Design of an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm for a Low-Cost Insole Sensor to Estimate the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) and Calibrate the Center of Pressure (CoP)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Hardware Design
2.2. Virtual Force Algorithm (VFA) Design
2.3. Artificial Neural Network Setting
3. Experimental Settings
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massion, J. Postural control system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1994, 4, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horack, F.B. Macpherson, Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35, ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.; Davids, J.R. Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 1992, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffard, V.; Nantel, J.; Therrien, M.; Vendittoli, P.A.; Lavigne, M.; Prince, F. Center of Mass Compensation during Gait in Hip Arthroplasty Patients: Comparison between Large Diameter Head Total Hip Arthroplasty and Hip Resurfacing. Rehabil. Res. Pract. 2011, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donelan, J.M.; Kram, R.; Kuo, A.D. Simultaneous positive and negative external mechanical work in human walking. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kong, K.; Byl, N.; Tomizuka, M. A Mobile Gait Monitoring System for Abnormal Gait Diagnosis and Rehabilitation: A Pilot Study for Parkinson Disease Patients. J. Biomech. Eng. 2011, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.R.; Olivier, J.; Pagel, A.; Bleuler, H.; Bouri, M.; Lambercy, O.; del R Millán, J.; Riener, R.; Vallery, H.; Gassert, R. Control strategies for active lower extremity prosthetics and orthotics: A review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaulian, H.; Solomonow-Avnon, D.; Herman, A.; Rozen, N.; Haim, A.; Wolf, A. The effect of center of pressure alteration on the ground reaction force during gait: A statistical model. Gait Posture 2018, 66, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liao, W.-H. Human Gait Modeling and Analysis Using a Semi-Markov Process with Ground Reaction Force. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.H.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.J.; Han, C.S. Development of Real-Time Gait Phase Detection System for a Lower Extremity Exoskeleton Robot. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2017, 18, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, P.; Huang, J.; Nakagawa, S.; Sekiyama, K.; Fukuda, T. Fall detection for elderly by using an intelligent cane robot based on center of pressure (COP) stability theory. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (MHS), Nagoya, Japan, 10–12 November 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, M.M.; Meyer, S.; Sandstad, S.; Wiskerke, E.; Thuwis, R.; Vandekerckhove, C.; Myny, C.; Ghosh, N.; Beyens, H.; Dejaeger, E.; et al. A cross-sectional study comparing lateral and diagonal maximum weight shift in people with stroke and healthy controls and the correlation with balance, gait and fear of falling. PLoS ONE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchioka, S.; Iwata, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Miyake, M.; Kanda, S.; Nishiyama, T. The Forward Velocity of the Center of Pressure in the Midfoot is a Major Predictor of Gait Speed in Older Adults. Int. J. Gerontol. 2015, 9, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.H.; Kim, W.S.; Ali, M.A.; Han, C.S. Development of Insole Sensor System and Gait Phase Detection Algorithm for Lower Extremity Exoskeleton. J. Korean Soc. Precis. Eng. 2015, 32, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, H.A.; Farris, R.J.; Goldfarb, M. Control and implementation of a powered lower limb orthosis to aid walking in paraplegic individuals. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Na, Y.; Gu, G.; Kim, J. Flexible insole ground reaction force measurement shoes for jumping and running. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner-Cordero, A.; Koopman, H.J.F.M.; Van der Helm, F.C.T. Inverse dynamics calculations during gait with restricted ground reaction force information from pressure insole. Gait Posture 2006, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claverie, L.; Ille, A.; Moretto, P. Discrete sensors distribution for accurate plantar pressure analyses. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, J.; Peng, D.; Sun, Z.; Qu, X. Estimation of Foot Plantar Center of Pressure Trajectories with Low-Cost Instrumented Insoles Using an Individual-Specific Nonlinear Model. Sensors 2018, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekscan Inc. FlexiForce Standard Model A401 Datasheet. Available online: https://www.tekscan.com/products-solutions/force-sensors/a401 (accessed on 8 December 2018).
- Hall, R.S.; Desmoulin, G.T.; Milner, T.E. A technique for conditioning and calibrating force-sensing resistors for repeatable and reliable measurement of compressive force. J. Biomech. 2008, 41, 3492–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Bates, B.T. Comparison of F-Scan in-sole and AMTI forceplate system in measuring vertical ground reaction force during gait. Int. J. Phys. Ther. 2000, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
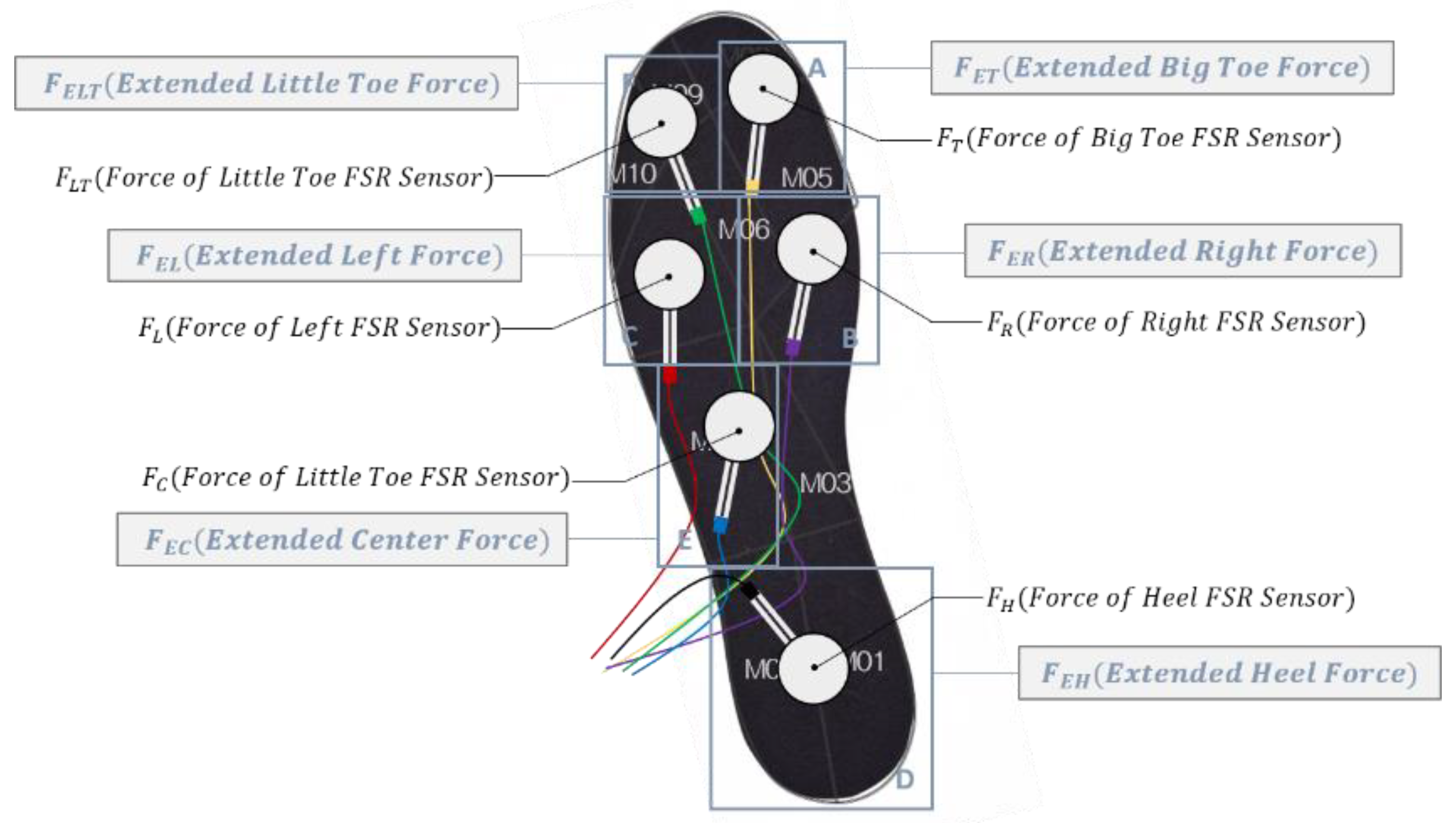

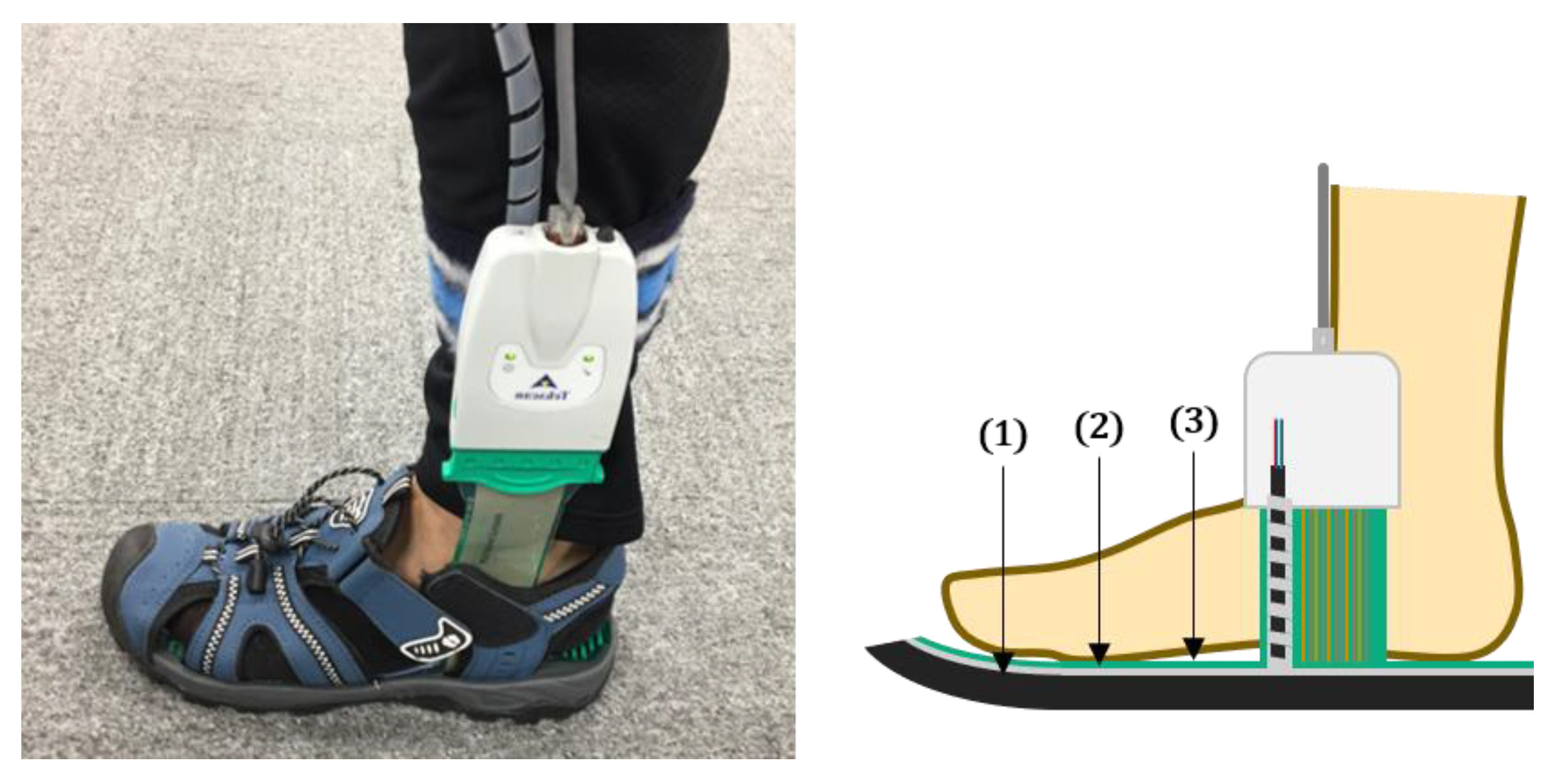
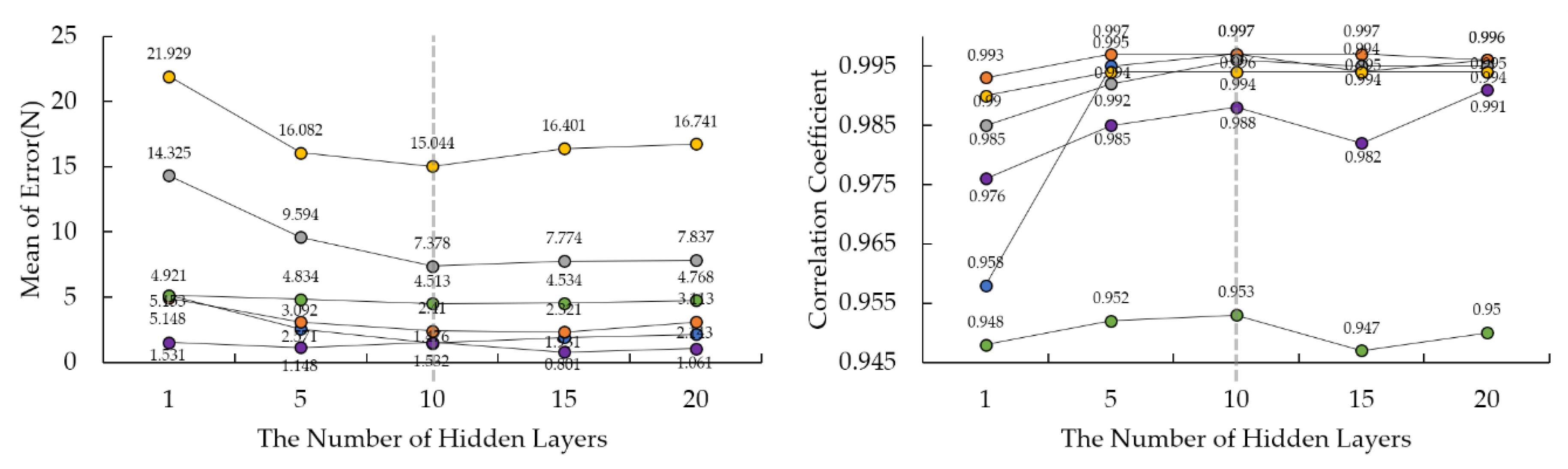
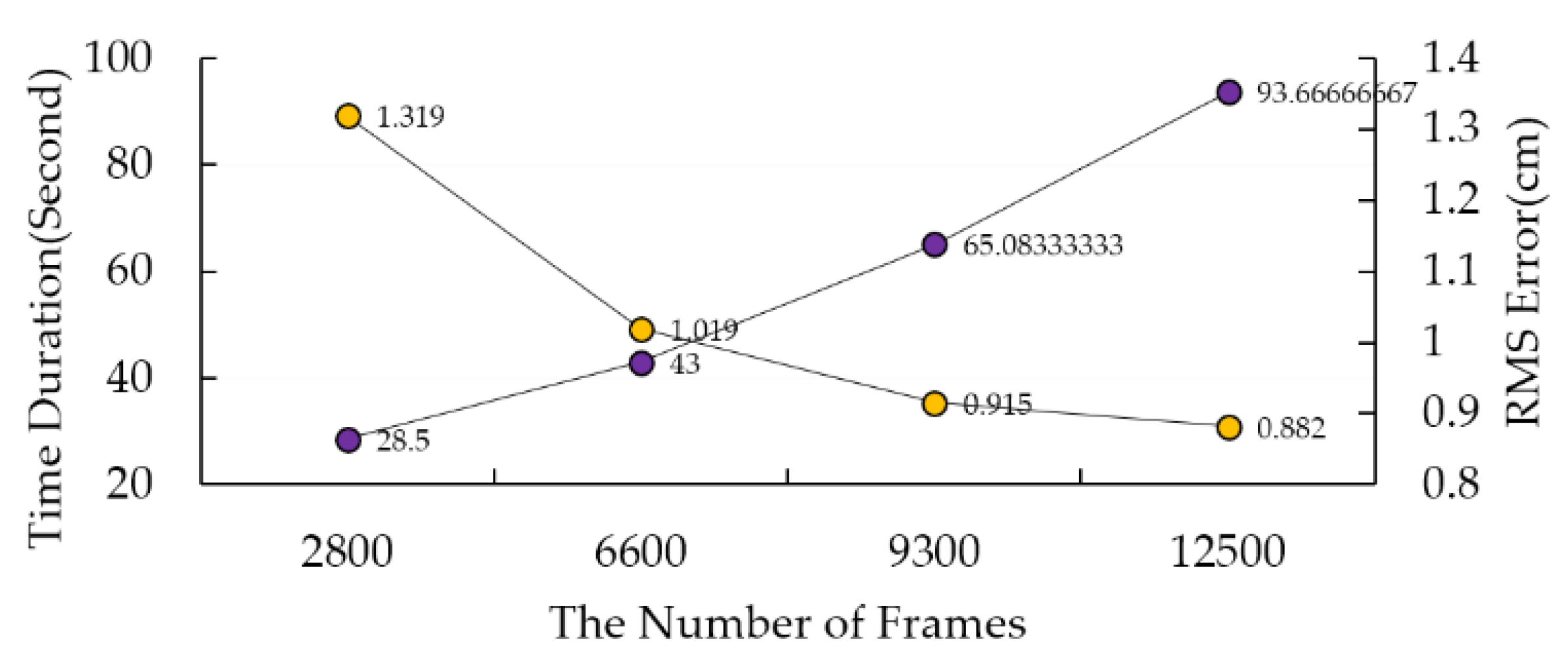
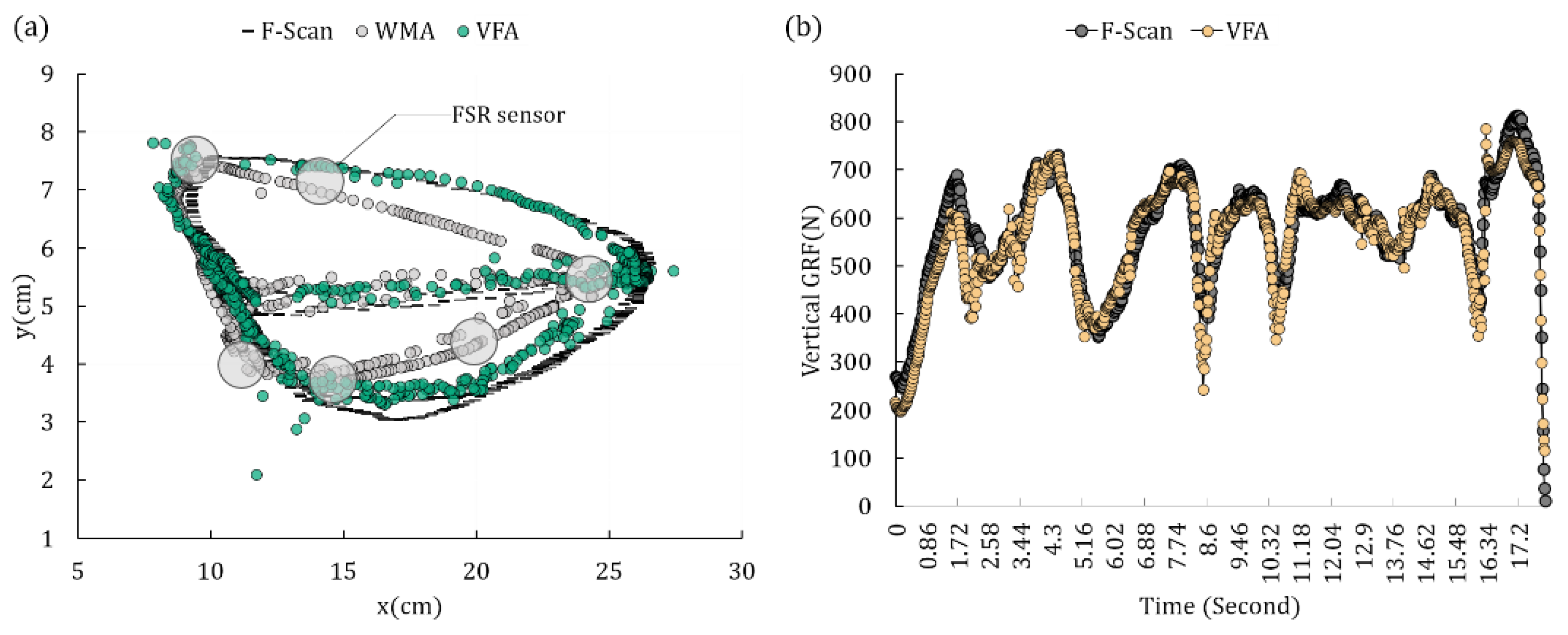
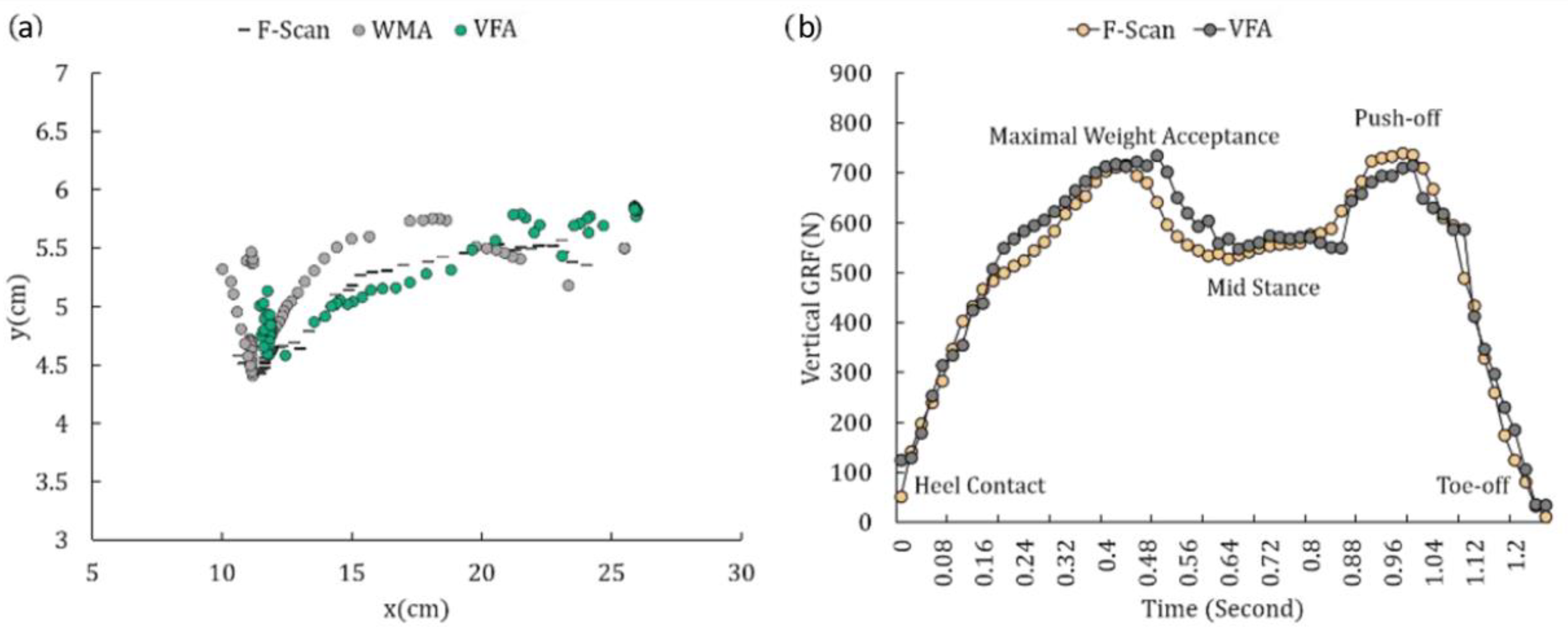
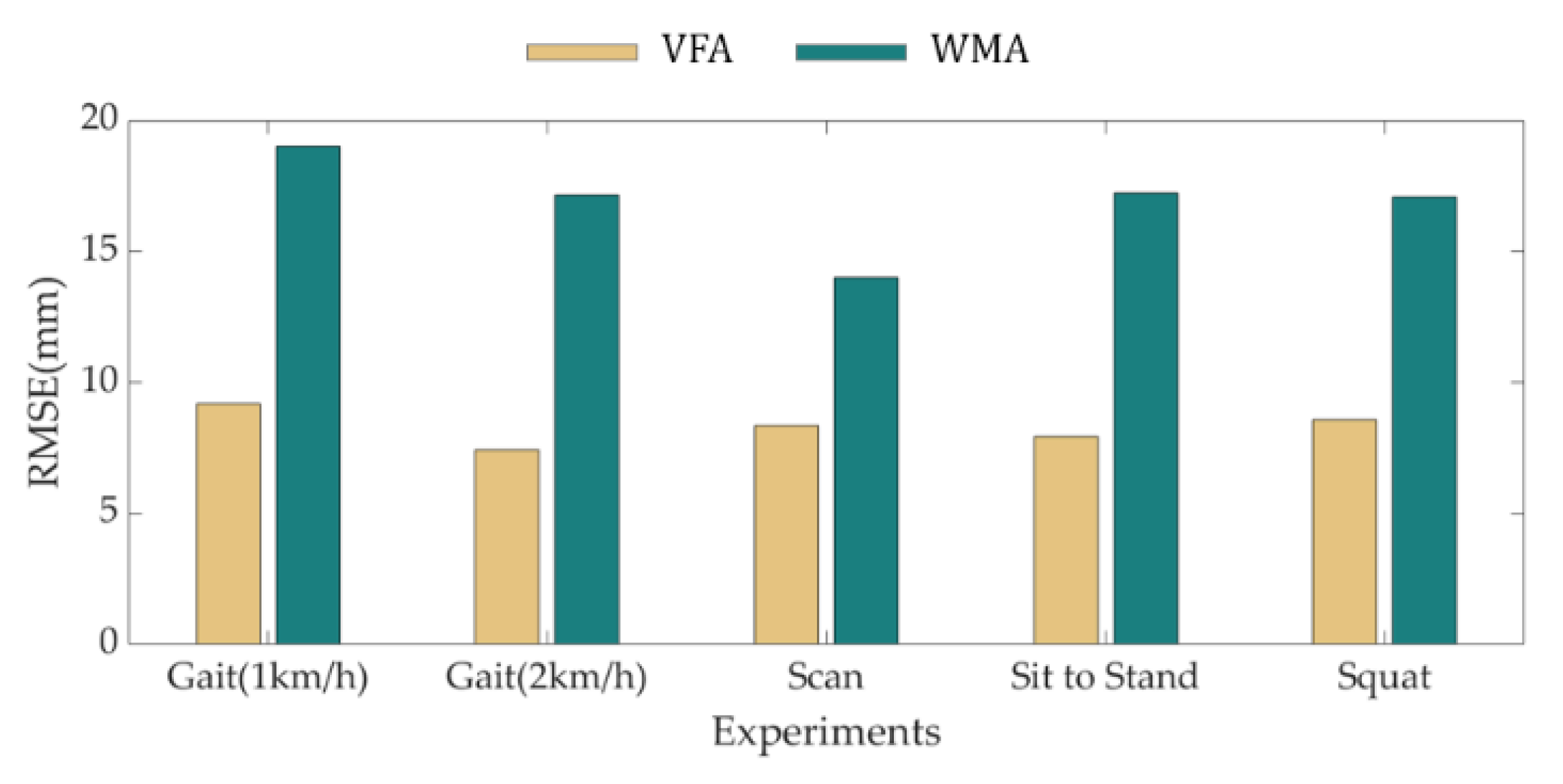

| Subject No. | Gender | Age | Height (cm) | Weight (kg) | Shoe Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 26 | 179 | 67 | US8 |
| 2 | Male | 27 | 180 | 74 | US8 |
| 3 | Male | 24 | 173 | 71 | US8 |
| 4 | Male | 24 | 185 | 77 | US8 |
| 5 | Male | 32 | 173 | 72 | US8 |
| 6 | Male | 34 | 171 | 70 | US8 |
| 7 | Male | 38 | 173 | 79 | US8 |
| 8 | Male | 35 | 169 | 74 | US8 |
| Subject No. | RMSE of GRF(N) by VFA | RMSE of CoP(mm) by VFA | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scan | Gait 1 | Gait 2 | Squat | STS | Scan | Gait 1 | Gait 2 | Squat | STS | |
| 1 | 21.43 | 26.46 | 26.79 | 25.08 | 19.00 | 7.43 | 8.47 | 6.14 | 10.56 | 7.44 |
| 2 | 23.99 | 35.55 | 46.28 | 32.17 | 16.97 | 5.38 | 5.79 | 8.71 | 7.36 | 9.56 |
| 3 | 27.65 | 45.70 | 28.11 | 29.51 | 17.39 | 9.94 | 13.65 | 10.28 | 4.38 | 0.80 |
| 4 | 28.83 | 34.28 | 40.35 | 44.60 | 38.30 | 9.74 | 11.31 | 4.64 | 5.75 | 5.60 |
| 5 | 27.70 | 23.57 | 28.41 | 40.48 | 20.69 | 8.38 | 8.70 | 7.05 | 15.5 | 10.29 |
| 6 | 33.75 | 29.74 | 32.98 | 32.88 | 15.66 | 9.40 | 15.79 | 8.37 | 11.90 | 14.71 |
| 7 | 32.45 | 54.58 | 30.80 | 32.58 | 20.56 | 9.49 | 4.87 | 7.23 | 8.58 | 7.00 |
| 8 | 32.86 | 22.19 | 18.04 | 20.92 | 14.37 | 6.98 | 4.75 | 7.06 | 4.61 | 8.06 |
| Avg. | 28.58 | 34.01 | 31.47 | 32.28 | 20.37 | 8.34 | 9.17 | 7.44 | 8.58 | 7.93 |
| RMSE of CoP(mm) by WMA | CC of GRF by VFA | |||||||||
| 1 | 15.07 | 14.27 | 14.15 | 14.70 | 15.40 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.93 |
| 2 | 11.34 | 23.07 | 22.20 | 18.77 | 14.19 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| 3 | 17.40 | 23.06 | 16.71 | 16.53 | 20.60 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 |
| 4 | 12.75 | 20.86 | 21.80 | 12.78 | 10.9 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.94 | 0.86 | 0.94 |
| 5 | 11.03 | 12.05 | 12.00 | 17.4 | 19.44 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.72 | 0.96 |
| 6 | 18.88 | 21.11 | 14.26 | 20.68 | 20.10 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 0.96 |
| 7 | 10.88 | 11.49 | 17.57 | 14.25 | 18.05 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.95 |
| 8 | 14.69 | 26.17 | 18.54 | 21.43 | 19.12 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.95 |
| Avg. | 14.01 | 19.01 | 17.15 | 17.07 | 17.23 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.95 |
| CC of CoP X by VFA | CC of CoP Y by VFA | |||||||||
| 1 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.46 |
| 2 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.60 | 0.65 | 0.77 |
| 3 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| 4 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.64 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.26 |
| 5 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.68 | 0.43 |
| 6 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.69 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.65 |
| 7 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.85 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 0.86 | 0.75 | 0.69 | 0.71 |
| 8 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.86 | 0.90 |
| Avg. | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.88 | 0.86 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 0.6 |
| CC of CoP X by WMA | CC of CoP Y by WMA | |||||||||
| 1 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.65 | 0.94 | 0.65 | 0.40 | 0.06 | 0.33 |
| 2 | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.92 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.67 | 0.35 | 0.58 | 0.69 |
| 3 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.62 |
| 4 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.96 | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.98 | 0.61 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 0.13 |
| 5 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.31 |
| 6 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.74 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.50 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.58 |
| 7 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| 8 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.93 | 0.78 | 0.31 | 0.78 | 0.86 |
| Avg. | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 0.70 | 0.55 | 0.52 | 0.51 |
| Numerical Value | Divided Area of Insole | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | F | |
| ADC Value | 55 | 132 | 0 | 154 | 0 | 0 |
| Estimated Virtual Force (N) | 23.418 | 104.242 | 0 | 286.743 | 0 | 0 |
| Proportional Rate of ADC Value | 1 | 2.4 | 0 | 2.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Proportional Rate of Estimated Virtual Force | 1 | 4.45 | 0 | 12.24 | 0 | 0 |
| X Coordinate of FSR Sensor | 7 | 12 | 12 | 25.5 | 9.25 | 3.5 |
| Estimated Moving X Coordinate of Divided Area | 5.684 | 12.034 | NaN | 25.692 | NaN | NaN |
| Constants | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 79.160 | 0.316 | 3.155 | 0.321 | −0.387 | −0.016 | −1.253 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.S.; Lee, C.H.; Shim, M.; Han, J.I.; Baek, Y.S. Design of an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm for a Low-Cost Insole Sensor to Estimate the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) and Calibrate the Center of Pressure (CoP). Sensors 2018, 18, 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124349
Choi HS, Lee CH, Shim M, Han JI, Baek YS. Design of an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm for a Low-Cost Insole Sensor to Estimate the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) and Calibrate the Center of Pressure (CoP). Sensors. 2018; 18(12):4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124349
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ho Seon, Chang Hee Lee, Myounghoon Shim, Jong In Han, and Yoon Su Baek. 2018. "Design of an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm for a Low-Cost Insole Sensor to Estimate the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) and Calibrate the Center of Pressure (CoP)" Sensors 18, no. 12: 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124349
APA StyleChoi, H. S., Lee, C. H., Shim, M., Han, J. I., & Baek, Y. S. (2018). Design of an Artificial Neural Network Algorithm for a Low-Cost Insole Sensor to Estimate the Ground Reaction Force (GRF) and Calibrate the Center of Pressure (CoP). Sensors, 18(12), 4349. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18124349





