Design and Manufacturing of a Disposable, Cyclo-Olefin Copolymer, Microfluidic Device for a Biosensor †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
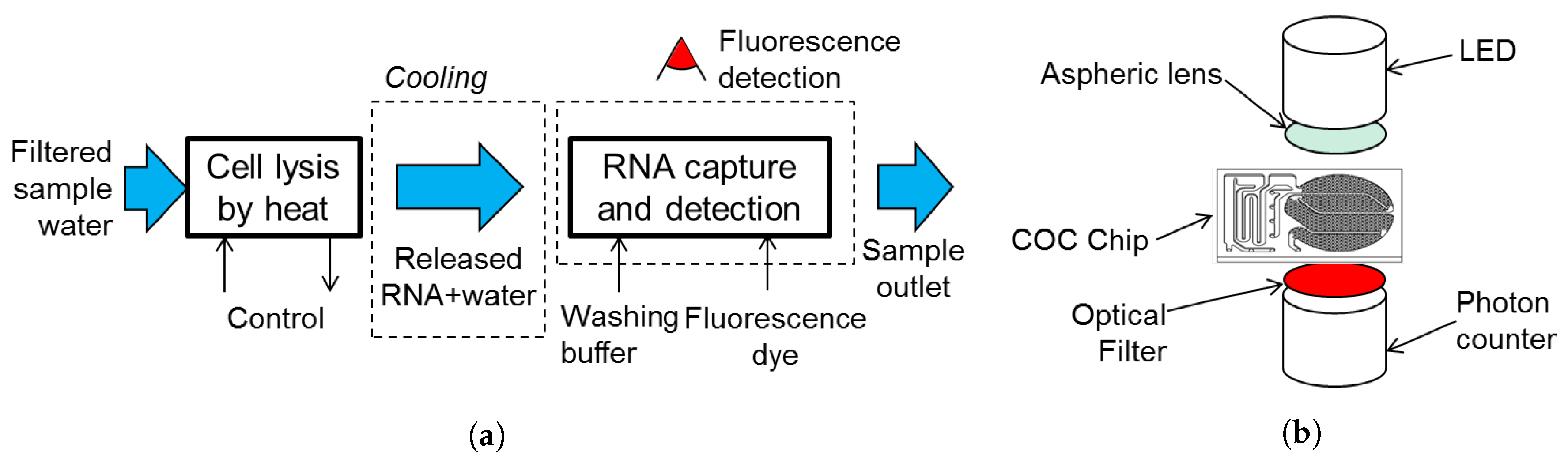
2.1. Biosensor Design and Preparation
2.2. Screen Printed Temperature Sensors
2.3. Cell Heat Lysis
2.4. Static Hybridization and Activated Biosensors
2.5. Closing of Microfluidics
2.6. Biosensor Experimental Setup
3. Results
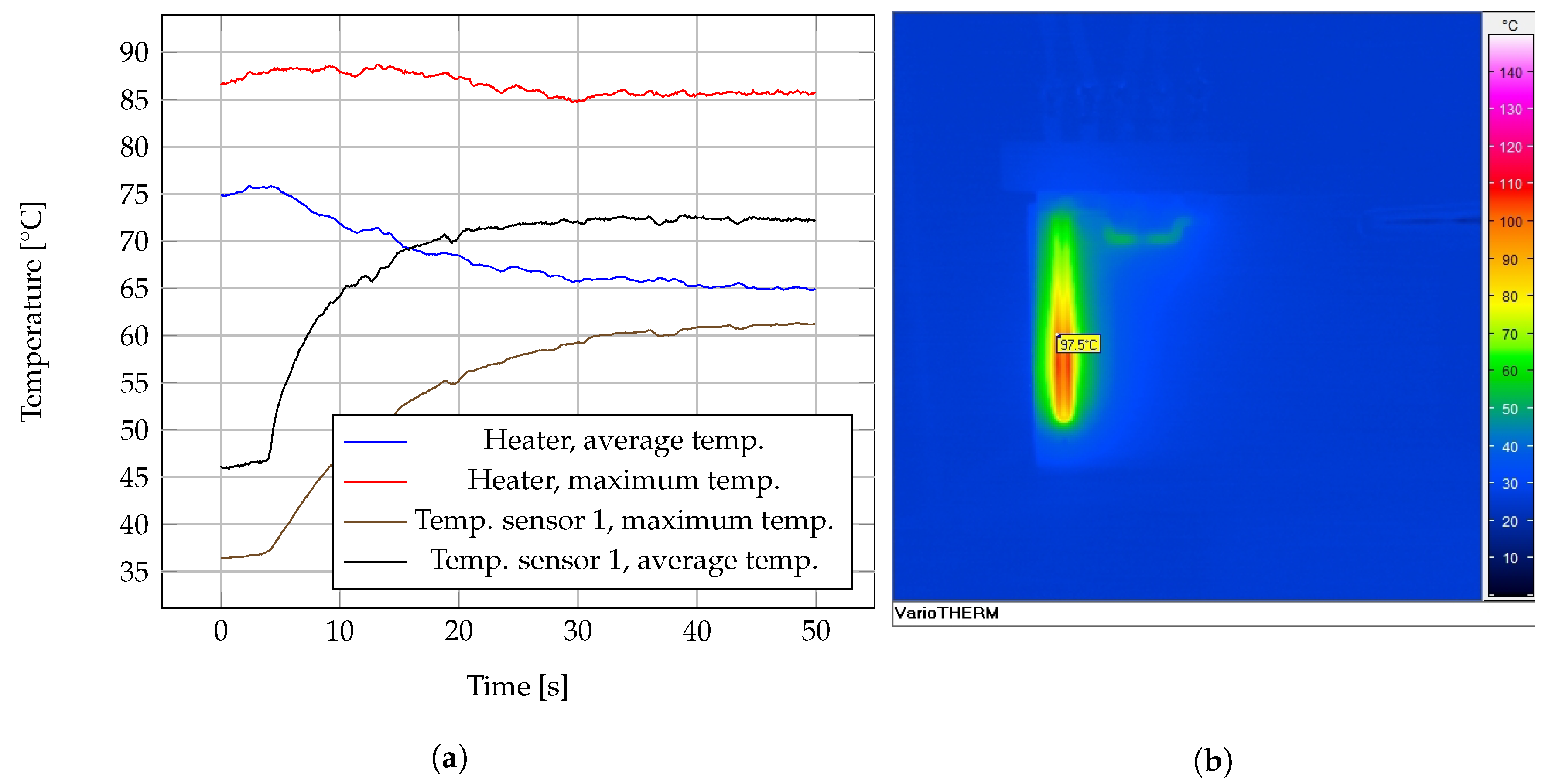
3.1. Screen Printed Temperature Sensors and Heater
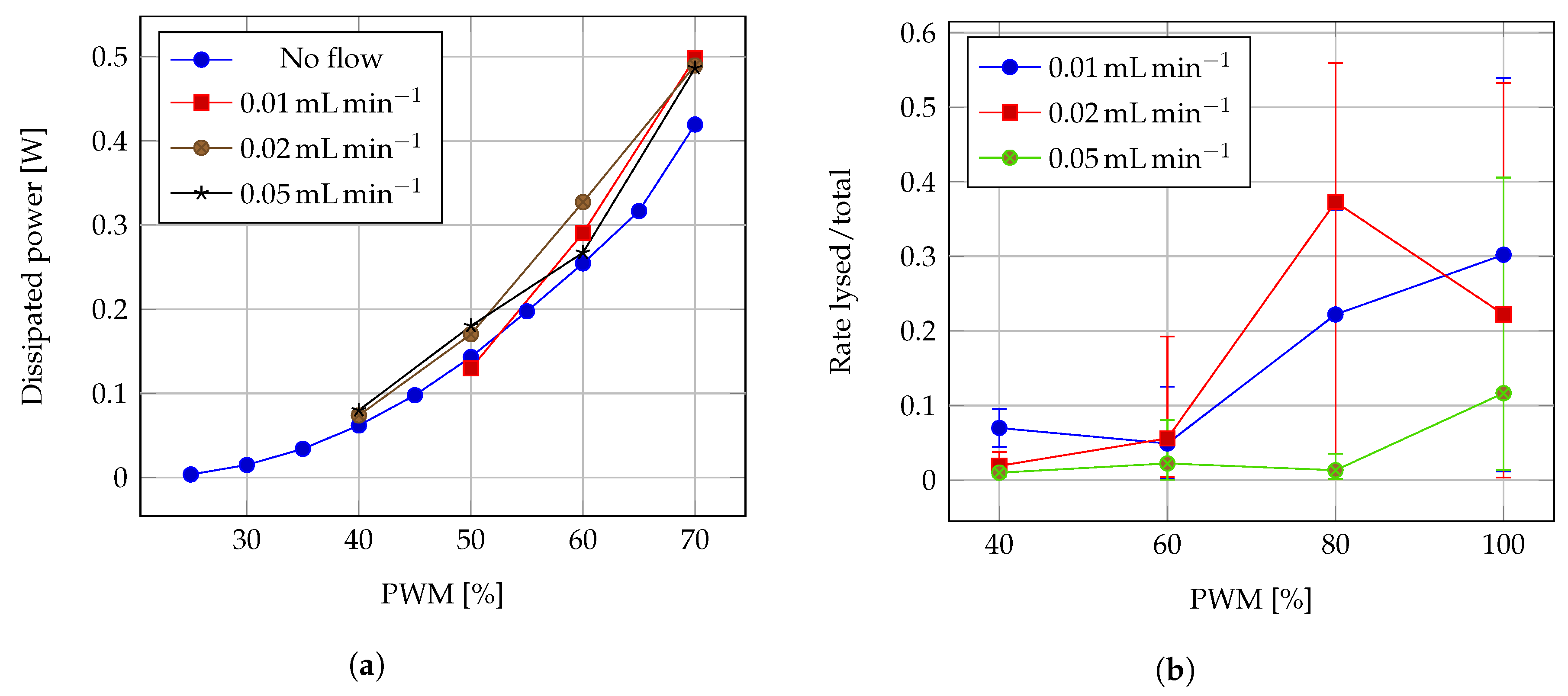
3.2. Cell Heat Lysis
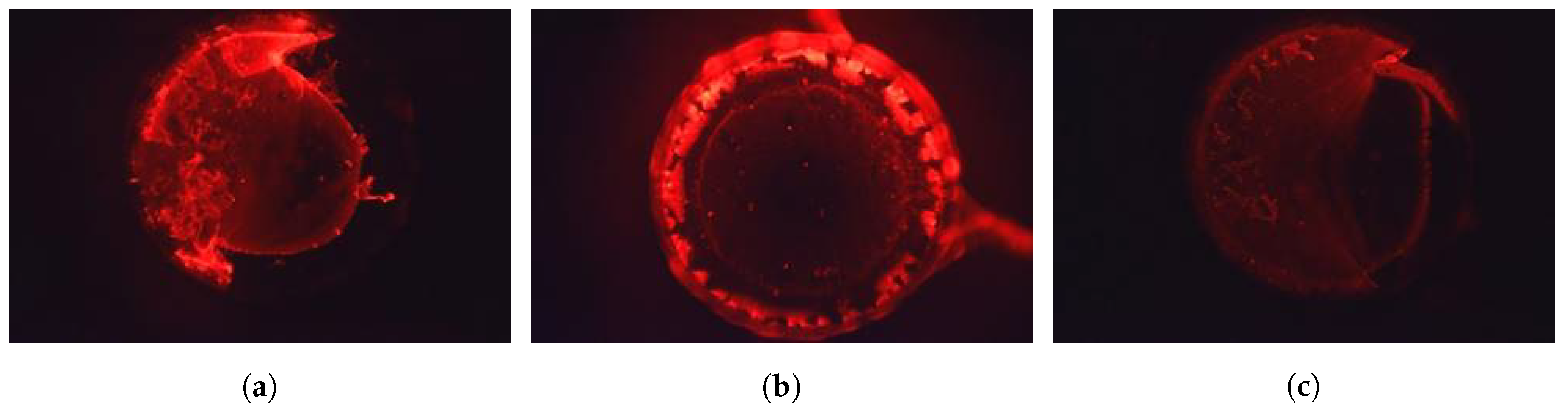
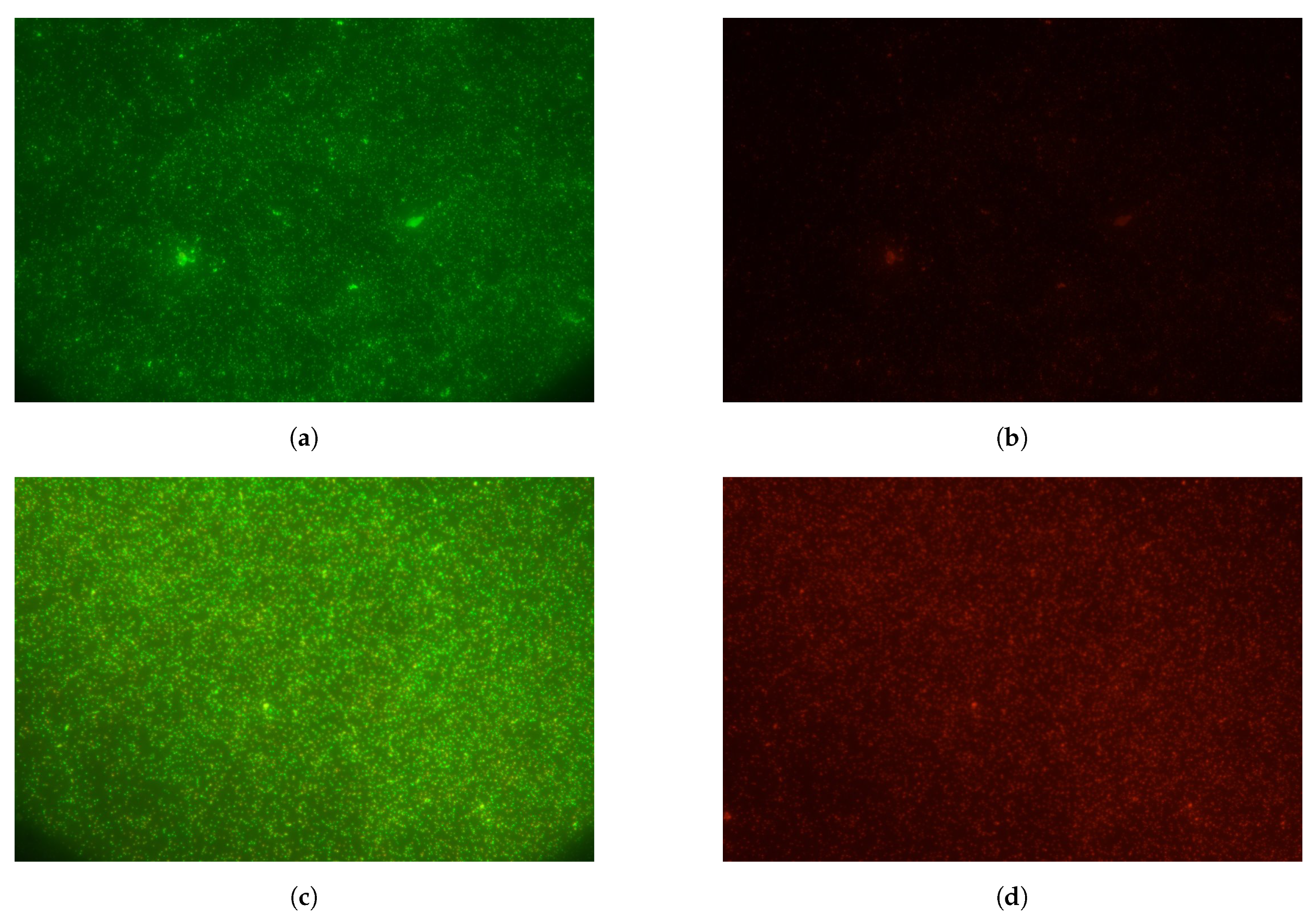
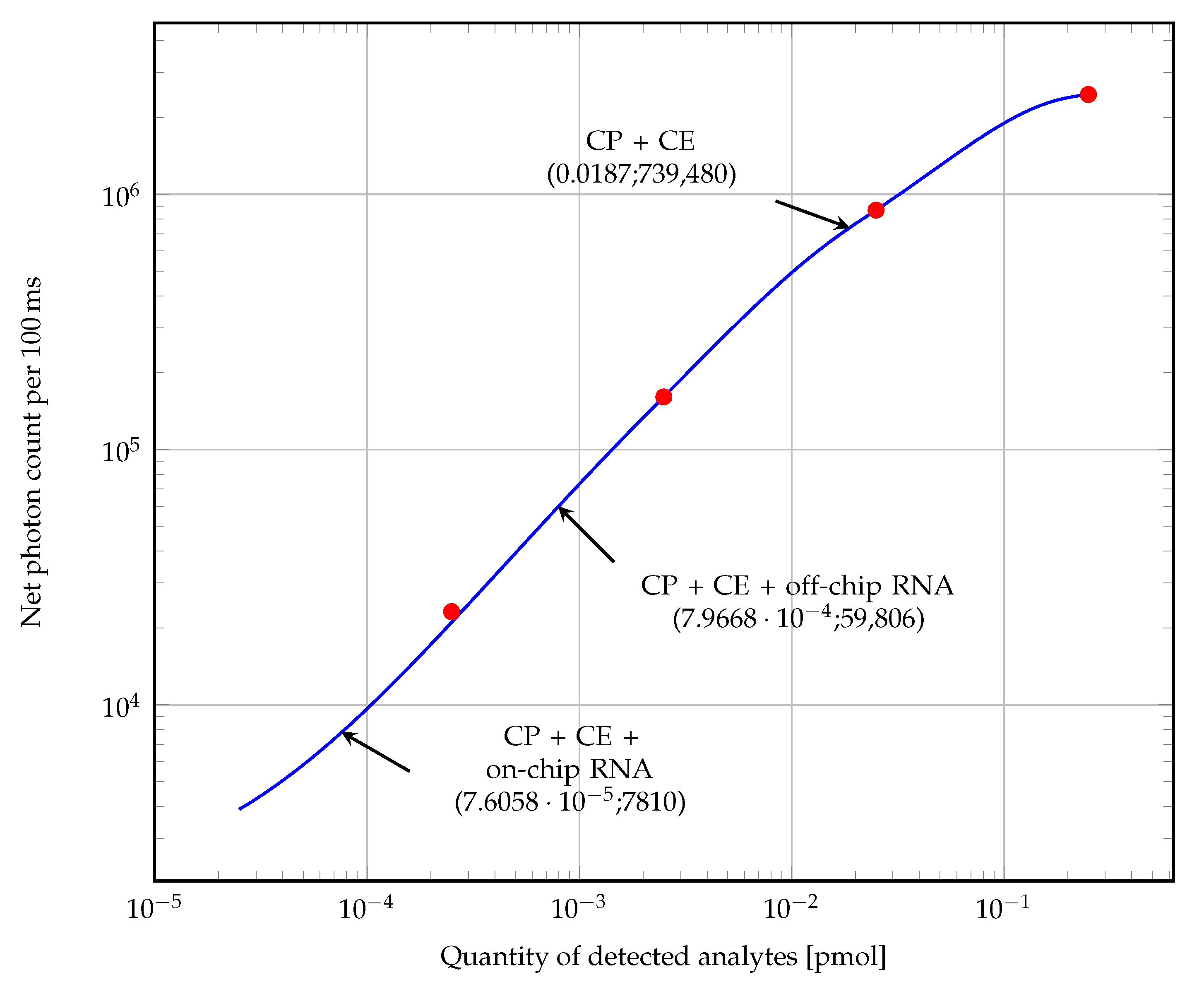
3.3. Fluorescence Tests on Biosensor
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirsch, J.; Siltanen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Revzin, A.; Simonian, A. Biosensor technology: Recent advances in threat agent detection and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, J.; Silberzan, P. Microfluidics for Biotechnology; Microelectromechanical Systems Series; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liana, D.D.; Raguse, B.; Gooding, J.J.; Chow, E.; Liana, D.D.; Raguse, B.; Gooding, J.J.; Chow, E. Recent Advances in Paper-Based Sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 11505–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.W. Polymer microfluidics: Simple, low-cost fabrication process bridging academic lab research to commercialized production. Micromachines 2016, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrifaiy, A.; Lindahl, O.A.; Ramser, K. Polymer-Based Microfluidic Devices for Pharmacy, Biology and Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2012, 4, 1349–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencturk, E.; Mutlu, S.; Ulgen, K.O. Advances in microfluidic devices made from thermoplastics used in cell biology and analyses. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 051502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worgull, M. Hot Embossing: Theory and Technology of Microreplication; William Andrew: Oxford, UK, 2009; p. 345. [Google Scholar]
- Sastri, V.R. Materials Used in Medical Devices. In Plastics in Medical Devices, 2nd ed.; Sastri, V.R., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2014; Chapter 3; pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worgull, M.; Kolew, A.; Heilig, M.; Schneider, M.; Dinglreiter, H.; Rapp, B. Hot embossing of high performance polymers. In Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on Design Test Integration and Packaging of MEMS/MOEMS (DTIP), Seville, Spain, 5–7 May 2010; pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar]
- Khanarian, G.; Celanese, H. Optical properties of cyclic olefin copolymers. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piruska, A.; Nikcevic, I.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, C.; Heineman, W.R.; Limbach, P.A.; Seliskar, C.J. The autofluorescence of plastic materials and chips measured under laser irradiation. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1348–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, P.S.; Ohlsson, P.D.; Ordeig, O.; Kutter, J.P. Cyclic olefin polymers: Emerging materials for lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydewitz, V.; Krumova, M.; Michler, G.; Park, J.; Kim, S. Morphology and micromechanical behaviour of ethylene cycloolefin copolymers (COC). Polymer 2005, 46, 5608–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, P.W. Hot embossing of cyclic olefin copolymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 055008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, P.W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y. Effect of norbornene content on deformation properties and hot embossing of cyclic olefin copolymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5364–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jung, T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, C.; Woo, K.; Seol, J.H.; Yang, S. A microfluidic device for label-free detection of Escherichia coli in drinking water using positive dielectrophoretic focusing, capturing, and impedance measurement. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasaki, H.; Yasui, T.; Yanagida, T.; Kaji, N.; Kanai, M.; Nagashima, K.; Kawai, T.; Baba, Y. A real-time simultaneous measurement on a microfluidic device for individual bacteria discrimination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.; Zhou, G.; Chang, J.; Pu, H.; Jin, B.; Sui, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, C.H.; Magruder, M.; Chen, J. Rapid detection of single E. coli bacteria using a graphene-based field-effect transistor device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.S.; Misra, S.K.; Dighe, K.; Wang, Z.; Schwartz-Duval, A.S.; Sar, D.; Pan, D. Electrically-receptive and thermally-responsive paper-based sensor chip for rapid detection of bacterial cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudeh, A.M.; Trigui, H.; Mendis, N.; Faucher, S.P.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Rapid and specific SPRi detection of L. pneumophila in complex environmental water samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 5541–5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Dong, M.; Rigatto, C.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F. Lab-on-chip technology for chronic disease diagnosis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassolas, A.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.; Blum, L.J. DNA biosensors and microarrays. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Kwok, Y.C. Polymeric microfluidic system for DNA analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 556, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaloglou, M.N.; Bahi, M.M.; Waugh, E.M.; Morgan, H.; Mowlem, M. On-chip real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification for RNA detection and amplification. Anal. Methods 2011, 3, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Wang, H.; Hupert, M.; Witek, M.; Dharmasiri, U.; Pingle, M.R.; Barany, F.; Soper, S.A. Modular microfluidic system fabricated in thermoplastics for the strain-specific detection of bacterial pathogens. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3348–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, M.A.; Halpern, J.M. Guide to Selecting a Biorecognition Element for Biosensors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudeh, A.M.; Daoud, J.T.; Faucher, S.P.; Veres, T.; Tabrizian, M. Sub-femtomole detection of 16s rRNA from Legionella pneumophila using surface plasmon resonance imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, S.M.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Optical Biosensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 423–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Zheng, S.; Quach, B.Q.; Tai, Y.C. A study of the autofluorescence of parylene materials for microTAS applications. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1826–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strianese, M.; Staiano, M.; Ruggiero, G.; Labella, T.; Pellecchia, C.; D’Auria, S. Fluorescence-Based Biosensors. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 875, 193–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, J.P.; Jönsson, A.; Senkbeil, S.; Kutter, J.P. Recent advances in lab-on-a-chip for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 213–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.B. Fluorescence Sensors and Biosensors; CRC, Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Rauch, C.B.; Stevens, R.L.; Lenigk, R.; Yang, J.; Rhine, D.B.; Grodzinski, P. DNA amplification and hybridization assays in integrated plastic monolithic devices. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, S.; Pinti, M.; Bhushan, B. Theory, fabrication and applications of microfluidic and nanofluidic biosensors. Philos. Trans. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 2269–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadler, D.; Changrani, R.; Roberts, P.; Chou, C.-F.; Zenhausern, F. Thermal management of BioMEMS: Temperature control for ceramic-based PCR and DNA detection devices. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Technol. 2003, 26, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temiz, Y.; Lovchik, R.D.; Kaigala, G.V.; Delamarche, E. Lab-on-a-chip devices: How to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliadou, R.; Nasr Esfahani, M.M.; Brown, N.J.; Welham, K.J. A Disposable Microfluidic Device with a Screen Printed Electrode for Mimicking Phase II Metabolism. Sensors 2016, 16, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Vestergaard, M.C.; Tamiya, E. Printable Electrochemical Biosensors: A Focus on Screen-Printed Electrodes and Their Application. Sensors 2016, 16, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionello, A.; Josserand, J.; Jensen, H.; Girault, H.H. Protein adsorption in static microsystems: Effect of the surface to volume ratio. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Perch-Nielsen, I.; Dufva, M.; Sabourin, D.; Bang, D.D.; Høgberg, J.; Wolff, A. Direct immobilization of DNA probes on non-modified plastics by UV irradiation and integration in microfluidic devices for rapid bioassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 11843-1:1997—Capability of Detection—Part 1: Terms and Definitions; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Allegrini, F.; Olivieri, A.C. IUPAC-Consistent Approach to the Limit of Detection in Partial Least-Squares Calibration. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 7858–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massart, D.L.; Vandeginste, B.G.; Buydens, L.M.C.; De Jong, S.; Lewi, P.J.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J.; Mann, C.K. (Eds.) Internal method validation. In Handbook of Chemometrics and Qualimetrics: Part A; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 20, Chapter 13; pp. 379–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.C.; Sarabia, L.A.; Sánchez, M.S. Tutorial on evaluation of type I and type II errors in chemical analyses: From the analytical detection to authentication of products and process control. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaytseva, N.V.; Montagna, R.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Microfluidic biosensor for the serotype-specific detection of dengue virus RNA. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7520–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.I.; Strohsahl, C.M.; Miller, B.L. Microfluidic nanoplasmonic-enabled device for multiplex DNA detection. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, C.S.; Fan, X.; Mustapha, A. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella in ground beef by a bead-free quantum dot-facilitated isolation method. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 156, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foudeh, A.M.; Brassard, D.; Tabrizian, M.; Veres, T. Rapid and multiplex detection of Legionella’s RNA using digital microfluidics. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, Ü.; Kasap, E.; Cetin, D.; Suludere, Z.; Boyaci, I.H.; Türkyılmaz, C.; Ertas, N.; Tamer, U. Rapid detection of bacteria based on homogenous immunoassay using chitosan modified quantum dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

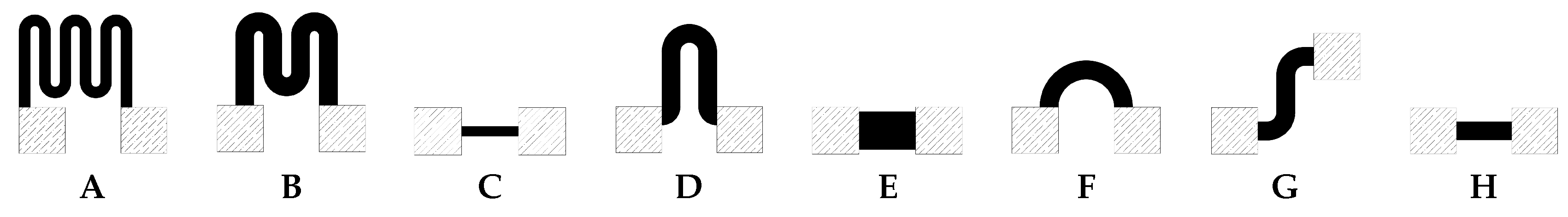




| Type | Length [mm] | Width [mm] | Ratio L/W | Resistance at Room temp. | TCR (from Room temp. to 95 C) | RMSE Polynomial Fitting | RMSE Exponential Fitting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [] | [] | [ppm/C] | [ppm/C] | ||||||||
| A | 28.14 | 0.6 | 46.9 | 997.59 | 115.86 | 4832.48 | 1851.4 | 2.615 | 1.292 | 3.527 | 1.810 |
| B | 18.57 | 1.0 | 18.57 | 286.74 | 40.24 | 4354.41 | 436.25 | 0.7923 | 0.409 | 1.099 | 0.411 |
| C | 3.0 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 138.88 | 15.76 | 5118.88 | 691.73 | 0.315 | 0.0624 | 0.604 | 0.162 |
| D | 10.71 | 1.0 | 10.71 | 166.06 | 19.86 | 4534.84 | 531.51 | 0.438 | 0.110 | 0.574 | 0.184 |
| E | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 32.88 | 3.73 | 4436.20 | 509.59 | 0.148 | 0.101 | 0.183 | 0.111 |
| F | 6.28 | 1.0 | 6.28 | 121.22 | 7.02 | 4863.82 | 450.97 | 0.337 | 0.0853 | 0.483 | 0.133 |
| G | 6.14 | 1.0 | 6.14 | 114.86 | 7.37 | 4393.73 | 437.12 | 0.312 | 0.0735 | 0.511 | 0.176 |
| H | 3.0 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 65.18 | 5.30 | 4885.04 | 441.92 | 0.304 | 0.386 | 0.4278 | 0.3799 |
| Empty COC Chip | 0.01 pmol/mL | 0.1 pmol/mL | 1.0 pmol/mL | 10 pmol/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background LED OFF | 54,567 | 62,784 | 64,853 | 61,896 | 57,863 |
| Signal at LED ON | 184,160 | 207,330 | 344,960 | 1,051,400 | 2,646,400 |
| Difference (LED ON minus LED ON, empty COC) | - | 23,170 | 160,800 | 867,240 | 2,462,240 |
| Capture Probe + Capture Extender | CP + CE + off-Chip RNA (1 × 10 CFU/mL) | CP + CE + on-Chip RNA (2 × 10 CFU/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background LED ON/LED OFF | 249,550/35,917 | 241,840/34,966 | 232,190/41,635 |
| Maximum intensity with detection solution (before washing)/LED OFF | 1,074,800/44,278 | 2,138,809/32,303 | 1,300,000 |
| Signal after hybridization and washing/LED OFF | 989,030/44,894 | 301,646/41,685 | 240,000 |
| Target | Detection | Limit of Detection | Year, Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli and Escherichia faecalis | PCR + surface hybridization | 50 | 2002, [34] |
| Dengue Virus | Magnetic bead-based sandwich | 2005, [46] | |
| DNA | Ag surface DNA hairpin probes. | 500 | 2012, [47] |
| E. coli | Immunoassay bead-free detection with quantum dots | 10 CFU/ | 2012, [48] |
| Legionella spp. | Hybridization on magnetic beads | 2015, [49] | |
| E. coli | Immunoassay on magnetic nanoparticles | 30 CFU/ | 2016, [50] |
| E. coli | RNA Hybridization on surface by capture probes | This work |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prada, J.; Cordes, C.; Harms, C.; Lang, W. Design and Manufacturing of a Disposable, Cyclo-Olefin Copolymer, Microfluidic Device for a Biosensor †. Sensors 2019, 19, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051178
Prada J, Cordes C, Harms C, Lang W. Design and Manufacturing of a Disposable, Cyclo-Olefin Copolymer, Microfluidic Device for a Biosensor †. Sensors. 2019; 19(5):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051178
Chicago/Turabian StylePrada, Jorge, Christina Cordes, Carsten Harms, and Walter Lang. 2019. "Design and Manufacturing of a Disposable, Cyclo-Olefin Copolymer, Microfluidic Device for a Biosensor †" Sensors 19, no. 5: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051178
APA StylePrada, J., Cordes, C., Harms, C., & Lang, W. (2019). Design and Manufacturing of a Disposable, Cyclo-Olefin Copolymer, Microfluidic Device for a Biosensor †. Sensors, 19(5), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051178





