Photo-Rheological Fluid-Based Colorimetric Ultraviolet Light Intensity Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
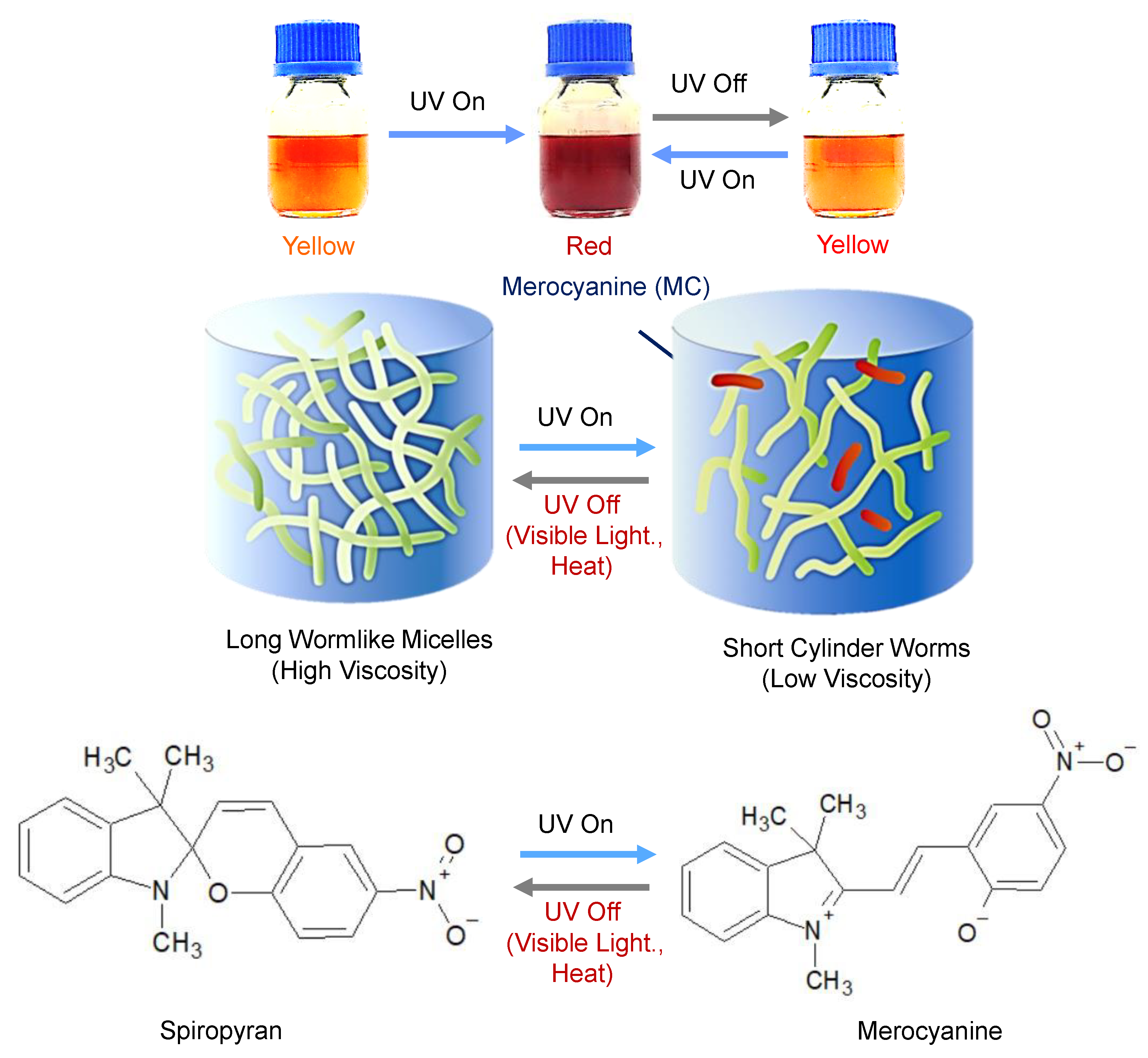
2. Overview of PR Fluids
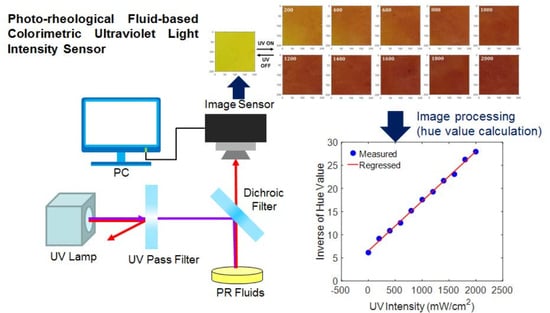
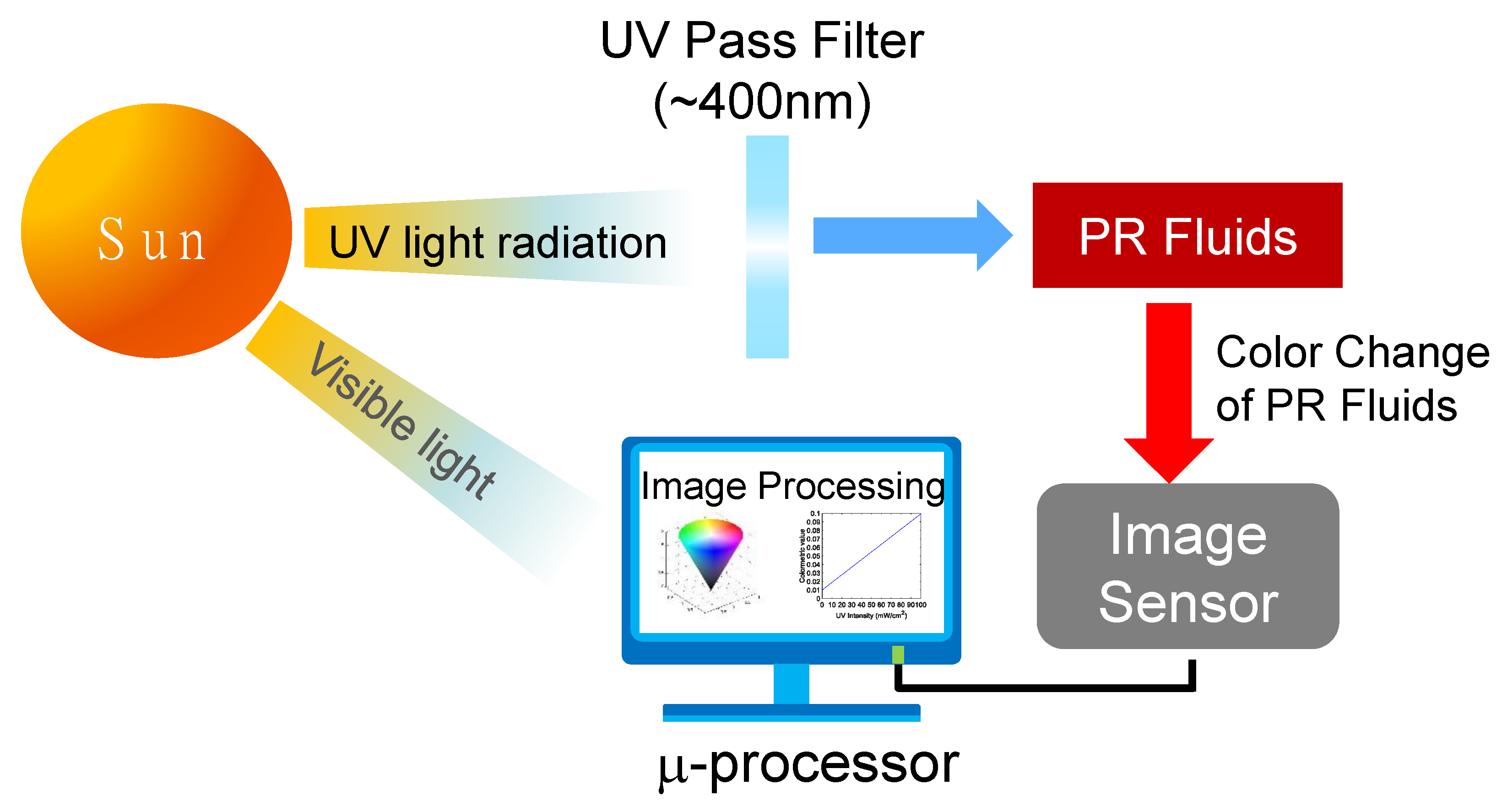
3. Working Principle of Colorimetric UV Intensity Sensor
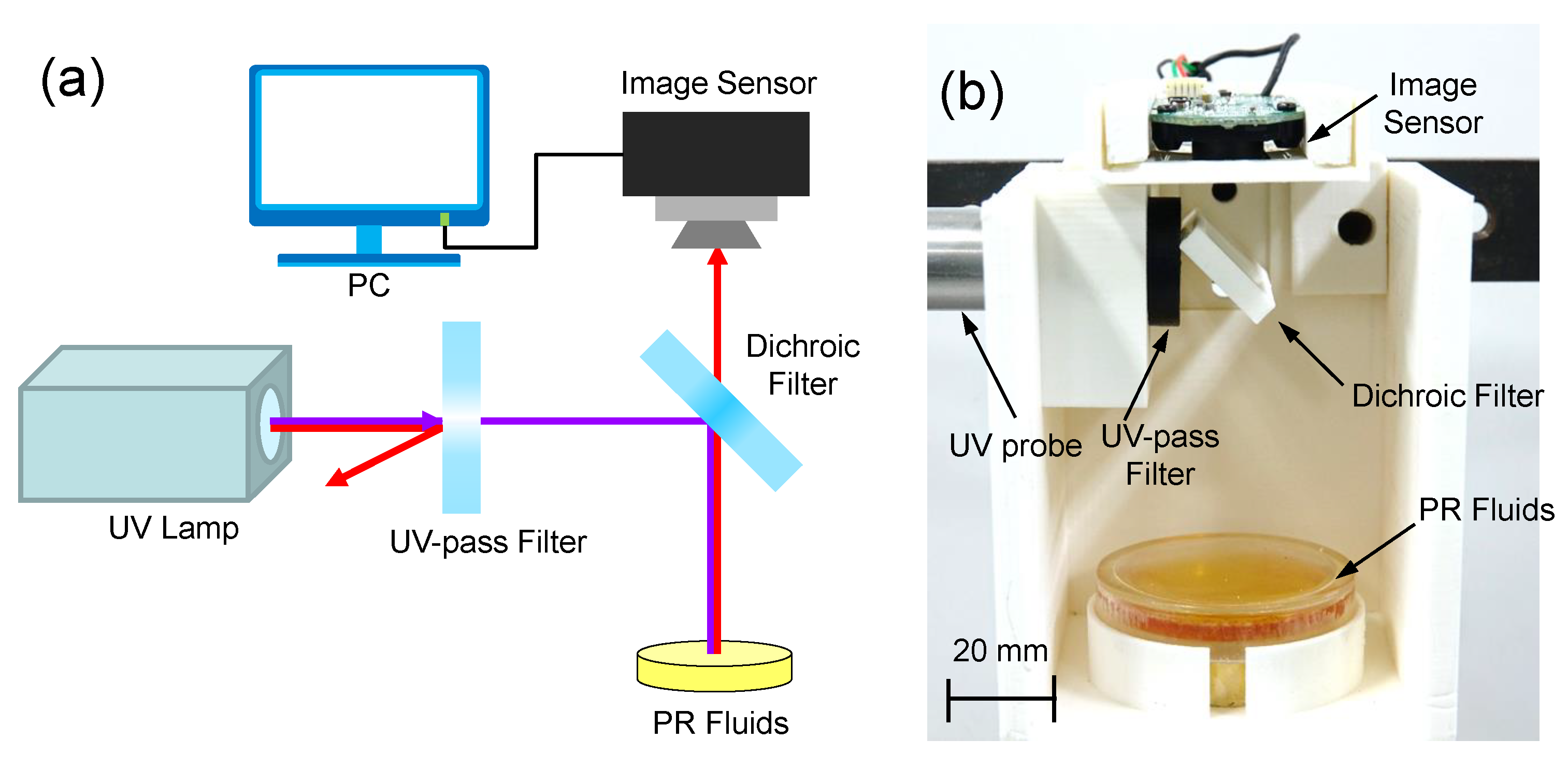
3.1. Design of Colorimetric UV Intensity Sensor
3.2. Digital Image Processing Algorithm
4. Experimental Validation
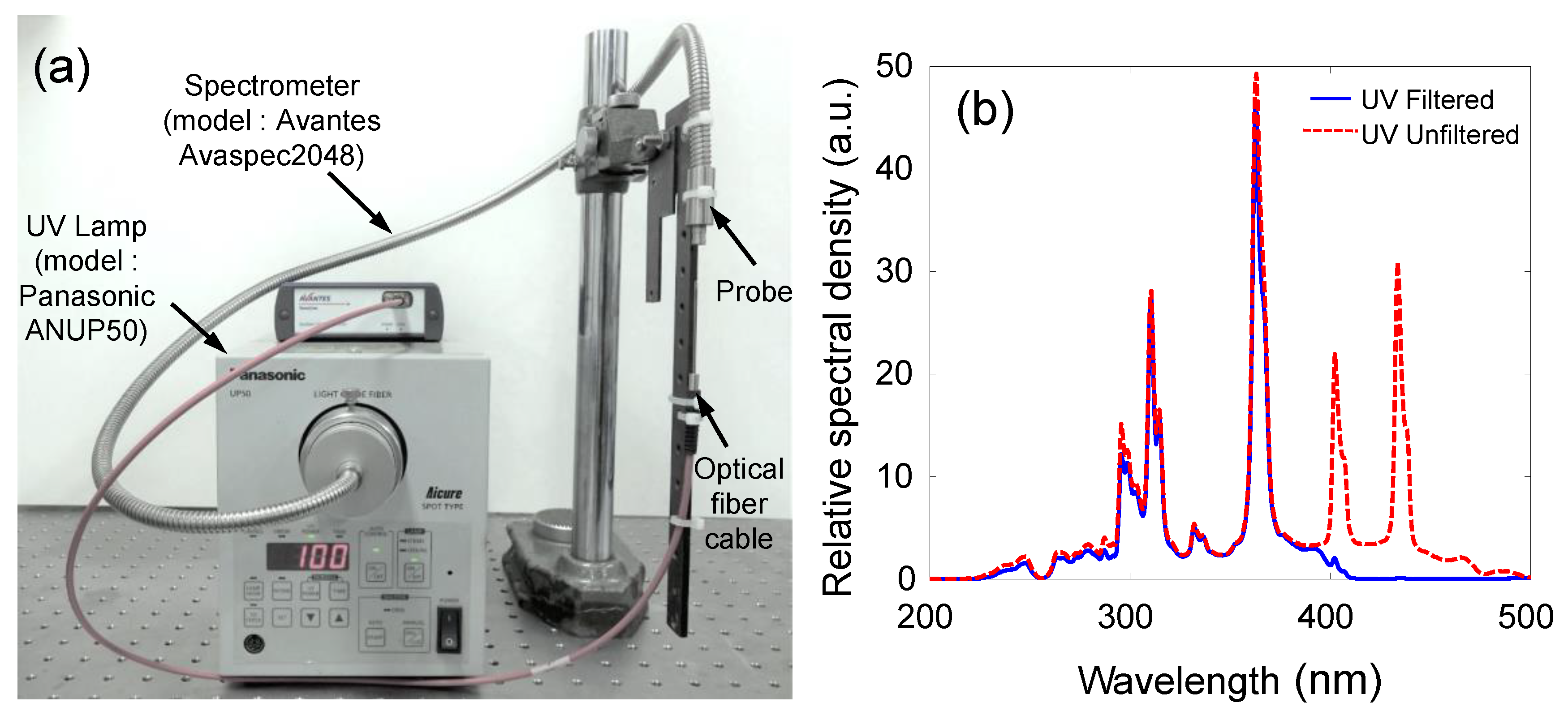
4.1. Experimental Setup
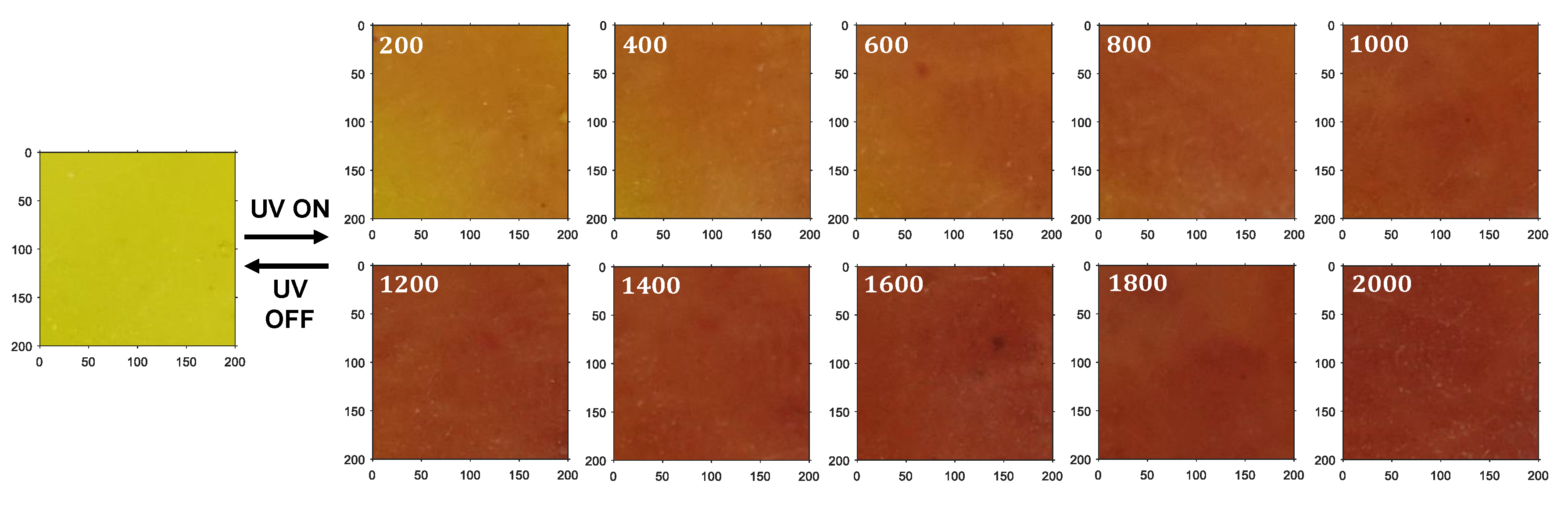
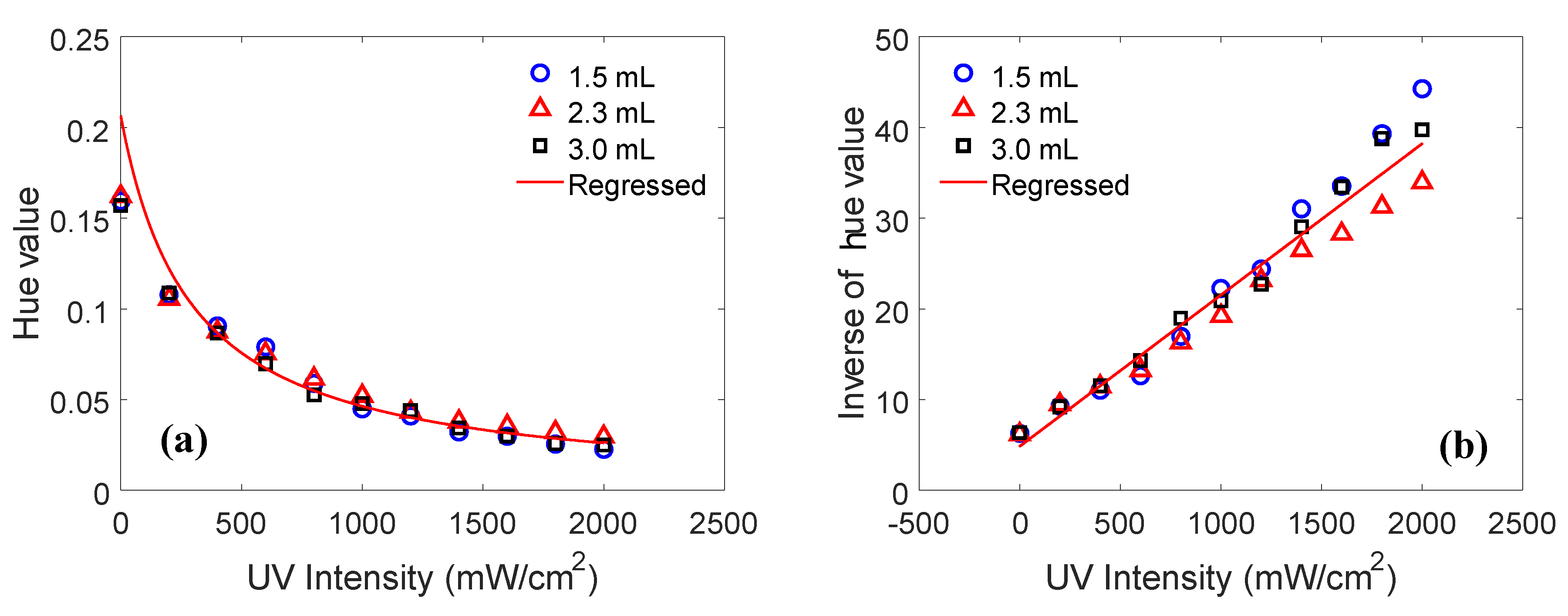
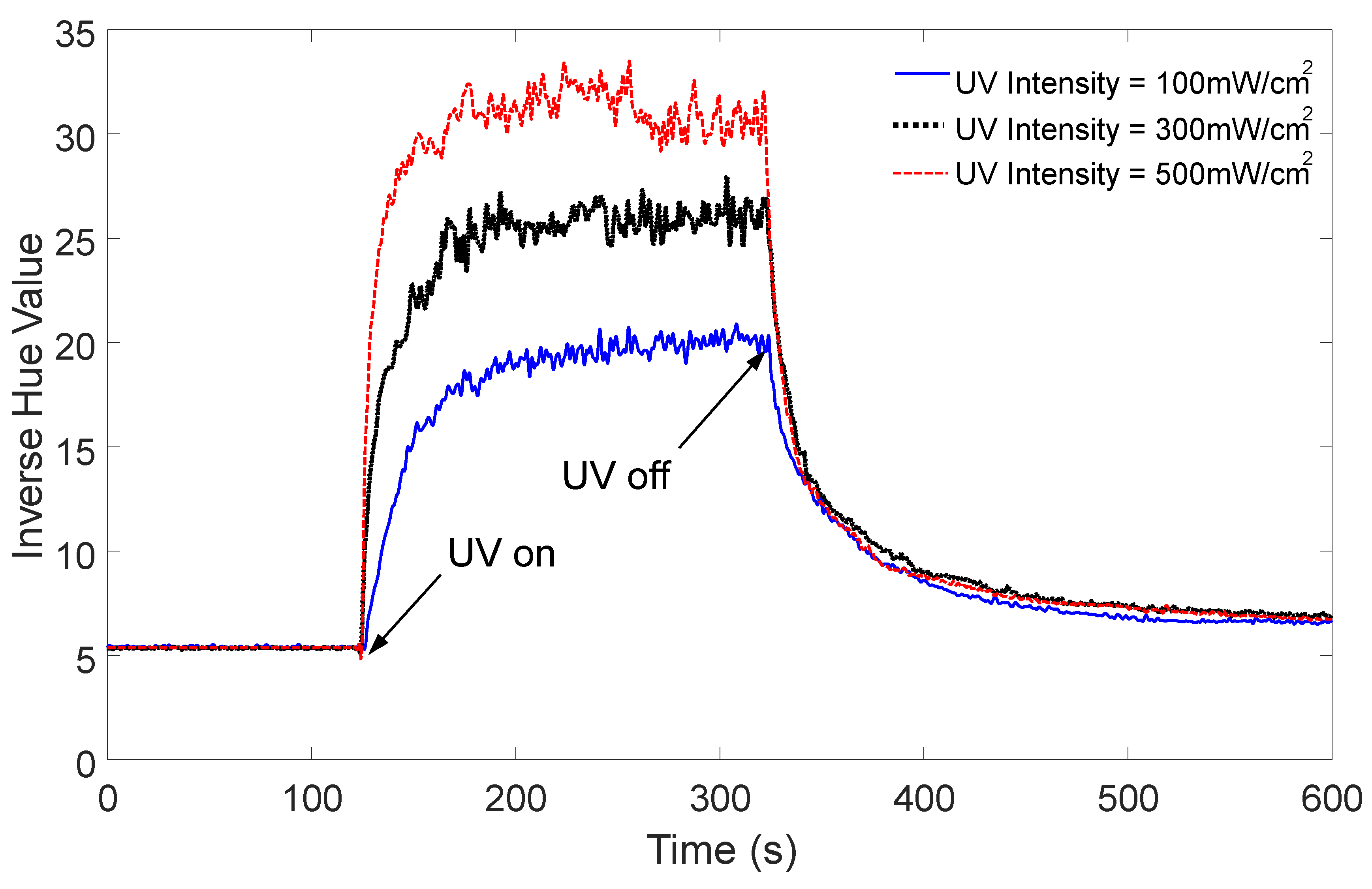
4.2. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Diehn, K.K.; Sun, K.; Chen, T.; Raghavan, S.R. Reversible Photorheological Fluids Based on Spiropyran-Doped Reverse Micelles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8461–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketner, A.M.; Kumar, R.; Davies, T.S.; Elder, P.W.; Raghavan, S.R. A Simple Class of Photorheological Fluids: Surfactant Solution with Viscosity Tunable by Light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomatsu, I.; Hashidzume, A.; Harada, A. Photoresponsive Hydrogel System Using Molecular Recognition of α-Cyclodextrin. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 5223–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Barrio, J.D.; Liu, J.; Scherman, O.A. Supramolecular polymer networks based on cucurbit[8]uril host-guest interactions as aqueous photo-rheological fluids. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 7652–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, J.; Choi, H.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, G. Ultraviolet Light-Responsive Photorheological Fluids: As a New Class of Smart Fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 54007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, S.B.; Kim, G.W. Non-Contact Tunable Damping of a Cantilever Beam Structure Embedded with Photo-Rheological Fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Liu, G.; Ji, J. Micelles and Reverse Micelles with a Photo and Thermo Double-Responsive Block Copolymer. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 2855–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Bando, Y.; Gautam, U.K.; Zhai, T.; Zeng, H.; Xu, X.; Liao, M.; Golberg, D. ZnO and ZnS Nanostructures: Ultraviolet-Light Emitters, Lasers, and Sensors. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2009, 34, 190–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Fang, X.; Liao, M.; Xu, X.; Zeng, H.; Yoshio, B.; Golberg, D. A Comprehensive Review of One-Dimensional Metal-Oxide Nanostructure Photodetectors. Sensors 2009, 9, 6504–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Sun, Z.; Ho, K.Y.; Tao, X.; Yan, F.; Kwok, W.; Zheng, Z. A Highly Sensitive Ultraviolet Sensor Based on a Facile in Situ Solution-Grown ZnO Nanorod/Graphene Heterostructure. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Bando, Y.; Liao, M.; Gautam, U.K.; Zhi, C.; Dierre, B.; Liu, B.; Zhai, T.; Sekiguchi, T.; Koide, Y.; et al. Single-Crystalline ZnS Nanobelts as Ultraviolet-Light Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2034–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Bando, Y.; Liao, M.; Zhai, T.; Gautam, U.K.; Li, L.; Koide, Y.; Golberg, D. An Efficient Way to Assemble ZnS Nanobelts as Ultraviolet-Light Sensors with Enhanced Photocurrent and Stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Manzoor, U.; Islam, M.; Bhatti, A.S.; Shah, N.A. Synthesis of ZnO Nanostructures for Low Temperature CO and UV Sensing. Sensors 2012, 12, 13842–13851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, E.; Calle, F.; Angulo, C.; Vila, P.; Sanz, A.; Garrido, J.A.; Calleja, E.M.; Oz, E.; Haffouz, S.; Beaumont, B.; et al. GaN-Based Solar-Ultraviolet Detection Instrument. Appl. Opt. 1998, 37, 5058–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Huang, F.; Zheng, R.; Wu, H. Low-Dimensional Structure Vacuum-Ultraviolet-Sensitive (Λ < 200 Nm) Photodetector with Fast-Response Speed Based on High-Quality AlN Micro/Nanowire. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 3921–3927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yagi, S. Highly Sensitive Ultraviolet Photodetectors Based on mg-Doped Hydrogenated GaN Films Grown at 380 °C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2000, 76, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, L.; Huo, K.; Gao, B.; Zhao, L.; Liao, M.; Chu, P.K.; Bando, Y.; Golberg, D. New Ultraviolet Photodetector Based on Individual Nb2O5 Nanobelts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3907–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Tachibana, T.; Kawakami, N.; Yokota, Y.; Kobashi, K.; Ishihara, H.; Uchida, K.; Nippashi, K.; Matsuoka, M. Durable Ultraviolet Sensors using Highly Oriented Diamond Films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2006, 15, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Park, Y.; Cho, Y. Hierarchically Structured Suspended TiO2 Nanofibers for use in UV and pH Sensor Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 12189–12195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sreenivas, K. Highly Sensitive Ultraviolet Detector Based on ZnO/LiNbO3 Hybrid Surface Acoustic Wave Filter. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3617–3619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Qiu, J.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Mou, X.; Li, L.; Li, A.; et al. Rutile Nanorod/Anatase Nanowire Junction Array as both Sensor and Power Supplier for High-Performance, Self-Powered, Wireless UV Photodetector. Small 2016, 12, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Tiwari, K.R.; Raghavan, S.R. Biopolymer Capsules Bearing Polydiacetylenic Vesicles as Colorimetric Sensors of pH and Temperature. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 3273–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Han, K.; Lee, I.; Yoon, Y.; Park, W.; Hong, S.; Yang, W.; Hwang, W. A Zero-Power, Low-Cost Ultraviolet-C Colorimetric Sensor using a Gallium Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Hybrid Via Photoelectrochemical Reactions. Catalysts 2017, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, J.; Qin, X.; Xian, X.; Tsow, F.; Forzani, E.S.; Wang, D.; Tao, N. Gradient-Based Colorimetric Sensors for Continuous Gas Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5375–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschos, G. Perceptually Uniform Color Spaces for Color Texture Analysis: An Empirical Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2001, 10, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, D.J.; Gupta, A.K.; Khan, F.A. Comparing the Performance of LAB and HSV Color Spaces with Respect to Color Image Segmentation. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1506.01472. [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell, K.; Erenas, M.M.; de Orbe-Payá, I.; Capitán-Vallvey, L.F. Use of the Hue Parameter of the Hue, Saturation, Value Color Space as a Quantitative Analytical Parameter for Bitonal Optical Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A. Color Gamut Transform Pairs. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1978, 12, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W. UV Intensity Sensor Using Photorheological Fluid. South Korea Patent Application No. 10-2018-0109564, 13 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- MATLAB/Image Processing ToolboxTM V7.4, User’s Guide; The Mathworks: Natick, MA, USA, 2017.



| Lecithin | Sodium Deoxycholate | Spiropyran |
|---|---|---|
| 0.1 mol | 0.0398 mol | 0.015 mol |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, K.-P.; Kim, G.-W. Photo-Rheological Fluid-Based Colorimetric Ultraviolet Light Intensity Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051128
Min K-P, Kim G-W. Photo-Rheological Fluid-Based Colorimetric Ultraviolet Light Intensity Sensor. Sensors. 2019; 19(5):1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051128
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Kyung-Pyo, and Gi-Woo Kim. 2019. "Photo-Rheological Fluid-Based Colorimetric Ultraviolet Light Intensity Sensor" Sensors 19, no. 5: 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051128
APA StyleMin, K.-P., & Kim, G.-W. (2019). Photo-Rheological Fluid-Based Colorimetric Ultraviolet Light Intensity Sensor. Sensors, 19(5), 1128. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19051128