Perrogator: A Portable Energy-Efficient Interrogator for Dynamic Monitoring of Wavelength-Based Sensors in Wearable Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
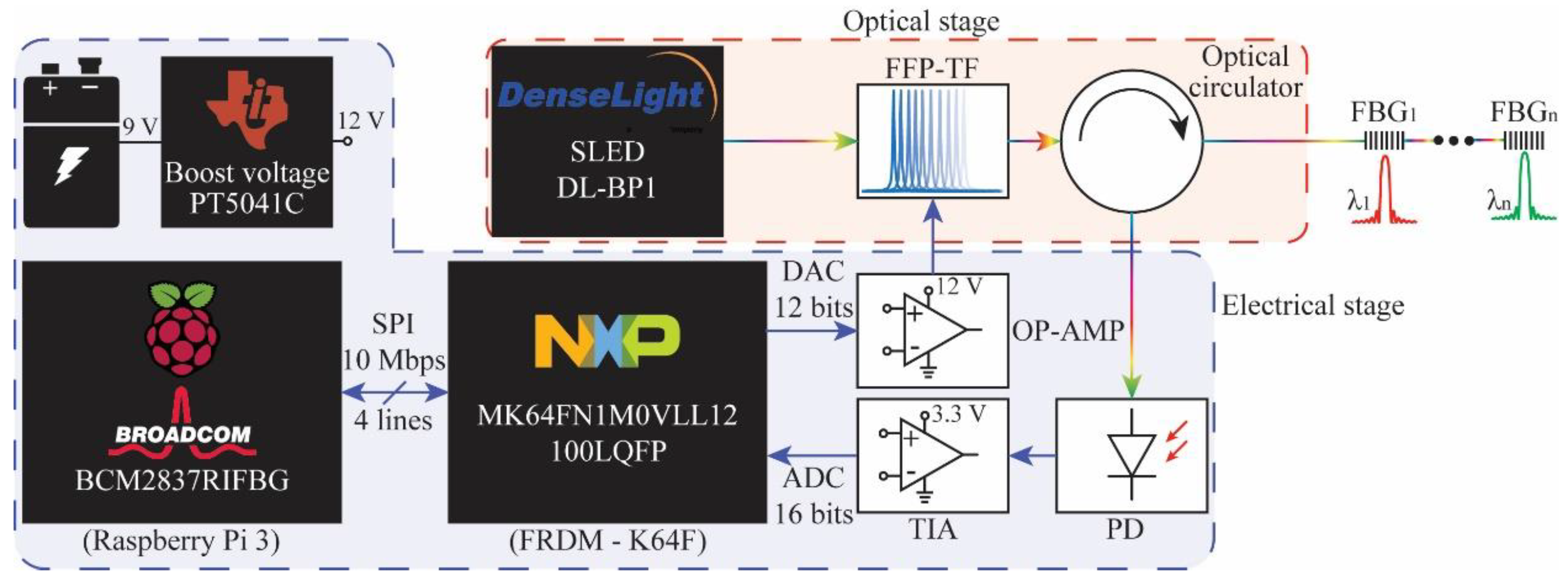
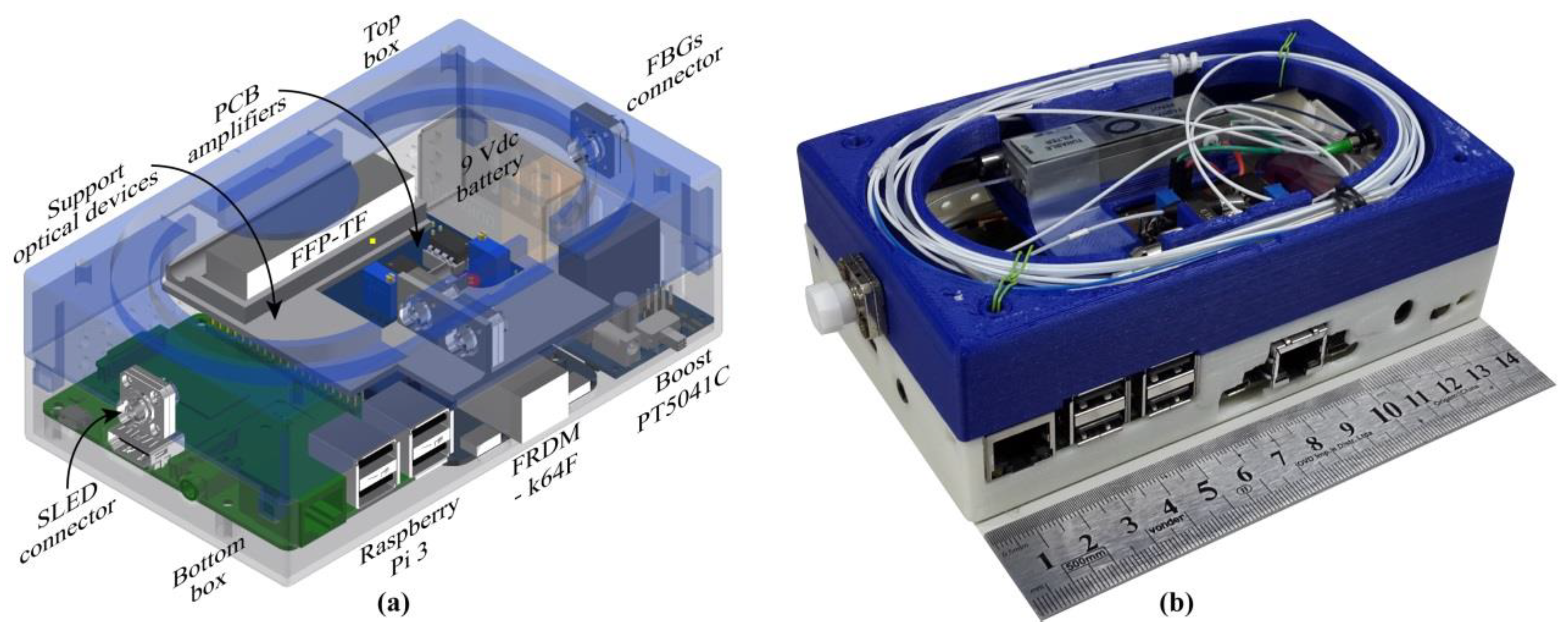
2.1. FBG Interrogator
2.2. Caracterization and Validation of the Proposed Interrogator
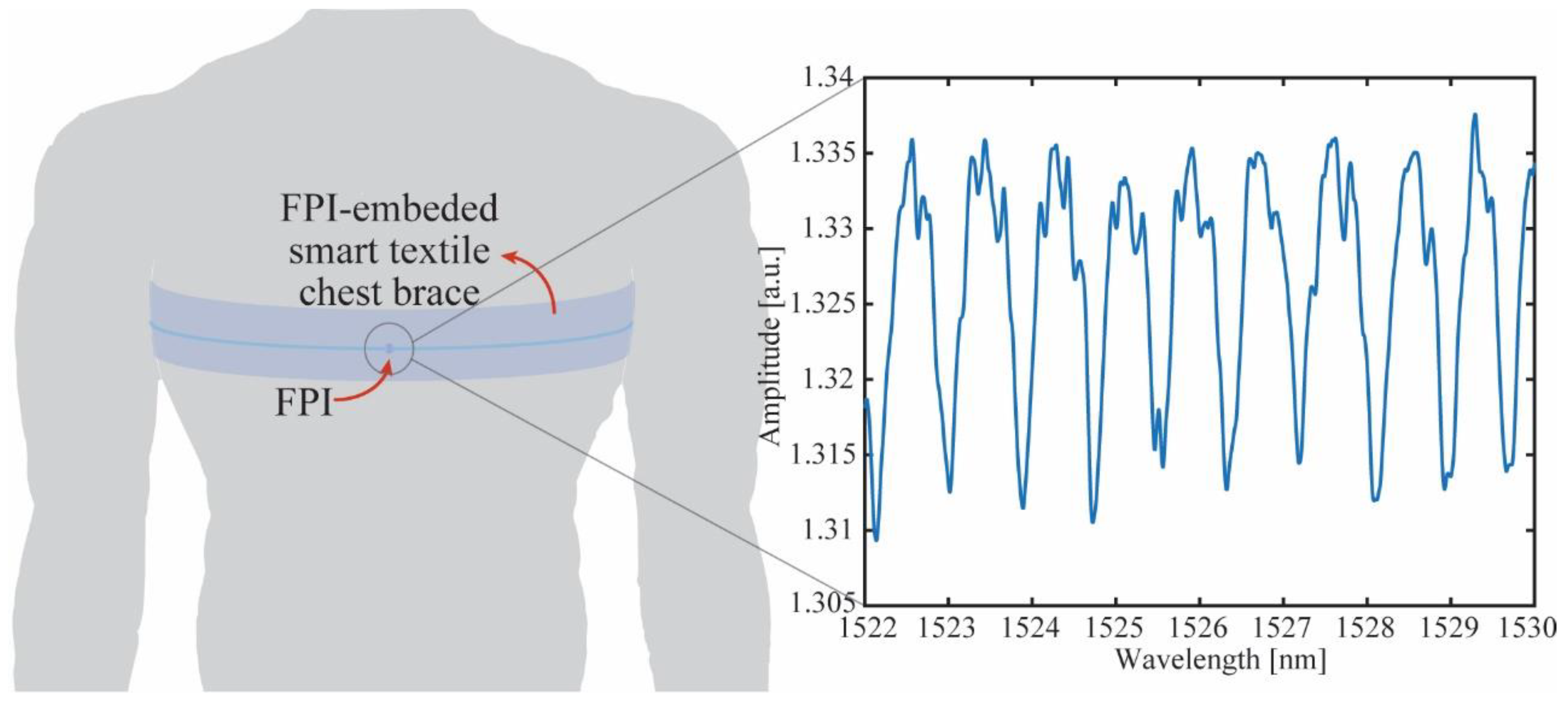
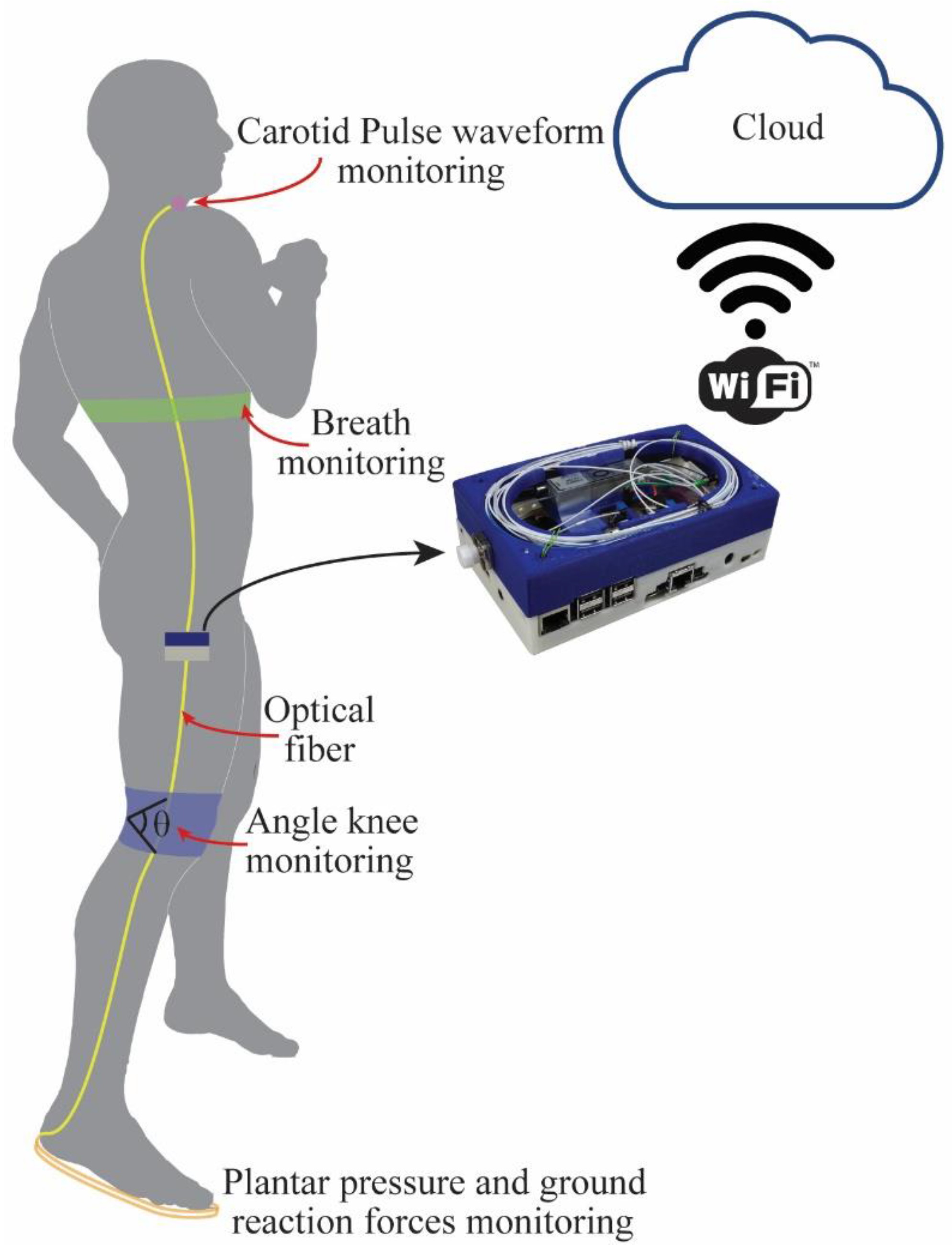
2.3. Wearable Application
3. Results and Discussions
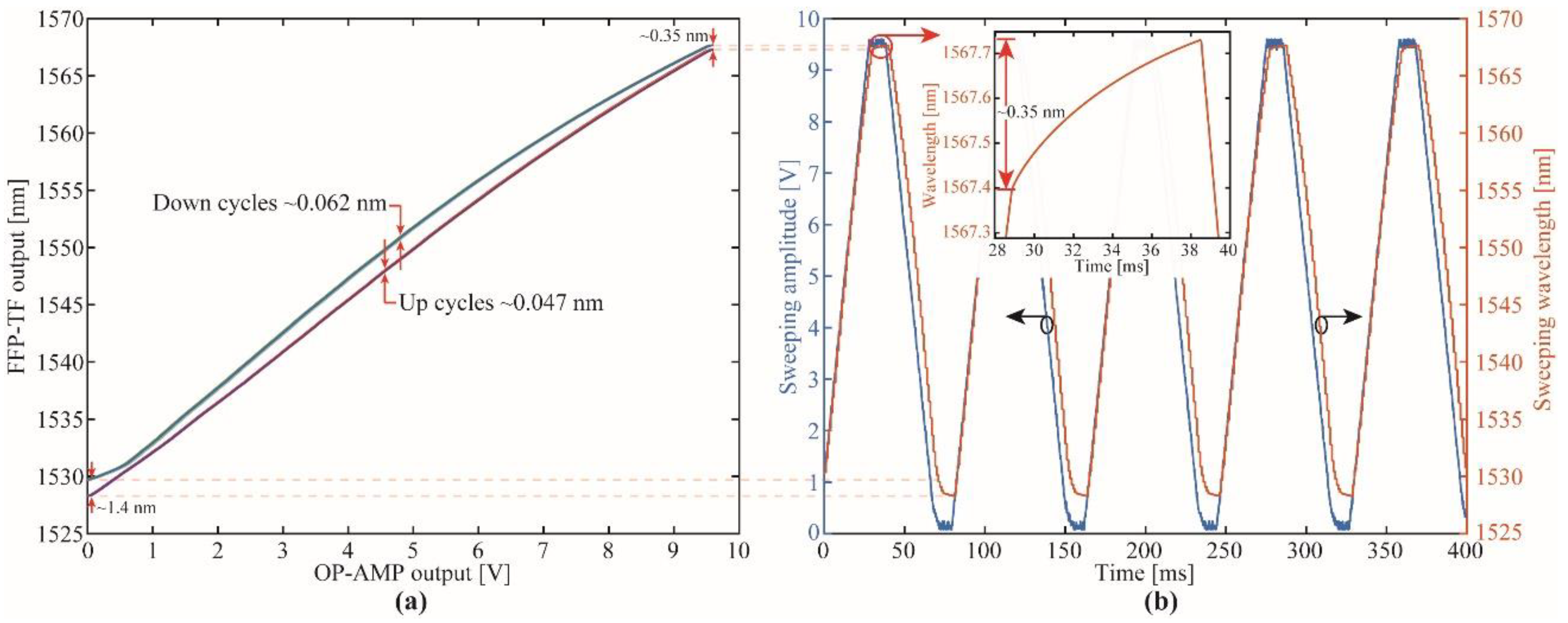
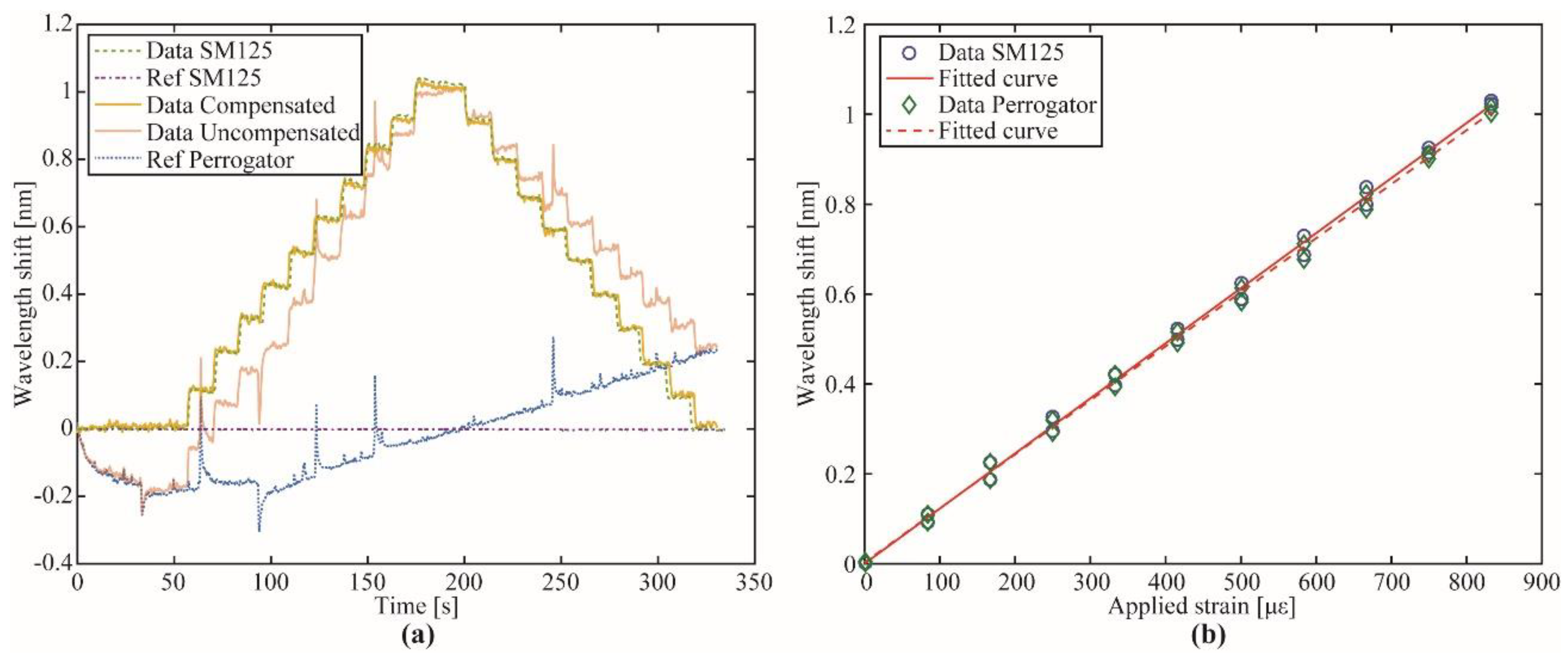
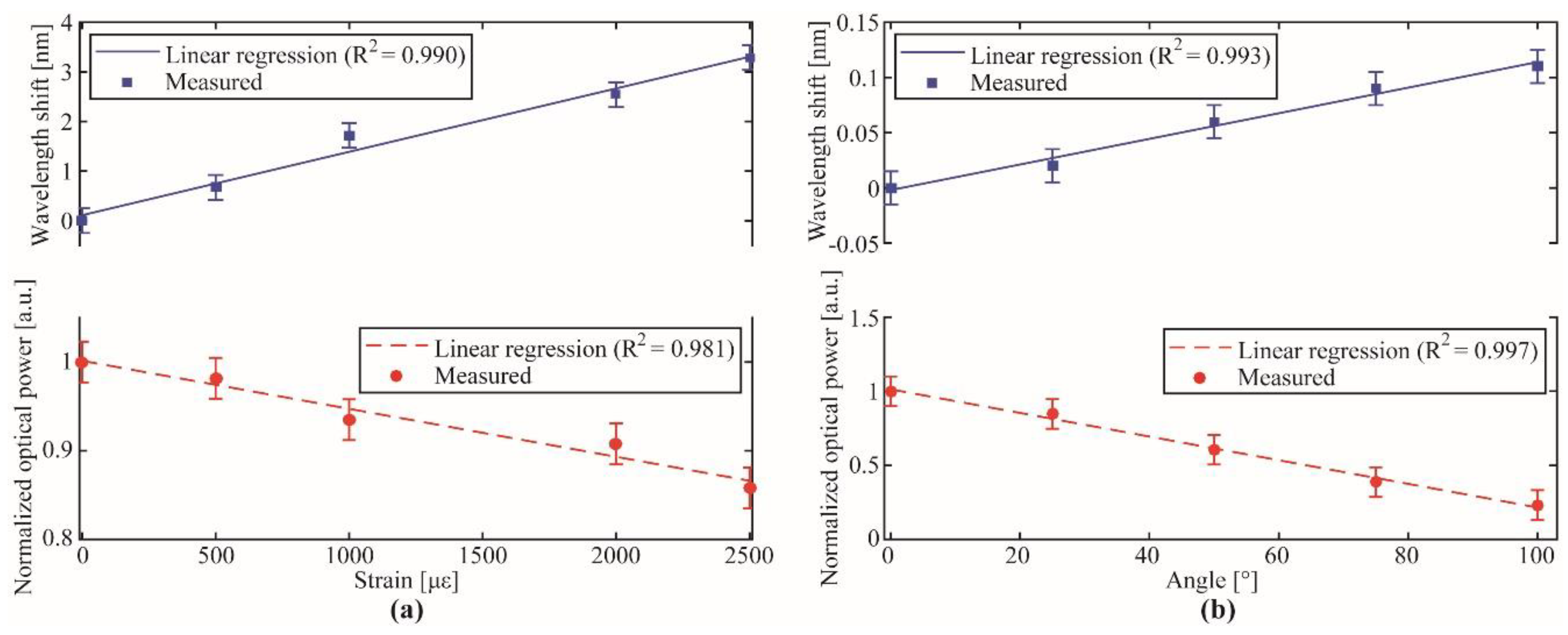
3.1. Portable Interrogator Characterization
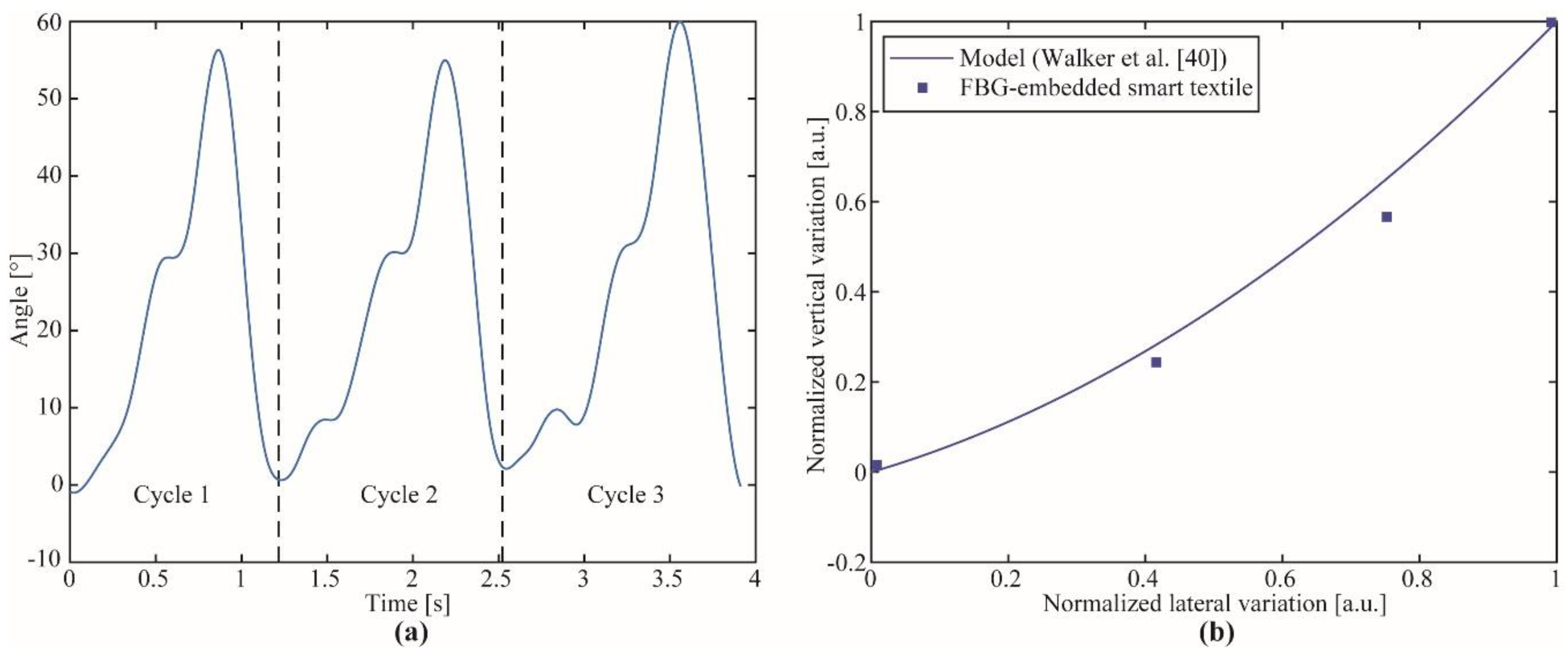
3.2. Study Case 1: Knee Joint Assessment
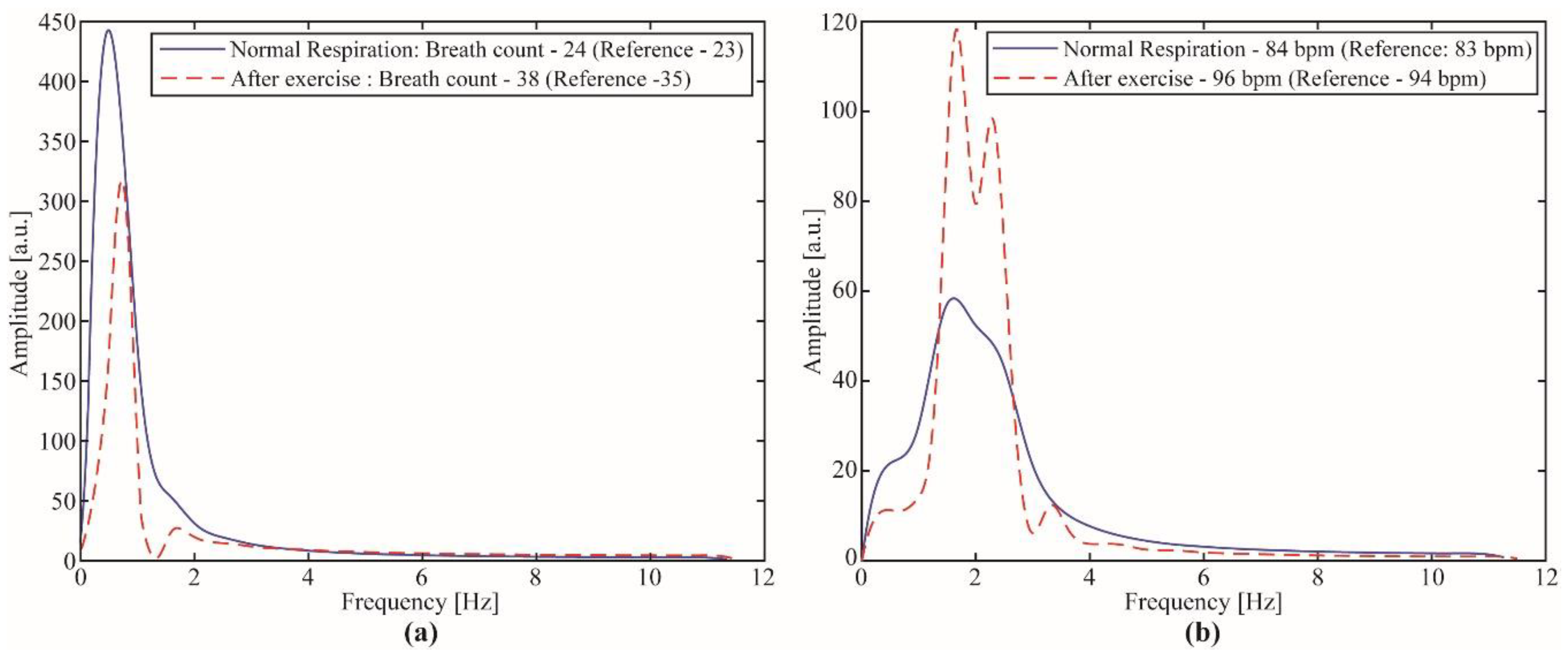
3.3. Study Case 2: Breath and Heart Rate Assessment
3.4. Comparisons with Commercial Solutions and Future Perpectives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cusano, A.; Cutolo, A.; Albert, J. Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors: Market. Overview and New Perspectives; Bentham Science Publishers: Potomac, MD, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Marques, C.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J. Multi-interface level in oil tanks and applications of optical fiber sensors. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 40, 40–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Singh, N.; Tiwari, U.; Kapur, P. Fiber grating sensors in medicine: Current and emerging applications. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2011, 167, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Vargas-Valencia, L.; dos Santos, W.M.; Bó, A.P.; Siqueira, A.A.; Pontes, M.J. Polymer optical fiber sensors in wearable devices: Toward novel instrumentation approaches for gait assistance devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 7085–7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Díaz, C.R.; Jiménez, M.F.; Leitão, C.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M.J.; Frizera, A. Polymer optical fiber based sensor system for smart walker instrumentation and health assessment. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 1748, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, K.T.V.; Sun, T. Fiber optic sensor technology: An overview. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 82, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M. Measuement of temperature and relative humidity with polymer optical fiber sensors based on the induced stress-optic effect. Sensors 2018, 18, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Ning, T.; .Zhang, C.; Wen, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, C. Liquid level and temperature sensor based on an asymmetrical fiber Mach-Zehnder interferometer combined with a fiber Bragg grating. Opt. Commun. 2016, 372, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Fukuda, H.; Song, K.Y.; Nakamura, K. Ultrahigh-speed distributed Brillouin reflectometry. Light Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, A.R.; Fontana, M.; Rodriguez-Cobo, L.; Lomer, M.; López-Higuera, J.M. Machine learning for turning optical fiber specklegram sensor into a spatially-resolved sensing system. Proof of concept. J. Light. Technol. 2018, 36, 3733–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Cheng, F.; Wang, H.; Peng, W. Surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on smart phone platforms. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.A.F.; Min, R.; Junior, A.L.; Antunes, P.; Fasano, A.; Woyessa, G.; Nielsen, H.K.; Rasmussen, B.O.; Bang, O. Fast and stable gratings inscription in POFs made of different materials with pulsed 248 nm KrF laser. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, D. Review of chirped fiber bragg grating (CFBG) fiber-optic sensors and their applications. Sensors 2018, 18, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Large, M.C.J.; Moran, J.; Ye, L. The role of viscoelastic properties in strain testing using microstructured polymer optical fibres (mPOF). Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 034014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilro, L.; Alberto, N.; Pinto, J.L.; Nogueira, R. Optical sensors based on plastic fibers. Sensors 2012, 12, 12184–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Theodosiou, A.; Min, R.; Casas, J.; Diaz, C.R.; dos Santos, W.M.; Pontes, M.J.; Siqueira, A.A.G.; Marques, C.A.F.; Kalli, K.; et al. Quasi-Distributed Torque and Displacement Sensing on a Series Elastic Actuator’s Spring using FBG arrays inscribed in CYTOP Fibers. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 1748, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Ali, M.; Lai, M.H.; Lim, K.S.; Ahmad, H. Chronology of fabry-perot interferometer fiber-optic sensors and their applications: A review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7451–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, C.A.; Marques, C.A.; Domingues, M.F.F.; Ribeiro, M.R.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Pontes, M.J.; André, P.S.; Antunes, P.F.C. A cost-effective edge-filter based FBG interrogator using catastrophic fuse effect micro-cavity interferometers. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2018, 124, 486–493. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, C.; Leitão, C.; Marques, C.; Domingues, M.; Alberto, N.; Pontes, M.; Frizera, A.; Ribeiro, M.R.N.; André, P.S.B.; Antunes, P.F.C. Low-Cost Interrogation Technique for Dynamic Measurements with FBG-Based Devices. Sensors 2017, 17, 2414. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Khattak, A.; Martz, C.; Zhou, D.P. Tunable Multimode Fiber Based Filter and Its Application in Cost-Effective Interrogation of Fiber-Optic Temperature Sensors. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachava, V.R.; Kamineni, S.; Madhuvarasu, S.S.; Putha, K.; Mamidi, V.R. FBG based high sensitive pressure sensor and its low-cost interrogation system with enhanced resolution. Photonic Sens. 2015, 5, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, W.; Luo, B.; Wang, P. High-speed FBG-based fiber sensor networks for semidistributed strain measurements. IEEE Photonics J. 2013, 5, 7200507. [Google Scholar]
- Babin, S.A.; Vlasov, A.A.; Dyshlyuk, A.V.; Shalagin, A.M.; Vitrik, O.B.; Kulchin, Y.N. Application of optical time-domain reflectometry for the interrogation of fiber Bragg sensors. Laser Phys. 2007, 17, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, D.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Pang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C. Interrogation of 5000 ultraweak fiber Bragg grating sensors using optical frequency domain reflectometry. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Wearable sensors for human activity monitoring: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Mondal, T.; Deen, M. Wearable sensors for remote health monitoring. Sensors 2017, 17, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Frizera, A.; Avellar, L.M.; Pontes, M.J. Design considerations, analysis, and application of a low-cost, fully portable, wearable polymer optical fiber curvature sensor. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Díaz, C.R.; Leitão, C.; Pontes, M.J.; Marques, C.; Frizera, A. Polymer optical fiber-based sensor for simultaneous measurement of breath and heart rate under dynamic movements. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 109, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, S.; Umesh, S.; Asokan, S. Knee angle measurement device using fiber bragg grating sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 10034–10040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, M.F.; Alberto, N.; Leitão, C.; Tavares, C.; de Lima, E.R.; Radwan, A.; Sucasas, V.; Rodriguez, J.; André, P.S.B.; Antunes, P.F.C. Insole optical fiber sensor architecturefor remote gait analysis—An eHealth Solution. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4662, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bonefacino, J.; Tam, H.Y.; Glen, T.S.; Cheng, X.; Pun, C.F.J.; Wang, J.; Lee, P.H.; Vincent Tse, M.L.; Boles, S.T. Ultra-fast polymer optical fibre Bragg grating inscription for medical devices. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Theodosiou, A.; Díaz, CR.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M.J.; Kalli, K.; Frizera, A. Simultaneous measurement of axial strain, bending and torsion with a Single fiber Bragg grating in CYTOP fiber. J. Light Technol. 2018, 37, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, C.A.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; Andre, P.S.; da Costa Antunes, P.F.; Pontes, M.J.; Frizera-Neto, A.; Ribeiro, M.R. Liquid level measurement based on FBG-embedded diaphragms with temperature compensation. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 18, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtley, C. Clinical Gait Analysis: Theory and Practice; Elsevier: Philadelphia, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, P.N.; Refshauge, K.M.; Scarvell, J.M. Development of the concepts of knee kinematics. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 1895–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Bilro, L.; Nogueira, R. Fabry-Pérot cavities based on photopolymerizable resins for sensing applications. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.F.; Bilro, L.; Nogueira, R.; Rocha, A.M.M. Adhesive based Fabry-Pérot hydrostatic pressure sensor with improved and controlled sensitivity. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 8724, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.S.; Ferreira, M.S.; Silva, S.O.; Kobelke, J.; Schuster, K.; Bierlich, J.; Frazão, O. Fiber Fabry-Perot interferometer for curvature sensing. Photonic Sens. 2016, 6, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, D.; Sadek, S.; Zaharia, G.; el Zein, G. Doppler radar for heartbeat rate and heart rate variability extraction. E Health Bioeng. 2011, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Pai, A.; Riepold, M.; Trächtler, A. Model-based precision position and force control of SMA actuators with a clamping application. Mechatronics 2018, 50, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepold, M.; Maslo, S.; Han, G.; Henke, C.; Trächtler, A. Open-loop linearization for piezoelectric actuator with inverse hysteresis model. Vibroeng. Procedia 2019, 22, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micron, O. FFP-TF2 Fiber Fabry-Perot Tunable Filter Technical Reference; Micron Optics Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sabat, R.G.; Mukherjee, B.K.; Ren, W.; Yang, G. Temperature dependence of the complete material coefficients matrix of soft and hard doped piezoelectric lead zirconate titanate ceramics. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 064111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzou, H.S.; Ye, R. Pyroelectric and thermal strain effects of piezoelectric (PVDF and PZT) devices. Mech. Syst. Signal. Process 1996, 10, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.S.; Kurosawa, H.; Rovick, J.S.; Zimmerman, R.A. External knee joint design based on normal motionc. J. Rehabil. Res. 1985, 22, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilro, L.; Oliveira, J.G.; Pinto, J.L.; Nogueira, R.N. A reliable low-cost wireless and wearable gait monitoring system based on a plastic optical fibre sensor. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 045801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner-Cordero, A.; Pons, J.L.; Turowska, E.A.; Schiele, A.; Baydal-Bertomeu, J.M.; Garrido, D.; Molla, F.; Belda-lois, J.M.; Poveda, R.; Barbera, R. Kinematics and Dynamics of Wearable Robots, in Wearable Robots, Chichester; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 47–85. [Google Scholar]
- Coppetti, T.; Brauchlin, A.; Müggler, S.; Attinger-Toller, A.; Templin, C.; Schönrath, F. Accuracy of smartphone apps for heart rate measurement. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| DAC Resolution | Full Scale FFP-TF Resolution (pm) | Maximum FFP-TF Resolution (pm) | Frequency Rate (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4096 | 11.01 | 3.82 | 26.65 |
| 2048 | 22.02 | 7.65 | 53.30 |
| 1024 | 44.04 | 11.47 | 106.61 |
| 512 | 88.08 | 15.30 | 213.22 |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength sensitivity—axial strain | sλ,ε | 1.28 pm/με |
| Reflectivity sensitivity—axial strain | sr,ε | −5.14 × 10−5 με−1 |
| Wavelength sensitivity—bending angle | sλ,α | 1.16 pm/° |
| Reflectivity sensitivity—bending angle | sr,α | −7.98 × 10−3/° |
| Interrogator/Parameter | SM125 | I-MON 256 HS | Perrogator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of channels | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Scan frequency (Hz) | 2 | 17000 | 213 |
| Accuracy (pm) | 1 | 5 | 12 |
| Repeatability (pm) | 0.5 | 5 | 60 |
| Dynamic range (dB) | 50 | 30 | 25 |
| Wavelength range (nm) | 80 | 45 | 45 |
| Battery powered | No | No | Yes |
| Wireless communication | No | No | Yes |
| Power consumption (W) | 20 | Not reported | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
R. Diaz, C.A.; Leal-Junior, A.G.; M. Avellar, L.; C. Antunes, P.F.; Pontes, M.J.; Marques, C.A.; Frizera, A.; N. Ribeiro, M.R. Perrogator: A Portable Energy-Efficient Interrogator for Dynamic Monitoring of Wavelength-Based Sensors in Wearable Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132962
R. Diaz CA, Leal-Junior AG, M. Avellar L, C. Antunes PF, Pontes MJ, Marques CA, Frizera A, N. Ribeiro MR. Perrogator: A Portable Energy-Efficient Interrogator for Dynamic Monitoring of Wavelength-Based Sensors in Wearable Applications. Sensors. 2019; 19(13):2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132962
Chicago/Turabian StyleR. Diaz, Camilo A., Arnaldo Gomes Leal-Junior, Letícia M. Avellar, Paulo F. C. Antunes, Maria J. Pontes, Carlos A. Marques, Anselmo Frizera, and Moisés R. N. Ribeiro. 2019. "Perrogator: A Portable Energy-Efficient Interrogator for Dynamic Monitoring of Wavelength-Based Sensors in Wearable Applications" Sensors 19, no. 13: 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132962
APA StyleR. Diaz, C. A., Leal-Junior, A. G., M. Avellar, L., C. Antunes, P. F., Pontes, M. J., Marques, C. A., Frizera, A., & N. Ribeiro, M. R. (2019). Perrogator: A Portable Energy-Efficient Interrogator for Dynamic Monitoring of Wavelength-Based Sensors in Wearable Applications. Sensors, 19(13), 2962. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19132962










