Application of Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
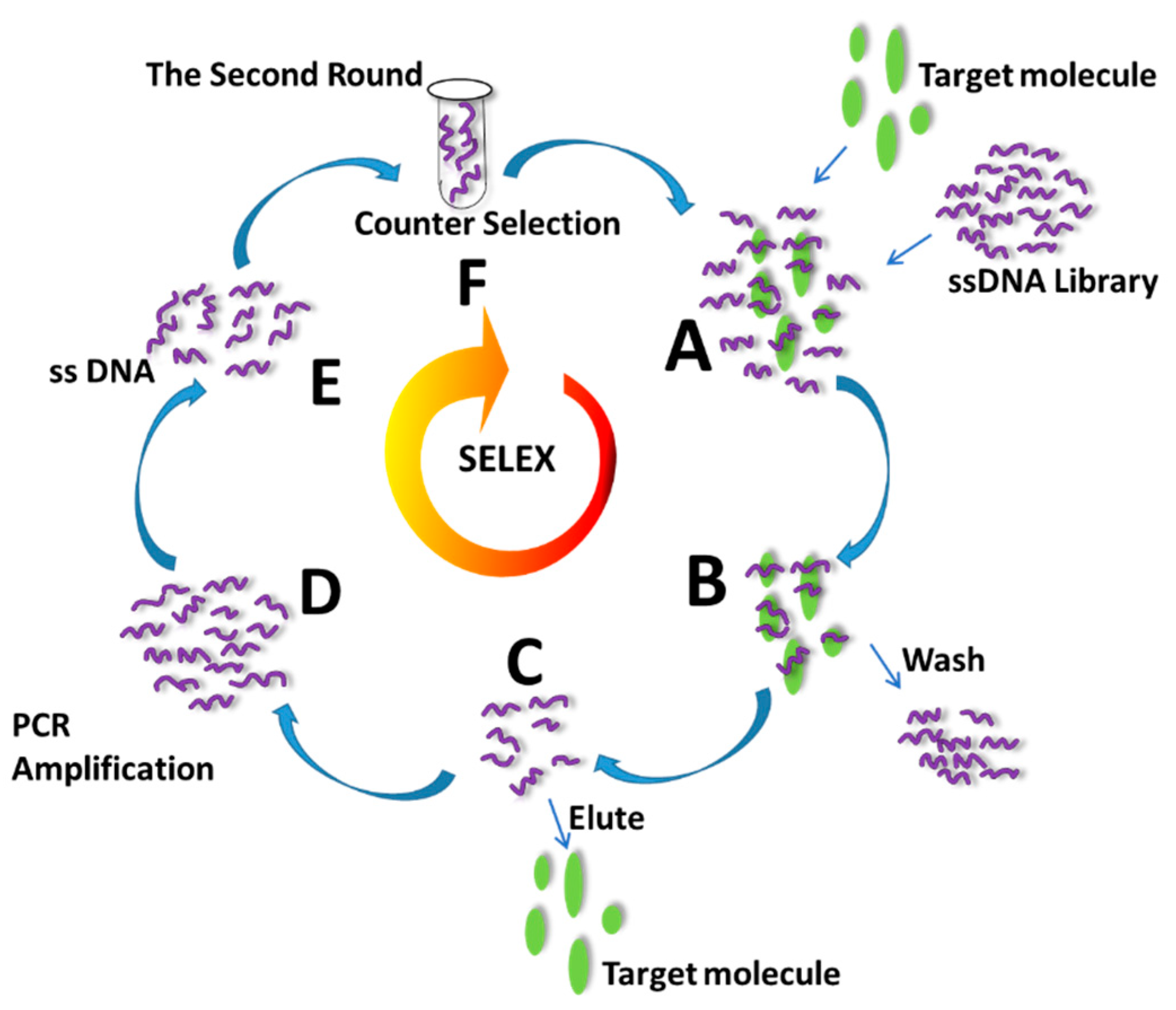
2. Screening of Pathogenic E. coli Aptamers by SELEX Technique
3. Aptamer-Based Optical Sensors for Pathogenic E. coli Detection
4. Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Pathogenic E. coli Detection
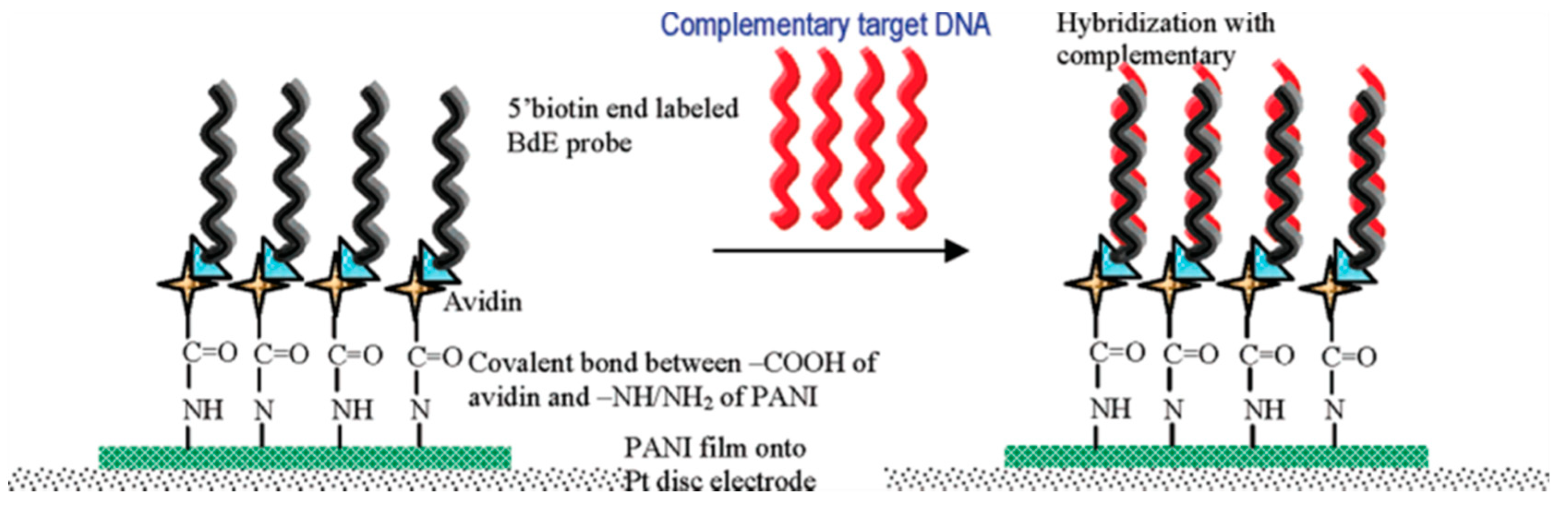
4.1. E. coli Genetic Testing by Aptamer-Electrochemical Sensor
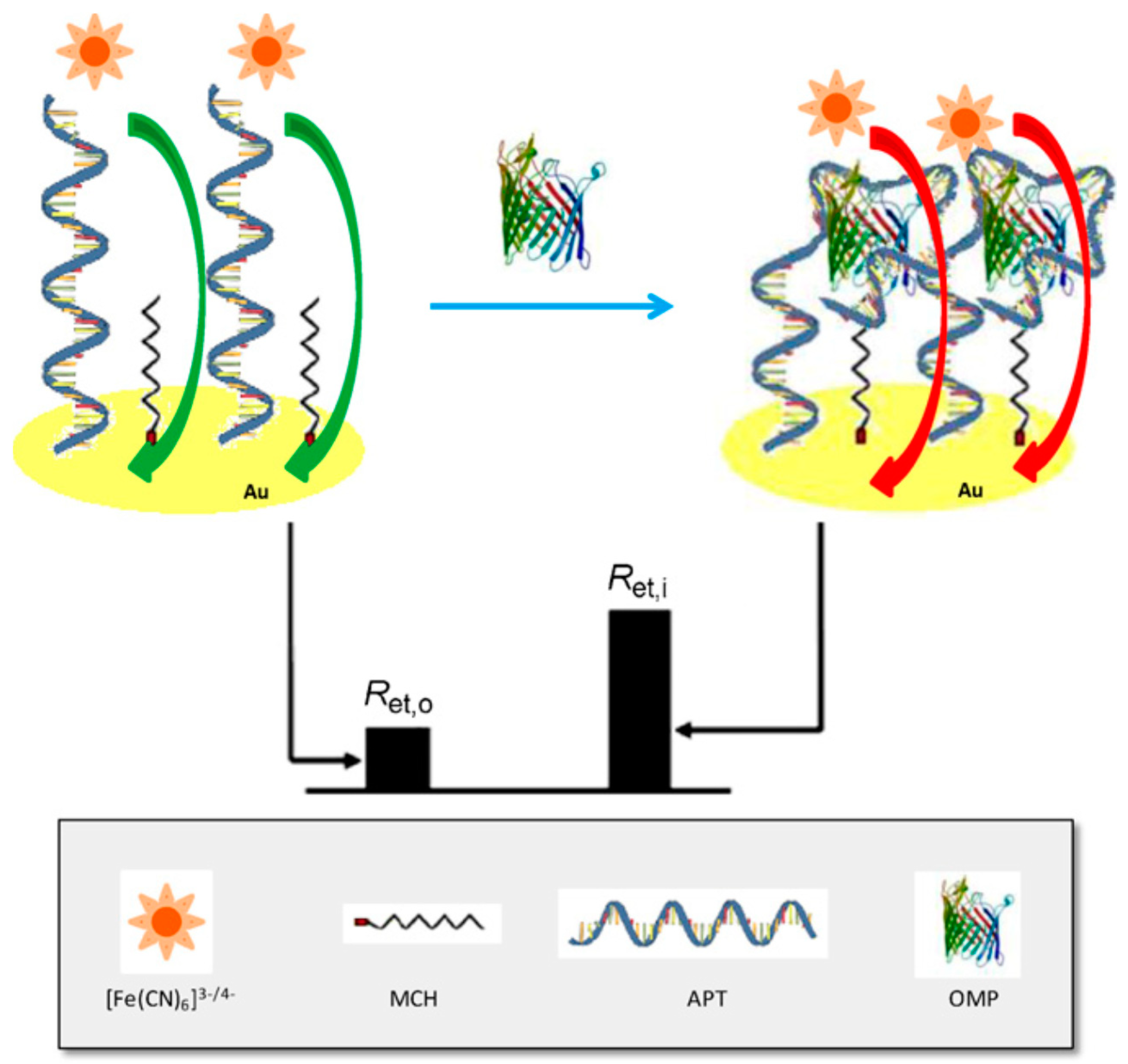
4.2. E. coli Protein Detection by Aptamer-Electrochemical Sensor
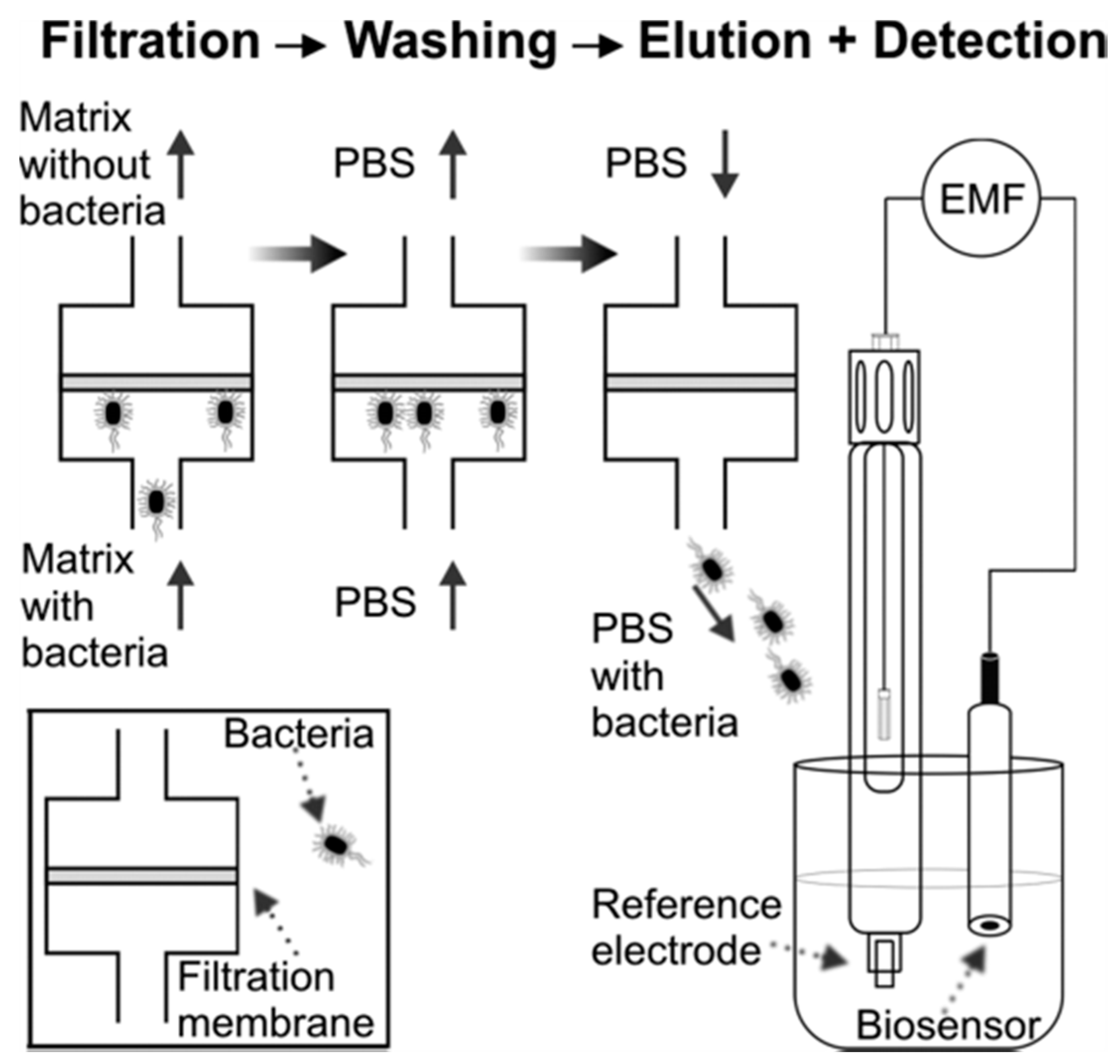
4.3. E. coli Cell Detection by Aptamer-Electrochemical Sensor
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| CFU | Colony forming units |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| SELEX | Exponentially enriched ligand system evolution |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| OMPs | Outer membrane proteins |
| PDA | Polydiacetylene |
| CR | Colorimetric responses |
| Au NPs | Gold nanoparticles |
| RFD-EC1 | Fluorogenic DNAzyme |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| BdE | Biotin-labeled E. coli capture probe |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetric |
| FIS | Faradaic impedance spectroscopy |
| Ret | Electron-transfer resistance |
| SWCNT | Single-walled carbon nanotubes |
| GCE | Glassy carbon electrode |
| 3DNGH | Three-dimensional graphene hydrogel |
| ECL | Electrochemiluminescence |
| IDEA | Interdigital array electrode |
| 3D-IDEA | Three-dimensional interdigital array electrode |
References
- Saxena, T.; Kaushik, P.; Krishna Mohan, M. Prevalence of E. coli O157:H7 in water sources: An overview on associated diseases, outbreaks and detection methods. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 82, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, S.D.; Motiwala, A.S.; Springman, A.C.; Qi, W.; Lacher, D.W.; Ouellette, L.M.; Mladonicky, J.M.; Somsel, P.; Rudrik, J.T.; Dietrich, S.E.; et al. Variation in virulence among clades of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with disease outbreaks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4868–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health of China. GB 4789.3-2016, Food microbiological examination: Enumeration of coliforms. In National Food Safety Standard of the People’s Republic of China; Ministry of Health of China: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Minaei, M.E.; Saadati, M.; Najafi, M.; Honari, H. Label-free, PCR-free DNA hybridization detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on electrochemical nanobiosensor. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Shelton, D.R.; Li, S.; Adams, D.L.; Karns, J.S.; Amstutz, P.; Tang, C.M. Detection of E. coli O157:H7 by immunomagnetic separation coupled with fluorescence immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, P.J.; Gannon, R.M.; Robin, K.K.; Elizabeth, J.G. Detection and characterization of the eae gene of shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli using polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1993, 31, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.R. Development of polymerase chain reaction-based assays for bacterial gene detection. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2000, 41, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Han, J.J.; Shan, S.; Liu, D.F.; Wu, S.S.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lai, W.H. DNA-based hybridization chain reaction and biotin-streptavidin signal amplification for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 through elisa. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Ying, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Evaluation of different micro/nanobeads used as amplifiers in qcm immunosensor for more sensitive detection of E. Coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Li, J.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Song, S.; Rong, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Lu, J. Gold nanoparticle-based enzyme-linked antibody-aptamer sandwich assay for detection of salmonella typhimurium. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 16974–16981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Wang, R.; Saeed, A.; Yang, Q.; Chen, H.; Ling, S.; Xiao, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, S. Preparation of anti-human podoplanin monoclonal antibody and its application in immunohistochemical diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipp, A.; Jorn, G.; Zoltan, K.; Hans, L.; Dolores, J.C. 3D protein microarrays: Performing multiplex immunoassays on a single chip. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4368–4372. [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.K.R. Monitoring intact viruses using aptamers. Biosensors 2016, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Brown, A.K.; Meng, X.; Cropek, D.M.; Istok, J.D.; Watson, D.B.; Lu, Y. A catalytic beacon sensor for uranium with parts-per-trillion sensitivity and millionfold selectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2056–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y. Using personal glucose meters and functional DNA sensors to quantify a variety of analytical targets. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.; Han, H.; Mao, D.; Jiang, Y.; Song, J. Qualitative and quantitative detection of prp(sc) based on the controlled release property of magnetic microspheres using surface plasmon resonance (SPR). Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.K.; Sharma, V.; Mishra, R.K. Electrochemical aptasensors for food and environmental safeguarding: A review. Biosensors 2018, 8, E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marton, S.; Cleto, F.; Krieger, M.A.; Cardoso, J. Isolation of an aptamer that binds specifically to E. Coli. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ding, X.; Peng, Z.; Deng, L.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; He, Q. Aptamer selection for the detection of Escherichia coli k88. Can. J. Microbiol. 2011, 57, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.M.; Aguirre, S.D.; Lazim, H.; Li, Y. Fluorogenic dnazyme probes as bacterial indicators. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3751–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.Y.; Lin, L.P.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, G.P. Establishment of a visual and rapid detection method for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli k88. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, K.; Prabhakar, N.; Chand, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Escherichia coli genosensor based on polyaniline. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6152–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setterington, E.B.; Alocilja, E.C. Electrochemical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of magnetically extracted bacterial pathogens. Biosensors 2012, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, F.J.; Ozalp, V.C. Graphene and other nanomaterial-based electrochemical aptasensors. Biosensors 2012, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghajari, R.; Azadbakht, A. Amplified detection of streptomycin using aptamer-conjugated palladium nanoparticles decorated on chitosan-carbon nanotube. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 547, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Electrochemical biosensors for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta 2017, 162, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Ye, Z.Z.; Si, C.Y.; Ying, Y.B. Application of aptamer based biosensors for detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2012, 40, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, D.; Maria, V.; Dmitrii, P.; Sidney, A.; Valentin, V.; Alya, V. Aptamers against pathogenic microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, J.; Luo, F.; Mohammed, A.B.; Zhang, X.L. Aptamer from whole-bacterium selex as new therapeutic reagent against virulent mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Han, S.R.; Maeng, J.S.; Cho, Y.J.; Lee, S.W. In vitro selection of Escherichia coli O157:H7-specific RNA aptamer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savory, N.; Nzakizwanayo, J.; Abe, K.; Yoshida, W.; Ferri, S.; Dedi, C.; Jones, B.V.; Ikebukuro, K. Selection of DNA aptamers against uropathogenic Escherichia coli NSM59 by quantitative PCR controlled cell-selex. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2014, 104, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Zhang, T.L.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, Z.P. Selection of an aptamer targeted to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2015, 6, 4803–4809. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, N.; Zhang, T.L.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, Z.P. An aptamer-based fluorescence assay for enteropathogenic escherichia coli. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Ling, M.; Ning, Y.; Deng, L. Rapid fluorescent detection of Escherichia coli k88 based on DNA aptamer library as direct and specific reporter combined with immuno-magnetic separation. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khang, J.; Kim, D.; Chung, K.W.; Lee, J.H. Chemiluminescent aptasensor capable of rapidly quantifying Escherichia coli O157:H7. Talanta 2016, 147, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jurng, J.; Kim, B.C. Isolation and characterization of DNA aptamers against Escherichia coli using a bacterial cell-systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment approach. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 436, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Dai, Z.; Tang, X.; Lin, Z.; Lo, P.K.; Meyyappan, M.; Lai, K.W.C. Graphene field-effect transistors for the sensitive and selective detection of Escherichia coli using pyrene-tagged DNA aptamer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Song, L.; Qian, C.; Ge, J.W. Screening and structure analysis of the aptamer target to Escherichia coli tolc protein. J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2014, 46, 698–702. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, J.G.; Carrillo, M.P.; Phillips, T. In vitro antibacterial effects of antilipopolysaccharide DNA aptamer–c1qrs complexes. Folia Microbiol. 2008, 53, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.Y.; Zhu, L.J.; Shao, X.L.; Huang, K.L.; Tian, J.J.; Xu, W.T. Highly sensitive detection of lipopolysaccharides using an aptasensor based on hybridization chain reaction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, J.G.; Carrillo, M.P.; Phillips, T.; Andrews, C.J. A novel screening method for competitive fret-aptamers applied to E. coli assay development. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.H.; Ding, J.W.; Qin, W. A chronopotentiometric flow injection system for aptasensing of E. coli O157. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, H.M.; Park, D.W.; Jeon, E.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, C.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Chang, H.; Lee, J.O. Detection and titer estimation of Escherichia coli using aptamer-functionalized single-walled carbon-nanotube field-effect transistors. Small 2008, 4, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Wu, W.P.; Ye, W.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. An aptamer-based biosensor for colorimetric detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Zou, S.; Cao, X.D. A simple dendrimer-aptamer based microfluidic platform for E. coli O157:H7 detection and signal intensification by rolling circle amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, S.; Mao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zeng, L. A sensitive lateral flow biosensor for Escherichia coli O157:H7 detection based on aptamer mediated strand displacement amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Whole-bacterium selex of DNA aptamers for rapid detection of E. coli o157:H7 using a qcm sensor. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 266, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dua, P.; Ren, S.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, H.S.; Jeong, O.C.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.K. Cell-selex based identification of an rna aptamer for Escherichia coli and its use in various detection formats. Mol. Cells 2016, 39, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amraee, M.; Oloomi, M.; Yavari, A.; Bouzari, S. DNA aptamer identification and characterization for E. Coli O157 detection using cell based selex method. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 536, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Shen, M.; Wang, Z. Selection, identification, and binding mechanism studies of an ssdna aptamer targeted to different stages of E. coli O157:H7. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5677–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.L. A Method for Detecting Enterotoxic Escherichia coli in Food Kit. Chinese Patent CN 106018802A, 27 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.; Qiu, Z.G.; Yang, D.; Jin, M.; Liu, W.L.; Li, J.W.; Xu, Q.Y.; Yuan, Z.K.; Shen, Z.Q. In vitro screening of Escherichia coli O157:H7-specific ssdna aptamer by whole-bacterium based subtractive selex. J. Environ. Health 2016, 33, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Qu, H.; Hao, L.Y.; Tian, B.H.; Gao, W.C.; Li, N.; Wang, X.W.; Li, Z.P.; Yi, L.; Li, Q.X.; et al. Devising a rapid and efficient method of detecting Escherichia coil O157:H7 based on aptamer-mediated surface-enhanced Ramam spectroscopy (SERS). J. Pathog. Biol. 2018, 13, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Lim, S.; Hahn, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Gunasekaran, S. Bifunctional linker-based immunosensing for rapid and visible detection of bacteria in real matrices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothikumar, P.; Narayanan, J.; Hill, V.R. Visual endpoint detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 using isothermal genome exponential amplification reaction (gear) assay and malachite green. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2014, 98, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, J.M.; Ramos, D.L.O.; Sousa, R.M.F.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Santana, M.H.P.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M. A portable electrochemical method for cocaine quantification and rapid screening of common adulterants in seized samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.I.; Maddaus, A.G.; Song, E. A low-cost inkjet-printed aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for the selective detection of lysozyme. Biosensors 2018, 8, E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, P.; Stoltenburg, R.; Strehlitz, B.; Frense, D.; Beckmann, D. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the detection of staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, E2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, C.M.; Singh, R.; Sumana, G.; Pandey, M.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical genosensor based on modified octadecanethiol self-assembled monolayer for Escherichia coli detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 151, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settu, K.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, J.T.; Chen, C.L.; Tsai, J.Z. Impedimetric method for measuring ultra-low E. coli concentrations in human urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L. Fe2O3@Au core/shell nanoparticle-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for Escherichia coli detection. Talanta 2011, 84, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. An interdigital array microelectrode aptasensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for detection of tetracycline. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 40, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Y. Development of cu nanoflowers modified the flexible needle-type microelectrode and its application in continuous monitoring glucose in vivo. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.; Roci, I.; Gurbuz, Y.; Niazi, J.H. An aptamer based competition assay for protein detection using cnt activated gold-interdigitated capacitor arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, P.; Zhang, X.; Teng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, M.; Jin, L.; Zhang, W. A DNA sequence-specific electrochemical biosensor based on alginic acid-coated cobalt magnetic beads for the detection of E. coli. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3325–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.H.; Chen, S.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Shen, T.Y.; Chang, C.A.; Lin, C.S. Disposable amperometric immunosensing strips fabricated by au nanoparticles-modified screen-printed carbon electrodes for the detection of foodborne pathogen Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, D.C.; Yu, T.X.; Yin, Y.B.; Ju, H.X.; Ding, S.J. Rapid and sensitive strategy for salmonella detection using an inva gene-based electrochemical DNA sensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 844–856. [Google Scholar]
- LaGier, M.J.; Scholin, C.A.; Fell, J.W.; Wang, J.; Goodwin, K.D. An electrochemical RNA hybridization assay for detection of the fecal indicator bacterium Escherichia coli. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kawde, A.N. Amplified label-free electrical detection of DNA hybridization. Analyst 2002, 127, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keer, J.T.; Birch, L. Molecular methods for the assessment of bacterial viability. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2003, 53, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, R.B.; de-los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Noronha, J.P.; Sales, M.G.F. A label-free DNA aptamer-based impedance biosensor for the detection of E. coli outer membrane proteins. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 181, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, C.H.; Mayuri, P.; Sankaran, K.; Kumar, A.S. An electrochemical immunosensor for efficient detection of uropathogenic E. coli based on thionine dye immobilized chitosan/functionalized-mwcnt modified electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, J.; Ma, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, C.; Han, E.; Yao, B.; He, Y. Optimized dendrimer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles and enhanced carbon nanotube nanoprobes for amplified electrochemical immunoassay of E. coli in dairy product based on enzymatically induced deposition of polyaniline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, H.; Shorie, M.; Sharma, M.; Ganguli, A.K.; Sabherwal, P. Bridged rebar graphene functionalized aptasensor for pathogenic E. coli O78:K80:H11 detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelada-Guillen, G.A.; Bhosale, S.V.; Riu, J.; Rius, F.X. Real-time potentiometric detection of bacteria in complex samples. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9254–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
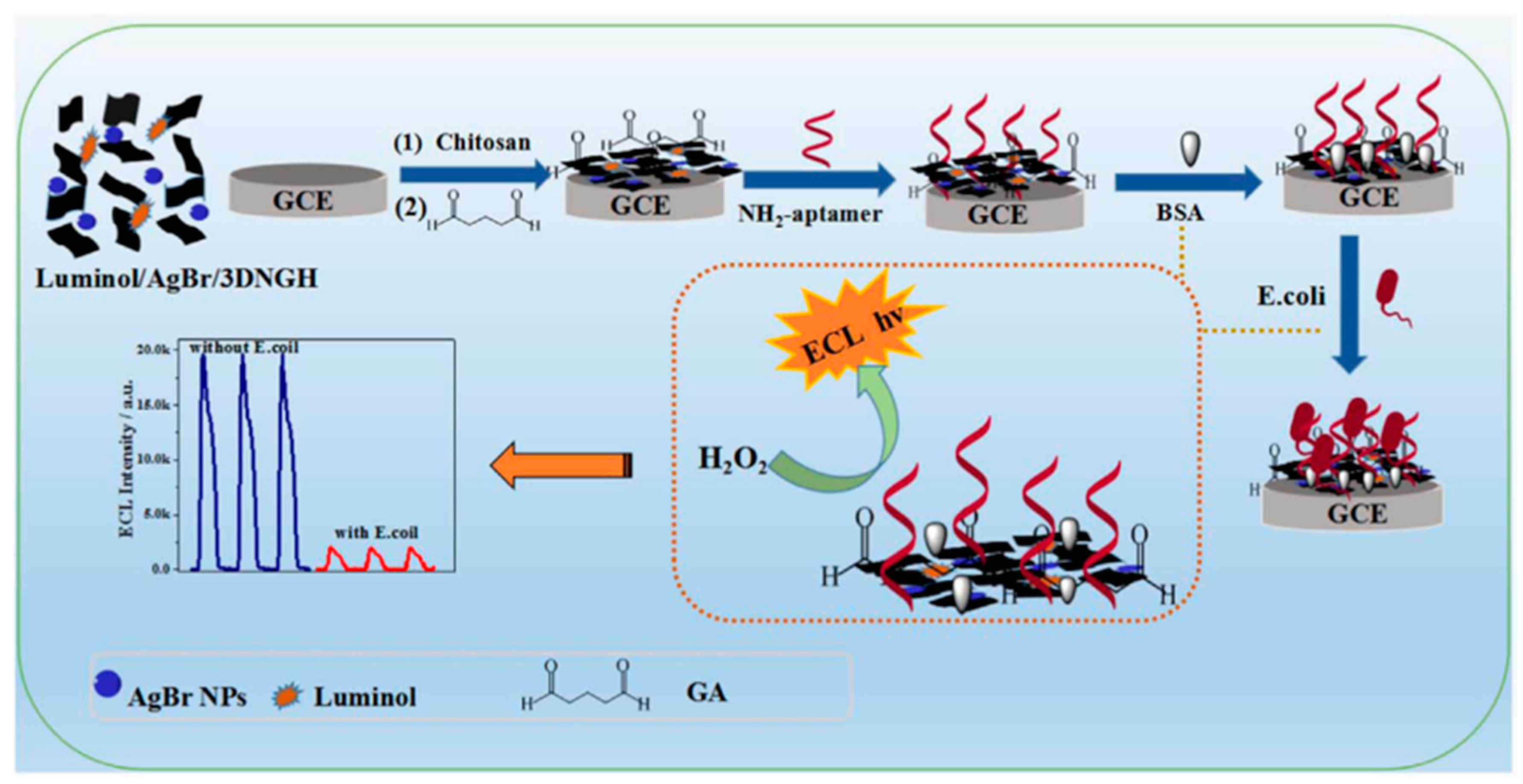
- Hao, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Hua, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qian, J.; Li, H.; Wang, K. Agbr nanoparticles/3D nitrogen-doped graphene hydrogel for fabricating all-solid-state luminol-electrochemiluminescence Escherichia coli aptasensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 97, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.W.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yu, P.P.; Dong, X.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Highly sensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay with enhanced amplification using horseradish peroxidase induced biocatalytic precipitation on a CdS quantum dots multilayer electrode. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Lei, Y.; Yan, L.; Yu, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ding, S.; Ju, H. A rapid and sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of Escherichia coli O111. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Tang, H.; Cheng, W.; Yan, L.; Zhang, D.; Ju, H.; Ding, S. A sensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor for specific detection of Enterobacteriaceae bacteria by Exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Mosher, C.; Lee, X.Y.; Das, S.R.; Cargill, A.A.; Tang, X.; Chen, B.; McLamore, E.S.; Gomes, C.; Hostetter, J.M.; et al. Rapid and label-free detection of interferon gamma via an electrochemical aptasensor comprising a ternary surface monolayer on a gold interdigitated electrode array. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergi, B.O.; Rubén, F.; Naroa, U.; Natalia, A.; Raimundo, G.; Francesc-Xavier, M.P.; Andrey, B. Novel impedimetric aptasensor for label-free detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 2988–2995. [Google Scholar]
- Burrs, S.L.; Bhargava, M.; Sidhu, R.; Kiernan-Lewis, J.; Gomes, C.; Claussen, J.C.; McLamore, E.S. A paper based graphene-nanocauliflower hybrid composite for point of care biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No. | Name | Sequence (5′ - 3′) | Target Strains of E. coli | Recognition Sites | Ref. | Follow up Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Seq.1 | ACCAGTAGACTTTCAACTTTACTGCCATCGTGTGCCCTAA | Enteropathogenic E. coli | Whole bacteria | [35] | [36] |
| 2 | Seq.28 | ACAGTGCTCGGGATATATCAATATGTCACCTCGGCTAATG | Enteropathogenic E. coli | Whole bacteria | [35] | [36] |
| 3 | aptamer37 | GGAGACCGTACCATCTGTTCGTGGAAGCGCTTTGCTCGTCCATTAGCCTTGTGCTCGTGC | Enterotoxigenic E. coli | Pilin protein | [21] | [37] |
| 4 | I-1 | UGAUUCCAUCUUCCUGGACUGUCGAAAAUUCAGUAUCGGGAGGUUACGUAUUUGGUUUAU | Enteropathogenic E. coli | Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) | [33] | [38] |
| 5 | EcA5-27 | GGCATAGCTGCCGGGAGGGGGGGG | Urethropathogenic E. coli | Whole bacteria | [34] | / |
| 6 | E2 | CCATGAGTGTTGTGAAATGTTGGGACACTAGGTGGCATAGAGCCG | E. coli KCTC 2571 | Whole bacteria | [39] | [40] |
| 7 | E1 | ACTTAGGTCGAGGTTAGTTTGTCTTGCTGGCGCATCCACTGAGCG | E. coli KCTC 2571 | Whole bacteria | [39] | / |
| 8 | E10 | GTTGCACTGTGCGGCCGAGCTGCCCCCTGGTTTGTGAATACCCTGGG | E. coli KCTC 2571 | Whole bacteria | [39] | / |
| 9 | E12 | GCGAGGGCCAACGGTGGTTACGTCGCTACGGCGCTACTGGTTGAT | E. coli KCTC 2571 | Whole bacteria | [39] | / |
| 10 | 20# | CGAACGAATATAATTATGGCGTCCCCGGGGTTTCG | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | Outer membrane proteins (OMPs) | [41] | / |
| 11 | L1F | CGTCGCTATGAAGTAACAAAGATAGGAGCAATCGGG | Enteropathogenic E. coli O111:B4 | LPS | [42] | [43] |
| 12 | Eco 4 Rev | ACGGCGCTCCCAACAGGCCTCTCCTTACGGCATATTA | E. coli strain 8739 | OMPs | [44] | / |
| 13 | Eco 3 Rev | GTCTGCGAGCGGGGCGCGGGCCCGGCGGGGGATGCG | E. coli strain 8739 | OMPs | [44] | [45] |
| 14 | / | GGGAGAGCGGAAGCGUGCUGGGUCGCAGUUUGCGCGCGUUCCAACUUCUCUCAUCACGGAAACAUAACCCAGAGGUCGAU | E. coli DH5α | Whole bacteria | [46] | [46] |
| 15 | E17F-37 | ATCAAATGTGCAGATATCAAGACGATTTGTACAAGAT | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | LPS | [47] | [45,47,48] |
| 16 | E18R-42 | CCGGACGCTTATGCCTTGCCATCTACAGAGCAGGTGTGACGG | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | LPS | [47] | [49] |
| 17 | S1 | TGGTCGTGGTGAGGTGCGTGTATGGGTGGTGGATGAGTGTGTGGC | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | Whole bacteria | [50] | [50] |
| 18 | Ec3 | GCACGAAUUUGCUGUGUUUUUGGGGGGGUCGGGGAGUAUA | E. coli DH5α | Whole bacteria | [51] | [51] |
| 19 | EA | CCGGACGCTTATGCCTTGCCATCTACAGAGCAGGTGTGACGG | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | Whole bacteria | [38] | [38] |
| 20 | AM-6 | GGGTGATGGGTGCATGTGATGAAAGGGGTTCGTGCTATGCTGTTTTGTCTAATAATACTAGTCCTTGCCAAGGTTTATTC | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | Whole bacteria | [52] | [53] |
| 21 | ETEC-1 | CTATAACTTTACTCCTAAGAACCCAAACAACACACA | Enterotoxigenic E.coli | Whole bacteria | [54] | / |
| 22 | Aptamer1 | CGCAGTTTGGGAAGGGTGATCGCACTATCAGAGGATTCCGTTCGG | Enterohemorrhagic E.coli | Whole bacteria | [55] | [56] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.-W.; Wang, H.-X.; Jia, G.-C.; Li, Z. Application of Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Sensors 2018, 18, 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082518
Zhao Y-W, Wang H-X, Jia G-C, Li Z. Application of Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082518
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yu-Wen, Hai-Xia Wang, Guang-Cheng Jia, and Zheng Li. 2018. "Application of Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082518
APA StyleZhao, Y.-W., Wang, H.-X., Jia, G.-C., & Li, Z. (2018). Application of Aptamer-Based Biosensor for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Sensors, 18(8), 2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082518




