Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using a Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
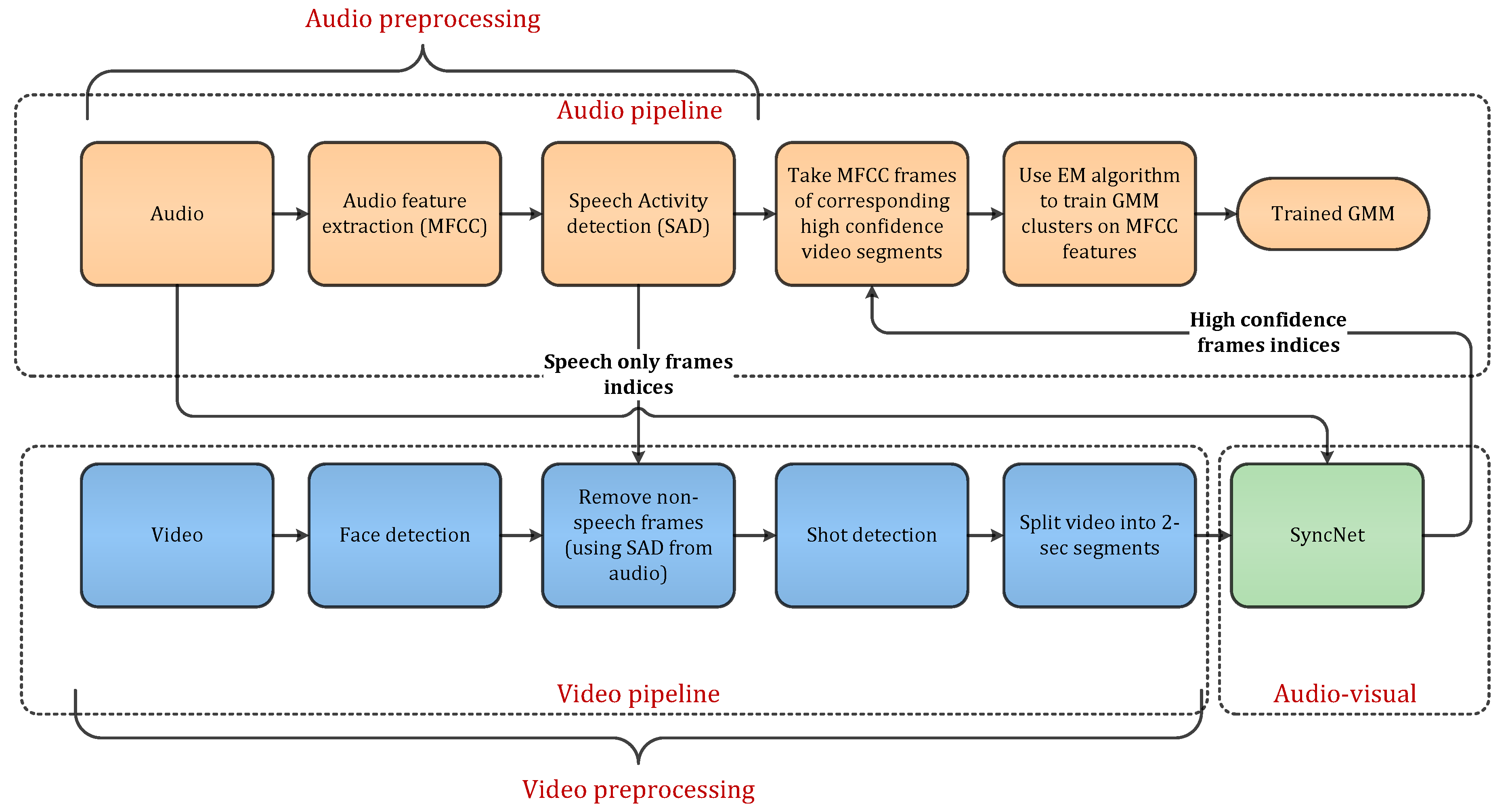
3. Methodology
3.1. Audio Preprocessing
3.2. Video Preprocessing
3.3. SyncNet Architecture and Inference
3.4. Complete Multimodal Diarization Pipeline
4. Experimentation Details
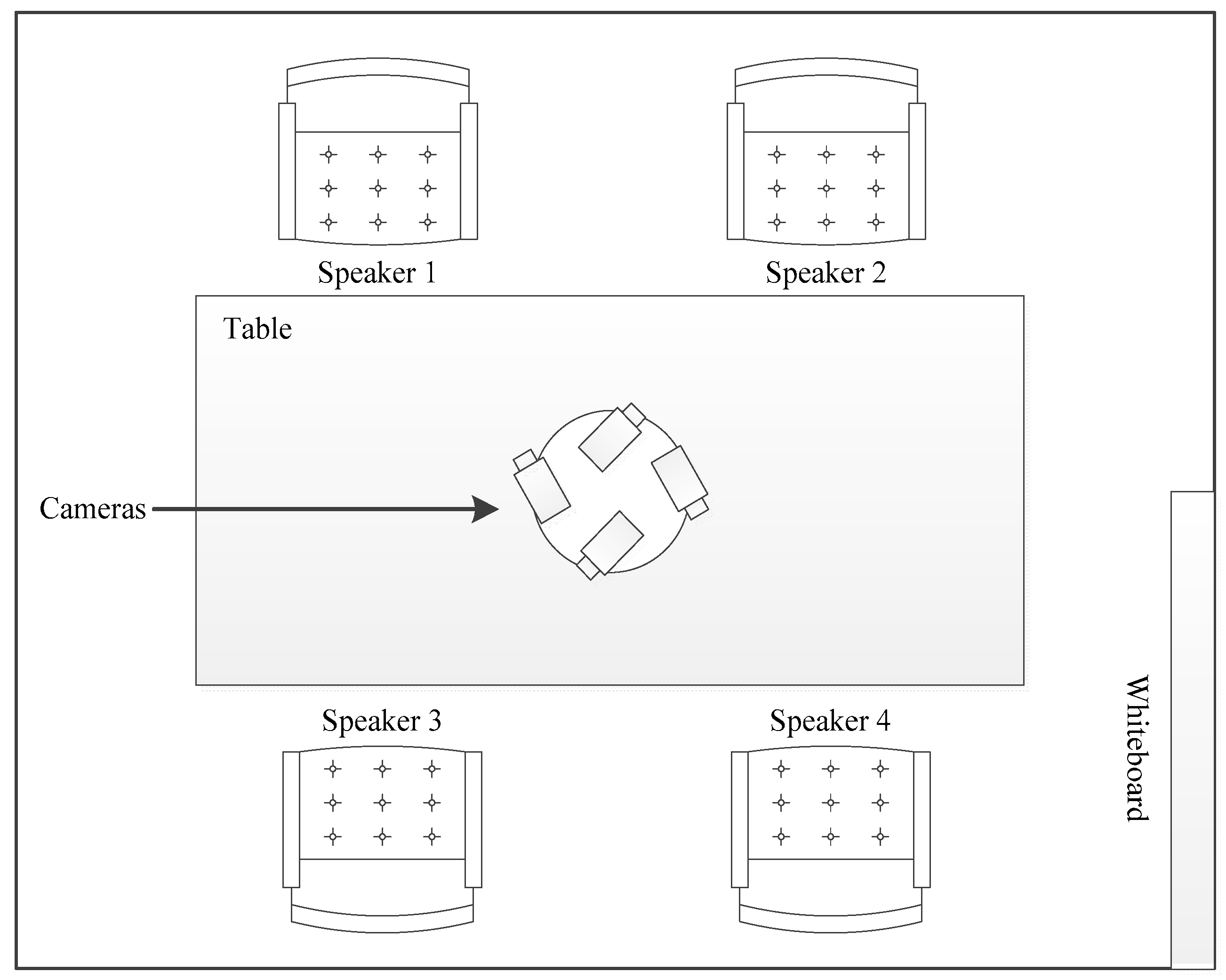
4.1. AMI Meeting Corpus
4.2. Audio Pipeline
4.3. Video Pipeline and SyncNet
4.4. Evaluation Metric
4.5. Comparison Methods
4.6. Environmental Setup
4.7. Computational Cost
4.8. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wooters, C.; Fung, J.; Peskin, B.; Anguera, X. Towards Robust Speaker Segmentation: The Icsi-Sri Fall 2004 Diarization System; International Computer Science Institute: Berkeley, CA, USA; Polytechnical University of Catalonia (UPC): Barcelona, Spain, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Anguera, X.; Wooters, C.; Pardo, J.M. Robust Speaker Diarization for Meetings. In Proceedings of the MLMI: International Workshop on Machine Learning for Multimodal Interaction, Bethesda, MD, USA, 1–4 May 2006; pp. 346–358. [Google Scholar]
- Anguera, X.; Wooters, C.; Peskin, B.; Aguiló, M. Robust speaker segmentation for meetings: The ICSI-SRI spring 2005 diarization system. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 3869, pp. 402–414. ISBN 3540325492. [Google Scholar]
- Anguera, X.; Wooters, C.; Hernando, J. Automatic cluster complexity and quantity selection: Towards robust speaker diarization. In International Workshop on Machine Learning for Multimodal Interaction, Bethesda, MD, USA, 1–4 May 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 4299, pp. 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.J.; Narayanan, S.S. Agglomerative hierarchical speaker clustering using incremental Gaussian mixture cluster modeling. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Interspeech, Brisbane, Australia, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wooters, C.; Huijbregts, M. The ICSI RT07s speaker diarization system. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4625, pp. 509–519. [Google Scholar]
- Fredouille, C.; Evans, N. The LIA RT’07 speaker diarization system. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4625, pp. 520–532. [Google Scholar]
- Imseng, D.; Friedland, G. Robust Speaker Diarization for short speech recordings. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, ASRU 2009, Merano/Meran, Italy, 13–17 December 2009; pp. 432–437. [Google Scholar]
- Gonina, E.; Friedland, G.; Cook, H.; Keutzer, K. Fast speaker diarization using a high-level scripting language. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, ASRU 2011, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 11–15 December 2011; pp. 553–558. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, G.; Janin, A.; Gottlieb, L.; Knox, M.T.; Vinyals, O.; Imseng, D.; Imseng, D.; Miro, X.A.; Huijbregts, M. The ICSI RT-09 Speaker Diarization System. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gopalakrishnan, P. Speaker, environment and channel change detection and clustering via the Bayesian Information Criterion. Proc. DARPA Broadcast News Transcr. Underst. Work. 1998, 6, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Molau, S.; Pitz, M.; Schluter, R.; Ney, H. Computing Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients on the power spectrum. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Proceedings (Cat. No.01CH37221), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 7–11 May 2001; pp. 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Dehak, N.; Kenny, P.; Dehak, R. Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. Audio Speech 2010, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, P.; Ouellet, P.; Dehak, N.; Gupta, V.; Dumouchel, P. A study of interspeaker variability in speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2008, 16, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sell, G.; Garcia-Romero, D. Speaker diarization with plda i-vector scoring and unsupervised calibration. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Workshop on Spoken Language Technology, SLT 2014-Proceedings, South Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 7–10 December 2014; pp. 413–417. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Mcloughlin, I.; Song, Y. Improved i-vector representation for speaker diarization. Cir. Syst. Signal Process. 2015, 35, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikeri, S.; Himawan, I.; Motlicek, P.; Ferras, M. Integrating online i-vector extractor with information bottleneck based speaker diarization system. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Dresden, Germany, 6–10 September 2015; pp. 3105–3109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Downey, C.; Wan, L.; Mansfield, P.A.; Moreno, I.L. Speaker diarization with LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5239–5243. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Garcia-Romero, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; Khudanpur, S. X-Vectors: Robust DNN Embeddings for Speaker Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 5329–5333. [Google Scholar]
- Cyrta, P.; Trzci, T.; Stokowiec, W. Speaker Diarization using Deep Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Speaker Embeddings, Proceedings of the Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Szklarska Poręba, Poland, 17–19 September 2017; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 655, pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Romero, D.; Snyder, D.; Sell, G.; Povey, D.; McCree, A. Speaker diarization using deep neural network embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 May 2017; pp. 4930–4934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Paisley, J.; Wang, C. Fully Supervised Speaker Diarization. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04719v7. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, R.; Bredin, H.; Barras, C. Neural speech turn segmentation and affinity propagation for speaker diarization. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bredin, H.; Gelly, G. Improving Speaker Diarization of TV Series using Talking-Face Detection and Clustering. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 September 2007; pp. 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Peruffo Minotto, V.; Rosito Jung, C.; Lee, B. Multimodal Multi-Channel On-Line Speaker Diarization Using Sensor Fusion Through SVM. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2015, 17, 1694–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, H.; Barras, C.; Guinaudeau, C. Multimodal person discovery in broadcast TV at MediaEval 2016. CEUR Workshop Proc. 2016, 1739, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sarafianos, N.; Giannakopoulos, T.; Petridis, S. Audio-visual speaker diarization using fisher linear semi-discriminant analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, X.; Linares, G.; Gueye, S. Audiovisual speaker diarization of TV series. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 19–24 April 2015; pp. 4799–4803. [Google Scholar]
- El Khoury, E.; Sénac, C.; Joly, P. Audiovisual diarization of people in video content. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2014, 68, 747–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noulas, A.; Englebienne, G.; Kröse, B.J.A. Multimodal Speaker diarization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsouras, I.; Tefas, A.; Nikolaidis, N.; Peeters, G.; Benaroya, L.; Pitas, I. Multimodal speaker clustering in full length movies. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 2223–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañas-Molero, P.; Lucena, M.; Fuertes, J.M.; Vera-Candeas, P.; Ruiz-Reyes, N. Multimodal speaker diarization for meetings using volume-evaluated SRP-PHAT and video analysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 27685–27707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, I.D.; Ba, S.; Li, X.; Horaud, R. Audio-Visual Speaker Diarization Based on Spatiotemporal Bayesian Fusion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. Out of time: Automated lip sync in the wild. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016; pp. 251–263. [Google Scholar]
- Komai, Y.; Ariki, Y.; Takiguchi, T. Audio-Visual Speech Recognition Based on AAM Parameter and Phoneme Analysis of Visual Feature, Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), Gwangju, Korea, 20–23 November 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 7087, pp. 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Potamianos, G.; Neti, C.; Gravier, G.; Garg, A.; Senior, A.W. Recent advances in the automatic recognition of audiovisual speech. IEEE 2003, 91, 1306–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivet, B.; Girin, L.; Jutten, C. Mixing audiovisual speech processing and blind source separation for the extraction of speech signals from convolutive mixtures. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2007, 15, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzelay, Z.; Schechner, Y.Y. Onsets coincidence for cross-modal analysis. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2010, 12, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.W.; Darrell, T.; Freeman, W.T.; Viola, P. Learning joint statistical models for audio-visual fusion and segregation. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–8 December 2001; pp. 772–778. [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa, M.R.; Fisher, J.W. Dynamic dependency tests for audio-visual speaker association. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing-Proceedings, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–20 April 2007; Volume 2, p. 9484814. [Google Scholar]
- Noulas, A.K.; Krose, B.J.A. On-line multi-modal speaker diarization, Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, ICMI’07, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan, 12–15 November 2007; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 350–357. [Google Scholar]
- Nock, H.J.; Iyengar, G.; Neti, C. Speaker localisation using audio-visual synchrony: An empirical study. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2003, 2728, 488–499. [Google Scholar]
- Friedland, G.; Hung, H.; Yeo, C.; Berkeley, U.C. Multi-modal speaker diarization of real-world meetings using compressed-domain video features int. Computer Science Institute Rue Marconi 19 CH-1920 Martigny. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Taipei, Taiwan, 19–24 April 2009; pp. 4069–4072. [Google Scholar]
- Garau, G.; Dielmann, A.; Bourlard, H. Audio-visual synchronisation for speaker diarisation. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Makuhari, Japan, 26–30 September 2010; pp. 2654–2657. [Google Scholar]
- Carletta, J.; Ashby, S.; Bourban, S.; Flynn, M.; Guillemot, M.; Hain, T.; Kadlec, J.; Karaiskos, V.; Kraaij, W.; Kronenthal, M.; et al. The AMI Meeting Corpus: A Pre-announcement Machine Learning for Multimodal Interaction. In International Workshop on Machine Learning for Multimodal Interaction, Edinburgh, UK, July 11–13 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; Volume 3869, pp. 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Rehan-Ahmad/MultimodalDiarization: Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model. Available online: https://github.com/Rehan-Ahmad/MultimodalDiarization (accessed on 23 November 2019).
- AMI Corpus. Available online: http://groups.inf.ed.ac.uk/ami/corpus/ (accessed on 24 November 2019).
- Yin, R.; Bredin, H.; Barras, C. Speaker change detection in broadcast TV using bidirectional long short-term memory networks. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 3827–3831. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Jaitly, N.; Mohamed, A.R. Hybrid speech recognition with Deep Bidirectional LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 8–12 December 2013; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Bredin, H. TristouNet: Triplet loss for speaker turn embedding. In Proceedings of the ICASSP, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 May 2017; pp. 5430–5434. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, B.J.; Dueck, D. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 2007, 315, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, I.D.; Ba, S.; Evangelidis, G.; Horaud, R. Tracking the Active Speaker Based on a Joint Audio-Visual Observation Model. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 11–12 December 2015; pp. 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Deleforge, A.; Horaud, R.; Schechner, Y.Y.; Girin, L. Co-Localization of Audio Sources in Images Using Binaural Features and Locally-Linear Regression. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 718–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcfee, B.; Raffel, C.; Liang, D.; Ellis, D.P.W.; Mcvicar, M.; Battenberg, E.; Nieto, O. librosa: Audio and Music Signal Analysis in Python. In Proceedings of the 14th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 6–12 July 2015; pp. 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.E. Dlib-ml: A Machine Learning Toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Bredin, H. Pyannote.metrics: A toolkit for reproducible evaluation, diagnostic, and error analysis of speaker diarization systems. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 3587–3591. [Google Scholar]

| Meeting ID | Conventional SD [9] | Proposed Multimodal | Difference (Improvement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IS1000a | 42.079 | 29.313 | 12.766 |
| IS1001a | 42.144 | 37.573 | 4.571 |
| IS1001b | 48.301 | 35.709 | 12.592 |
| IS1001c | 52.889 | 24.389 | 28.5 |
| IS1003b | 51.681 | 22.169 | 29.512 |
| IS1003d | 68.443 | 48.655 | 19.788 |
| IS1006b | 52.65 | 42.861 | 9.789 |
| IS1006d | 66.849 | 58.497 | 8.352 |
| IS1008a | 16.172 | 10.946 | 5.226 |
| IS1008b | 12.075 | 12.715 | -0.64 |
| IS1008c | 40.59 | 22.217 | 18.373 |
| IS1008d | 35.503 | 21.376 | 14.127 |
| Average | 44.11 | 30.535 | - |
| Average Improvement | 13.58 | ||
| Meeting ID | Fully Supervised SD [23] | Recording Set | Proposed Multimodal | Difference (Improvement) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IS1000a | 46.55 | Train | 29.313 | 17.237 |
| IS1001a | 43.31 | Train | 37.573 | 5.737 |
| IS1001b | 26.77 | Train | 35.709 | -8.939 |
| IS1001c | 25.74 | Train | 24.389 | 1.351 |
| IS1003d | 59.56 | Train | 48.655 | 10.905 |
| IS1006b | 29.87 | Train | 42.861 | -12.991 |
| IS1006d | 51.06 | Train | 58.497 | -7.437 |
| IS1008a | 13.84 | Dev | 10.946 | 2.894 |
| IS1008b | 14.97 | Dev | 12.715 | 2.255 |
| IS1008c | 22.26 | Dev | 22.217 | 0.043 |
| IS1008d | 26.25 | Dev | 21.376 | 4.874 |
| Average | 32.74 | 31.29 | - | |
| Average Improvement | 1.44 | |||
| Meeting ID | MMSD [32] | Proposed Multimodal | Difference (Improvement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| IS | 21.68 | 22.24 | −0.56 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, R.; Zubair, S.; Alquhayz, H.; Ditta, A. Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using a Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model. Sensors 2019, 19, 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235163
Ahmad R, Zubair S, Alquhayz H, Ditta A. Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using a Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model. Sensors. 2019; 19(23):5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235163
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Rehan, Syed Zubair, Hani Alquhayz, and Allah Ditta. 2019. "Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using a Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model" Sensors 19, no. 23: 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235163
APA StyleAhmad, R., Zubair, S., Alquhayz, H., & Ditta, A. (2019). Multimodal Speaker Diarization Using a Pre-Trained Audio-Visual Synchronization Model. Sensors, 19(23), 5163. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19235163






