Computationally Efficient Automatic Coast Mode Target Tracking Based on Occlusion Awareness in Infrared Images
Abstract
:1. Introduction
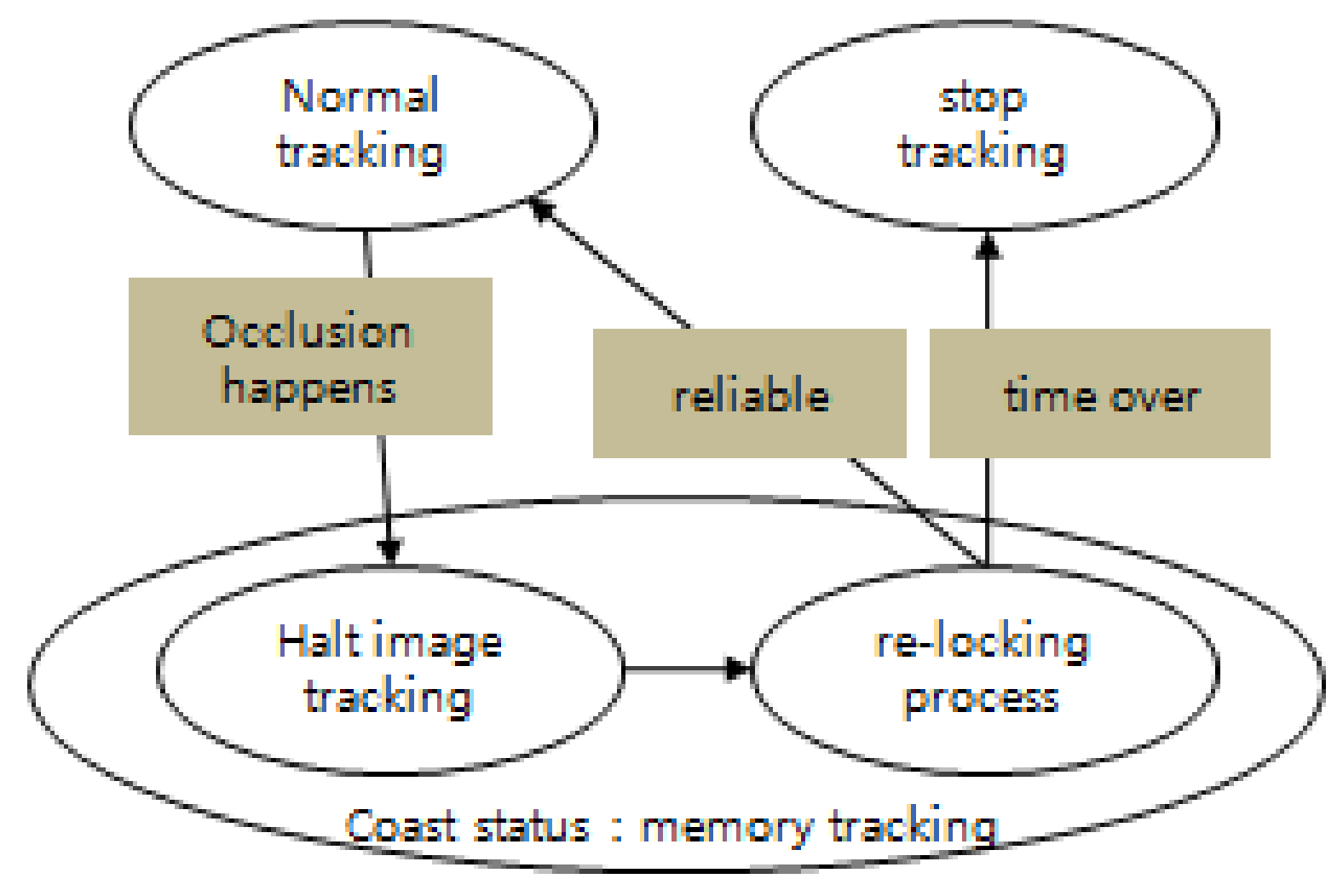
2. Background of Coast Mode Tracking
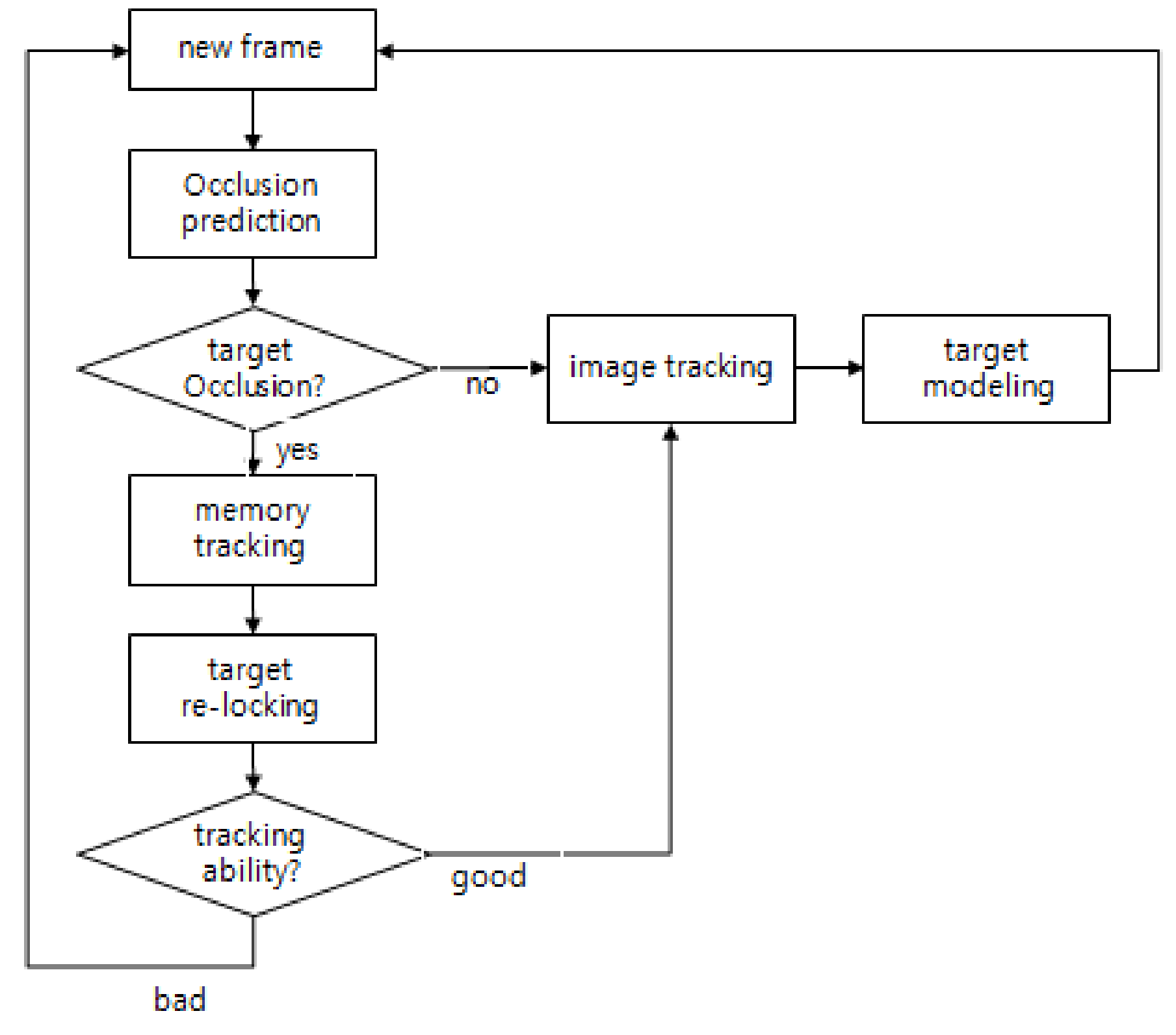
3. Proposed OA-CMT Based Infrared Target Tracker
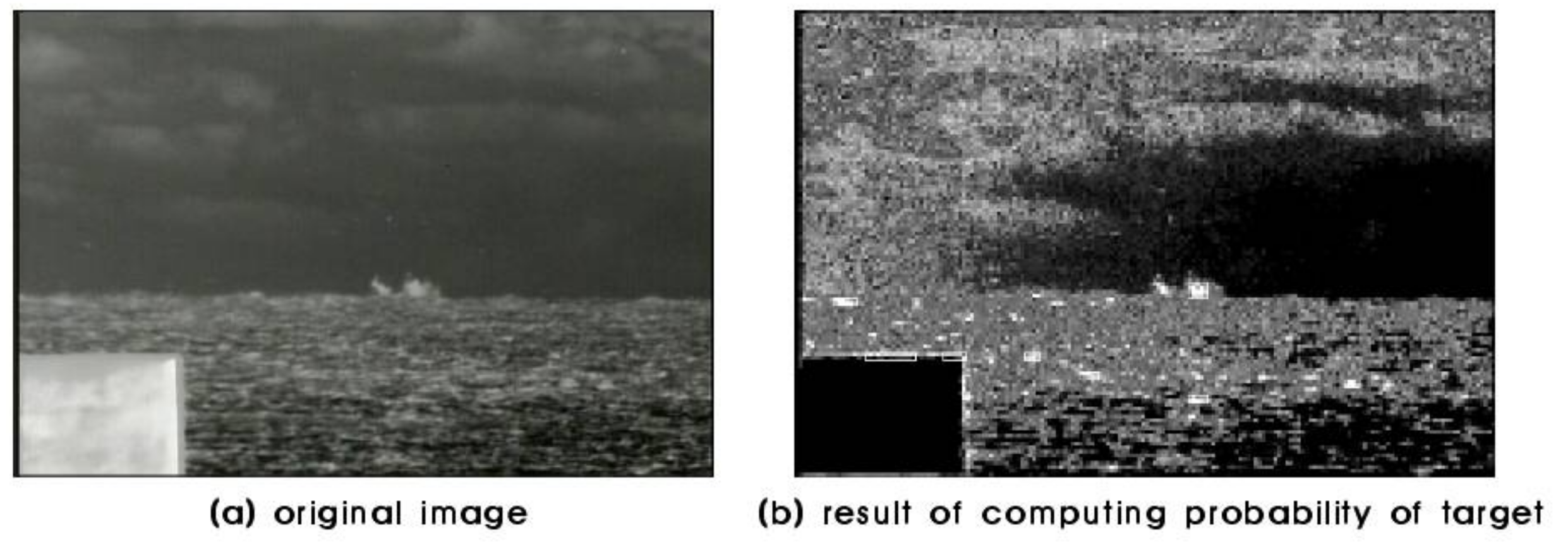
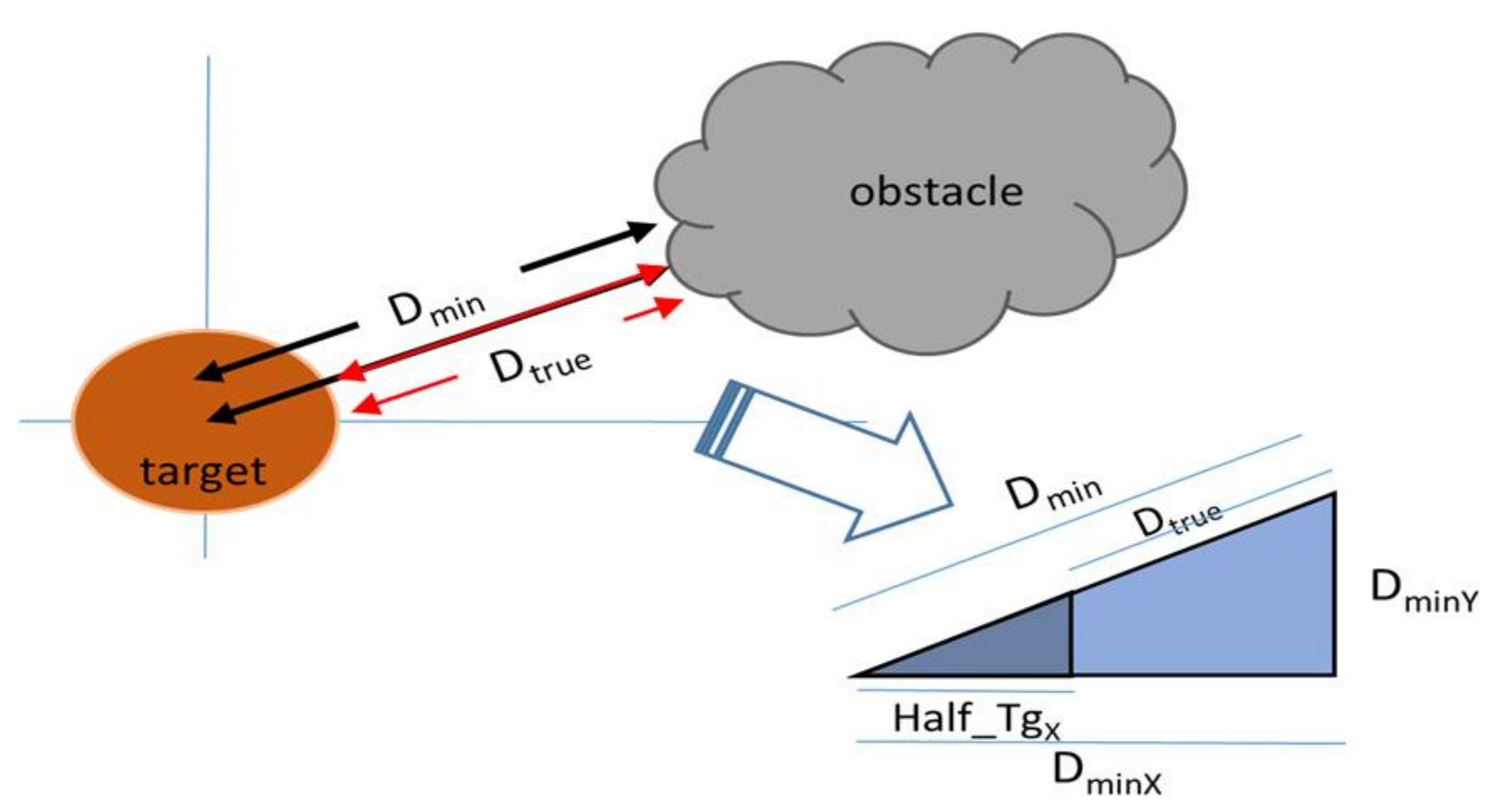
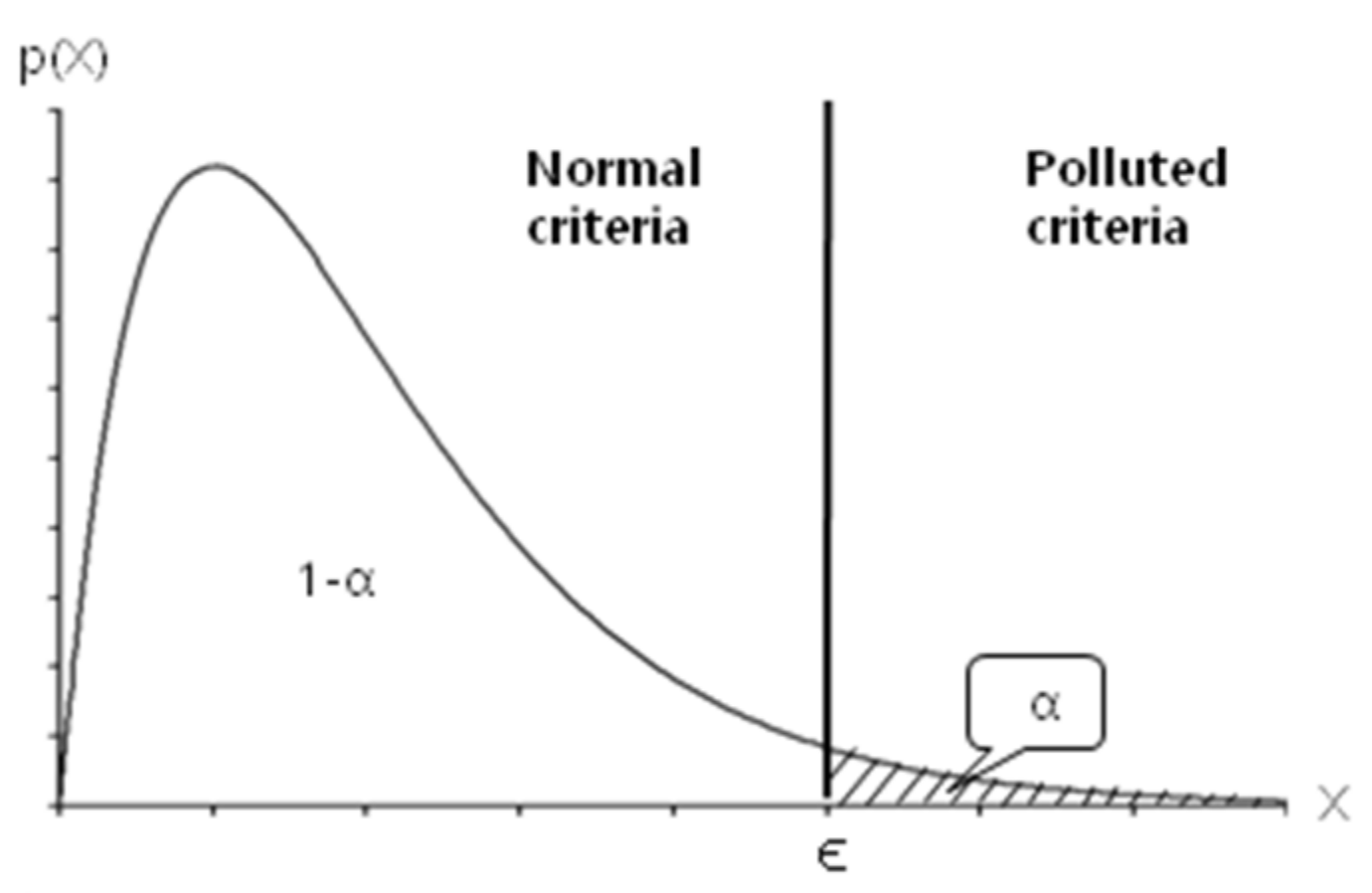
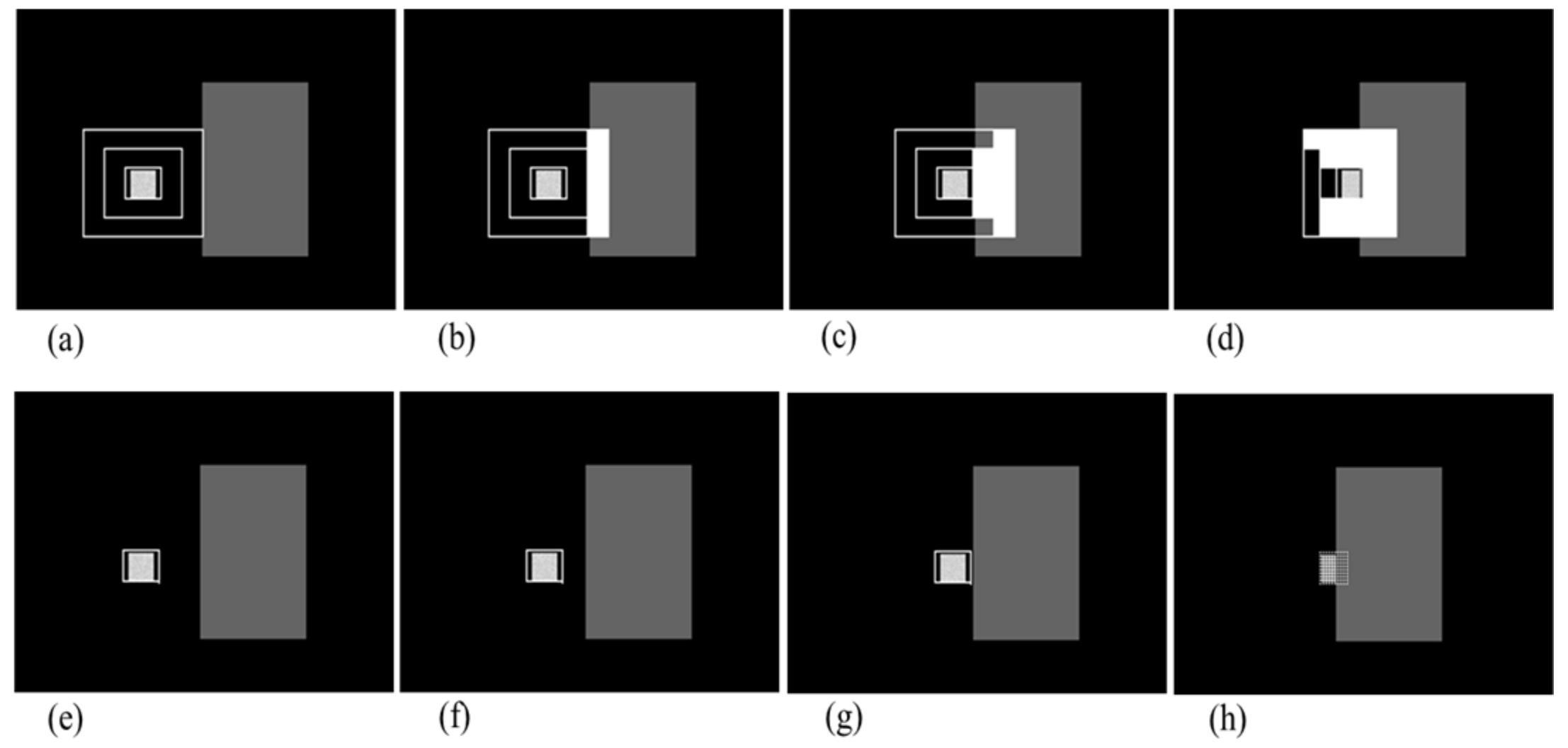
3.1. Prediction of Target’s Obstruction
3.2. Memory Tracking Using Tracking Filter
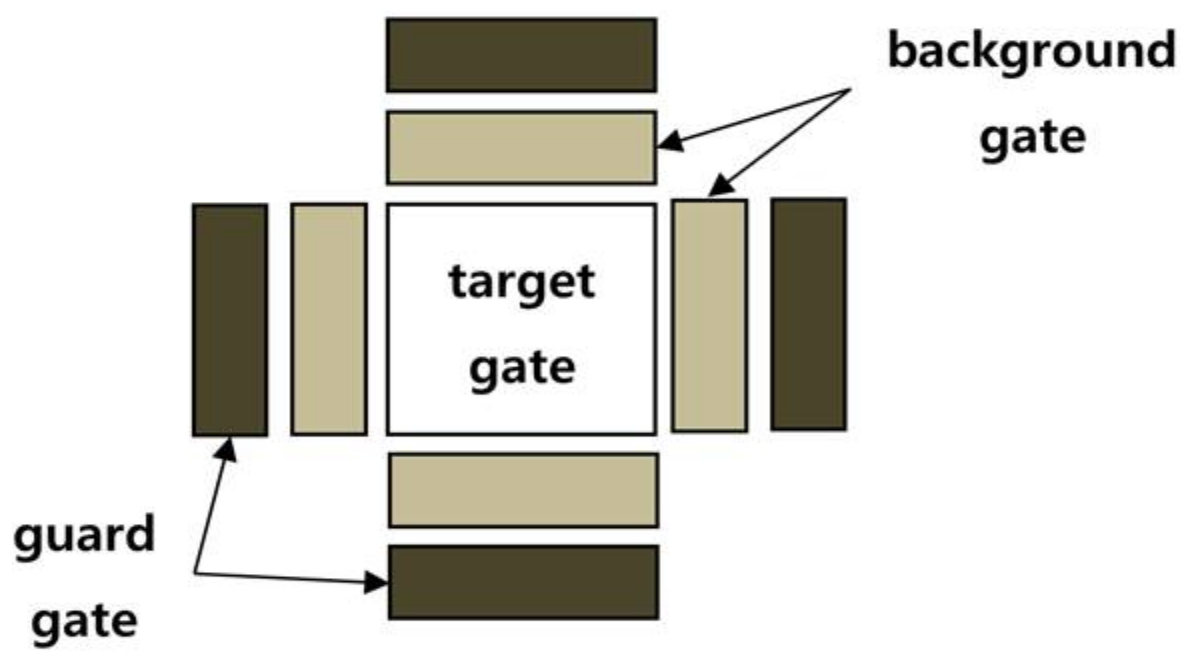
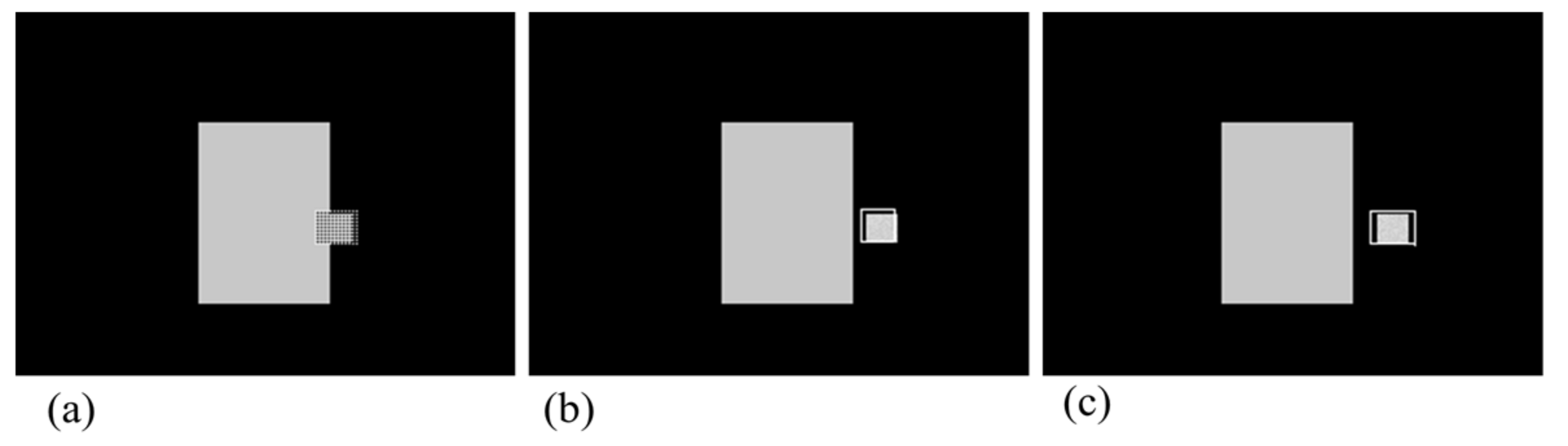
3.3. Target’s Re-Locking
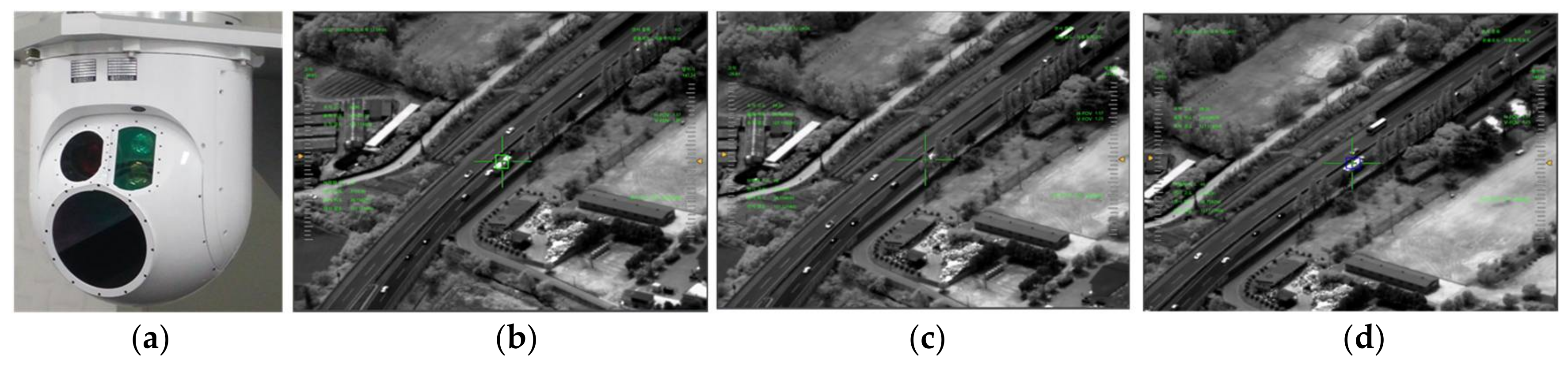
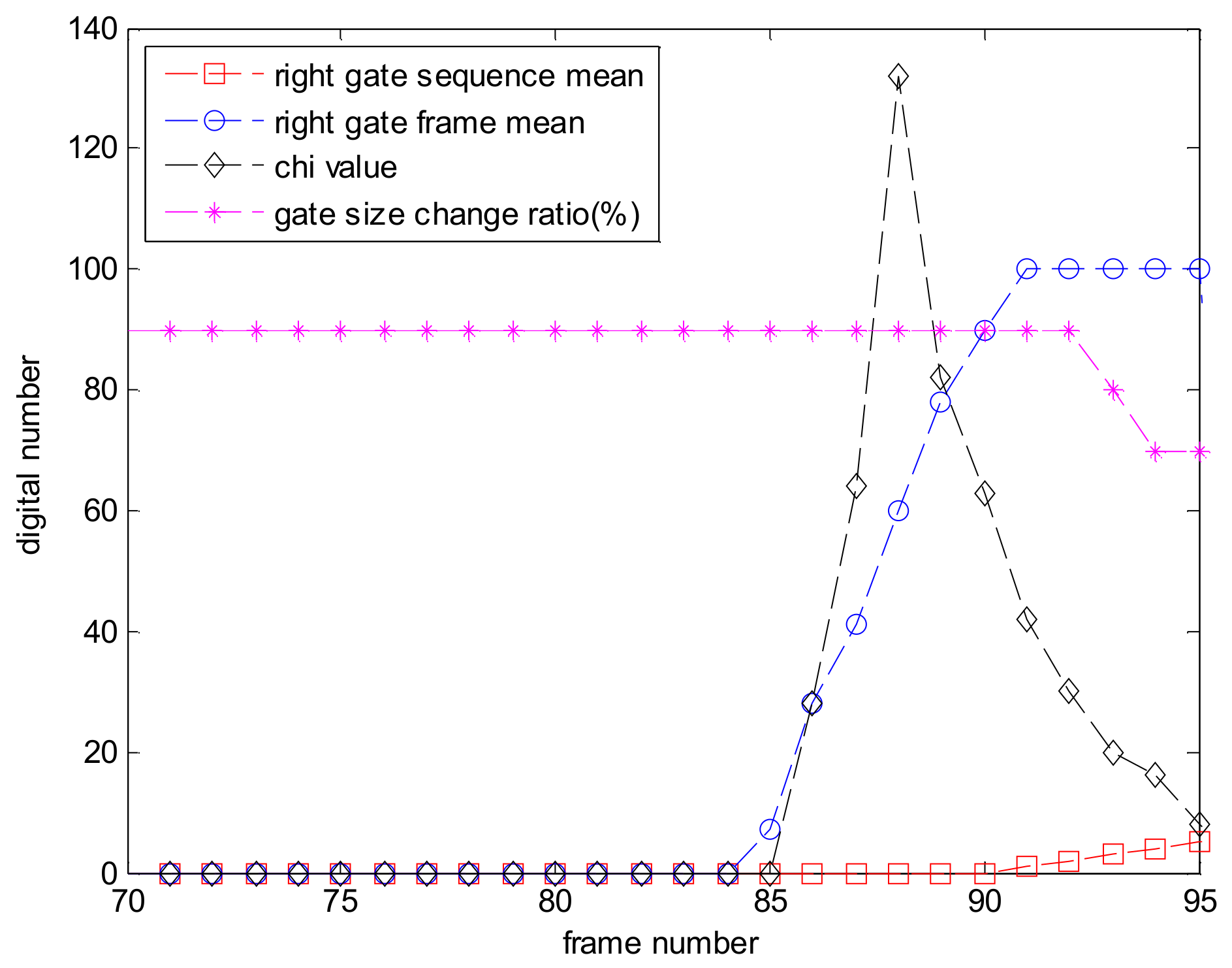
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Senior, A.; Hampapur, A.; Tian, Y.; Brown, L.; Pankanti, S.; Bolle, R. Appearance models for occlusion handling. Image Vis. Comput. 2006, 24, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Smeulders, A.W.M. Fast occluded object tracking by a robust appearance filter. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, Y.; Essa, I. Tracking multiple object through occlusions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Davis, L. On-line density-based appearance modeling for object tracking. In Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, A.; Fleet, D.; El-Maraghi, T. Robust online appearance models for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, D.; Lim, J.; Yang, M. Adaptive probabilistic visual tracking with incremental subspace update. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Jung, J.; Park, D.; Choi, B.; Choi, S. Automatic tracking system with target classification. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 April 2009; Volume 7335. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Hu, B. Robust Occlusion Handling in Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, T.; Gong, S.; Ong, E. Tracking multiple people under occlusion using multiple cameras. In Proceedings of the 11th British Machine Vision Conference, Bristol, UK, 11–14 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Dockstander, S.L.; Tekalp, A.M. Multiple camera fusion for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Workshop on Multi-Object Tracking, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8 July 2001; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Fleuret, F.; Berclaz, J.; Lengagne, R.; Fua, P. Multi-camera people tracking with a probabilistic occupancy map. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Shi, Q.; Shen, C.; Zhang, Y.; van den Hengel, A. Part-based visual tracking with online latent structural learning. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Wu, Y.; Hua, G. Spatial selection for attentional visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Jia, K.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ahuja, N. Partial occlusion handling for visual tracking via robust part matching. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Isard, M.; Blake, A. Condensation-Conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1998, 29, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isard, M.; Blake, A. Contour tracking by stochastic propagation of conditional density. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Computer Vision, Cambridge, UK, 15–18 April 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, A.; Freitas, N.; Gordon, N. Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.-H. Robust object tracking via sparsity-based collaborative model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, X.; Ling, G.; Wu, Y.; Blasch, E.; Bai, L. Minimum error bounded efficient L1 tracker with occlusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, X.; Blasch, E.P. Efficient minimum error bounded particle resampling L1 tracker with occlusion detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 2661–2675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Luan, S.; Chen, C.; Han, J.; Wang, W.; Perina, A.; Sha, L. Latent constrained correlation filter. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, D.; Thrun, S.; Savarese, S. Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sadeghian, A.; Alahi, A.; Savarese, S. Tracking the untrackable: Learning to track multiple cues with long-term dependencies. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; You, T.; Kwak, S.; Han, B. Online tracking by learning discriminative saliency map with convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Jang, G.; Kwon, K.H.; Jung, J.H. Design of autocoast tracking algorithm by the prediction of target occlusion and its on-based implementation. J. Korea Inst. Mil. Sci. Technol. 2009, 12, 354–359. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Jang, G. Decision method of tracking possibility under the firing flame influence in IR image. In Proceedings of the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea Fall Conference, Daejeon, Korea, 26–27 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Li, X.R.; Kirubarajan, T. Estimation with Applications to Tracking and Navigation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, F.; Gunnarsson, F.; Bergman, N.; Forssell, U.; Jansson, J.; Karlsson, R.; Nordlund, P.-J. Particle filters for positioning, navigation and tracking. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2002, 50, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalata, P.R. A generalized parameter for α-β and α-β-γ target trackers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1984, AES-20, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, W.H.; Jeong, D.S. Object tracking method using back projection of multiple color histogram models. Circuits Syst. 2003, 2, 668–671. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J. Design of re-locking algorithm using target modeling of histogram ratio during coast tracking mode in infrared image. In Proceedings of the Unmanned/Unattended Sensors and Sensor Networks IX, Edinburgh, UK, 24–27 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Mao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Ship target detection and tracking in cluttered infrared imagery. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 057207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalal, Z.; Matas, J.; Mikolajczyk, K. P-N Learning: Bootstrapping Binary Classifiers by Structural Constraints. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]







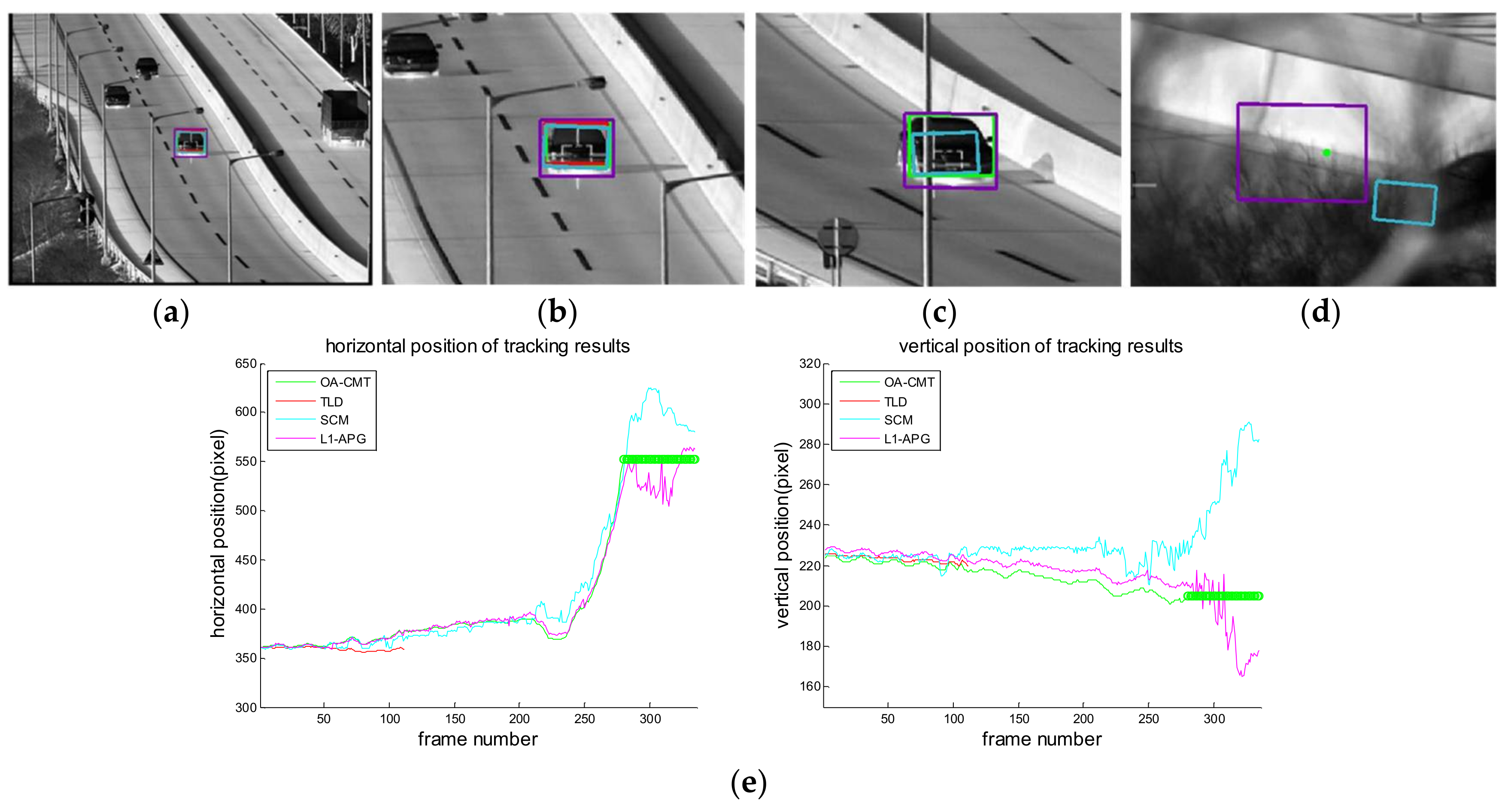




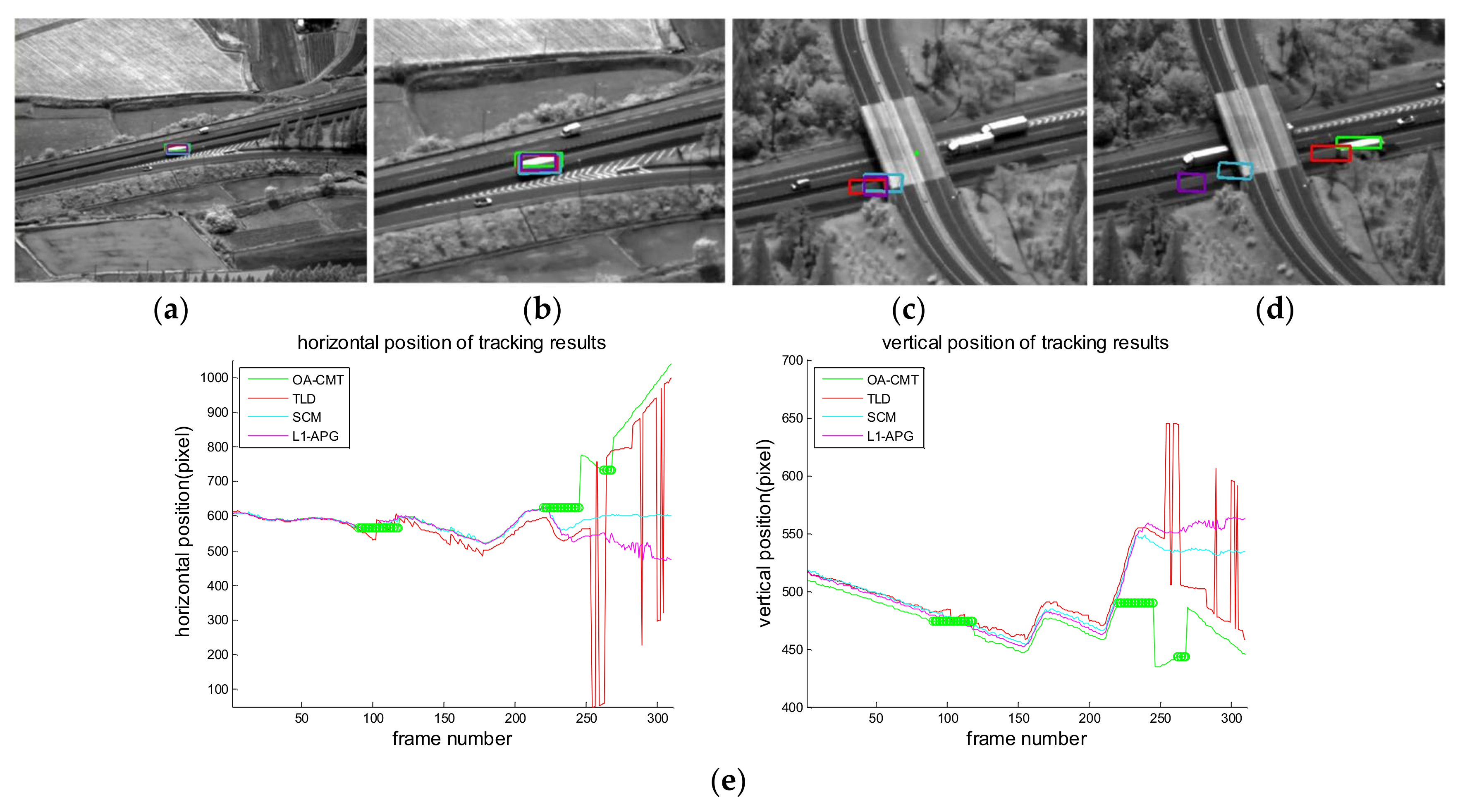
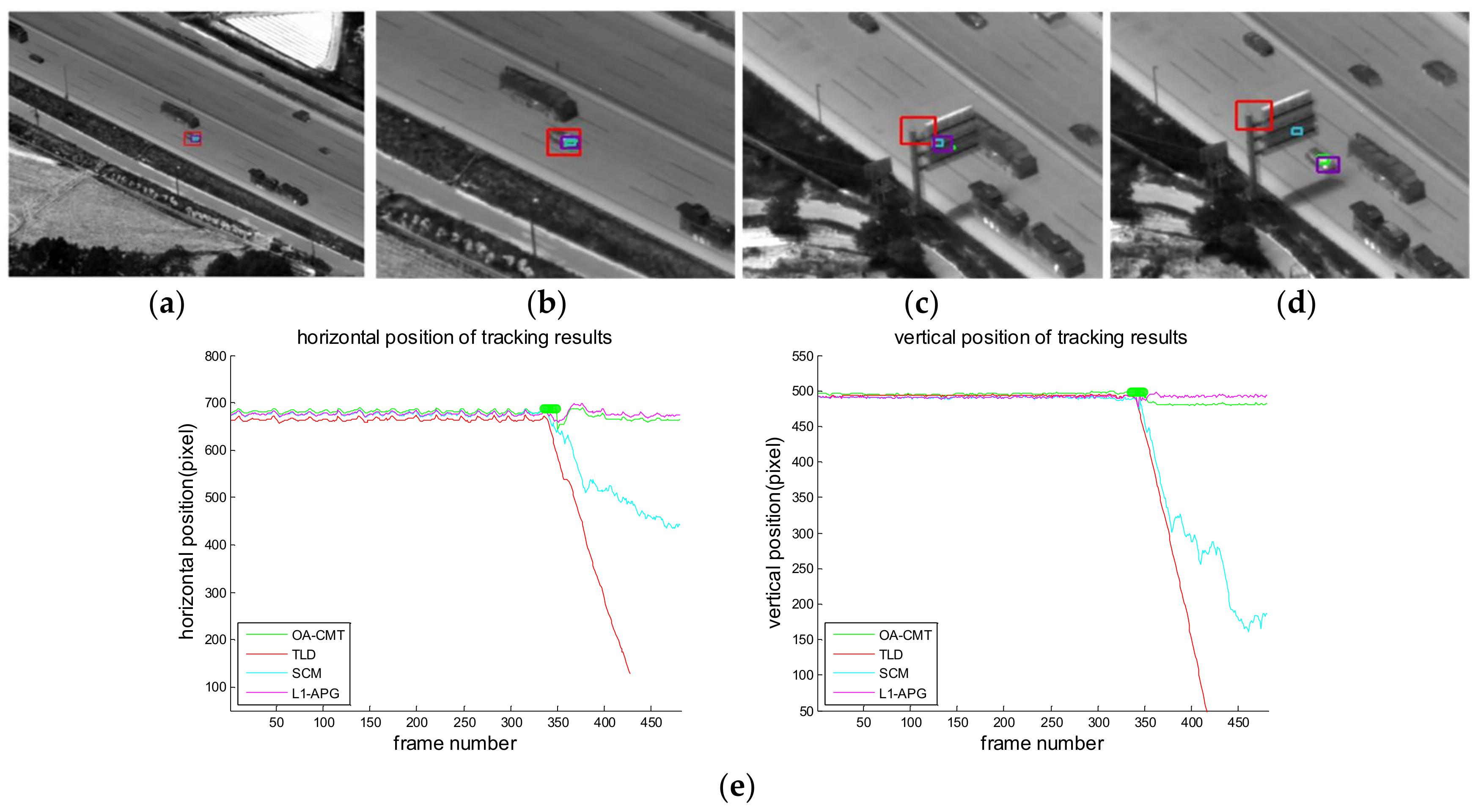
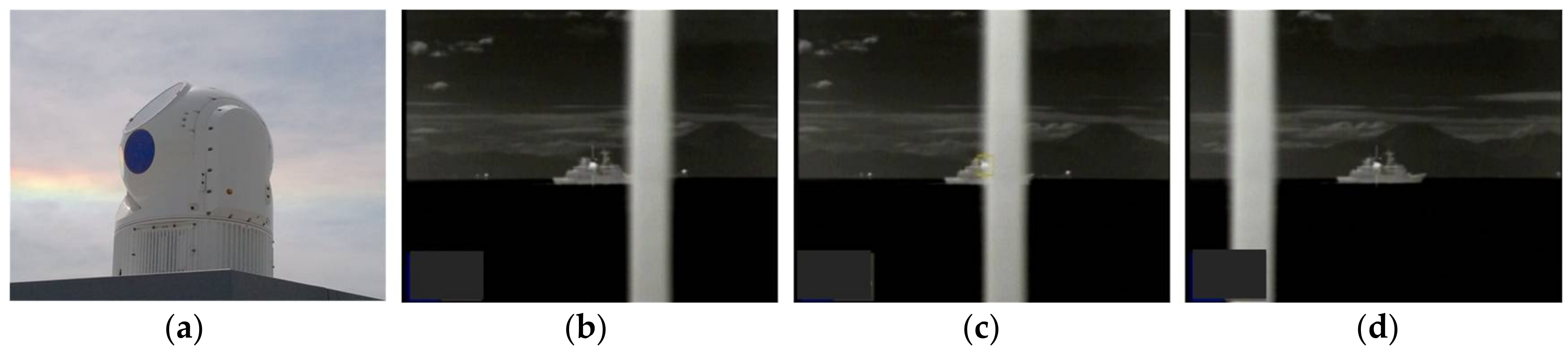

| ID | Imagery Sequences | Sensor | Obstacle Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | IR | Background screening | Car screened by bush |
| 2 |  | IR | Background screening | Truck screened by street lamp & trees |
| 3 |  | IR | Target likelihood obstacle | Tank screened by human |
| 4 |  | IR | Background screening | Car screened by building |
| 5 |  | EO | Background obstacle | Car screened by trees |
| 6 |  | EO | Background screening | Bus screened by trees & bridge |
| 7 |  | IR | Target likelihood obstacle | Car screened by traffic sign |
| ID | Image Size | Target Size | Frames Per Second | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLD | L1-APG | SCM | OA-CMT (Proposed) | |||
| 1 | 720 × 480(336 frames) | 56 × 48 | 7.05 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 42 |
| 2 | 720 × 480(831 frames) | 28 × 24 | 6.39 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 30.81 |
| 3 | 640 × 480(130 frames) | 36 × 14 | 3.88 | 2.54 | 2.89 | 71.5 |
| 4 | 640 × 480(283 frames) | 10 × 8 | 10.5 | 3.42 | 1.48 | 71 |
| 5 | 320 × 240(300 frames) | 90 × 40 | 9.87 | 2.92 | 2.18 | 149.5 |
| 6 | 1280 × 1024(310 frames) | 94 × 26 | 2.13 | 2.64 | 1.18 | 6.6 |
| 7 | 1280 × 1024(480 frames) | 24 × 16 | 1.37 | 0.3 | 1.43 | 6.67 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.; Jang, G.-I.; Kim, S.; Kim, J. Computationally Efficient Automatic Coast Mode Target Tracking Based on Occlusion Awareness in Infrared Images. Sensors 2018, 18, 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040996
Kim S, Jang G-I, Kim S, Kim J. Computationally Efficient Automatic Coast Mode Target Tracking Based on Occlusion Awareness in Infrared Images. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040996
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sohyun, Gwang-Il Jang, Sungho Kim, and Junmo Kim. 2018. "Computationally Efficient Automatic Coast Mode Target Tracking Based on Occlusion Awareness in Infrared Images" Sensors 18, no. 4: 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040996
APA StyleKim, S., Jang, G.-I., Kim, S., & Kim, J. (2018). Computationally Efficient Automatic Coast Mode Target Tracking Based on Occlusion Awareness in Infrared Images. Sensors, 18(4), 996. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18040996






