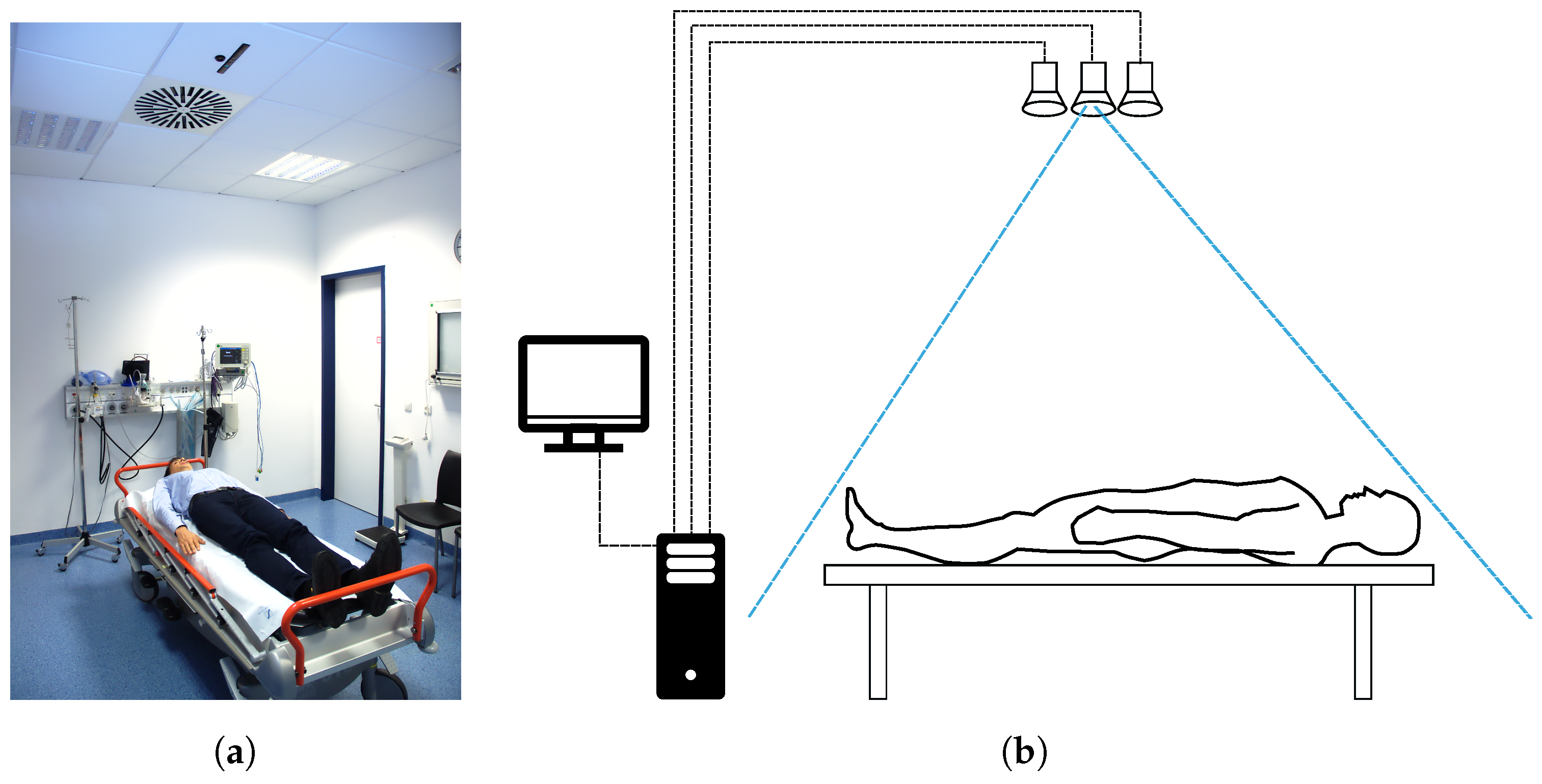
3.1. System Description
The system uses different sensors, depending on the recorded dataset. It was developed for previous work [
15,
20] to be integrated into the clinical environment. There the system includes a Microsoft Kinect, a Microsoft Kinect One and an Optris PI400 thermal camera. A single depth sensor is sufficient for body weight extraction. However, the developed algorithm should not depend on the applied sensor. Therefore, experiments are performed with different sensors.
Table 2 compares the sensors to each other.
Both the Kinect and the Kinect One are RGB-D cameras providing a color stream RGB, and a depth per pixel D. The first Kinect camera was released in 2011 bringing a low-cost consumer product into robotics. The sensor brought multiple applications and made an impact well beyond the gaming industry [
29]. The Kinect holds a sensor for infrared (IR) and a sensor for color. Both sensors are calibrated to each other. The structured light principle obtains depth: A projector emits a known pattern in the environment. This pattern is seen by the IR sensor from a different pose to calculate the depth for an arbitrary pixel. Khoshelham and Elberink [
30] illustrate the sensor’s characteristics in image quality and noise.
In contrast to that, the Kinect One works by the Time-of-Flight (ToF) principle [
31]: Having a highly precise measurement device for the time, it would be possible to calculate the distance between a light source and an object by measuring the time. The range of a given point can be calculated by the time
t the light travels with the help of the speed of light
c with
. Due to the fast traveling light, the distance measurement is obtained by modulated light: A source emits a light pulse towards an object. The frequency for modulation is known, and a phase shift can be measured from the reflected signal.
The here applied depth sensors differ not only in their resolution, but also the different principle provides a diverse characteristic of depth. Both sensors are compared to each other by Sarbolandi et al. [
32]. Today, there exist various types of RGB-D sensors, which are suitable for the body weight estimation approach, e.g., Asus Xtion cameras from the Intel RealSense series [
33]. The thermal camera is state of the art and is added to the sensor set to ease segmentation based on a simple thermal threshold. In this presented sensor configuration, the thermal camera is the most expensive part. It was used because it was already available from an earlier project. However, a cheaper thermal camera with a lower resolution and frame rate can be used for the segmentation. Pfitzner et al. [
20] illustrated that the visual body weight estimation is possible without a thermal camera, but outliers due to insufficient segmentation can occur.
The algorithm—including the sensor fusion, the feature extraction and the forwarding to an artificial neural network—is implemented on a conventional desktop computer, which is installed in the trauma room. The computer in the trauma room, which is equipped with an Intel i7 of the 4th generation, can provide the result in body weight estimation within 300 ms, including the saving of the sensor data. The software does not rely on specialized hardware, like a high-end graphics card, although the processing speed could benefit from parallelization. For offline processing, a mobile computer (Dell M4800) is used, having a maximum power consumption of less than 80 Watt [
34]. Therefore, the complete hardware could be designed with less than 100 W, including the mobile computer, the thermal camera (<2.5 Watt) and the Microsoft Kinect (12 Watt).
Table 3 illustrates that the processing time for the desktop computer and the mobile computer is similar. A small experiment in our laboratory showed that the approach is also suitable for small size embedded computers, e.g., a Raspberry PI. With a reduced visualization, and without the saving of the sensor’s data to the database, this configuration provided the estimation of body weight in around 5 s, see
Table 3. The system is then limited in real-time visualization, as well as process time, and the estimation of the body weight is available with a higher delay. However, the embedded computer can have the benefit of lower power consumption and a smaller footprint, which provides easier integration in the clinical environment.
3.2. Sensor Fusion
All applied projective depth, color, and thermal sensors are calibrated intrinsically based on the method presented by Zhang [
35]. Therefore, a single calibration pattern is used, which is visible in depth, color, and thermal frame. Gonzalez-Jorge et al. [
36] present different types of suitable calibration targets. The here applied calibration target consists of a metal plate on the back which is colored white and a black wooden plate on top. The wooden plate has holes in a circular pattern. The metal plate can be heated. Because of a space between the metal and the wood plate, a thermal gradient is visible, and the wholes appear to be warmer than the top surface. The circle pattern is therefore visible in the spectrum of the thermal camera [
15].
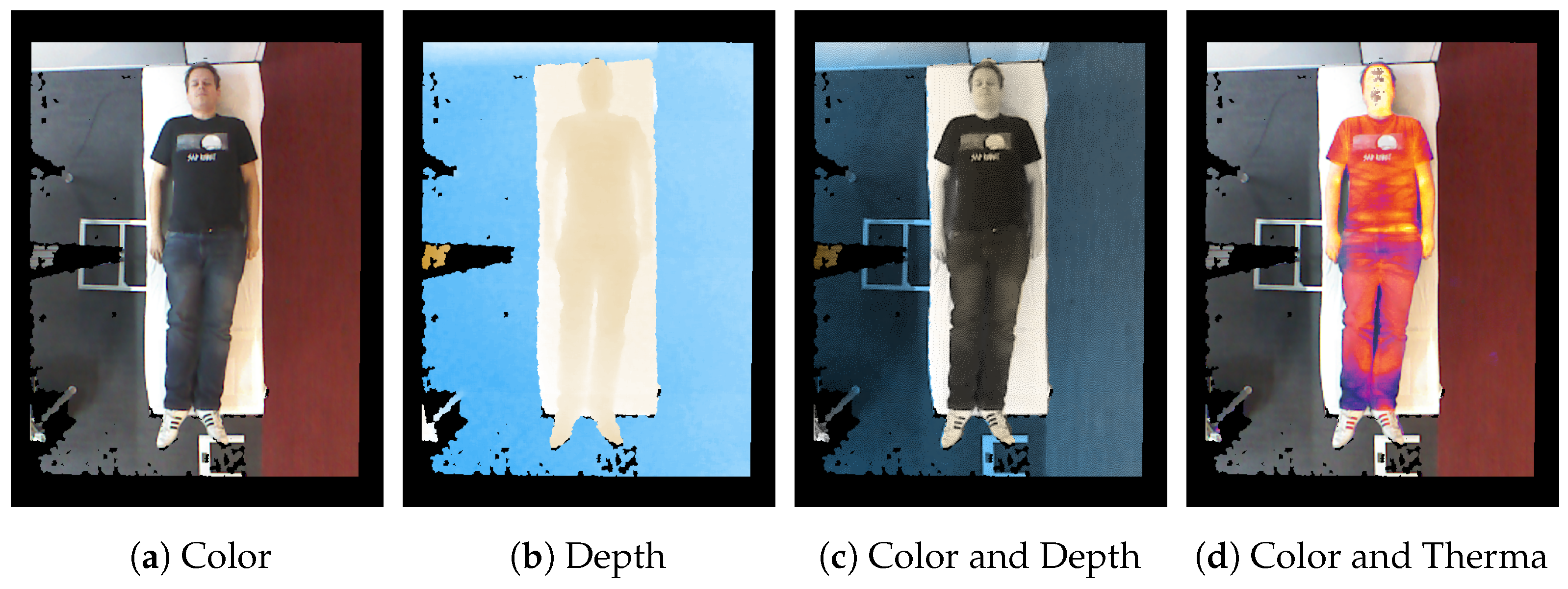
The results of sensor fusion can be displayed in different settings. Besides the typical representation on the screen as a color image of the scene, the depth can be visualized by a color mapping. Furthermore, it is also possible to illustrate the scene as a false-color representation for temperature or fused with the color stream, similar to that presented by Vidas et al. [
37]. This is achieved by comparing the color channel of every point in the cloud.
Figure 3 illustrates the sensor fusion and its visualizations: In
Figure 3c, the data from the color sensor of the Kinect camera is fused with its depth stream. In the fused image, the color stream provides the intensity of each pixel as a grayscale, while the color of a pixel arranges the depth in the scene, as shown in
Figure 3b. In addition, the color data and the thermal data are aligned to be visible at the same time, see
Figure 3d. From the given data, further data can be calculated to enhance the point cloud or the depth image, e.g., with normals.
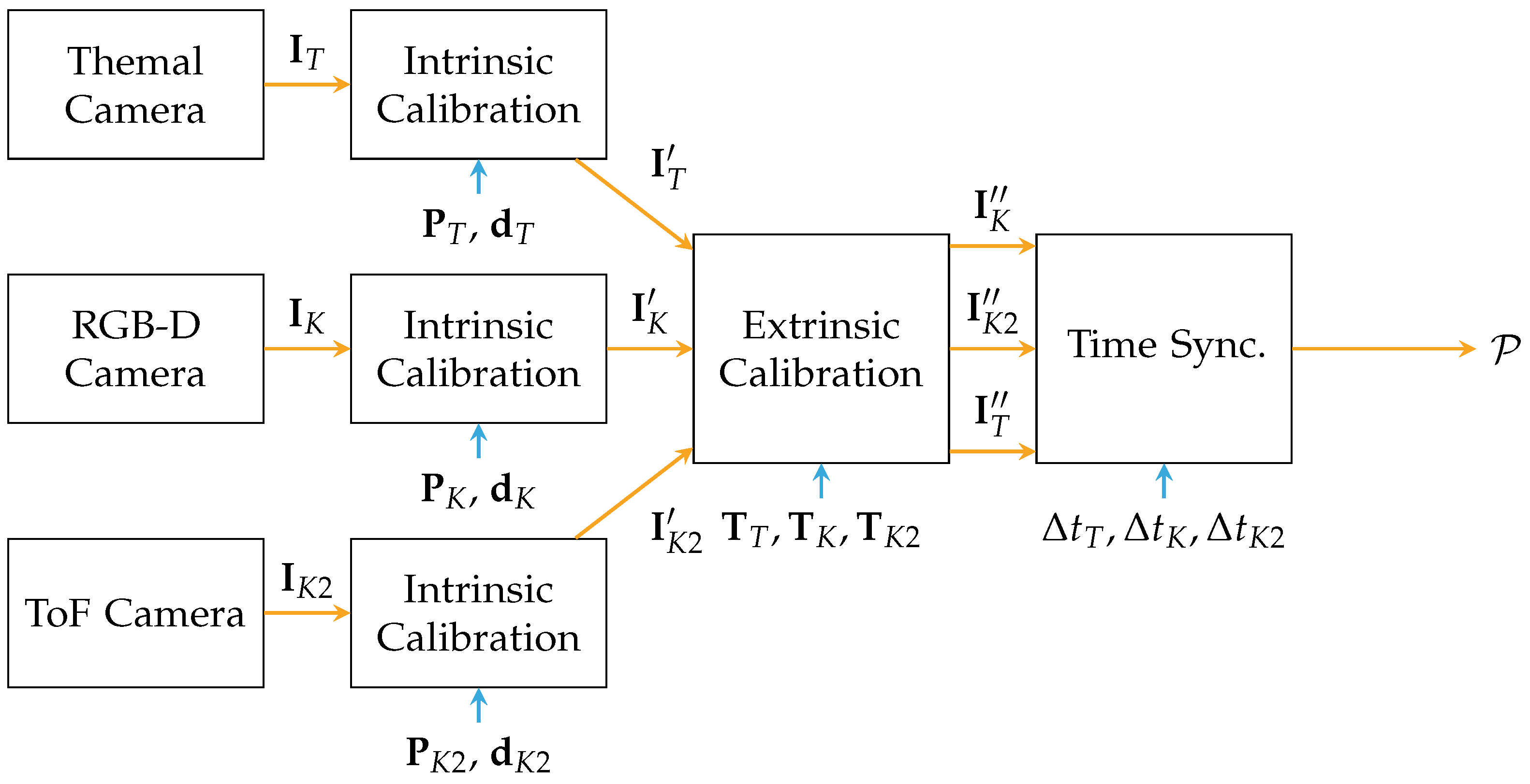
Figure 4 presents the process of calibration for sensor fusion: The frames from the sensor are differentiated by indices,
K for the Kinect,
for the Kinect One and
T for the thermal camera. All three sensors are calibrated intrinsically. First, the raw streams from the sensors
are forwarded to rectification based on the determined intrinsic parameters
and
[
35]. Second, the rectified images
are then calibrated extrinsically based on the previously estimated transformations
. Third, the aligned data
is synchronized in time by the method presented by Lussier and Thrun [
38] with
. Finally, a point cloud
containing
n points, can be generated with the help of the pinhole camera model.
The intrinsic calibration aims to remove the aberrations from the lens, bringing the image in the form of the pinhole camera model. For the intrinsic calibration, the projection matrix has to be determined. The matrix contains the focal length , as well as the offset to the sensor’s center. Therefore, based on the pinhole camera model, a point can be projected onto the sensor as a pixel . For the extrinsic calibration, the world frame’s origin is set the same as the origin of the infrared sensor of the Kinect. The extrinsic factory calibration of both Kinect cameras is left as it is. The transformations between the two Kinect cameras and the thermal camera is estimated with the help of the same calibration pattern.
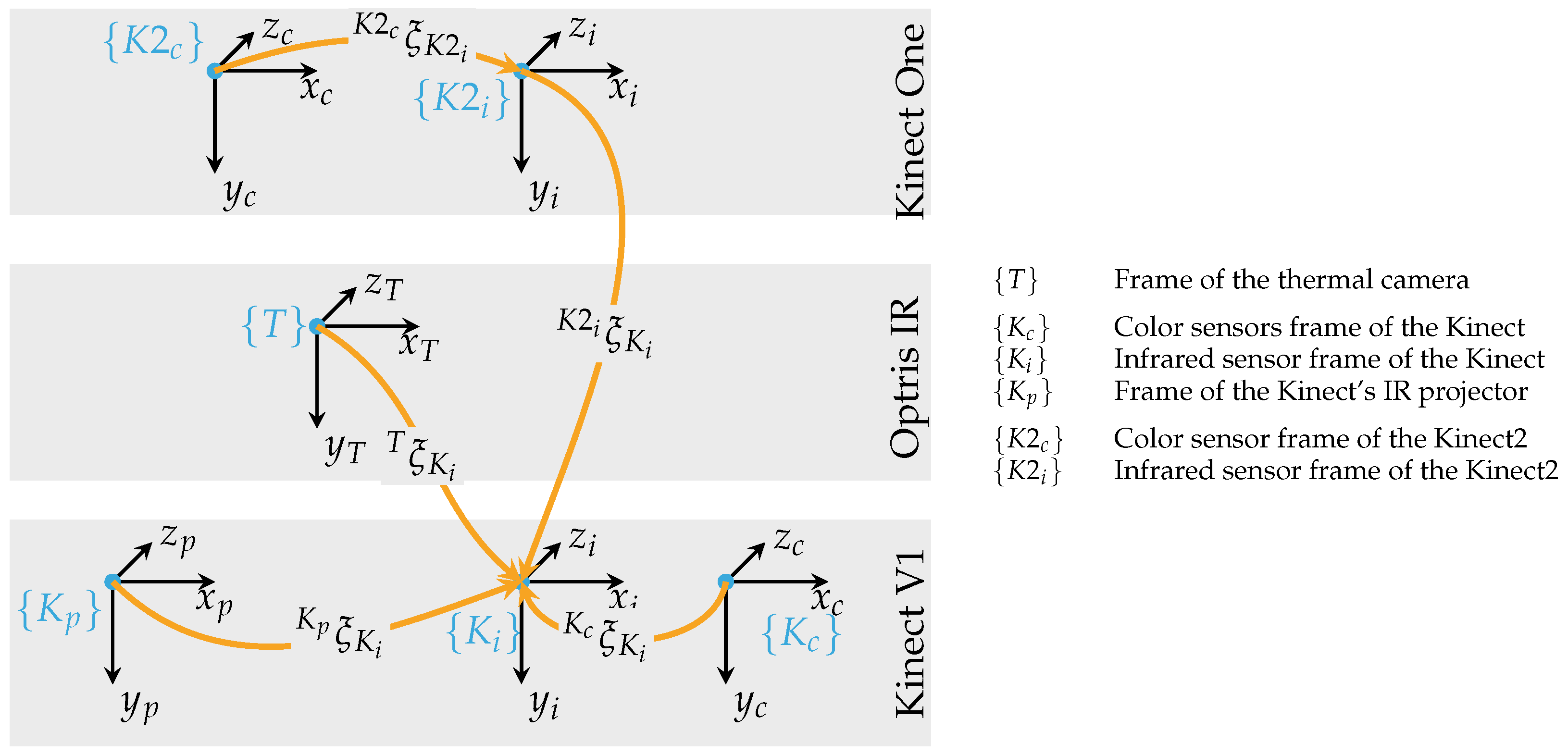
Figure 5 illustrates the transformation between the sensors. The extrinsic parameters—the rotation
and the translation
—are combined to a pose
describing the relative pose of
with respect to
. After sensor fusion, every point can contain the Cartesian coordinates
, color (
) and thermal data (
t) with
. For calibration and sensor fusion, OpenCV was applied [
39].
3.3. Segmentation
The process of segmentation differs with the scene: A patient lying on a medical stretcher with physicians on his side is harder to segment than someone standing in an empty room with a clear distance to the wall behind him. The point cloud
is segmented in a set belonging to the person
and a set for the environment
with
. Therefore, a point can only belong to the person’s point cloud, or the environment. The segmentation for clinical applications is described by Pfitzner et al. [
15]. For the reader’s convenience, it is also presented as follows: The patient is placed in a set range within the field of view (FOV) of the sensors mounted on the ceiling. This range is visible with markers on the floor. In an initial step, the amount of data in the point cloud is reduced. Therefore, the floor and all data outside the range of the markers on the floor is removed from the point cloud. After this step, the point cloud should contain mostly the patient and the stretcher he or she is lying on. Based on the available thermal data from the thermal camera, the segmentation can be done with a threshold in temperature. Points having a higher temperature than a fixed limit are included in the patient’s point set
. Physicians or family members close to the patient can be removed by finding the most significant contour easily under the assumption that the most significant part of the remaining scene is the patient and the stretcher. Based on the Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) algorithm [
40], the surface of the stretcher is obtained with a model for a plane. On one side, this is necessary to improve the outcome of segmentation. On the other side, the surface of the stretcher is necessary for the upcoming feature extraction. Morphological operations like erosion and dilation improve the outcome of segmentation [
41]. Finally, the scene’s point cloud
is segmented, and the patient’s point cloud
is available. To check if a patient is within the FOV of the camera, state of the art algorithms like the histogram of oriented gradients can be used [
42]. Further, the measurement can be started by the medical staff by pressing a button attached to the wall in the trauma room. The segmentation in this medical scenario is reliable and robust. The data from the thermal camera provides good results in segmentation, sufficient for feature extraction. However, also without a thermal camera, the segmentation can be achieved, but outliers can occur, as illustrated in previous work [
20].
The segmentation of a standing or walking person is less complex: To segment the person from the background, a reference frame
without the person is recorded in advance. The current frame containing the person is subtracted from the reference frame
. Due to the sensor’s noise, a threshold in distance should be applied to get a good outcome of background subtraction. Furthermore, to improve the outcome of the segmentation on the floor, the RANSAC algorithm can be applied to detect points on the floor and remove them from the scene’s point cloud. Therefore, the segmentation of the feet gets more accurate and robust. Outliers and jumping edge errors can be removed by morphological filters or statistical outlier filters.
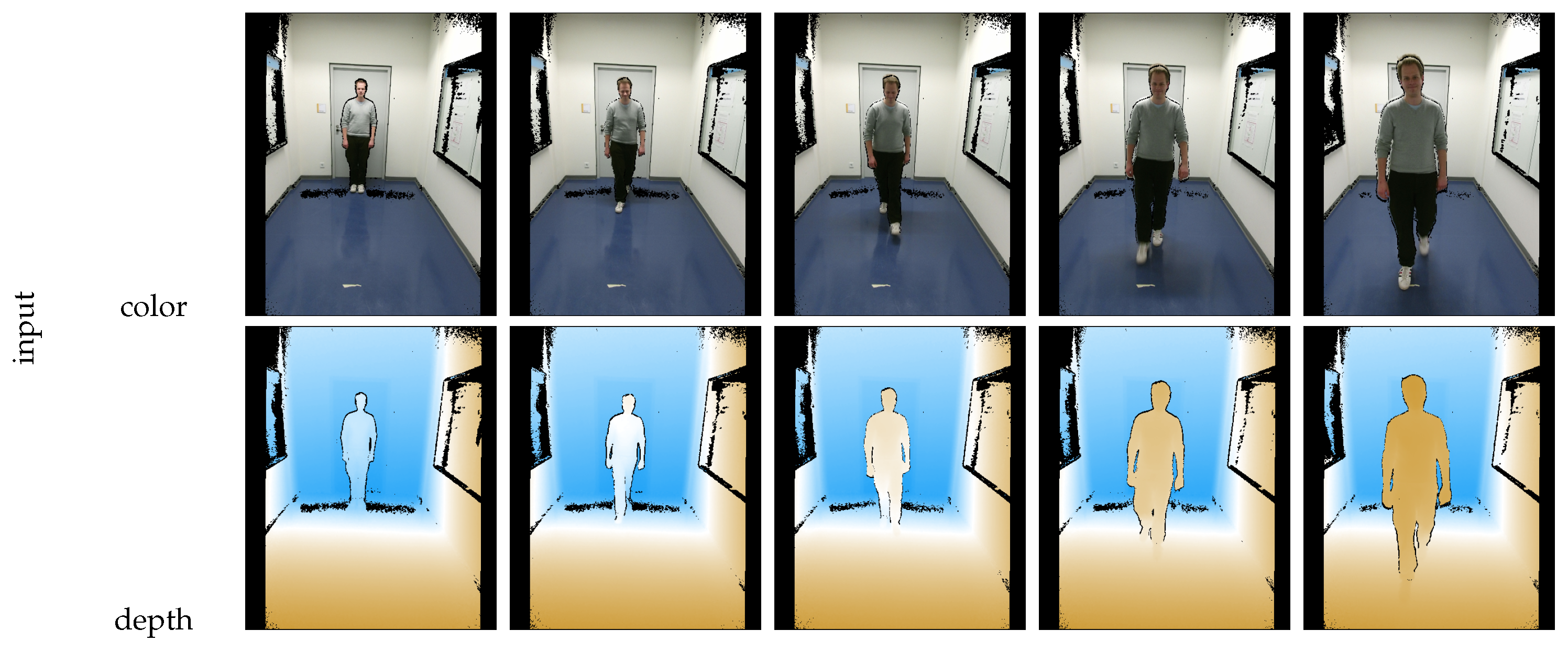
Figure 6 illustrates the segmentation based on background subtraction with a person walking towards the camera. This procedure is similar as presented in related work by Labati et al. [
27] and Nguyen et al. [
26].
3.4. Feature Extraction
Based on the segmentation, features are obtained from the person’s point cloud . The position of a patient does not vary much in the clinical scenario with the patient on a medical stretcher in a previously defined position of the bed and in a fixed distance from the sensors. In contrast to that, the pose of multiple persons standing in front of a camera can vary more; while walking the pose of the person changes from frame to frame. Therefore, it is necessary that the extracted features are robust against changes in scale, translation, and perspective. The difference in posture is small for most people standing in front of the camera or lying on a stretcher: most of them have their arms aside their body and a few have their arms crossed over their stomach.
The extracted features are presented in
Table 4. The correlation of those features to the ground truth body weight is shown in Pfitzner et al. [
22]. A good feature is invariant against scale (s), rotation (r), translation (t), perspective (pe) and posture of the person (po) in front of the camera. However, while most of the here presented features are invariant for scale, due to the applied 3D data, no feature is invariant against changes in posture. Therefore, the data applied for training the model should cover many different common postures for standing and walking people.
The features can be grouped: The features
to
are simple geometric features. The estimation of the volume is only possible due to the stretcher the patient is lying on. The volume is calculated based on a triangle mesh of the person’s frontal surface
s. The not visible surface on the back of the person is modeled by a single plane. The calculation of the volume is presented in detail in Pfitzner et al. [
20]. Further, the triangle mesh is taken to calculate the frontal surface of a person. Although both features, the volume, and the surface, are only estimations and can be far from ground truth values, they can be a hint for an estimator: A person having a higher value for volume tends to be heavier compared to someone having a lower volume value. In addition, this first feature group contains the number of points belonging to the person’s point cloud
and the calculated density of the scene, setting the number of points from the person in relation to the number of points of the whole scene
.
The second group of features ( to ) is based on eigenvalues and the eigenvalues itself: The normalized eigenvalues have the benefit that they are invariant against coordinate transformations like scale, rotation, and translation. Therefore, the features based on these eigenvalues—sphericity, flatness, and linearity—are also invariant against transformations.
The third group consists of features from statistics: Compactness and kurtosis are normalized and therefore invariant against scale, rotation, and translation.
Features from the silhouette of a person are grouped in the fourth section: The area and length of the contour and the convex hull are invariant against rotation, and translation, but not against scale. However, a small change in posture can change the outcome from the calculation of contour and convex hull.
Related work showed that the body weight estimation could be improved if the gender is known [
26]. The gender was here taken from ground truth, but could also be estimated by algorithm [
26,
43]. Apparently, the gender does not change in any way with applied transformation. Further, the cited algorithms are robust in detecting gender [
43].
Table 5 demonstrates the changes in the feature values with different postures: The first scene shows a subject standing straight with the arms aside. The features are listed and calculated by the previously presented equations. In the second scene, the subject raises both hands a bit. The values for surface and density do not change much. In addition, the first eigenvalue nearly stays the same. However, the value for the third eigenvalue changes, due to the arms raised in front of the person. Flatness and sphericity—which correlate with the third eigenvalue—also change significantly. Compared to the third scene, where the subject stands with legs apart, the second eigenvalue changes most. Therefore, flatness and also linearity change. Comparing the first and the fourth scene, the subject crosses the arms: The surface lowers, as well as all features from contour and convex hull. The second eigenvalue lowers while the third eigenvalue increases. In the last scene, the subject is wearing a backpack. Comparing the features from this scene with the first scene, most of the features are within the same range. However, there are differences due to slight differences in posture. Apparently, the body weight estimation can ignore such objects as backpacks, if not visible to the sensor.
Concerning all the poses presented here, the features from contour and convex hull are able to vary the most: A subject having the arms aside can cause a much higher length in contour when there is a small gap between the body and the arm. However, as shown in [
22], the length and area of the contour correlate with the body weight and therefore it can be useful to enclose such features for body weight estimation.
Machine learning minimizes the invariances in selected features. However, a suitable set for training and testing should cover most of the various poses, especially when the subject is moving during body weight estimation.
3.6. Estimation of a Sensor Stream
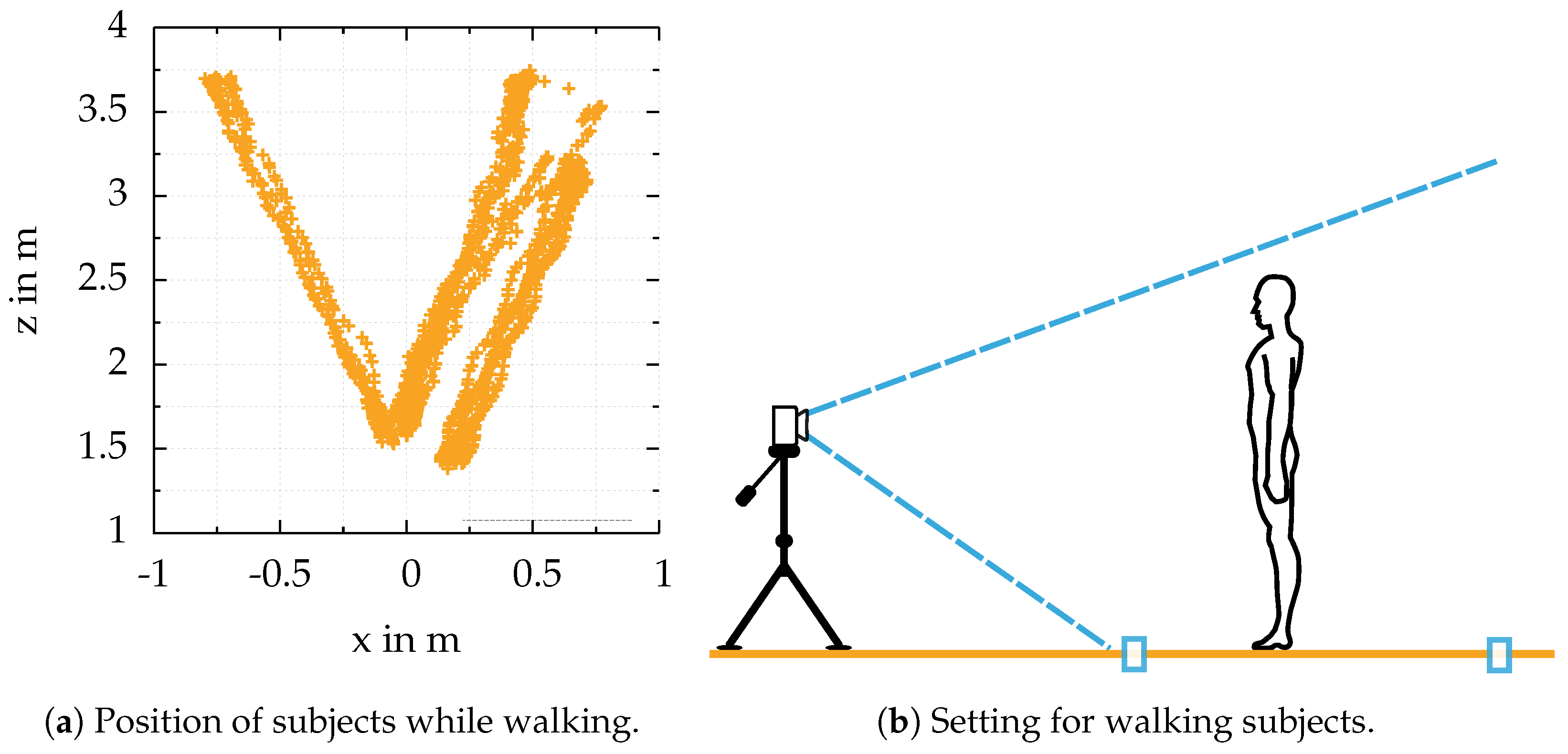
The FOV, the person’s height, and the maximum distance for 3D data acquisition mark the starting and end markers on the floor, see
Figure 7b.
Figure 7a illustrates the poses of all people walking towards the camera. Due to different settings for the experiments, the path people tend to walk differs. Further, the camera did not always have the same orientation towards the floor and was not always mounted at the same height.
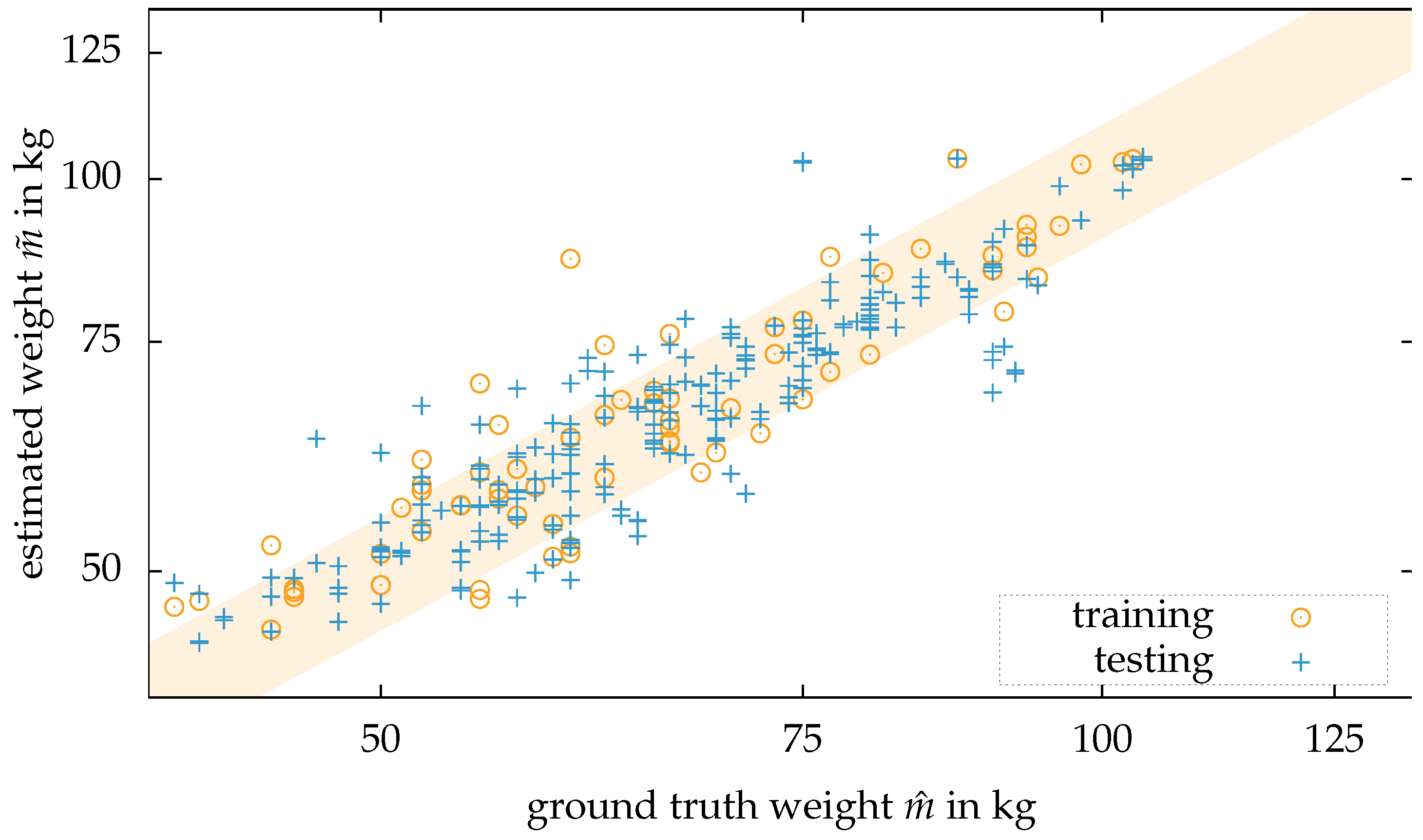
First, the person is segmented from the background by the methods described in the previous section. Second, for every frame of the dataset, the body weight estimation is applied. In a scatter plot together with the ground truth body weight, a line becomes visible for every single person. Some of the estimations are close to the ground truth body weight. Even outliers of more than 30 percent occur. Therefore, taking an arbitrary frame from a person’s dataset will likely lead to a close to random result. Third, a clustering method is applied, so not only an arbitrary frame from a person’s dataset provides an estimation of the body weight. A Euclidean clustering method is applied to improve the outcome. The clustering is applied as follows: A dataset of a person consists out of N frames from the sensor . Every frame consists of a point cloud .
For every frame in the dataset estimate the body weight based on the calculated features .
Calculate the mean distance
for every estimation of a dataset
to all other estimations by
and store the calculated average distances in a vector
.
Sort the calculated distances in an ascending order .
Remove values with the highest distances. Keep a fixed amount of distances, e.g., 20 percent.
Calculate the centroid of the remaining estimations containing
estimations
which is the result of the body weight estimation based on a stream of data.
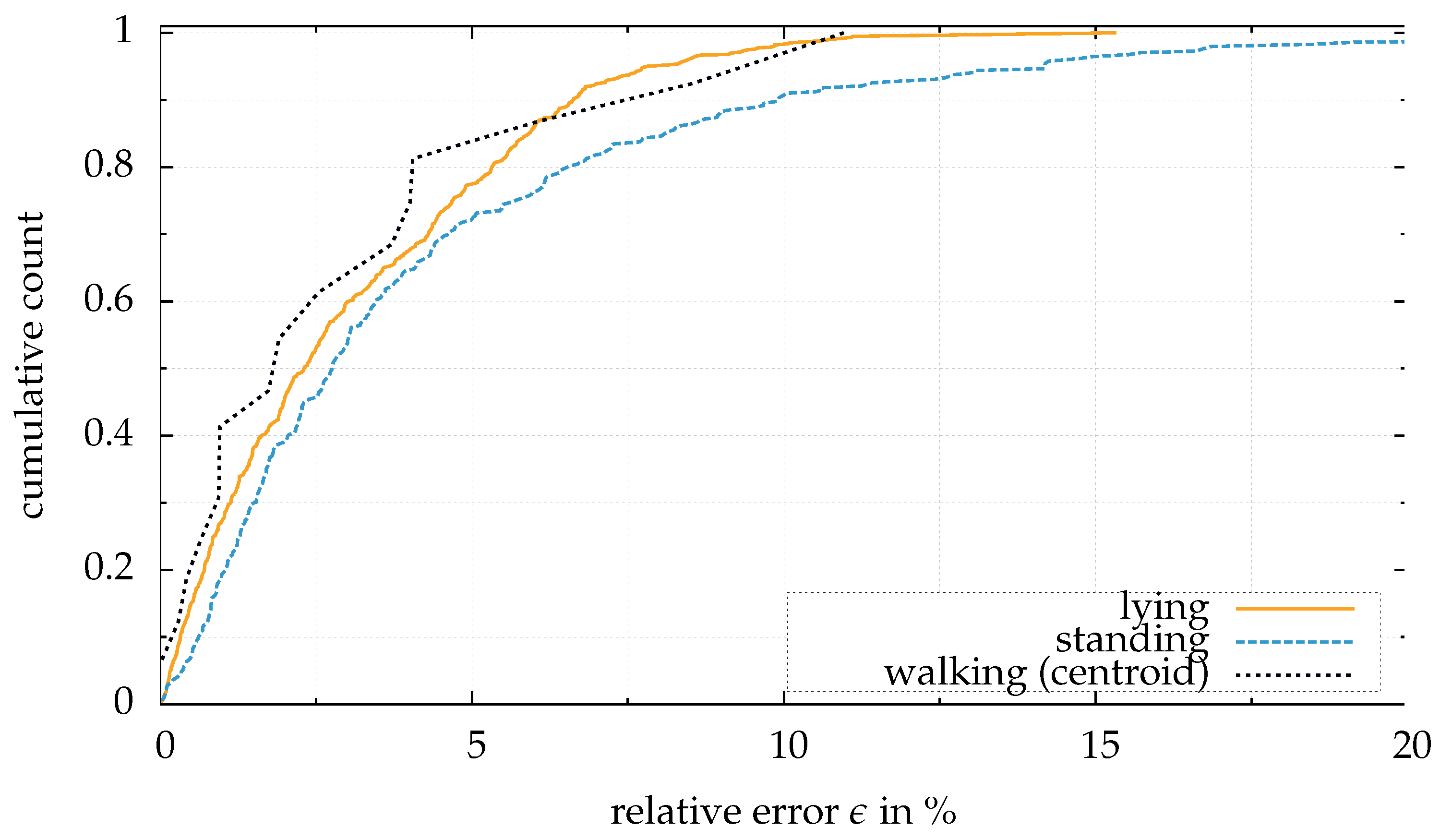
The principle in clustering is demonstrated in the upcoming section with experiments.