Robust and Accurate Hand–Eye Calibration Method Based on Schur Matric Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
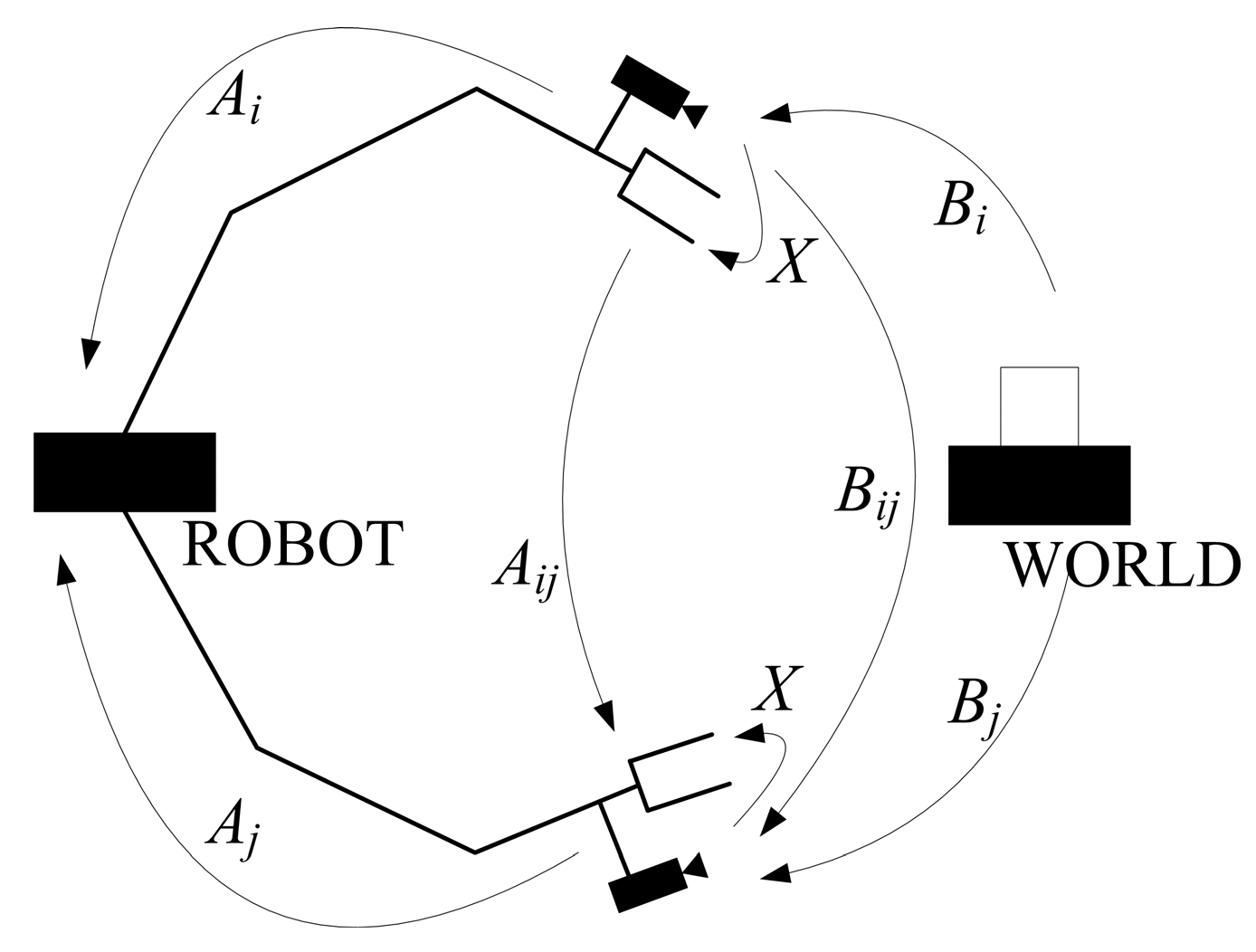
2. Description of Hand–Eye Calibration Problem
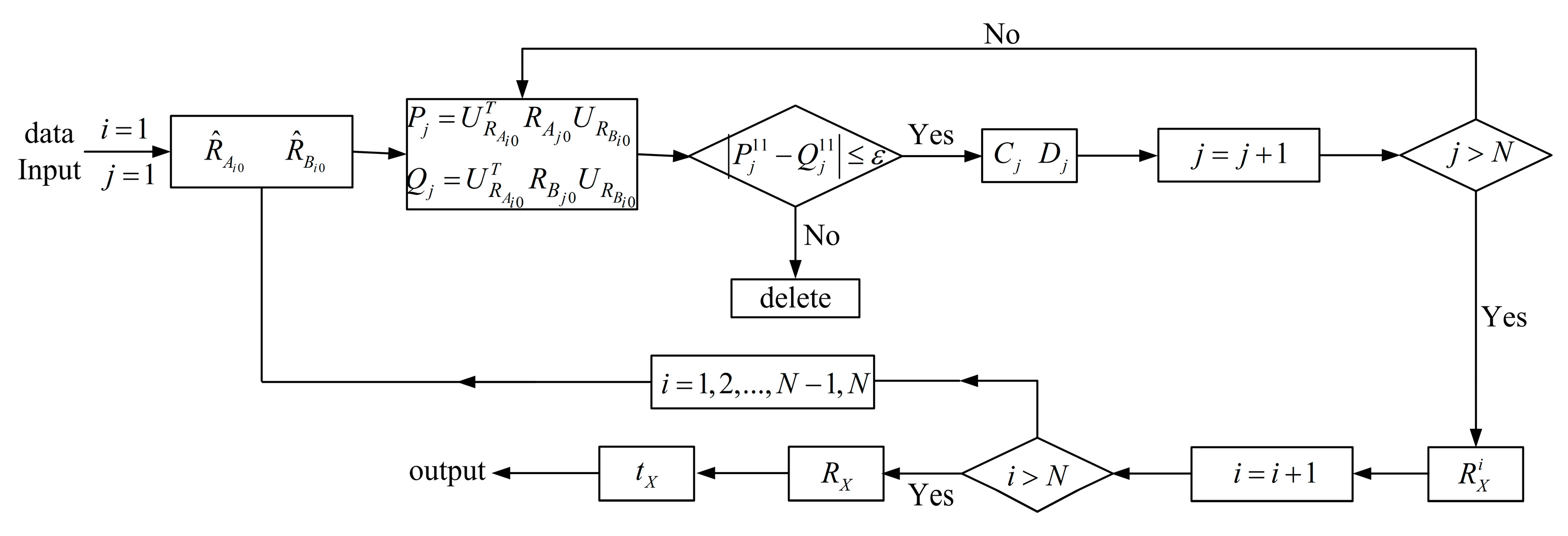
3. Hand–Eye Calibration Method
3.1. Schur Matric Decomposition
3.2. Hand–Eye Calibration Principle
3.3. Outlier Detection
3.4. Unique Solution Conditions
4. Results
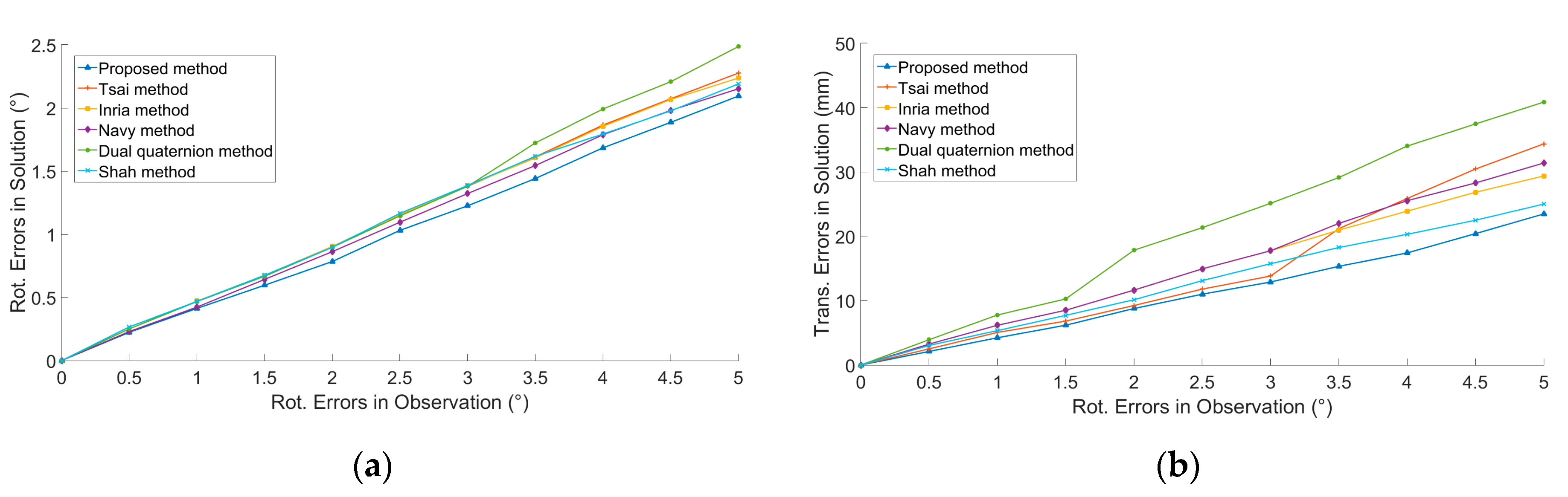
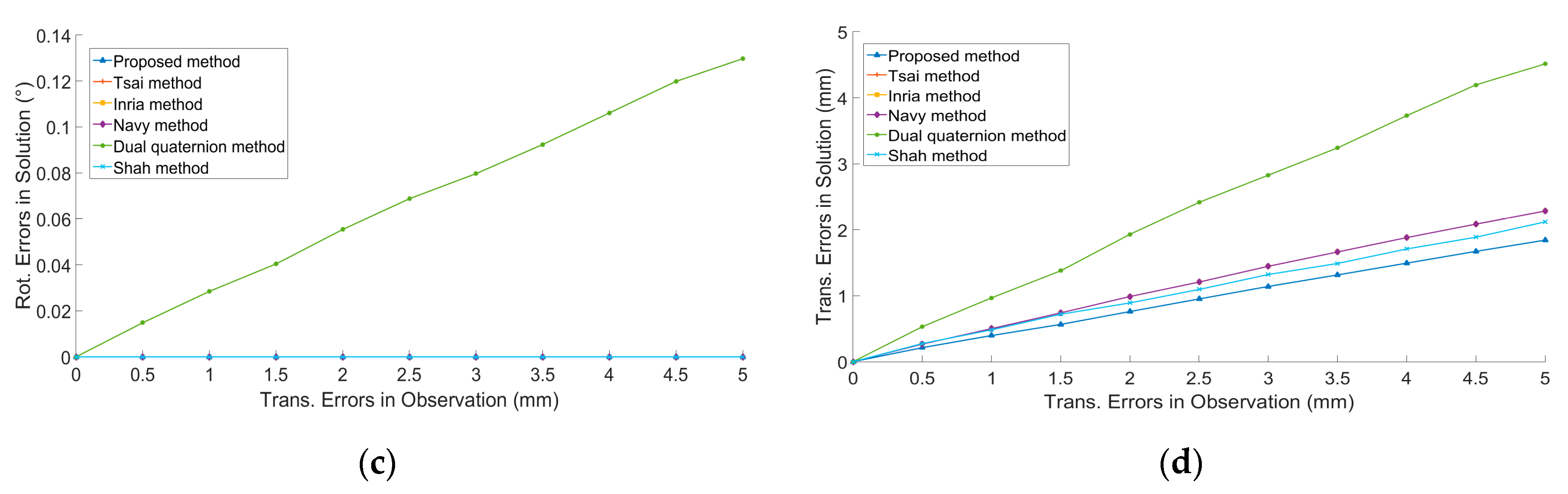
4.1. Simulations
4.1.1. Analysis of Noise Sensitivity
4.1.2. Relationship between Number of Movements and Accuracy
4.1.3. Outlier Detection
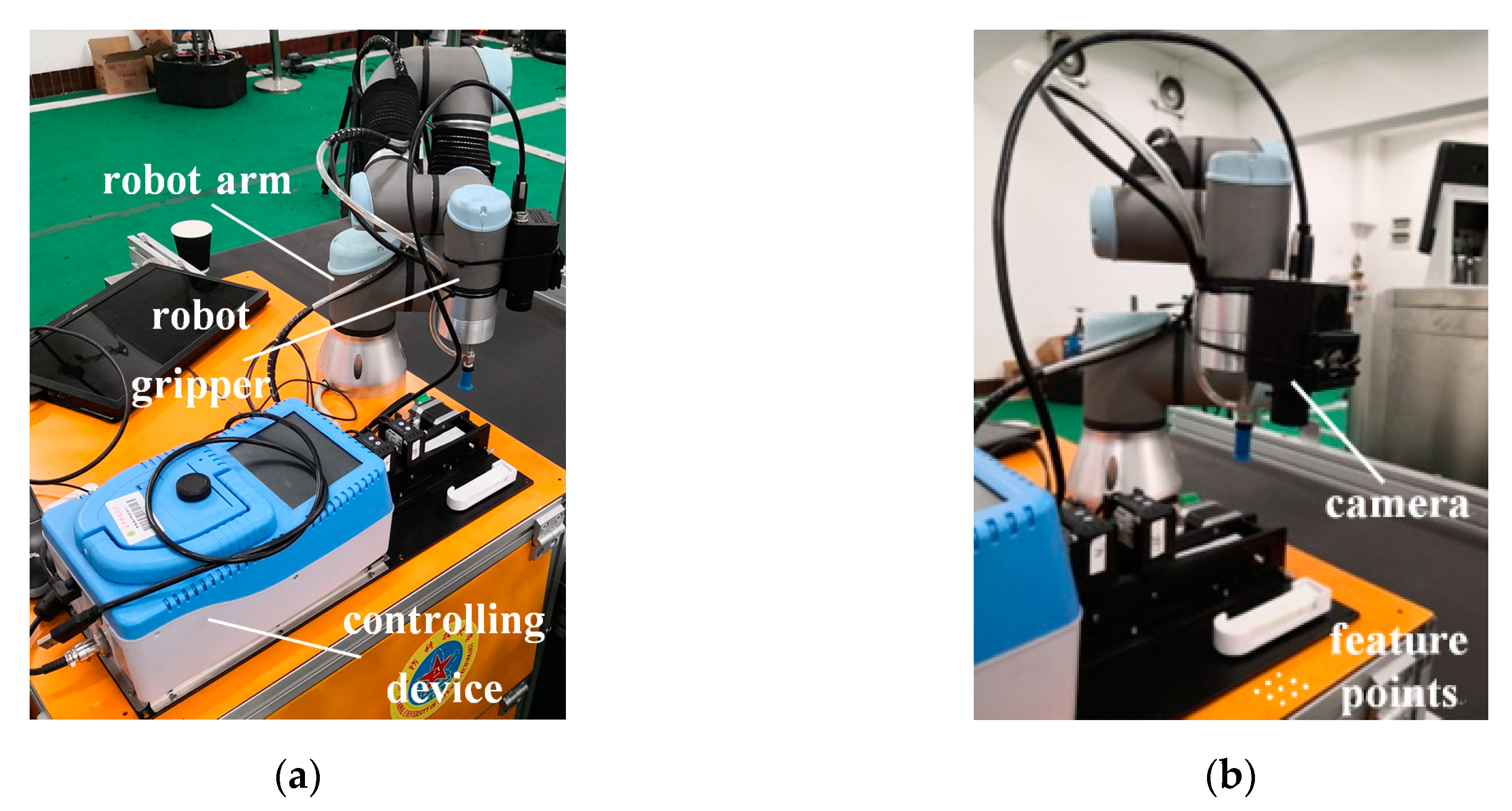
4.2. Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Knight, J.; Reid, I. Automated alignment of robotic pan-tilt camera units using vision. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2006, 68, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschelbach, M.; Aghaeifar, A.; Bause, J.; Handwerker, J.; Anders, J.; Engel, E.M.; Thielscher, A.; Scheffler, K. Comparison of prospective head motion correction with NMR field probes and an optical tracking system. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 81, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lian, B.; Sun, T. Kinematic calibration of a 5-DOF parallel kinematic machine. Precis. Eng. 2016, 45, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, N.L.; Qin, Y.S. A closed-form solution to eye-to-hand calibration towards visual grasping. Ind. Robot 2014, 41, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Suominen, O.; Gotchev, A.; Morales, E.R. Methods for simultaneous robot-world-hand-eye calibration: A comparative study. Sensors 2019, 19, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, Y.C.; Ahmad, S. Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX = XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3D robotics hand-eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, A.; Liu, Y.H.; Kim, S.; Deguet, A.; Reiter, A.; Kazanzides, P.; Taylor, R.H. Vision-based calibration of dual RCM-based robot arms in human-robot collaborative minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.Z. A computationally efficient method for hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, T.; Chirikjian, G.S. Simultaneous hand-eye and robot-world calibration by solving the AX = XB problem without correspondence. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2015, 8, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidis, K. Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1999, 18, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, F.C.; Martin, B.J. Robot sensor calibration: Solving AX = XB on the Euclidean group. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. Lett. 1994, 10, 717–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M. Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the Kronecker product. J. Mech. Robot. 2013, 5, 031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachtrachai, K.; Vasconcelos, F.; Chadebecq, F.; Allan, M.; Hailes, S.; Pawar, V.; Stoyanov, D. Adjoint transformation method for hand-eye calibration with applications in robotics assisted surgery. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassi, I.; Legnani, G. Hand to sensor calibration: A geometrical interpretation of the matric equation AX = XB. J. Robot. Syst. 2005, 22, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dong, M.L.; Lu, N.G. Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration without a calibration object. Sensors 2018, 18, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.T.; Do, V.P.; Lee, B.Y. A novel indirect calibration approach for robot positioning error compensation based on neural network and hand-eye vision. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruland, T.; Pajdla, T.; Kruger, L. Robust hand-eye self-calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Washington, DC, USA, 5–7 October 2011; pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Niemann, H. Data-selection for hand–eye calibration: A vector quantization approach. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 1027–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Zhang, B.; Tang, Y.Y. Multi-view classification via a fast and effective multi-view nearest-subspace classifier. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 49669–49679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Iwata, S.; Nakatsukasa, Y.; Takeda, A. Solving the trust-region subproblem by a generalized eigenvalue problem. SIAM J. Optim. 2017, 27, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Gerstoft, P.; Seonng, W. Grid-free compressive mode extraction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horaud, R.; Dornaika, F. Hand-eye calibration. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1995, 14, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, L.H.; Cheng, L. Pose estimation from line correspondences: A complete analysis and a series of solutions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1209–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

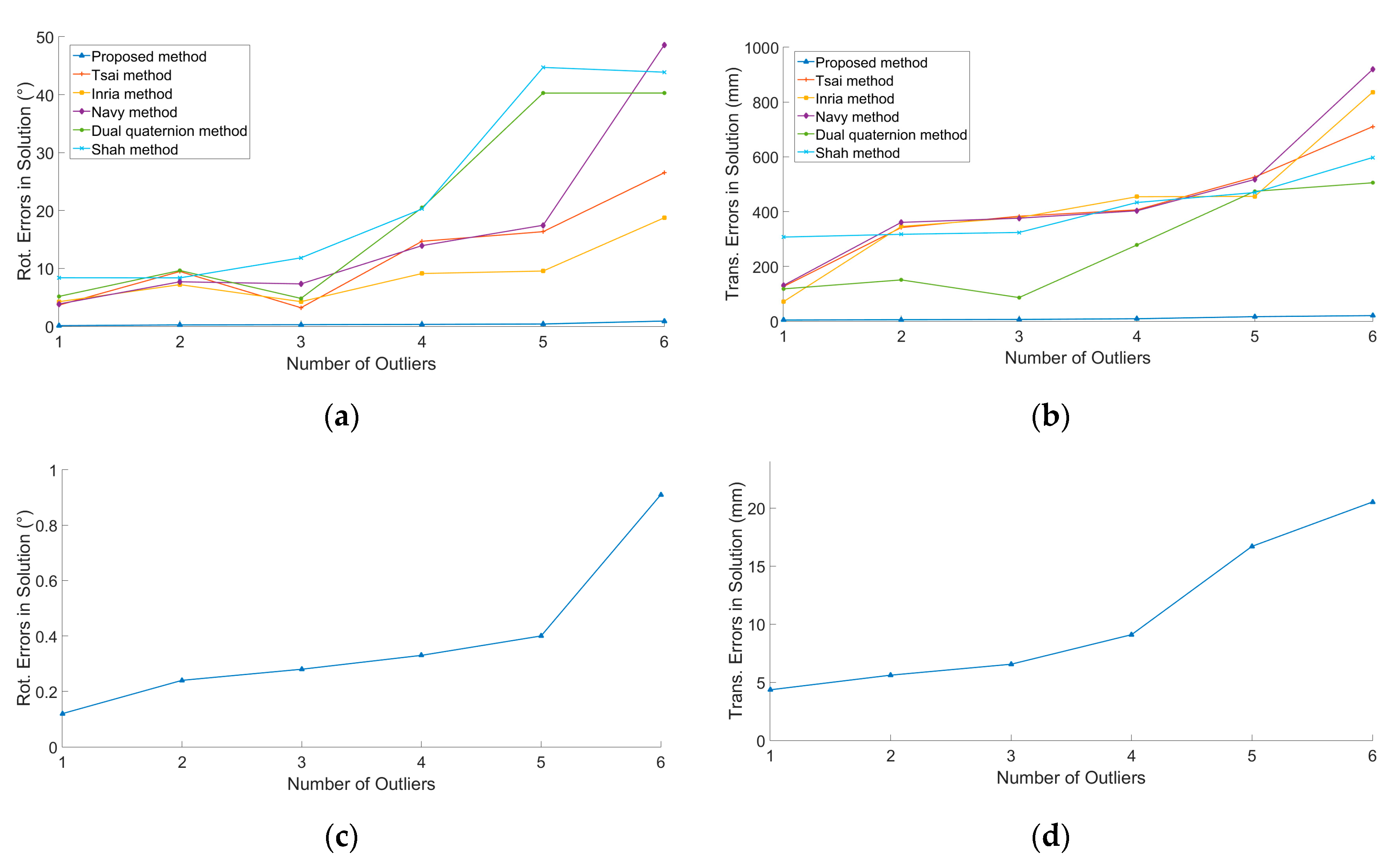
| N | Proposed | Tsai | Inria | Navy | Dual Quaternion | Shah | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θerror | terror | θerror | terror | θerror | terror | θerror | terror | θerror | terror | θerror | terror | |
| 2 | 10.14 | 5.49 | 10.14 | 7.06 | 10.14 | 6.23 | 10.17 | 5.25 | 10.21 | 8.70 | 10.14 | 5.63 |
| 3 | 10.10 | 4.63 | 10.10 | 6.21 | 10.14 | 6.20 | 10.14 | 5.10 | 10.14 | 7.08 | 10.10 | 4.71 |
| 4 | 10.07 | 4.06 | 10.10 | 5.77 | 10.10 | 4.74 | 10.10 | 4.97 | 10.14 | 6.18 | 10.10 | 4.16 |
| 5 | 9.83 | 3.94 | 10.07 | 4.15 | 10.07 | 3.79 | 10.07 | 4.62 | 10.10 | 4.17 | 9.86 | 4.04 |
| 6 | 0.96 | 2.46 | 0.96 | 3.67 | 1.30 | 3.61 | 2.16 | 3.54 | 3.81 | 3.98 | 1.34 | 2.60 |
| 7 | 0.44 | 1.57 | 0.51 | 3.51 | 0.51 | 3.60 | 0.51 | 1.87 | 1.78 | 3.64 | 0.72 | 1.75 |
| 8 | 0.37 | 1.15 | 0.37 | 2.76 | 0.41 | 2.51 | 0.44 | 1.77 | 0.44 | 2.27 | 0.37 | 1.20 |
| 9 | 0.06 | 1.01 | 0.27 | 2.47 | 0.34 | 2.27 | 0.41 | 1.19 | 0.41 | 1.82 | 0.20 | 1.05 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Wu, J.; Li, X. Robust and Accurate Hand–Eye Calibration Method Based on Schur Matric Decomposition. Sensors 2019, 19, 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204490
Liu J, Wu J, Li X. Robust and Accurate Hand–Eye Calibration Method Based on Schur Matric Decomposition. Sensors. 2019; 19(20):4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinbo, Jinshui Wu, and Xin Li. 2019. "Robust and Accurate Hand–Eye Calibration Method Based on Schur Matric Decomposition" Sensors 19, no. 20: 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204490
APA StyleLiu, J., Wu, J., & Li, X. (2019). Robust and Accurate Hand–Eye Calibration Method Based on Schur Matric Decomposition. Sensors, 19(20), 4490. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204490





