Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi–Uda-Like Antennas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background Theory
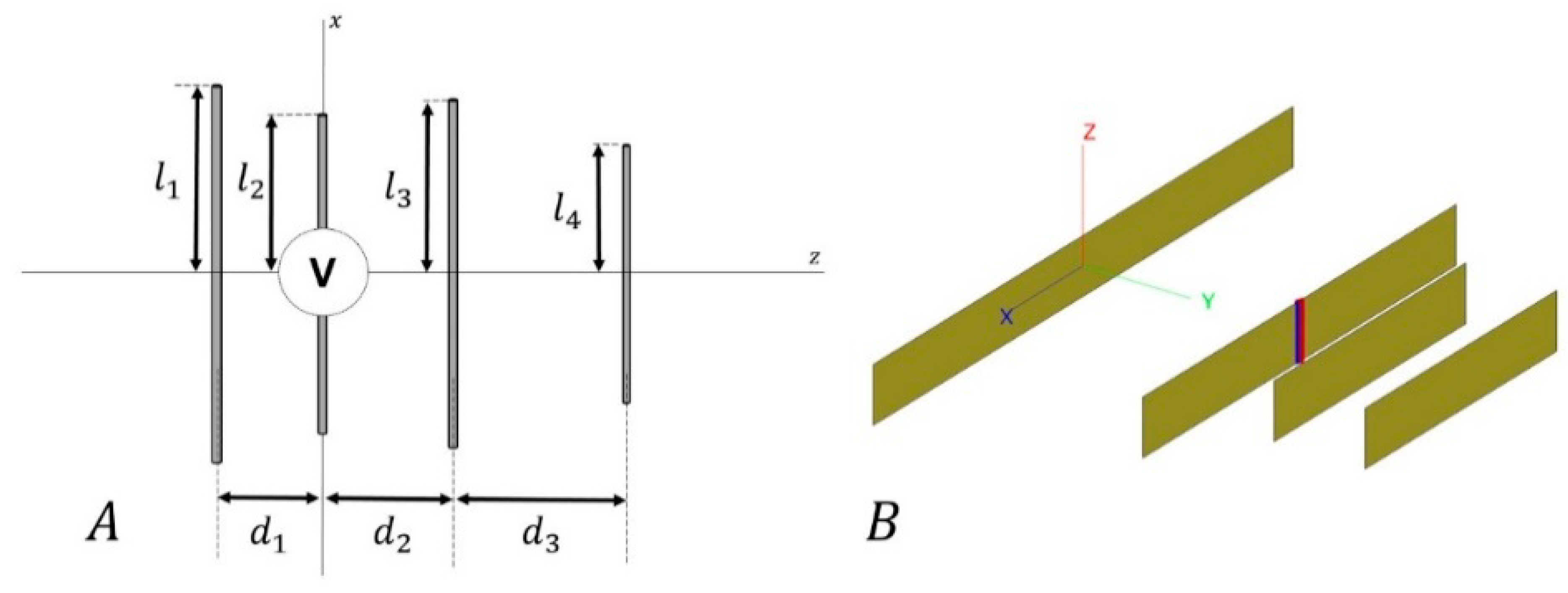
2.1.1. Main Antenna Parameters
2.1.2. Relative Permittivity of Air in Presence of PM
- Temperatures of −50 °C to +40 °C;
- Pressures of 200 mbar to 1100 mbar;
- Water vapor partial pressures up to 30 mbar;
- Frequency range up to 30 GHz.
2.1.3. Input Impedance of a Yagi–Uda-like Antenna
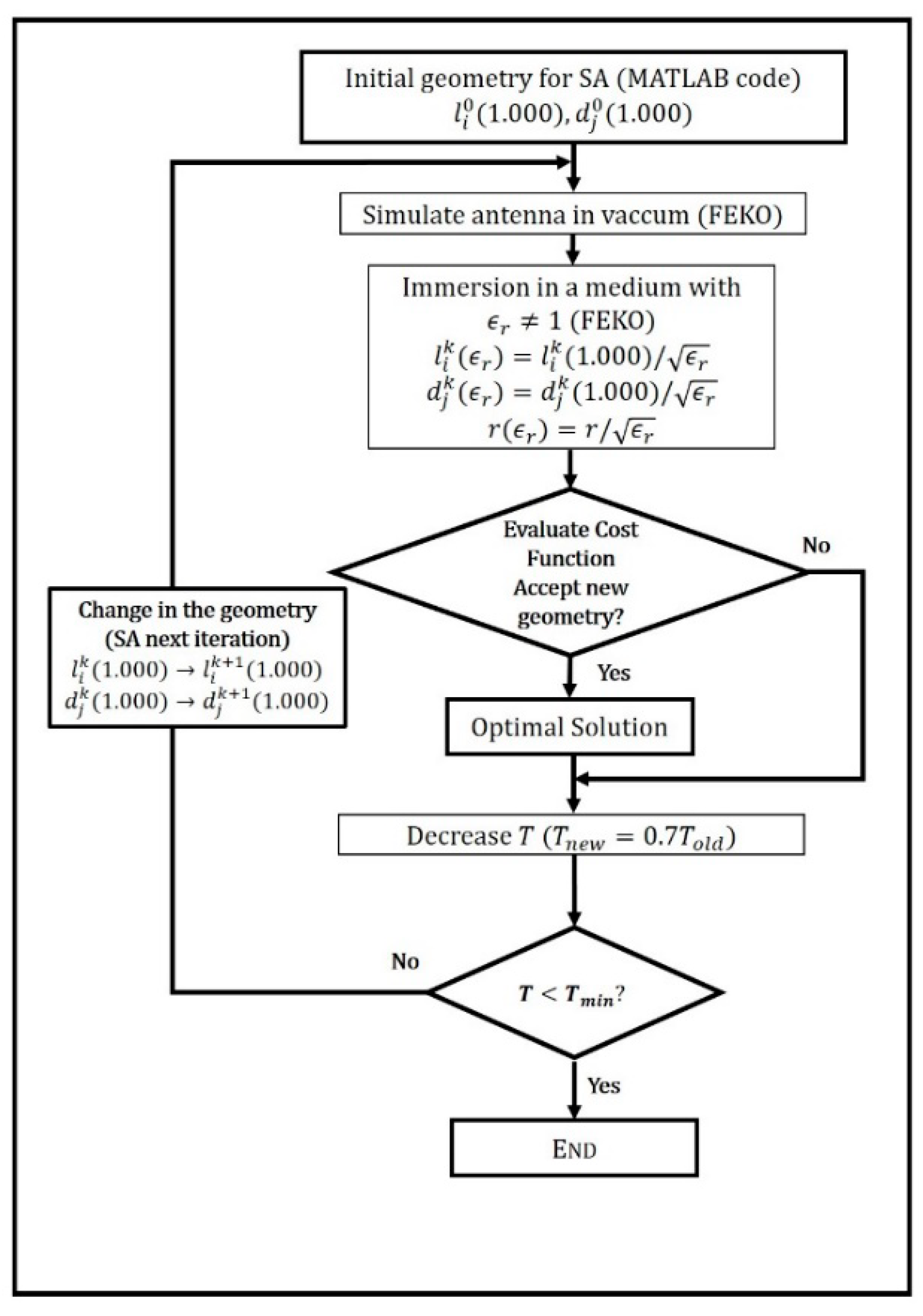
2.2. Numerical Simulation Settings
2.2.1. Antenna Model and Environmental Scenario
2.2.2. Optimization Strategy
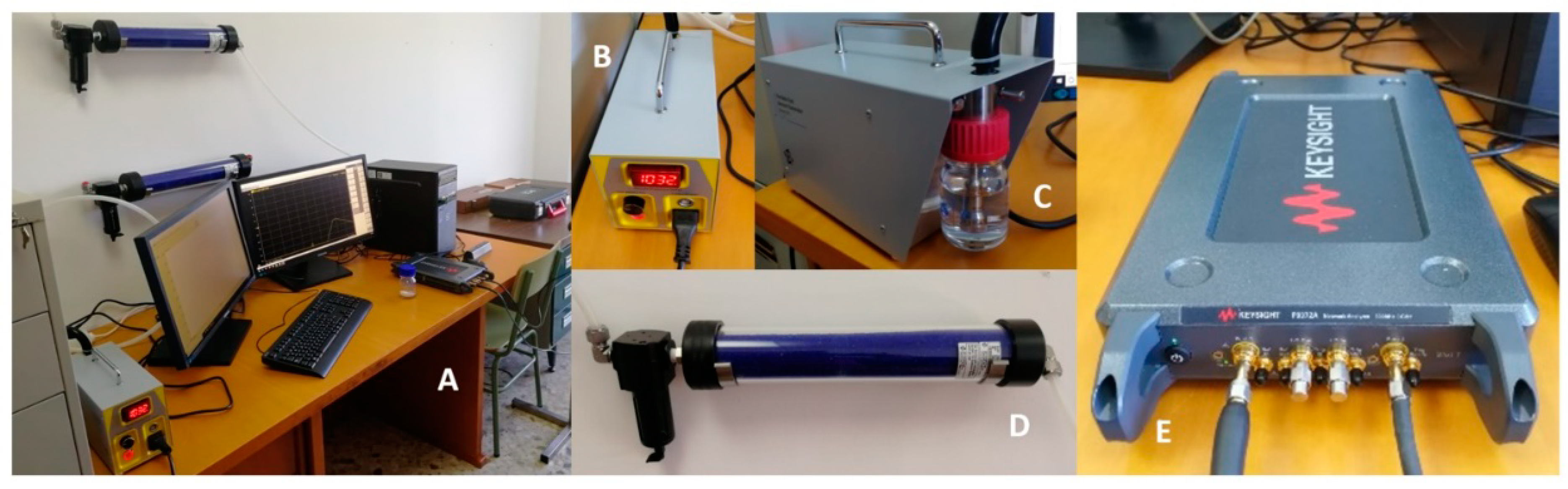
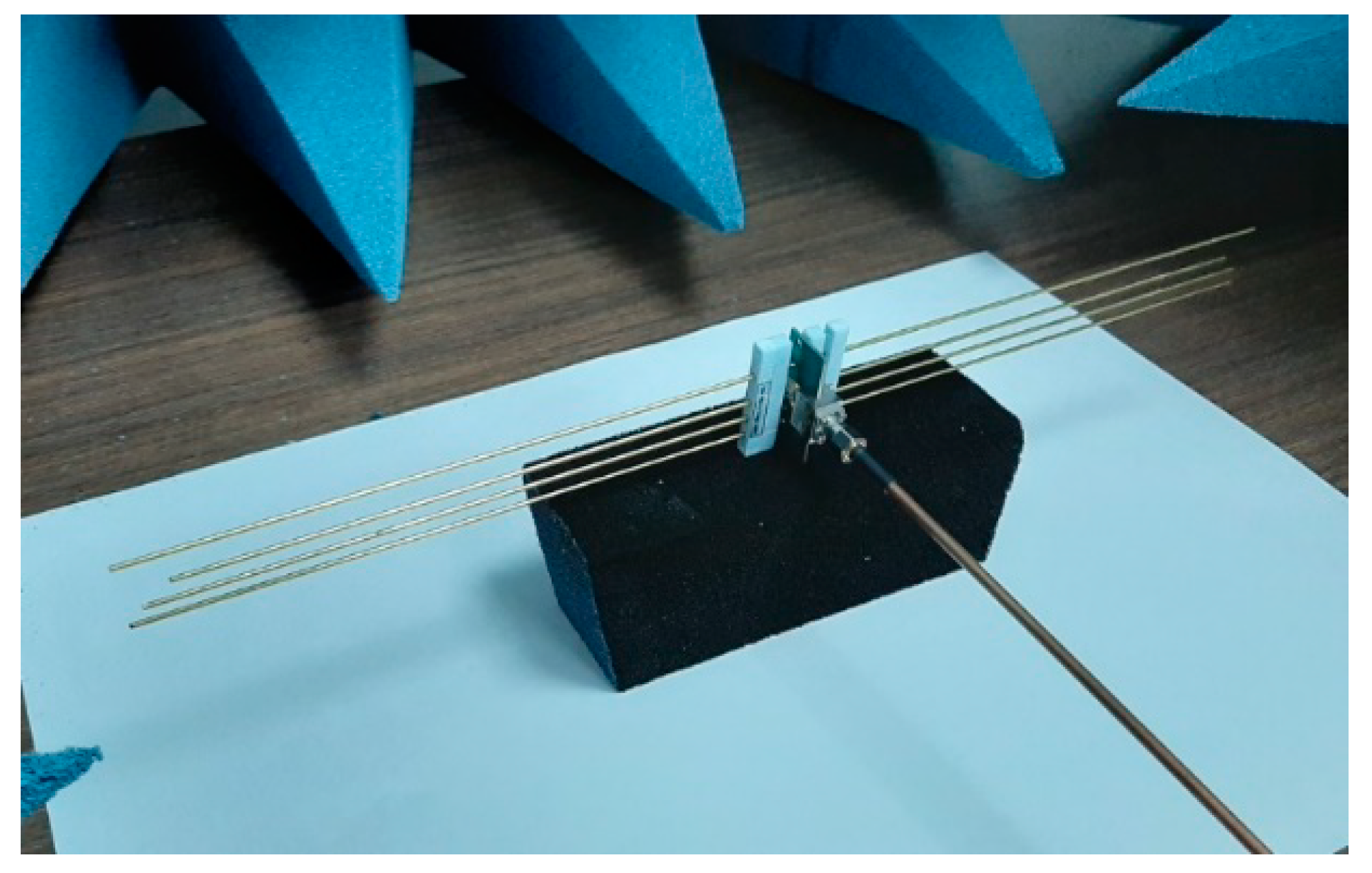
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results
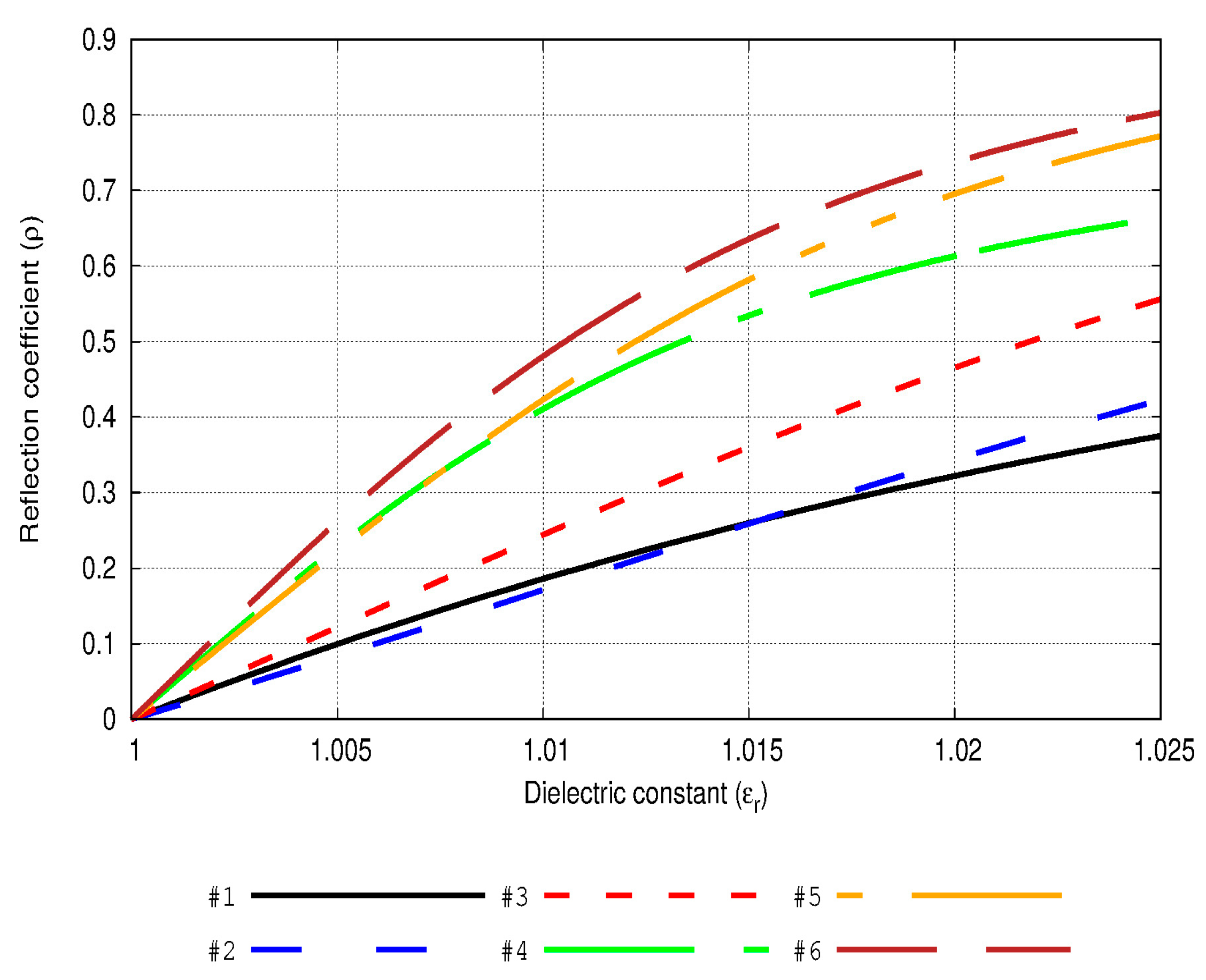
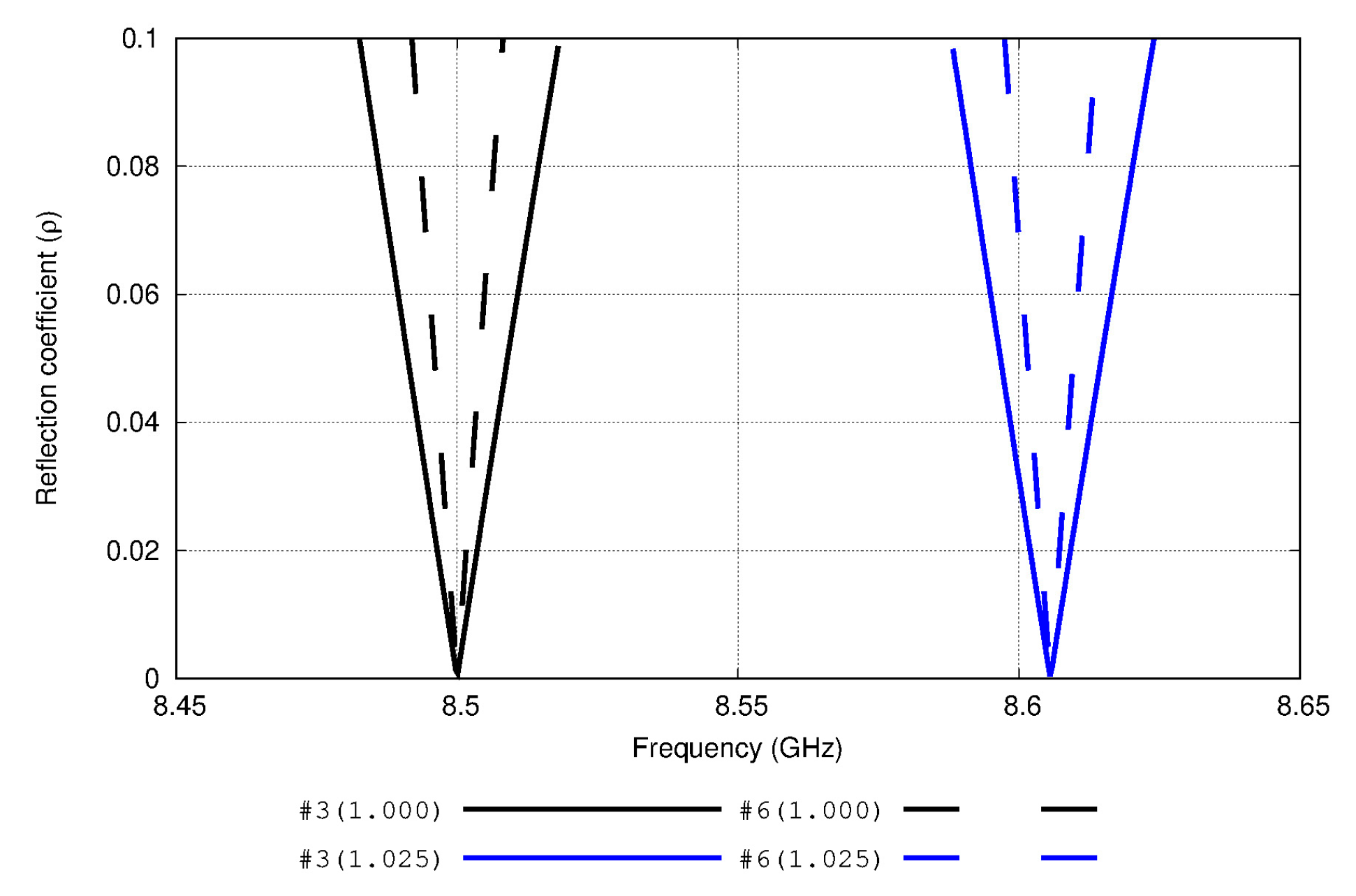
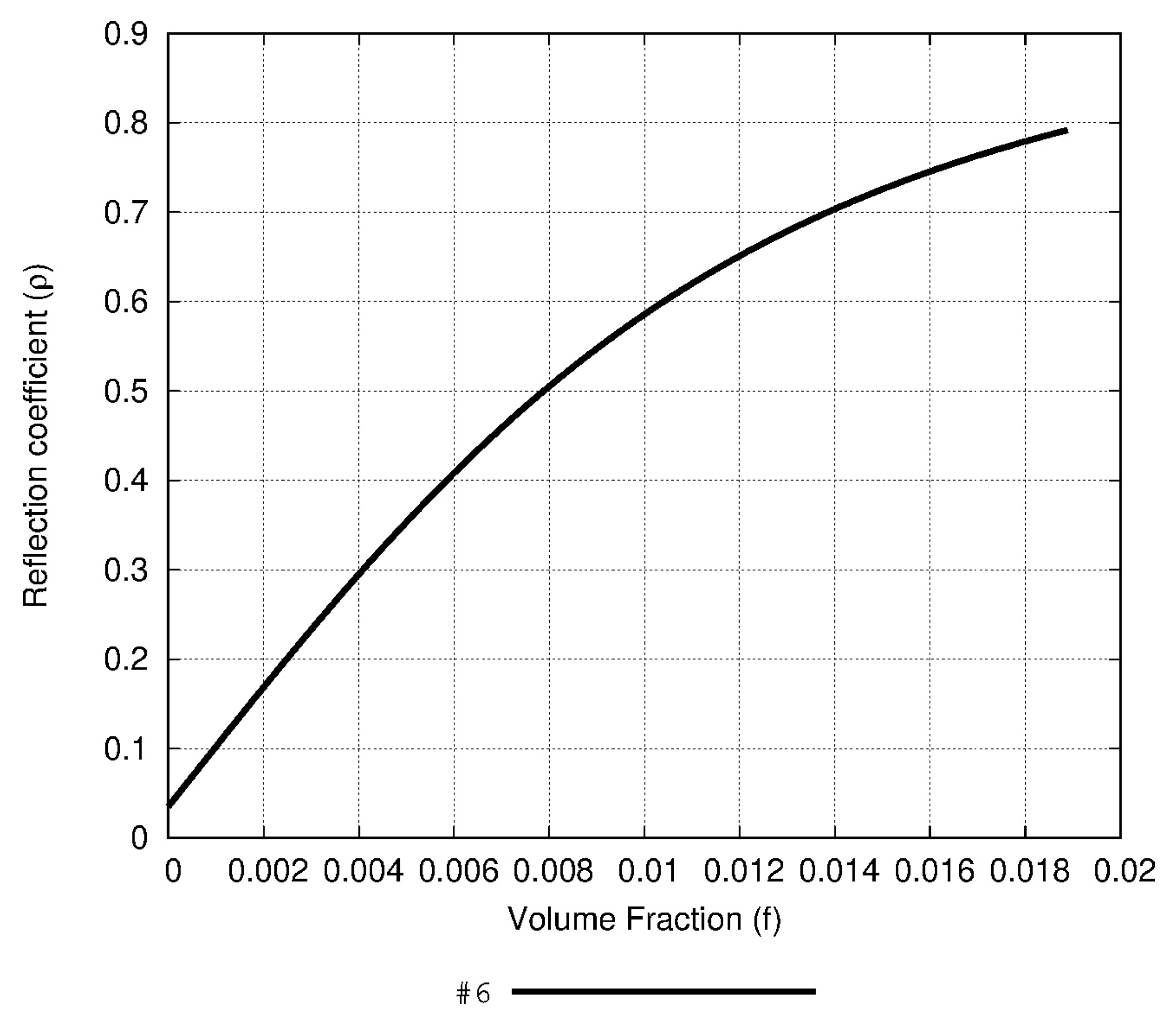
3.1. Numerical Results
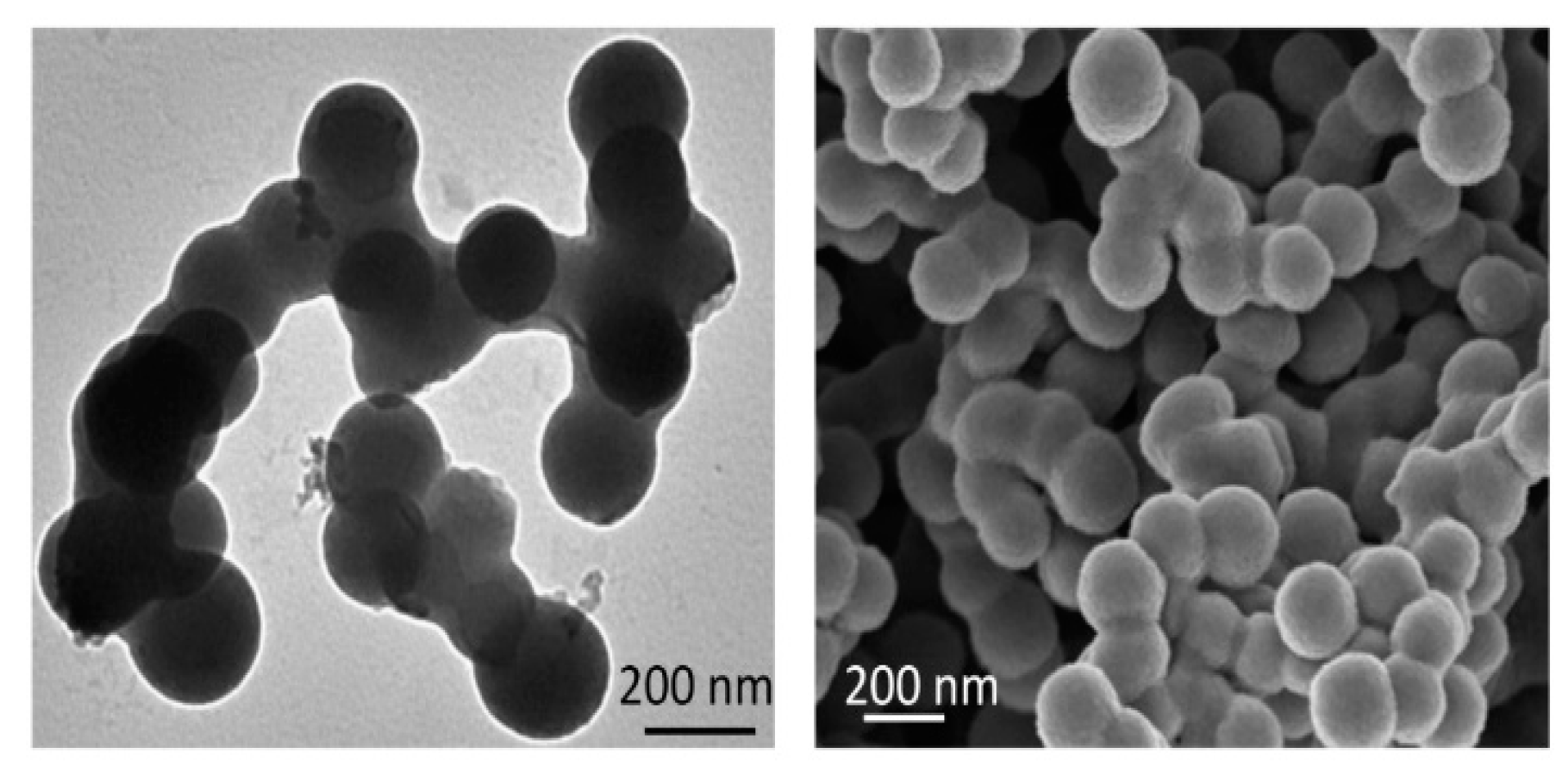
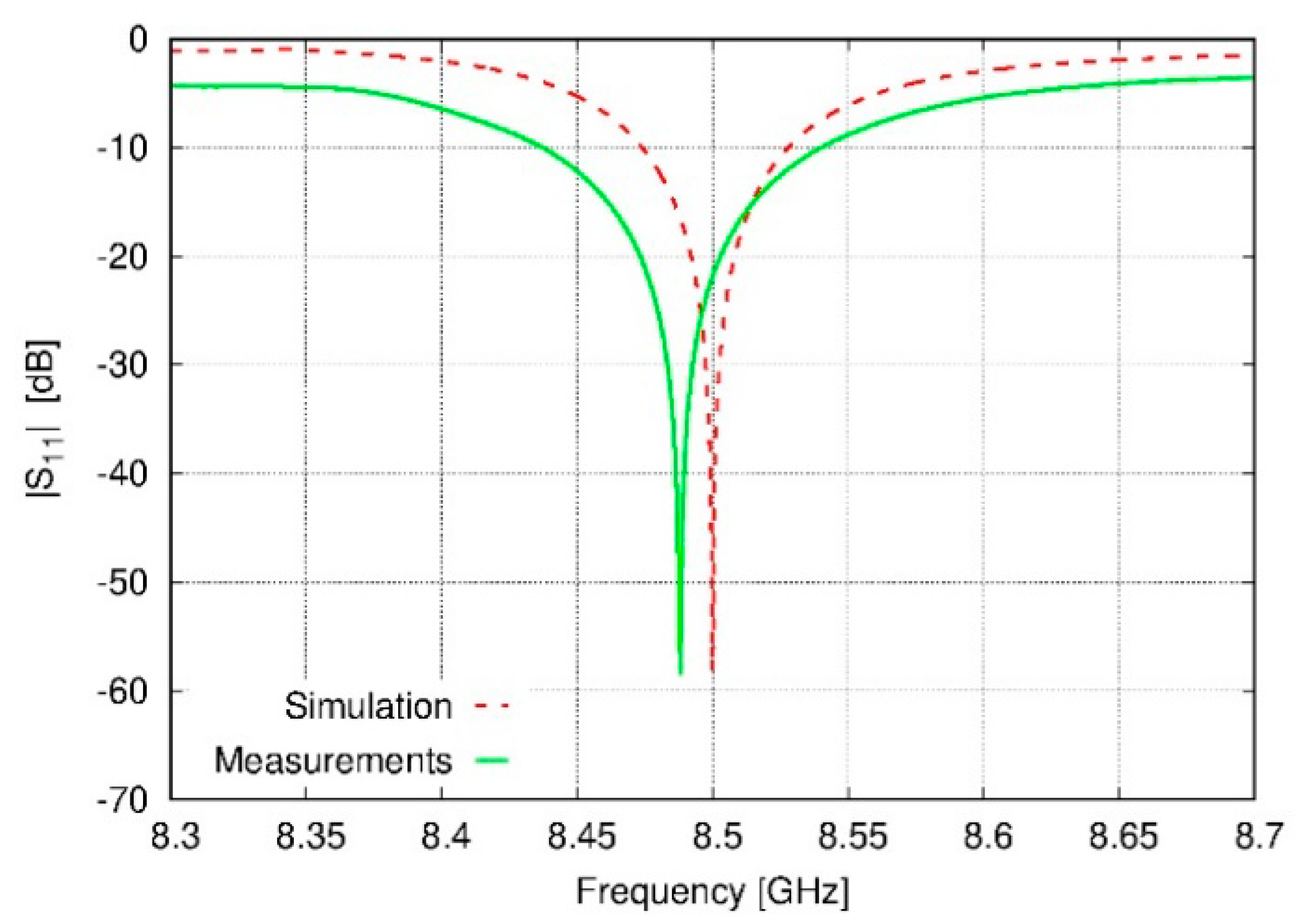
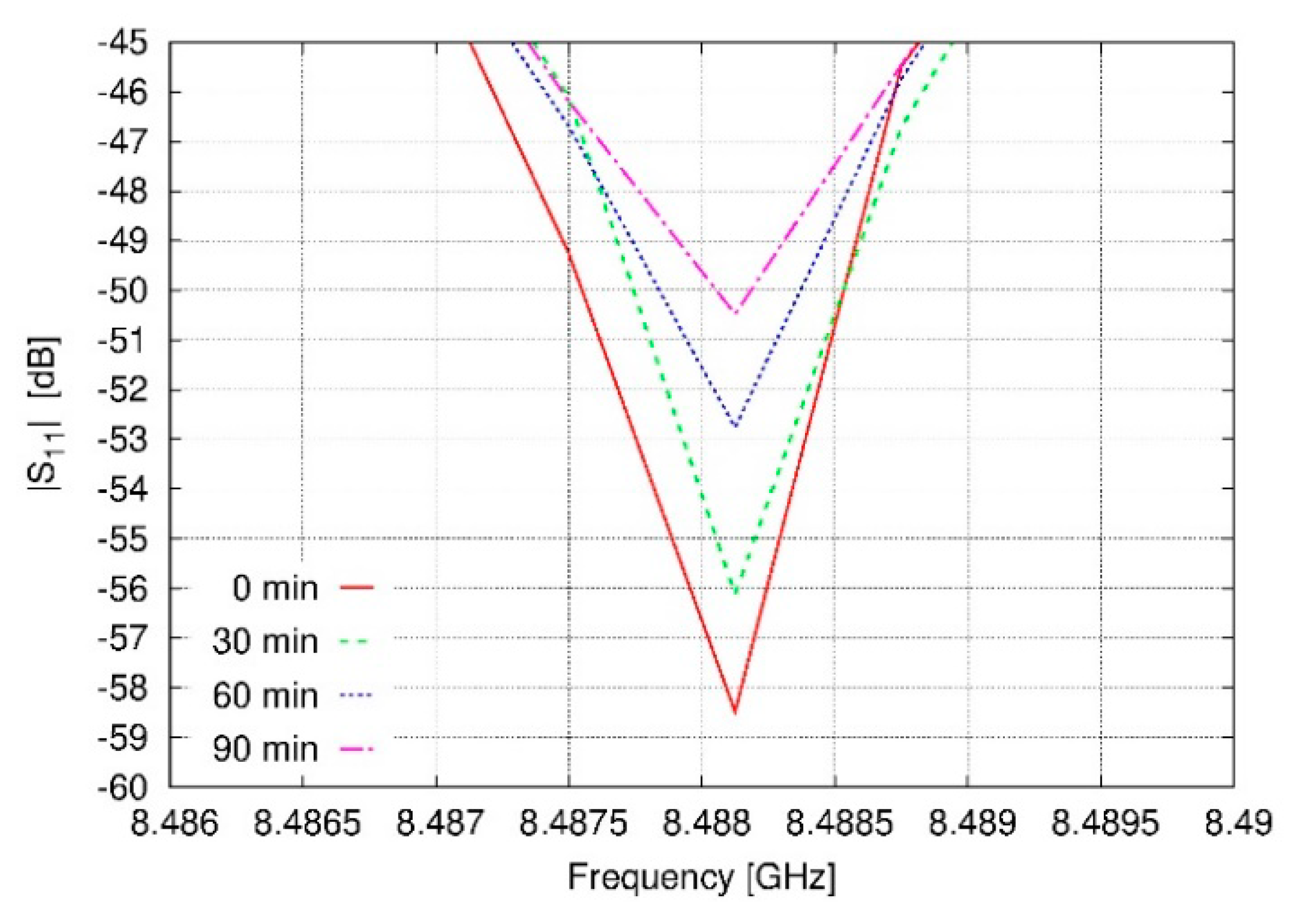
3.2. Prototyping and Experimental Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Environment Agency. Air Quality in Europe—2018 Report. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu//publications/air-quality-in-europe-2018 (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Nawrot, T.S.; Perez, L.; Künzli, N.; Munters, E.; Nemery, B. Public health importance of triggers of myocardial infarction: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet 2011, 377, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Veronesi, B.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Gehr, P.; Chen, L.C.; Geiser, M.; Reed, W.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Schürch, S.; Schulz, H. Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Mora-Tiscareno, A.; Ontiveros, E.; Gómez-Garza, G.; Barragán-Mejía, G.; Broadway, J.; Chapman, S.; Valencia-Salazar, G.; Jewells, V.; Maronpot, R.R.; et al. Air pollution, cognitive deficits and brain abnormalities: a pilot study with children and dogs. Brain Cogn. 2008, 68, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Outdoor Air Pollution—IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Volume. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/_publications/media/download/4317/b1f528f1fca20965a2b48a220f47447c1d94e6d1.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- U.S. EPA. Current Knowledge of Particulate Matter (pm) Continuous Emission Monitoring. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA-454/R-00-039. 2000. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/emc/cem/pmcemsknowfinalrep.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- U.S. EPA. Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter (Final Report, 2019). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, EPA/600/R-19/188. 2019. Available online: http://ofmpub.epa.gov/eims/eimscomm.getfile?p_download_id=539935 (accessed on 4 June 2009).
- Simões Amaral, S.; Andrade de Carvalho Jr., J.; Martins Costa, M.A.; Pinheiro, C. An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 2015, 1327–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Arnott, W.P.; Rogers, C.F.; Bowen, J.L.; Gillies, J.; Pierson, W.R.; Collins, J.F.; Durbin, T.D.; Norbeck, J.M. Time Resolved Characterization of Diesel Particulate Emissions. 1. Instruments for Particle Mass Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehadi, A.; Moosmüller, H.; Campbell, D.E.; Ham, W.; Schweizer, D.; Tarnay, L.; Hunter, J. Laboratory and Field Evaluation of Real-time and Near Real-time PM2.5 Smoke Monitors. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2020, 70, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Arnott, W.P.; Rogers, C.F. Methods for Real Time, in Situ Measurement of Aerosol Light Absorption. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Arnott, W.P. Aerosol Light Absorption and its Measurement: A Review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, H. Atmospheric Light Absorption—A Review. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 27A, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanre, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenue, F.; et al. An emerging ground based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría-Salazar, S.M.; Holmes, H.A.; Patrick Arnott, W.; Barnard, J.C.; Moosmüller, H. Evaluation of MODIS Columnar Aerosol Retrievals Using AERONET in Semi-Arid Nevada and California, U.S.A. during the Summer of 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Nakajima, T. Remote Sensing of Tropospheric Aerosols from Space: Past, Present, and Future. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1999, 80, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.I.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A Satellite View of Aerosols in the Climate System. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote Sensing of Particulate Pollution from Space: Have We Reached the Promised Land? J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkelaar, A.V.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Gehrig, R.; Lee, Y.; Kumar, N. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, C.; Kuhns, H.D.; Moosmüller, H. Monitoring automotive particulate matter emissions with lidar: A review. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1077–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grusha, G.V. Antennas for the remote measurement systems of the gaseous pollution concentration. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Antenna Theory and Techniques, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 9–12 September 2003; pp. 574–576. [Google Scholar]
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; López-Martín, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Technique for determination of particulate matter pollution in the atmosphere using waveguide slot linear array antennas: A feasibility study. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 13, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, E.A.; Joines, W.T. Design of Yagi-Uda antennas using genetic algorithms. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1997, 45, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.S. Antenna Theory and Design, rev. ed.; IEEE Press: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; López-Martín, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Design of polyimide-coated Yagi-Uda antennas for monitoring the relative humidity level. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 14, 961–963. [Google Scholar]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, R.S. An Introduction to Guided Waves and Microwave Circuits; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.K.; Weintraub, S. The constants in the equation for atmospheric refractive index at radio frequencies. Proc. IRE 1953, 41, 1035–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihvola, A.H. How strict are theoretical bounds for dielectric properties of mixtures? IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2002, 40, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EM Software and Systems. Feko v2017.1. Available online: https://altairhyperworks.com/product/FEKO (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- MathWorks, MATLAB, Version 2016b. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/products/new_products/release2016b.html (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D., Jr.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Vetterling, W.T.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Flannery, B.P. Numerical Recipes in C, 2nd ed.; Cambridge Univeristy Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Lack, D.A.; Moosmüller, H.; McMeeking, G.R.; Chakrabarty, R.K.; Baumgardner, D. Characterizing Elemental, Equivalent Black, and Refractory Black Carbon Aerosol Particles: A Review of Techniques, Their Limitations and Uncertainties. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the Role of Black Carbon in the Climate System: A Scientific Assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSI Incorporated, Portable Test Aerosol Generator Model 3073. Available online: https://www.tsi.com/getmedia/e5d8a77a-7533-4631-a85a-470f11828a1c/5002118_US_3073_Portable%20Test%20Aerosol%20Generator_Web?ext=.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2020).
- Michel, R.P.; Bacain, R.; Schubert, E. Soot particle properties in the microwave range. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Microwave Conference, Madrid, Spain, 6–9 September 1993; pp. 959–960. [Google Scholar]
- Koven, C.D.; Fung, I. Inferring dust composition from wavelength dependent absorption in aerosol robotic network (aeronet) data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; López-Furelos, A.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J.; López-Martín, M.E. Validation of Potential Effects on Human Health of in Vivo Experimental Models Studied in Rat Exposed to Sub-Thermal Radiofrequency. Possible Health Risks Due to the Interaction of Electromagnetic Pollution and Environmental Particles. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79186–79198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Relative permittivity of the inclusions | Dimensionless | |
| Volume fraction of the inclusions | Dimensionless | |
| Relative permittivity of the host material | Dimensionless | |
| ν | Control parameter for changing the model (MG, BG, CPA) * | Dimensionless |
| Resulting effective relative permittivity of the mixture | Dimensionless |
| Antenna | Elem | Lengths | Spacing | Antenna | Elem | Lengths | Spacing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 [0.1–0.5] * | 1 | 0.4732 | 0.3414 | #4 [2.5–4.0] * | 1 | 3.1841 | 0.2895 |
| 2 a | 0.3525 | 0.1108 | 2 a | 3.1646 | 0.3277 | ||
| 3 | 0.2157 | 0.1435 | 3 | 3.3171 | 0.2652 | ||
| 4 | 0.4768 | - | 4 | 3.2444 | - | ||
| #2 [0.5–2.0] * | 1 | 1.2267 | 0.3109 | #5 [3.5–5.0] * | 1 | 4.2677 | 0.2303 |
| 2 a | 1.1679 | 0.2663 | 2 a | 4.1525 | 0.2103 | ||
| 3 | 1.2770 | 0.2722 | 3 | 4.3593 | 0.2568 | ||
| 4 | 1.2867 | - | 4 | 4.1907 | - | ||
| #3 [1.5–3.0] * | 1 | 2.2643 | 0.2340 | #6 [4.5–6.0] * | 1 | 5.3820 | 0.2633 |
| 2 a | 2.1643 | 0.2465 | 2 a | 5.1481 | 0.1688 | ||
| 3 | 2.3371 | 0.2328 | 3 | 5.2826 | 0.1858 | ||
| 4 | 2.2473 | - | 4 | 5.3174 | - |
| Antenna Number | (Ω) | (°) | (Ω) | (°) | (Ω) | (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 102.16 | 311.434 | −28.039 | 50.000 | 0.000 | 268.334 | 146.936 |
| 311.747 | −25.392 | 84.647 | −30.663 | 227.591 | 156.566 | ||
| #2 | 78.41 | 92.574 | −49.308 | 49.997 | −0.001 | 70.951 | 98.397 |
| 99.712 | −56.485 | 42.973 | −45.174 | 58.187 | 115.186 | ||
| #3 | 116.98 | 99.672 | −46.001 | 50.000 | 0.001 | 74.235 | 105.019 |
| 111.222 | −57.070 | 52.560 | −58.100 | 58.679 | 123.853 | ||
| #4 | 225.34 | 103.189 | −42.328 | 50.000 | 0.000 | 74.290 | 110.723 |
| 117.807 | −57.406 | 80.894 | −64.256 | 38.712 | 137.026 | ||
| #5 | 212.50 | 107.002 | −45.370 | 49.999 | 0.000 | 80.201 | 108.292 |
| 129.922 | −60.104 | 77.961 | −72.933 | 56.617 | 137.698 | ||
| #6 | 254.33 | 108.903 | −44.823 | 50.000 | 0.000 | 81.458 | 109.539 |
| 137.228 | −60.802 | 89.242 | −74.403 | 54.676 | 141.769 |
| Element | Lengths (cm) | Spacing (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.0171 | 0.9528 |
| 2 a | 18.1553 | 0.6031 |
| 3 | 18.5847 | 0.6483 |
| 4 | 18.8143 | - |
| Time of Exposure (min) | |S11| @ 8.488GHz (dB) |
|---|---|
| 0 | −58.49 |
| 10 | −57.68 |
| 20 | −56.36 |
| 30 | −56.12 |
| 40 | −54.78 |
| 50 | −53.26 |
| 60 | −52.76 |
| 70 | −51.31 |
| 80 | −50.81 |
| 90 | −50.48 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; Rauch, J.; López-Martín, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Franceschetti, G.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi–Uda-Like Antennas. Sensors 2020, 20, 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113225
Salas-Sánchez AA, Rauch J, López-Martín ME, Rodríguez-González JA, Franceschetti G, Ares-Pena FJ. Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi–Uda-Like Antennas. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113225
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalas-Sánchez, Aarón A., Julian Rauch, M. Elena López-Martín, J. Antonio Rodríguez-González, Giorgio Franceschetti, and Francisco J. Ares-Pena. 2020. "Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi–Uda-Like Antennas" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113225
APA StyleSalas-Sánchez, A. A., Rauch, J., López-Martín, M. E., Rodríguez-González, J. A., Franceschetti, G., & Ares-Pena, F. J. (2020). Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi–Uda-Like Antennas. Sensors, 20(11), 3225. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113225





