Comparison of Gas Sensing Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Obtained by Two Different Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Material 1—oxidation: Modification of Hummer’s method (Method 1), reduction: thermal reduction.
- Material 2—oxidation: Modification of Tour’s method (Method 2), reduction: thermal reduction.
- H—Hummers’ method;
- T—modified Tour’s method;
- GO1—graphite oxide prepared using Hummers’ method;
- GO2—graphite oxide prepared using modified Tour’s method;
- TRGO1—graphene oxide obtained after thermally reduction of GO1;
- TRGO2—graphene oxide obtained after thermally reduction of GO2;
- Sample 1—a measuring structure with TRGO1;
- Sample 2—a measuring structure with TRGO2.
2.1.1. Oxidation
2.1.2. Exfoliation and Reduction
- The graphite oxide sample (10 g), after being placed in the retort, was purged with nitrogen (5 mL/min) at room temperature for 30 min;
- The retort with the sample was then placed in an oven preheated to 900 °C and kept at this temperature for 5 min.
2.2. Preparation of Sensing Structures
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Gas Measurement System
2.3.2. Porous Texture Analysis Using N2 Sorption
2.3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Structures
3.1.1. Porous Texture Analysis Using the N2 Sorption Method
3.1.2. Imaging of the rGO Structures
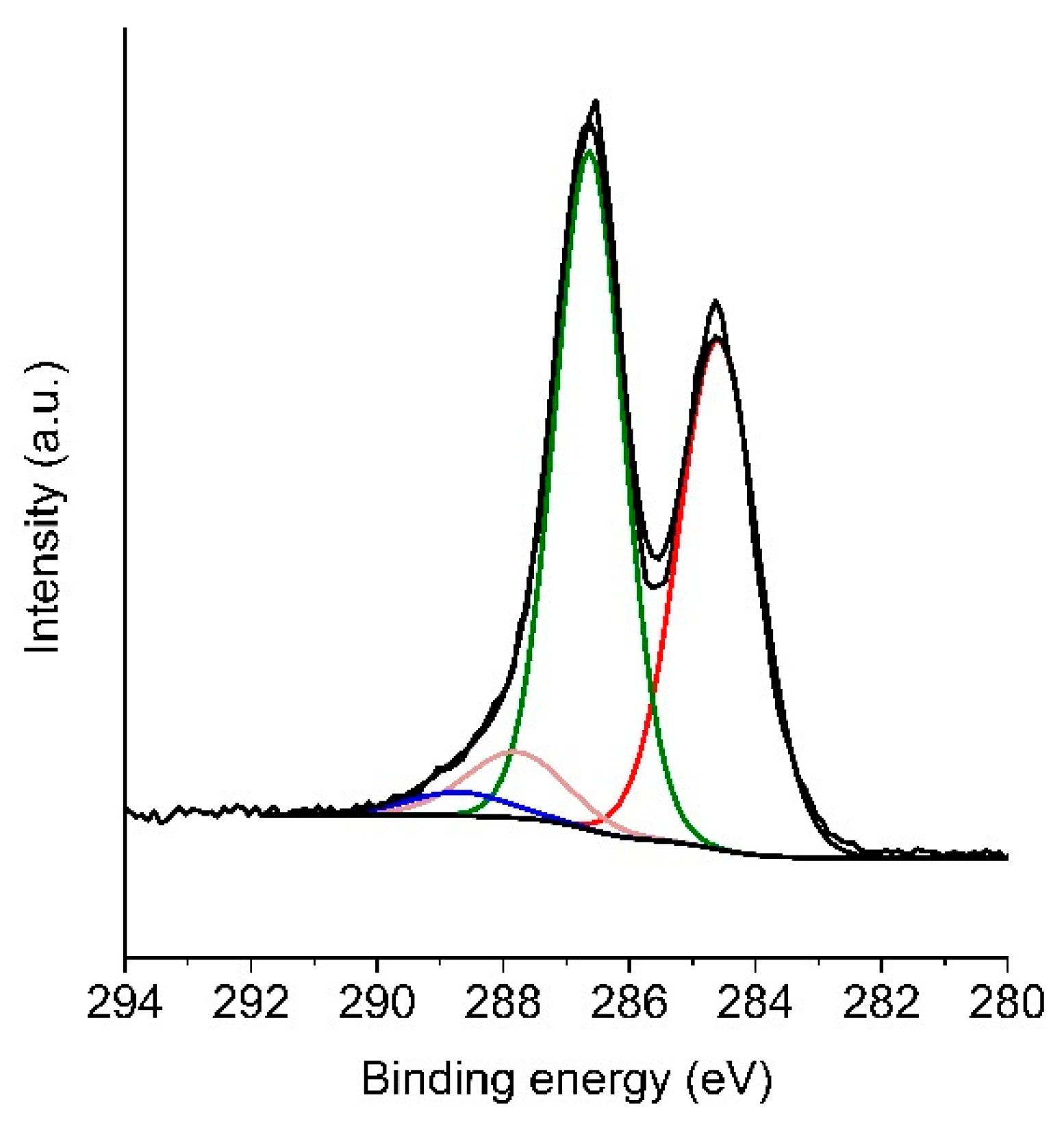
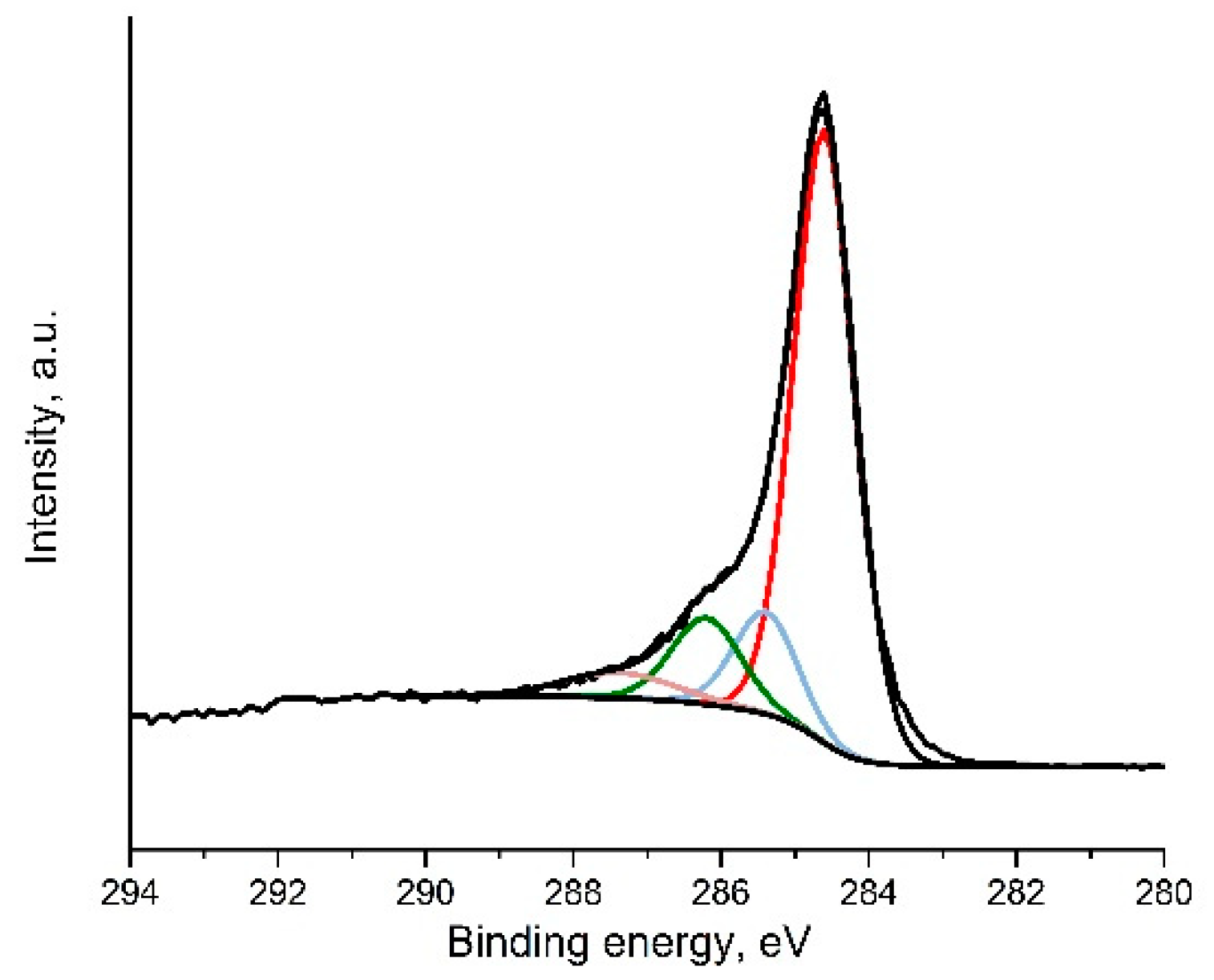
3.1.3. Composition Analysis Using X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
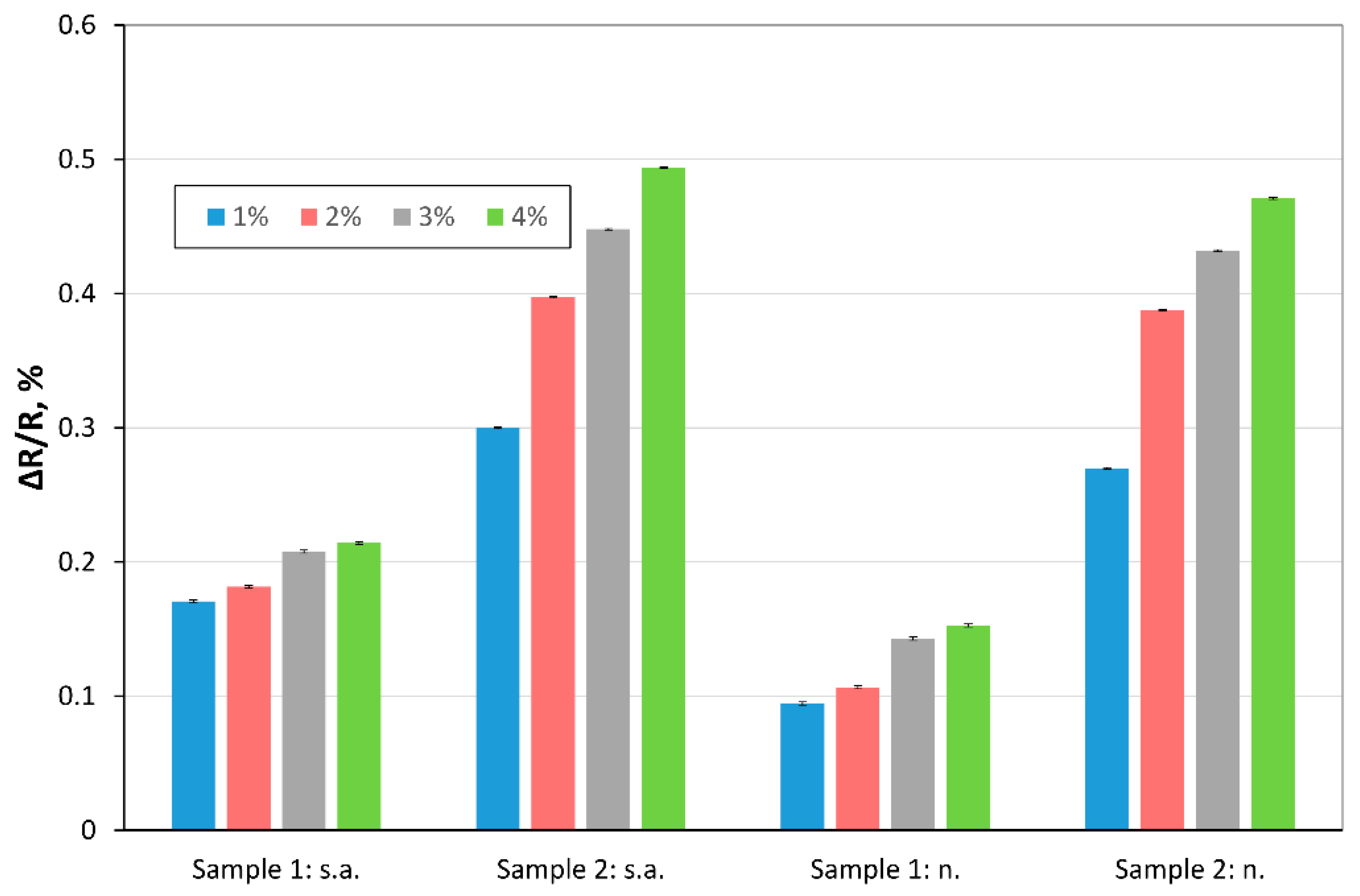
3.2. Study of the Sensitivity of Receptor Layers
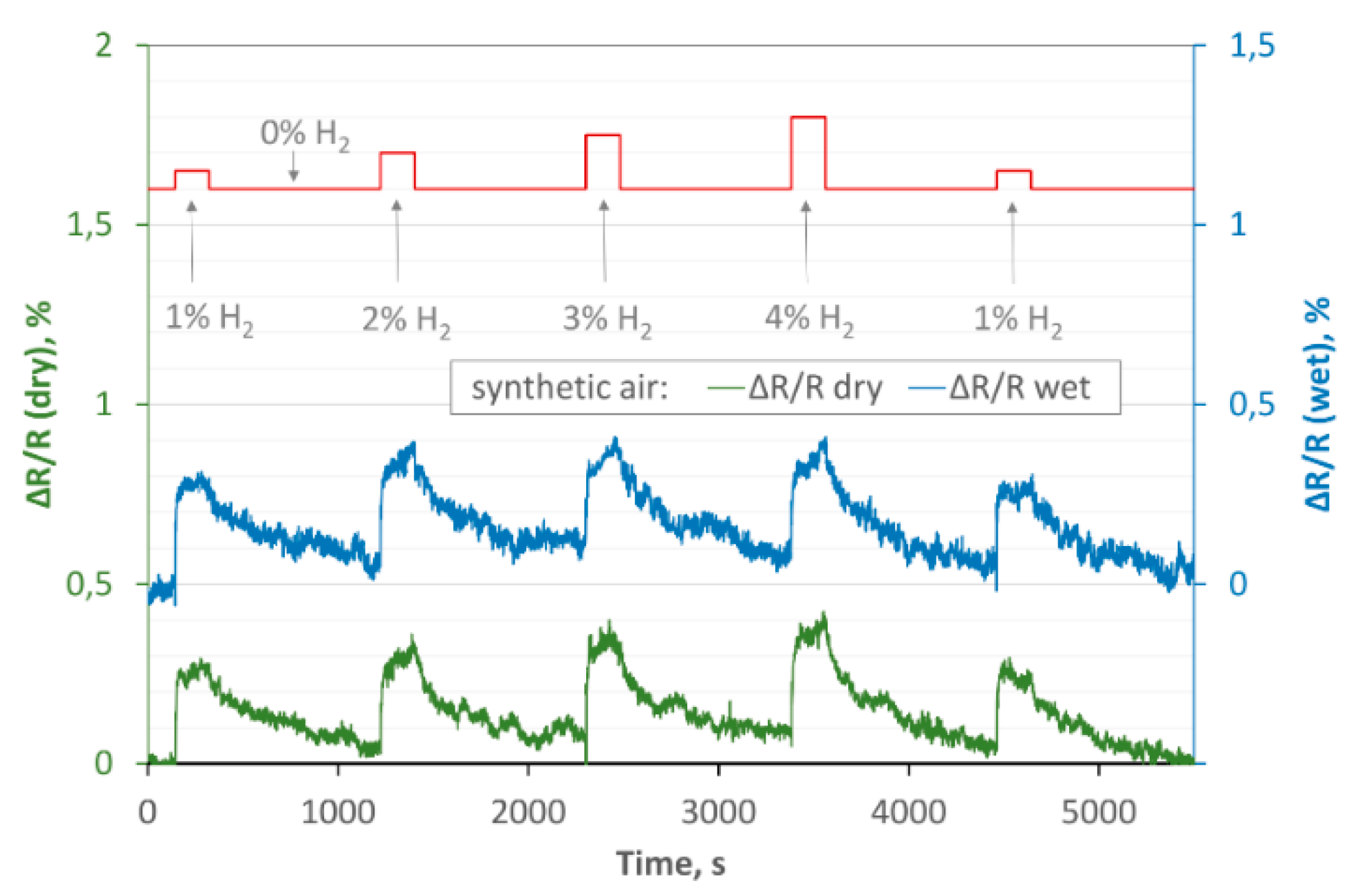
3.2.1. Hydrogen Action in Dry Carrier Gas on rGO Structures
- RX- resistance of target gas (structure is affected by testing gas);
- RC- resistance of the structure affected by carrier gas.
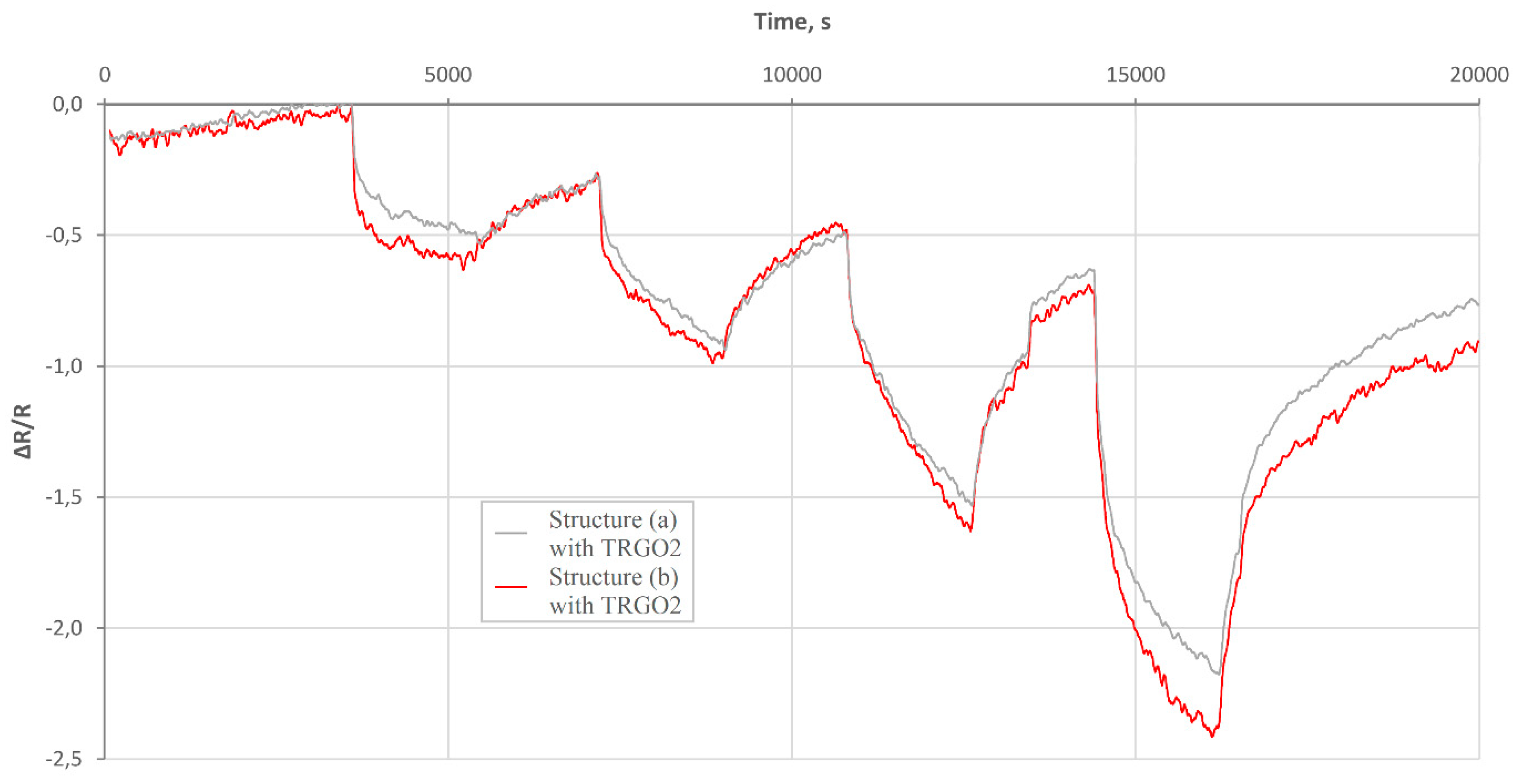
3.2.2. Hydrogen Action in Wet Carrier Gas on rGO Structures
- for the same concentration of hydrogen and the same temperature but different humidity of the carrier gas, the trc times are comparable (for each sample);
- the trc is slightly shorter for Sample 2;
- treg is much longer than trc, for all cases.
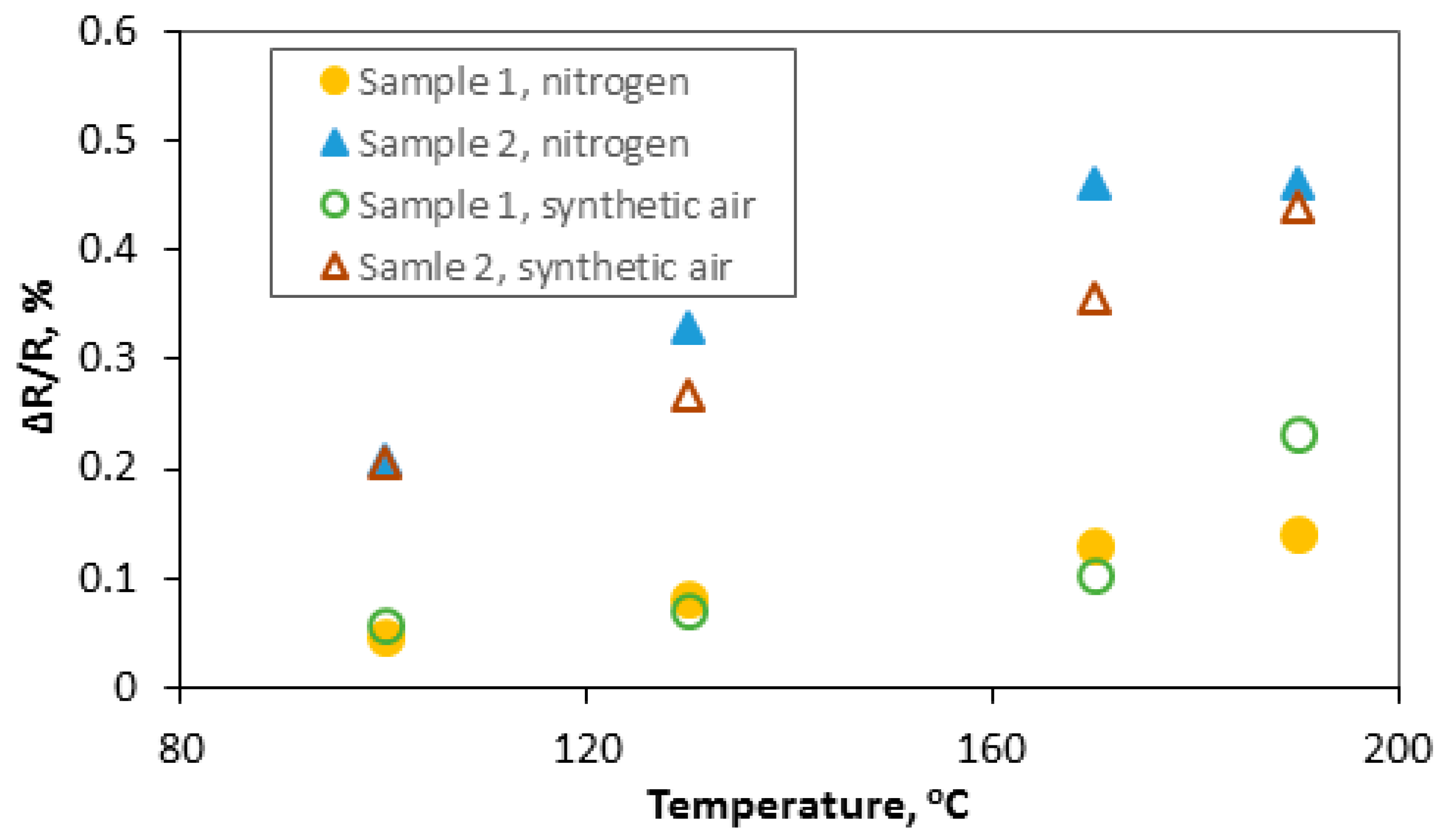
3.2.3. Ammonia and Nitrogen Dioxide Action on rGO Structures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- fast changes in resistance as a result of the presence of hydrogen in nitrogen/synthetic air (much shorter than for nitrogen dioxide);
- lack of sensitivity or poor sensitivity to humidity (an unquestionable advantage of both structures);
- selectivity: different reactions of the samples when mixture with hydrogen, ammonia or nitrogen dioxide are introduced to the atmosphere ( is positive for the measurement with hydrogen, negative for the measurement with nitrogen dioxide and there is no reaction when NH3 was dosed). Our results are consistent with the literature which says that the structure can interact with NO2, but the interaction with NH3 is weak [29]. The absolute changes of the responses are much larger when in contact with NO2 than H2, for both structures.
- due to the potential sensor’s application of structures, the research was carried out at relatively low temperatures (i.e., 150 °C).
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Material | Csp2 284.5 ± 0.1 eV | Csp3 285.4 ± 0.2 eV | C-OH, C-O-C 286.5 ± 0.3 eV | C=O 287.6 ± 0.2 eV | O=C-OH 288.9 ± 0.3 eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO1 | 46 | 3 | 39 | 7 | 5 |
| GO2 | 41 | 1 | 46 | 10 | 2 |
| TRGO1 | 78 | 8 | 11 | 3 | 0 |
| TRGO2 | 80 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 0 |



References
- Ferrari, A.C. Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: Disorder, electron-phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 2007, 143, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, L.; Lee, W.B.; Ng, M.C. Structure of graphene and its disorders: A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2018, 19, 613–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Facile and highly efficient preparation of semi-transparent, patterned and large-sized reduced graphene oxide films by electrochemical reduction on indium tin oxide glass surface. Thin Solid Films 2019, 692, 137626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeta Rani, B.; Sai Bhargava Reddy, M.; Kailasa, S.; Maseed, H.; Bikshalu, K.; Venkateswara Rao, K. Comparative gas sensing analysis of green and chemically reduced graphene oxide. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115624. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon N. Y. 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, A.; Dennis, J.O.; Mohamed Saheed, M.S.; Mohamed, N.M.; Irshad, M.I.; Mumtaz, A.; Jose, R. Physical reduction of graphene oxide for supercapacitive charge storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 822, 153636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, K.; Mahanandia, P. Conducting reduced graphene oxide film as transparent electrode. Thin Solid Films 2019, 692, 137594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, B.S.; Bernardi, M.I.B.; Mastelaro, V.R. Wavelength effect of ns-pulsed radiation on the reduction of graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 506, 144808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, H.; Karakalos, S.; Ma, K.; Fu, Z.; Swihart, M.T.; Wu, G. Engineering reduced graphene oxides with enhanced electrochemical properties through multiple-step reductions. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovský, O.; Marvan, P.; Nováček, M.; Luxa, J.; Mazánek, V.; Klímová, K.; Sedmidubský, D.; Sofer, Z. Synthesis procedure and type of graphite oxide strongly influence resulting graphene properties. Appl. Mater. Today 2016, 4, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sali, S.; Mackey, H.R.; Abdala, A.A. Effect of graphene oxide synthesis method on properties and performance of polysulfone-graphene oxide mixed matrix membranes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chng, E.L.K.; Pumera, M. The Toxicity of Graphene Oxides: Dependence on the Oxidative Methods Used. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 8227–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzyka, R.; Drewniak, S.; Pustelny, T.; Chrubasik, M.; Gryglewicz, G. Characterization of graphite oxide and reduced graphene oxide obtained from different graphite precursors and oxidized by different methods using Raman spectroscopy. Materials 2018, 11, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, K.; Srivastava, S.; Solanki, P.R.; Puri, N.K. Electrochemical Hydrogen Gas Sensing Employing Palladium Oxide/Reduced Graphene Oxide (PdO-rGO) Nanocomposites. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 8262–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.Y.; Sung, S.J.; Jang, H.W.; Park, C.R. Band gap engineering of graphene oxide for ultrasensitive NO2 gas sensing. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 159, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Hao, Y.W.; Li, P.L.; Song, J.F.; Yang, R.Z.; Fu, X.Y.; Xie, S.Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.L. Improved NO2 Gas Sensing Properties of Graphene Oxide Reduced by Two-beam-laser Interference. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Sun, Q.; Si, P.; Zhang, L.; Ci, L. Reduced graphene oxide/SnO2@Au heterostructure for enhanced ammonia gas sensing. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 737, 136829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Graiti, W.; Foroughi, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Hybrid Graphene/Conducting Polymer Strip Sensors for Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Detection of Serotonin. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 22169–22177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Yoo, Y.K.; Chae, M.S.; Hwang, K.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hur, D.; Lee, J.H. Highly selective reduced graphene oxide (rGO) sensor based on a peptide aptamer receptor for detecting explosives. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddeppa, M.; Park, B.-G.; Kim, M.-D.; Rao, K.; Duc, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.-G.; Murali, G. H2, H2S gas sensing properties of rGO/GaN nanorods at room temperature: Effect of UV illumination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 264, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, A.; Sun, L.; Han, N.; Chu, H.; Bai, S.; Shu, X.; Luo, R. rGO decorated CdS/CdO composite for detection of low concentration NO2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 299, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Sharma, V.; Vyas, R.; Kumari, M.; Kaushal, A.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, S.K.; Sachdev, K. A new sustainable green protocol for production of reduced graphene oxide and its gas sensing properties. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanov, Y.S.; Skryshevsky, V.A.; Slobodian, O.M.; Pustovyi, D.O.; Tang, X.; Raskin, J.P.; Nazarov, A.N. Influence of Gas Adsorption on the Impedance of Graphene Oxide. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 39th International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology, ELNANO 2019- Proceedings (ELNANO), Kyiv, Ukraine, 16–18 April 2019; pp. 155–158. [Google Scholar]
- Drewniak, S.; Muzyka, R.; Stolarczyk, A.; Pustelny, T.; Kotyczka-Morańska, M.; Setkiewicz, M. Studies of reduced graphene oxide and graphite oxide in the aspect of their possible application in gas sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biring, S.; Sadhu, A.S.; Deb, M. An Effective Optical Dual Gas Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Oxygen and Ammonia. Sensors 2019, 19, 5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Ocola, L.E.; Chen, J. Reduced graphene oxide for room-temperature gas sensors. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 445502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, J.; Zhao, L. Room-Temperature NH3 sensing of graphene oxide film and its enhanced response on the laser-Textured silicon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, W. Research Progress of Gas Sensor Based on Graphene and Its Derivatives: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatskiv, R.; Grym, J. Hydrogen sensing using reduced graphene oxide sheets supported by Pd nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 450, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, C.; Tang, C. Doping composite of polyaniline and reduced graphene oxide with palladium nanoparticles for. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 5396–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abideen, Z.U.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, S.S. An ultra-sensitive hydrogen gas sensor using reduced graphene oxide-loaded ZnO nanofibers. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15418–15421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
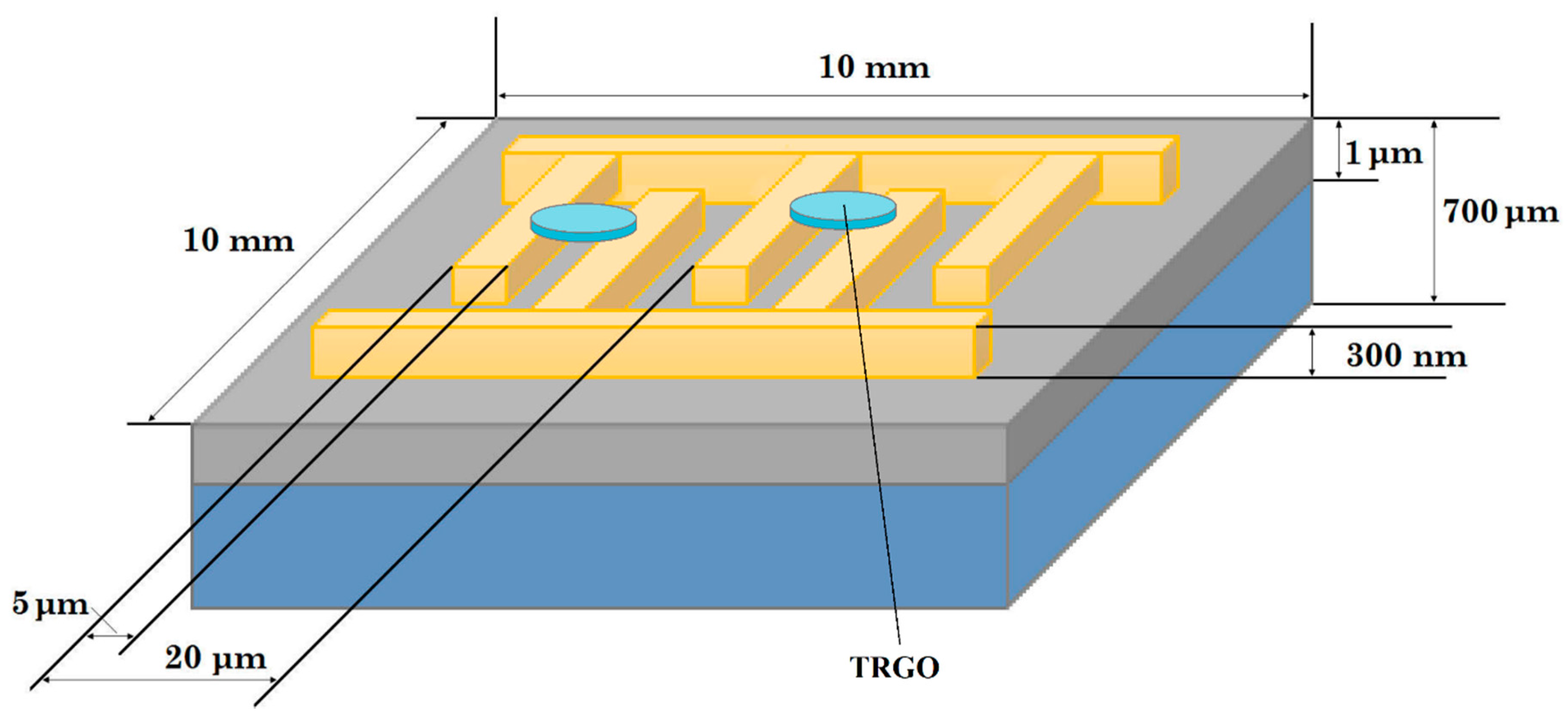


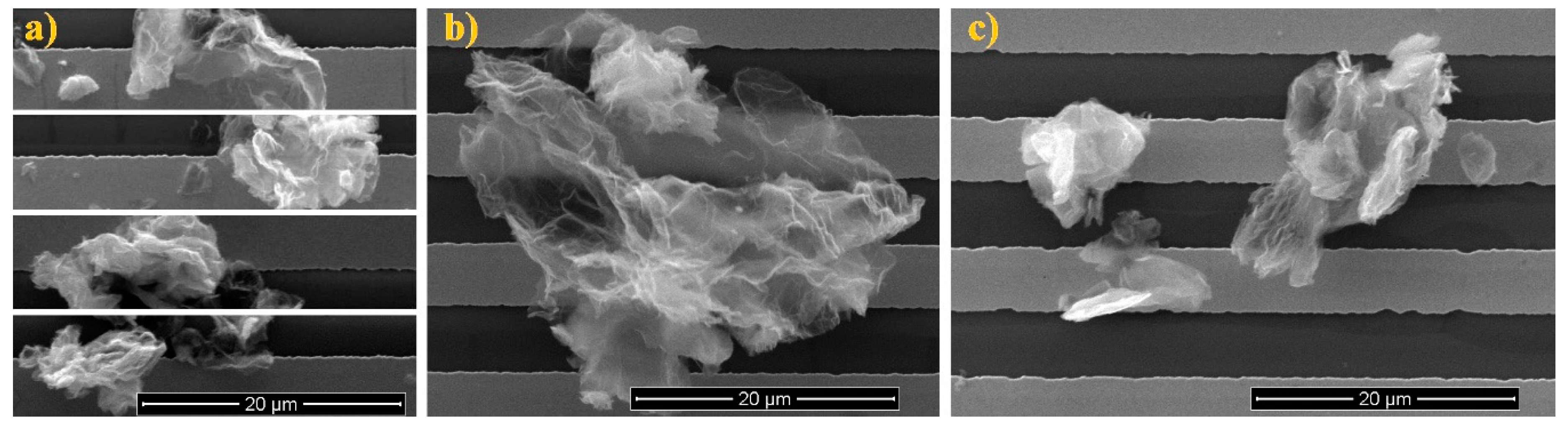




| Method of Oxidation | Reagents | Time, h | Obtained Graphite Oxide |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | H2SO4 (30 mL); NaNO3 (3 g); KMnO4 (3 g) | 2 | GO1 |
| T | H2SO4 (45 mL); H3PO4 (5 mL); KNO3 (1.5 g); KMnO4 (5 g) | 5 | GO2 |
| Material | Surface Area (SBET) m2 g−1 | Total Pore Volume (VT) cm3 g−1 | Micropore Volume (VDR) cm3 g−1 | Mesopore Volume (Vmez) cm3g−1 | Vmez/VT | Average Pore Diameter (dav) nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRGO1 | 183 ± 13 | 0.41 | 0.06 | 0.35 | 0.87 | 9.6 |
| TRGO2 | 965 ± 39 | 2.32 | 0.29 | 2.05 | 0.88 | 9.6 |
| Concentration of Hydrogen, % | Pch |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.9402 ± 0.0025 |
| 2 | 0.9213 ± 0.0020 |
| 3 | 0.9667 ± 0.0019 |
| 4 | 1.0297 ± 0.0020 |
| trc Dry, s | trc Wet, s | treg Dry, s | treg Wet, s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 22 | 21 | 527 | 481 |
| Sample 2 | 17 | 16 | 594 | 564 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drewniak, S.; Procek, M.; Muzyka, R.; Pustelny, T. Comparison of Gas Sensing Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Obtained by Two Different Methods. Sensors 2020, 20, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113175
Drewniak S, Procek M, Muzyka R, Pustelny T. Comparison of Gas Sensing Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Obtained by Two Different Methods. Sensors. 2020; 20(11):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113175
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrewniak, Sabina, Marcin Procek, Roksana Muzyka, and Tadeusz Pustelny. 2020. "Comparison of Gas Sensing Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Obtained by Two Different Methods" Sensors 20, no. 11: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113175
APA StyleDrewniak, S., Procek, M., Muzyka, R., & Pustelny, T. (2020). Comparison of Gas Sensing Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide Obtained by Two Different Methods. Sensors, 20(11), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20113175







