RGB-D SLAM Using Point–Plane Constraints for Indoor Environments †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We exploited point and plane features, which provide reliable constraints for the estimation of poses and reconstruction of the scene’s map for the majority of indoor environments.
- We added the MW constraint to point–plane-based cost functions, resulting in the provision of fixed-plane normals as global landmarks for more accurate pose estimation.
- We evaluated our proposed approach on two public available datasets, and we obtained robust and accurate performance.
2. Related Work
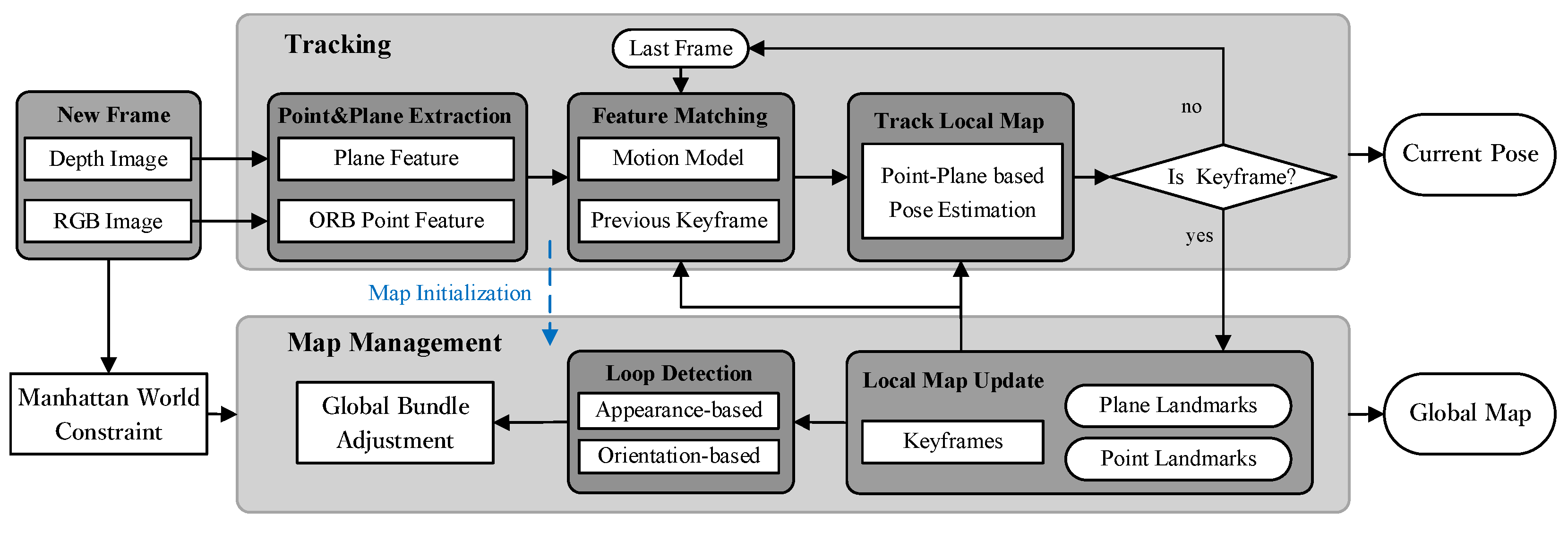
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Preliminaries
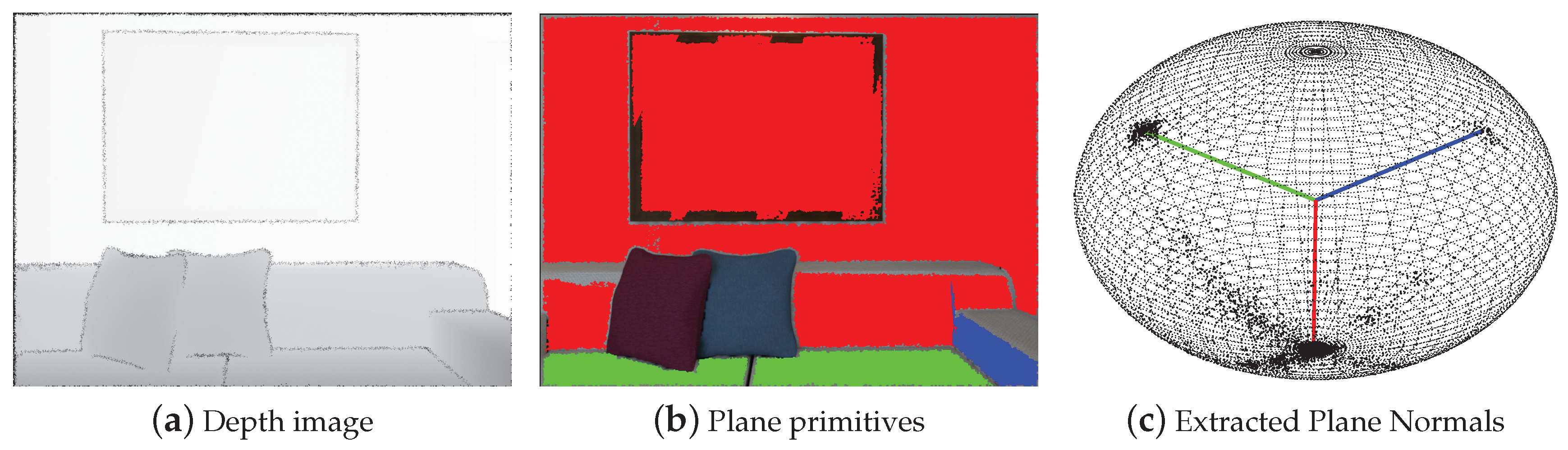
3.1.1. Point and Plane Representation
3.1.2. State Transformation
3.1.3. Distance Measurement
3.2. Pose Estimation with Point and Plane Features
3.2.1. Point and Plane Feature Tracking
3.2.2. Robust Pose Estimation
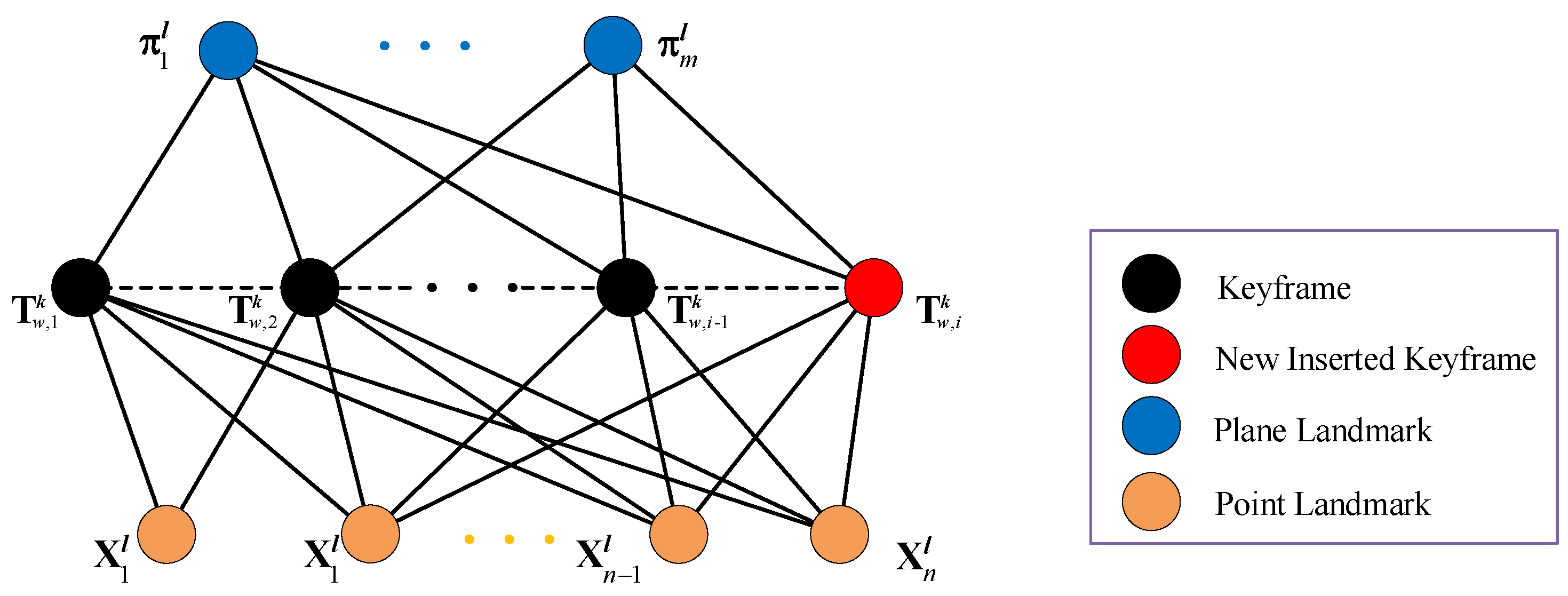
3.3. Map Management and Loop Detection
3.3.1. Local Map Update
3.3.2. Loop Detection based on Appearance and Orientation Constraints
3.3.3. Global Map Generation
3.4. Pose and Plane Optimization with the MW Constraint
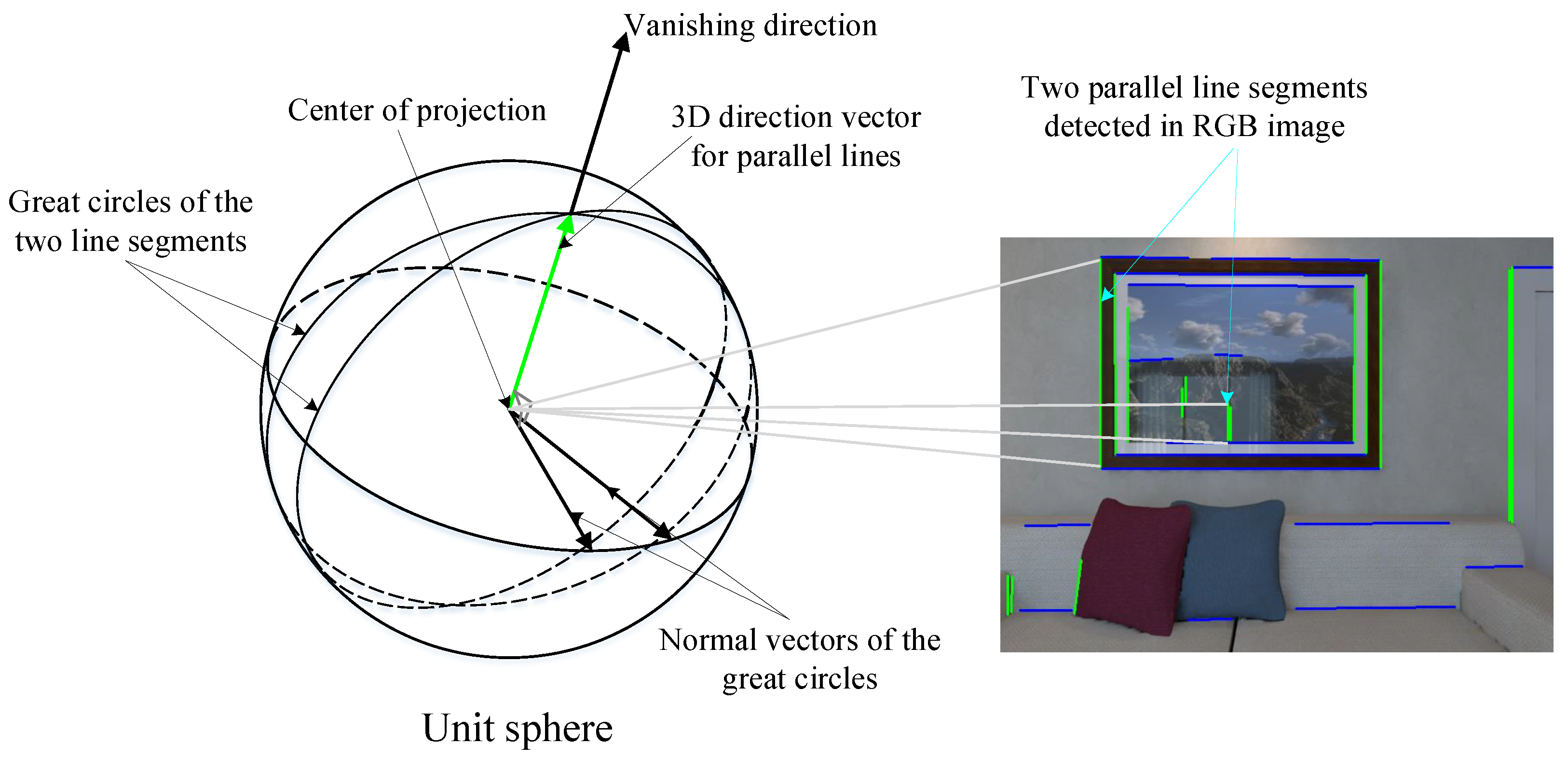
3.4.1. MW Axes Extraction
3.4.2. Optimization with Fixed Plane Normal
4. Results
- The ICL-NUIMdataset comprises images from a hand-held RGB-D camera in synthetically generated environments. These sequences were captured in a living room and an office with perfect ground-truth poses to fully quantify the accuracy of a given visual odometry or SLAM system. Depth and RGB noise models were used to alter the ground images to simulate realistic sensor noise. Some image sequences are in low-texture environments, which makes it difficult to estimate the poses of the whole images in these sequences.
- The TUM RGB-D dataset is a famous benchmark that is used to evaluate the accuracy of a given visual odometry or visual SLAM system. It contains various indoor sequences captured by a Kinect RGB-D sensor. The sequences were recorded in real environments at a frame rate of 30 Hz with a resolution, and their ground-truth trajectories were obtained from a high-accuracy motion-capture system. The TUM dataset is more challenging than the ICL dataset because includes some blurred images and inaccurate alignment image pairs that make it difficult to estimate the camera poses.
4.1. Evaluation on Synthetic Dataset
4.2. Evaluation on Real-World Data
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, R.; Zhou, D.; Peng, K.; Liu, Y. Plane Based Visual Odometry for Structural and Low-Texture Environments Using RGB-D Sensors. In Proceedings of the BigComp 2019, 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Kyoto, Japan, 27 February–2 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Mei, Y.; Yang, K.; Cai, B. IMU-Assisted 2D SLAM Method for Low-Texture and Dynamic Environments. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, F. Automatic Estimation of Dynamic Lever Arms for a Position and Orientation System. Sensors 2018, 18, 4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhou, D.; Peng, K.; Fan, W.; Liu, Y. Improved real-time odometry estimation method for incremental RGB-D mapping by fusing IMU data. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), Gui-lin, China, 12–15 June 2016; pp. 2991–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, P.; Dong, W.; Li, J.; Ai, M.; Wu, X.; Hu, Q. An Eight-Direction Scanning Detection Algorithm for the Mapping Robot Pathfinding in Unknown Indoor Environment. Sensors 2018, 18, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Rad, A.B.; Wong, Y.K. Sensor fusion of monocular cameras and laser rangefinders for line-based simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) tasks in autonomous mobile robots. Sensors 2012, 12, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payá, L.; Reinoso, O.; Jiménez, L.M.; Juliá, M. Estimating the position and orientation of a mobile robot with respect to a trajectory using omnidirectional imaging and global appearance. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Kim, T. Development of Stereo Visual Odometry Based on Photogrammetric Feature Optimization. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, W.; Li, H.; Tang, F.; Wu, Y. Robust and Efficient CPU-Based RGB-D Scene Reconstruction. Sensors 2018, 18, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Orb-slam2: An open-source slam system for monocular, stereo, and rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; Schöps, T.; Cremers, D. LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular SLAM. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 834–849. [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan, J.M.; Yuille, A.L. Manhattan world: Compass direction from a single image by bayesian inference. In Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 941–947. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, K.; Oh, T.H.; Kim, J.; So Kweon, I. Globally optimal Manhattan frame estimation in real-time. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, J.; Bhandari, N.; Leonard, J.J.; Fisher, J.W. Real-time manhattan world rotation estimation in 3d. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1913–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Kneip, L.; Li, H. Real-time rotation estimation for dense depth sensors in piece-wise planar environments. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 2271–2278. [Google Scholar]
- Straub, J.; Freifeld, O.; Rosman, G.; Leonard, J.J.; Fisher, J.W. The manhattan frame model—Manhattan world inference in the space of surface normals. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.K.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.; An, S.; Oh, S.Y. Indoor mapping using planes extracted from noisy RGB-D sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 1727–1733. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, Y.; Jian, Y.D.; Ramalingam, S.; Feng, C. Point-plane SLAM for hand-held 3D sensors. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 5182–5189. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshelham, K. Direct 6-DoF pose estimation from point-plane correspondences. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Image Computing, Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Adelaide, SA, Australia, 23–25 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.; Sugimoto, A. Modeling large-scale indoor scenes with rigid fragments using RGB-D cameras. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2017, 157, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaess, M. Simultaneous localization and mapping with infinite planes. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 25–30 May 2015; Volume 1, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Newcombe, R.A.; Izadi, S.; Hilliges, O.; Molyneaux, D.; Kim, D.; Davison, A.J.; Kohi, P.; Shotton, J.; Hodges, S.; Fitzgibbon, A. KinectFusion: Real-time dense surface mapping and tracking. In Proceedings of the 2011 10th IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Basel, Switzerland, 26–29 October 2011; pp. 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Whelan, T.; Kaess, M.; Johannsson, H.; Fallon, M.; Leonard, J.J.; McDonald, J. Real-time large-scale dense RGB-D SLAM with volumetric fusion. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 598–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerl, C.; Sturm, J.; Cremers, D. Dense visual SLAM for RGB-D cameras. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 2100–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Prisacariu, V.A.; Kähler, O.; Golodetz, S.; Sapienza, M.; Cavallari, T.; Torr, P.H.; Murray, D.W. InfiniTAM v3: A framework for large-scale 3D reconstruction with loop closure. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.00783. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Kneip, L.; Rodriguez, C.; Li, H. Divide and conquer: Efficient density-based tracking of 3D sensors in Manhattan worlds. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.; Coltin, B.; Kim, H.J. Low-drift visual odometry in structured environments by decoupling rotational and translational motion. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 7247–7253. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, P.; Coltin, B.; Jin Kim, H. Linear RGB-D SLAM for planar environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Taguchi, Y.; Kamat, V.R. Fast plane extraction in organized point clouds using agglomerative hierarchical clustering. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–5 June 2014; pp. 6218–6225. [Google Scholar]
- Kümmerle, R.; Grisetti, G.; Strasdat, H.; Konolige, K.; Burgard, W. g2o: A general framework for graph optimization. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3607–3613. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, J.H.; Baldwin, T. An empirical evaluation of doc2vec with practical insights into document embedding generation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1607.05368. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, R.; Peng, K.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Y. Robust visual compass using hybrid features for indoor environments. Electronics 2019, 8, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gioi, R.G.; Jakubowicz, J.; Morel, J.M.; Randall, G. LSD: A line segment detector. Image Process. Line 2012, 2, 35–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, A.; Whelan, T.; Mcdonald, J.; Davison, A.J. A benchmark for RGB-D visual odometry, 3D reconstruction and SLAM. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Hong Kong, China, 31 May–5 June 2014; pp. 1524–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, J.; Engelhard, N.; Endres, F.; Burgard, W.; Cremers, D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 573–580. [Google Scholar]

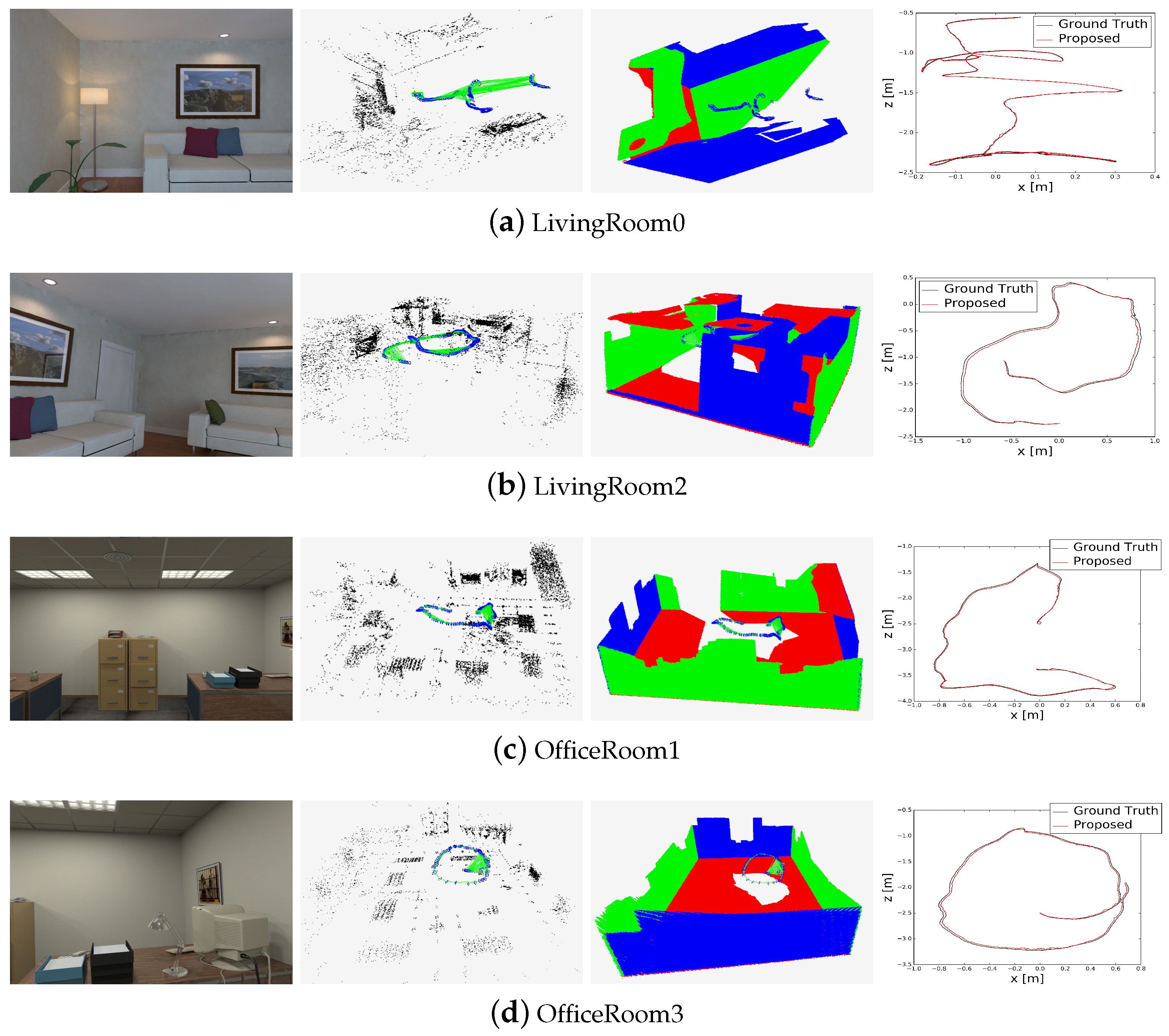
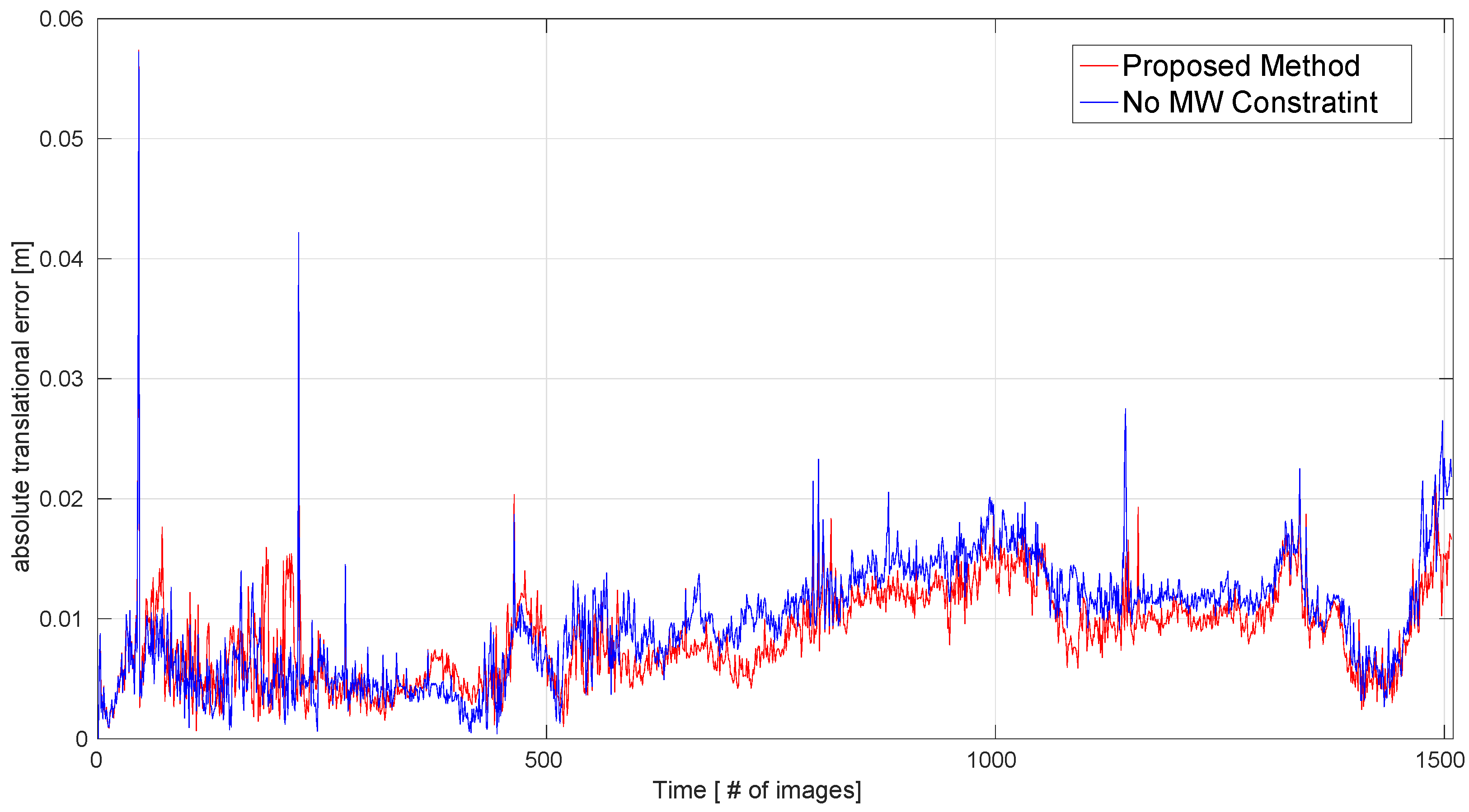

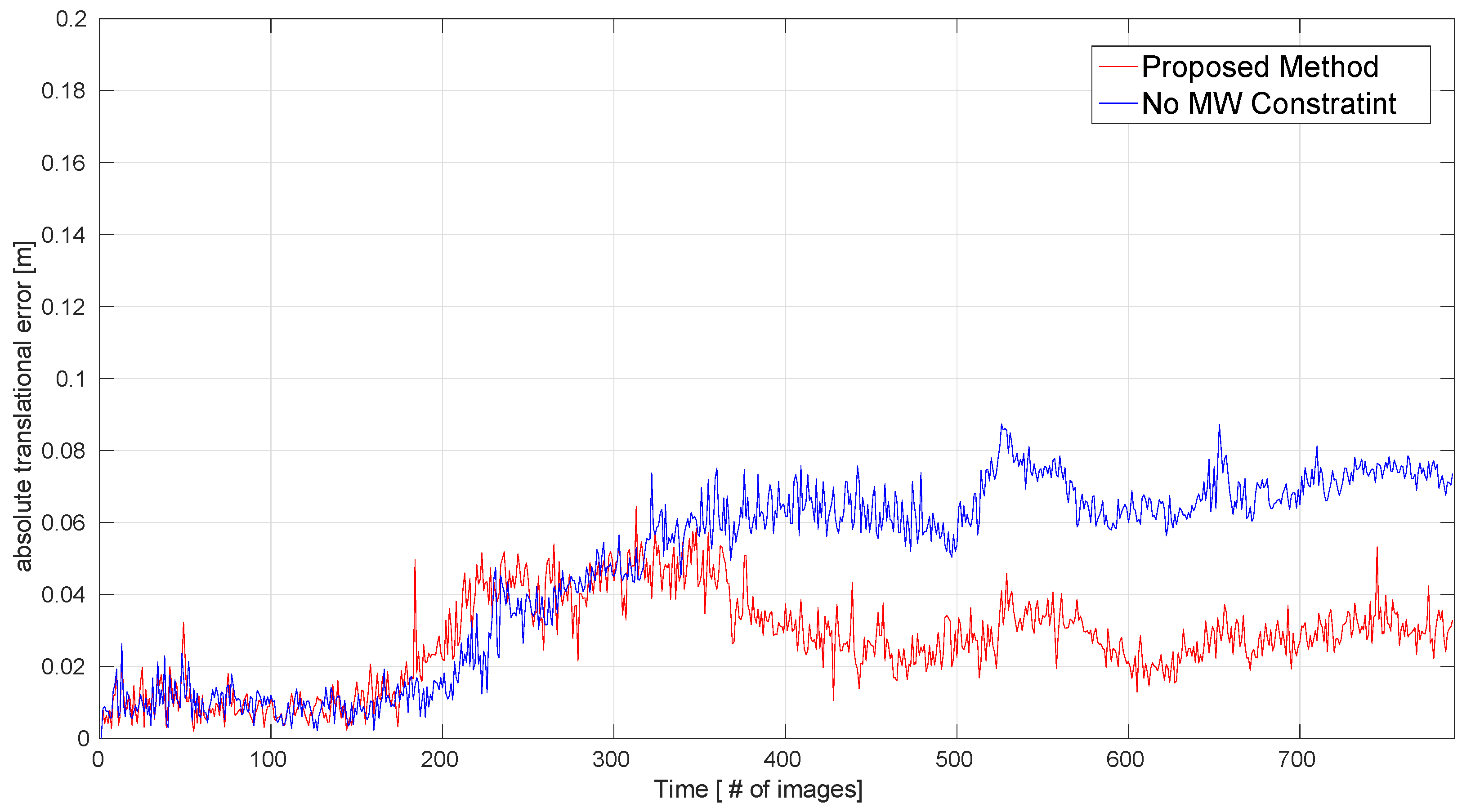
| Sequence | Proposed | No MW | ORB-SLAM2 | DVO | InfiniTAM | LPVO | L-SLAM | Frames |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Living Room 0 | 0.006 | 0.007 | 0.010 | 0.108 | × | 0.015 | 0.012 | 1508 |
| Living Room 1 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.185 | 0.059 | 0.006 | 0.039 | 0.027 | 965 |
| Living Room 2 | 0.026 | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.375 | 0.013 | 0.034 | 0.053 | 880 |
| Living Room 3 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.433 | × | 0.102 | 0.143 | 1240 |
| Office Room 0 | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.049 | 0.244 | 0.042 | 0.061 | 0.020 | 1507 |
| Office Room 1 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.079 | 0.178 | 0.025 | 0.052 | 0.015 | 965 |
| Office Room 2 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.099 | × | 0.039 | 0.026 | 880 |
| Office Room 3 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 0.065 | 0.079 | 0.010 | 0.030 | 0.011 | 1240 |
| Sequence | Proposed | No MW | ORB-SLAM2 | DVO | InfiniTAM | LPVO | L-SLAM | Frames |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fr3_struc_notex_far | 0.017 | 0.029 | 0.276 | 0.213 | 0.037 | 0.075 | 0.141 | 790 |
| fr3_struc_tex_far | 0.011 | 0.012 | 0.024 | 0.048 | 0.030 | 0.174 | 0.212 | 904 |
| fr3_struc_notex_near | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.652 | 0.076 | 0.022 | 0.080 | 0.066 | 1031 |
| fr3_struc_tex_near | 0.011 | 0.013 | 0.019 | 0.031 | 0.034 | 0.115 | 0.156 | 1054 |
| fr3_cabinet | 0.012 | 0.013 | × | 0.690 | 0.035 | 0.520 | 0.291 | 926 |
| fr3_large_cabinet | 0.074 | 0.094 | 0.179 | 0.979 | 0.512 | 0.279 | 0.140 | 979 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, R.; Peng, K.; Fan, W.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, Y. RGB-D SLAM Using Point–Plane Constraints for Indoor Environments. Sensors 2019, 19, 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122721
Guo R, Peng K, Fan W, Zhai Y, Liu Y. RGB-D SLAM Using Point–Plane Constraints for Indoor Environments. Sensors. 2019; 19(12):2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122721
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ruibin, Keju Peng, Weihong Fan, Yongping Zhai, and Yunhui Liu. 2019. "RGB-D SLAM Using Point–Plane Constraints for Indoor Environments" Sensors 19, no. 12: 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122721
APA StyleGuo, R., Peng, K., Fan, W., Zhai, Y., & Liu, Y. (2019). RGB-D SLAM Using Point–Plane Constraints for Indoor Environments. Sensors, 19(12), 2721. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122721





