Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Health Monitoring for Assessing Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Structures
3. Theoretical Background
3.1. The Silver/Silver Chloride Ion-Selective Electrode (Ag/AgCl ISE)
3.2. The Iridium/Iridium Oxide (IrOx) Electrode
4. Experimental Protocol
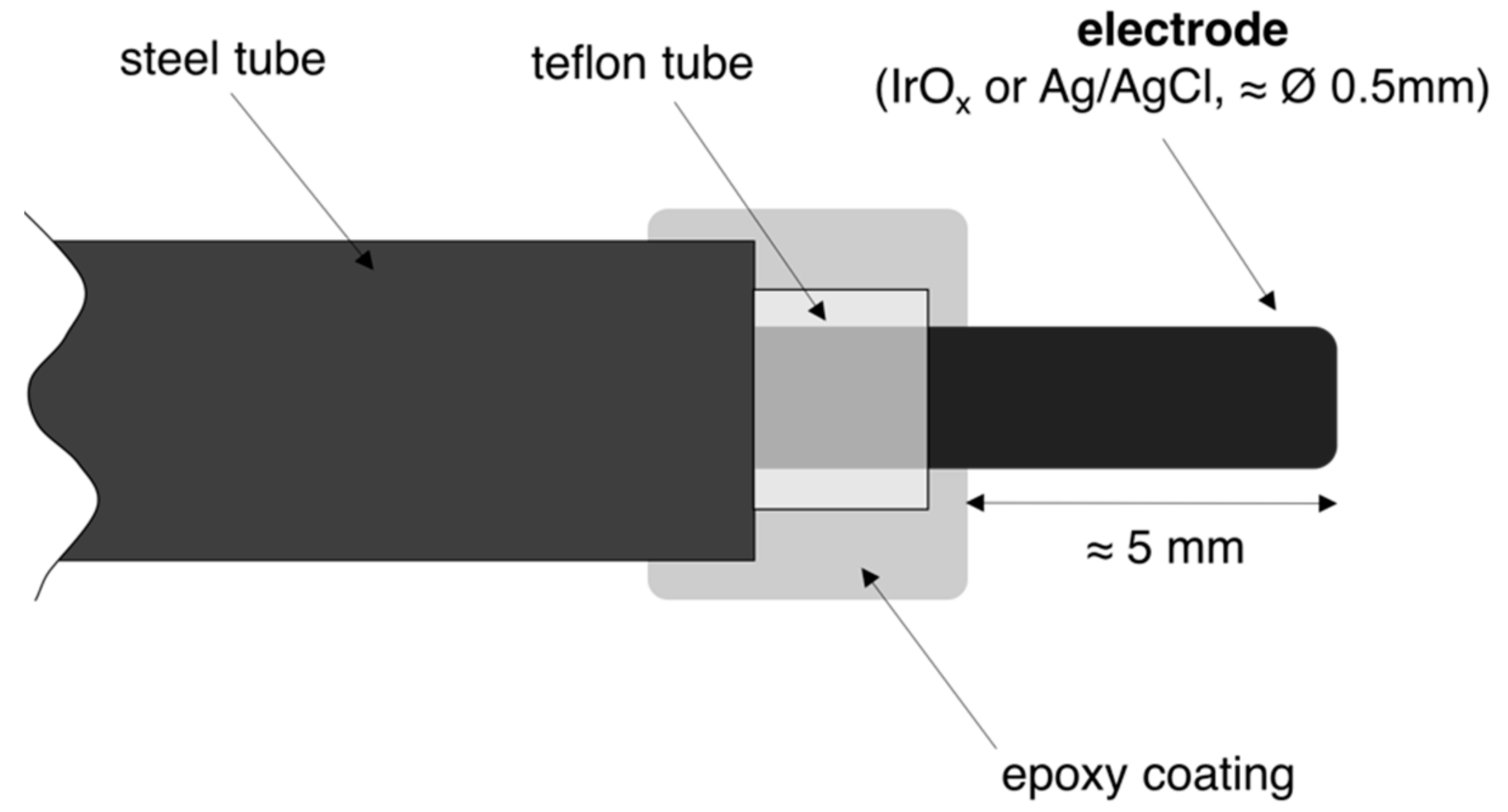
4.1. Electrodes Set-Up
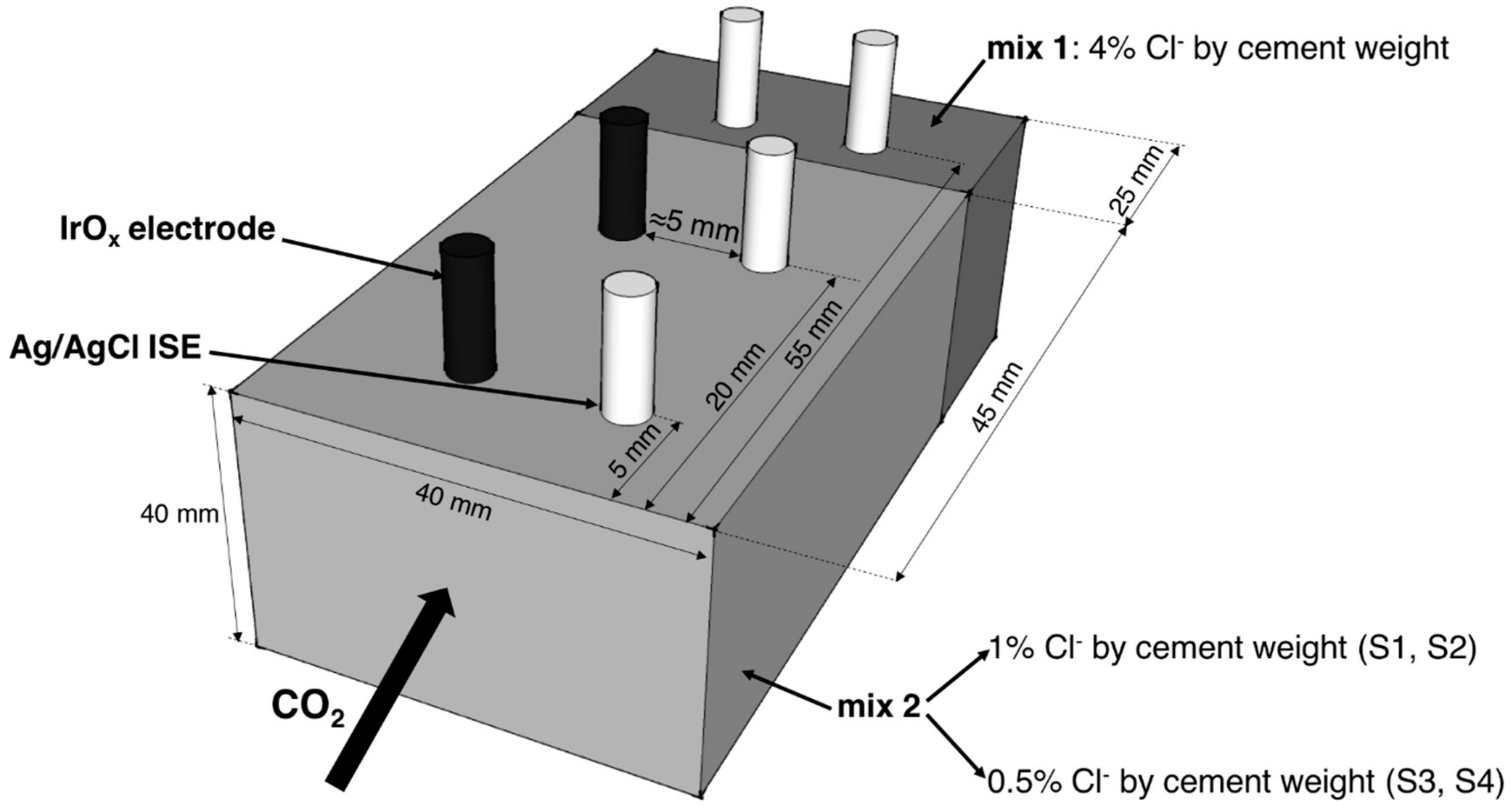
4.2. Mortar Samples Preparation
4.3. Measurement Procedure
5. Results
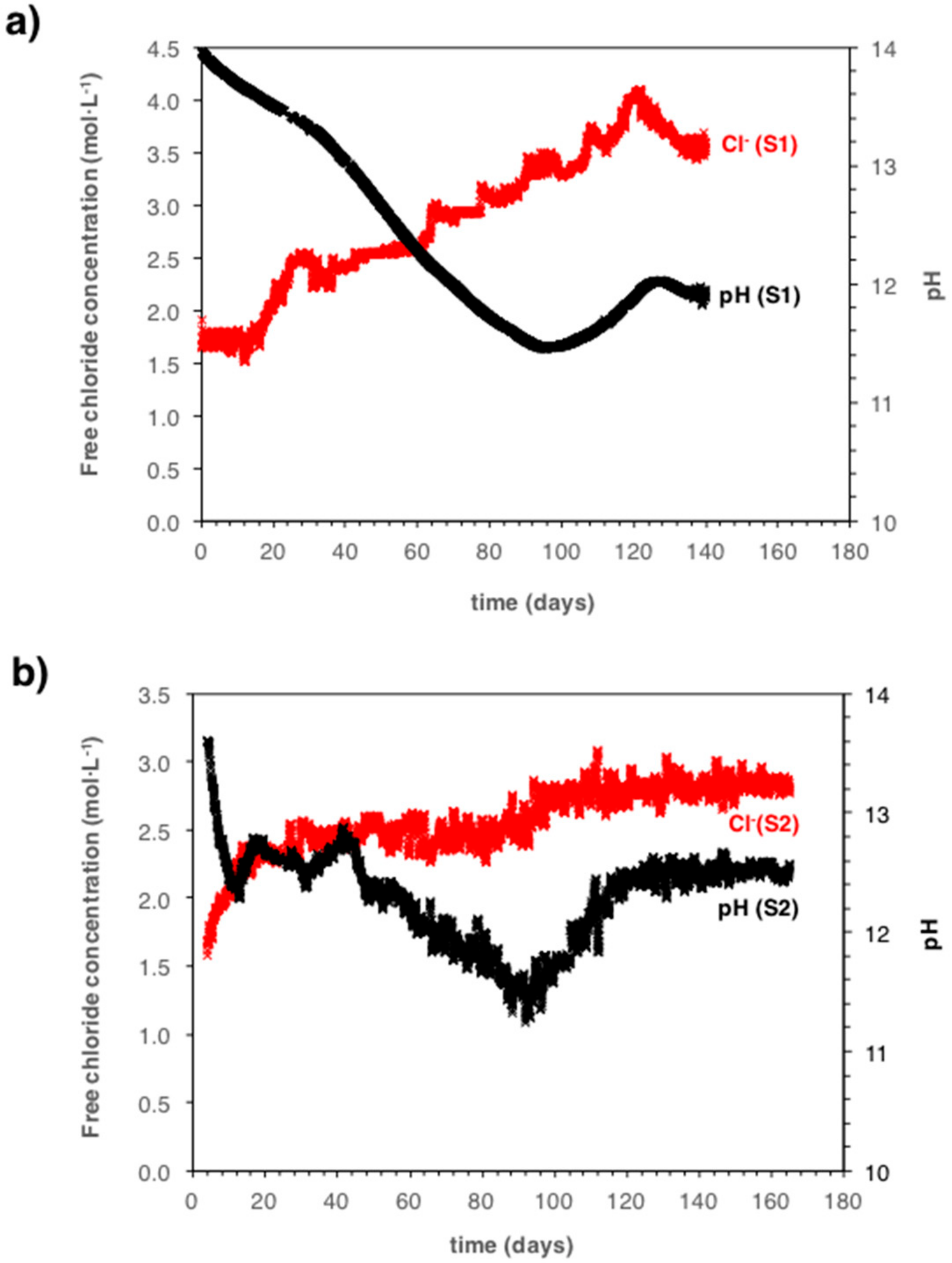
5.1. Monitoring the Pore Solution pH during Carbonation Propagation
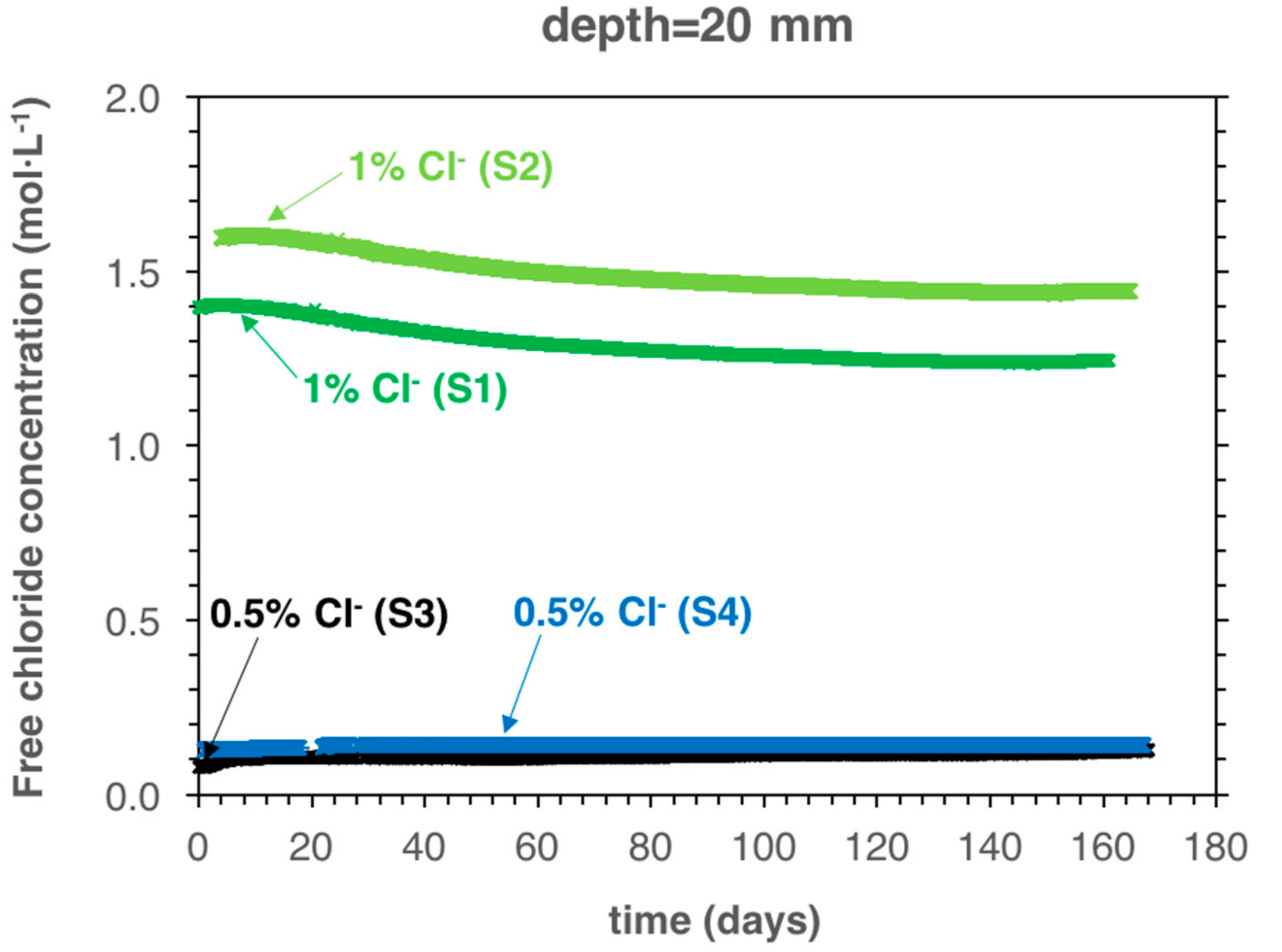
5.2. Monitoring the Chloride Concentration during Carbonation Propagation
6. Discussion
6.1. Implications on the Carbonation Process in Mortar Samples Containing Chlorides
6.2. Implications for the Risk of Corrosion
6.3. Suggestions for Further Research
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flatt, R.J.; Roussel, N.; Cheeseman, C.R. Concrete: An eco material that needs to be improved. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlen, C.; Matthews, S.; Osterminski, K.; Straub, D.; Kessler, S.; Mayer, T.F.; Greve-Dierfeld, V.S.; Zintel, M. Condition Control and Assessment of Reinforced Concrete Structures Exposed to Corrosive Environments; Technical Report for International Federation of Structural Concrete (FIB): Lausanne, Switzerland, May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.E.K.; Marsh, B.; Clark, L.; Seymour, D.; Basheer, P.; Long, A. Development of An Holistic Approach to Ensure the Durability of New Concrete Construction; British Cement Association: Camberley, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Raupach, M.; Elsener, B.; Polder, R.; Miet, J. Corrosion of Reinforcement in Concrete; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E.; Polder, R.P. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete: Prevention, Diagnosis, Repair, 2nd ed.; Join Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G.H.; Brongers, M.P.H.; Thomson, N.G.; Virmani, Y.P.; Payer, J.H. Corrosion Cost and Preventive Strategies in the United States; Technical report for Federal Highway Administration, US Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, March 2002.
- Polder, R.B.; Peelen, W.H.A.; Courage, W.M.G. Non-traditional assessment and maintenance methods for aging concrete structures—Technical and non-technical issues. Mater. Corros. 2012, 63, 1147–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.M. Challenges and opportunities in corrosion of steel in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G. Cost of corrosion. In Trends in Oil and Gas Corrosion Research and Technologies, 1st ed.; El-Sherik, A.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 3–30. [Google Scholar]
- Schiegg, Y.; Steiner, L. Cost effectiveness and application of online monitoring in reinforced concrete structures. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, R. Electrochemical sensors for monitoring the corrosion conditions of reinforced concrete structures: A review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.; Schießl, P. Macrocell sensor systems for monitoring of the corrosion risk of the reinforcement in concrete structures. NDT E Int. 2001, 34, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M.; Schiessl, P. Monitoring system for the penetration of chlorides, carbonation and the corrosion risk for the reinforcement. Constr. Build. Mater. 1997, 11, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Jin, W. A new corrosion sensor to determine the start and development of embedded rebar corrosion process at coastal concrete. Sensors 2013, 13, 13258–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiessl, P.; Raupach, M. Monitoring system for the corrosion risk of steel in concrete structures. Concr. Int. 1992, 14, 52–55. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, C.K.Y.; Wan, K.T.; Chen, L. A novel optical fiber sensor for steel corrosion in concrete structures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1960–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiessl, P.; Breit, W. Monitoring of the depth-dependent moisture content of concrete using multi-ring electrodes. In Proceedings of the Concrete Under Severe Conditions: Environment and Loading, Sapporo, Japan, 2–4 August 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Potentiometric determination of the chloride ion activity in cement based materials. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F.; Alves, J.H.; Simões, A.M.; Fernandes, J.C.S.; Lourenço, Z.; Costa, A.J.S.; Appleton, A.J.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Multiprobe chloride sensor for in situ monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Zimmermann, L.; Böhni, H. Non destructive determination of the free chloride content in cement based materials. Mater. Corros. 2003, 54, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.G.; Hu, R.G.; Huang, R.S.; Lin, C.J. In situ measurement of Cl− concentrations and pH at the reinforcing steel/Concrete interface by combination sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.G.; Lin, C.J.; Hu, R.G.; Li, L.Q.; Du, R.G. Effective monitoring of corrosion in reinforcing steel in concrete constructions by a multifunctional sensor. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandía-Romero, J.M.; Campos, I.; Valcuende, M.; García-Breijo, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Payá, J.; Soto, J. Potentiometric thick-film sensors for measuring the pH of concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 68, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrdal, R. The Electrochemistry and Characteristics of Embeddable Reference Electrodes for Concrete, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Willey: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, U.; Vennesland, Ø.; Myrdal, R. Diffusion potentials as source of error in electrochemical measurements in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí Femenias, Y. Electrochemical Durability Monitoring in Reinforced Concrete. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Seguí Femenias, Y.; Angst, U.; Caruso, F.; Elsener, B. Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrodes in neutral and alkaline environments containing interfering ions. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí Femenias, Y.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. Monitoring chloride concentrations in concrete by means of Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrodes. In Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Concrete Repair, Leipzig, Germany, 5–7 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Koryta, J. Theory and applications of ion-selective electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1972, 61, 329–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreir, L. Corrosion control. In Corrosion, 3rd ed.; Shreir, L., Jarman, R.A., Burstein, G.T., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1994; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, C.P.; Carter, M.A.; Scantlebury, J.D. Sources of error in using silver/silver chloride electrodes to monitor chloride activity in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí Femenias, Y.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. Monitoring pH in corrosion engineering by means of thermally-produced iridium oxide electrodes. Mater. Corros. 2018, 69, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí Femenias, Y.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. PH-monitoring in mortar with thermally-oxidized iridium electrodes. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2017, 2, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrdal, R. Potential Gradients in Concrete Caused by Charge Separations in a Complex Electrolyte; NACE International: New Orleans, LA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Myrdal, R. Phenomena that Disturb the Measurement of Potentials in Voncrete; NACE International: Denver, CO, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Schiegg, Y.; Büchler, M.; Brem, M. Potential mapping technique for the detection of corrosion in reinforced concrete structures: Investigation of parameters influencing the measurement and determination of the reliability of the method. Mater. Corros. 2009, 60, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterji, S. Transportation of ions through cement based materials. Part 3. Experimental evidence for the basic equations and some important deductions. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Glass, G.K.; Lim, P.J.; Buenfeld, N.R. On the corrosion risk presented by chloride bound in concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justnes, H. A review of chloride binding in cementitious systems. Nordic Concr. Res. 1998, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, J.; Easterbrook, D.; Liu, Q.-F.; Li, L.Y. Effect of carbonation on release of bound chlorides in chloride-contaminated concrete. Mag. Concr. Res 2016, 68, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, H.; Dong, Z.; Xing, F.; Zhang, H.; Lo, T.Y. Carbonation of concrete made with dredged marine sand and its effect on chloride binding. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuutti, K. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete. Ph.D. Thesis, Swedish Cement and Concrete Research Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, January 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Suryavanshi, A.K.; Swamy, R.N. Stability of friedel’s salt in carbonated concrete structural elements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vehmas, T.; Kronlöf, A.; Cwirzen, A. Calcium chloride acceleration in ordinary portland cement. Mag. Concr. Res. 2018, 70, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, J.; Jeknavorian, A.; Roberts, L.; Silva, D. Impact of admixtures on the hydration kinetics of portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1289–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, A.K.; Scantlebury, J.D.; Lyon, S.B. Pore size distribution of opc & srpc mortars in presence of chlorides. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, G.K.; Page, C.L.; Short, N.R. Factors affecting the corrosion rate of steel in carbonated mortars. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Domingo, C.; Garcia, C.; Petit, S.; Andrade, C.; Alonso, C. Microstructural changes induced in Portland cement-based materials due to natural and supercritical carbonation. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.; Page, C.L.; Vassie, P.R.W. Investigations of reinforcement corrosion. 2. Electrochemical monitoring of steel in chloride-contaminated concrete. Mater. Struct. 1991, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.K.; Buenfeld, N.R. The presentation of the chloride threshold level for corrosion of steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 1997, 39, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, D.A. Corrosion of steel in concrete—How does it occur? J. Mater. Prot. 1967, 6, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, M.; Morris, W.; Alvarez, M.G.; Duffó, G.S. Corrosion of reinforcing steel in simulated concrete pore solutions. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 2681–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chiang, K.T.K.; Yang, L. Threshold chloride level and characteristics of reinforcement corrosion initiation in simulated concrete pore solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plusquellec, G.; Geiker, M.R.; Lindgård, J.; Duchesne, J.; Fournier, B.; Weerdt, K.D. Determination of the pH and the free alkali metal content in the pore solution of concrete: Review and experimental comparison. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 96, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Chung, C.W. The application of various indicators for the estimation of carbonation and pH of cement based materials. J. Test. Eval. 2010, 38, 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Trejo, D.; Isgor, O.B.; Weiss, W.J. The allowable admixed chloride conundrum: A review of how ACI Committee documents define maximum chlorides in fresh concrete. Concr. Int. 2016, 38, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, T.; Hover, K.; Poston, R.; Broomfield, J.; Joseph, T.; Price, R.; Clear, K.; Khan, M.; Reddy, D.V.; Clifton, J.; et al. Protection of Metals in Concrete against Corrosion; Technical report for ACI Committee 222: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanoni, M.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. Corrosion rate of carbon steel in carbonated concrete—A critical review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 103, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, K.; Colombo, A.; Coppola, L.; Justnes, H.; Geiker, M.R. Impact of the associated cation on chloride binding of Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 68, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Geiker, M.R.; De Weerdt, K.; Østnor, T.A.; Lothenbach, B.; Winnefeld, F.; Skibsted, J. Role of calcium on chloride binding in hydrated Portland cement–metakaolin–limestone blends. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 95, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

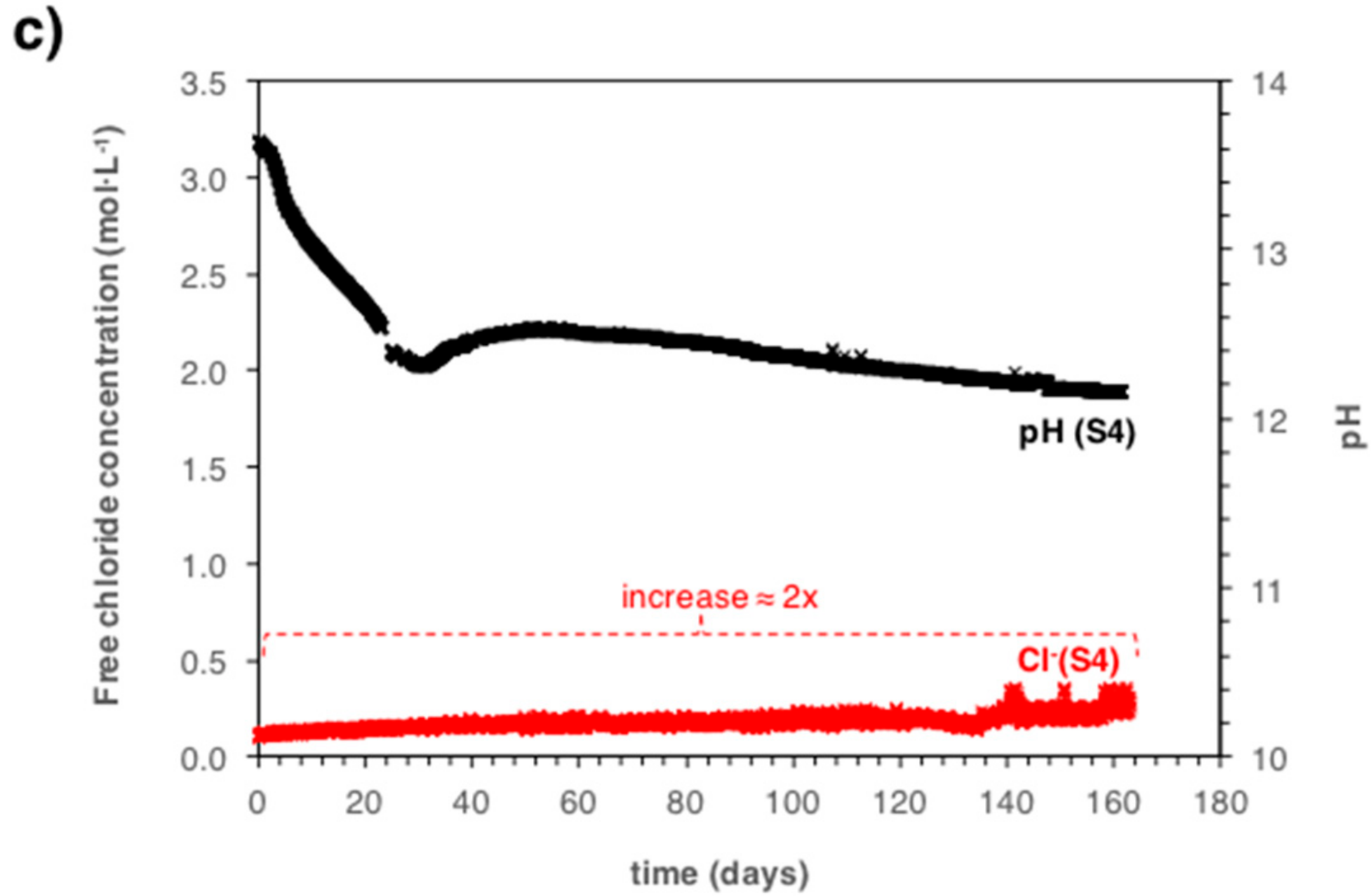

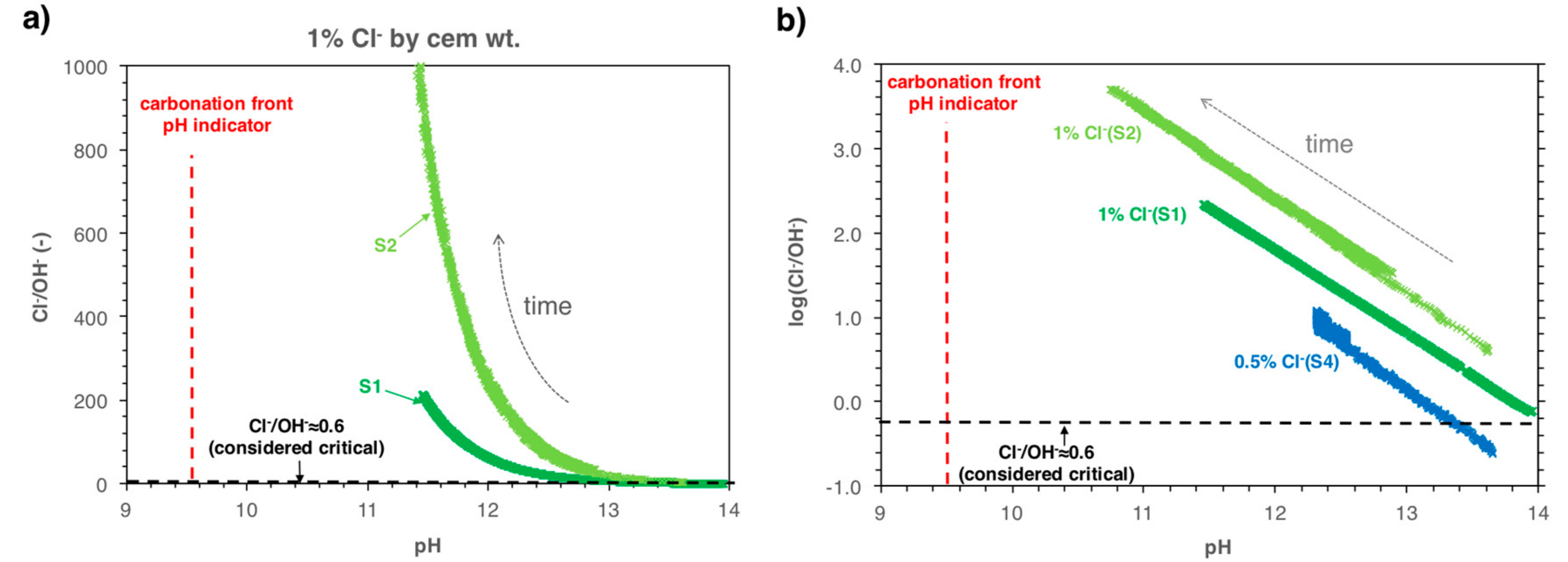
| Sample Name | Amount of Chlorides in Mix 2 (% by Cement Weight) |
|---|---|
| S1 | 1% |
| S2 | 1% |
| S3 | 0.5% |
| S4 | 0.5% |
| Sample Name | Initial Measured Free Chloride Concentration (mol·L−1) | Total Chloride Content—Initially Admixed Chlorides (% by Cement Weight) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mm depth | 20 mm depth | ||
| S1 | 1.58 | 1.40 | 1.0 |
| S2 | 1.54 | 1.60 | 1.0 |
| S3 | - | 0.08 | 0.5 |
| S4 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Femenias, Y.S.; Angst, U.; Moro, F.; Elsener, B. Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration. Sensors 2018, 18, 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093101
Femenias YS, Angst U, Moro F, Elsener B. Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration. Sensors. 2018; 18(9):3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093101
Chicago/Turabian StyleFemenias, Yurena Seguí, Ueli Angst, Fabrizio Moro, and Bernhard Elsener. 2018. "Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration" Sensors 18, no. 9: 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093101
APA StyleFemenias, Y. S., Angst, U., Moro, F., & Elsener, B. (2018). Development of a Novel Methodology to Assess the Corrosion Threshold in Concrete Based on Simultaneous Monitoring of pH and Free Chloride Concentration. Sensors, 18(9), 3101. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18093101





