Targeting FRET-Based Reporters for cAMP and PKA Activity Using AKAP79
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.2. Isolation and Culture of Cardiomyocytes
2.3. Pull Down Experiments and Western Blotting
2.4. FRET Imaging
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
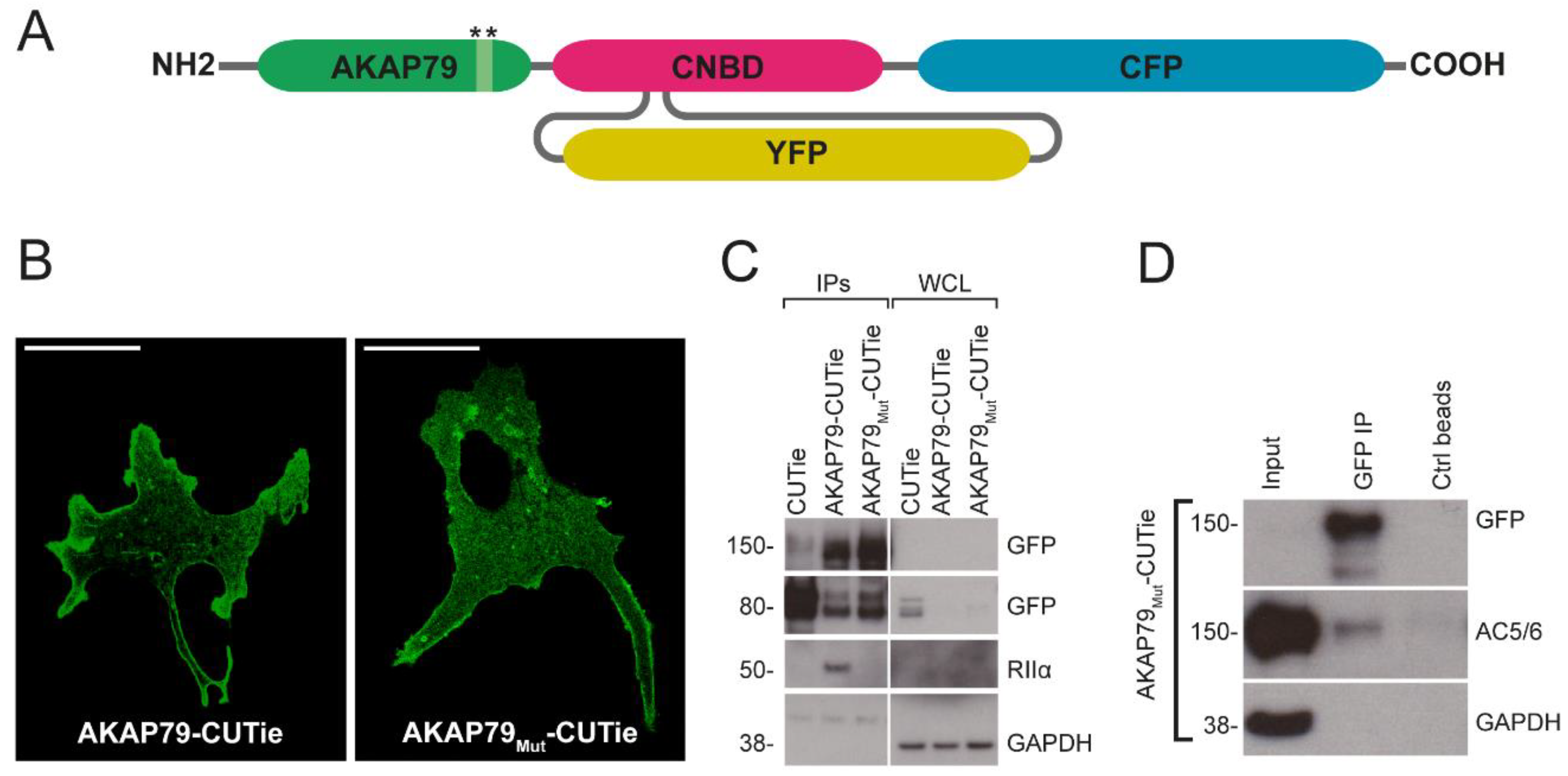
3.1. AKAP79 as Targeting Domain for the cAMP FRET-Based Sensor CUTie
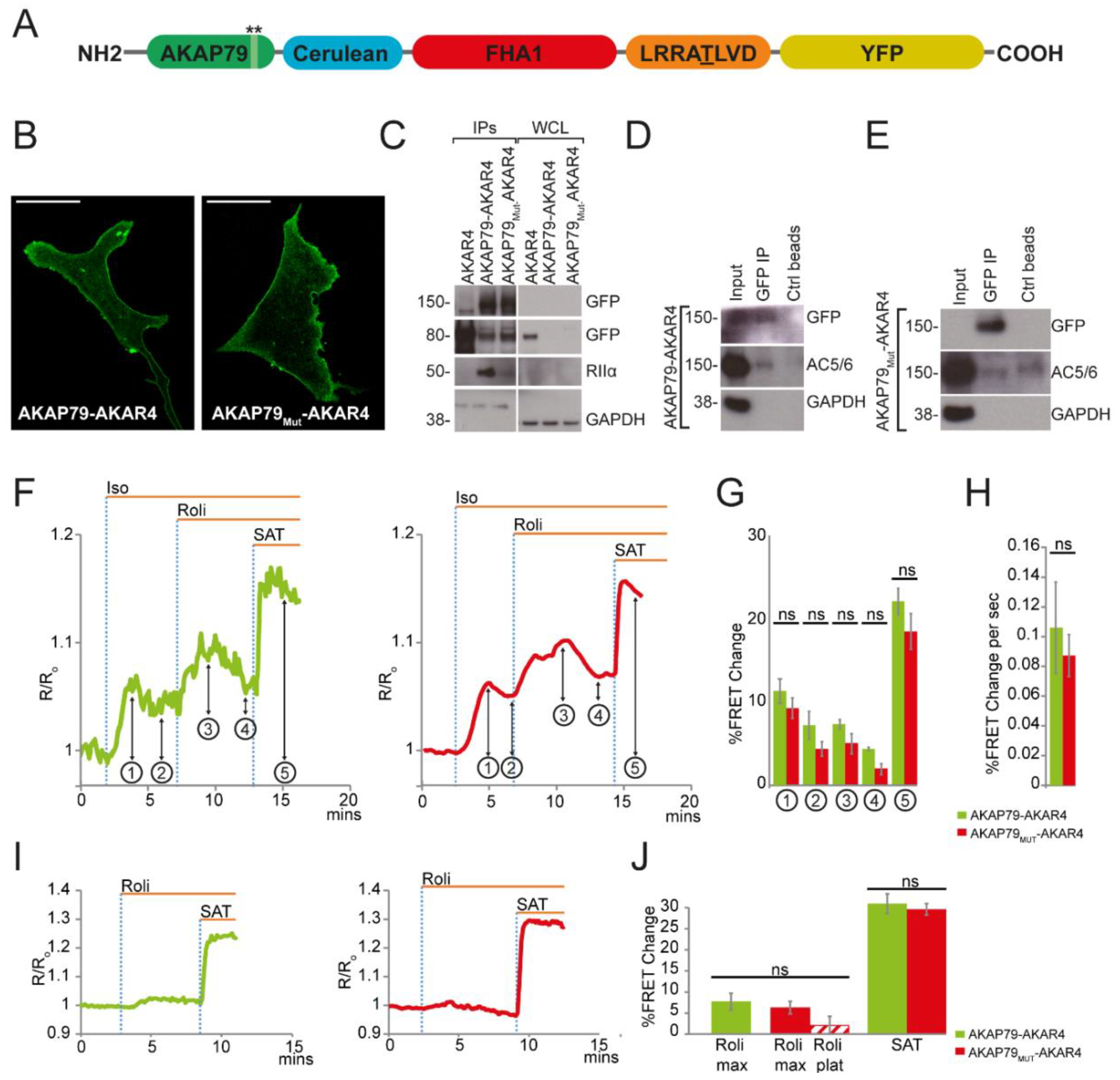
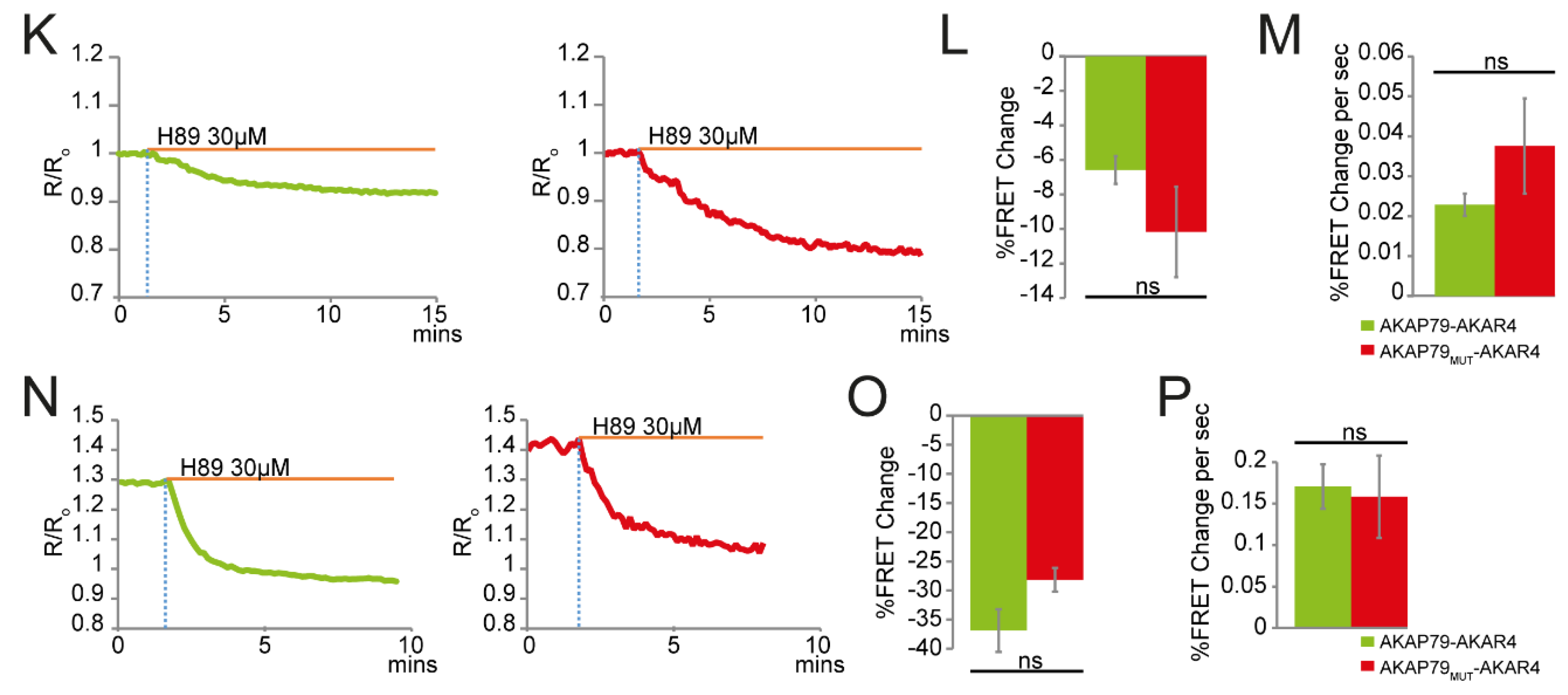
3.2. AKAP79 as a Targeting Domain for the PKA Activity FRET-Based Sensor AKAR4
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Musheshe, N.; Schmidt, M.; Zaccolo, M. cAMP: From Long-Range Second Messenger to Nanodomain Signalling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.; Scott, J.D. AKAP signalling complexes: Focal points in space and time. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, M.; Beavo, J. Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: Essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coghlan, V.M.; Perrino, B.A.; Howard, M.; Langeberg, L.K.; Hicks, J.B.; Gallatin, W.M.; Scott, J.D. Association of protein kinase A and protein phosphatase 2B with a common anchoring protein. Science 1995, 267, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccolo, M.; Pozzan, T. Discrete microdomains with high concentration of cAMP in stimulated rat neonatal cardiac myocytes. Science 2002, 295, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, G.; Zoccarato, A.; Lissandron, V.; Terrin, A.; Li, X.; Houslay, M.D.; Baillie, G.S.; Zaccolo, M. Protein kinase A type I and type II define distinct intracellular signaling compartments. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, R.K.; Sprenger, J.U.; Steinbrecher, J.H.; Hübscher, D.; Lehnart, S.E.; Abesser, M.; Schuh, K.; El-Armouche, A.; Nikolaev, V.O. Microdomain switch of cGMP-regulated phosphodiesterases leads to ANP-induced augmentation of beta-adrenoceptor-stimulated contractility in early cardiac hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorshkov, K.; Mehta, S.; Ramamurthy, S.; Ronnett, G.V.; Zhou, F.Q.; Zhang, J. AKAP-mediated feedback control of cAMP gradients in developing hippocampal neurons. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surdo, N.C.; Berrera, M.; Koschinski, A.; Brescia, M.; Machado, M.R.; Carr, C.; Wright, P.; Gorelik, J.; Morotti, S.; Grandi, E.; et al. FRET biosensor uncovers cAMP nano-domains at beta-adrenergic targets that dictate precise tuning of cardiac contractility. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaccolo, M.; De Giorgi, F.; Cho, C.Y.; Feng, L.; Knapp, T.; Negulescu, P.A.; Taylor, S.S.; Tsien, R.Y.; Pozzan, T. A genetically encoded, fluorescent indicator for cyclic AMP in living cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiPilato, L.M.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J. Fluorescent indicators of cAMP and Epac activation reveal differential dynamics of cAMP signalling within discrete subcellular compartments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16513–16518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefkimmiatis, K.; Leronni, D.; Hofer, A.M. The inner and outer compartments of mitochondria are sites of distinct cAMP/PKA signaling dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveria, S.F.; Gomez, L.L.; Dell’Acqua, M.L. Imaging kinase—AKAP79—Phosphatase scaffold complexes at the plasma membrane in living cells using FRET microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nooh, M.M.; Bahouth, S.W. Role of AKAP79/150 protein in beta1-adrenergic receptor trafficking and signaling in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 33797–33812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.X.; Cooper, D.M. AKAP79, PKC, PKA and PDE4 participate in a Gq-linked muscarinic receptor and adenylate cyclase 2 cAMP signalling complex. Biochem. J. 2013, 455, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, D.; Halls, M.L.; Everett, K.L.; Ciruela, A.; Skroblin, P.; Klussmann, E.; Cooper, D.M. A key phosphorylation site in AC8 mediates regulation of Ca(2+)-dependent cAMP dynamics by an AC8-AKAP79-PKA signalling complex. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125 Pt 23, 5850–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, D.W.; Hausken, Z.E.; Fraser, I.D.; Stofko-Hahn, R.E.; Scott, J.D. Association of the type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase with a human thyroid RII-anchoring protein. Cloning and characterization of the RII-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13376–13382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dell’Acqua, M.L.; Faux, M.C.; Thorburn, J.; Thorburn, A.; Scott, J.D. Membrane-targeting sequences on AKAP79 bind phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 2246–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauck, T.M.; Faux, M.C.; Labudda, K.; Langeberg, L.K.; Jaken, S.; Scott, J.D. Coordination of three signaling enzymes by AKAP79, a mammalian scaffold protein. Science 1996, 271, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveria, S.F.; Dell’Acqua, M.L.; Sather, W.A. AKAP79/150 anchoring of calcineurin controls neuronal L-type Ca2+ channel activity and nuclear signaling. Neuron 2007, 55, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efendiev, R.; Samelson, B.K.; Nguyen, B.T.; Phatarpekar, P.V.; Baameur, F.; Scott, J.D.; Dessauer, C.W. AKAP79 Interacts with Multiple Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) Isoforms and Scaffolds AC5 and -6 to A-Amino-3-Hydroxyl-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazole-Propionate (AMPA) Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14450–14458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Harry, A.; Li, J.; Smit, M.J.; Bai, X.; Magnusson, R.; Pieroni, J.P.; Weng, G.; Iyengar, R. Adenylyl cyclase 6 is selectively regulated by protein kinase A phosphorylation in a region involved in Galphas stimulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14100–14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sette, C.; Vicini, E.; Conti, M. The rat PDE3/IVd phosphodiesterase gene codes for multiple proteins differentially activated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18271–18274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, S.J.; Baillie, G.S.; McPhee, I.; MacKenzie, C.; Seamons, R.; McSorley, T.; Millen, J.; Beard, M.B.; van Heeke, G.; Houslay, M.D. Long PDE4 cAMP Specific Phosphodiesterases Are Activated by Protein Kinase A-Mediated Phosphorylation of a Single Serine Residue in Upstream Conserved Region 1 (UCR1). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 136, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodge-Kafka, K.L.; Soughayer, J.; Pare, G.C.; Carlisle Michel, J.J.; Langeberg, L.K.; Kapiloff, M.S.; Scott, J.D. The protein kinase A anchoring protein mAKAP coordinates two integrated cAMP effector pathways. Nature 2005, 437, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, D.; Wong, W.; Schaack, J.; Scott, J.D.; Cooper, D.M. An anchored PKA and PDE4 complex regulates subplasmalemmal cAMP dynamics. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.J.; Baillie, G.S.; Mohamed, A.; Li, X.; Maisonneuve, C.; Klussmann, E.; van Heeke, G.; Houslay, M.D. RNA silencing identifies PDE4D5 as the functionally relevant cAMP phosphodiesterase interacting with beta arrestin to control the protein kinase A/AKAP79-mediated switching of the beta2-adrenergic receptor to activation of ERK in HEK293B2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33178–33189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, G.S.; Scott, J.D.; Houslay, M.D. Compartmentalisation of phosphodiesterases and protein kinase A: Opposites attract. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3264–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depry, C.; Allen, M.D.; Zhang, J. Visualization of PKA activity in plasma membrane microdomains. Mol. Biol. Syst. 2011, 7, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangherlin, A.; Gesellchen, F.; Zoccarato, A.; Terrin, A.; Fields, L.A.; Berrera, M.; Surdo, N.C.; Craig, M.A.; Smith, G.; Hamilton, G.; et al. cGMP Signals Modulate cAMP Levels in a Compartment-Specific Manner to Regulate Catecholamine-Dependent Signaling in Cardiac Myocytes. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.G.; Stengel, F.; Nygren, P.J.; Weisbrod, C.R.; Bruce, J.E.; Robinson, C.V.; Barford, D.; Scott, J.D. Architecture and dynamics of an A-kinase anchoring protein 79 (AKAP79) signaling complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6426–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Musheshe, N.; Lobo, M.J.; Schmidt, M.; Zaccolo, M. Targeting FRET-Based Reporters for cAMP and PKA Activity Using AKAP79. Sensors 2018, 18, 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072164
Musheshe N, Lobo MJ, Schmidt M, Zaccolo M. Targeting FRET-Based Reporters for cAMP and PKA Activity Using AKAP79. Sensors. 2018; 18(7):2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072164
Chicago/Turabian StyleMusheshe, Nshunge, Miguel J. Lobo, Martina Schmidt, and Manuela Zaccolo. 2018. "Targeting FRET-Based Reporters for cAMP and PKA Activity Using AKAP79" Sensors 18, no. 7: 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072164
APA StyleMusheshe, N., Lobo, M. J., Schmidt, M., & Zaccolo, M. (2018). Targeting FRET-Based Reporters for cAMP and PKA Activity Using AKAP79. Sensors, 18(7), 2164. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072164





