Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
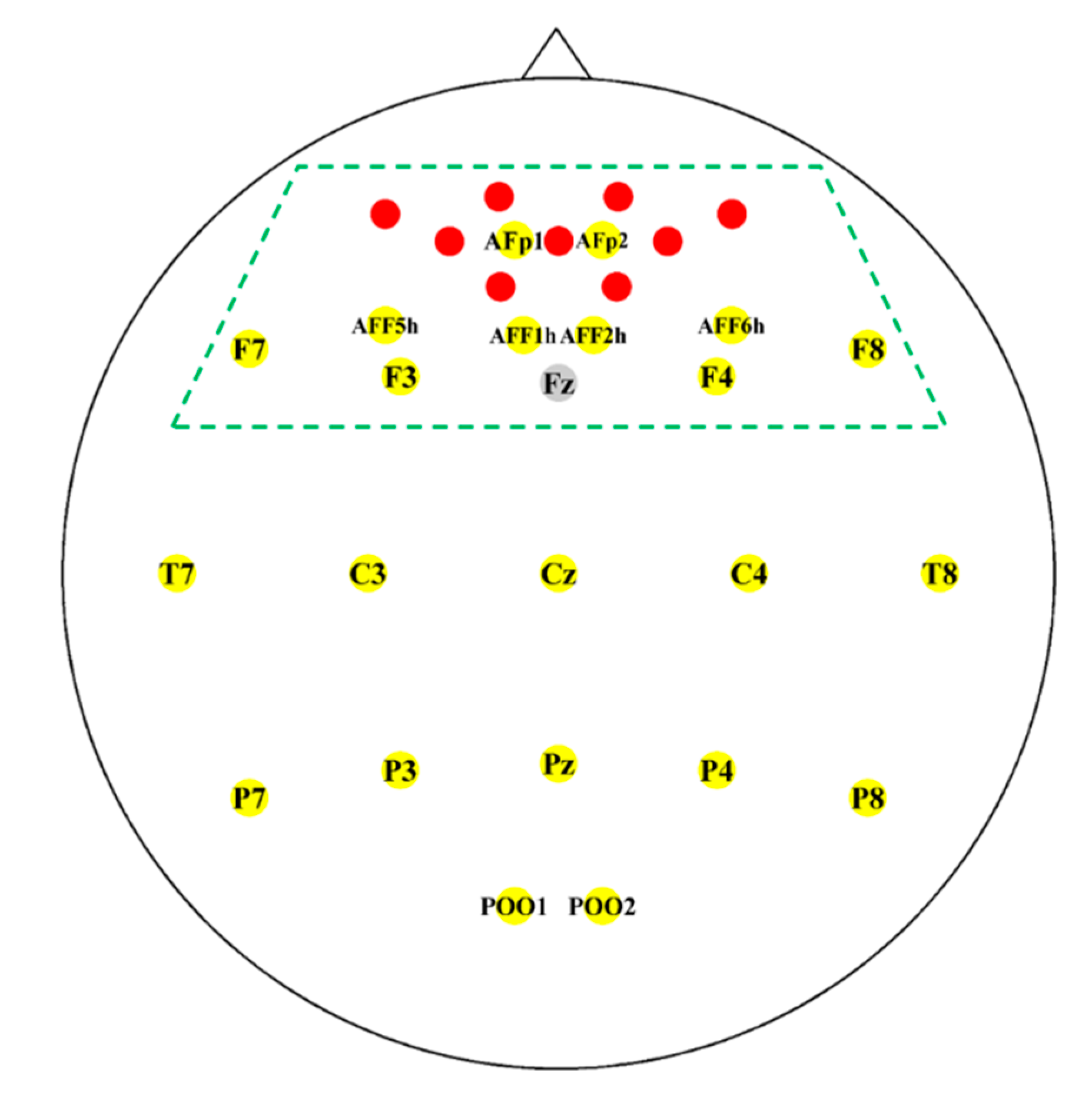
2.2. Instrumentation
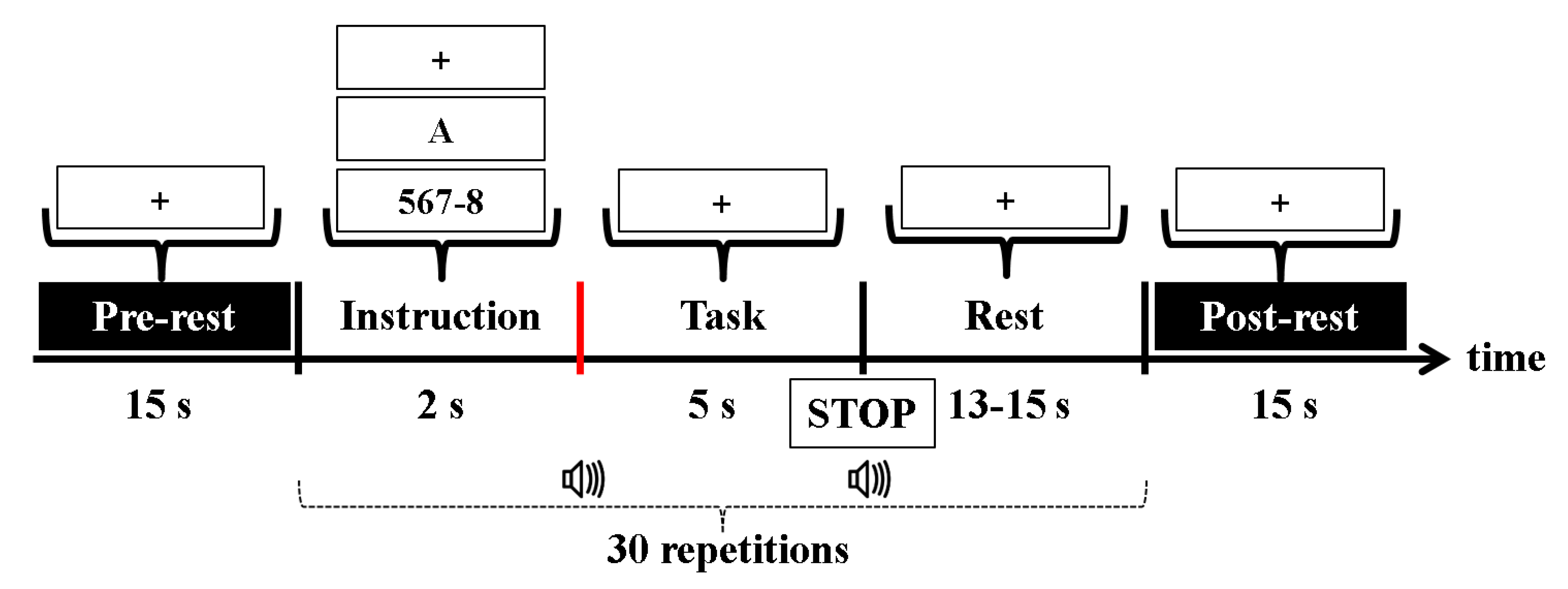
2.3. Experimental Paradigm
2.4. Preprocessing
2.5. Features
2.6. Classification
2.7. Information Transfer Rate
2.8. Statistical Test
3. Experimental Results
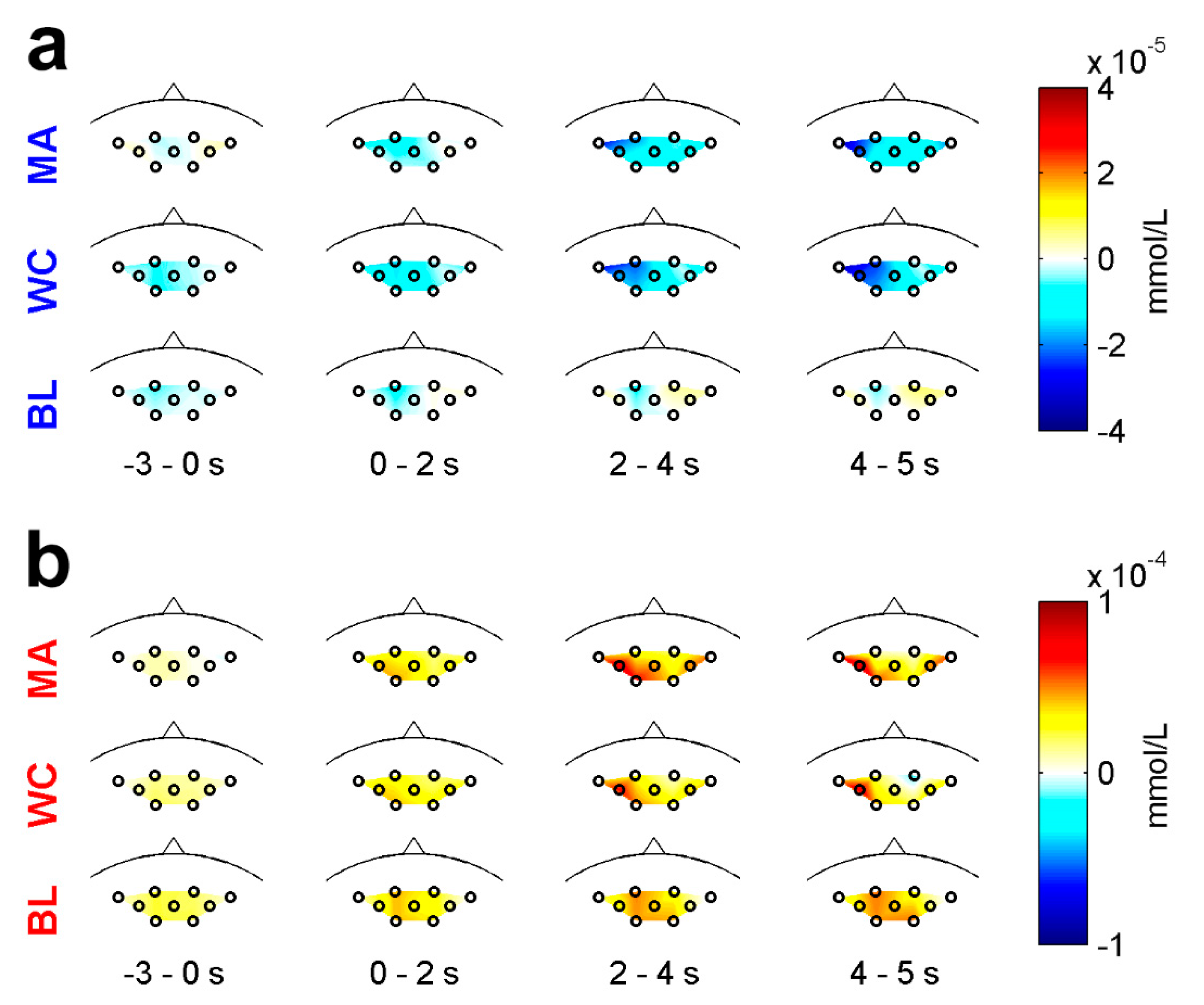
3.1. EEG Characteristics
3.2. NIRS Characteristics
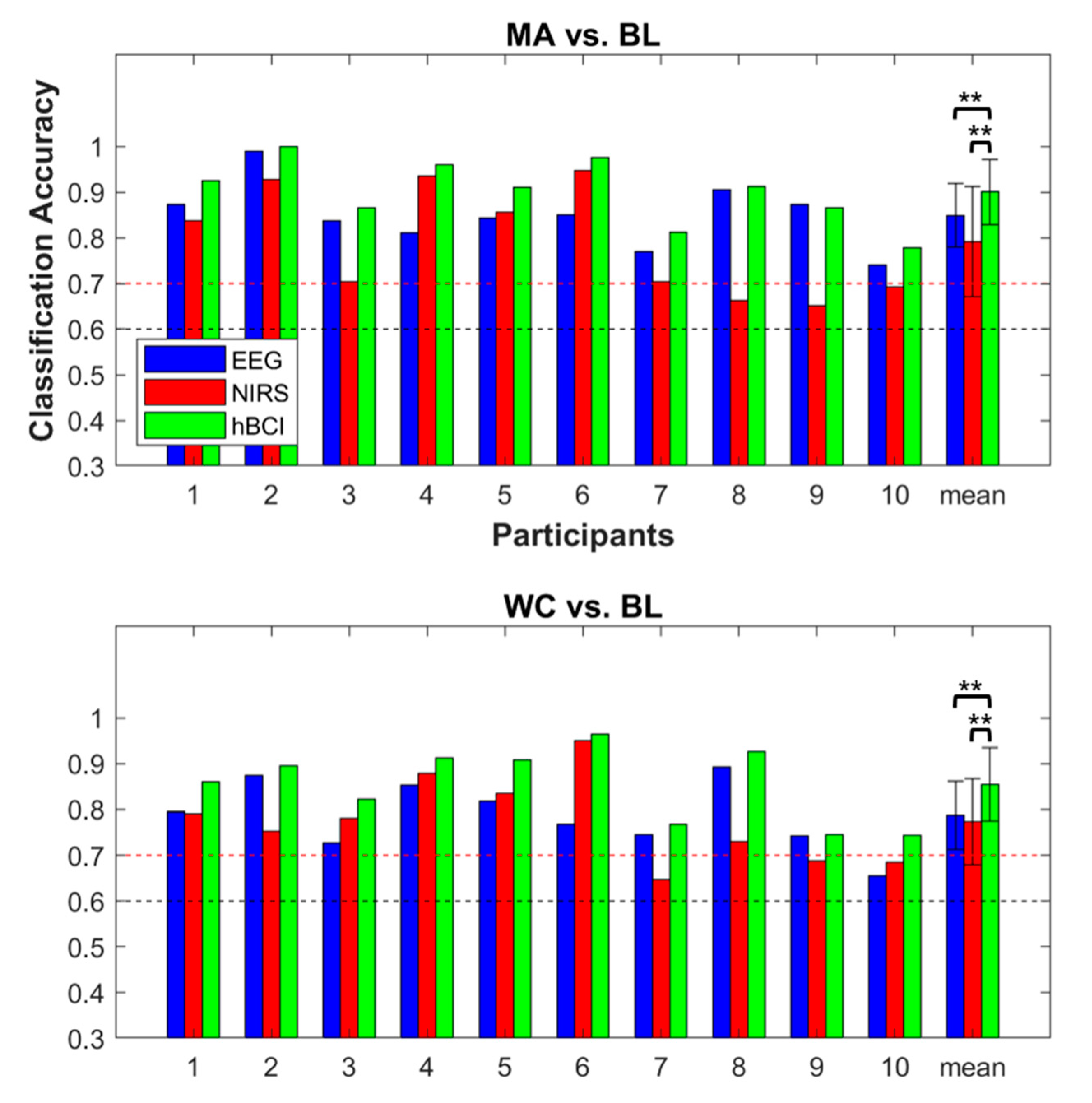
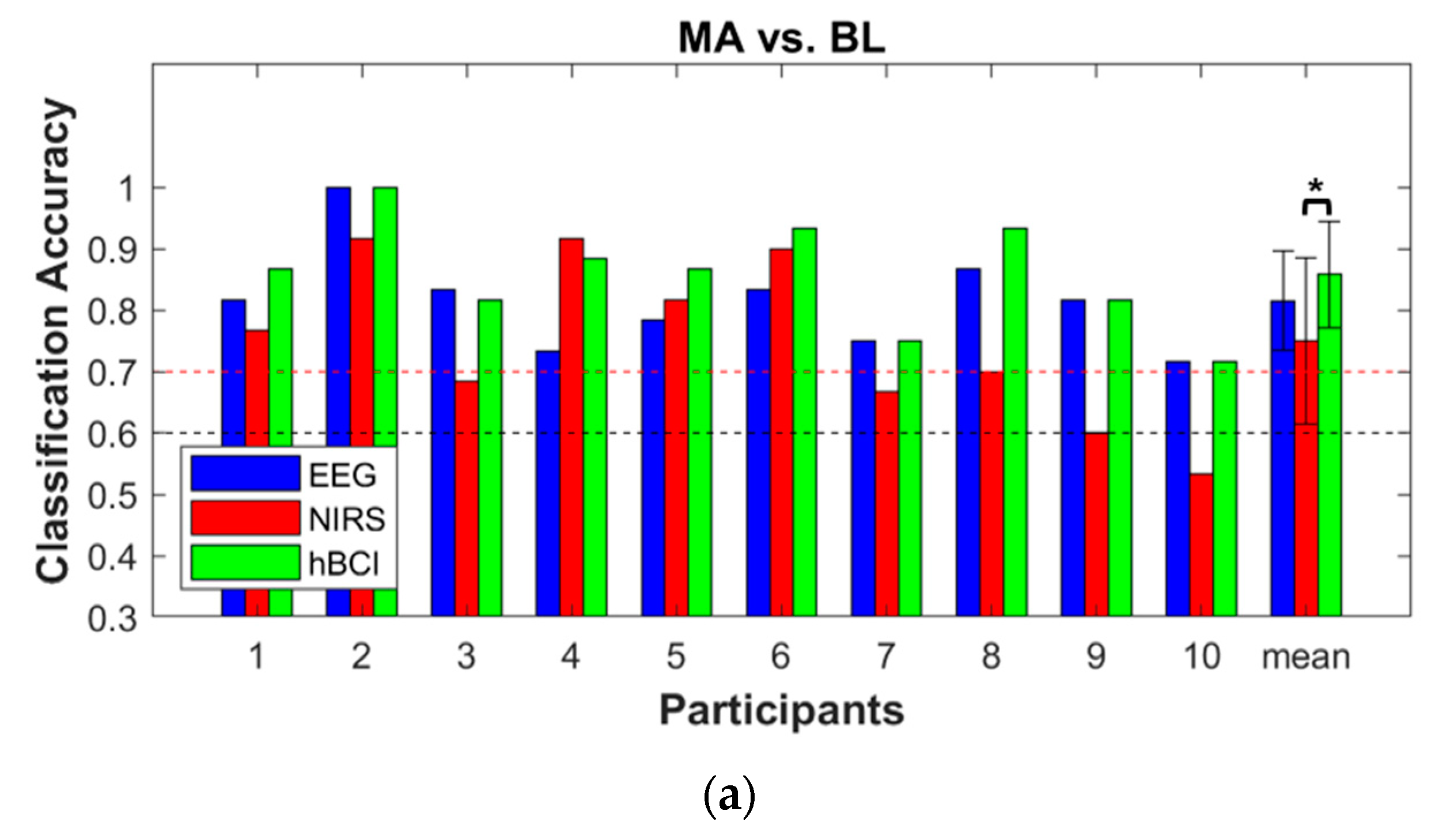
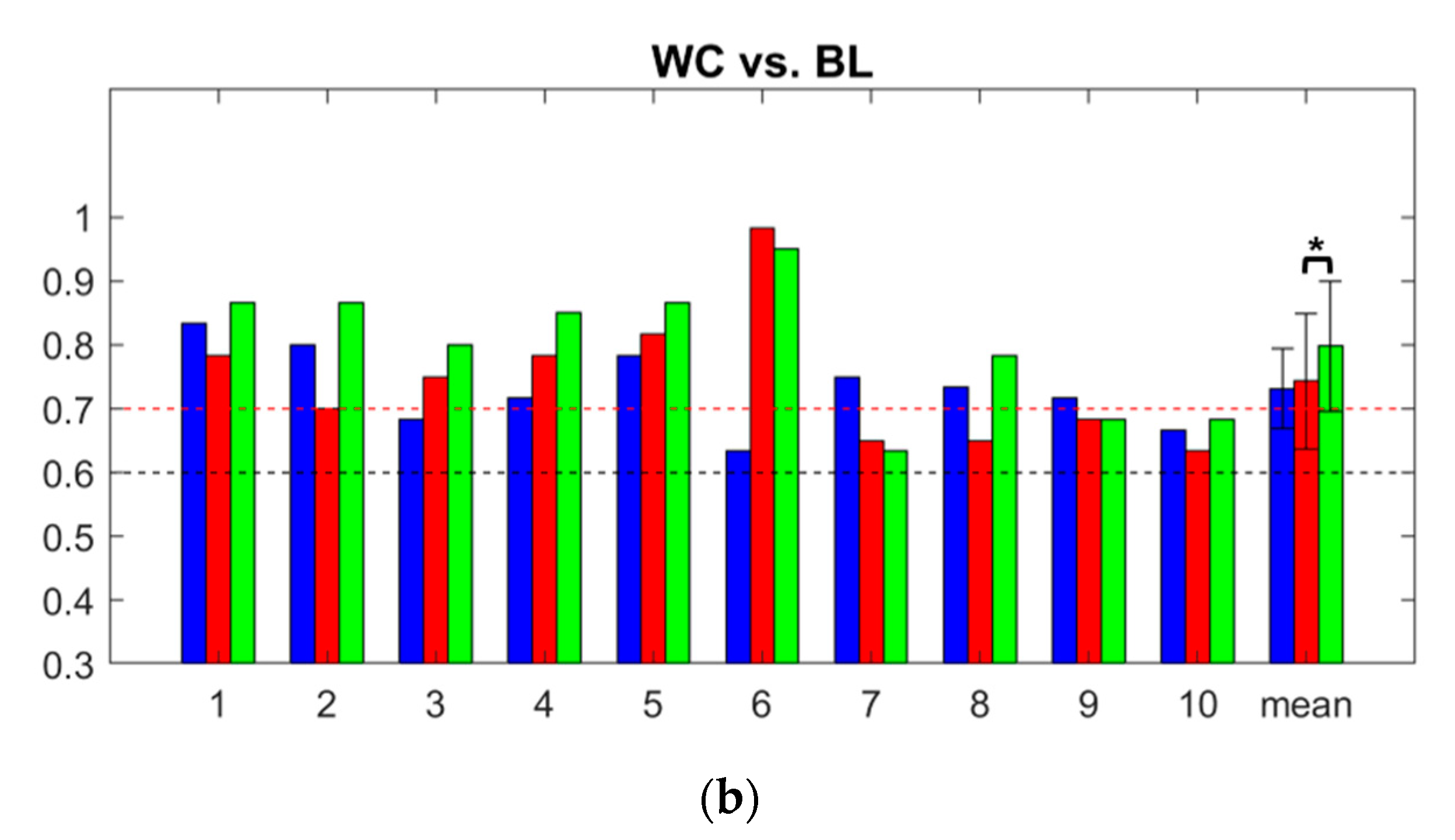
3.3. Classification Accuracy
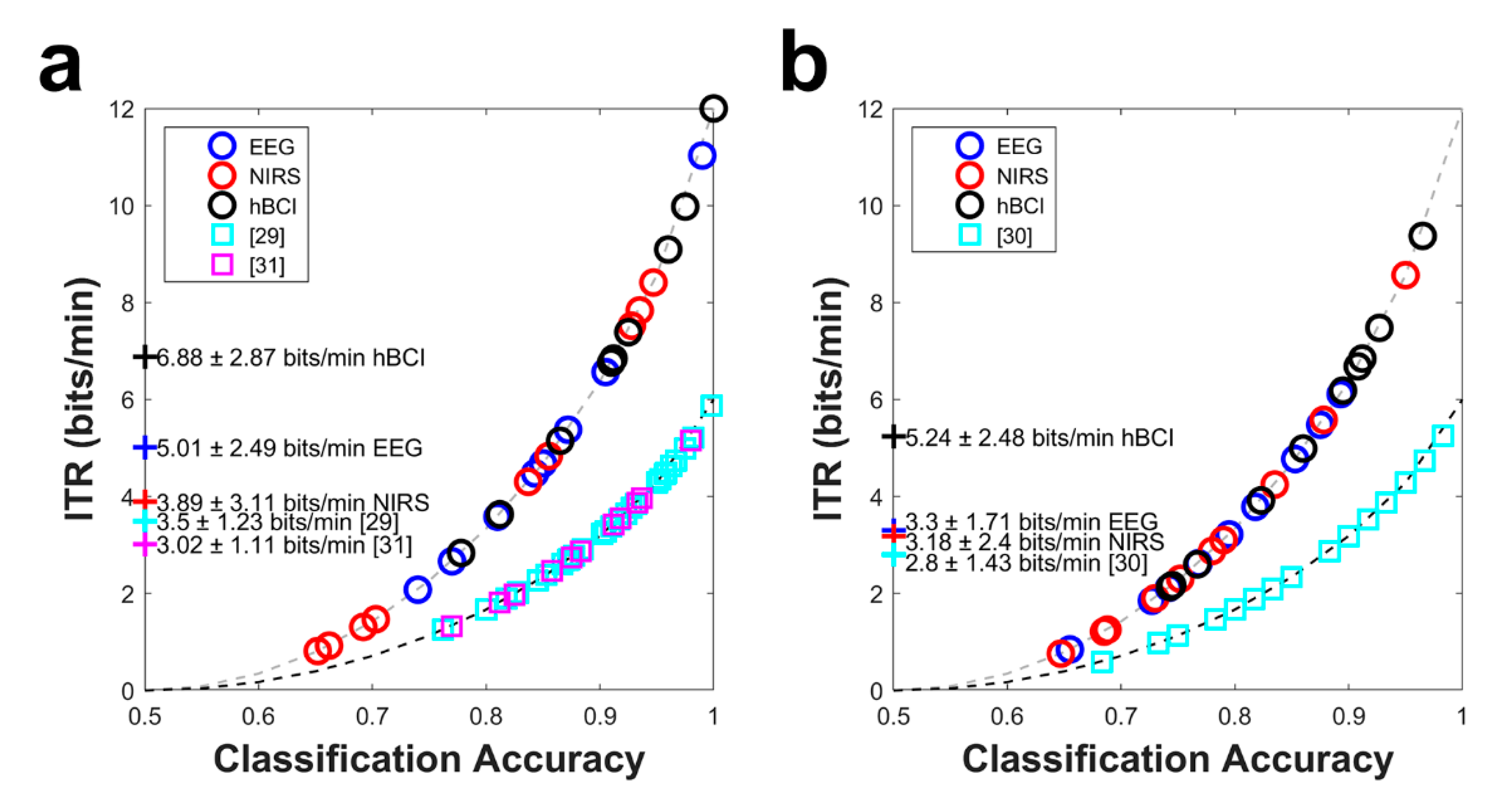
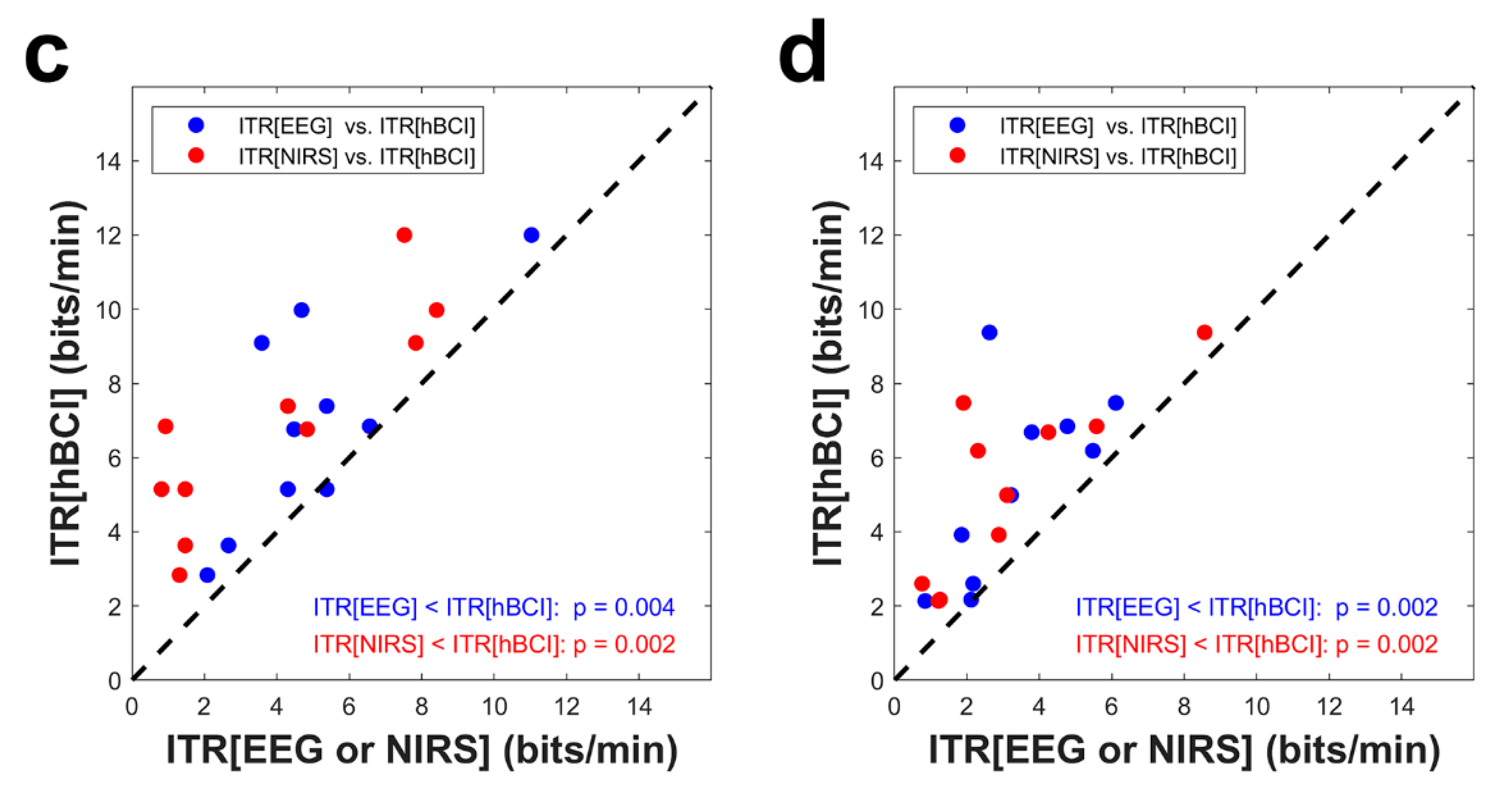
3.4. Information Transfer Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Allison, B.Z.; Brunner, C.; Bauernfeind, G.; Solis-Escalante, T.; Scherer, R.; Zander, T.O.; Müller-Putz, G.; Neuper, C.; Birbaumer, N. The hybrid BCI. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpaw, J.; Wolpaw, E.W. Brain-Computer Interfaces: Principles and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dornhege, G.; Millán, J.R.; Hinterberger, T.; McFarland, D.; Müller, K.-R. Toward Brain-Computer Interfacing; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Höhne, J.; Holz, E.; Staiger-Salzer, P.; Muller, K.R.; Kubler, A.; Tangermann, M. Motor imagery for severely motor-impaired patients: Evidence for brain-computer interfacing as superior control solution. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazli, S.; Mehnert, J.; Steinbrink, J.; Curio, G.; Villringer, A.; Müller, K.-R.; Blankertz, B. Enhanced performance by a hybrid NIRS-EEG brain computer interface. NeuroImage 2012, 59, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskopf, N.; Mathiak, K.; Bock, S.W.; Scharnowski, F.; Veit, R.; Grodd, W.; Goebel, R.; Birbaumer, N. Principles of a brain-computer interface (BCI) based on real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.I.; Stern, J.M.; Engel, J.; Cohen, M.S. Simultaneous EEG and fMRI of the alpha rhythm. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 2487–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitaram, R.; Weiskopf, N.; Caria, A.; Veit, R.; Erb, M.; Birbaumer, N. fMRI brain-computer interfaces. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Fox, S.; Blasi, A.; Elwell, C.E. Illuminating the developing brain: The past, present and future of functional near infrared spectroscopy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, P.; Villringer, A. Simultaneous EEG-fMRI. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, S.; Fazel-Rezai, R.; Asadpour, V. A review of hybrid brain-computer interface systems. Adv. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2013, 2013, 187024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, B.Z.; Brunner, C.; Kaiser, V.; Müller-Putz, G.R.; Neuper, C.; Pfurtscheller, G. Toward a hybrid brain-computer interface based on imagined movement and visual attention. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfurtscheller, G.; Solis-Escalante, T.; Ortner, R.; Linortner, P.; Müller-Putz, G.R. Self-paced operation of an SSVEP-based orthosis with and without an imagery-based “brain switch”: A feasibility study towards a hybrid BCI. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, C.; Allison, B.Z.; Altstatter, C.; Neuper, C. A comparison of three brain-computer interfaces based on event-related desynchronization, steady state visual evoked potentials, or a hybrid approach using both signals. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panicker, R.C.; Puthusserypady, S.; Sun, Y. An asynchronous P300 BCI with SSVEP-based control state detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeb, R.; Sagha, H.; Chavarriaga, R.; Millan, J.D. A hybrid brain-computer interface based on the fusion of electroencephalographic and electromyographic activities. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, X.; Fatourechi, M.; Ward, R.K.; Birch, G.E. The design of a point-and-click system by integrating a self-paced brain-computer interface with an eye-tracker. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2011, 1, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Putz, G.; Leeb, R.; Tangermann, M.; Höhne, J.; Kübler, A.; Cincotti, F.; Mattia, D.; Rupp, R.; Müller, K.-R.; Millán, J.R. Towards noninvasive hybrid brain–computer interfaces: Framework, practice, clinical application, and beyond. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 926–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Sejnowski, T.; Makeig, S. Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using higher-order statistics and independent component analysis. NeuroImage 2007, 34, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseer, N.; Hong, K.-S. fNIRS-based brain-computer interfaces: A review. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, K.T.; Ayaz, H.; Ward, T.E.; Izzetoglu, M.; McLoone, S.F.; Onaral, B. A methodology for validating artifact removal techniques for physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2012, 16, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.; Chau, T. Single-trial classification of NIRS signals during emotional induction tasks: Towards a corporeal machine interface. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, T.H.; Guirgis, M.; Power, S.; Chau, T. Taking NIRS-BCIs outside the lab: Towards achieving robustness against environment noise. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Bryant, D.M.; Glover, G.H.; Reiss, A.L. A quantitative comparison of NIRS and fMRI across multiple cognitive tasks. NeuroImage 2011, 54, 2808–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazli, S.; Lee, S.-W. Brain computer interfacing: A multi-modal perspective. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dähne, S.; Bießmann, F.; Samek, W.; Haufe, S.; Goltz, D.; Gundlach, C.; Villringer, A.; Fazli, S.; Müller, K.-R. Multivariate machine learning methods for fusing multimodal functional neuroimaging data. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1507–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli, S.; Dähne, S.; Samek, W.; Bießmann, F.; Müller, K.-R. Learning from more than one data source: Data fusion techniques for sensorimotor rhythm-based brain–computer interfaces. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, M.J.; Hong, K.-S. Decoding of four movement directions using hybrid NIRS-EEG brain-computer interface. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.X.; Xu, B.L.; Jiang, C.H.; Fu, Y.F.; Wang, Z.D.; Li, H.Y.; Shi, G. A hybrid BCI based on EEG and fNIRS signals improves the performance of decoding motor imagery of both force and speed of hand clenching. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; von Lühmann, A.; Blankertz, B.; Kim, D.-W.; Jeong, J.; Hwang, H.-J.; Müller, K.-R. Open access dataset for EEG+NIRS single-trial classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1735–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; von Lühmann, A.; Kim, D.-W.; Mehnert, J.; Hwang, H.-J.; Müller, K.-R. Simultaneous acquisition of EEG and NIRS during cognitive tasks for an open access dataset. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Müller, K-R.; Schmitz, C.H.; Kim, D.-W.; Hwang, H.-J. Evaluation of a compact hybrid brain-computer interface system. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Lühmann, A.; Wabnitz, H.; Sander, T.; Müller, K.-R. M3BA: A mobile, modular, multimodal biosignal acquisition architecture for miniaturized EEG-NIRS based hybrid BCI and monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1199–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Bray, S.; Reiss, A.L. Speeded near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) response detection. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaurre, C.; Blankertz, B. Towards a cure for BCI illiteracy. Brain Topogr. 2010, 23, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Sannelli, C.; Halder, S.; Hammer, E.M.; Kübler, A.; Müller, K.R.; Curio, G.; Dickhaus, T. Neurophysiological predictor of SMR-based BCI performance. NeuroImage 2010, 51, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combrisson, E.; Jerbi, K. Exceeding chance level by chance: The caveat of theoretical chance levels in brain signal classification and statistical assessment of decoding accuracy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2015, 250, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaurre, C.; Sannelli, C.; Müller, K.-R.; Blankertz, B. Machine-learning-based coadaptive calibration for brain-computer interfaces. Neural Comput. 2011, 23, 791–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidaurre, C.; Sannelli, C.; Müller, K.-R.; Blankertz, B. Co-adaptive calibration to improve BCI efficiency. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 025009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Müller, K.-R.; Hwang, H.-J. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) based eyes-closed brain-computer interface (BCI) using prefrontal cortex activation due to mental arithmetic. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kwon, J.; Choi, J.; Im, C.-H. Performance enhancement of a brain-computer interface using high-density multi-distance NIRS. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, Y.; Toichi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Mason, R.A.; Coconcea, C.M.; Findling, R.L.; Yamamoto, K.; Calabrese, J.R. Prefrontal activation during verbal fluency tests in schizophrenia—A near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) study. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 77, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, S.D.; Falk, T.H.; Chau, T. Classification of prefrontal activity due to mental arithmetic and music imagery using hidden Markov models and frequency domain near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Kwon, J.; Im, C.-H. A multi-class hybrid EEG-NIRS brain-computer interface for the classification of brain activation patterns during mental arithmetic, motor imagery, and idle state. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 23, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.J.; Hong, K.-S. Hybrid EEG–fNIRS-based eight-command decoding for BCI: Application to quadcopter control. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.; Lee, H.-G.; Nam, Y.; Kang, H.; Koh, C.; Shin, H.-C.; Choi, S. A hybrid NIRS-EEG system for self-paced brain computer interface with online motor imagery. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2015, 244, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Herrero, G.; De Clercq, W.; Anwar, H.; Kara, O.; Egiazarian, K.; Van Huffel, S.; Van Paesschen, W. Automatic removal of ocular artifacts in the EEG without an EOG reference channel. In Proceedings of the 7th Nordic Signal Processing Symposium, Reykjavik, Iceland, 7–9 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, L.; Herman, P.; Eke, A. The modified Beer–Lambert law revisited. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, N91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, E.V.C.; Scherer, R.; Neuper, C. Stability of event-related (de-) synchronization during brain–computer interface-relevant mental tasks. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 124, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Kawanabe, M.; Tomioka, R.; Hohlefeld, F.; Müller, K.-R.; Nikulin, V.V. Invariant common spatial patterns: Alleviating nonstationarities in brain-computer interfacing. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Koles, Z.J.; Soong, A.C.K. EEG source localization: Implementing the spatio-temporal decomposition approach. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 107, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankertz, B.; Tomioka, R.; Lemm, S.; Kawanabe, M.; Müller, K.-R. Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankertz, B.; Tangermann, M.; Vidaurre, C.; Fazli, S.; Sannelli, C.; Haufe, S.; Maeder, C.; Ramsey, L.; Sturm, I.; Curio, G.; et al. The Berlin brain–computer interface: Non-medical uses of BCI technology. Front. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Acqualagna, L.; Dähne, S.; Haufe, S.; Schultze-Kraft, M.; Sturm, I.; Ušćumlic, M.; Wenzel, M.A.; Curio, G.; Müller, K.-R. The Berlin brain-computer interface: Progress beyond communication and control. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Regularized discriminant analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1989, 84, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BBCI Toolbox. Available online: https://github.com/bbci/bbci_public/ (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Ledoit, O.; Wolf, M. A well-conditioned estimator for large-dimensional covariance matrices. J. Multivar. Anal. 2004, 88, 365–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, J.; Strimmer, K. A Shrinkage approach to large-scale covariance matrix estimation and implications for functional genomics. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2005, 4, 2194–6302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankertz, B.; Lemm, S.; Treder, M.; Haufe, S.; Müller, K.R. Single-trial analysis and classification of ERP components—A tutorial. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemm, S.; Blankertz, B.; Dickhaus, T.; Müller, K.-R. Introduction to machine learning for brain imaging. NeuroImage 2011, 56, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, S.D.; Kushki, A.; Chau, T. Towards a system-paced near-infrared spectroscopy brain–computer interface: Differentiating prefrontal activity due to mental arithmetic and mental singing from the no-control state. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 066004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, S.D.; Kushki, A.; Chau, T. Automatic single-trial discrimination of mental arithmetic, mental singing and the no-control state from prefrontal activity: Toward a three-state NIRS-BCI. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schudlo, L.C.; Chau, T. Dynamic topographical pattern classification of multichannel prefrontal NIRS signals: II. Online differentiation of mental arithmetic and rest. J. Neural Eng. 2014, 11, 016003. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, K.S.; Naseer, N. Reduction of delay in detecting initial dips from functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals using vector-based phase analysis. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2016, 26, 1650012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, A.; Hong, K.S. Detection and classification of three-class initial dips from prefrontal cortex. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacoub, E.; Shmuel, A.; Pfeuffer, J.; Van de Moortele, P.F.; Adriany, G.; Ugurbil, K.; Hu, X.P. Investigation of the initial dip in fMRI at 7 Tesla. NMR Biomed. 2001, 14, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.J.; Mechelli, A.; Turner, R.; Price, C.J. Nonlinear responses in fMRI: The balloon model, volterra kernels, and other hemodynamics. NeuroImage 2000, 12, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-J.; Lim, J.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Im, C.-H. Evaluation of various mental task combinations for near-infrared spectroscopy-based brain-computer interfaces. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauernfeind, G.; Scherer, R.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Neuper, C. Single-trial classification of antagonistic oxyhemoglobin responses during mental arithmetic. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.-S.; Naseer, N.; Kim, Y.-H. Classification of prefrontal and motor cortex signals for three-class fNIRS-BCI. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, E.A.; Stokes, M.J. Learning to control brain activity: A review of the production and control of EEG components for driving brain–computer interface (BCI) systems. Brain Cognit. 2003, 51, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faress, A.; Chau, T. Towards a multimodal brain–computer interface: Combining fNIRS and fTCD measurements to enable higher classification accuracy. NeuroImage 2013, 77, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecklmann, M.; Ehlis, A.C.; Plichta, M.M.; Fallgatter, A.J. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy: A long-term reliable tool for measuring brain activity during verbal fluency. NeuroImage 2008, 43, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, M.J.; Ehlis, A.C.; Fallgatter, A.J. Frontal activation during a verbal-fluency task as measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 61, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, J.; Kim, D.-W.; Müller, K.-R.; Hwang, H.-J. Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses. Sensors 2018, 18, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061827
Shin J, Kim D-W, Müller K-R, Hwang H-J. Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses. Sensors. 2018; 18(6):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061827
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Jaeyoung, Do-Won Kim, Klaus-Robert Müller, and Han-Jeong Hwang. 2018. "Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses" Sensors 18, no. 6: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061827
APA StyleShin, J., Kim, D.-W., Müller, K.-R., & Hwang, H.-J. (2018). Improvement of Information Transfer Rates Using a Hybrid EEG-NIRS Brain-Computer Interface with a Short Trial Length: Offline and Pseudo-Online Analyses. Sensors, 18(6), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18061827





