Joint Center Estimation Using Single-Frame Optimization: Part 1: Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Equations of Motion
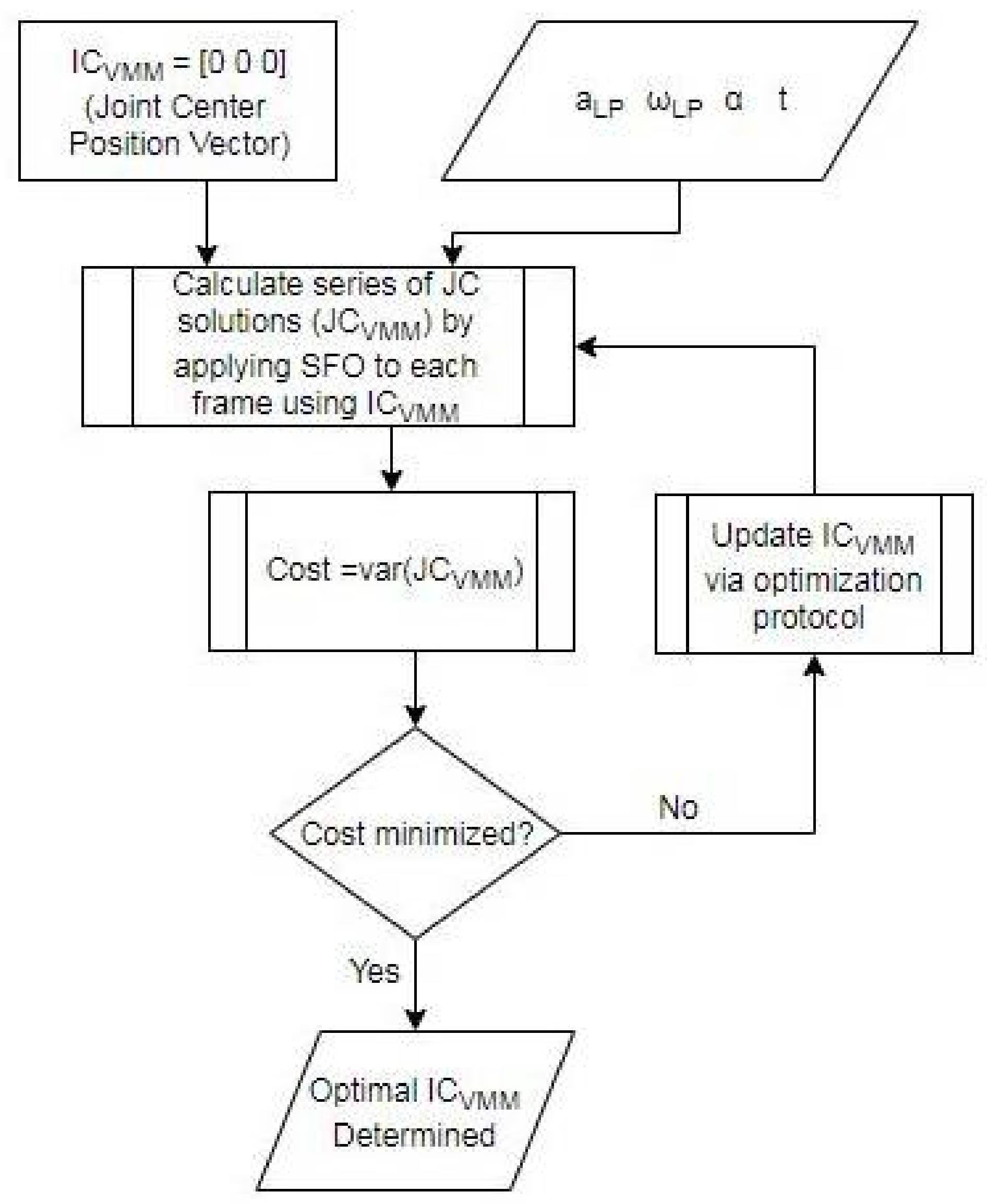
2.2. Spanned Single-Frame Optimization
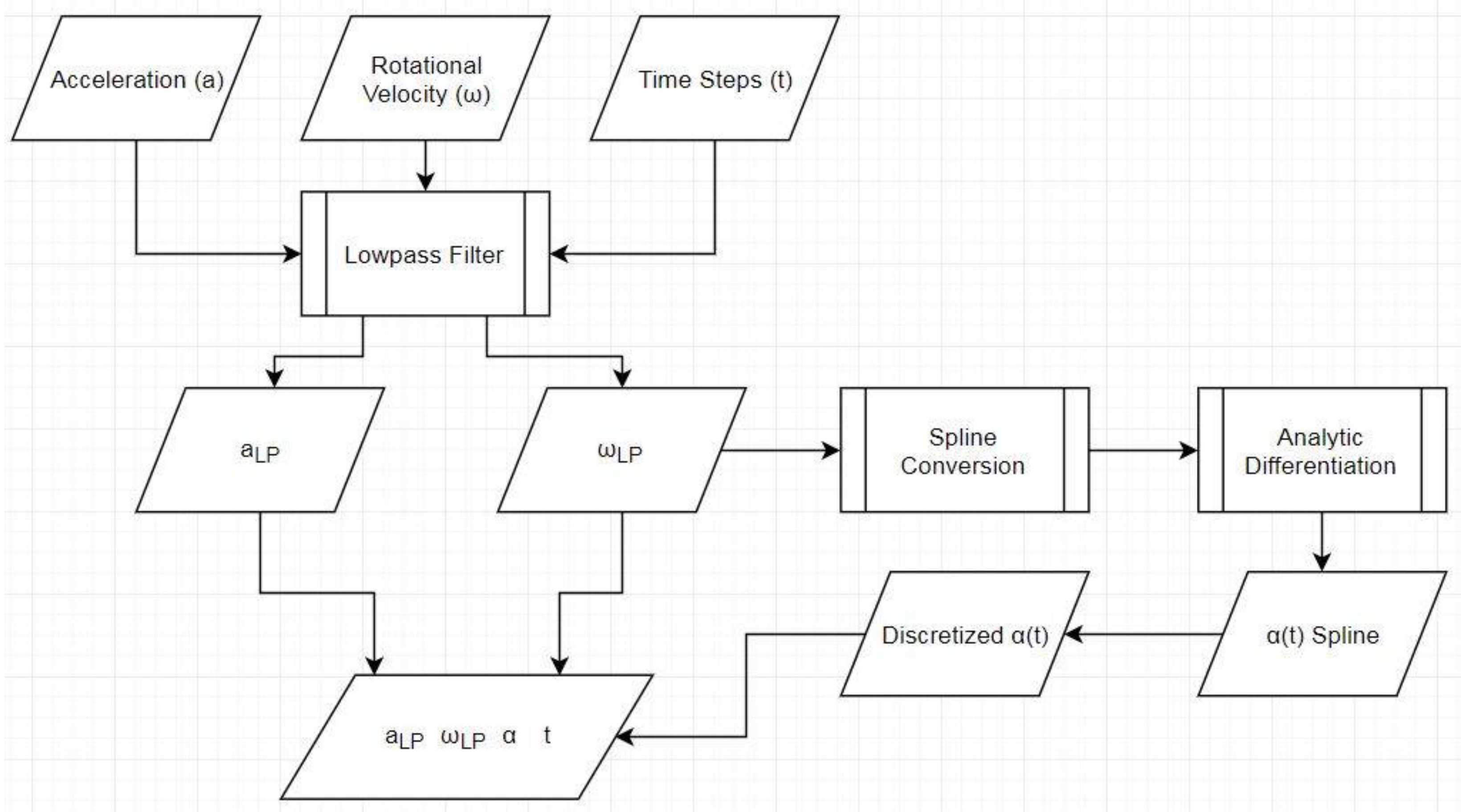
2.3. Data Preparation
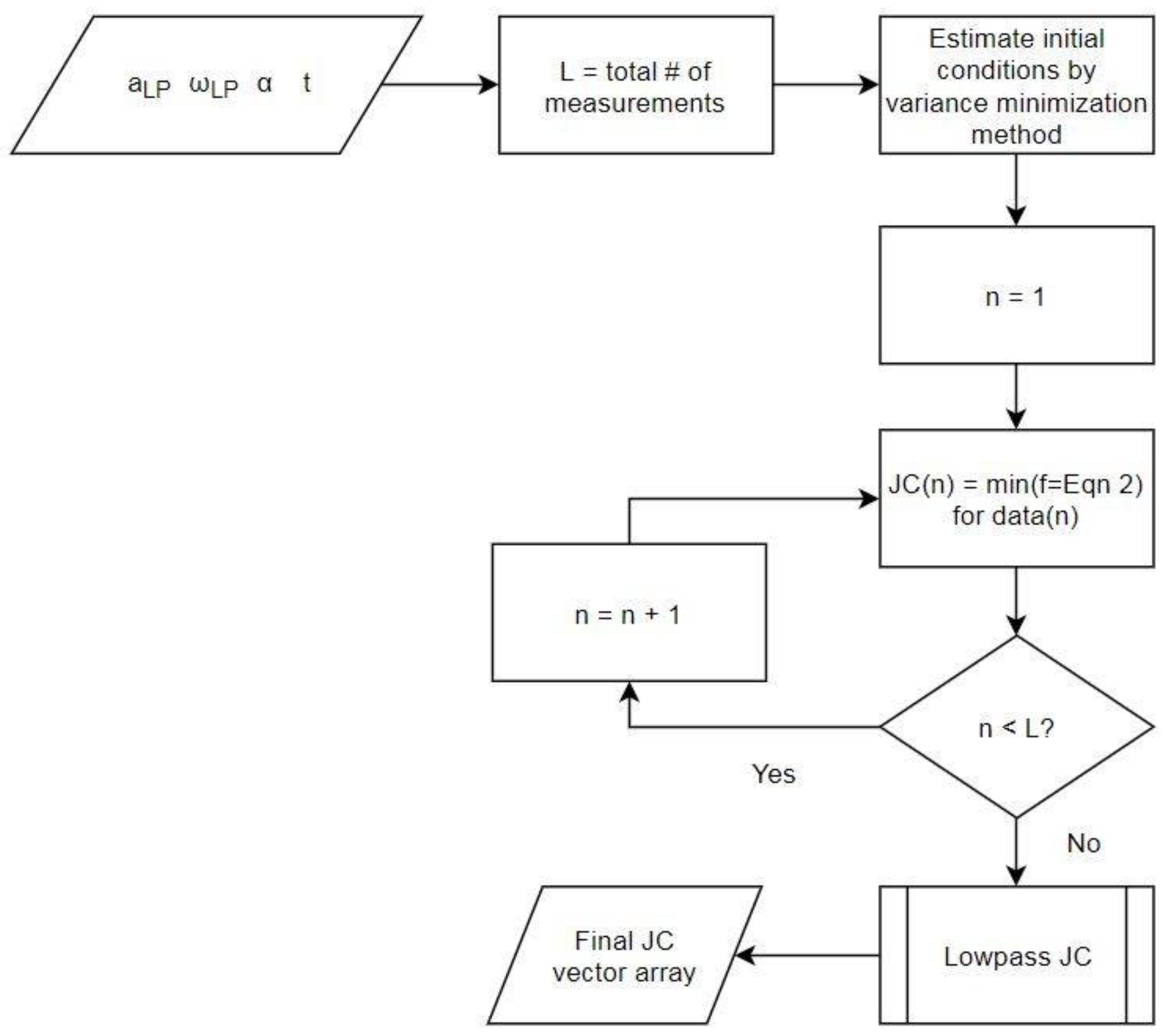
2.4. Variance Minimization Method
2.5. Comparator for SFO Validation
2.6. Numerical Examples
- Rigid link with added noise (control simulation)
- Rigid link with added noise and spring motion
- Rigid link with added noise and relative rotation
- Rigid link with added noise, spring motion, and relative rotation
- Rigid link with added noise, multimodal spring motion, and multimodal relative rotation
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Interpreting SFO Results
4.2. Comparison with SOM
4.3. Assumptions and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barris, S.; Button, C. A review of vision-based motion analysis in sport. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmatalla, S.; Xia, T.; Contratto, M.; Kopp, G.; Wilder, D.; Frey-Law, L.; Ankrum, J. 3D motion capture protocol for seated operators in whole body vibration. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2008, 38, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manal, K.; McClay, D.; Galinat, B.; Stanhope, S. The accuracy of estimating proximal tibial translation during natural cadence walking: Bone vs. skin mounted target. Clin. Biomech. 2003, 18, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, D. On simulating human reach motions for ergonomics analyses. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. 2002, 12, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, C.E.; Babcock, J.H.; Forrest, J.H.; Stuart, C.M.; Tonnemacher, M.J.; Wang, W.-S. Multiple User Motion Capture and Systems Engineering. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Systems and Information, Engineering Design Symposium, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 29 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kadaba, M.P.; Ramakrishnan, H.K.; Wootten, M.E. Measurement of lower extremity kinematics during level walking. J. Orthop. Res. 1990, 8, 8383–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.B., III; Ounpuu, S.; Tyburski, D.; Gage, J.R. A gait analysis data collection and reduction technique. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1991, 10, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrig, R.M.; Taylor, W.R.; Duda, G.N.; Heller, M.O. A survey of formal methods for determining the centre of rotation of ball joints. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2798–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrig, R.M.; Taylor, W.R.; Duda, G.N.; Heller, M.O. A survey of formal methods for determining functional joint axes. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kainz, H.; Carty, C.P.; Modenese, L.; Boyd, R.N.; Lloyd, D.G. Estimation of the hip joint centre in human motion analysis: A systematic review. Clin. Biomech. 2015, 30, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Siegler, S.; Allard, P.; Kirtley, C.; Leardini, A.; Rosenbaum, D.; Whittle, M.; D’Lima, D.D.; Cristofolini, L.; Witte, H. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate system of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion—Part I: Ankle, hip, and spine, Letter to the editor. J. Biomech. 2001, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besier, T.F.; Sturnieks, D.L.; Alderson, J.A.; Lloyd, D.G. Repeatability of gait data using a functional hip joint centre and a mean helical knee axis. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, M.E.; Zavatsky, A.B.; Lawson, S.E.; Yuan, Z.; Theologis, T.N. Prediction of the hip joint centre in adults, children, and patients with cerebral palsy based on magnetic resonance imaging. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, P.; Bégin, M.A.; Schauer, T.; Seel, T. Alignment-free, self-calibrating elbow angles measurement using inertial sensors. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidig, D.; Müller, P.; Seel, T. Automatic anatomical calibration for IMU-based elbow angle measurement in disturbed magnetic fields. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 3, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentino, N.M.; Atkins, P.R.; Kutschke, M.J.; Goebel, J.M.; Foreman, K.B.; Anderson, A.E. Soft tissue artifact causes significant errors in the calculation of joint angles and range of motion at the hip. Gait Posture 2017, 55, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barré, A.; Jolles, B.M.; Theumann, N.; Aminian, K. Soft tissue artifact distribution on lower limbs during treadmill gait: Influence of skin markers’ location on cluster design. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1965–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaim, A.; Moissenet, F.; Duprey, S.; Begon, M.; Chèze, L. Effect of various upper limb multibody models on soft tissue artefact correction: A case study. J. Biomech. 2017, 62, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.S.; Damsgaard, M.; Rasmussen, J.; Ramsey, D.K.; Benoit, D.L. A linear soft tissue artefact model for human movement analysis: Proof of concept using in vivo data. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, D.L.; Damsgaard, M.; Andersen, M.S. Surface marker cluster translation, rotation, scaling and deformation: Their contribution to soft tissue artefact and impact on knee joint kinematics. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 2124–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, R.; Camomilla, V.; Bonci, T.; Chèze, L.; Cappozzo, A. What portion of the soft tissue artefact requires compensation when estimating joint kinematics? J. Biomech. Eng. 2015, 137, 064502-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camomilla, V.; Bonci, T.; Dumas, R.; Chèze, L.; Cappozzo, A. A model of the soft tissue artefact rigid component. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barré, A.; Aissaoui, R.; Aminian, K.; Dumas, R. Assessment of the lower limb soft tissue artefact at marker-cluster level with a high-density marker set during walking. J. Biomech. 2017, 62, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapron, A.L.; Aoki, S.K.; Peters, C.L.; Maas, S.A.; Bey, M.J.; Zauel, R.; Anderson, A.E. Accuracy and feasibility of dual fluoroscopy and model-based tracking to quantify in vivo hip kinematics during clinical exams. J. Appl. Biomech. 2014, 30, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarshahi, M.; Schache, A.G.; Fernandez, J.W.; Baker, R.; Banks, S.; Pandy, M.G. Non-invasive assessment of soft-tissue artifact and its effect on knee joint. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, D.T.-P.; Chan, Y.-Y. The use of wearable inertial motion sensors in human lower limb biomechanics studies: A systematic revie. Sensors 2010, 10, 11556–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippeschi, A.; Schmitz, N.; Miezal, M.; Bleser, G.; Ruffaldi, E.; Stricker, D. Survey of motion tracking methods based on inertial sensors: A focus on upper limb human motion. Sensors 2017, 17, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seel, T.; Raisch, J.; Schauer, T. IMU-based joint angle measurement for gait analysis. Sensors 2014, 14, 6891–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner-Cordero, A.; Mateu-Arce, M.; Forner-Cordero, I.; Alcantara, E.; Moreno, J.C.; Pons, J.L. Study of the motion artefacts of skin-mounted inertial sensors under different attachment conditions. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, N21–N31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Liu, T.; Zheng, R.; Feng, H. Gait analysis using wearable sensors. Sensors 2012, 12, 2255–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seel, T.; Schauer, T.; Raisch, J. Joint Axis and Position Estimation from Inertial Measurement Data by Exploiting Kinematic Constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control Applications (CCA), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 3–5 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis, R.S.; Perkins, N.C. Inertial sensor based method for identifying spherical joint center of rotation. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2546–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MATLAB and Optimization Toolbox Release 2016a (R2016a); The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2016.
- Bellusci, G.; Dijkstra, F.; Slycke, P. Xsens MTw: Miniature Wireless Inertial Motion Tracker for Highly Accurate 3D Kinematic Applications; Xsens Technologies: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Hill, J.O. A method for measuring mechanical work and work efficiency during human activities. J. Biomech. 1993, 26, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathie, M.J.; Coster, A.C.F.; Lovell, N.H.; Celler, B.G. Accelerometry: Providing an integrated, practical method for long-term, ambulatory monitoring of human movement. Physiol. Meas. 2004, 25, R1–R20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.A.; Sidwall, H.G.; Hobson, D.A. Measurement and reduction of noise in kinematics of locomotion. J. Biomech. 1974, 7, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappozzo, A. Low frequency self-generated vibration during ambulation in normal men. J. Biomech. 1982, 15, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



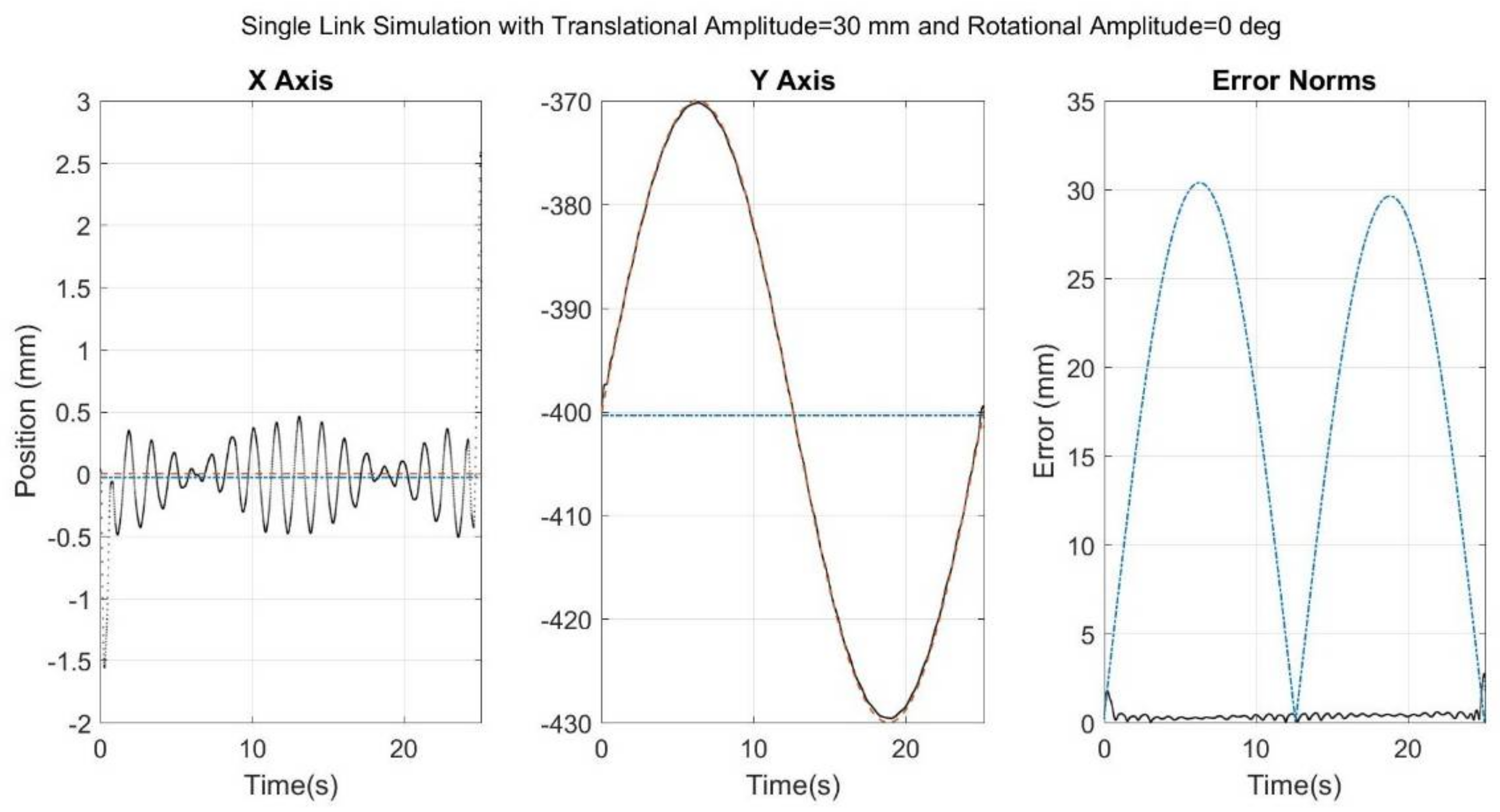




| Simulated Case | SFO | SOM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude (mm) | Rotation (°) | RMSE (mm) | RMSE (mm) | |||
| Case 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | - | 0.00 | 0.10 |
| Case 2 | 30 | 0 | 0.474 | - | 1.00 | 21.22 |
| Case 3 | 0 | 5 | 7.80 | 0.97 | 0.33 | 24.70 |
| Case 4 | 30 | 5 | 7.83 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 32.53 |
| Case 5 | Multimodal * | Multimodal ** | 7.53 | 0.825 | 0.90 | 13.85 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frick, E.; Rahmatalla, S. Joint Center Estimation Using Single-Frame Optimization: Part 1: Numerical Simulation. Sensors 2018, 18, 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041089
Frick E, Rahmatalla S. Joint Center Estimation Using Single-Frame Optimization: Part 1: Numerical Simulation. Sensors. 2018; 18(4):1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041089
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrick, Eric, and Salam Rahmatalla. 2018. "Joint Center Estimation Using Single-Frame Optimization: Part 1: Numerical Simulation" Sensors 18, no. 4: 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041089
APA StyleFrick, E., & Rahmatalla, S. (2018). Joint Center Estimation Using Single-Frame Optimization: Part 1: Numerical Simulation. Sensors, 18(4), 1089. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18041089





