An Anti-Jamming Null-Steering Control Technique Based on Double Projection in Dynamic Scenes for GNSS Receivers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
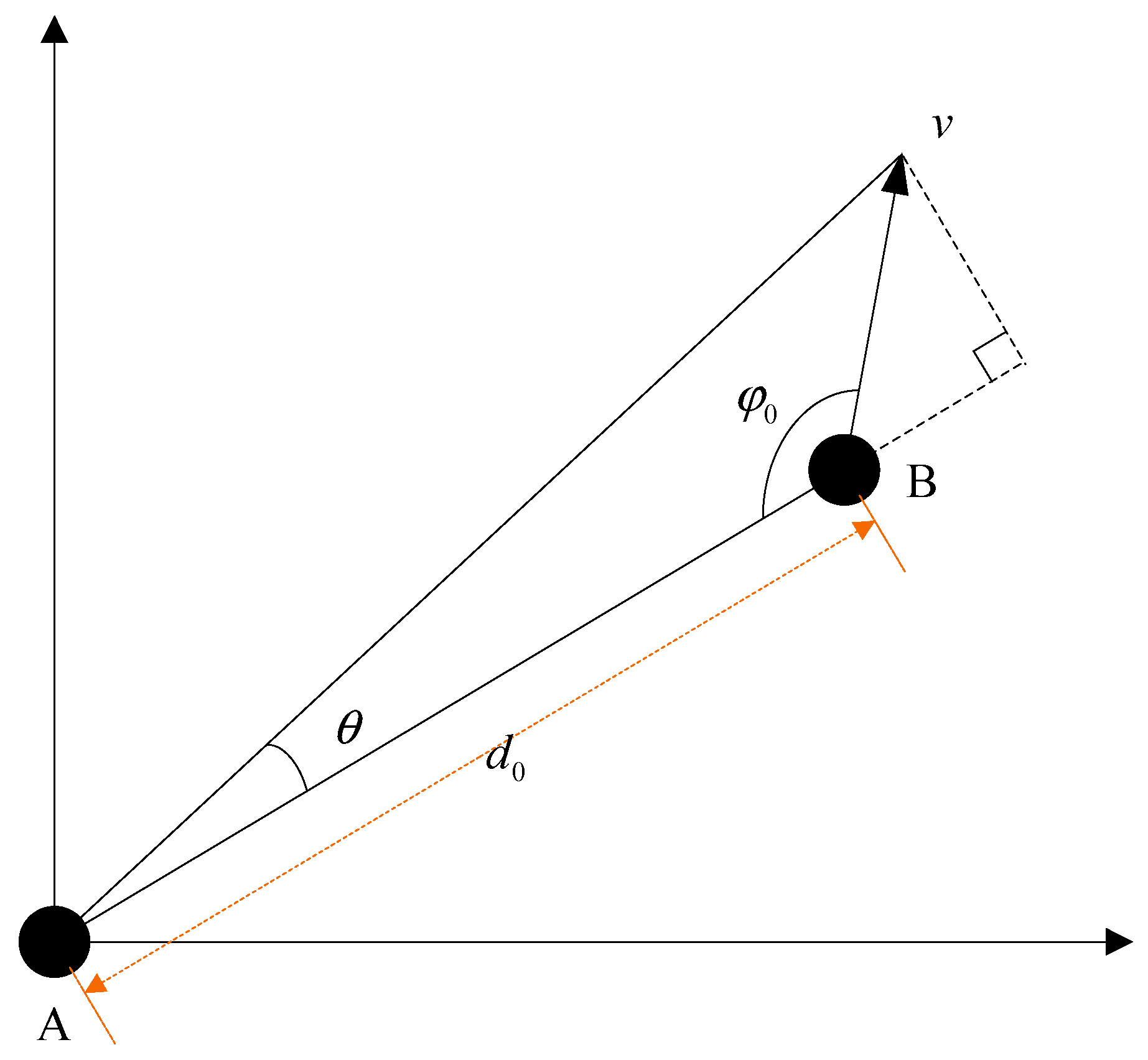
2. Dynamic Model and Signal Model
3. Analysis of Spatial Filtering Performance in Static and Dynamic Scenes
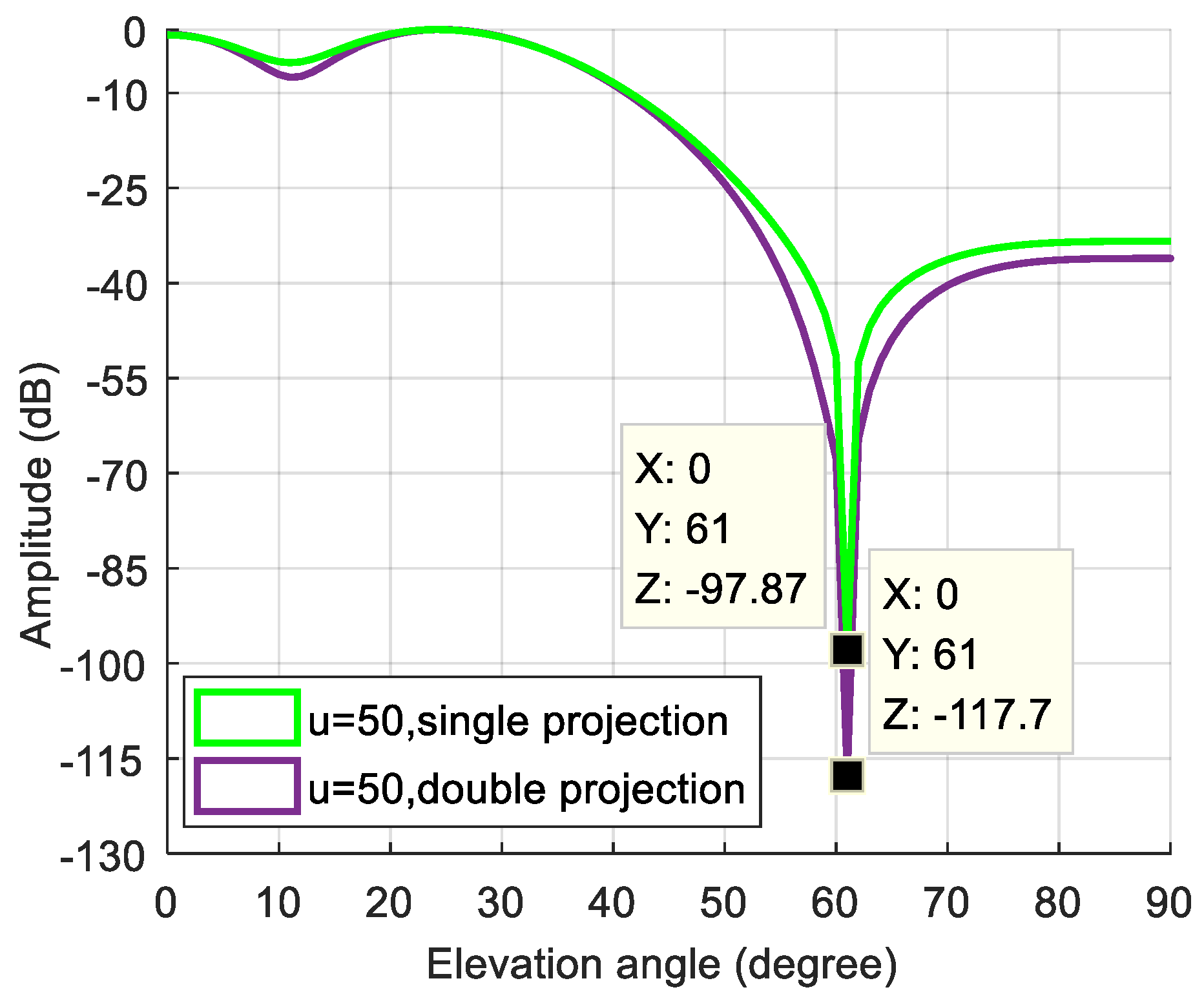
3.1. Static Scene
3.2. Dynamic Scene
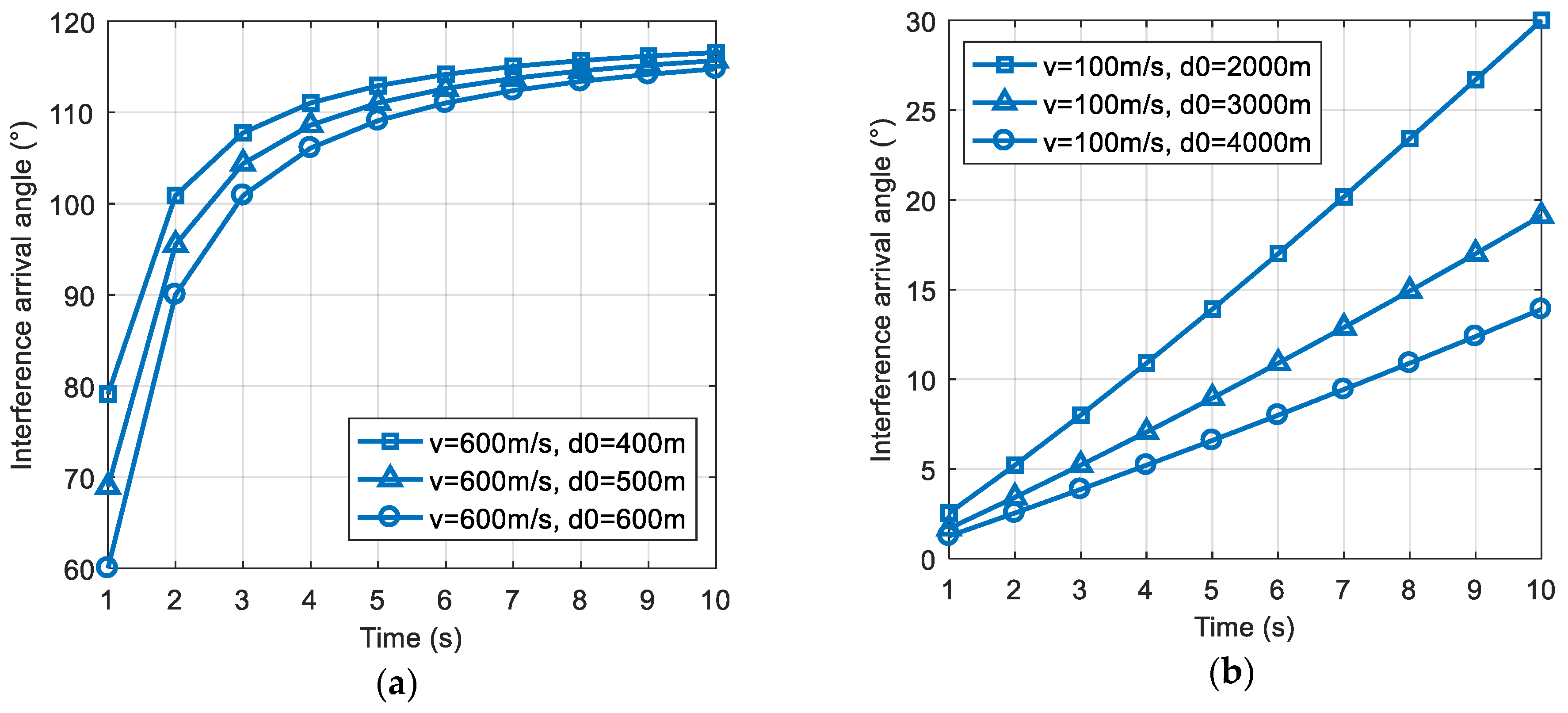
3.2.1. Lower Dynamic
3.2.2. Higher Dynamic
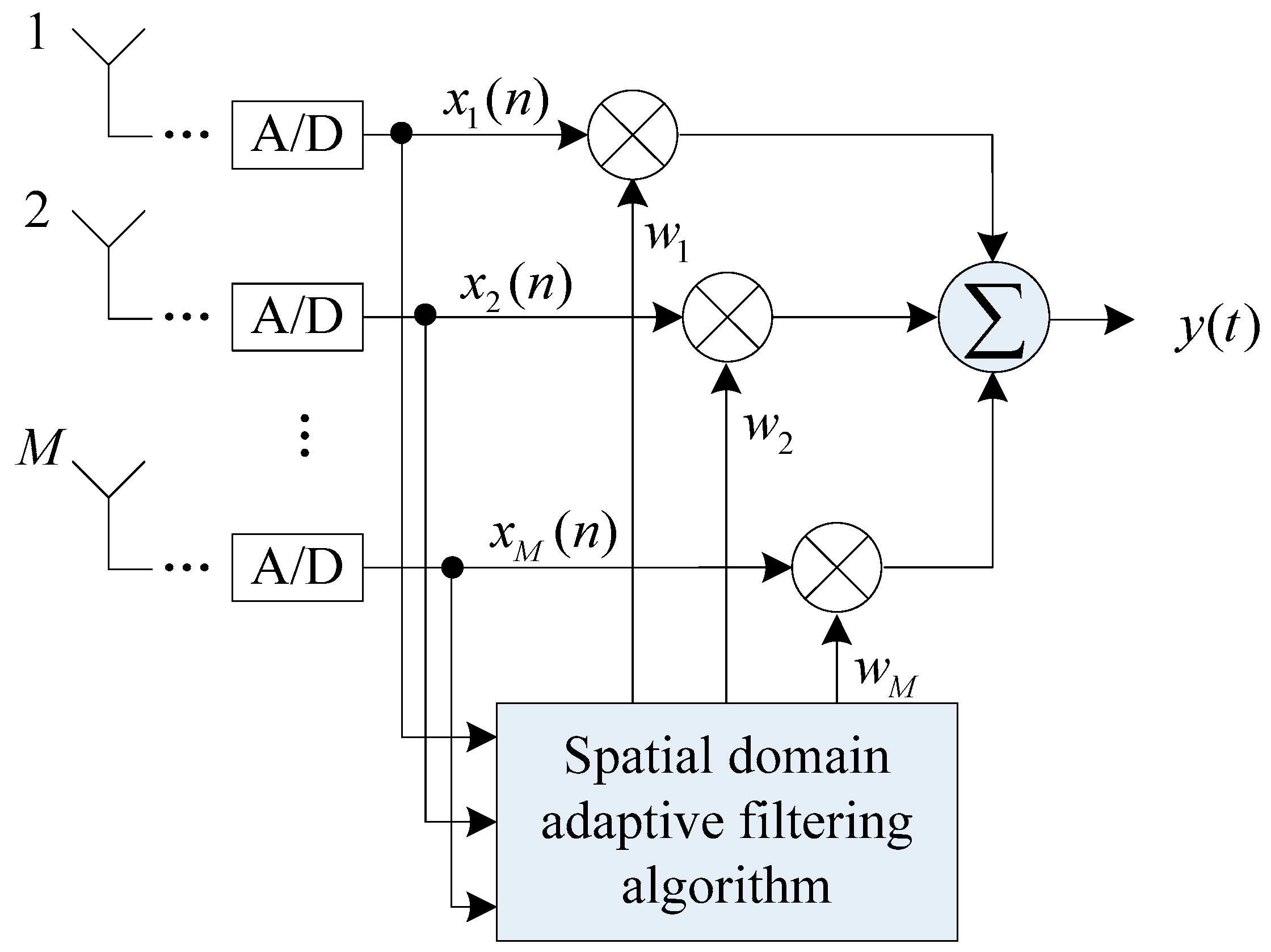
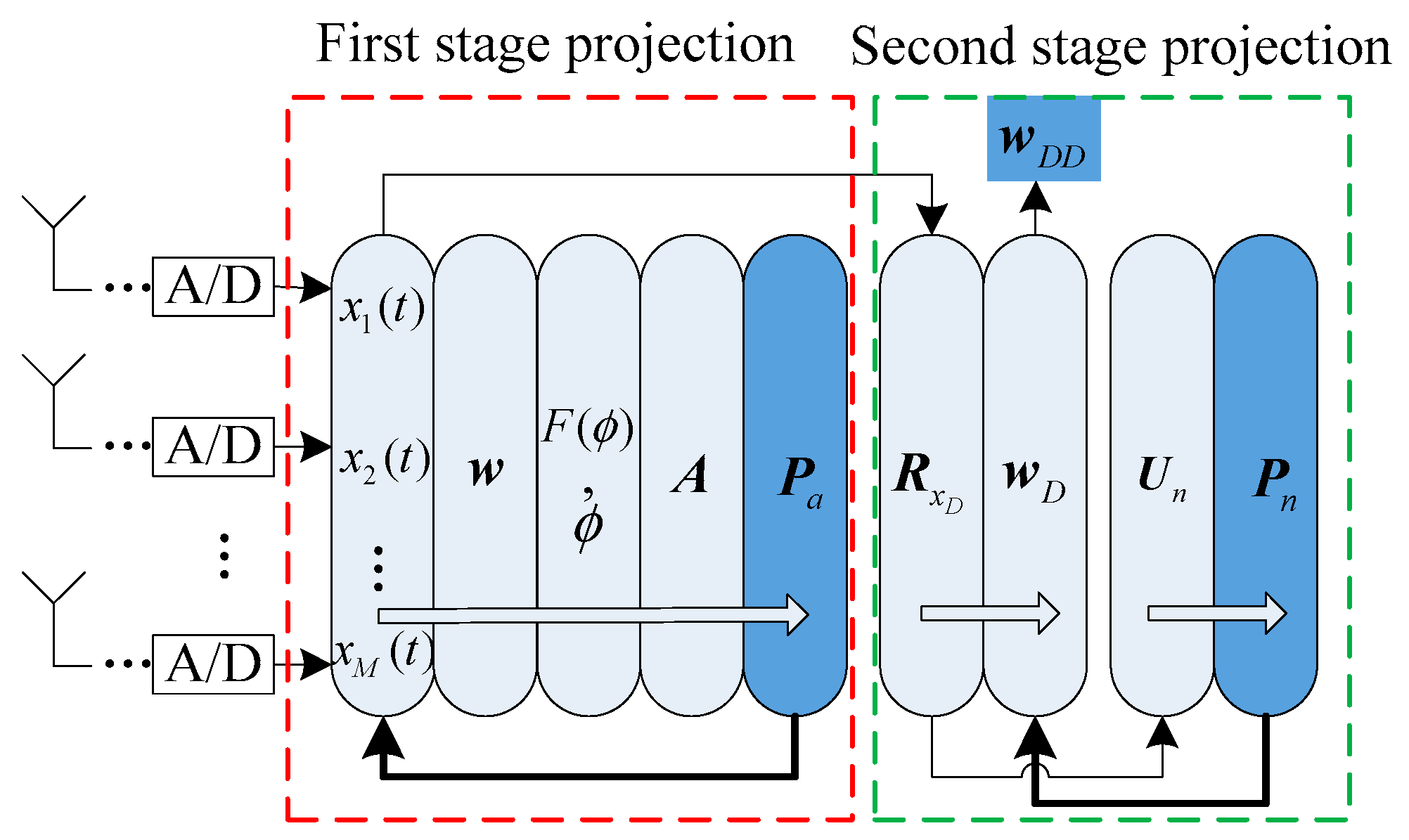
4. Interference-Nulling Control Algorithm
- Solve the anti-jamming weight vector according to spatial filtering algorithm;
- Calculate the spatial spectral function about the anti-jamming vector and determine the direction angle corresponding to the null, and the steering vector of the interference signal can be obtained;
- Calculate the projection matrix , project the sampled signal into the noise subspace and calculate the autocorrelation matrix , then calculate the anti-jamming vector ;
- Perform eigen decomposition on , construct a noise subspace , and calculate the corresponding projection matrix ;
- Project the anti-jamming weight vector to the noise subspace and obtain .
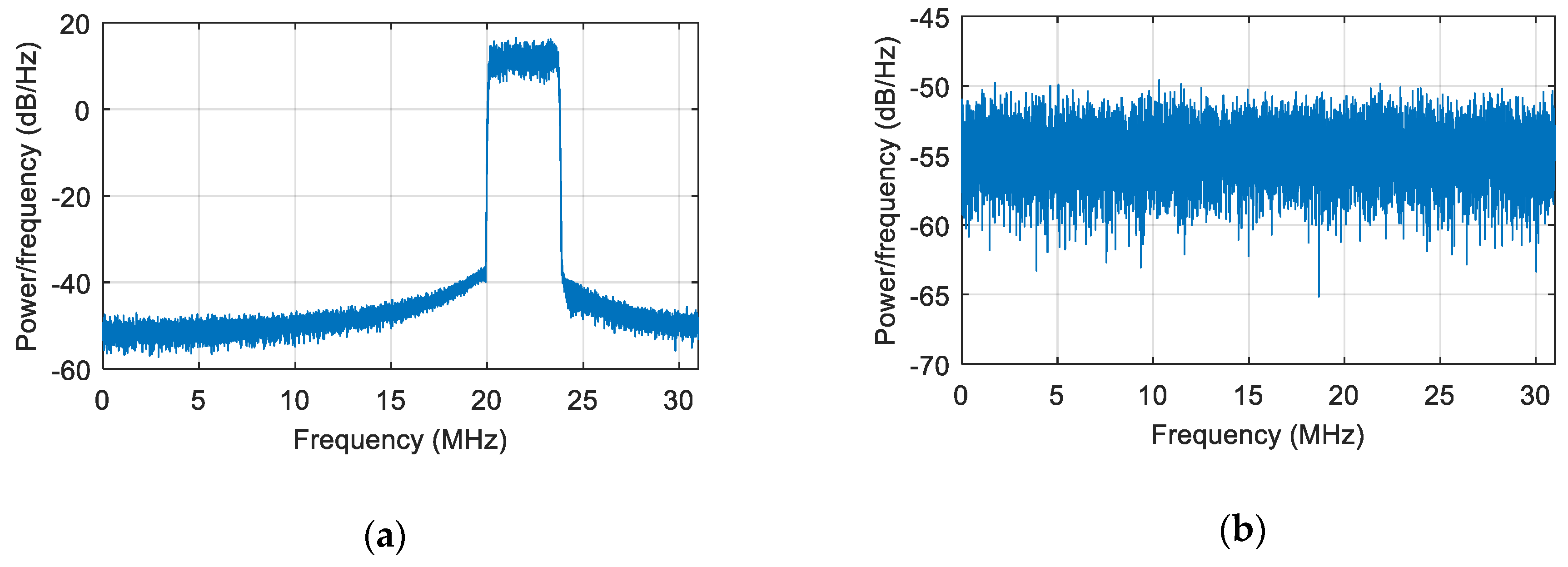
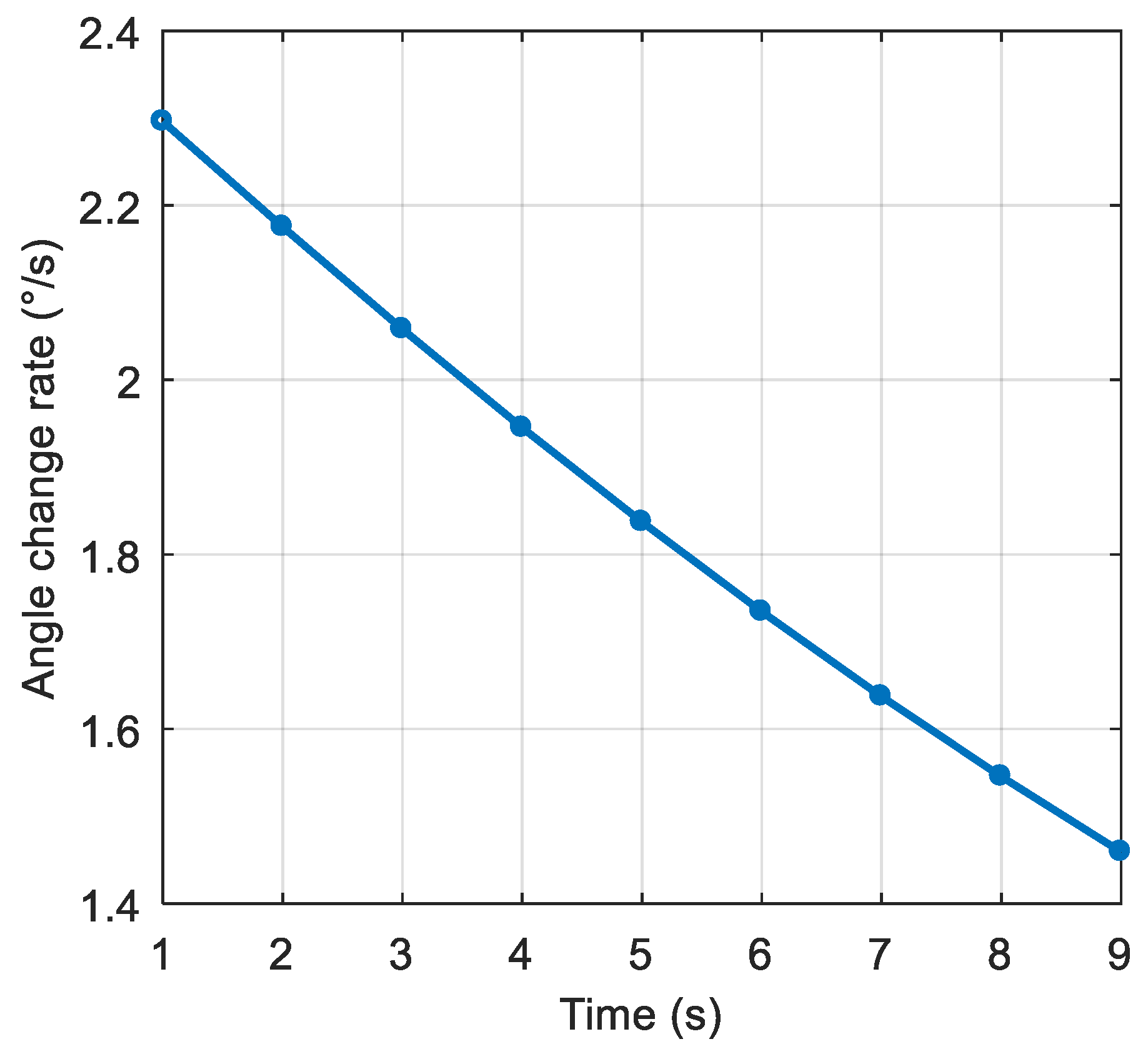
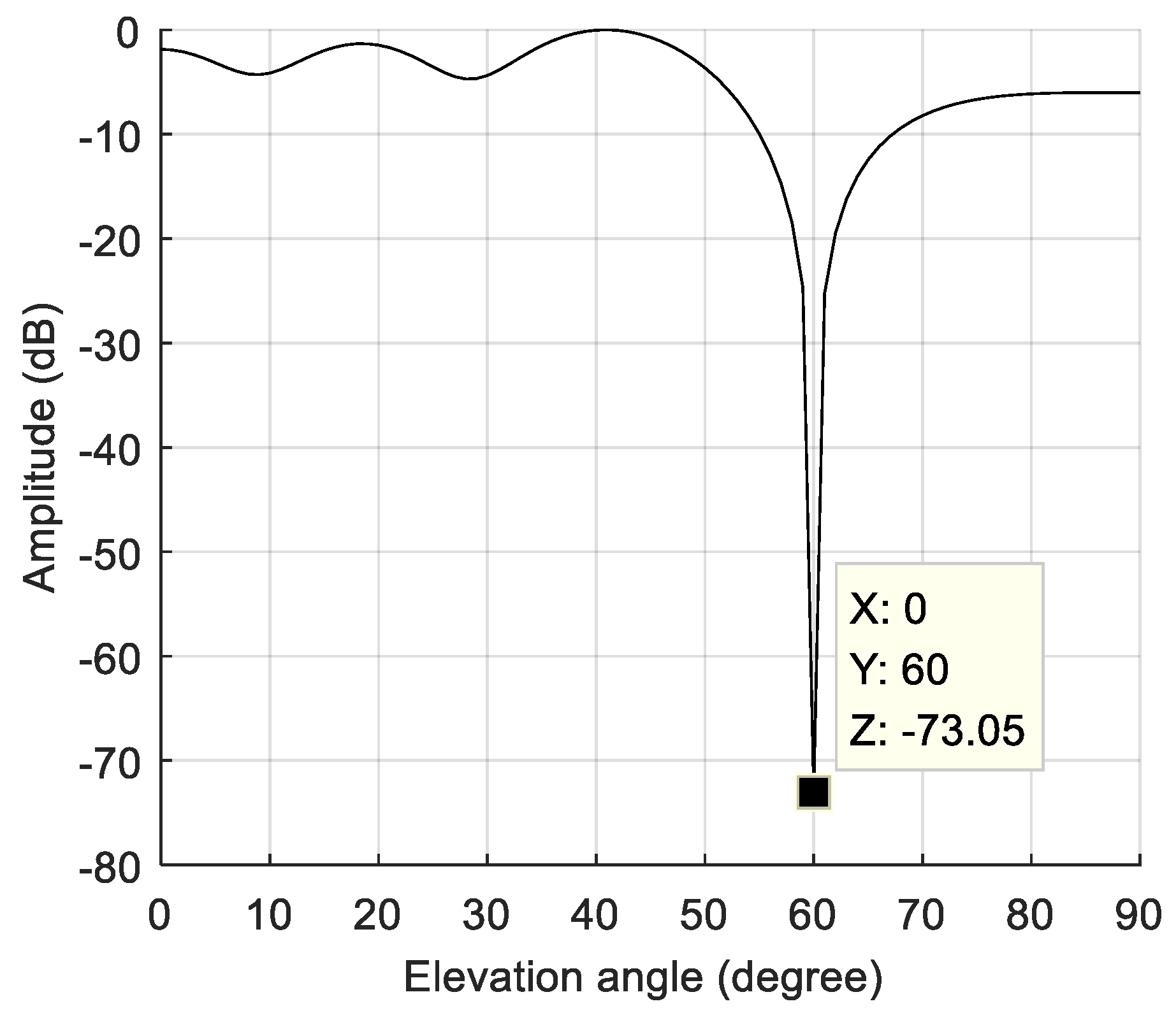
5. Simulation and Test
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, R.; Su, Z.; Zhou, K.; Mou, S. A Robust Signal Driven Method for GNSS Signals Interference Detection. Chin. J. Electron. 2018, 27, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.G.; Borio, D.; Zhang, Y.D.; Galleani, L.J.I.S.P.M. Time-Frequency Analysis for GNSSs: From interference mitigation to system monitoring. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liao, G.; Feng, W. Sparse Representation Based Algorithm for Airborne Radar in Beam-Space Post-Doppler Reduced-Dimension Space-Time Adaptive Processing. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5896–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshmand, S.; Jahromi, A.J.; Broumandan, A.; Lachapelle, G. GNSS space-time interference mitigation and attitude determination in the presence of interference signals. Sensors 2015, 15, 12180–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delikaris-Manias, S.; Vilkamo, J.; Pulkki, V. Signal-Dependent Spatial Filtering Based on Weighted-Orthogonal Beamformers in the Spherical Harmonic Domain. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2016, 24, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Prades, C.; Arribas, J.; Closas, P. Robust GNSS Receivers by Array Signal Processing: Theory and Implementation. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, G.; Choo, H.; Kim, S. Improvement of Pattern Null Depth and Width Using a Curved Array With Two Subarrays for CRPA Systems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2015, 63, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Li, Y.P. An effective method on increasing the null depth of beam forming via virtual array transformation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Science & Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 4–6 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Zheng, J. A Broadened and Deepened Anti-Jamming Technology for High-Dynamic GNSS Array Receivers. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2016, 99, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Tan, Q.; Pan, H.; Ma, H.; Sun, X.-L. Robust anti-jamming method for high dynamic global positioning system receiver. IET Signal Process. 2016, 10, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Ser, W. Adaptive null steering beamformer implementation for flexible broad null control. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, L.; Wu, R.; Wang, W. Robust widenull anti-jamming algorithm for high dynamic GPS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 21–25 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, X. A Robust Anti-Jamming Navigation Receiver with Antenna Array and GPS/SINS. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2014, 18, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, F.; Nie, J.; Ou, G. Blind adaptive channel mismatch equalisation method for GNSS antenna arrays. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Nie, J.; Chen, F.; Ou, G. Distortionless space-time adaptive processor based on MVDR beamformer for GNSS receiver. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2017, 11, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igambi, D.; Yang, X.; Jalal, B. Robust Adaptive Beamforming Based on Desired Signal Power Reduction and Output Power of Spatial Matched Filter. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 50217–50228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cui, X.; Lu, M. An SDR-Based Real-Time Testbed for GNSS Adaptive Array Anti-Jamming Algorithms Accelerated by GPU. Sensors 2016, 16, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazos, S.; Hurtado, M.; Muravchik, C. On Sparse Methods for Array Signal Processing in the Presence of Interference. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2015, 14, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, F.; Zhao, C.; He, C. An Orthogonal Projection Algorithm to Suppress Interference in High-Frequency Surface Wave Radar. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.T.; Seif, N.P.A.; Ahmed, W.A.E.M. Hermite-Gaussian-like eigenvectors of the discrete Fourier transform matrix based on the direct utilization of the orthogonal projection matrices on its eigenspaces. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 2815–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zheng, J.-S.; Dong, Z.-C.; Panayirci, E.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Qingnuobu, R. An Improved Adaptive Subspace Tracking Algorithm Based on Approximated Power Iteration. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 43136–43145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, W.; Pesavento, M.; Zoubir, A.M. Performance Analysis of the Decentralized Eigendecomposition and ESPRIT Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2016, 64, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



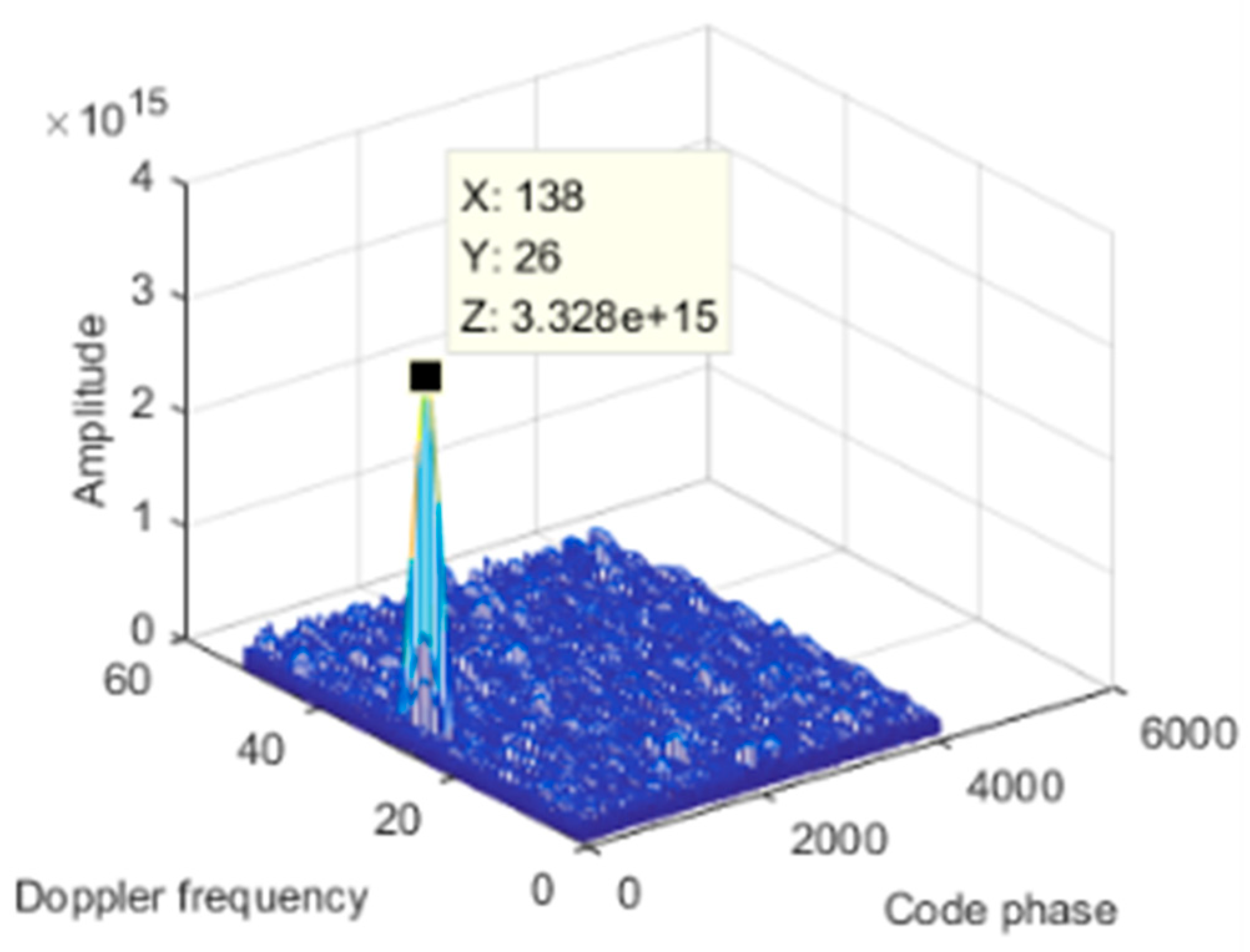

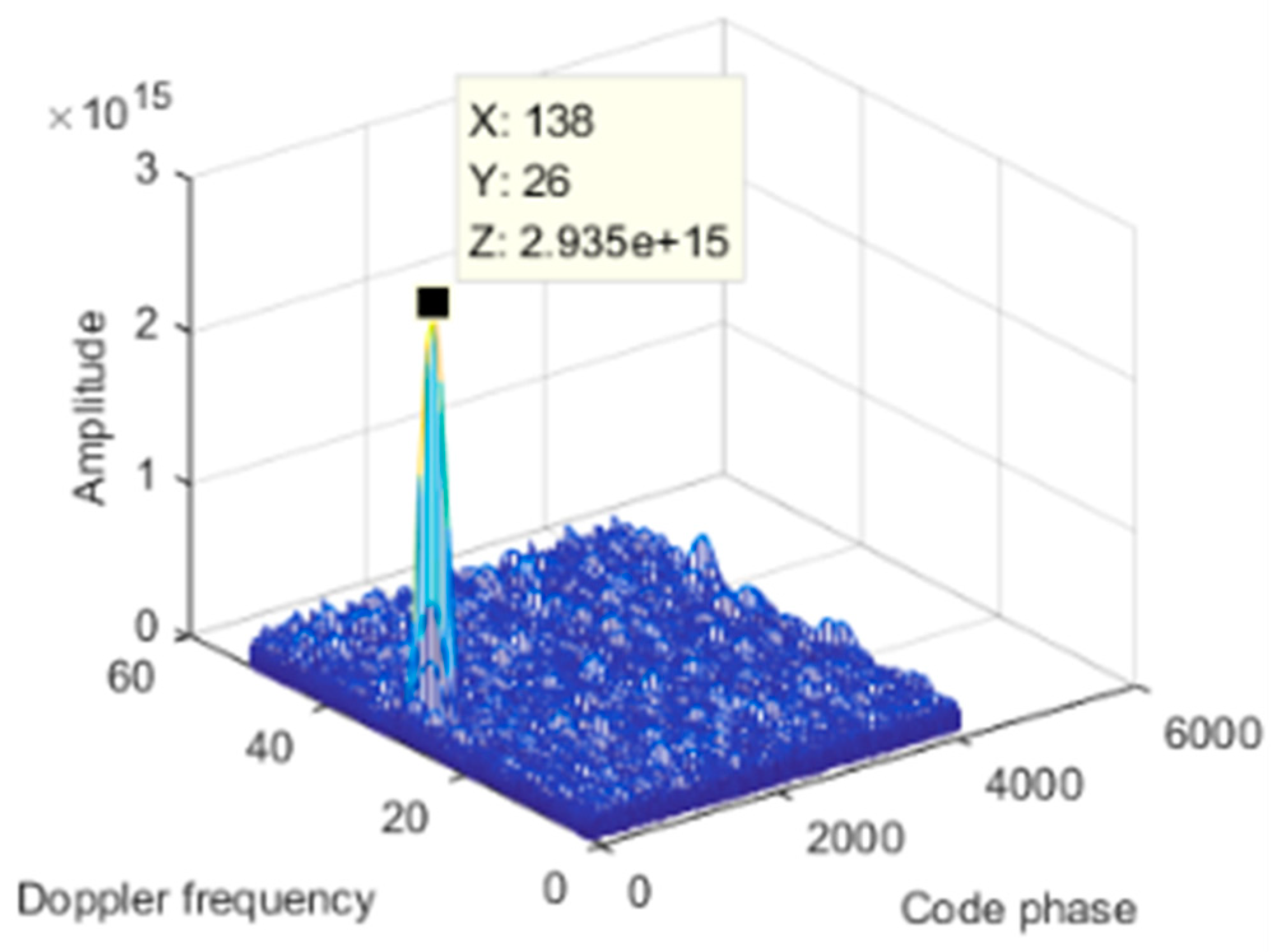

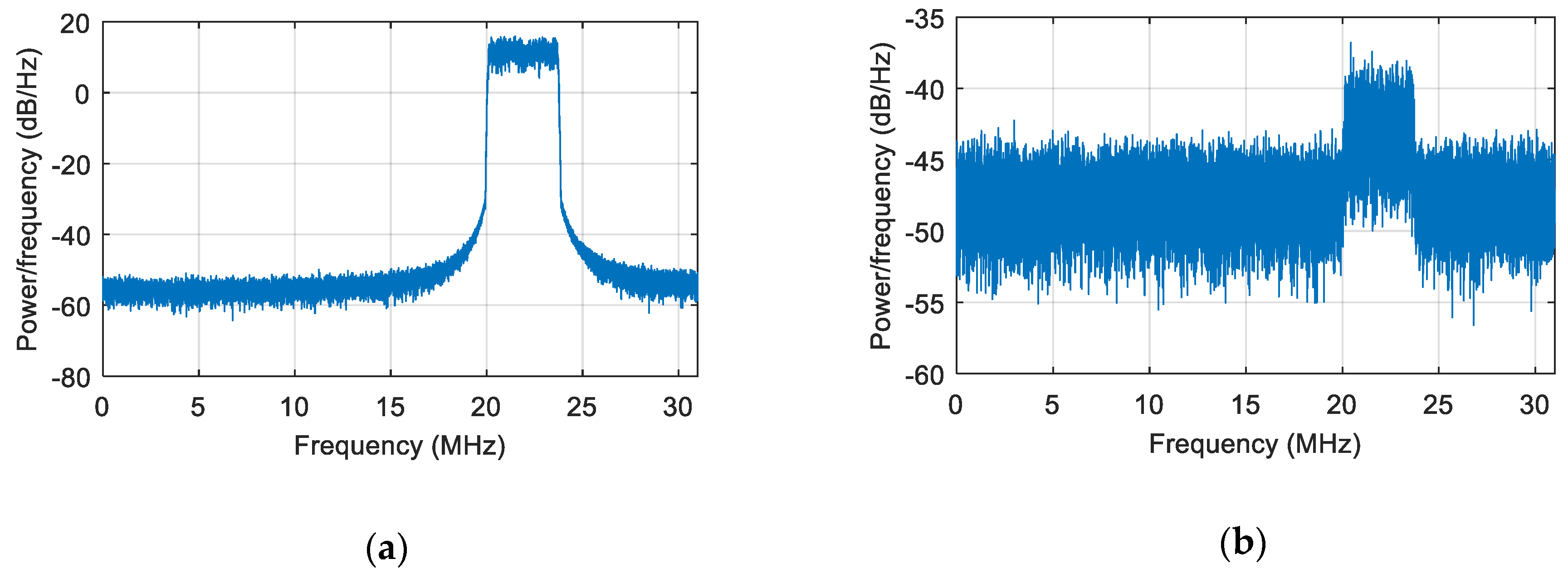





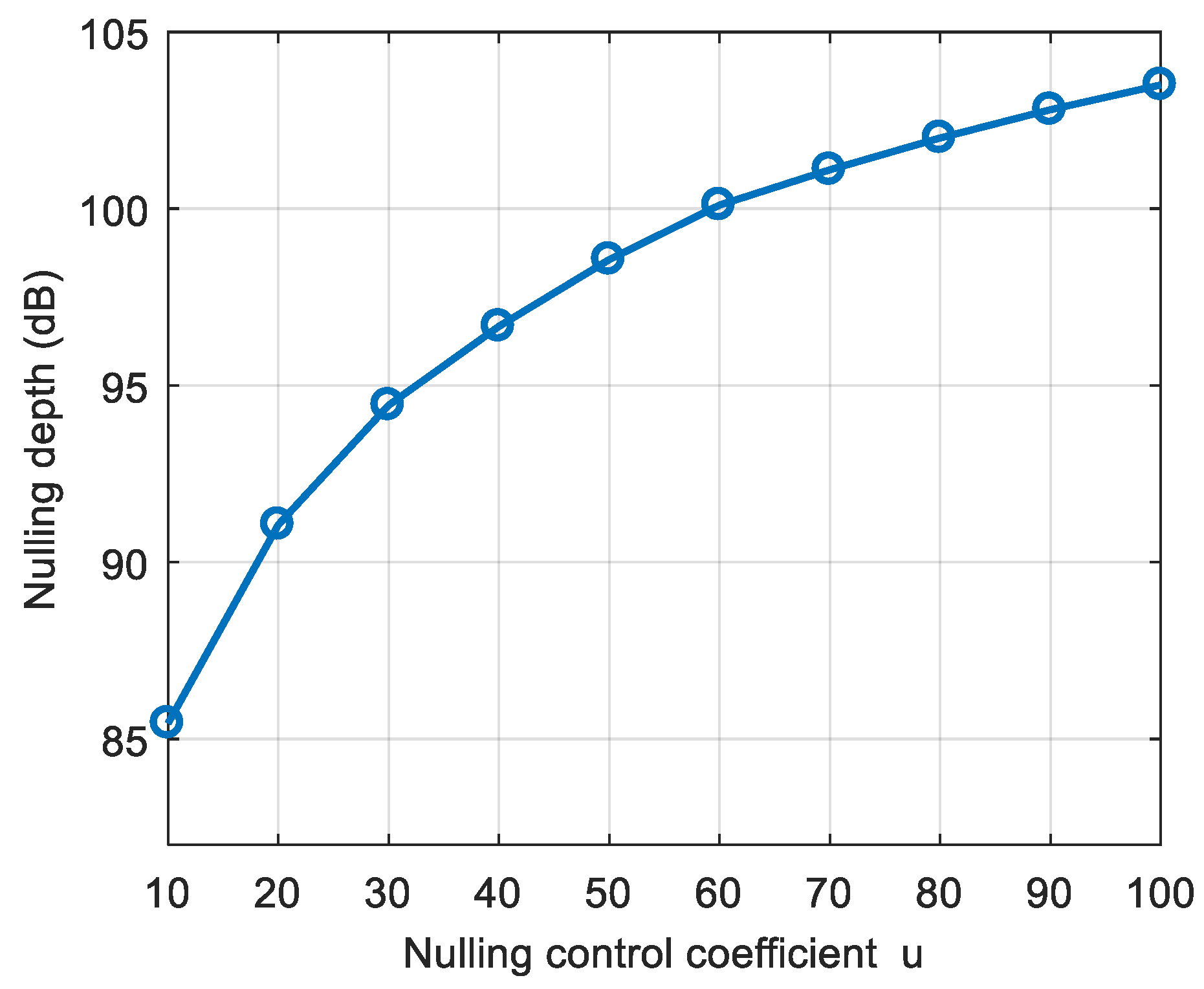
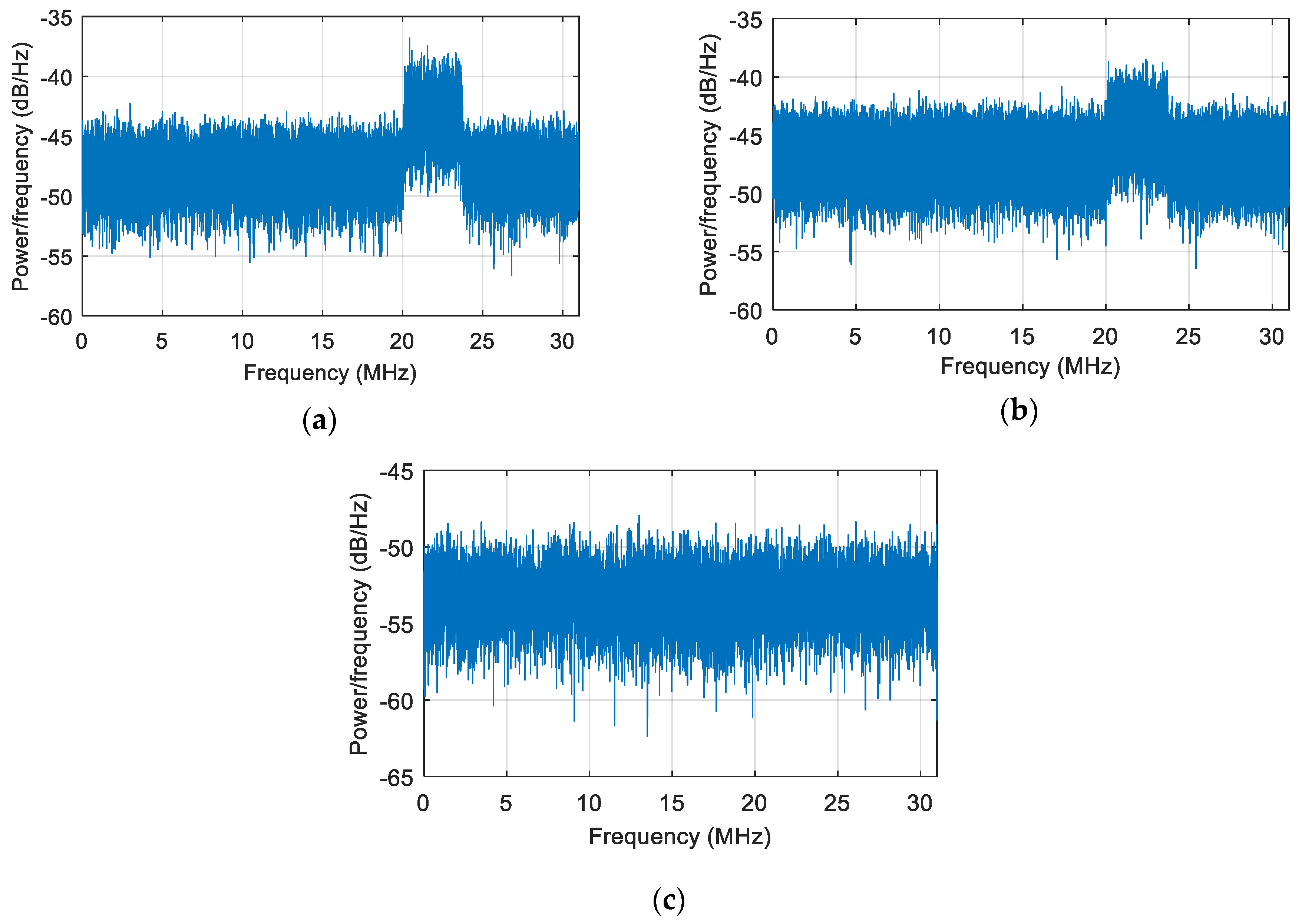

| Category | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite signal parameters | Sampling frequency | 62 MHz |
| RF frequency | 1561.098 MHz | |
| Intermediate frequency | 40.098 MHz | |
| Code rate | 2.046 MHz | |
| Signal bandwidth | 4.092 MHz | |
| Carrier-to-noise ratio | 45 dBHz | |
| Signal direction (angle of pitch) | 40° | |
| Interference parameters | Type of interference | Gaussian interference |
| Interference bandwidth | 4.092 MHz | |
| Jamming-to-signal ratio (JSR) | 80 dB | |
| Initial direction of interference (angle of pitch) | 60° | |
| Array parameters | Array type | Linetype |
| Number of array elements | 7 | |
| Element spacing | Half-wavelength | |
| Anti-jamming algorithm parameter | Weight vector update time | 1 ms |
| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Relative speed | 100 m/s | |
| The angle between the relative motion direction and the radial connection | 120° | |
| Initial distance | 2000 m | |
| Maximum rate of change of the interference arrival angle | 0.0023 °/ms |
| Symbol | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Relative speed | 700 m/s | |
| The angle between the relative motion direction and the radial connection | 20° | |
| Initial distance | 1000 m | |
| Maximum rate of change of the interference arrival angle | 0.09 °/ms |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Chang, Q.; Xu, Y. An Anti-Jamming Null-Steering Control Technique Based on Double Projection in Dynamic Scenes for GNSS Receivers. Sensors 2019, 19, 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071661
Wang H, Chang Q, Xu Y. An Anti-Jamming Null-Steering Control Technique Based on Double Projection in Dynamic Scenes for GNSS Receivers. Sensors. 2019; 19(7):1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071661
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Qing Chang, and Yong Xu. 2019. "An Anti-Jamming Null-Steering Control Technique Based on Double Projection in Dynamic Scenes for GNSS Receivers" Sensors 19, no. 7: 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071661
APA StyleWang, H., Chang, Q., & Xu, Y. (2019). An Anti-Jamming Null-Steering Control Technique Based on Double Projection in Dynamic Scenes for GNSS Receivers. Sensors, 19(7), 1661. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19071661




