Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a longitudinal IoT deployment in the shared open space within the University campus. We discuss the lessons we have learned based on our experience in equipping public open space with IoT technology at the University campus.
- We present a number of studies exploring how this shared open space is actually used, how its state can be communicated, and how users can interact with this space.
- We share experiences in using this IoT deployment in teaching and development activities. We discuss challenges and possibilities to bring the users of the space along with its further development.
2. Related Work
2.1. Smart Shared Spaces
2.2. Smart Campuses
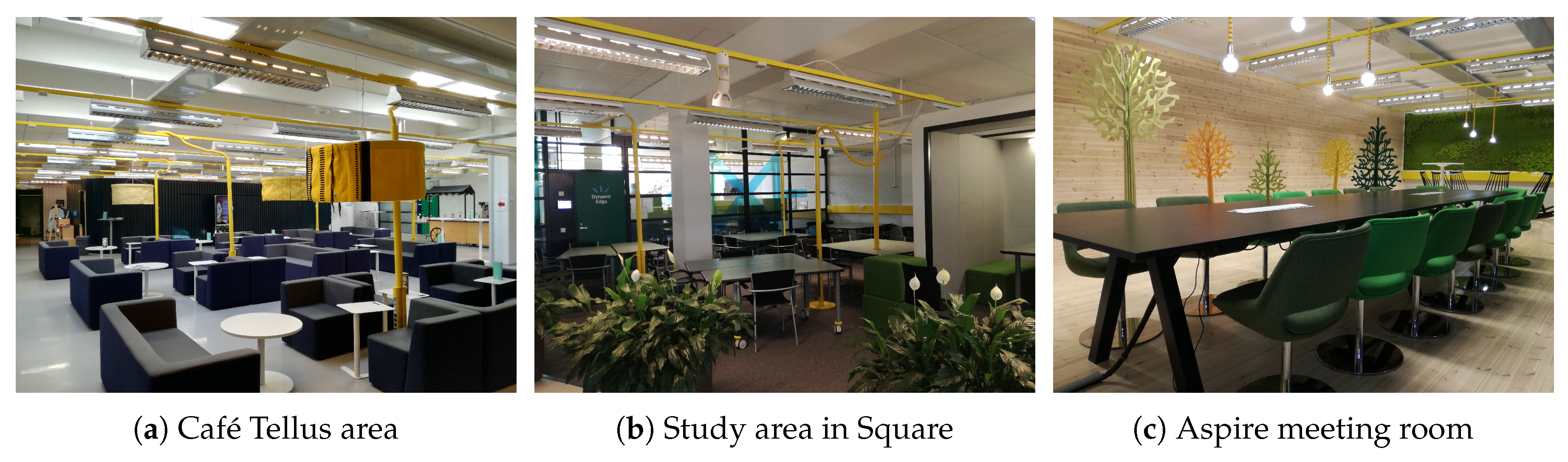
3. Tellus: Towards a Smart Space
3.1. Tellus Infrastructure
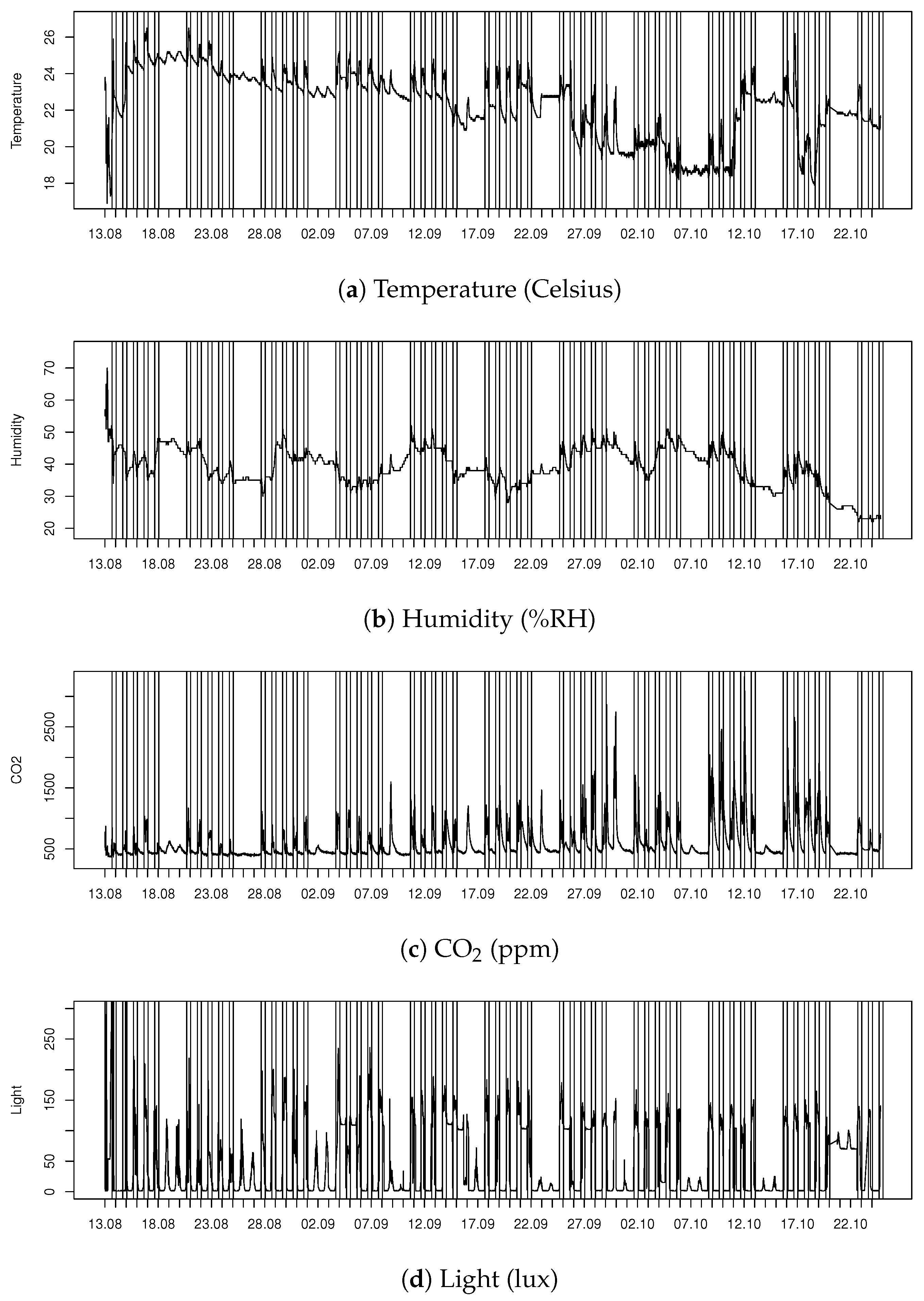
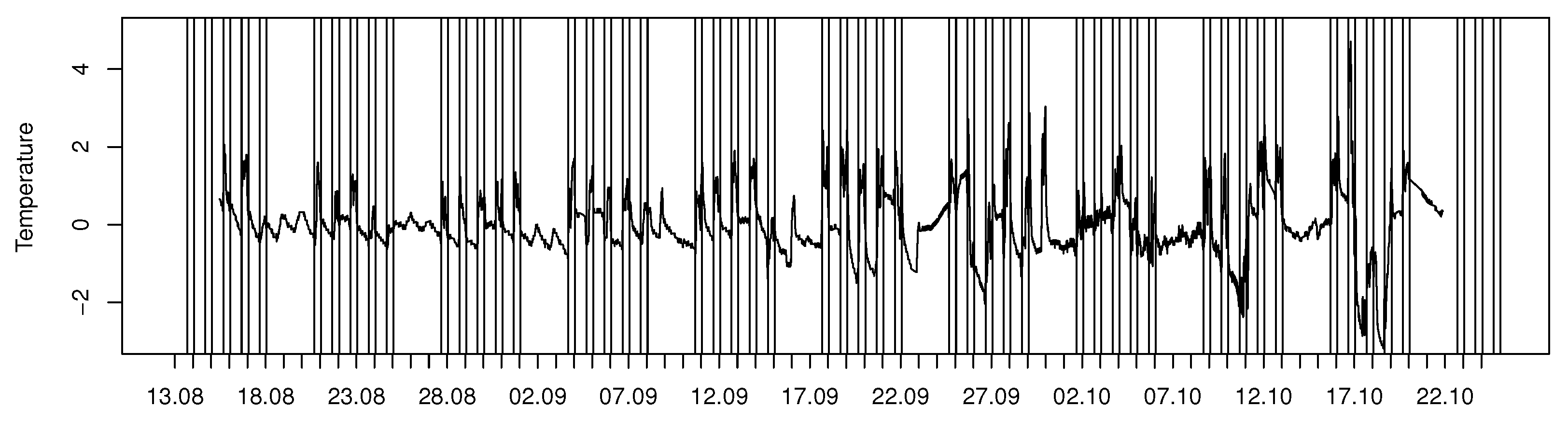
3.2. Data Patterns
3.3. Features of Deployed Infrastructure for Data Analysis
4. Tellus: Insights and Experiments
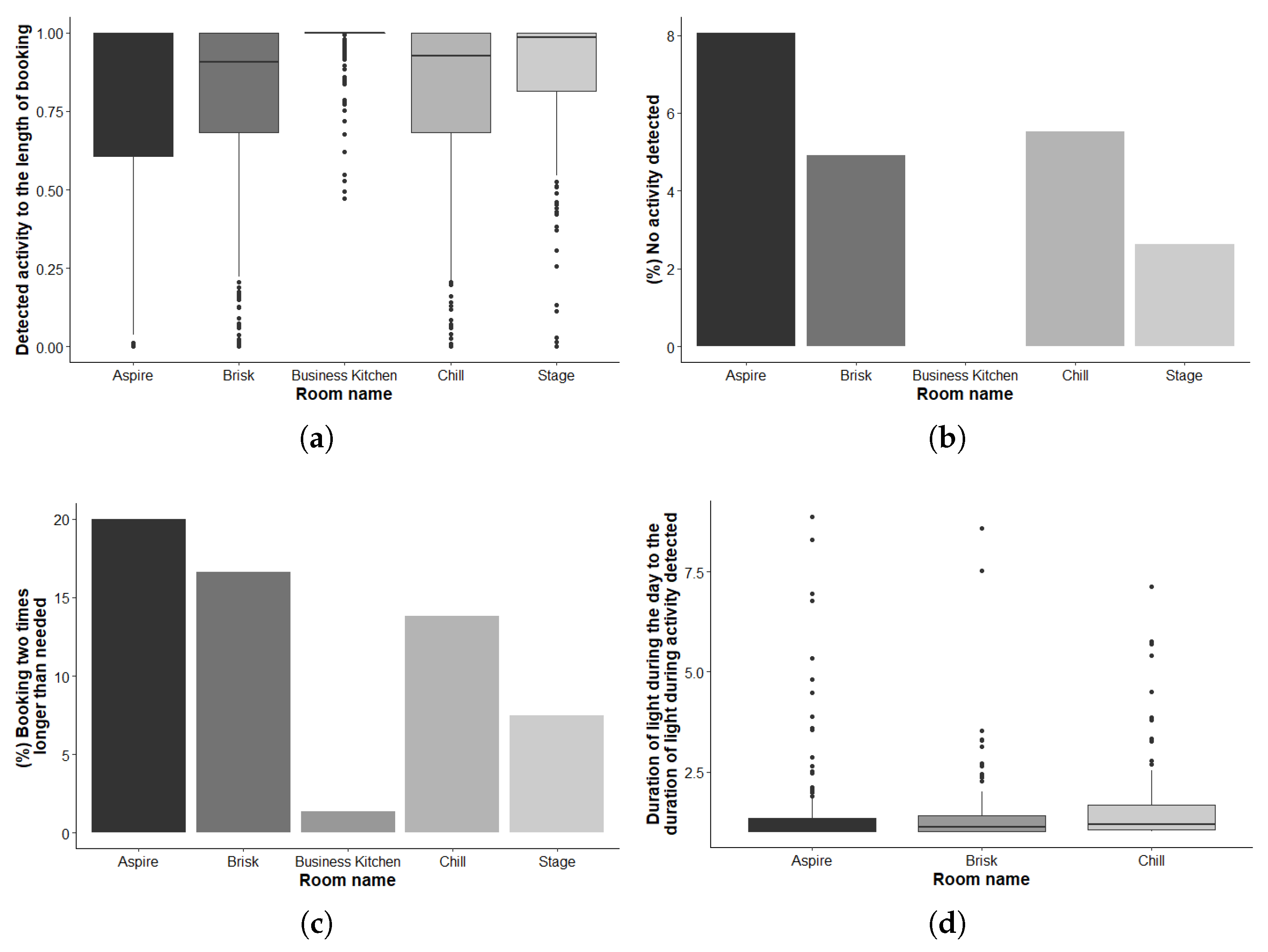
4.1. Tellus Efficiency
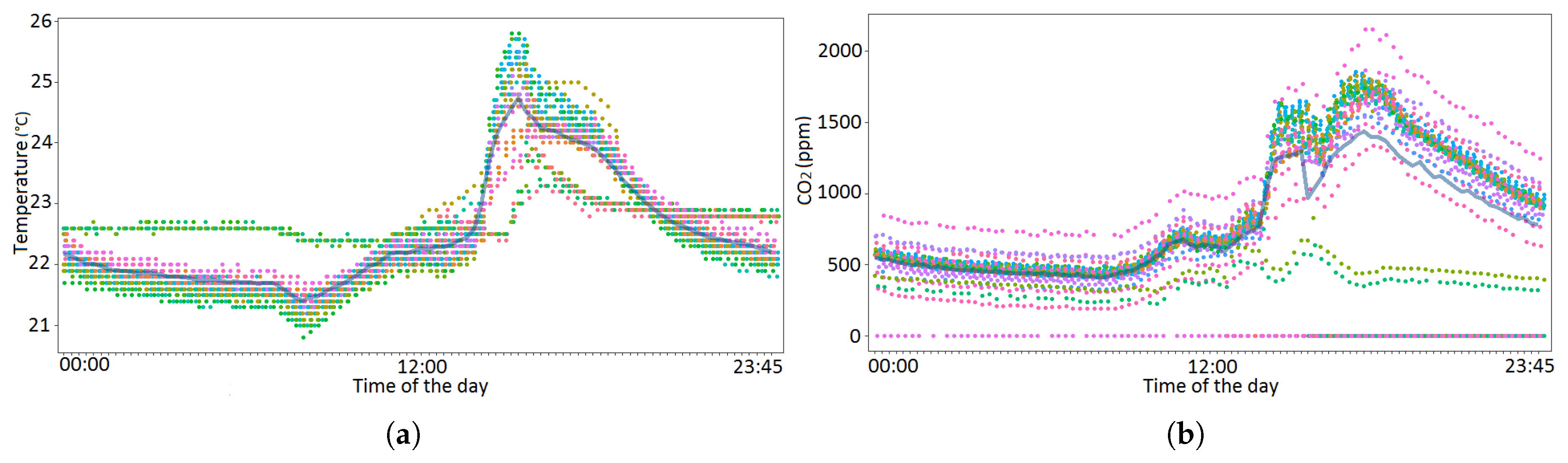
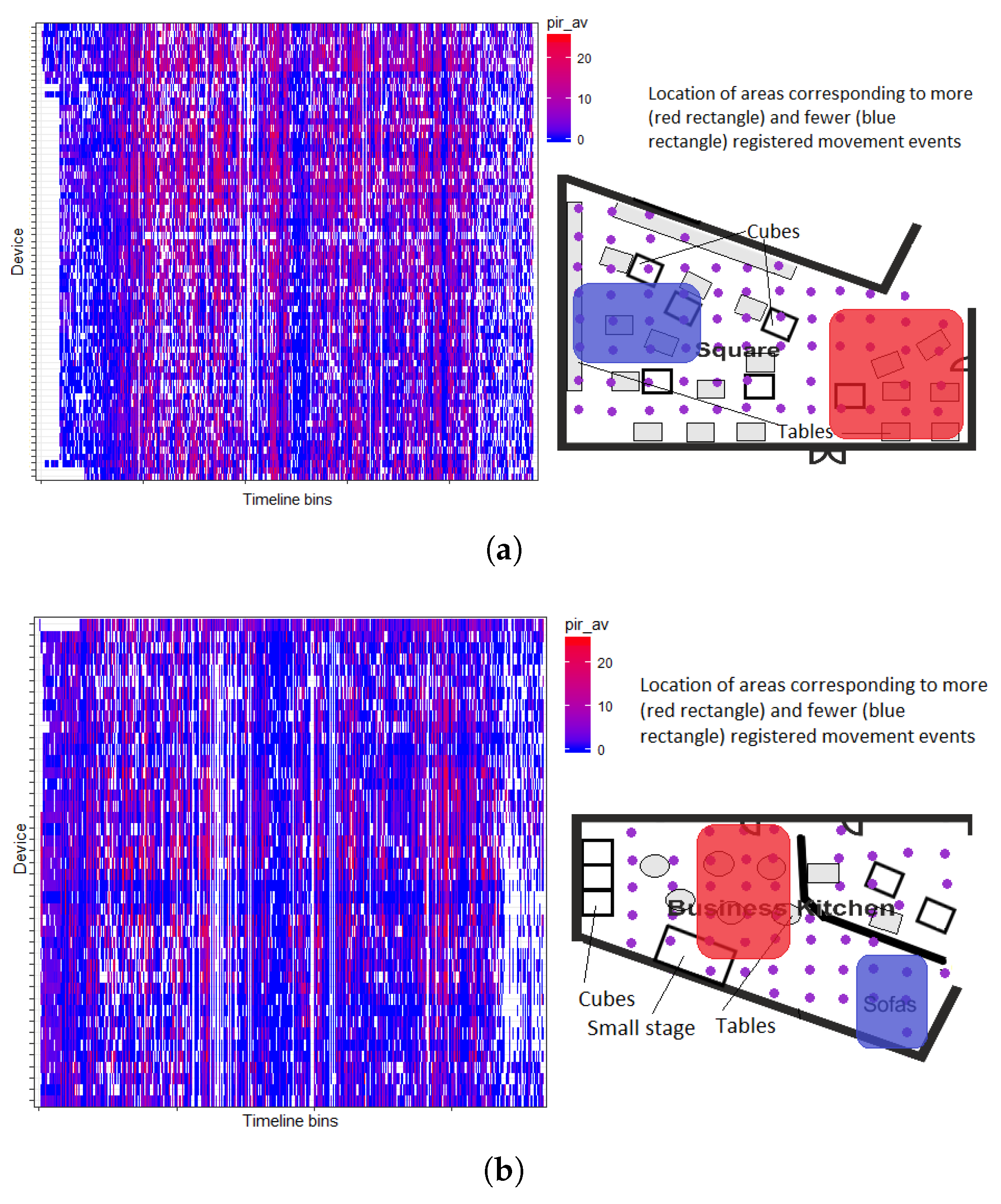
4.2. Space Usage Patterns
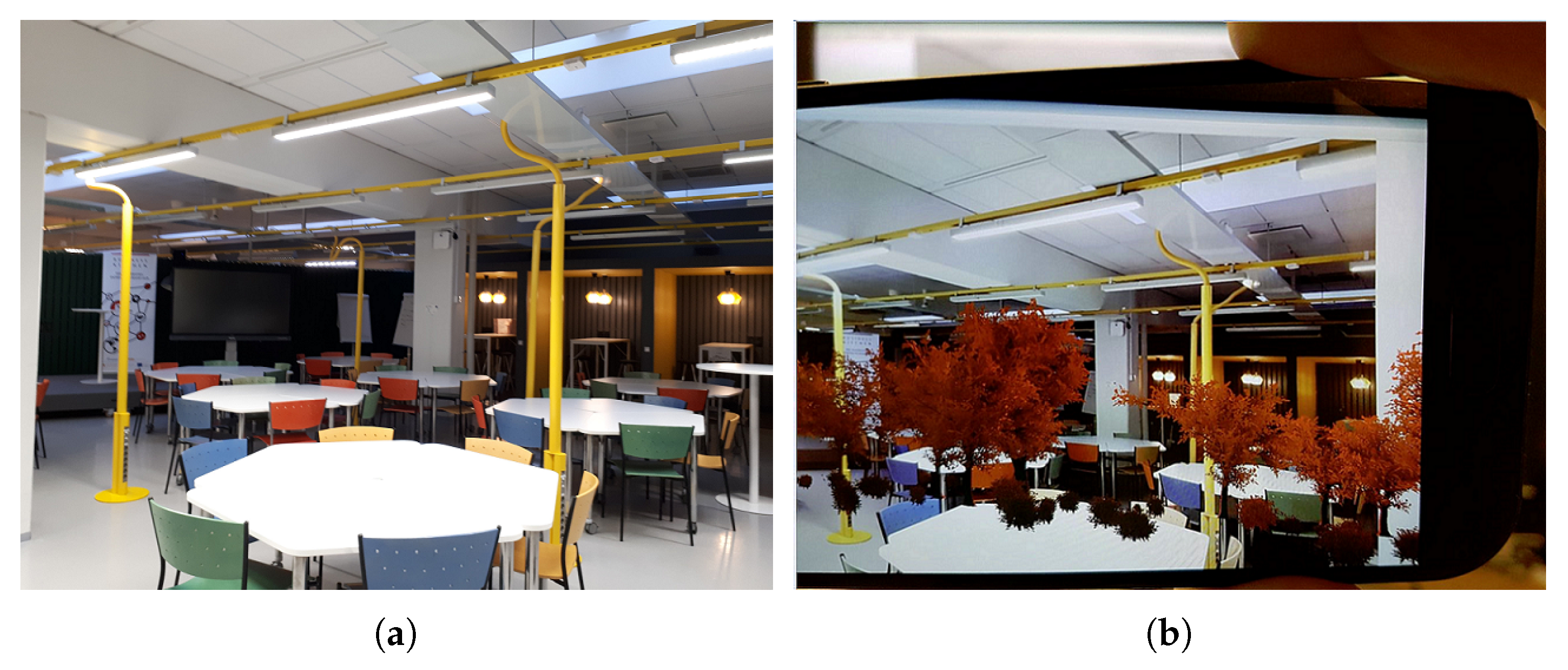
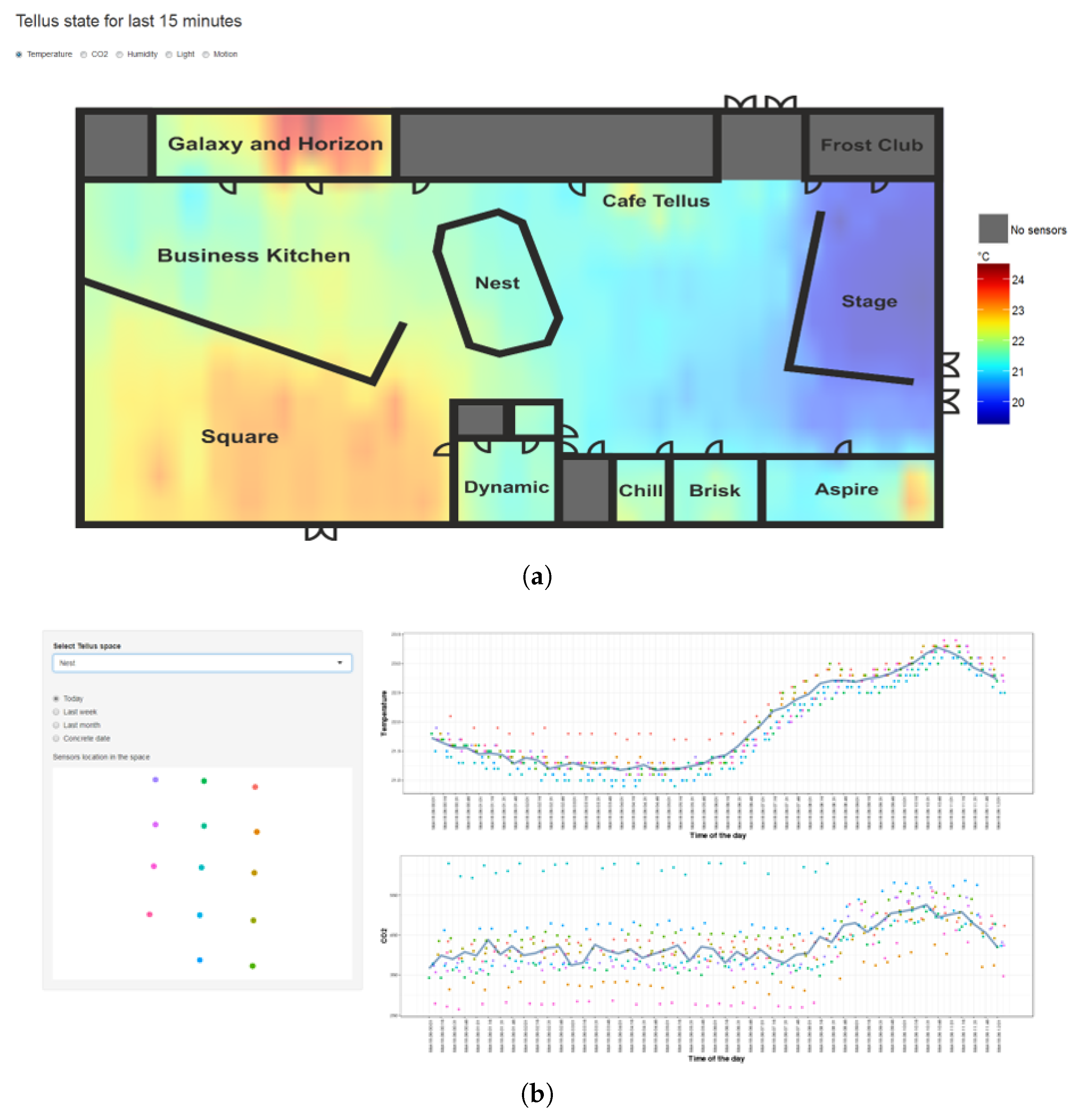
4.3. State Visualization
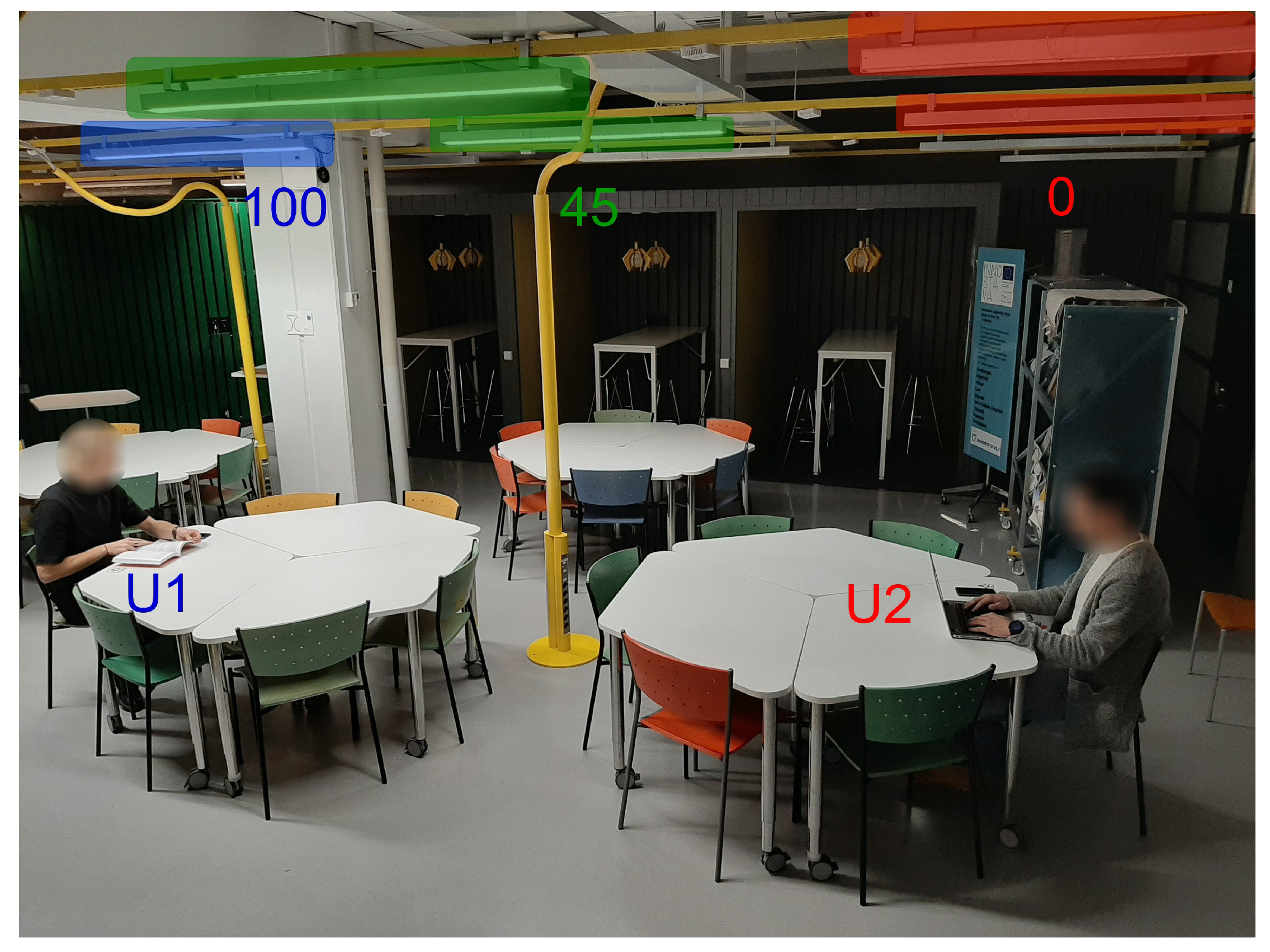
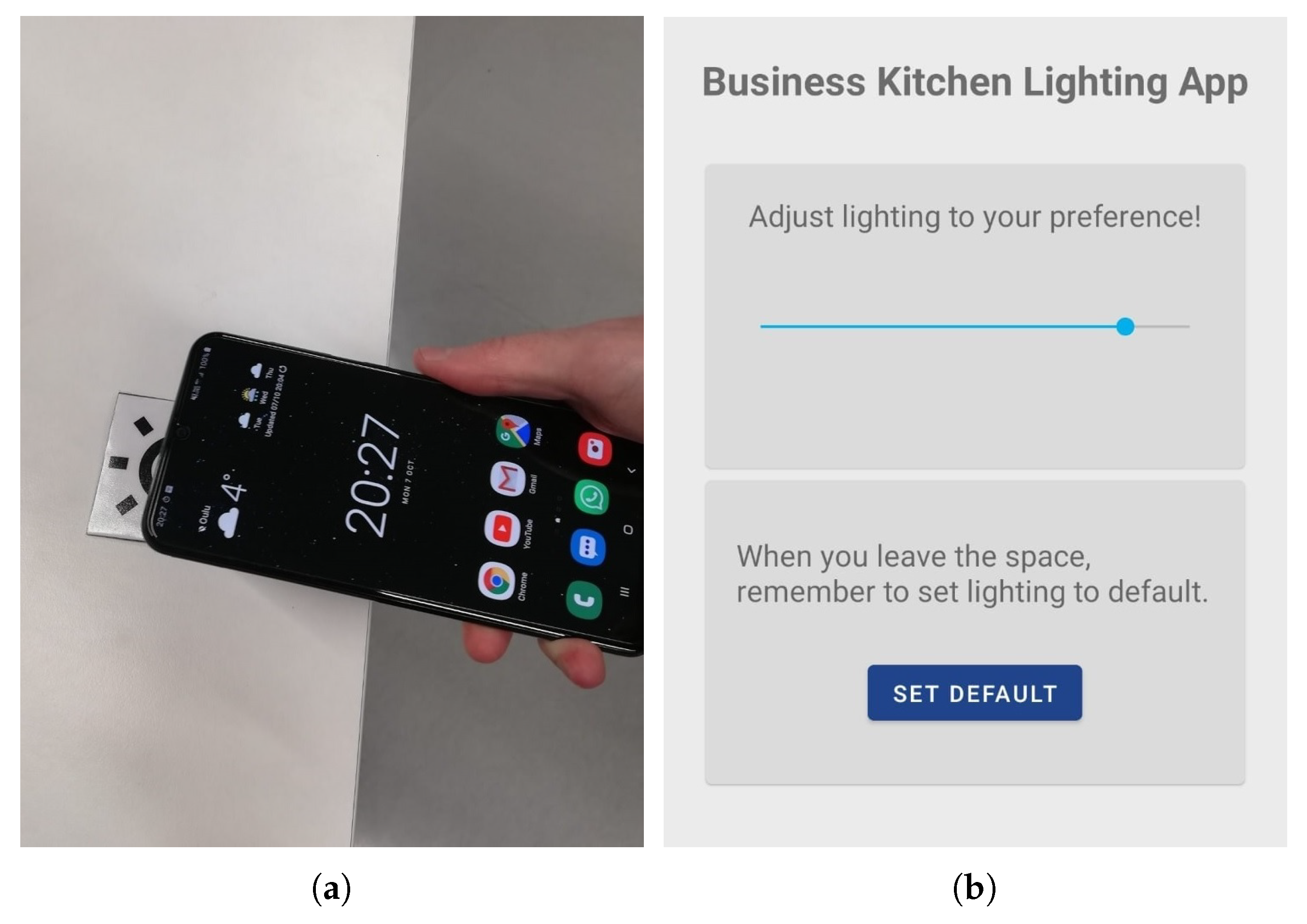
4.4. Space Interaction
4.5. Use for Teaching and Development Activities
- –
- Working with a real-life, large-scale data set.
- –
- Understanding implementation and operation of smart spaces through concrete work.
- –
- Learning how to develop functional applications for real environments with real end-users.
- –
- Rehearsing innovation and design skills during the group work.
- –
- Possibility to be creative and brainstorm novel innovative ideas.
- –
- The use of weather data could improve the results of the analysis and the additional information, like speed of users walking or some physiological measurements of the people of the area, could provide valuable information about the health aspects.
- –
- Larger perspective to consider the air quality was proposed as it affects also the building.
- –
- Possibilities to estimate the number of people in the area based on the sensed information.
5. Challenges and Lessons Learned
5.1. Infrastructure
5.2. Data Related Aspects
5.3. Ethics
5.4. User Involvement
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, D.J.; Das, S.K. (Eds.) Smart Environments: Technology, Protocols, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, E.; Sánchez, I.S.; Cortés, M.; Riekki, J. Towards User Support in Ubiquitous Learning Systems. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2015, 8, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, T.G.; Vrakas, D.; Vlahavas, I. A Survey of Service Composition in Ambient Intelligence Environments. Artifi. Intell. Rev. 2013, 40, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, M.; Holleis, P.; Schmidt, A. Embedded interaction: Interacting with the internet of things. IEEE Int. Comput. 2010, 14, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Woo, W. Service conflict management framework for multi-user inhabited smart home. JUCS 2009, 15, 2330–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitz, N.; Charitos, D.; Kaptein, M.; Böhlen, M. Grand challenges for ambient intelligence and implications for design contexts and smart societies. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2019, 11, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, R.; Rodrigues, L.; Hughes, N.; Greenhalgh, C.; Goulden, M.; Tennison, J. What Smart Campuses Can Teach Us about Smart Cities: User Experiences and Open Data. Information 2018, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, O.; Friday, A. Beyond Data in the Smart City: Repurposing Existing Campus IoT. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2017, 16, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzamany, E.; Barrett, J. Smart Campus: A Route Using 4G and 5G to Serve the Smart City; JISC Report; JISC: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A.K. Understanding and Using Context. Int. J. Person. Ubiquitous Comput. 2001, 5, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M. The computer for the 21st century. SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 1999, 3, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, J.C. Ambient Intelligence: The Confluence of Ubiquitous/Pervasive Computing and Artificial Intelligence. In Intelligent Computing Everywhere; Shuster, A.J., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2007; pp. 213–234. ISBN 978-1-84628-942-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sadri, F. Ambient intelligence: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2011, 43, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.J.; Augusto, J.C.; Jakkula, V.R. Ambient intelligence: Technologies, applications, and opportunities. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2009, 5, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychoudhury, V.; Cao, J.; Kumar, M.; Zhang, D. Middleware for pervasive computing: A survey. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2013, 9, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikakis, A.; Patkos, T.; Antoniou, G.; Plexousakis, D. A survey of semantics-based approaches for context reasoning in ambient intelligence. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2008, 11, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ben Allouch, S.; van Dijk, J.A.G.M.; Peters, O. The Acceptance of Domestic Ambient Intelligence Appliances by Prospective Users. In Pervasive Computing; Tokuda, H., Beigl, M., Friday, A., Brush, A.J.B., Tobe, Y., Eds.; LNCS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 5538. [Google Scholar]
- Wiegerling, K. The Question of Ethics in Ambient Intelligence. In Ubiquitous Computing in the Workplace; Kinder-Kurlanda, K., Nihan, C.E., Eds.; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 333. [Google Scholar]
- Acampora, G.; Cook, D.J.; Rashidi, P.; Vasilakos, A.V. A Survey on Ambient Intelligence in Health Care. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 2470–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Robledo, L.A.; Peña-Ayala, A. Ubiquitous learning: A systematic review. Telematics Inf. 2018, 35, 1097–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tentori, M.; Escobedo, L.; Balderas, G. A Smart Environment for Children with Autism. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2015, 14, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, M.A.; Haavisto, E.; Liikanen, E.; Kääriäinen, M. Students’ perceptions on the use of a ubiquitous 360° learning environment in histotechnology: A pilot study. J. Histotechnol. 2018, 41, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.D.; Favela, J.; Preciado, A.; Vizcaino, A. Agent-based ambient intelligence for healthcare. AI Commun. 2005, 18, 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Yang, T.-C.; Tsai, C.-C.; Yang, S.J.H. A context-aware ubiquitous learning environment for conducting complex science experiments. Comput. Educ. 2009, 53, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kray, C.; Kortuem, G.; Wasinger, R. Concepts and issues in interfaces for multiple users and multiple devices. In Workshop on Multi-User and Ubiquitous User Interfaces (MU3I) at IUI 2004; Funchal: Madeira, Portugal, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bettini, C.; Brdiczka, O.; Henricksen, K.; Indulska, J.; Nicklas, D.; Ranganathan, A.; Riboni, D. A survey of context modelling and reasoning techniques. Pervasive Mobile Comput. 2010, 6, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, C.; Zaslavsky, A.; Christen, P.; Georgakopoulos, D. Context Aware Computing for The Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 414–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Dobson, S.; McKeever, S. Situation identification techniques in pervasive computing: A review. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2012, 8, 36–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, J.; Thomas, B.L.; Cook, D.J.; Wang, X. Activity Learning as a Foundation for Security Monitoring in Smart Homes. Sensors 2017, 17, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaull, J.; Augusto, J.C.; Mulvenna, M.; McCullagh, P. Data and Information Quality Issues in Ambient Assisted Living Systems. J. Data Inf. Q. 2012, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henricksen, K.; Indulska, J. Modelling and using imperfect context information. In Proceedings of the IEEE Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops, Orlando, FL, USA, 14–17 March 2004; pp. 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Budde, M.; Schankin, A.; Hoffmann, J.; Danz, M.; Riedel, T.; Beigl, M. Participatory Sensing or Participatory Nonsense?—Mitigating the Effect of Human Error on Data Quality in Citizen Science. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmansour, A.; Bouchachia, A.; Feham, M. Multioccupant Activity Recognition in Pervasive Smart Home Environments. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 48, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, A.; Cook, D.J. Learning Activity Models for Multiple Agents in a Smart Space. In Handbook of Ambient Intelligence and Smart Environments; Nakashima, H., AghajanJuan, H., Augusto, J.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 751–769. [Google Scholar]
- Alhamoud, A.; Muradi, V.; Böhnstedt, D.; Steinmetz, R. Activity Recognition in Multi-User Environments Using Techniques of Multi-label Classification. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on the Internet of Things (IoT’16), Stuttgart, Germany, 7–9 November 2016; pp. 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ditzler, G.; Roveri, M.; Alippi, C.; Polikar, R. Learning in Nonstationary Environments: A Survey. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2015, 10, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, J.; Žliobaitė, I.; Bifet, A.; Pechenizkiy, M.; Bouchachia, A. A survey on concept drift adaptation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2014, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidyuk, O.; Sánchez, I.M.; Gilman, E.; Riekki, J. An overview of interactive application composition approaches. Open Comput. Sci. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemantsverdriet, K.; Broekhuijsen, M.; van Essen, H.; Eggen, B. Designing for Multi-User Interaction in the Home Environment: Implementing Social Translucence. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM Conference on Designing Interactive Systems (DIS ’16), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 4–8 June 2016; pp. 1303–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Davidyuk, O.; Gilman, E.; Sánchez, I.M.; Makipelto, J.; Pyykkonen, M.; Riekki, J. iCompose: Context-aware physical user interface for application composition. Central Eur. J. Comput. Sci. 2011, 1, 442–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurmu, M.; Perttunen, M.; Riekki, J. Lease-Based Resource Management in Smart Spaces. In Proceedings of the Fifth Annual IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerComW’07), White Plains, NY, USA, 19–23 March 2007; pp. 622–626. [Google Scholar]
- Pakanen, M.; Lovén, L.; Alavesa, P.; Gilman, E.; Terken, J.; Eggen, B.; Pirttikangas, S. Design Challenges of Wellbeing Supporting Smart Environment in Collaborative Use Situations. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM International Joint Conference and 2018 International Symposium on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and Wearable Computers (UbiComp ’18), Singapore, 8–12 October 2018; pp. 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Niemantsverdriet, K.; Essen, H.; Eggen, B. A perspective on multi-user interaction design based on an understanding of domestic lighting conflicts. Personal Ubiquitous Comput. 2017, 21, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, R. The ethics of smart cities and urban science. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2016, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, G.; Botterman, M.; Neisse, R. Ethical Design in the Internet of Things. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2018, 24, 905–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ienca, M.; Wangmo, T.; Jotterand, F.; Kressig, R.W.; Elger, B. Ethical Design of Intelligent Assistive Technologies for Dementia: A Descriptive Review. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2018, 24, 1035–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The IEEE Global Initiative on Ethics of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems, Ethically Aligned Design, 1st ed.; A Vision for Prioitizing Human Well-being with Autonomous and Intelligent Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- High-Level Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence; Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- Muhamad, W.; Kurniawan, N.B.; Yazid, S. Smart campus features, technologies, and applications: A systematic literature review. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 October 2017; pp. 384–391. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, L. A vision for the development of i-campus. Smart Learn. Environ. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galego, D.; Giovannella, C.; Mealha, O. Determination of the Smartness of a University Campus: The Case Study of Aveiro. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 223, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atif, Y.; Mathew, S.S.; Lakas, A. Building a smart campus to support ubiquitous learning. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 2015, 6, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caramés, T.M.; Fraga-Lamas, P. Towards Next Generation Teaching, Learning, and Context-Aware Applications for Higher Education: A Review on Blockchain, IoT, Fog and Edge Computing Enabled Smart Campuses and Universities. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R.; Pombeiro, H.; Silva, C.; Carreira, P.; Carvalho, M.; Almeida, G.; Domingues, P.; Ferrão, P. Towards a Smart Campus: Building-User Learning Interaction for Energy Efficiency, the Lisbon Case Study. In Handbook of Theory and Practice of Sustainable Development in Higher Education; World Sustainability Series; Leal Filho, W., Brandli, L., Castro, P., Newman, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Saez, B.; Szczechowicz, J.; Ruisi, J.; Kraft, T.; Toscano, S.; Vacco, Z.; Nicolas, K. A smart campus internet of things framework. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 8th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 498–503. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, J.; Hume, D. Campus IoT Collaboration and Governance Using the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. In Proceedings of the IoT-2018, London, UK, 28–29 March 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Prandi, C.; Monti, L.; Ceccarini, C.; Salomoni, P. Smart Campus: Fostering the Community Awareness through an Intelligent Environment. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2020, 25, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, Y. The research of smart campus based on Internet of Things & cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM 2015), Shanghai, China, 21–23 September 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Haghi, A.; Burney, K.; Kidd, F.S.; Valiente, L.; Peng, Y. Fast-paced development of a smart campus IoT platform. In Proceedings of the 2017 Global Internet of Things Summit (GIoTS), Geneva, Switzerland, 6–9 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shou, G.; Hu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, H.; Peng, F.; Seah, H.S. Towards a smart campus: Innovative applications with WiCloud platform based on mobile edge computing. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Computer Science and Education (ICCSE), Houston, TX, USA, 22–25 August 2017; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Celdrán, A.H.; Garcia, F.; Saenz, J.; De La Torre, L.; Salzmann, C.; Gillet, D. Self-Organized Laboratories for Smart Campus. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2019, 13, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, R.; Petäjäjärvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pouttu, A. Large and Dense LoRaWAN Deployment to Monitor Real Estate Conditions and Utilization Rate. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Bologna, Italy, 9–12 September 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmin, R.; Salminen, M.; Gilman, E.; Petäjäjärvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pakanen, M.; Niemelä, A.; Riekki, J.; Pirttikangas, S.; Pouttu, A. Combining IoT Deployment and Data Visualization: Experiences within campus maintenance use-case. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on the Networks of the Future, Poznań, Poland, 19–21 November 2018; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.A.; Waibel, A.; Soundararajan, E. Anomaly Prediction in Non-Stationalry Signals using Neural Network Based Multi-Perspective Analysis. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, J.; Mishra, B. Customized IoT Enabled Wireless Sensing and Monitoring Platform for Smart Buildings. Procedia Tech. 2016, 23, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.; Pitarma, R. An Indoor Monitoring System for Ambient Assisted Living Based on Internet of Things Architecture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F.; Trilles, S.; Torres-Sospedra, J.; Perales, F.J. New Trends in Using Augmented Reality Apps for Smart City Contexts. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.; Kim, G.J. AR Enabled IoT for a Smart and Interactive Environment: A Survey and Future Directions. Sensors 2019, 19, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.-P.; van Treeck, C.; Frisch, J. Visualization of indoor thermal environment on mobile devices based on augmented reality and computational fluid dynamics. Autom. Constr. 2019, 103, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.; Feiner, S. SiteLens: Situated visualization techniques for urban site visits. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ’09), Boston, MA, USA, 4–9 April 2009; pp. 1117–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Gilman, E.; Davidyuk, O.; Su, X.; Riekki, J. Towards interactive smart spaces. J. Ambient Intell. Smart Environ. 2013, 5, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bakker, C.; Aarts, M.; Kort, H.; Rosemann, A. The feasibility of highly granular lighting control in open-plan offices: Exploring the comfort and energy saving potential. Build. Environ. 2018, 142, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, H.; Chien, S.-C.; Xie, L.; Spanos, C.J. WinLight: A WiFi-based occupancy-driven lighting control system for smart building. Energy Build. 2018, 158, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G Test Network. Available online: https://5gtn.fi (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Fabrication Laboratory (Fab Lab). Available online: https://www.oulu.fi/fablab (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Zhao, K.; Ge, L. A Survey on the Internet of Things Security. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security, Leshan, China, 14–15 December 2013; pp. 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Bettini, C.; Riboni, D. Privacy protection in pervasive systems: State of the art and technical challenges. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2015, 17, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU General Data Protection Regulation. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:32016R0679&from=EN (accessed on 30 June 2020).
- Acquisti, A.; Gross, R.; Stutzman, F.D. Face Recognition and Privacy in the Age of Augmented Reality. J. Priv. Confid. 2014, 6, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Cornelius, C.; Peebles, D.; Kapadia, A.; Kotz, D.; Triandopoulos, N. AnonySense: A system for anonymous opportunistic sensing. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2011, 7, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilman, E.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Tamminen, S.; Pirttikangas, S.; Röning, J.; Riekki, J. Personalised assistance for fuel-efficient driving. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2015, 58, 681–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutjarittham, T.; Gharakheili, H.H.; Kanhere, S.S.; Sivaraman, V. Realizing a Smart University Campus: Vision, Architecture, and Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Networks and Telecommunications Systems (ANTS), Indore, India, 16–19 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rohunen, A.; Liinasuo, M.; Peltola, J.; Immonen, M.; Siirtola, P.; Jukkanen, M.; Malmivaara, M.; Hiekkanen, K.; Pirttikangas, S. Artificial intelligence application utilising employees’ personal data: Data privacy legislation’s requirements, employee perspective and ethical considerations. in press.
- Kostakos, V.; Rogstadius, J.; Ferreira, D.; Hosio, S.; Goncalves, J. Human Sensors. In Participatory Sensing, Opinions and Collective Awareness, Understanding Complex Systems; Loreto, V., Haklay, M., Hotho, A., Servedio, V.D.P., Stumme, G., Theunis, J., Tria, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gilman, E.; Tamminen, S.; Yasmin, R.; Ristimella, E.; Peltonen, E.; Harju, M.; Lovén, L.; Riekki, J.; Pirttikangas, S. Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 3716. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133716
Gilman E, Tamminen S, Yasmin R, Ristimella E, Peltonen E, Harju M, Lovén L, Riekki J, Pirttikangas S. Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study. Sensors. 2020; 20(13):3716. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133716
Chicago/Turabian StyleGilman, Ekaterina, Satu Tamminen, Rumana Yasmin, Eemeli Ristimella, Ella Peltonen, Markus Harju, Lauri Lovén, Jukka Riekki, and Susanna Pirttikangas. 2020. "Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study" Sensors 20, no. 13: 3716. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133716
APA StyleGilman, E., Tamminen, S., Yasmin, R., Ristimella, E., Peltonen, E., Harju, M., Lovén, L., Riekki, J., & Pirttikangas, S. (2020). Internet of Things for Smart Spaces: A University Campus Case Study. Sensors, 20(13), 3716. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20133716






