Control Methods for Transradial Prostheses Based on Remnant Muscle Activity and Its Relationship with Proprioceptive Feedback
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Amputation
2.2. Proprioception
2.3. Prosthesis Control
3. Approaches Proven for Prosthetic Control
3.1. Electromyography
- Monopolar configuration acquiring a signal using a single electrode with respect to a reference (ground) electrode usually placed on an electrically neutral tissue (in the vicinity of a bone).
- Bipolar configuration—the signal is acquired using two active electrodes (placed 1–2 cm from each other) with the help of a reference electrode. The signals from the two measuring sites are collected with respect to a common ground provided by the reference electrode and then amplified. This helps in the mitigation of ambient electromagnetic noise.
- Multipolar configurations—similar to the bipolar configuration but uses more than two active electrodes. This configuration further reduces crosstalk and noise.
3.2. Electrical Impedance Tomography
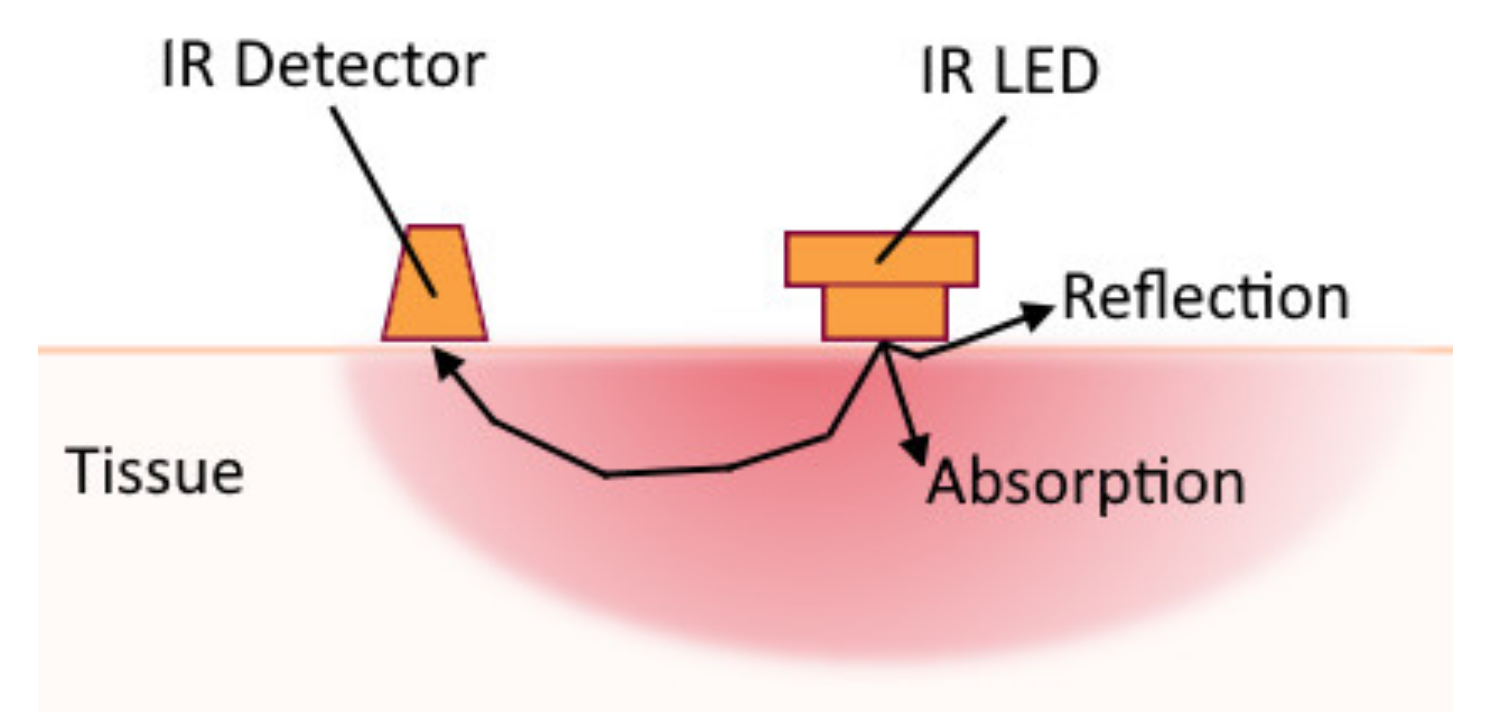
3.3. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
3.4. Sonomyography
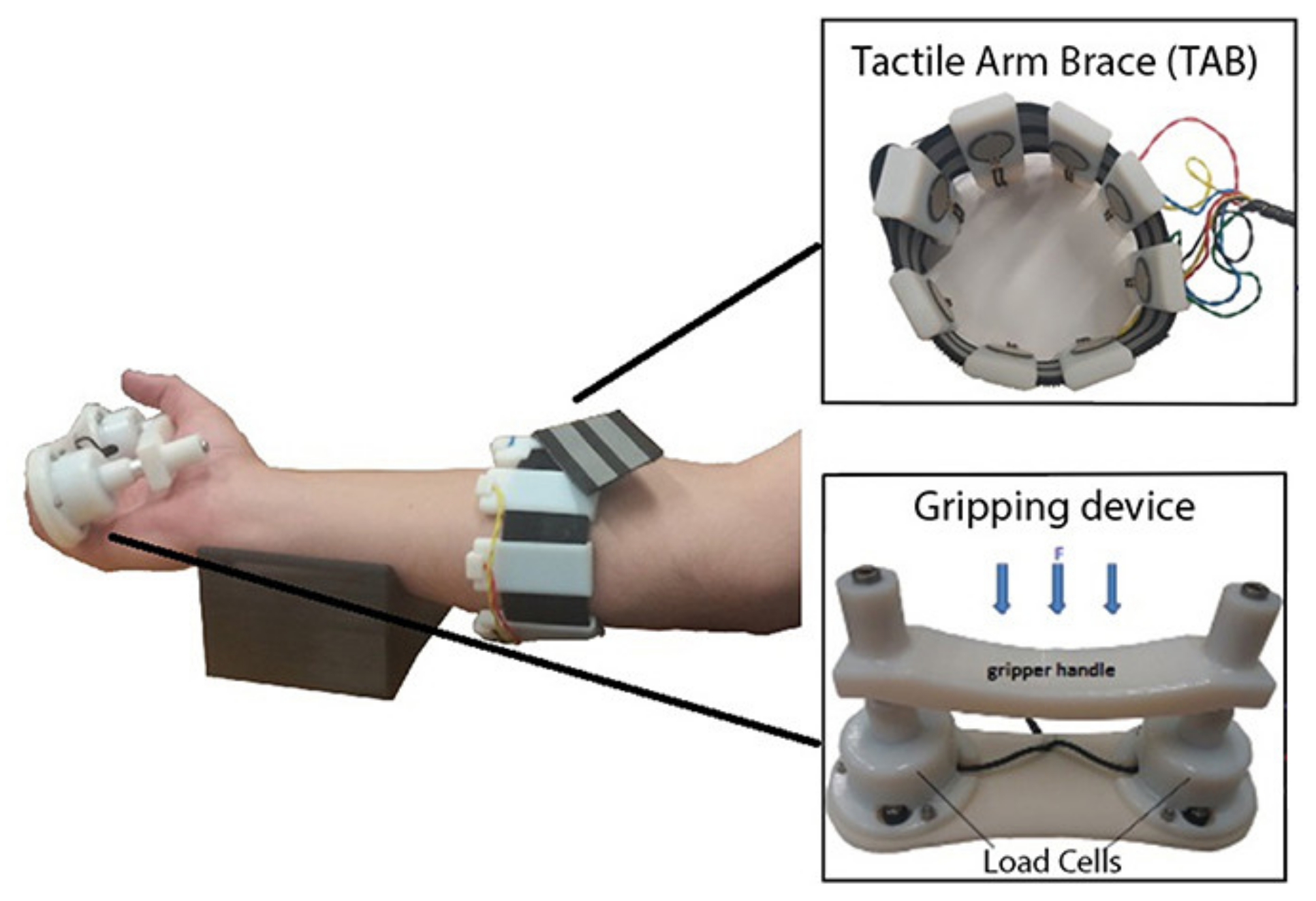
3.5. Force Myography
3.6. Phonomyography
4. Promising Control Approaches
4.1. Control Approaches without Proprioceptive Feedback
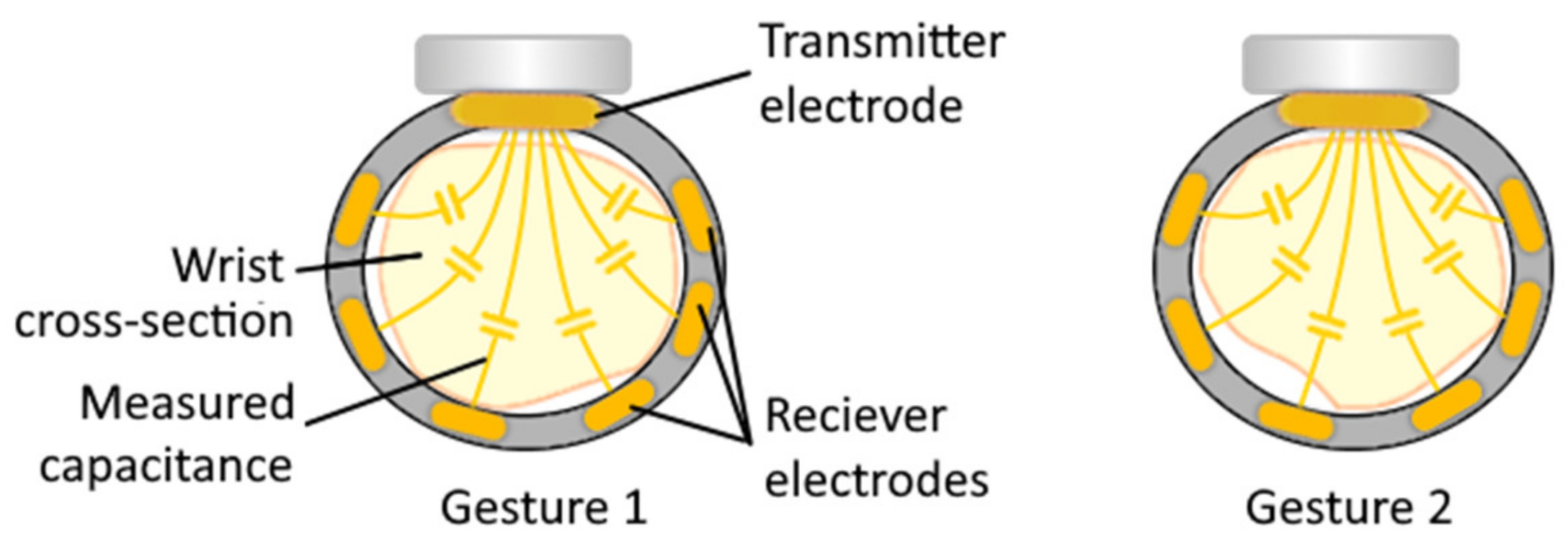
4.1.1. Capacitance Sensing
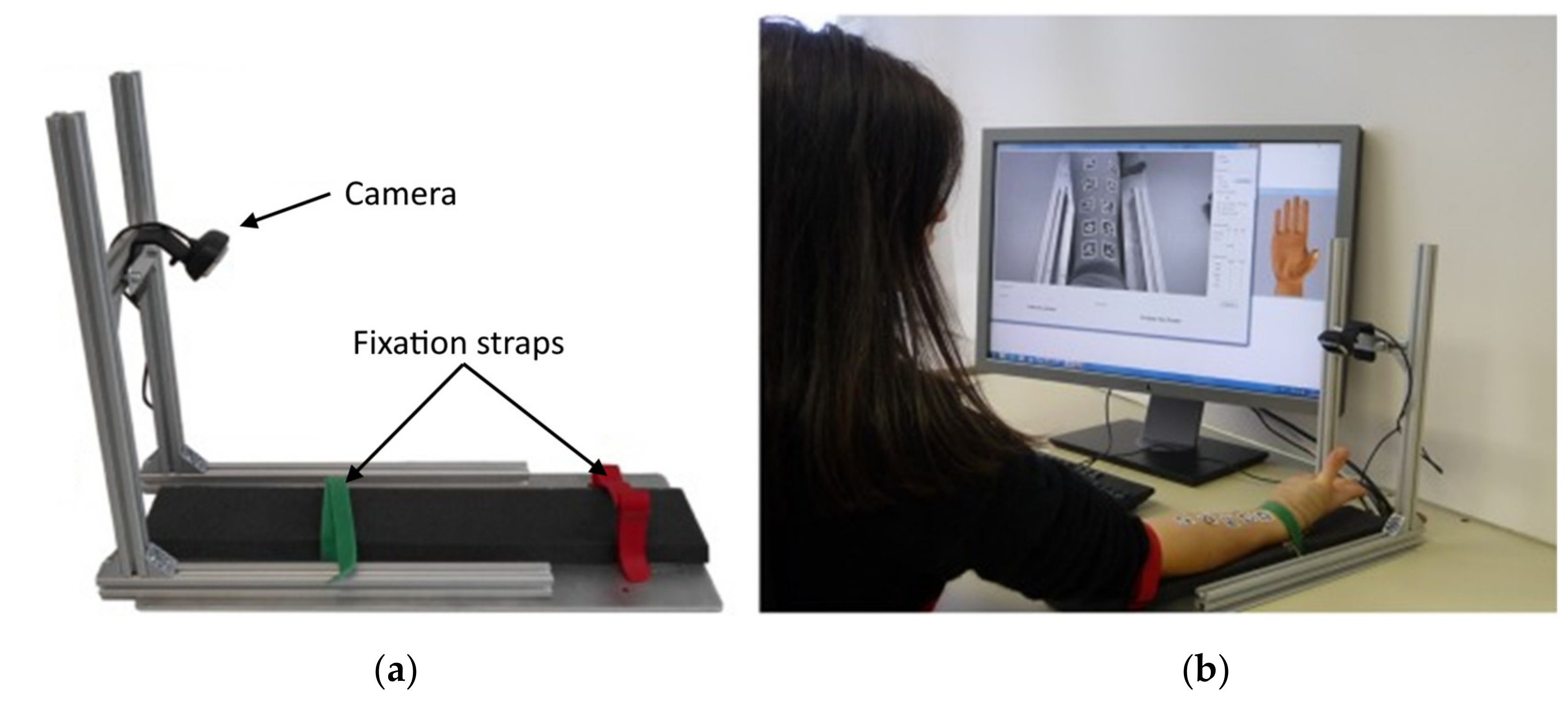
4.1.2. Optical Myography
4.1.3. Magnetomyography
4.2. Control Approaches Enabling Proprioceptive Feedback
4.2.1. Cineplasty
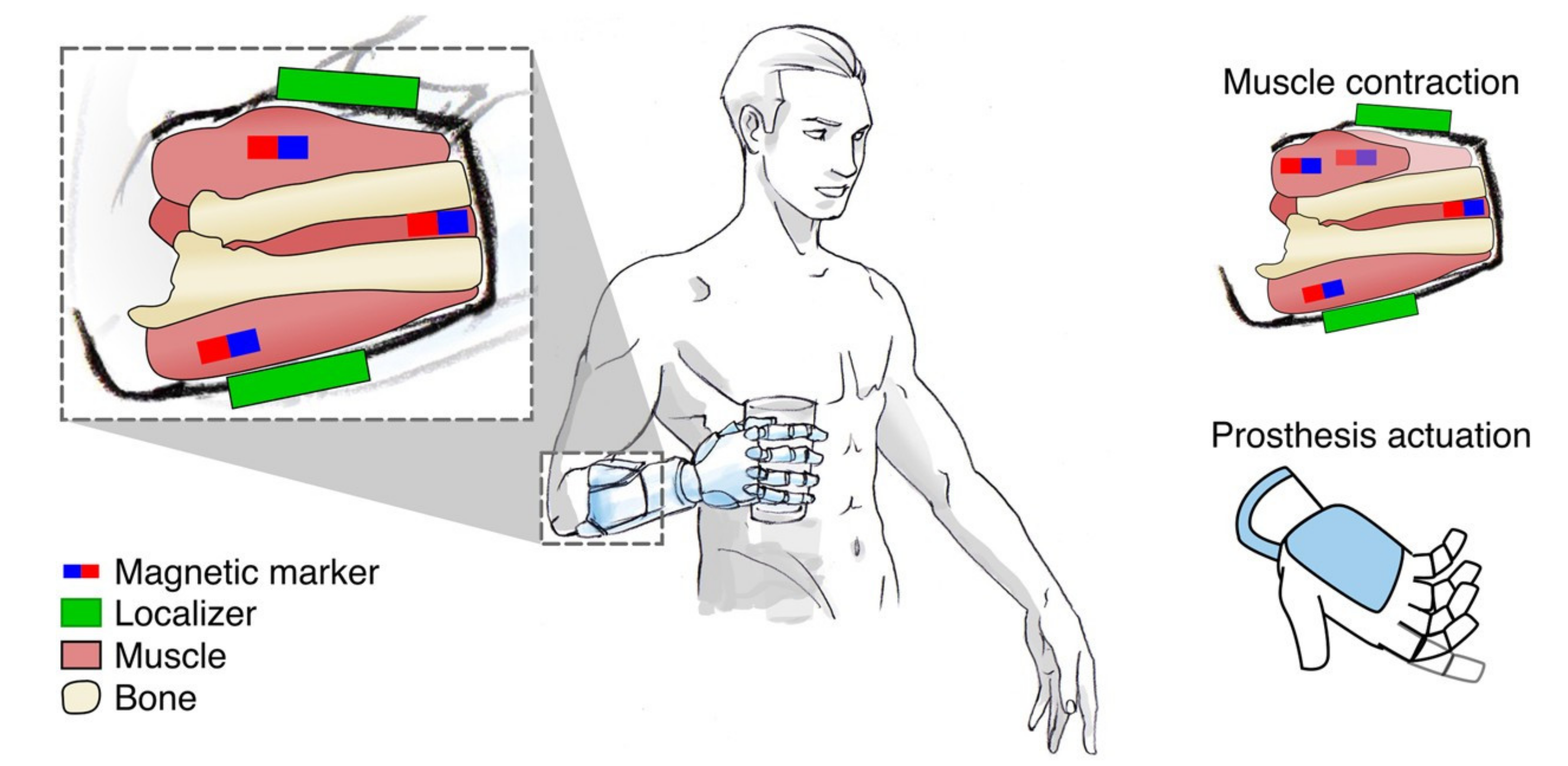
4.2.2. Myokinetic Control
5. Enabling Intuitive Proprioceptive Feedback
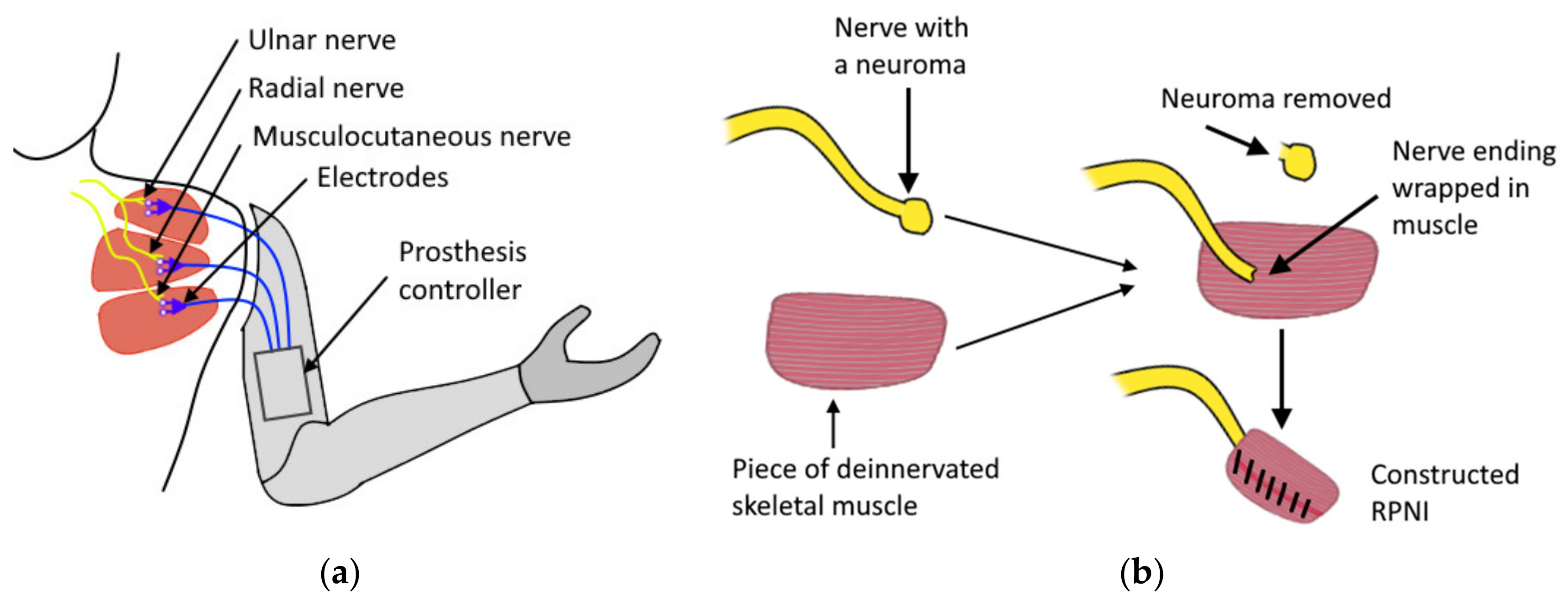
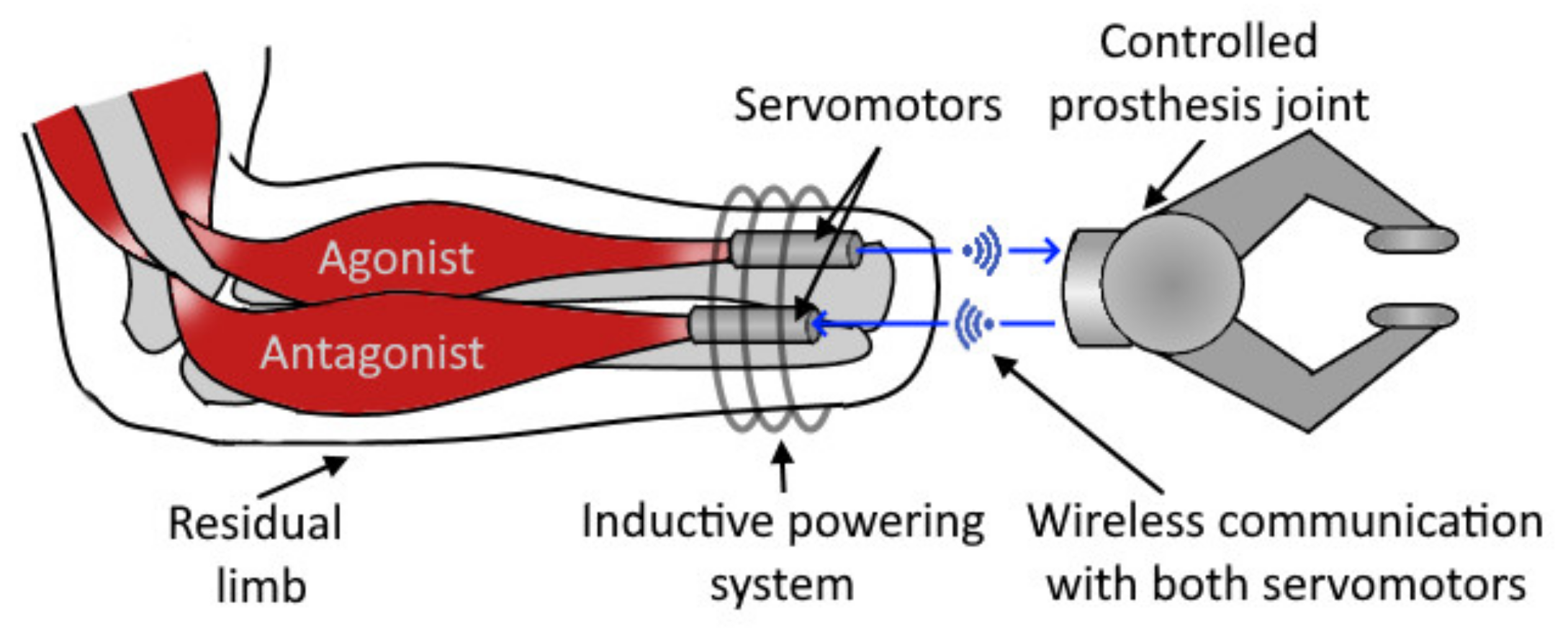
5.1. Agonist–Antagonist Myoneural Interface
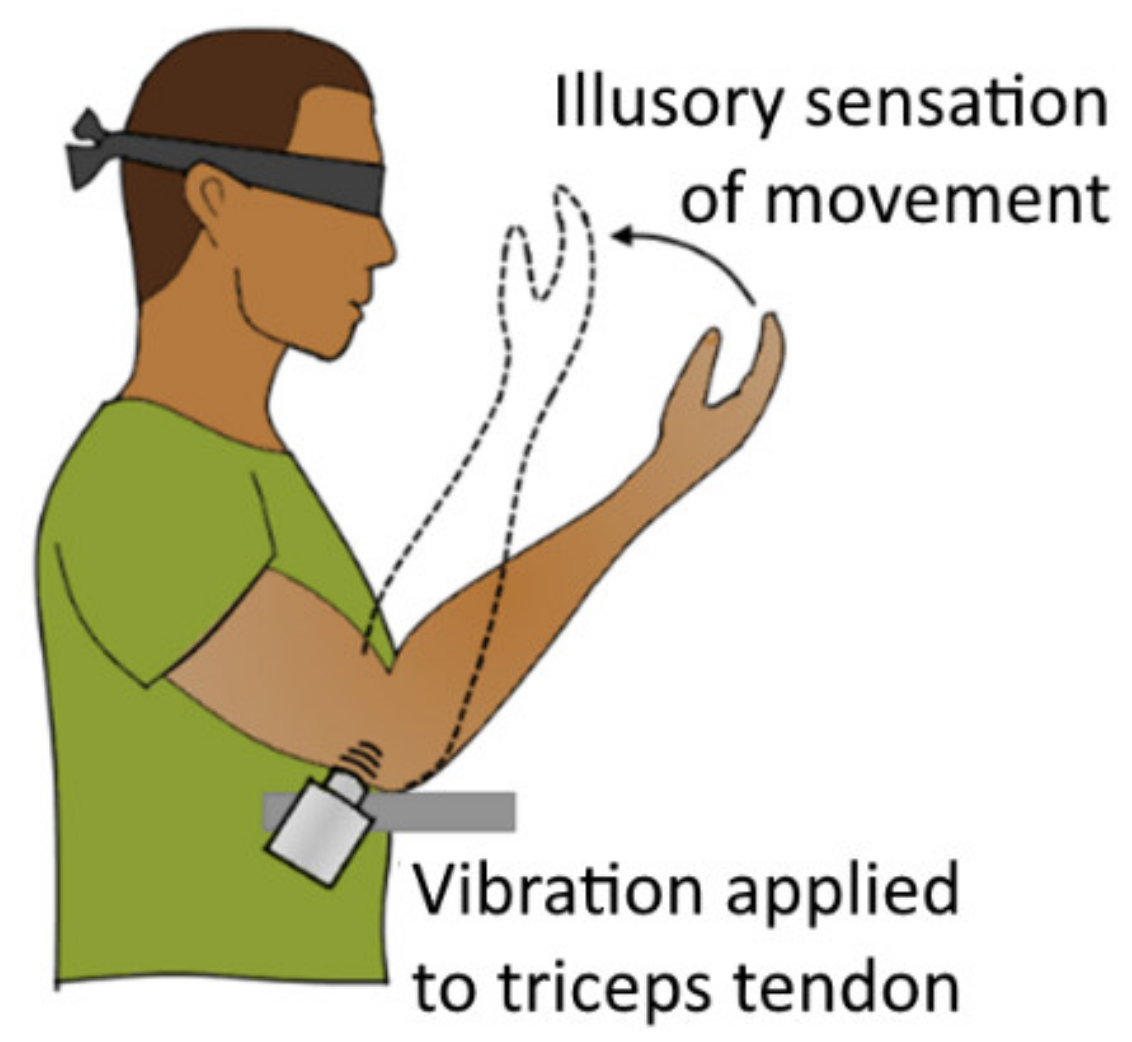
5.2. Kinaesthetic Illusion
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuiken, T.A.; Childress, D.S.; Rymer, W.Z. The hyper-reinnervation of rat skeletal muscle. Brain Res. 1995, 676, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, J.; Elzinga, K.; Chan, K.; Olson, J.; Morhart, M. Updates in Targeted Sensory Reinnervation for Upper Limb Amputation. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2014, 2, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.; Langhals, N.; Martin, D.; Johnson, P.; Cederna, P.; Urbanchek, M. Regenerative Peripheral Nerve Interface Viability and Signal Transduction with an Implanted Electrode. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 1380–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambani, S.; Urbanchek, M.; Zheng, X.; Leach, M.; Moon, J.; Cederna, P.; Langhals, N. Partial Skeletal Muscle Grafts for Prosthetic Control. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Woollard, A.; Konczalik, W. New surgical options to improve the quality of life of amputees. Surgery 2019, 37, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.L.; Kung, T.A.; Brown, D.L.; Leonard, J.A.; Kelly, B.M.; Cederna, P.S. Regenerative Peripheral Nerve Interfaces for the Treatment of Postamputation Neuroma Pain: A Pilot Study. Plast. Reconstr Surg.–Glob. Open 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, C.A.; Kemp, S.W.P.; Cederna, P.S. Regenerative Peripheral Nerve Interface for Management of Postamputation Neuroma. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 681–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumanian, G.A.; Potter, B.K.; Mioton, L.M.; Ko, J.H.; Cheesborough, J.E.; Souza, J.M.; Ertl, W.J.; Tintle, S.M.; Nanos, G.P.; Valerio, I.L.; et al. Targeted Muscle Reinnervation Treats Neuroma and Phantom Pain in Major Limb Amputees: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Surg. 2019, 270, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.N.; Kyle Potter, B.; Souza, J.M.; Tintle, S.M.; Nanos, G.P.I. Targeted Muscle Reinnervation for Transradial Amputation: Description of Operative Technique. Tech. Hand Up. Extrem. Surg. 2016, 20, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubblefield, K.A.; Miller, L.A.; Lipschutz, R.D.; Kuiken, T.A. Occupational therapy protocol for amputees with targeted muscle reinnervation. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2009, 46, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, B.A.; Potter, B.K. Residual Limb Complications and Management Strategies. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2014, 2, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engdahl, S.M.; Christie, B.P.; Kelly, B.; Davis, A.; Chestek, C.A.; Gates, D.H. Surveying the interest of individuals with upper limb loss in novel prosthetic control techniques. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peerdeman, B.; Boere, D.; Witteveen, H.; Hermens, H.; Stramigioli, S.; Rietman, H.; Veltink, P.; Misra, S. Myoelectric forearm prostheses: State of the art from a user-centered perspective. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilk, K.E.; Hooks, T.R. 12-Neuromuscular Training After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. In Noyes’ Knee Disorders: Surgery, Rehabilitation, Clinical Outcomes, 2nd ed.; Noyes, F.R., Barber-Westin, S.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 330–342. ISBN 978-0-323-32903-3. [Google Scholar]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S. The Proprioceptive Senses: Their Roles in Signaling Body Shape, Body Position and Movement, and Muscle Force. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1651–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemann, B.; Lephart, S. The Sensorimotor System, Part II: The Role of Proprioception in Motor Control and Functional Joint Stability. J. Athl. Train. 2002, 37, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Marasco, P.D.; Hebert, J.S.; Sensinger, J.W.; Shell, C.E.; Schofield, J.S.; Thumser, Z.C.; Nataraj, R.; Beckler, D.T.; Dawson, M.R.; Blustein, D.H.; et al. Illusory movement perception improves motor control for prosthetic hands. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, L.; Elangovan, N.; Contu, S.; Khosravani, S.; Konczak, J.; Masia, L. Robot-Aided Assessment of Wrist Proprioception. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Anson, J.; Liu, Y. Assessing proprioception: A critical review of methods. J. Sport Health Sci. 2015, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosker, J.; Sarabon, N. Kinaesthesia and methods for its assessment. Sport Sci. Rev. 2010, 19, 165–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contu, S.; Hussain, A.; Kager, S.; Budhota, A.; Deshmukh, V.A.; Kuah, C.W.K.; Yam, L.H.L.; Xiang, L.; Chua, K.S.G.; Masia, L.; et al. Proprioceptive assessment in clinical settings: Evaluation of joint position sense in upper limb post-stroke using a robotic manipulator. PLoS ONE 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, S.; Immink, M.; Thewlis, D. Assessing Proprioception: A Systematic Review of Possibilities. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2015, 29, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Anson, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R. Proprioceptive performance of bilateral upper and lower limb joints: Side-general and site-specific effects. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 226, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Waddington, G.; Adams, R.; Anson, J. Ability to discriminate movements at multiple joints around the body: Global or site-specific. Percept. Mot. Skills 2013, 116, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuthill, J.C.; Azim, E. Proprioception. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R194–R203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribot-Ciscar, E.; Roll, J.-P. Ago-antagonist muscle spindle inputs contribute together to joint movement coding in man. Brain Res. 1998, 791, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.S.; Carty, M.J.; Calvaresi, P.W.; Clites, T.R.; Maimon, B.E.; Taylor, C.R.; Zorzos, A.N.; Herr, H. On prosthetic control: A regenerative agonist-antagonist myoneural interface. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaan2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, M.A.; Graczyk, E.L.; Sidik, S.M.; Tan, D.W.; Tyler, D.J. Artificial tactile and proprioceptive feedback improves performance and confidence on object identification tasks. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, A.; Okamura, A.M.; Kuchenbecker, K.J. Identifying the role of proprioception in upper-limb prosthesis control: Studies on targeted motion. Acm Trans. Appl. Percept. 2008, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, S.; Dhawan, A.S.; Mukherjee, B.; Alzamani, M.; Joiner, W.M.; Sikdar, S. Evaluation of the Role of Proprioception During Proportional Position Control Using Sonomyography: Applications in Prosthetic Control. IEEE Int. Conf. Rehabil. Robot. 2019, 2019, 830–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens-Fripp, B.; Alici, G.; Mutlu, R. A Review of Non-Invasive Sensory Feedback Methods for Transradial Prosthetic Hands. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 6878–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemah, M.N.; Low, C.Y.; Aldulaymi, O.H.; Ong, P.; Ismail, A.E.; Qasim, A.A. A Review of Non-Invasive Haptic Feedback stimulation Techniques for Upper Extremity Prostheses. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, W.M.; Norman, S.E.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Implanted neural interfaces: Biochallenges and engineered solutions. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saal, H.P.; Bensmaia, S.J. Biomimetic approaches to bionic touch through a peripheral nerve interface. Neuropsychologia 2015, 79, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, A.D.; Rehbaum, H.; Farina, D.; Aszmann, O.C. Prosthetic Myoelectric Control Strategies: A Clinical Perspective. Curr. Surg. Rep. 2014, 2, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- i-Limb® Ultra. Available online: https://www.ossur.com/en-us/prosthetics/arms/i-limb-ultra,/prosthetics/arms/i-limb-ultra (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Smith, L.H.; Hargrove, L.J. Comparison of surface and intramuscular EMG pattern recognition for simultaneous wrist/hand motion classification. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 4223–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, P. Myoelectric control of prosthetic hands: State-of-the-art review. Med. Devices 2016, 9, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, K.A.; Shin, A.Y.; Kaufman, K.R. Interfaces with the peripheral nervous system for the control of a neuroprosthetic limb: A review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, K.; Weir, R.F.; Kuiken, T.A. Neural machine interfaces for controlling multifunctional powered upper-limb prostheses. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2007, 4, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, A.; Yang, J. Control of Hand Prostheses: A Literature Review; American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME): New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, C.J.D. Surface electromyography detection and recording. Delsys. Inc. 2002, 10, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Muceli, S.; Bergmeister, K.D.; Hoffmann, K.-P.; Aman, M.; Vukajlija, I.; Aszmann, O.C.; Farina, D. Decoding motor neuron activity from epimysial thin-film electrode recordings following targeted muscle reinnervation. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 16, 016010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
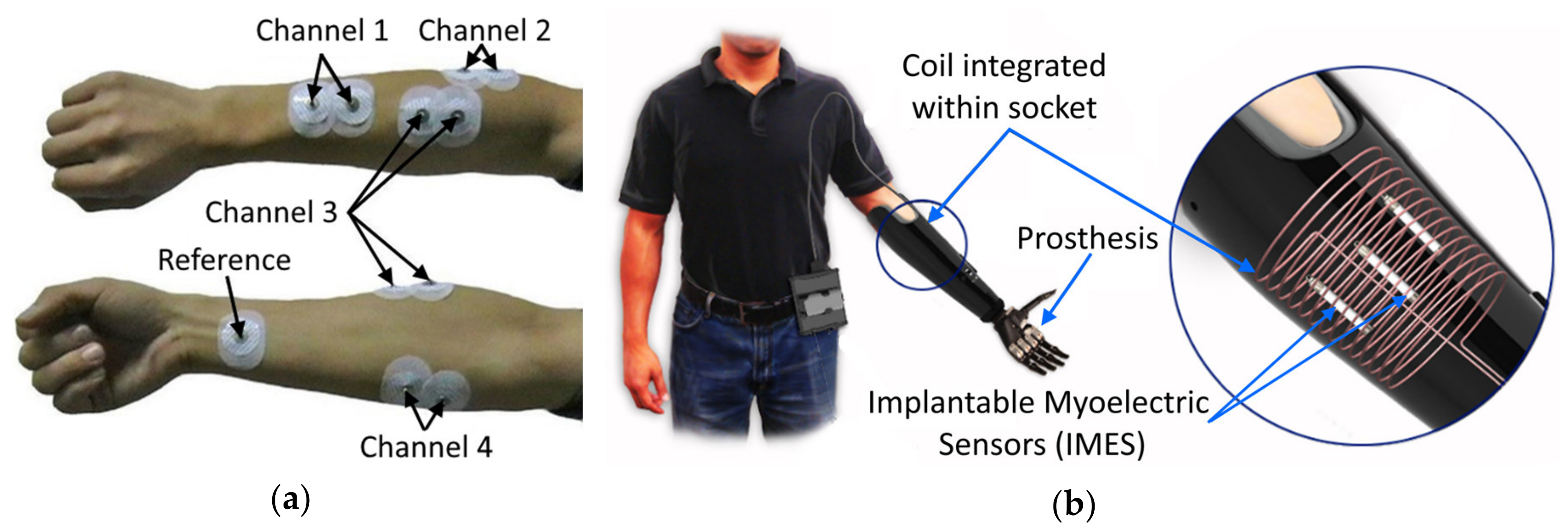
- Weir, R.F.F.; Troyk, P.R.; DeMichele, G.A.; Kerns, D.A.; Schorsch, J.F.; Maas, H. Implantable Myoelectric Sensors (IMESs) for Intramuscular Electromyogram Recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 56, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquina, P.F.; Evangelista, M.; Carvalho, A.J.; Lockhart, J.; Griffin, S.; Nanos, G.; McKay, P.; Hansen, M.; Ipsen, D.; Vandersea, J.; et al. First-in-man demonstration of a fully implanted myoelectric sensors system to control an advanced electromechanical prosthetic hand. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 244, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, B. Online Finger Gesture Recognition Using Surface Electromyography Signals. J. Signal Inf. Process. 2013, 4, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muceli, S.; Farina, D. Simultaneous and Proportional Estimation of Hand Kinematics From EMG During Mirrored Movements at Multiple Degrees-of-Freedom. IEEE Trans. Neural. Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 20, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amma, C.; Krings, T.; Böer, J.; Schultz, T. Advancing Muscle-Computer Interfaces with High-Density Electromyography. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems—CHI ’15, Seoul, Korea, 18–23 April 2015; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 929–938. [Google Scholar]
- Artemiadis, P.K.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. An EMG-Based Robot Control Scheme Robust to Time-Varying EMG Signal Features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, D.; Jiang, N.; Rehbaum, H.; Holobar, A.; Graimann, B.; Dietl, H.; Aszmann, O.C. The extraction of neural information from the surface EMG for the control of upper-limb prostheses: Emerging avenues and challenges. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahne, J.M.; Farina, D.; Jiang, N.; Liebetanz, D. A Novel Percutaneous Electrode Implant for Improving Robustness in Advanced Myoelectric Control. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddiss, E.A.; Chau, T.T. Upper limb prosthesis use and abandonment: A survey of the last 25 years. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2007, 31, 236–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Electrical Impedance Tomography; Adam Hilger: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Staats, W.L.; Spieker, A.; Sung, M.; Rutkove, S.B. A Technique for Performing Electrical Impedance Myography in the Mouse Hind Limb: Data in Normal and ALS SOD1 G93A Animals. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orschulik, J.R.; Menden, T. Optimizing the Measurement Frequency in Electrical Impedance Tomography; Czech Technical University: Prague, Czech Republic, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Hao, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. An optimal Electrical Impedance Tomography drive pattern for human-computer interaction applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowrick, T.; Blochet, C.; Holder, D. In vivo bioimpedance measurement of healthy and ischaemic rat brain: Implications for stroke imaging using electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.; Bayford, R.; Demosthenous, A. A Human-Machine Interface Using Electrical Impedance Tomography for Hand Prosthesis Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Harrison, C. Tomo: Wearable, Low-Cost Electrical Impedance Tomography for Hand Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software & Technology-UIST ’15, Daegu, Kyungpook, Korea, 8–11 November 2015; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Harrison, C. Advancing Hand Gesture Recognition with High Resolution Electrical Impedance Tomography. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 16–19 October 2016; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 843–850. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, M.S.; Wania, V.; Bastin, B.; Schmalz, U.; Kienbaum, P.; Beiderlinden, M.; Treschan, T.A. Electrical impedance tomography during major open upper abdominal surgery: A pilot-study. BMC Anesth. 2014, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bera, T.K.; Nagaraju, J. A multifrequency Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) system for biomedical imaging. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM), Bangalore, India, 22–25 July 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Izzetoglu, K.; Bunce, S.; Izzetoglu, M.; Onaral, B.; Pourrezaei, K. Functional near-infrared neuroimaging. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; Volume 2, pp. 5333–5336. [Google Scholar]
- Paleari, M.; Luciani, R.; Ariano, P. Towards NIRS-based hand movement recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 1506–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Development of a Multi-Channel Compact-Size Wireless Hybrid sEMG/NIRS Sensor System for Prosthetic Manipulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 16, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Towards Low-cost Sign Language Gesture Recognition Leveraging Wearables. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everdell, N.L.; Airantzis, D.; Kolvya, C.; Suzuki, T.; Elwell, C.E. A portable wireless near-infrared spatially resolved spectroscopy system for use on brain and muscle. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 1692–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.; Attenberger, A.; Buchenrieder, K. Prostheses Control with Combined Near-Infrared and Myoelectric Signals. In Computer Aided Systems Theory—EUROCAST 2011; Moreno-Díaz, R., Pichler, F., Quesada-Arencibia, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 6928, pp. 601–608. ISBN 978-3-642-27578-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, T.; Zambarbieri, D.; Beltrami, G.; Verni, G. NIRS monitoring of muscle contraction to control a prosthetic device. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Sensors, Fibers, and Optical Delivery Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–12 September 1998; pp. 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Toward an Enhanced Human-Machine Interface for Upper-Limb Prosthesis Control with Combined EMG and NIRS Signals. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2017, 47, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.P.; Chan, M.M.F.; Shi, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.H. Sonomyography: Monitoring morphological changes of forearm muscles in actions with the feasibility for the control of powered prosthesis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2006, 28, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Huang, Q.-H.; Chen, X. Continuous monitoring of sonomyography, electromyography and torque generated by normal upper arm muscles during isometric contraction: Sonomyography assessment for arm muscles. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Hertkorn, K.; Sagardia, M.; González, D.S.; Nowak, M. A virtual piano-playing environment for rehabilitation based upon ultrasound imaging. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014; pp. 548–554. [Google Scholar]
- Castellini, C.; Passig, G. Ultrasound image features of the wrist are linearly related to finger positions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Castellini, C.; Passig, G.; Zarka, E. Using Ultrasound Images of the Forearm to Predict Finger Positions. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2012, 20, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.; Baker, C.A.; Lahlou, M.; Zafar, H.; Murthy, K.G.; Rangwala, H.; Kosecka, J.; Joiner, W.M.; Pancrazio, J.J.; Sikdar, S. Real-Time Classification of Hand Motions Using Ultrasound Imaging of Forearm Muscles. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, A.S.; Mukherjee, B.; Patwardhan, S.; Akhlaghi, N.; Diao, G.; Levay, G.; Holley, R.; Joiner, W.M.; Harris-Love, M.; Sikdar, S. Proprioceptive Sonomyographic Control: A novel method for intuitive and proportional control of multiple degrees-of-freedom for individuals with upper extremity limb loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, J.; Marzo, A.; Fraser, M.; Phillips, C. EchoFlex: Hand Gesture Recognition using Ultrasound Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; Association for Computing Machinery (ACM): New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1923–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Sikdar, S.; Rangwala, H.; Eastlake, E.B.; Hunt, I.A.; Nelson, A.J.; Devanathan, J.; Shin, A.; Pancrazio, J.J. Novel Method for Predicting Dexterous Individual Finger Movements by Imaging Muscle Activity Using a Wearable Ultrasonic System. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 22, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Towards Wearable A-Mode Ultrasound Sensing for Real-Time Finger Motion Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, N.; Ju, Z.; Liu, H. A New Wearable Ultrasound Muscle Activity Sensing System for Dexterous Prosthetic Control. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Hong Kong, China, 9–12 October 2015; pp. 1415–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; He, K.; Sun, X.; Liu, H. Human-machine interface based on multi-channel single-element ultrasound transducers: A preliminary study. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Munich, Germany, 14–16 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xingchen, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, Z.; Ding, H.; Liu, H. A Proportional Pattern Recognition Control Scheme for Wearable A-mode Ultrasound Sensing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravantchi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Bernitsas, E.; Goel, M.; Harrison, C. Interferi: Gesture Sensing using On-Body Acoustic Interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, 4–9 May 2019; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Kenney, L.P.; Xie, H.-B. Evaluation of sonomyography (SMG) for control compared with electromyography (EMG) in a discrete target tracking task. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–6 September 2009; pp. 1549–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Youjia, H.; Liu, H. Performances of surface EMG and Ultrasound signals in recognizing finger motion. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th International Conference on Human System Interactions (HSI), Portsmouth, UK, 6–8 July 2016; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, D.; He, K.; Liu, H. Ultrasound-Based Sensing Models for Finger Motion Classification. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Li, K.; Cointet, C.; Liu, H. Ultrasonography and electromyography based hand motion intention recognition for a trans-radial amputee: A case study. Med. Eng. Phys. 2020, 75, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, M.; Hoffmann, P.; Öberg, T. Morphological changes during early trans-tibial prosthetic fitting. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 1998, 22, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, R.; Thiebaud, R.S.; Loenneke, J.P.; Loftin, M.; Abe, T. Time course for arm and chest muscle thickness changes following bench press training. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2012, 4, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Towards Zero Re-Training for Long-Term Hand Gesture Recognition via Ultrasound Sensing. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2019, 23, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; He, K.; Liu, H. Toward Portable Hybrid Surface Electromyography/A-Mode Ultrasound Sensing for Human–Machine Interface. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dementyev, A.; Paradiso, J. WristFlex: Low-power gesture input with wrist-worn pressure sensors. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology, Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liang, X.; Assaad, M.; Heidari, H. Wearable Wristworn Gesture Recognition Using Echo State Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 26th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Genova, Italy, 27–29 November 2019; pp. 875–878. [Google Scholar]
- Amft, O.; Junker, H.; Lukowicz, P.; Troster, G.; Schuster, C. Sensing muscle activities with body-worn sensors. In Proceedings of the Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN) 2006, International Workshop, Cambridge, UK, 3–5 April 2006; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 4–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, E.; Wu, Y.T.; Suzuki, C.K.; de Andrade, D.T.G.; Neto, A.R.; Rohmer, E. Optical fiber force myography sensor for applications in prosthetic hand control. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), Tokyo, Japan, 9–11 March 2018; pp. 342–347. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, H.; Vu, T.; Zhang, S.; Muncuk, U.; Nguyen, P.; Bui, N.; Nguyen, A.; Lv, Q.; Chowdhury, K.; Dinh, T. CapBand: Battery-free Successive Capacitance Sensing Wristband for Hand Gesture Recognition. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems, Shenzhen, China, 4–7 November 2018; pp. 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kenney, L.P.J.; Lisitsa, I.; Bowker, P.; Heath, G.H.; Howard, D. Dimensional change in muscle as a control signal for powered upper limb prostheses: A pilot study. Med. Eng. Phys. 1999, 21, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, P.B.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, X. Hand Gesture Recognition and Finger Angle Estimation via Wrist-Worn Modified Barometric Pressure Sensing. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, L.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Gu, G. Stretchable E-Skin Patch for Gesture Recognition on the Back of the Hand. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, T.; Chance, G.; Assaf, T.; Dogramadzi, S. Tactile Signatures and Hand Motion Intent Recognition for Wearable Assistive Devices. Front. Robot. AI 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyea, A.; Englehart, K.; Scheme, E. FMG Versus EMG: A Comparison of Usability for Real-Time Pattern Recognition Based Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radmand, A.; Scheme, E.; Englehart, K. High-density force myography: A possible alternative for upper-limb prosthetic control. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2016, 53, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodayan, A.; Jiang, X.; Menon, C. Continuous Prediction of Finger Movements Using Force Myography. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarangani, G.P.; Jiang, X.; Simpson, L.A.; Eng, J.J.; Menon, C. Force Myography for Monitoring Grasping in Individuals with Stroke with Mild to Moderate Upper-Extremity Impairments: A Preliminary Investigation in a Controlled Environment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Chen, R.; Merhi, L.-K.; Xiao, Z.; Pousett, B.; Menon, C. Force Myography to Control Robotic Upper Extremity Prostheses: A Feasibility Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Gao, Q.; Liu, H.; Shull, P.B. A novel, co-located EMG-FMG-sensing wearable armband for hand gesture recognition. Sens. Actuators A: Phys. 2020, 301, 111738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orizio, C. Muscle sound: Bases for the introduction of a mechanomyographic signal in muscle studies. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1993, 21, 201–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Courteville, A.; Gharbi, T.; Cornu, J.Y. MMG measurement: A high-sensitivity microphone-based sensor for clinical use. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1998, 45, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalise, L.; Casaccia, S.; Marchionni, P.; Ercoli, I.; Tomasini, E.P. Muscle activity characterization by laser Doppler Myography. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 459, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalise, L.; Casaccia, S.; Marchionni, P.; Ercoli, I.; Tomasini, E. Laser doppler myography (LDMi): A novel non-contact measurement method for the muscle activity. Laser 2013, 22, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaccia, S.; Scalise, L.; Casacanditella, L.; Tomasini, E.P.; Rohrbaugh, J.W. Non-contact assessment of muscle contraction: Laser Doppler Myography. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Torino, Italy, 7–9 May 2015; pp. 610–615. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, D.T.; Leonard, J.A.; Gitter, A.J.; Ball, R.D. Acoustic myography as a control signal for externally powered prosthesis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1986, 67, 267–269. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.; Heim, W.; Chau, T. A Self-Contained, Mechanomyography-Driven Externally Powered Prosthesis. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.; Vaidyanathan, R. Upper-limb prosthetic control using wearable multichannel mechanomyography. IEEE Int. Conf. Rehabil. Robot. 2017, 2017, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Chau, T.; Goldenberg, A.A. MMG-Based Multisensor Data Fusion for Prosthesis Control. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 3, pp. 2909–2912. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, D.; Andreozzi, E.; Fratini, A.; Gargiulo, G.D.; Savino, S.; Niola, V.; Bifulco, P. A Piezoresistive Sensor to Measure Muscle Contraction and Mechanomyography. Sensors 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.F.; Tsai, W.-W.; Lin, W.-Y.; Lee, M.-Y. MMG-torque estimation under dynamic contractions. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Anchorage, AK, USA, 9–12 October 2011; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 585–590. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, D.; Chen, X.; Yi, W.; Zheng, Y.-P.; Zhu, Z.; Chan, S.-C. In vivo behavior of human muscle during isometric ramp contraction: A simultaneous EMG, MMG and ultrasonography investigation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing (ICSPCC 2012), Hong Kong, China, 12–15 August 2012; pp. 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Sheng, X.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Mechanomyography Assisted Myoeletric Sensing for Upper-Extremity Prostheses: A Hybrid Approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregori, B.; Galié, E.; Accornero, N. Surface electromyography and mechanomyography recording: A new differential composite probe. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2003, 41, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekimoto, J. GestureWrist and GesturePad: Unobtrusive wearable interaction devices. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Zurich, Switzerland, 8–9 October 2001; pp. 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Bahle, G.; Lukowicz, P. A simple wristband based on capacitive sensors for recognition of complex hand motions. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE SENSORS, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Amft, O.; Bahle, G.; Lukowicz, P. Designing Sensitive Wearable Capacitive Sensors for Activity Recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3935–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissler, C.; Mouriki, N.; Castellini, C.; Belagiannis, V.; Navab, N. OMG: Introducing optical myography as a new human machine interface for hand amputees. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 937–942. [Google Scholar]
- Nissler, C.; Mouriki, N.; Castellini, C. Optical Myography: Detecting Finger Movements by Looking at the Forearm. Front. Neurorobot. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Fujiwara, E.; Suzuki, C.K. Optical myography system for posture monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 28–30 September 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Fujiwara, E.; Suzuki, C.K. Evaluation of Optical Myography Sensor as Predictor of Hand Postures. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5299–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, J.; Harrison, D.; Myers, T.; Allyn, K. Effects of elevated vacuum on in-socket residual limb fluid volume: Case study results using bioimpedance analysis. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 1231–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Givler, E. Magnetomyography: Magnetic fields around the human body produced by skeletal muscles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1972, 21, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.K.; Wikswo, J.P. A model of the magnetic fields created by single motor unit compound action potentials in skeletal muscle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1997, 44, 948–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Heidari, H.; Farina, D.; Nazarpour, K. Miniaturized Magnetic Sensors for Implantable Magnetomyography. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinin, M.H.; Ustinin, M. Reconstruction of the Human Hand Functional Structure Based on a Magnetomyogram. Maтeмaтичecкaя Биoлoгия И Биoинφopмaтикa 2018, 13, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reincke, M. Magnetomyographie mit dem SQUID—Magnetomyography with the SQUID. Biomed. Tech. Eng. 1993, 38, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, H.; Zuo, S.; Krasoulis, A.; Nazarpour, K. CMOS Magnetic Sensors for Wearable Magnetomyography. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2116–2119. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, S.; Schmalz, J.; Ozden, M.-O.; Gerken, M.; Su, J.; Niekiel, F.; Lofink, F.; Nazarpour, K.; Heidari, H. Ultrasensitive Magnetoelectric Sensing System for pico-Tesla MagnetoMyoGraphy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzenheimer, E.; Laufs, H.; Schulte-Mattler, W.; Schmidt, G. Magnetic Measurement of Electrically Evoked Muscle Responses with Optically Pumped Magnetometers. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Endo, H.; Takeda, T. Magnetic fields produced by single motor units in human skeletal muscles. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1999, 110, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, P.; Mazzoni, A.; Micera, S.; Corbo, M. Giuliano Vanghetti and the innovation of “cineplastic operations”. Neurology 2017, 89, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, R.W. The Tendon Exteriorization Cineplasty, A Preliminary Report. Inter-Clin. Inf. Bull. 1966, 5, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, D.C. The choice of control system for the multimovement prosthesis: Extended physiological proprioception (EPP). In The Control of Upper-Extremity Prostheses and Orthoses; Charles C Thomas Publisher: Springfield, IL, USA, 1974; pp. 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Doubler, J.A.; Childress, D.S. An analysis of extended physiological proprioception as a prosthesis-control technique. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1984, 21, 5–18. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, R.F.; Heckathorne, C.W.; Childress, D.S. Cineplasty as a control input for externally powered prosthetic components. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2001, 38, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Mablekos-Alexiou, A.; Bertos, G.A.; Papadopoulos, E. A biomechatronic Extended Physiological Proprioception (EPP) controller for upper-limb prostheses. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 6173–6178. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogiannopoulos, S.; Vangelatos, Z.; Bertos, G.A.; Papadopoulos, E. A Biomechatronic EPP upper-limb prosthesis controller and its performance comparison to other topologies. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1755–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogiannopoulos, S.; Bertos, G.A.; Papadopoulos, E. A “Biomechatronic EPP” Upper-Limb Prosthesis Control Configuration and its performance comparison to other control configurations. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2020, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukoulas, N.; Bertos, G.A.; Mablekos-Alexiou, A.; Papadopoulos, E. A Biomechatronic EPP upper-limb prosthesis teleoperation system implementation using Bluetooth Low Energy. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 17–21 July 2018; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantino, S.; Clemente, F.; Barone, D.; Controzzi, M.; Cipriani, C. The myokinetic control interface: Tracking implanted magnets as a means for prosthetic control. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ERC. Myki—A Bidirectional MYoKinetic Implanted Interface for Natural Control of Artificial Limbs; European Research Council (ERC): Brussels, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, F.; Ianniciello, V.; Gherardini, M.; Cipriani, C. Development of an Embedded Myokinetic Prosthetic Hand Controller. Sensors 2019, 19, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, S.; Clemente, F.; De Simone, A.; Cipriani, C. Feasibility of Tracking Multiple Implanted Magnets with a Myokinetic Control Interface: Simulation and Experimental Evidence Based on the Point Dipole Model. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Anna, E.; Valle, G.; Mazzoni, A.; Strauss, I.; Iberite, F.; Patton, J.; Petrini, F.M.; Raspopovic, S.; Granata, G.; Iorio, R.D.; et al. A closed-loop hand prosthesis with simultaneous intraneural tactile and position feedback. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clites, T.R.; Carty, M.J.; Ullauri, J.B.; Carney, M.E.; Mooney, L.M.; Duval, J.-F.; Srinivasan, S.S.; Herr, H.M. Proprioception from a neurally controlled lower-extremity prosthesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clites, T.R.; Carty, M.J.; Srinivasan, S.; Zorzos, A.N.; Herr, H.M. A murine model of a novel surgical architecture for proprioceptive muscle feedback and its potential application to control of advanced limb prostheses. J. Neural Eng. 2017, 14, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, G.M.; McCloskey, D.I.; Matthews, P.B. The contribution of muscle afferents to kinaesthesia shown by vibration induced illusions of movement and by the effects of paralysing joint afferents. Brain 1972, 95, 705–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.W.; Taylor, J.L.; Seizova-Cajic, T. Muscle Vibration-Induced Illusions: Review of Contributing Factors, Taxonomy of Illusions and User’s Guide. Multisens. Res. 2017, 30, 25–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.S.; Dawson, M.R.; Carey, J.P.; Hebert, J.S. Characterizing the effects of amplitude, frequency and limb position on vibration induced movement illusions: Implications in sensory-motor rehabilitation. Technol. Health Care 2015, 23, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, G.; Hagbarth, K.E. Normal variability of tonic vibration reflexes in man. Exp. Neurol. 1966, 16, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmotti, M.B.; Olmedo, D.G.; Cabrini, R.L. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontology 2019, 79, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.A.; Thomsen, P.; Palmquist, A. Osseointegration and current interpretations of the bone-implant interface. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasoulis, A.; Kyranou, I.; Erden, M.S.; Nazarpour, K.; Vijayakumar, S. Improved prosthetic hand control with concurrent use of myoelectric and inertial measurements. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radmand, A.; Scheme, E.; Englehart, K. On the Suitability of Integrating Accelerometry Data with Electromyography Signals for Resolving the Effect of Changes in Limb Position during Dynamic Limb Movement. J. Prosthet. Orthot. 2014, 26, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushaba, R.N.; Al-Timemy, A.; Kodagoda, S.; Nazarpour, K. Combined influence of forearm orientation and muscular contraction on EMG pattern recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 61, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of the Method | Measured Property | Applications | Provides Proprioceptive Feedback | Requires Surgical Procedure | Requires Contact of Sensor/Electrodes with Tissues |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electromyography (EMG, sEMG, iEMG) | Muscle electric potentials | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 27 gestures [48]) | No | sEMG–no iEMG–yes | Yes |
| Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) | Tissue impedance | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 8 gestures [60]) | No | No | Yes |
| Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) | Tissue oxygenation (through the amount of scattered light) | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 9 gestures [66]) | No | No | Yes |
| Sonomyography (SMG) | Change of muscle morphology | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 15 gestures [76]) | No | No | Yes |
| Force myography (FMG) | Change of muscle morphology measured on the skin surface | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 8 gestures [103]) | No | No | Yes |
| Phonomyography (PMG) | Muscle fibre oscillations | Prosthesis control, Hand gesture prediction (up to 5 gestures [115]) | No | No | No (possible contactless measurement [110]) |
| Capacitance sensing | Tissue capacitance | Hand gesture prediction (up to 2 gestures [122]) | No | No | No |
| Optical myography (OMG) | Change of muscle morphology measured on the skin surface | Hand gesture prediction (up to 8 gestures [128]) | No | No | No |
| Magnetomyography (MMG) | Magnetic fields generated by muscle | Concept | No | No (possible implantation) | No |
| Cineplasty | Muscle length | Prosthesis control (original approach), Concept | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Myokinetic control (MYKI) | Change of muscle morphology (through magnetic fields) | Concept | Yes | Yes | No |
| Name of the Method | Sensors/Electrodes Placement | Susceptibility | Monitoring Deep Muscles | Tested Hybrid Approaches | Typical Number of Channels/Electrodes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electromyography (EMG, sEMG, iEMG) | Over/inside targeted muscle | Sweating, Muscle fatigue, Electromagnetic noise | sEMG–no, iEMG - yes | NIRS, PMG, FMG, SMG | 2–32, up to 192 |
| Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) | Over targeted muscle, Over related tendons | Sweating, Electromagnetic noise | Yes | – | 8, up to 64 |
| Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) | Over targeted muscle | Ambient light, Muscle fatigue | No | EMG | 2–4 |
| Sonomyography (SMG) | Over targeted muscle, Over related tendons | Probe shift | Yes | EMG | Probe with 128 transducers (up to 512) A-mode: 4 transducers |
| Force myography (FMG) | Over targeted muscle, Over related tendons | Muscle fatigue | No | EMG | 8, up to 126 |
| Phonomyography (PMG) | Over targeted muscle | Ambient acoustic noise, Adjacent muscle crosstalk, Sensor movement | No | EMG | 6 |
| Capacitance sensing | Over targeted muscle, Over related tendons | Sweating, Electromagnetic noise | Yes | – | 3 (receiver electrodes) |
| Optical myography (OMG) | Over targeted muscle, Over related tendons | Ambient light, Muscle fatigue | No | – | Single camera, 10–18 skin markers |
| Magnetomyography (MMG) | Over/inside targeted muscle | Magnetic interference | No | – | – |
| Cineplasty | Wrist | Infections | Yes | – | Single sensor for each muscle pair |
| Myokinetic control (MYKI) | Over targeted muscle | Magnetic interference | Yes | – | 6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grushko, S.; Spurný, T.; Černý, M. Control Methods for Transradial Prostheses Based on Remnant Muscle Activity and Its Relationship with Proprioceptive Feedback. Sensors 2020, 20, 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174883
Grushko S, Spurný T, Černý M. Control Methods for Transradial Prostheses Based on Remnant Muscle Activity and Its Relationship with Proprioceptive Feedback. Sensors. 2020; 20(17):4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174883
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrushko, Stefan, Tomáš Spurný, and Martin Černý. 2020. "Control Methods for Transradial Prostheses Based on Remnant Muscle Activity and Its Relationship with Proprioceptive Feedback" Sensors 20, no. 17: 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174883
APA StyleGrushko, S., Spurný, T., & Černý, M. (2020). Control Methods for Transradial Prostheses Based on Remnant Muscle Activity and Its Relationship with Proprioceptive Feedback. Sensors, 20(17), 4883. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174883







