Fluorescence Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Percolation Water and Lateral Seepage Affected by Soil Solution (S-S) in a Lysimeter Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Method and Material
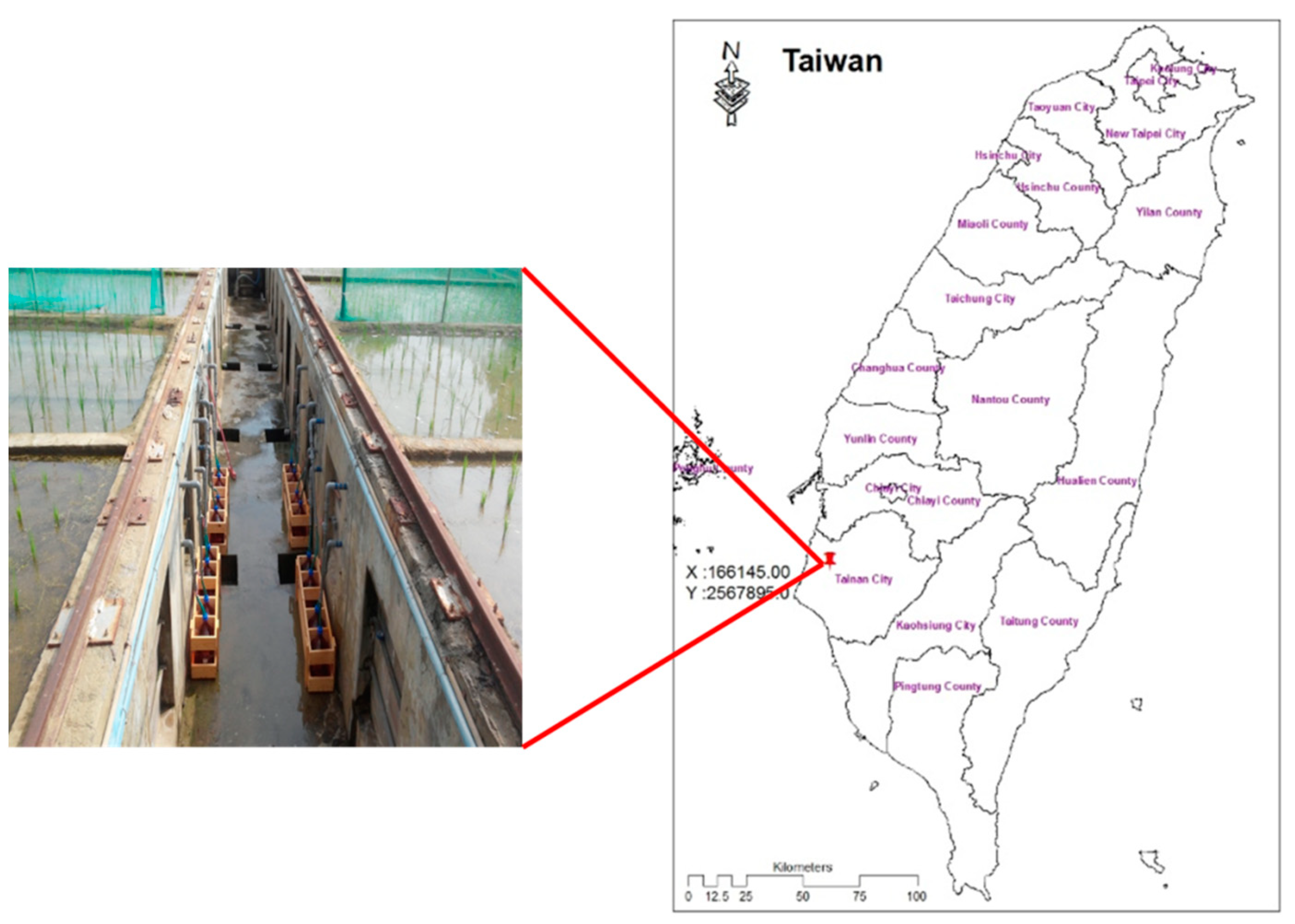
2.1. Research Site and Sample Collection
2.2. Water Samples Collection
2.3. Soil Collection and Extraction
2.4. UV/Vis and Fluorescence Spectrophotometer Measurement
2.5. Optical Index
2.6. Statistic
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DOC Concentrations of DOM and S-S
3.2. Optical Indices
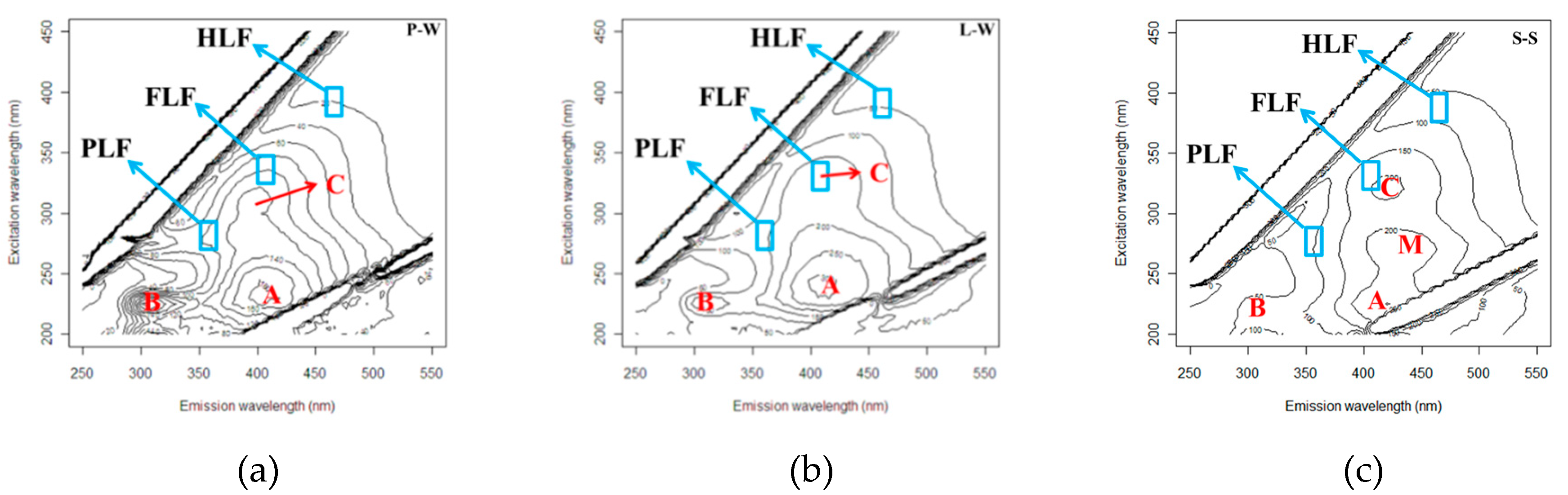
3.3. Fluorescence EEM
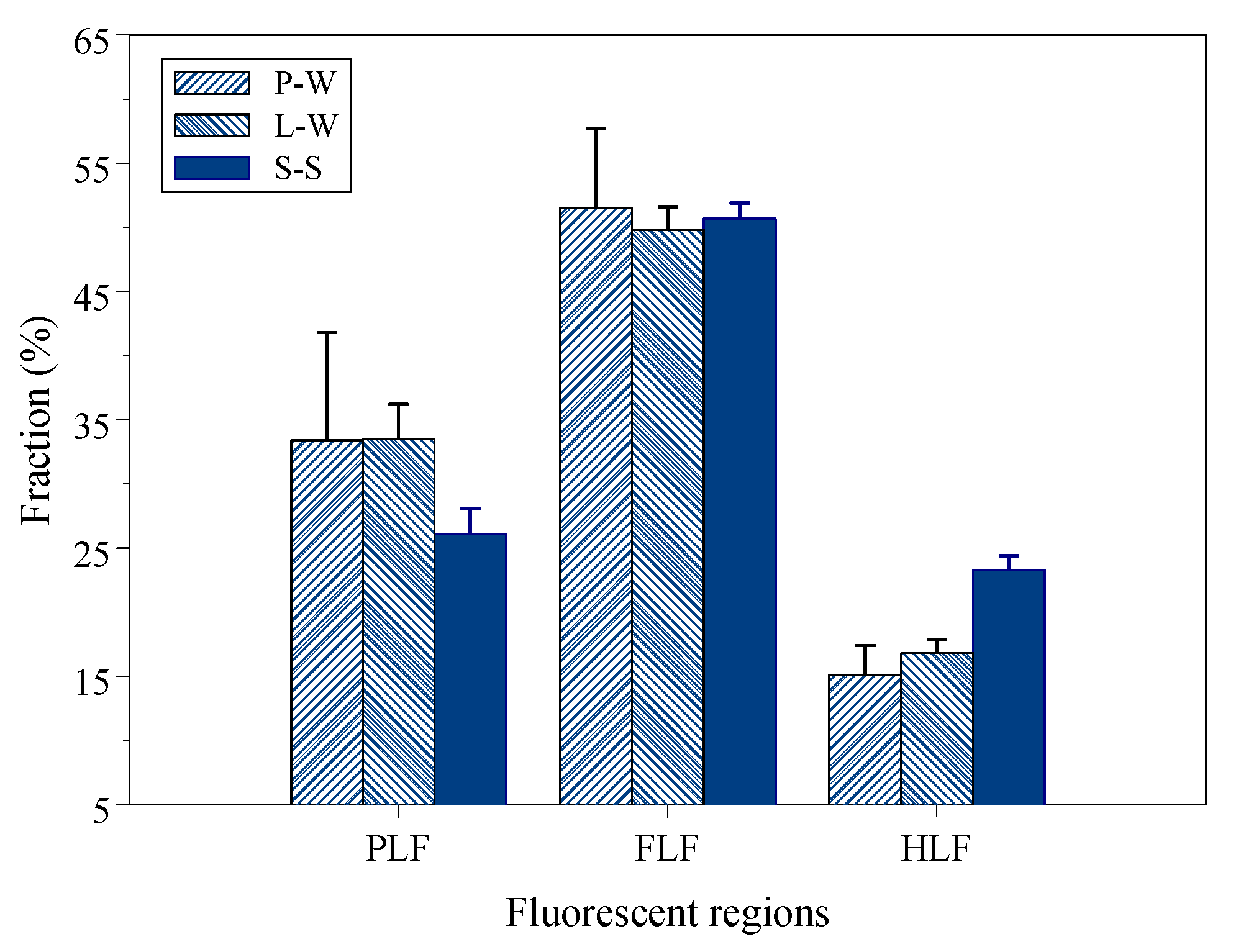
3.4. Protein- (PLF), Fulvic- (FLF) and Humic-Like (HLF) Fluorescence
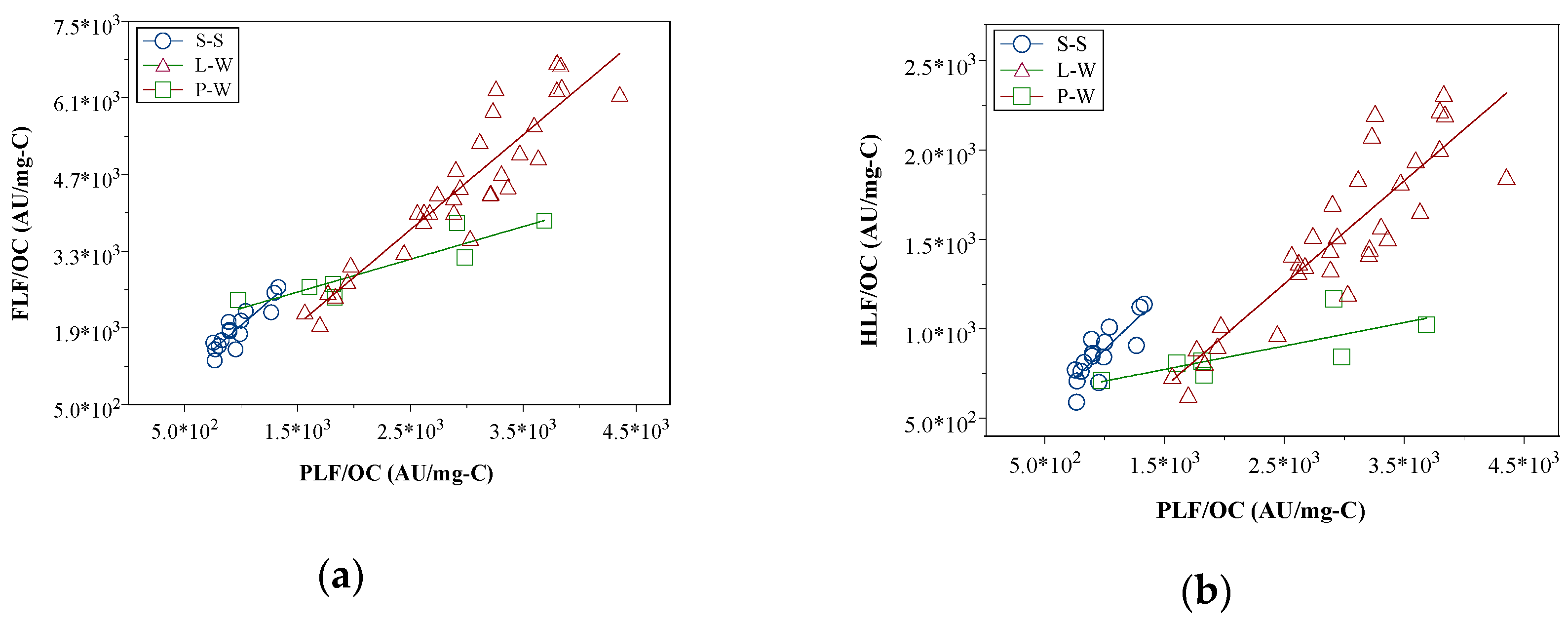
3.5. Percolation Mechanisms in the Lysimeter
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chow, J.; Kopp, R.J.; Portney, P.R. Energy resources and global development. Science 2003, 302, 1528–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalm, M.; Zeitz, J. Concentrations of dissolved organic carbon in peat soils as influenced by land use and site characteristics—A lysimeter study. Catena 2015, 127, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, B.; Kalbitz, K. Controls of bioavailability and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter in soils. Geoderma 2003, 113, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Kalbitz, K. Cycling downwards–Dissolved organic matter in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.E.; Rothstein, D.E. The dynamic exchange of dissolved organic matter percolating through six diverse soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chapelle, F.H.; Strom, E.W.; Benner, R. Origins and bioavailability of dissolved organic matter in groundwater. Biogeochemistry 2015, 122, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, R.T.; Butman, D.E.; Wilson, H.F.; Raymond, P.A. Riverine export of aged carbon driven by flow path depth and residence time. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulet, N.; Moore, T.R. Environmental chemistry: Browning the waters. Nature 2006, 444, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, S.; Pizzeghello, D.; Bragazza, L.; Gerdol, R. Low-molecular-weight organic acids and hormone-like activity of dissolved organic matter in two forest soils in N Italy. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzeghello, D.; Zanella, A.; Carletti, P.; Nardi, S. Chemical and biological characterization of dissolved organic matter from silver fir and beech forest soils. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebbioso, A.; Piccolo, A. Molecular characterization of dissolved organic matter (DOM): A critical review. Analyt. Bioanalyt. Chem. 2013, 405, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Hur, J. Pre-treatments, characteristics, and biogeochemical dynamics of dissolved organic matter in sediments: A review. Water Res. 2015, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—A review. River Res. Applicat. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, C.; Shen, G.; Lv, J.; Wu, H. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in various agricultural soils throughout China. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, A.M.; Kraus, T.E.; Pellerin, B.A.; Fleck, J.A.; Downing, B.D.; Bergamaschi, B.A. Optical properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM): Effects of biological and photolytic degradation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Hornberger, G.M.; Bencala, K.E.; Boyer, E.W. In-stream sorption of fulvic acid in an acidic stream: A stream-scale transport experiment. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdwell, J.E.; Engel, A.S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.K.; Baker, A.; Murphy, K.; Hambly, A.; Stuetz, R.; Khan, S. Fluorescence as a potential monitoring tool for recycled water systems: A review. Water Res. 2009, 43, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellman, J.B.; Spencer, R.G.; Hernes, P.J.; Edwards, R.T.; D’Amore, D.V.; Hood, E. The impact of glacier runoff on the biodegradability and biochemical composition of terrigenous dissolved organic matter in near-shore marine ecosystems. Mar. Chem. 2010, 121, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Westerhoff, P.; Leenheer, J.A.; Booksh, K. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5701–5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalán, N.; Obrador, B.; Felip, M.; Pretus, J.L. Higher reactivity of allochthonous vs. autochthonous DOC sources in a shallow lake. Aquatic Sci. 2013, 75, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, J.; Park, M.-H.; Schlautman, M.A. Microbial transformation of dissolved leaf litter organic matter and its effects on selected organic matter operational descriptors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofa, K.M.; Yoshioka, T.; Konohira, E.; Tanoue, E. Dynamics and characteristics of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the groundwater, river and lake water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 184, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.; Gooddy, D.; Allen, D.; Old, G. Understanding groundwater, surface water, and hyporheic zone biogeochemical processes in a Chalk catchment using fluorescence properties of dissolved and colloidal organic matter. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, G00F02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Price, R.M.; Yamashita, Y.; Jaffé, R. Comparative study of dissolved organic matter from groundwater and surface water in the Florida coastal Everglades using multi-dimensional spectrofluorometry combined with multivariate statistics. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.M.; Boyer, E.W.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Doran, P.T.; Kulbe, T.; Andersen, D.T. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.; Hwang, S.-J.; Shin, J.-K. Using synchronous fluorescence technique as a water quality monitoring tool for an urban river. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 191, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Kinniburgh, D. An R script for visualising and analysing fluorescence excitation–emission matrices (EEMs). Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longnecker, K.; Kujawinski, E.B. Composition of dissolved organic matter in groundwater. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2011, 75, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Yang, L.; Hur, J. Lipid biomarkers and spectroscopic indices for identifying organic matter sources in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2017, 112, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Jean, J.-S.; Chou, M.-L. Association between arsenic and different-sized dissolved organic matter in the groundwater of black-foot disease area, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-C.; Liao, C.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Shih, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-C.; Zehetner, F.; Hein, T. Differences in N loading affect DOM dynamics during typhoon events in a forested mountainous catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-L.; Yeh, K.-J.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yu, W.-C.; Lee, M.-H.; Chen, T.-C. Use of fluorescence quenching method to measure sorption constants of phenolic xenoestrogens onto humic fractions from sediment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edzwald, J.K.; Tobiason, J.E. Enhanced coagulation: US requirements and a broader view. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Fujii, M.; Terao, K.; Jiwei, R.; Lee, Y.P.; Yoshimura, C. Correlations between aromaticity of dissolved organic matter and trace metal concentrations in natural and effluent waters: A case study in the Sagami River Basin, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.G.; Butler, K.D.; Aiken, G.R. Dissolved organic carbon and chromophoric dissolved organic matter properties of rivers in the USA. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2012, 117, G03001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.-J.; Zhao, C.; Shi, Z.-H.; Zhong, J.; Liu, J.-G.; Li, J.-Q. Spectroscopic characteristics of dissolved organic matter in afforestation forest soil of Miyun District, Beijing. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavelescu, G.; Ghervase, L.; Ioja, C.; Dontu, S.; Spiridon, R. Spectral fingerprints of groundwater organic matter in rural areas. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2013, 65, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar]
- Coble, P.G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy. Mar. Chem. 1996, 51, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Lamont-BIack, J. Fluorescence of dissolved organic matter as a natural tracer of ground water. Groundwater 2001, 39, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H. Spectroscopic characterization of dissolved organic matter and its interactions with metals in surface waters using size exclusion chromatography. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Gooddy, D.; Butcher, A.; Morris, B. Tracing groundwater flow and sources of organic carbon in sandstone aquifers using fluorescence properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM). Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 3384–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naden, P.S.; Old, G.H.; Eliot-Laize, C.; Granger, S.J.; Hawkins, J.M.; Bol, R.; Haygarth, P. Assessment of natural fluorescence as a tracer of diffuse agricultural pollution from slurry spreading on intensely-farmed grasslands. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröberg, M.; Berggren Kleja, D.; Hagedorn, F. The contribution of fresh litter to dissolved organic carbon leached from a coniferous forest floor. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 58, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | pH | EC μS/cm | DO mg/L | OM% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P-W | 7.61 ± 0.42 | 1840 ± 240 | 1.44 ± 0.16 | - * |
| L-W | 7.90 ± 0.11 | 110.3 ± 5.8 | - | - |
| S-S | 8.24 ± 0.08 | - | - | 2.92 ± 0.37 |
| DOC * | SUVA254 | S275-295 | FI * | BIX * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/L | L/mg-C/m | 1/nm | |||
| P-W | 1.24 ± 0.35 | 2.68 ± 1.60 | 0.026 ± 0.011 | 1.94 ± 0.03 | 1.10 ± 0.07 |
| L-W | 2.01 ± 0.55 | 3.37 ± 0.69 | 0.019 ± 0.002 | 1.84 ± 0.05 | 0.98 ± 0.05 |
| S-S | 34.0 ± 11.0 a | 3.84 ± 0.55 | 0.011 ± 0.001 | 1.56 ± 0.05 | 0.71 ± 0.03 |
| PLF (au) | FLF (au) | HLF (au) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| P-W | 2640 ± 1482 (2048 ± 1064) | 3583 ± 1259 (2868 ± 697) | 1042 ± 365 (833 ± 188) |
| L-W | 5687 ± 1389 (2940 ± 710) | 8642 ± 2937 (4456 ± 1335) | 2931 ± 1067 (1505 ± 462) |
| S-S | 32,128 ± 7646 (966 ± 193) | 61,901 ± 10,632 (1886 ± 385) | 28,520 ± 5480 (862 ± 152) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, T.-P.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Fluorescence Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Percolation Water and Lateral Seepage Affected by Soil Solution (S-S) in a Lysimeter Test. Sensors 2019, 19, 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19184016
Chiu T-P, Huang W-S, Chen T-C, Yeh Y-L. Fluorescence Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Percolation Water and Lateral Seepage Affected by Soil Solution (S-S) in a Lysimeter Test. Sensors. 2019; 19(18):4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19184016
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Teng-Pao, Wei-Shiang Huang, Ting-Chien Chen, and Yi-Lung Yeh. 2019. "Fluorescence Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Percolation Water and Lateral Seepage Affected by Soil Solution (S-S) in a Lysimeter Test" Sensors 19, no. 18: 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19184016
APA StyleChiu, T.-P., Huang, W.-S., Chen, T.-C., & Yeh, Y.-L. (2019). Fluorescence Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Percolation Water and Lateral Seepage Affected by Soil Solution (S-S) in a Lysimeter Test. Sensors, 19(18), 4016. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19184016




