Fabrications and Performance of Wireless LC Pressure Sensors through LTCC Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
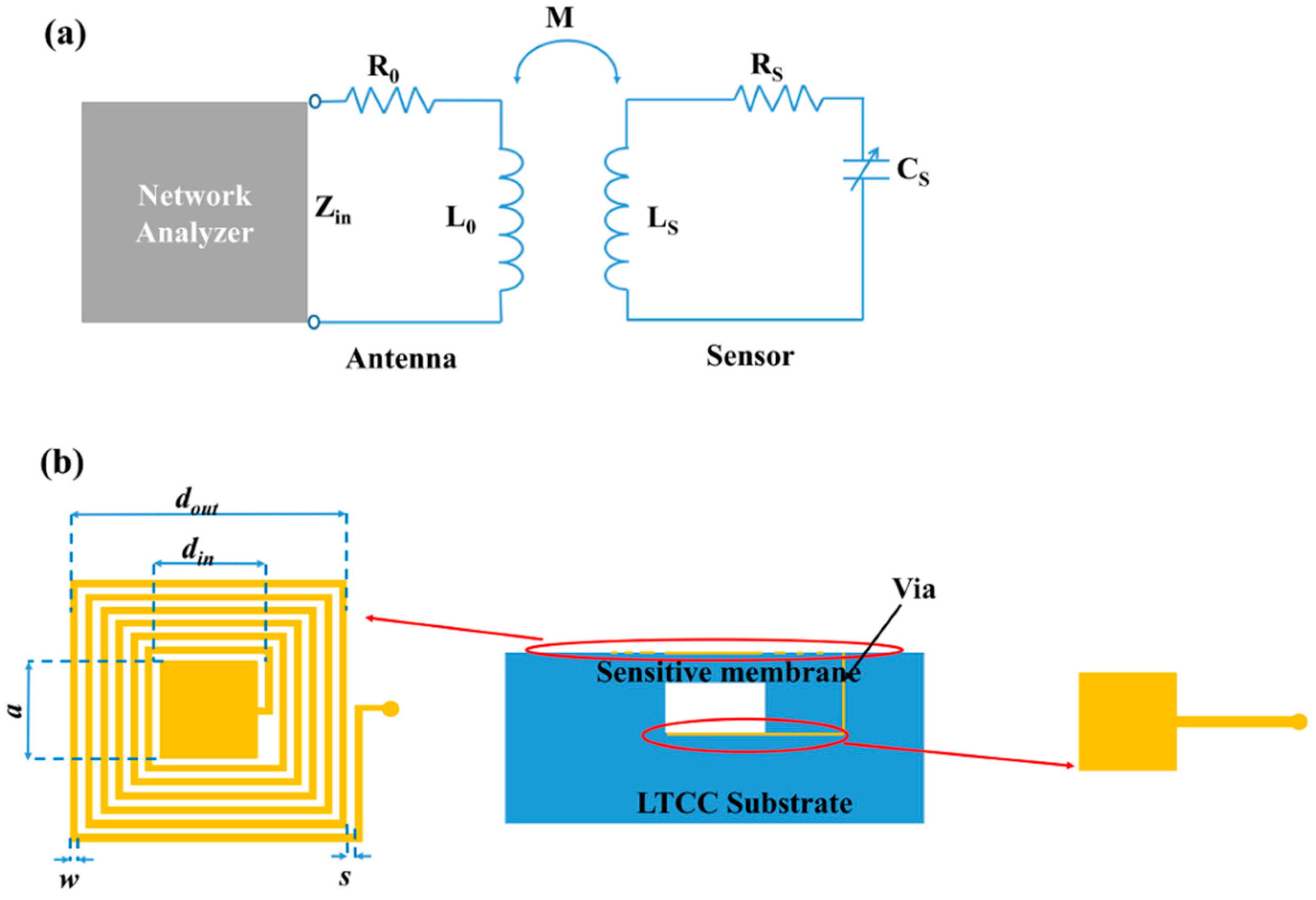
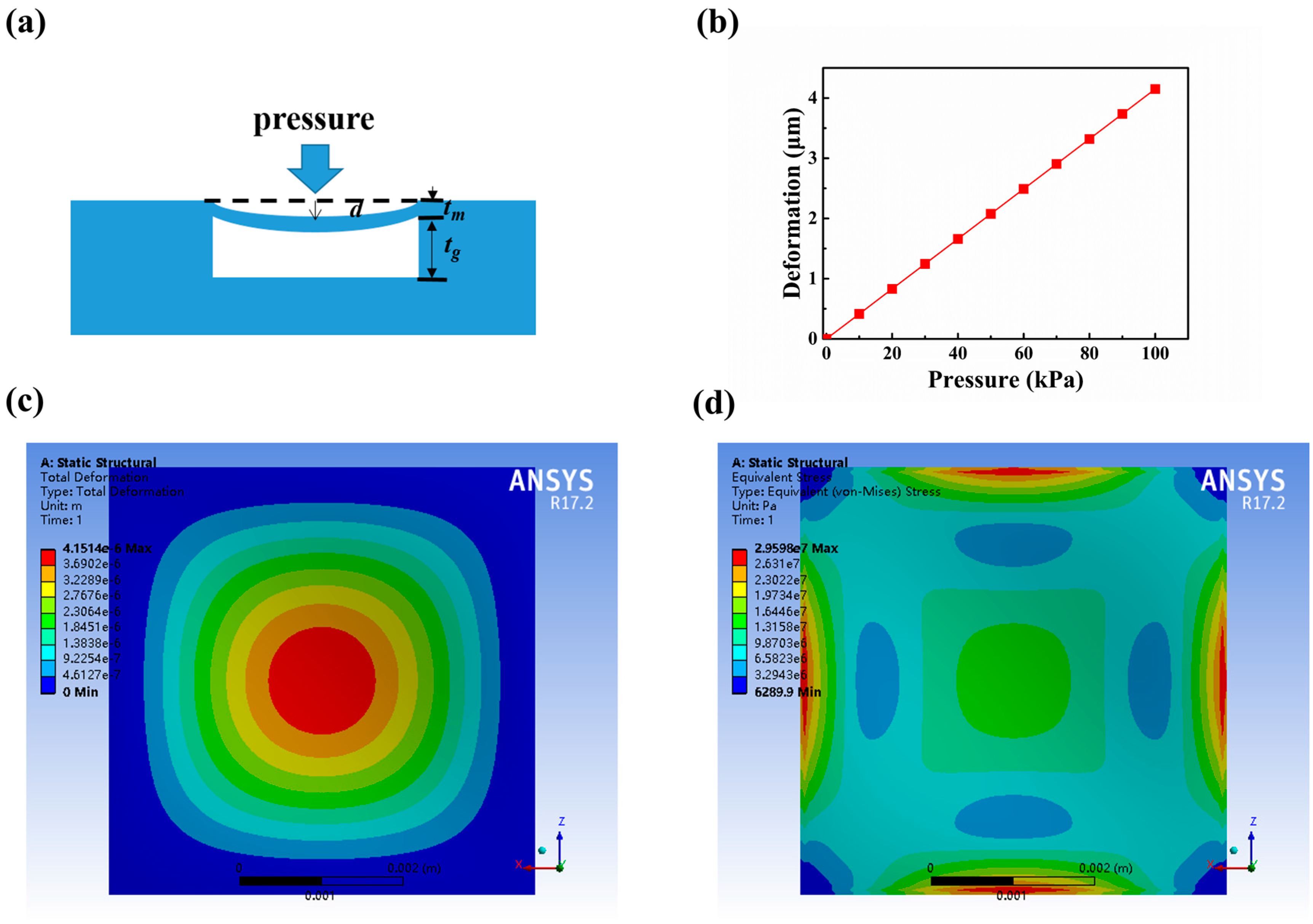
2. Sensor Design
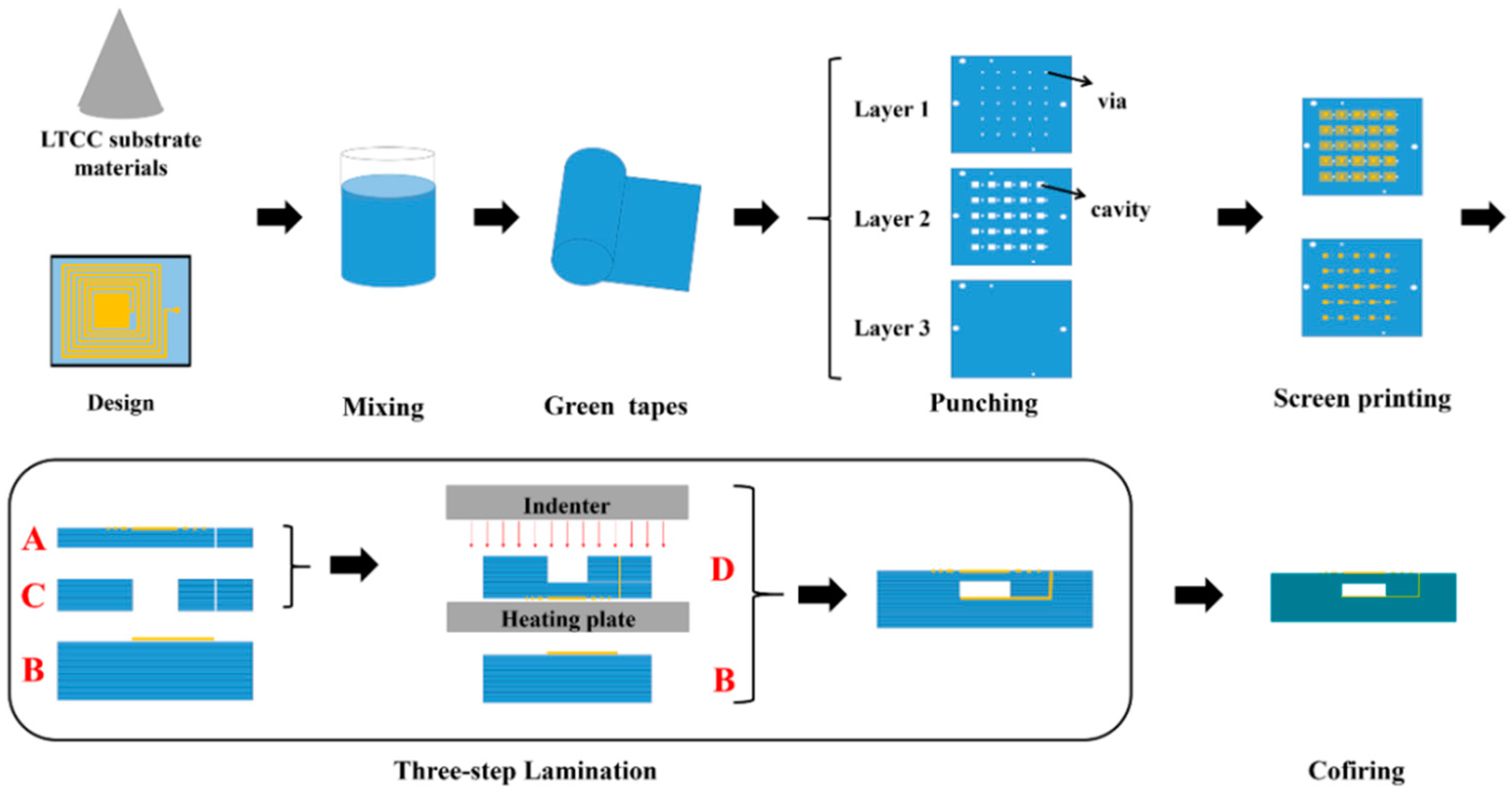
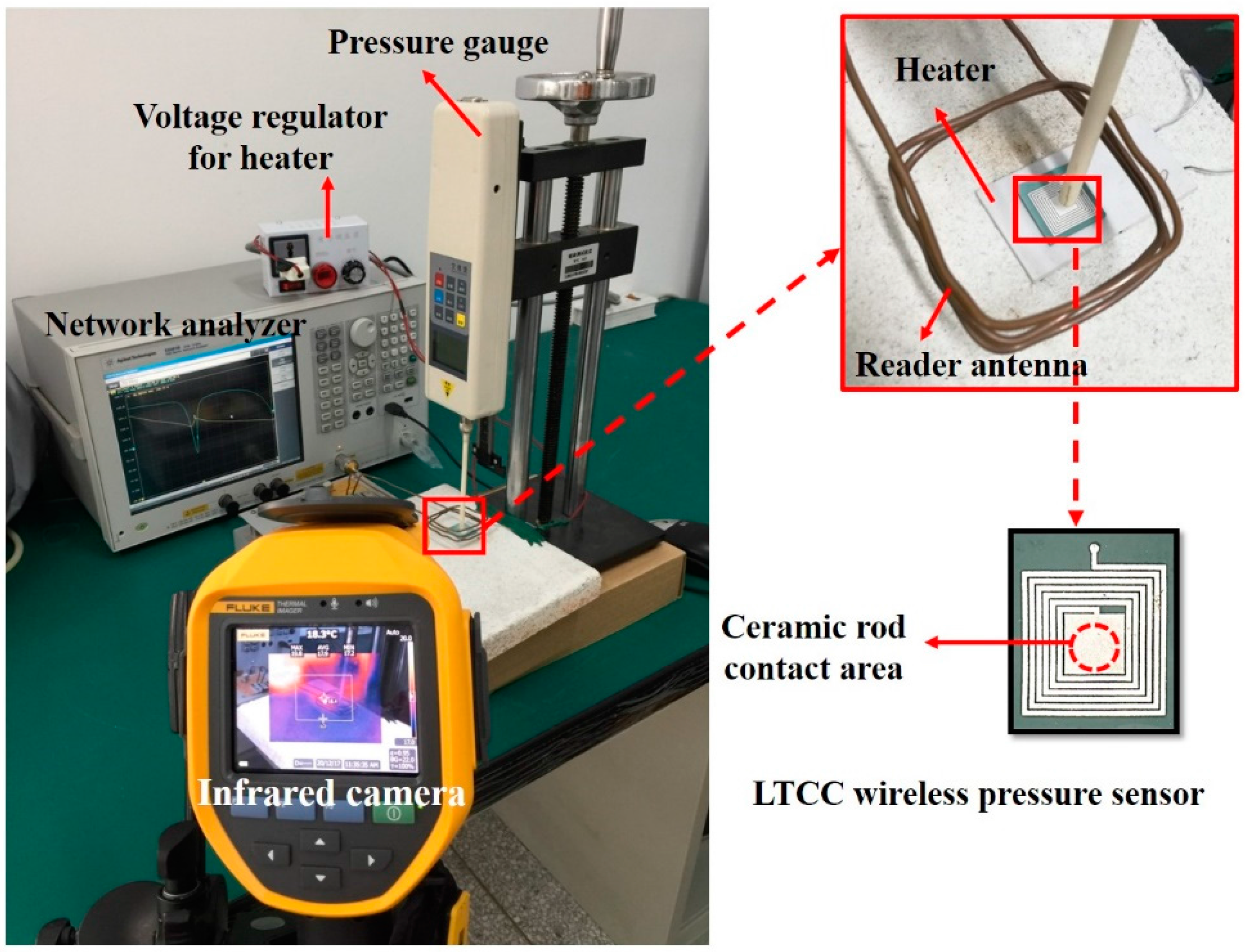
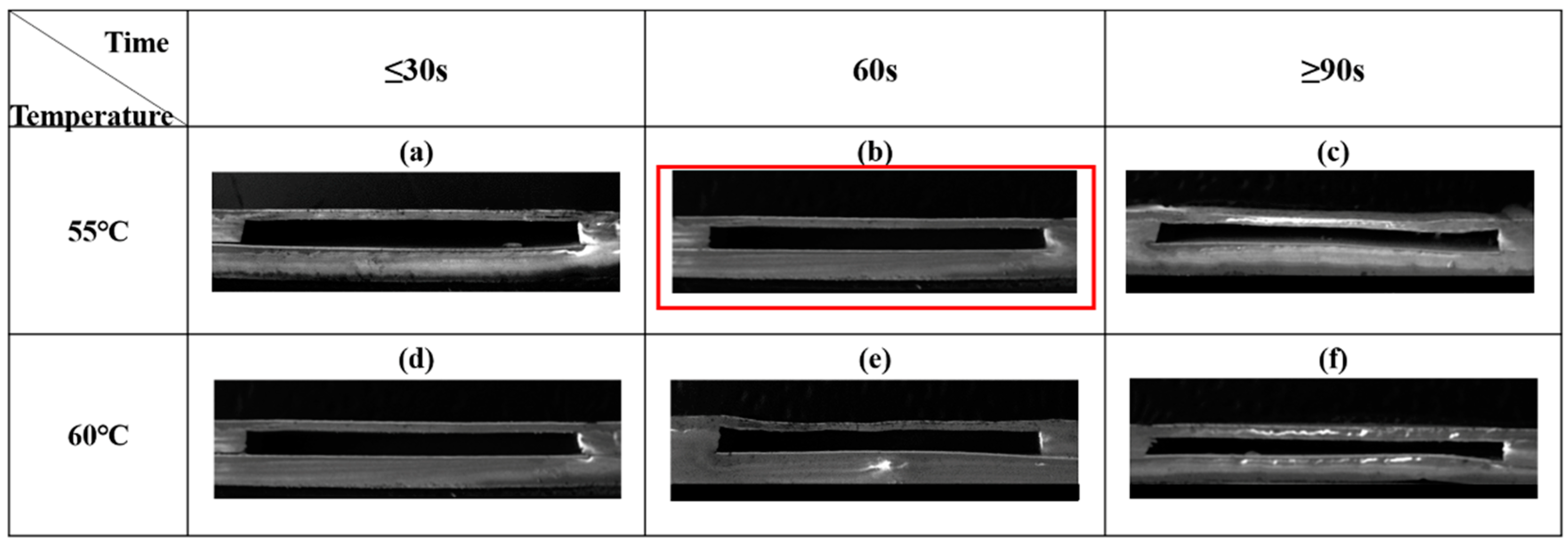
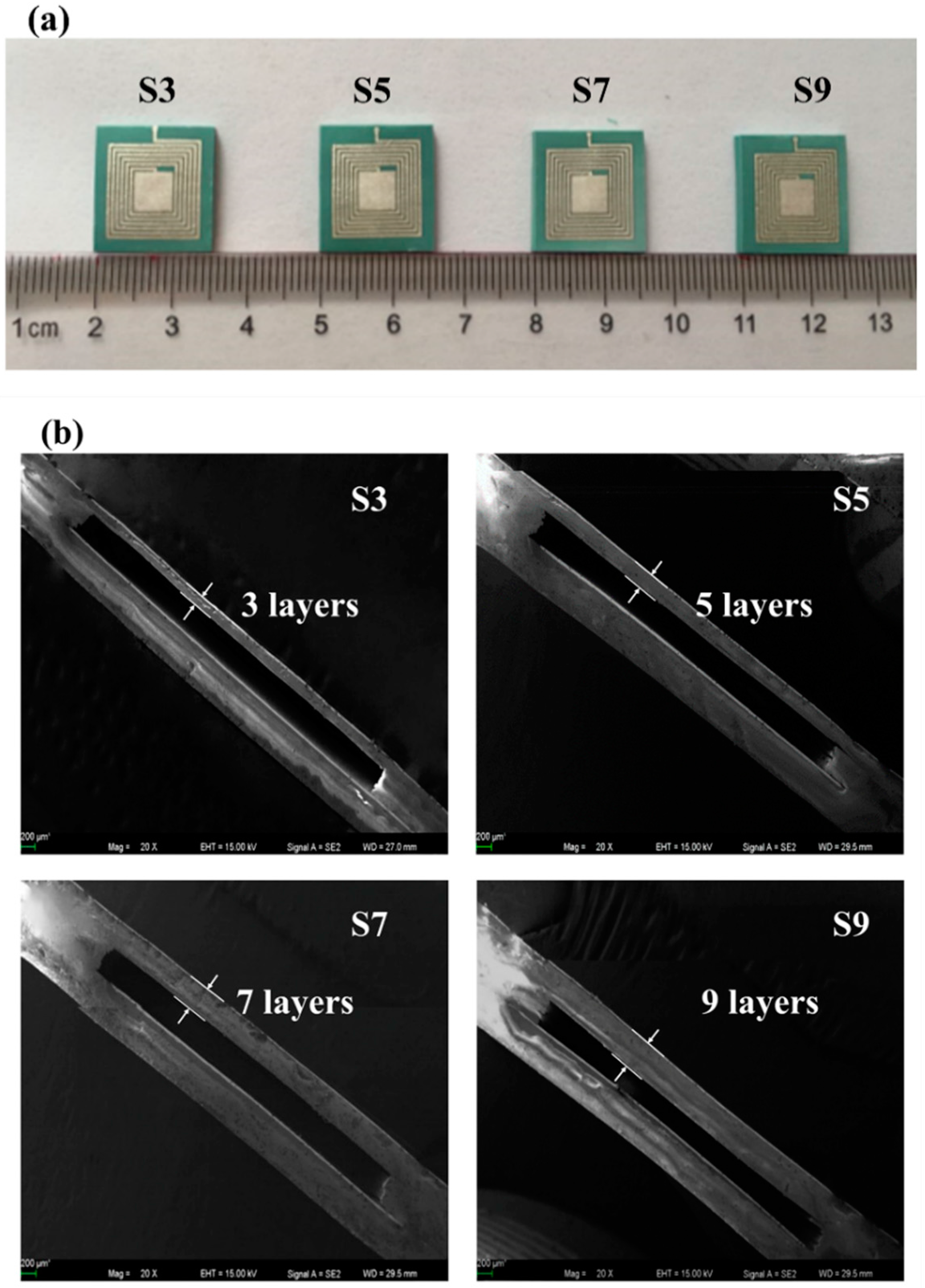
3. Pressure Sensor Fabrication and Test
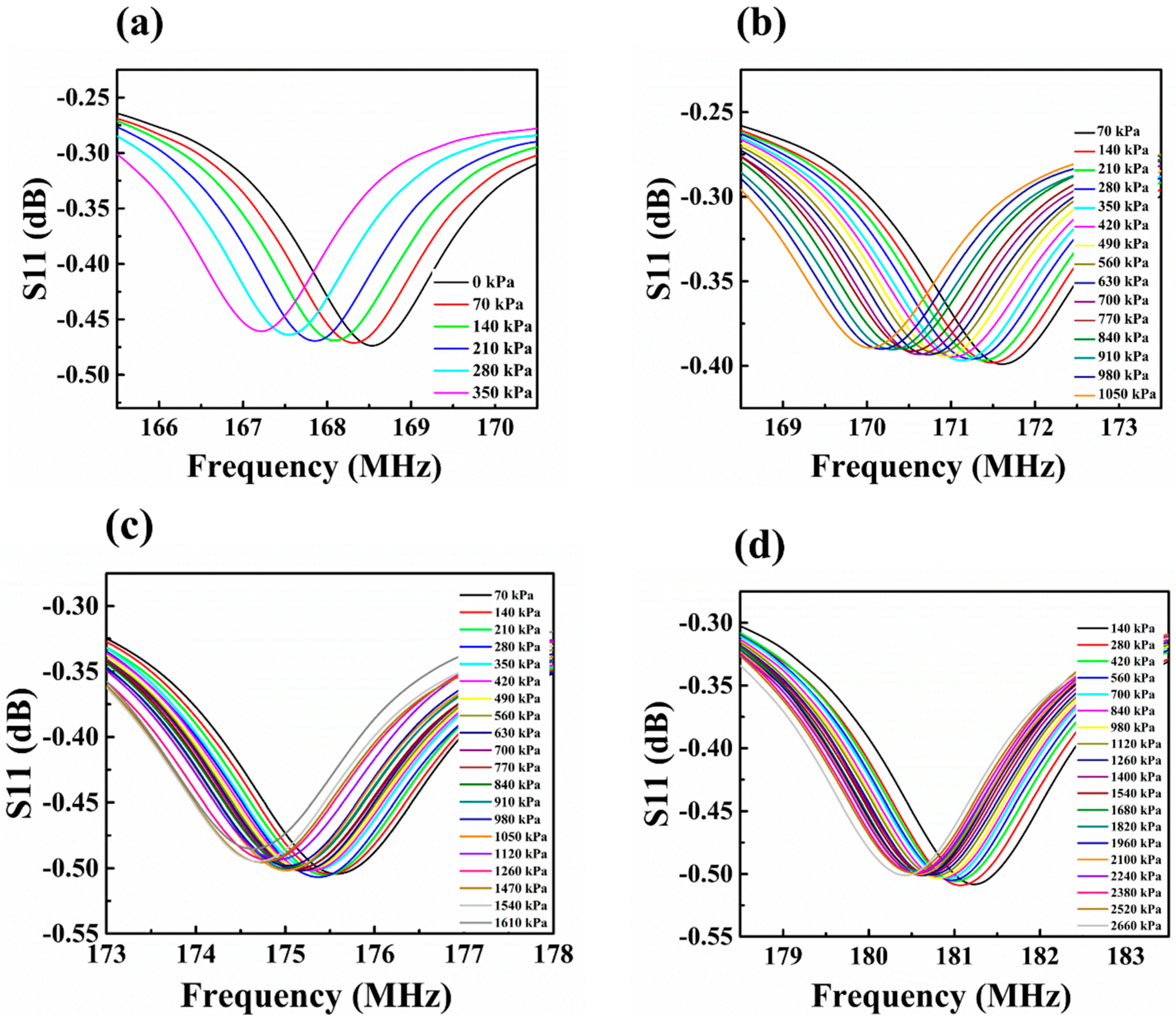
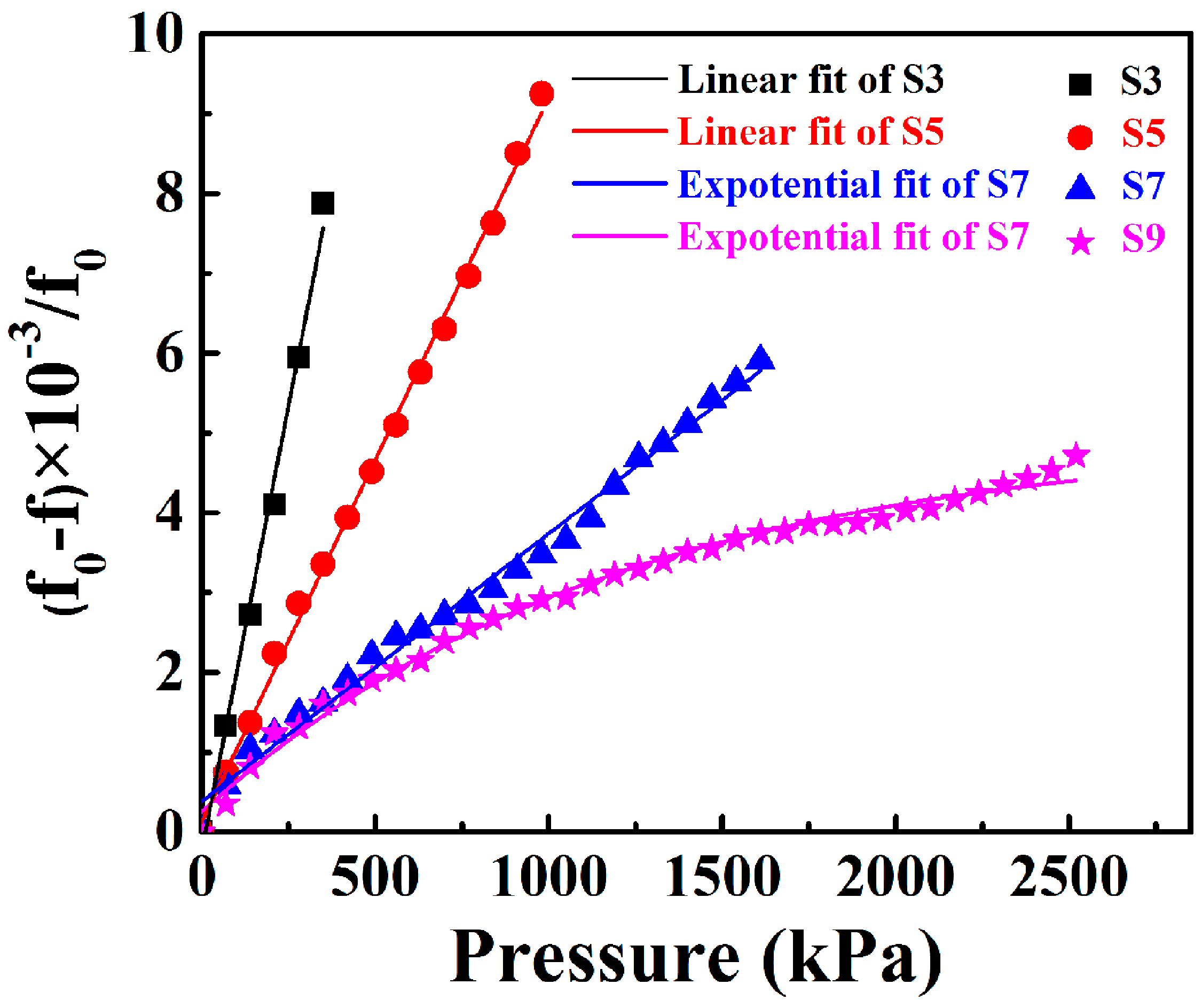
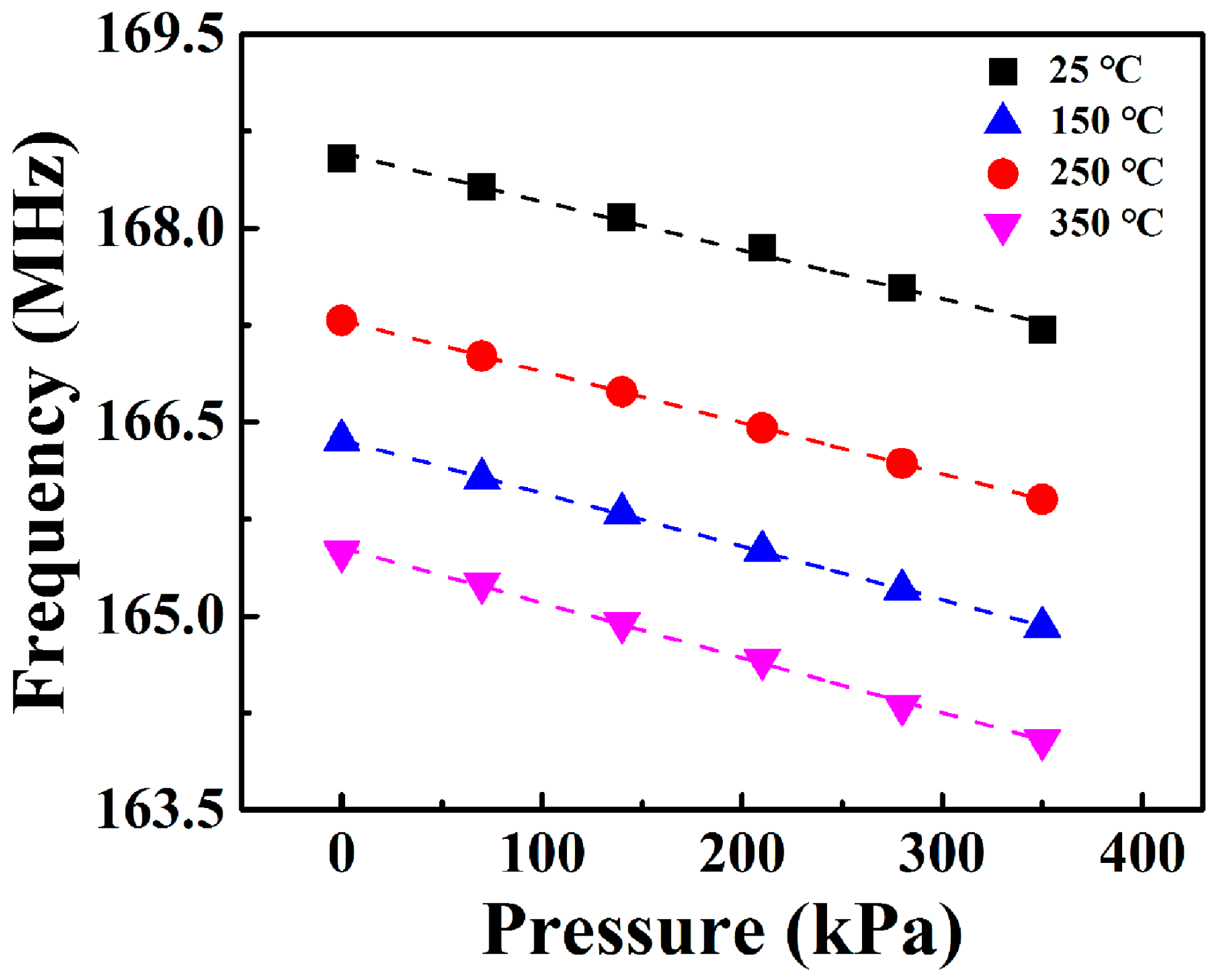
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, W.C.; Atkinson, G.M. Passive wireless sensor applications for NASA’s extreme aeronautical environments. IEEE Sen. J. 2014, 14, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Lee, J.; Qiao, S.; Ghaffari, R.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Song, C.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, D.J.; Jun, S.W.; et al. Multifunctional wearable devices for diagnosis and therapy of movement disorders. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Chortos, A.L.; Schwartz, G.; Tse, V.; Lipomi, D.J.; Wong, H.-S.; McConnell, M.V.; Bao, Z. Continuous wireless pressure monitoring and mapping with ultra-small passive sensors for health monitoring and critical care. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.J.; Saati, S.; Varma, R.; Humayun, M.S.; Tai, Y.C. Wireless intraocular pressure sensing using microfabricated minimally invasive flexible-coiled LC sensor implant. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturesson, P.; Khaji, Z.; Knaust, S.; Klintberg, L.; Thornell, G. Thermomechanical properties and performance of ceramic resonators for wireless pressure reading at high temperatures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 095016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, J.Q.; Huang, Q.A. An LC-type passive wireless humidity sensor system with portable telemetry unit. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2015, 24, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, A.A.; Pisliakov, A.V.; Sokolov, A.V.; Samotaev, N.N.; Soloviev, S.A.; Oblov, K.; Guarnieri, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Brunelli, J.; Maglione, A.; et al. Non-silicon MEMS platforms for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 224, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, W.; Li, A.L.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, L.Y.; Sun, D.H. Design and manufacturing of a passive pressure sensor based on LC resonance. Micromachines 2016, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoong, L.E.; Tan, Y.M.; Lam, Y.C. Overview on fabrication of three-dimensional structures in multi-layer ceramic substrate. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudev, A.; Jones, K.; Kaushik, A.; Bhansali, S. Prospects of low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) based microfluidic systems for point-of-care biosensing and environmental sensing. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 14, 683–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurków, D.; Maeder, T.; Dabrowski, A.; Zarnik, M.S.; Belavic, D.; Bartsch, H.; Muller, J. Overview on low temperature co-fired ceramic sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2015, 233, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.A.; English, J.M.; Arx, M.; Allen, M.G. Wireless micromachined ceramic pressure sensor for high-temperature applications. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.L.; Luo, T.; Wei, T.Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.W.; Xiong, J.J. A wireless passive pressure and temperature sensor via a dual LC resonant circuit in harsh environments. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radosavljevic, G.; Smetana, W.; Maric, A.; Živanov, L.; Unger, M.; Stojanovi, G. Micro force sensor fabricated in the LTCC technology. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Microelectronics, Nis, Serbia, 16–19 May 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.S.; Khan, H.; Shan, W.; Wang, Y.; Ou, J.Z.; Liu, Z.F.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Li, Y.X. A novel wireless gas sensor based on LTCC technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.H.; Liu, Z.F.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, Z.M.; Li, Y.X. High performance low temperature sintered microwave dielectric ceramics prepared by solid-state reaction. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop Series on Advanced Materials and Processes for RF and THz Applications (IMWS-AMP), Suzhou, China, 1–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Wang, L.F.; Huang, Q.A. Implementation of multiparameter monitoring by an LC-type passive wireless sensor through specific winding stacked inductors. IEEE Internet Things 2015, 2, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nopper, R.; Niekrawietz, R.; Reindl, L. Wireless readout of passive LC Sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.P.; Lin, C.W.; Lau, Y.D. A study on the effects of humidity, temperature, and pressure sensor on the piezoresistive film co-structure. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on MEMS, NANO and Smart Systems, Banff, AB, Canada, 24–27 July 2005; ISBN 0-7695-2398-6/05. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Haber, J.; Renken, A.; Muralt, P.; Kiwi-Minsker, L.; Maeder, T. Fine structuration of low-temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) microreactors. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoong, L.E.; Tan, Y.M.; Lam, Y.C. Study of deformation and porosity evolution of low temperature co-fired ceramic for embedded structures fabrication. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecha, K. Fabrication of cavities in low loss LTCC materials for microwave applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 125004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.P.; Lee, J.B.; Allen, M.G. Robust capacitive pressure sensor array. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2002, 101, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, M.A. Polymer/Ceramic Wireless MEMS Pressure Sensors for Harsh Environments: High Temperature and Biomedical Applications. Ph.D. Dissertion, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atalanta, GA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S.P.; Woinowsky-Krieger, S. Theory of Plates and Shells; McGraw Hill: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
| Symbol | Design Value |
|---|---|
| dout (mm) | 15.5 |
| din (mm) | 7.75 |
| w (mm) | 0.5 |
| s (mm) | 0.25 |
| n | 6 |
| a (mm) | 6.52 |
| Feature | SICCAS-K5F3 | DuPont 951 |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness (μm) | 60 | 50/114/250 |
| Young’s Modulus (GPa) | 65 | 120 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | >200 | 320 |
| Dielectric Constant (@10 GHz) | 6.2 | 7.8 |
| Dielectric Loss (@10 GHz) | <0.002 | 0.005 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, L.; Ma, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y. Fabrications and Performance of Wireless LC Pressure Sensors through LTCC Technology. Sensors 2018, 18, 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020340
Lin L, Ma M, Zhang F, Liu F, Liu Z, Li Y. Fabrications and Performance of Wireless LC Pressure Sensors through LTCC Technology. Sensors. 2018; 18(2):340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020340
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Lin, Mingsheng Ma, Faqiang Zhang, Feng Liu, Zhifu Liu, and Yongxiang Li. 2018. "Fabrications and Performance of Wireless LC Pressure Sensors through LTCC Technology" Sensors 18, no. 2: 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020340
APA StyleLin, L., Ma, M., Zhang, F., Liu, F., Liu, Z., & Li, Y. (2018). Fabrications and Performance of Wireless LC Pressure Sensors through LTCC Technology. Sensors, 18(2), 340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18020340






