Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
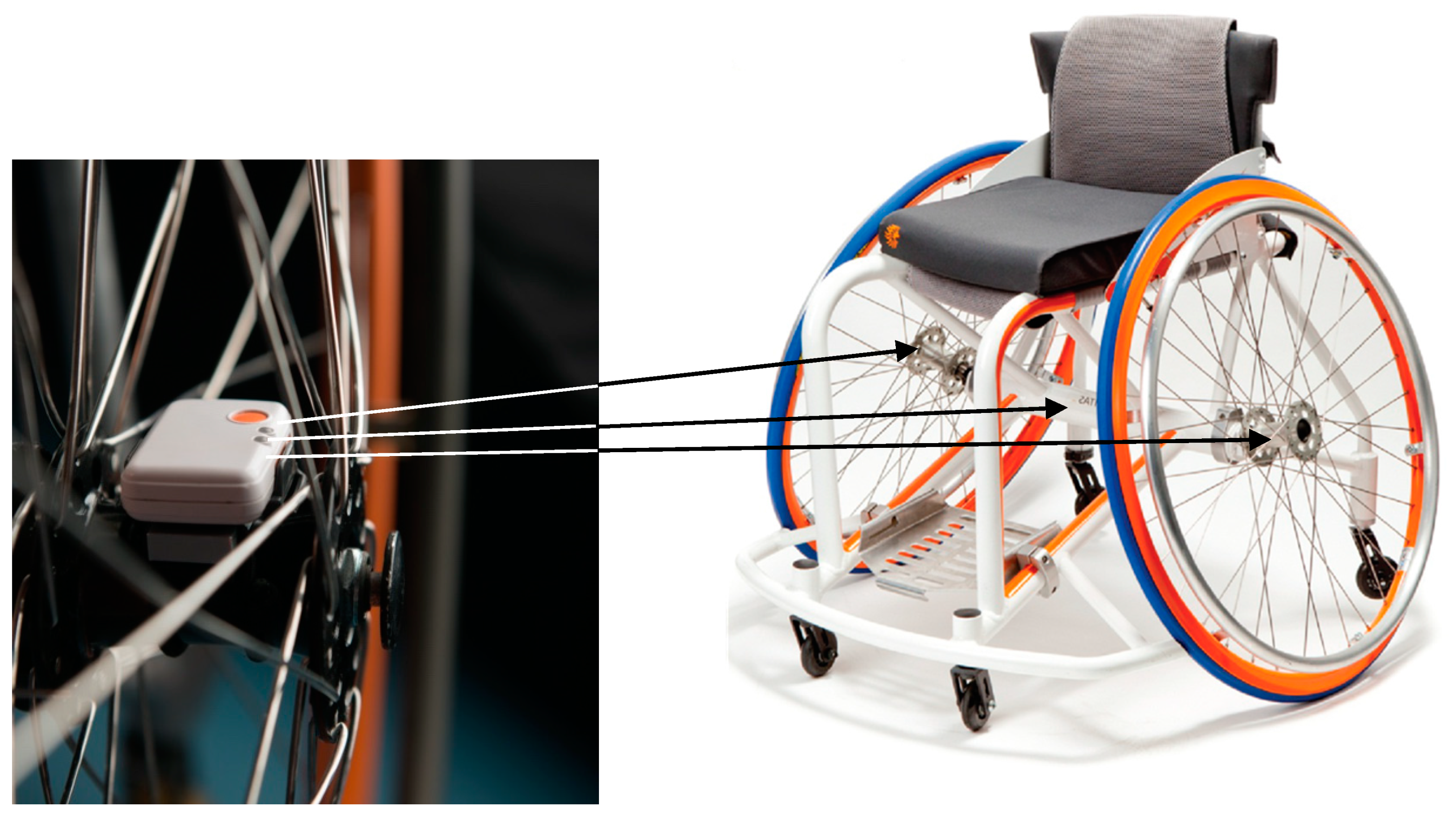
2.2. Methodology
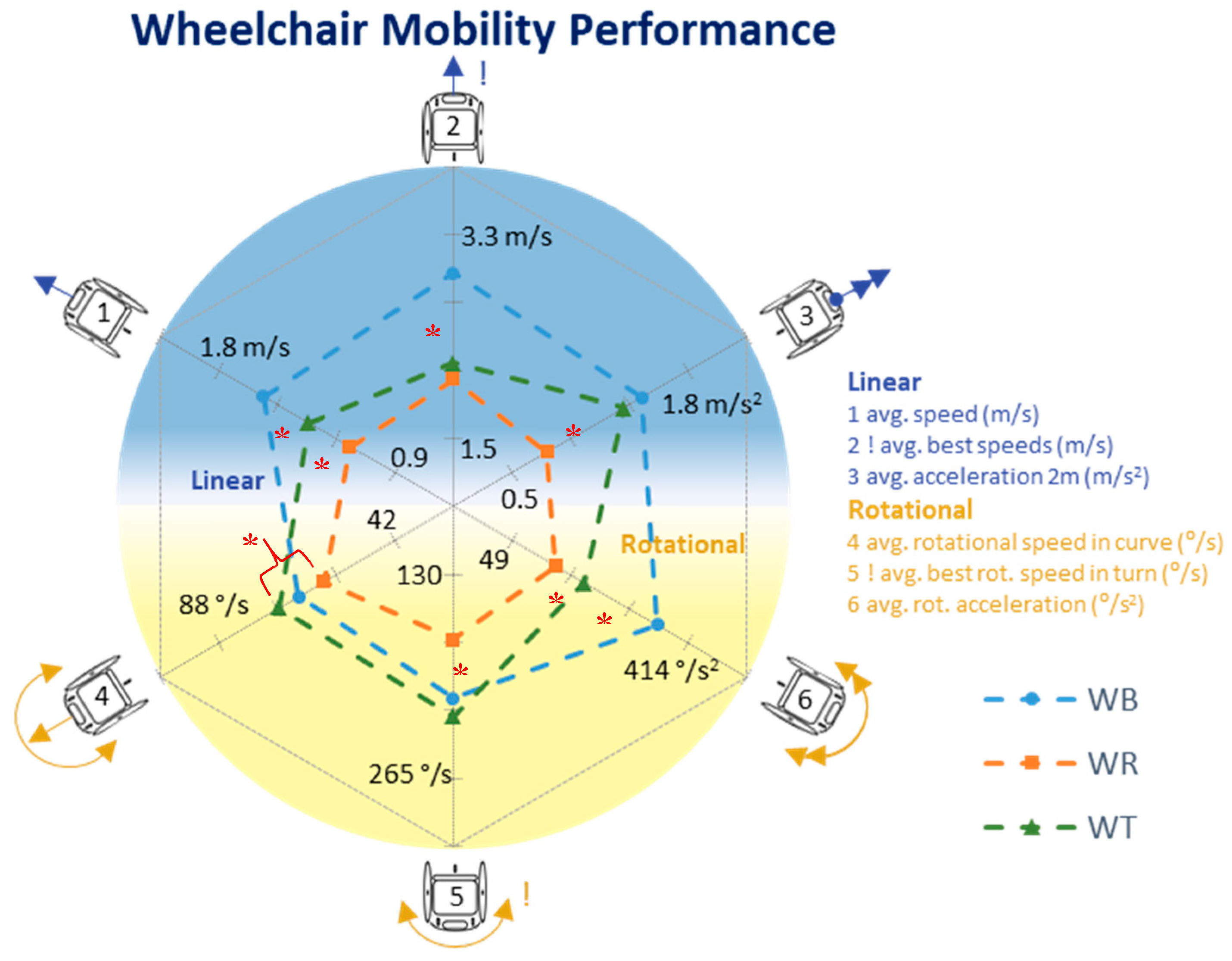
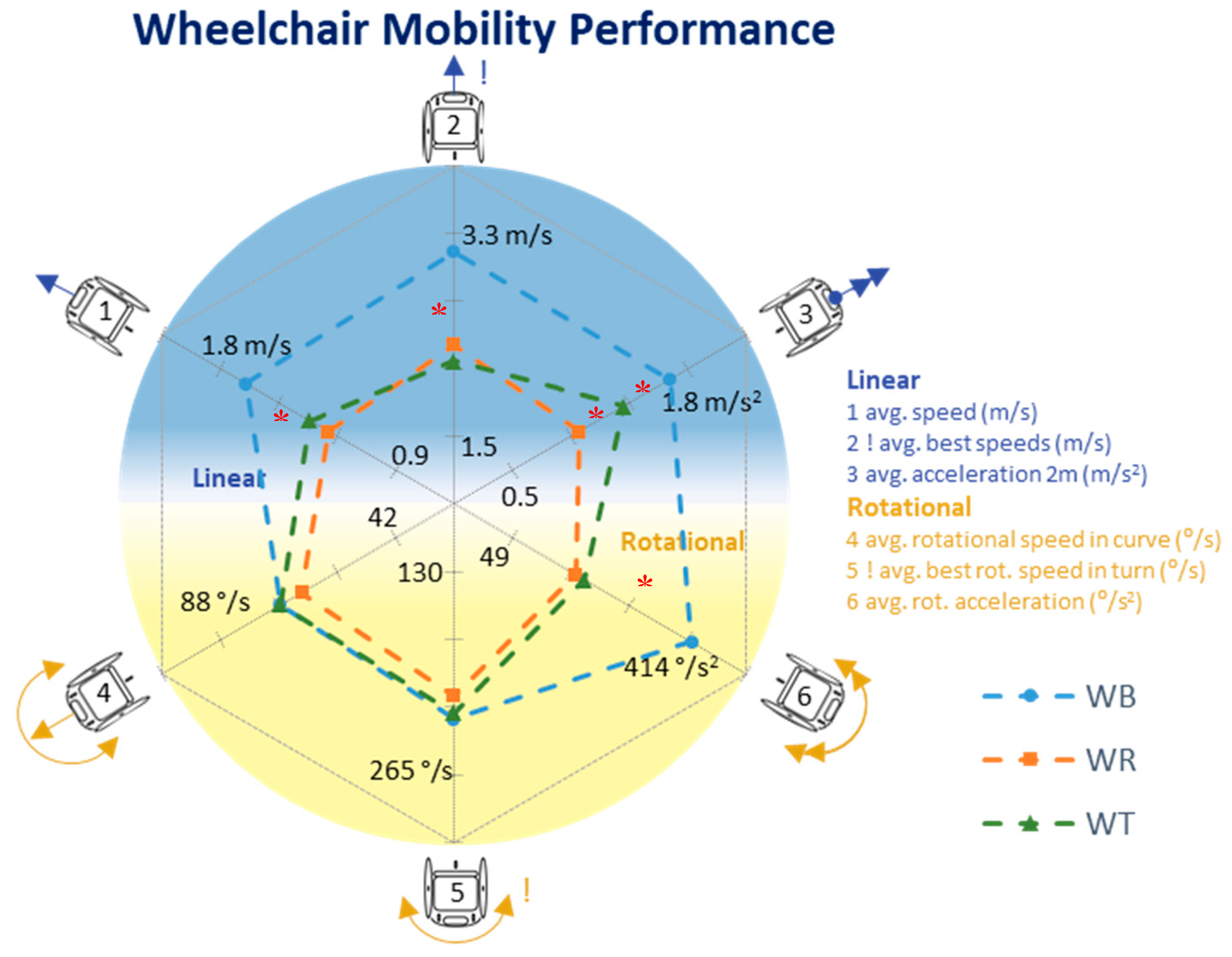
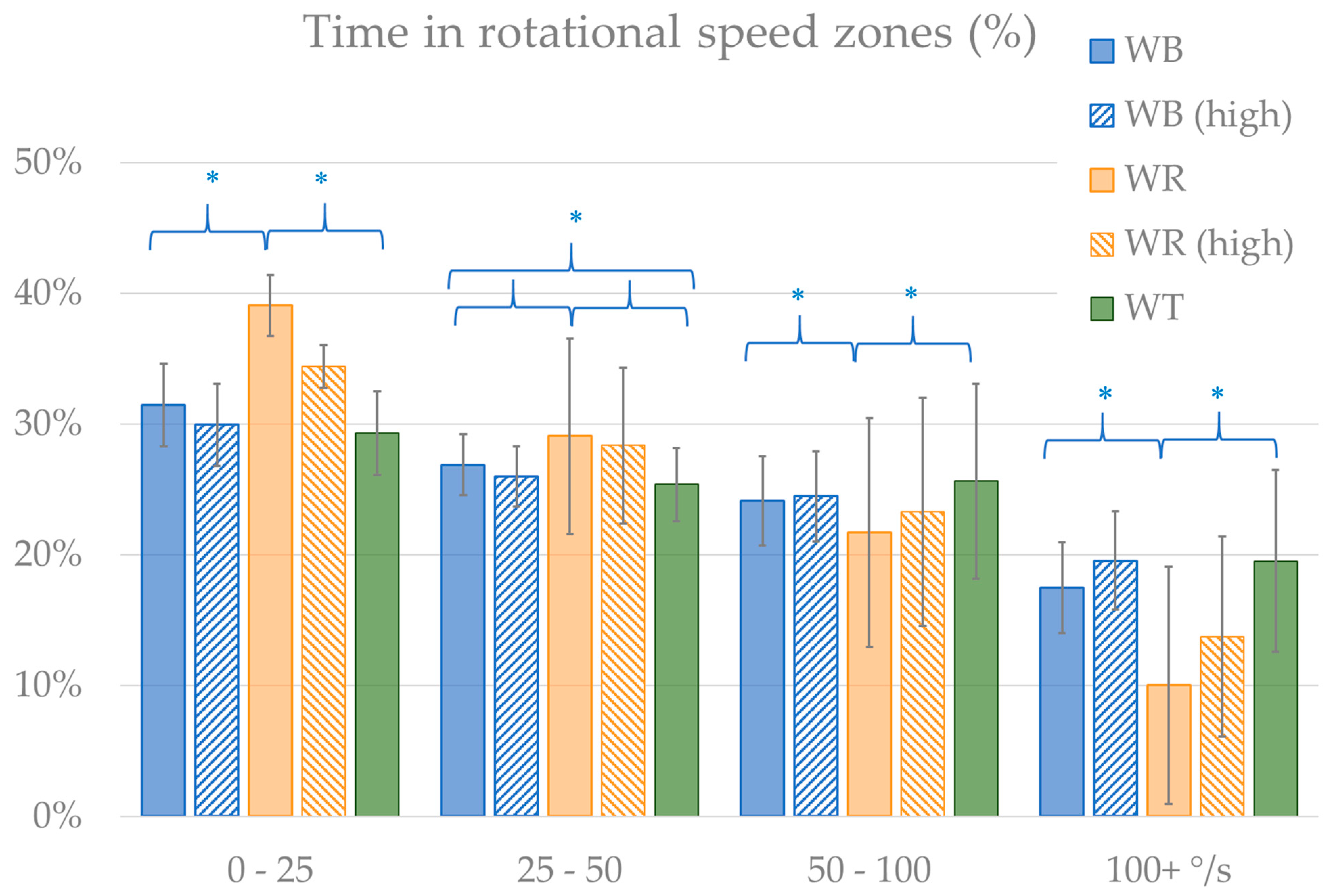
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Wheelchair Mobility Performance Quantified
4.2. Implications for Classification and Training
4.3. WMPM Use in Sports Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Wheelchair Components
- Wheelchair weight and dimensions
Appendix A.2. Sport Components
- Court dimensions and ratio
- Ball and racket handling
- Physiology and intensity
Appendix A.3. Differences Quantified
| Wheelchair Basketball vs. Wheelchair Rugby | Wheelchair Basketball vs. Wheelchair Tennis | Wheelchair Tennis vs. Wheelchair Rugby | ||||||||||||||||||||
| All | 95% | Confidence | Effect Size | 95% | Confidence | 95% | Confidence | |||||||||||||||
| Interval | Interval | Interval | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | ||||||||
| Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | ||
| WMP | Avg. forward speed (m/s) | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.000 | 0.32 | 0.57 | 2.13 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.07 | 0.38 | 1.79 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.06 | 0.003 | 0.06 | 0.36 | 1.01 | 0.20 |
| Best forward speed (m/s) | 0.94 | 0.11 | 0.000 | 0.68 | 1.20 | 2.11 | 0.25 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 0.000 | 0.47 | 1.11 | 4.18 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.746 | −0.17 | 0.47 | 0.35 | 0.09 | |
| Avg. acceleration to 2 m (m/s2) | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.000 | 0.51 | 0.89 | 2.25 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.541 | −0.11 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.10 | 0.000 | 0.33 | 0.80 | 1.77 | 0.25 | |
| Avg. rotational speed in a curve (°/s) | 6.59 | 3.84 | 0.272 | −2.82 | 16.00 | 0.41 | 0.10 | −5.14 | 4.76 | 0.853 | −16.81 | 6.53 | −0.63 | −0.14 | 11.72 | 4.69 | 0.044 | 0.24 | 23.21 | 0.75 | 0.16 | |
| Best rotational speed in a turn (°/s) | 38.8 | 10.2 | 0.001 | 13.8 | 63.9 | 0.94 | 0.19 | −12.5 | 12.7 | 0.979 | −43.6 | 18.5 | −0.44 | −0.11 | 51.4 | 12.5 | 0.000 | 20.8 | 81.9 | 1.22 | 0.22 | |
| Avg. rotational acceleration (°/s2) | 211.7 | 19.2 | 0.000 | 164.6 | 258.7 | 2.52 | 0.24 | 152.0 | 23.8 | 0.000 | 93.6 | 210.4 | 1.90 | 0.25 | 59.7 | 23.4 | 0.039 | 2.2 | 117.1 | 1.67 | 0.25 | |
| Max | Maximal forward speed (m/s) | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.000 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.11 | 0.25 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.039 | 0.0 | 1.1 | 1.40 | 0.23 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.000 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 1.36 | 0.23 |
| Maximal rotational speed (°/s) | 85.4 | 18.1 | 0.000 | 41.0 | 129.7 | 1.14 | 0.21 | 18.6 | 23.0 | 1.000 | −37.7 | 74.9 | 0.32 | 0.08 | 66.8 | 22.6 | 0.013 | 11.3 | 122.2 | 1.04 | 0.21 | |
| Speed zones | Speed <0 m/s | 3.5% | 0.7% | 0.000 | 1.7% | 5.3% | 1.25 | 0.22 | 3.8% | 0.9% | 0.000 | 1.6% | 6.1% | 1.21 | 0.22 | −0.4% | 0.9% | 1.000 | −2.5% | 1.8% | −0.13 | −0.03 |
| Speed between 0–0.5 m/s | −7.2% | 1.3% | 0.000 | −10.5% | −3.9% | −1.30 | −0.23 | 1.8% | 1.7% | 0.809 | −2.2% | 5.9% | 0.72 | 0.16 | −9.1% | 1.6% | 0.000 | −13.1% | −5.0% | −1.60 | −0.24 | |
| Speed between 0.5–1.5 m/s | −11.4% | 1.8% | 0.000 | −15.8% | −7.1% | −1.72 | −0.25 | −9.8% | 2.2% | 0.000 | −15.2% | −4.5% | −1.69 | −0.25 | −1.6% | 2.2% | 1.000 | −6.9% | 3.7% | −0.20 | −0.05 | |
| Speed between 1.5–2.5 m/s | 3.6% | 1.8% | 0.149 | −0.8% | 8.0% | 0.52 | 0.12 | −7.1% | 2.2% | 0.006 | −12.6% | −1.7% | −1.30 | −0.23 | 10.7% | 2.2% | 0.000 | 5.4% | 16.1% | 1.33 | 0.23 | |
| Speed above 2.5 m/s | 11.6% | 1.2% | 0.000 | 8.7% | 14.4% | 2.39 | 0.25 | 11.3% | 1.5% | 0.000 | 7.7% | 14.8% | 3.72 | 0.21 | 0.3% | 1.4% | 1.000 | −3.2% | 3.8% | 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| Rota-tional speed zones | Abs. rot. speed betw. 0–25 °/s | −7.6% | 1.2% | 0.000 | −10.6% | −4.6% | −1.55 | −0.24 | 2.2% | 1.5% | 0.474 | −1.6% | 5.9% | 0.66 | 0.15 | −9.8% | 1.5% | 0.000 | −13.4% | −6.1% | −1.87 | −0.25 |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 25–50 °/s | −2.2% | 0.4% | 0.000 | −3.1% | −1.2% | −1.61 | −0.24 | 1.5% | 0.5% | 0.008 | 0.3% | 2.7% | 0.87 | 0.18 | −3.7% | 0.5% | 0.000 | −4.9% | −2.5% | −2.10 | −0.25 | |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 50–100 °/s | 2.4% | 0.6% | 0.000 | 1.0% | 3.9% | 1.09 | 0.21 | −1.5% | 0.7% | 0.129 | −3.2% | 0.3% | −0.91 | −0.19 | 3.9% | 0.7% | 0.000 | 2.2% | 5.7% | 1.52 | 0.24 | |
| Abs. rot. speed above 100 °/s | 7.4% | 1.0% | 0.000 | 4.9% | 10.0% | 2.01 | 0.25 | −2.1% | 1.3% | 0.349 | −5.2% | 1.1% | −0.48 | −0.11 | 9.5% | 1.3% | 0.000 | 6.4% | 12.6% | 2.00 | 0.25 | |
| Wheelchair basketball vs. wheelchair rugby | Wheelchair basketball vs. wheelchair tennis | Wheelchair tennis vs. wheelchair rugby | ||||||||||||||||||||
| “High-class” | 95% Confidence Interval | Effect size | 95% Confidence Interval | 95% Confidence Interval | ||||||||||||||||||
| Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | Mean | Std. | Lower | Upper | Cohen’s | ||||||||
| Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | Diff. | Error | Sig. | Bound | Bound | d | ryλ | ||
| WMP | Avg. forward speed (m/s) | 0.42 | 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 2.04 | 0.25 | 0.33 | 0.07 | 0.000 | 0.15 | 0.50 | 2.76 | 0.24 | 0.10 | 0.07 | 0.532 | −0.08 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.11 |
| Best forward speed (m/s) | 0.83 | 0.14 | 0.000 | 0.47 | 1.18 | 1.93 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.13 | 0.000 | 0.63 | 1.31 | 6.54 | 0.14 | −0.14 | 0.13 | 0.870 | −0.48 | 0.19 | −0.34 | −0.08 | |
| Avg. acceleration to 2 m (m/s2) | 0.68 | 0.13 | 0.000 | 0.35 | 1.00 | 2.02 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.12 | 0.024 | 0.04 | 0.65 | 1.34 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.031 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 0.93 | 0.19 | |
| Avg. rotational speed in a curve (°/s) | 5.61 | 4.21 | 0.572 | −4.95 | 16.18 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.06 | 3.99 | 1.000 | −9.97 | 10.09 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 5.55 | 3.99 | 0.518 | −4.47 | 15.58 | 0.46 | 0.11 | |
| Best rotational speed in a turn (°/s) | 15.1 | 12.1 | 0.656 | −15.2 | 45.4 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 3.5 | 11.4 | 1.000 | −25.2 | 32.2 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 0.953 | −17.1 | 40.3 | 0.36 | 0.09 | |
| Avg. rotational acceleration (°/s2) | 241.3 | 28.6 | 0.000 | 169.4 | 313.2 | 2.76 | 0.24 | 223.1 | 27.2 | 0.000 | 154.9 | 291.3 | 2.59 | 0.24 | 18.2 | 27.2 | 1.000 | −50.0 | 86.4 | 0.62 | 0.14 | |
| Max | Maximal forward speed (m/s) | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.000 | 0.7 | 1.9 | 1.85 | 0.25 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.003 | 0.2 | 1.4 | 2.02 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.163 | −0.1 | 1.0 | 0.67 | 0.15 |
| Maximal rotational speed (°/s) | 57.0 | 25.2 | 0.090 | −6.4 | 120.4 | 0.81 | 0.17 | 54.2 | 24.3 | 0.096 | −6.9 | 115.3 | 0.84 | 0.18 | 2.8 | 24.3 | 1.000 | −58.3 | 63.9 | 0.05 | 0.01 | |
| Speed zones | Speed <0 m/s | 3.3% | 1.1% | 0.018 | 0.5% | 6.2% | 1.33 | 0.23 | 4.3% | 1.1% | 0.001 | 1.6% | 7.0% | 1.36 | 0.23 | −1.0% | 1.1% | 1.000 | −3.7% | 1.7% | −0.38 | −0.09 |
| Speed between 0–0.5 m/s | −5.5% | 1.6% | 0.005 | −9.6% | −1.5% | −1.22 | −0.22 | 1.1% | 1.5% | 1.000 | −2.7% | 5.0% | 0.44 | 0.11 | −6.7% | 1.5% | 0.000 | −10.5% | −2.8% | −1.43 | −0.24 | |
| Speed between 0.5–1.5 m/s | −10.0% | 2.8% | 0.004 | −17.2% | −2.9% | −1.51 | −0.24 | −11.9% | 2.7% | 0.000 | −18.7% | −5.1% | −2.04 | −0.25 | 1.9% | 2.7% | 1.000 | −4.9% | 8.6% | 0.23 | 0.06 | |
| Speed between 1.5–2.5 m/s | 2.0% | 2.6% | 1.000 | −4.6% | 8.5% | 0.33 | 0.08 | −7.0% | 2.5% | 0.022 | −13.3% | −0.8% | −1.26 | −0.23 | 9.0% | 2.5% | 0.003 | 2.8% | 15. | 1.24 | 0.22 | |
| Speed above 2.5 m/s | 10.2% | 1.9% | 0.000 | 5.5% | 15.0% | 1.86 | 0.25 | 13.5% | 1.8% | 0.000 | 9.0% | 18.0% | 4.58 | 0.18 | −3.2% | 1.8% | 0.233 | −7.7% | 1.2% | −0.61 | −0.14 | |
| Rota-tional speed zones | Abs. rot. speed betw. 0–25 °/s | −4.4% | 1.4% | 0.012 | −8.1% | −0.8% | −1.31 | −0.23 | 0.6% | 1.4% | 1.000 | −2.8% | 4.1% | 0.20 | 0.05 | −5.1% | 1.4% | 0.002 | −8.5% | −1.6% | −1.30 | −0.23 |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 25–50 °/s | −2.4% | 0.6% | 0.002 | −4.0% | −0.8% | −1.98 | −0.25 | 0.6% | 0.6% | 0.973 | −0.9% | 2.2% | 0.39 | 0.09 | −3.0% | 0.6% | 0.000 | −4.5% | −1.4% | −1.69 | −0.25 | |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 50–100 °/s | 1.2% | 0.8% | 0.504 | −0.9% | 3.3% | 0.58 | 0.13 | −1.1% | 0.8% | 0.474 | −3.1% | 0.8% | −0.69 | −0.15 | 2.3% | 0.8% | 0.018 | 0.3% | 4.3% | 0.97 | 0.20 | |
| Abs. rot. speed above 100 °/s | 5.8% | 1.5% | 0.002 | 1.9% | 9.7% | 2.43 | 0.25 | 0.0% | 1.5% | 1.000 | −3.6% | 3.7% | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.8% | 1.5% | 0.001 | 2.1% | 9.4% | 1.39 | 0.23 | |
References
- Goosey-Tolfrey, V. Supporting the Paralympic athlete: Focus on wheeled sports. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Veeger, H.E.J. From big data to rich data: The key features of athlete wheelchair mobility performance. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3340–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Lagerberg, A.H.; Veeger, H.E.J. Opportunities for measuring wheelchair kinematics in match settings; reliability of a three inertial sensor configuration. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 3398–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Veeger, H.E.J. Wheel Skid Correction is a Prerequisite to Reliably Measure Wheelchair Sports Kinematics Based on Inertial Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2015, 112, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, T.; Vegter, R.J.; Van der Slikke, R.M.; Hoekstra, A.E.; Van der Woude, L.H.; De Groot, S. Wheelchair mobility performance of elite wheelchair tennis players during four field tests: Inter-trial reliability and construct validity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, B.S.; Van der Woude, L.H.V.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. The ergonomics of wheelchair configuration for optimal performance in the wheelchair court sports. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydon, D.S.; Pinder, R.A.; Grimshaw, P.N.; Robertson, W.S. Wheelchair Rugby chair configurations: An individual, Robust design approach. Sports Biomech. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeger, T.T.; De Witte, A.M.; Berger, M.A.; Van der Slikke, R.M.; Veeger, D.H.; Hoozemans, M.J. Improving mobility performance in wheelchair basketball. J. Sport Rehabil. 2019, 28, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedy, S.M.; Vanlandewijck, Y.C. International Paralympic Committee position stand—Background and scientific principles of classification in Paralympic sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.; Bregman, D.J.; Berger, M.A.; De Witte, A.M. The future of classification in wheelchair sports: Can data science and technological advancement offer an alternative point of view? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pansiot, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lo, B.; Yang, Z.G. WISDOM: Wheelchair inertial sensors for displacement and orientation monitoring. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 105801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, F.K. Speed measurements in wheelchair sports–theory and application. Sports Technol. 2012, 5, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.M.; Mason, B.S.; Malone, L.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Effect of team rank and player classification on activity profiles of elite wheelchair rugby players. J. Sports Sci. 2015, 33, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sindall, P.; Lenton, J.P.; Whytock, K.; Tolfrey, K.; Oyster, M.L.; Cooper, R.A.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Criterion validity and accuracy of global positioning satellite and data logging devices for wheelchair tennis court movement. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2013, 36, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.S.; Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hutchinson, M.J.; Berger, M.A.M.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. The effect of small-sided game formats on physical and technical performance in wheelchair basketball. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 13, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.S.; Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Hutchinson, M.J.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Division, result and score margin alter the physical and technical performance of elite wheelchair tennis players. J. Sports Sci. 2020, 38, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Mason, B.S.; Berger, M.A.M.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L. Speed profiles in wheelchair court sports; comparison of two methods for measuring wheelchair mobility performance. J. Biomech. 2017, 65, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Berger, M.A.M.; Veeger, H.E.J. Wheelchair Mobility Performance enhancement by changing wheelchair properties; what is the effect of grip, seat height and mass? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.; Bos, F.; Koopman, J.; Hoekstra, A.; Vegter, R. Effect of holding a racket on propulsion technique of wheelchair tennis players. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.A.; De Luigi, A.J. Adaptive sports technology and biomechanics: Wheelchairs. PM&R 2014, 6, S31–S39. [Google Scholar]
- Vanlandewijck, Y.C.; Verellen, J.; Tweedy, S. Towards evidence-based classification in wheelchair sports: Impact of seating position on wheelchair acceleration. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Witte, A.M.H.; van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Hoozemans, M.J.; Veeger, H.E.J.; van der Woude, L.H.V. Effects of seat height, wheelchair mass and additional grip on a field-based wheelchair basketball mobility performance test. Technol. Disabil. 2020, 32, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L.; Moss, A.D. Wheelchair velocity of tennis players during propulsion with and without the use of racquets. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2005, 22, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, L.; Dybrus, S.; Lenton, J.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.A. Comparison of the physiological demands of wheelchair basketball and wheelchair tennis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, K. Heart rates of participants in wheelchair sports. Spinal Cord 1988, 26, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barfield, J.; Malone, L.A.; Arbo, C.; Jung, A.P. Exercise intensity during wheelchair rugby training. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, T.; Platen, P.; Vega, S.R.; Schneider, S.; Strüder, H. Energy expenditure in ball games for wheelchair users. Spinal Cord 2008, 46, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Hilsdale, N.J., Ed.; Lawrence Earlbaum Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]

| Sport | Class | Class | Sex | Level | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.5 | NA | Low/High | M/F | Int./Nat. | |
| Basketball | 29 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 17/12 | 20/9 | 12/17 | |||
| Rugby | 32 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 20/12 | 29/3 | 13/19 | |||
| Tennis | 15 | 15 | 0/15 | 4/11 | 5/10 |
| All | Total (n = 76) | Basketball (n = 29) | Rugby (n = 32) | Tennis (n = 15) | |||||
| Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | ||
| WMP | Avg. forward speed (m/s) | 1.34 | 0.28 | 1.57 | 0.13 | 1.13 | 0.27 | 1.34 | 0.13 |
| Best forward speed (m/s) | 2.41 | 0.60 | 2.96 | 0.23 | 2.02 | 0.59 | 2.17 | 0.14 | |
| Avg. acceleration to 2 m (m/s2) | 1.14 | 0.45 | 1.46 | 0.26 | 0.76 | 0.35 | 1.33 | 0.29 | |
| Avg. rotational speed in a curve (°/s) | 65 | 15 | 67 | 9 | 60 | 21 | 72 | 8 | |
| Best rotational speed in a turn (°/s) | 198 | 45 | 212 | 28 | 173 | 52 | 224 | 29 | |
| Avg. rotational acceleration (°/s2) | 232 | 122 | 351 | 110 | 139 | 44 | 199 | 26 | |
| Max | Maximal forward speed (m/s) | 4.19 | 1.02 | 4.98 | 0.43 | 3.37 | 0.99 | 4.40 | 0.40 |
| Maximal rotational speed (°/s) | 348 | 80 | 388 | 71 | 303 | 79 | 369 | 43 | |
| Speed zones | Speed <0 m/s | 11.2% | 3.3% | 13.4% | 3.2% | 9.9% | 2.3% | 9.6% | 3.2% |
| Speed between 0 to 0.5 m/s | 16.4% | 6.5% | 13.7% | 2.3% | 20.9% | 7.5% | 11.9% | 2.8% | |
| Speed between 0.5 to 1.5 m/s | 38.4% | 8.7% | 31.7% | 3.4% | 43.1% | 8.8% | 41.5% | 7.5% | |
| Speed between 1.5 to 2.5 m/s | 23.6% | 8.0% | 23.7% | 3.5% | 20.1% | 9.1% | 30.8% | 6.9% | |
| Speed above 2.5 m/s | 10.4% | 7.2% | 17.5% | 3.4% | 5.9% | 6.0% | 6.2% | 2.7% | |
| Rotational speed zones | Abs. rot. speed betw. 0 to 25 °/s | 34.3% | 6.3% | 31.5% | 2.7% | 39.1% | 6.4% | 29.3% | 3.8% |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 25 to 50 °/s | 27.5% | 2.1% | 26.9% | 1.3% | 29.1% | 1.4% | 25.4% | 2.1% | |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 50 to 100 °/s | 23.4% | 2.7% | 24.1% | 1.0% | 21.7% | 3.0% | 25.6% | 2.1% | |
| Abs. rot. speed above 100 °/s | 14.7% | 5.8% | 17.5% | 3.1% | 10.0% | 4.2% | 19.5% | 5.2% | |
| “High-class” | Total (n = 39) | Basketball (n = 12) | Rugby (n = 12) | Tennis (n = 15) | |||||
| Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | Mean | Stdev. | ||
| WMP | Avg. forward speed (m/s) | 1.41 | 0.25 | 1.67 | 0.10 | 1.25 | 0.27 | 1.34 | 0.13 |
| Best forward speed (m/s) | 2.52 | 0.54 | 3.14 | 0.16 | 2.32 | 0.58 | 2.17 | 0.14 | |
| Avg. acceleration to 2 m (m/s2) | 1.33 | 0.41 | 1.67 | 0.23 | 0.99 | 0.42 | 1.33 | 0.29 | |
| Avg. rotational speed in a curve (°/s) | 70 | 10 | 72 | 7 | 67 | 15 | 72 | 8 | |
| Best rotational speed in a turn (°/s) | 222 | 29 | 228 | 22 | 213 | 36 | 224 | 29 | |
| Avg. rotational acceleration (°/s2) | 262 | 128 | 422 | 119 | 181 | 33 | 199 | 26 | |
| Max | Maximal forward speed (m/s) | 4.51 | 0.78 | 5.22 | 0.41 | 3.94 | 0.89 | 4.40 | 0.40 |
| Maximal rotational speed (°/s) | 386 | 66 | 424 | 80 | 367 | 59 | 369 | 43 | |
| Speed zones | Speed <0 m/s | 11.2% | 3.3% | 13.9% | 3.1% | 10.5% | 1.7% | 9.6% | 3.2% |
| Speed between 0 to 0.5 m/s | 14.3% | 4.8% | 13.0% | 2.3% | 18.5% | 6.0% | 11.9% | 2.8% | |
| Speed between 0.5 to 1.5 m/s | 37.3% | 8.6% | 29.6% | 3.4% | 39.7% | 8.7% | 41.5% | 7.5% | |
| Speed between 1.5 to 2.5 m/s | 25.9% | 7.4% | 23.8% | 3.8% | 21.8% | 7.6% | 30.8% | 6.9% | |
| Speed above 2.5 m/s | 11.3% | 7.3% | 19.7% | 3.2% | 9.4% | 7.1% | 6.2% | 2.7% | |
| Rotational speed zones | Abs. rot. speed betw. 0 to 25 °/s | 31.1% | 4.1% | 30.0% | 2.5% | 34.4% | 4.1% | 29.3% | 3.8% |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 25 to 50 °/s | 26.5% | 2.0% | 26.0% | 0.9% | 28.4% | 1.4% | 25.4% | 2.1% | |
| Abs. rot. speed betw. 50 to 100 °/s | 24.6% | 2.2% | 24.5% | 1.1% | 23.3% | 2.7% | 25.6% | 2.1% | |
| Abs. rot. speed above 100 °/s | 17.8% | 4.6% | 19.6% | 2.1% | 13.8% | 2.7% | 19.5% | 5.2% | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van der Slikke, R.M.A.; Berger, M.A.M.; Bregman, D.J.J.; Veeger, D.H.E.J. Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training. Sensors 2020, 20, 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123518
van der Slikke RMA, Berger MAM, Bregman DJJ, Veeger DHEJ. Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training. Sensors. 2020; 20(12):3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123518
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan der Slikke, Rienk M. A., Monique A. M. Berger, Daan J. J. Bregman, and Dirkjan H. E. J. Veeger. 2020. "Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training" Sensors 20, no. 12: 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123518
APA Stylevan der Slikke, R. M. A., Berger, M. A. M., Bregman, D. J. J., & Veeger, D. H. E. J. (2020). Wearable Wheelchair Mobility Performance Measurement in Basketball, Rugby, and Tennis: Lessons for Classification and Training. Sensors, 20(12), 3518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123518





_Veeger.png)

