Employing Ray-Tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines for Localisation †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Methodology
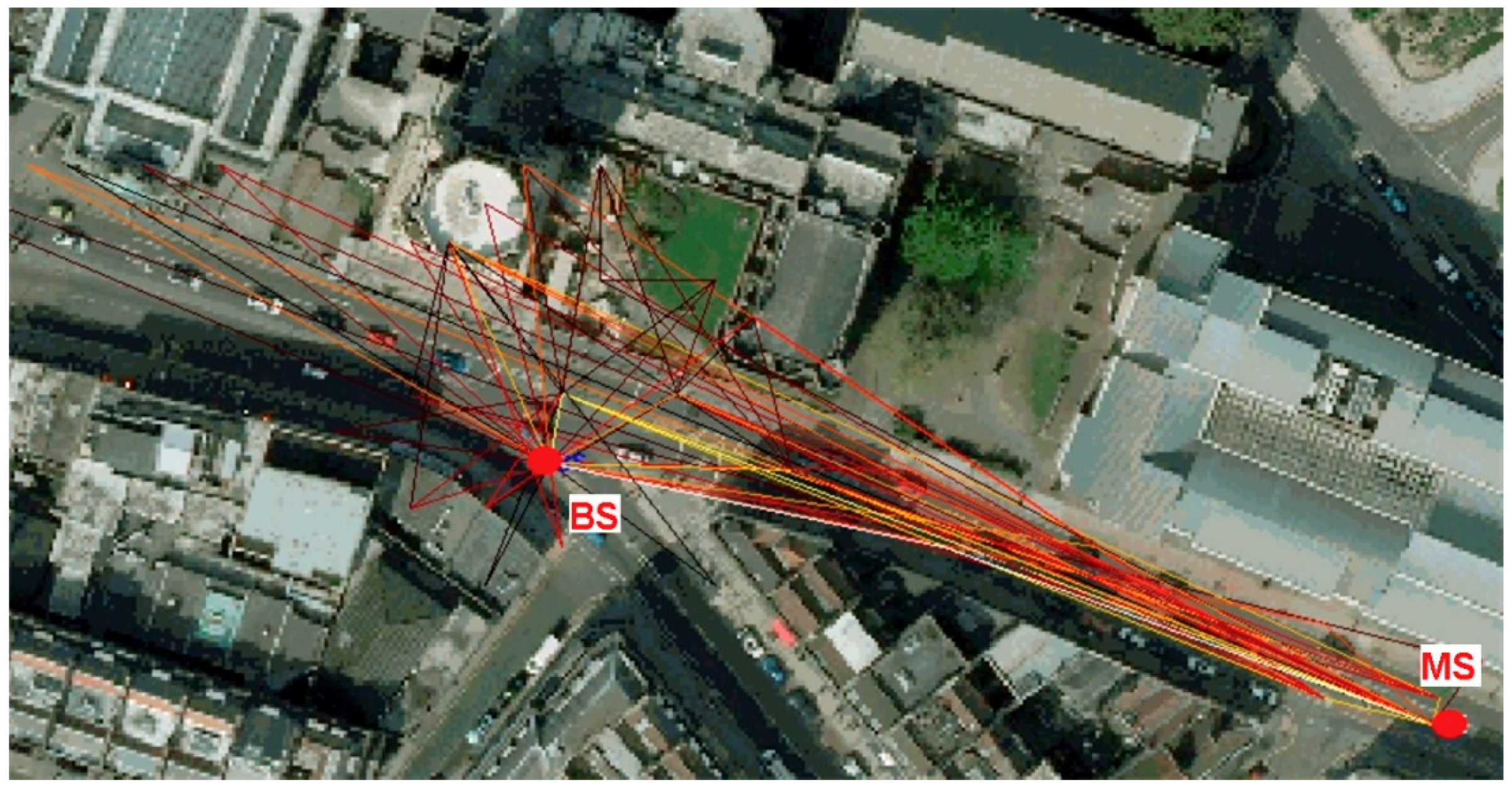
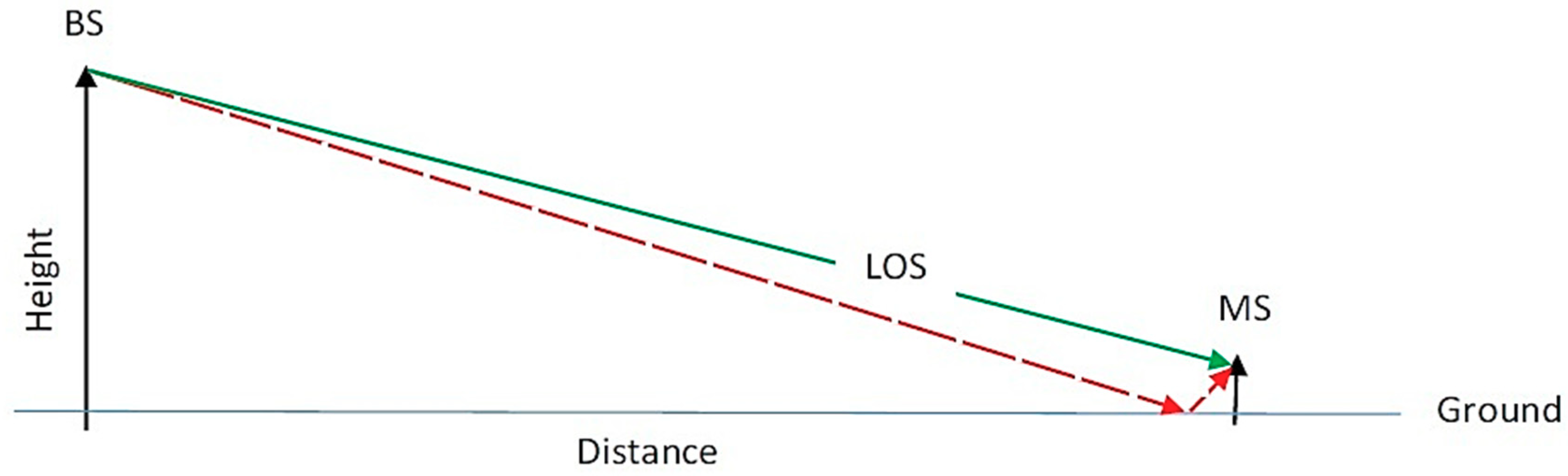
2.1. Ray Tracing
2.2. Assumptions
- Channel reciprocity
- Network deployment and capability
- Noise
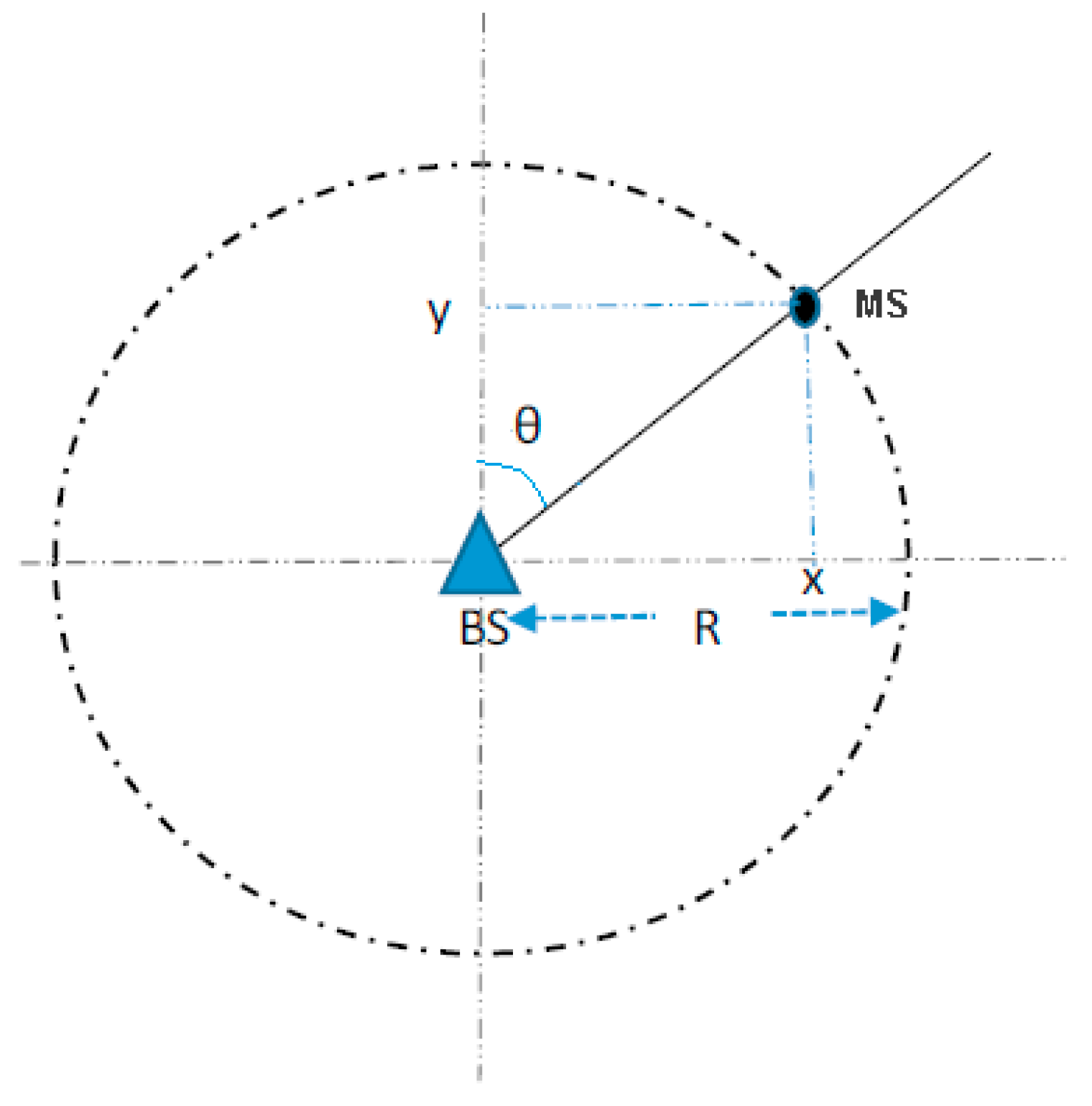
2.3. Localisation Algorithms Used for Comparison
2.4. Data Pre-Processing
2.5. Least-Square Support Vector Machines
2.6. Direct LSSVM Localisation Method
2.6.1. Training and Estimation
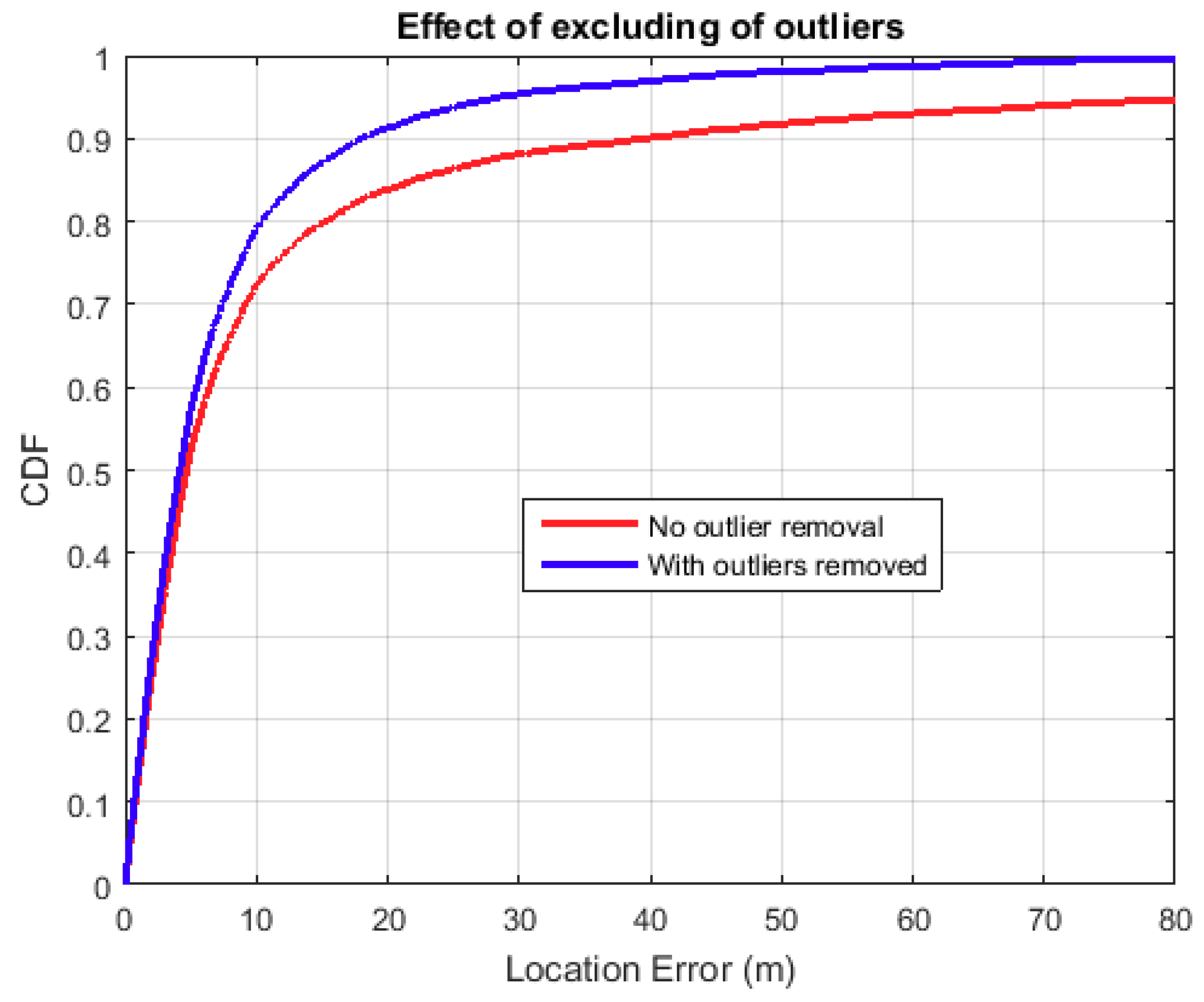
2.6.2. Post-Processing and Outlier Removal
2.7. Localisation Performance
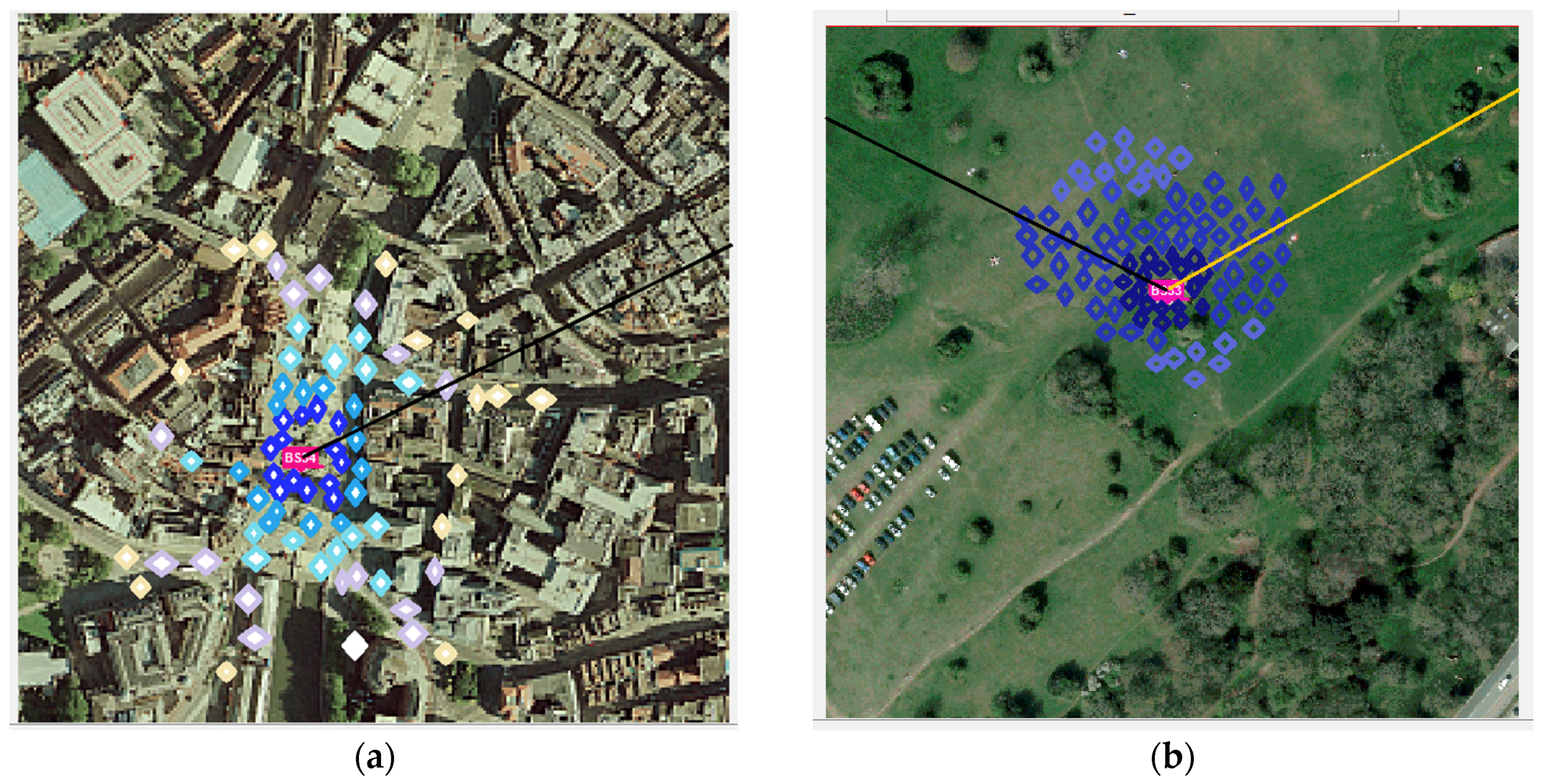
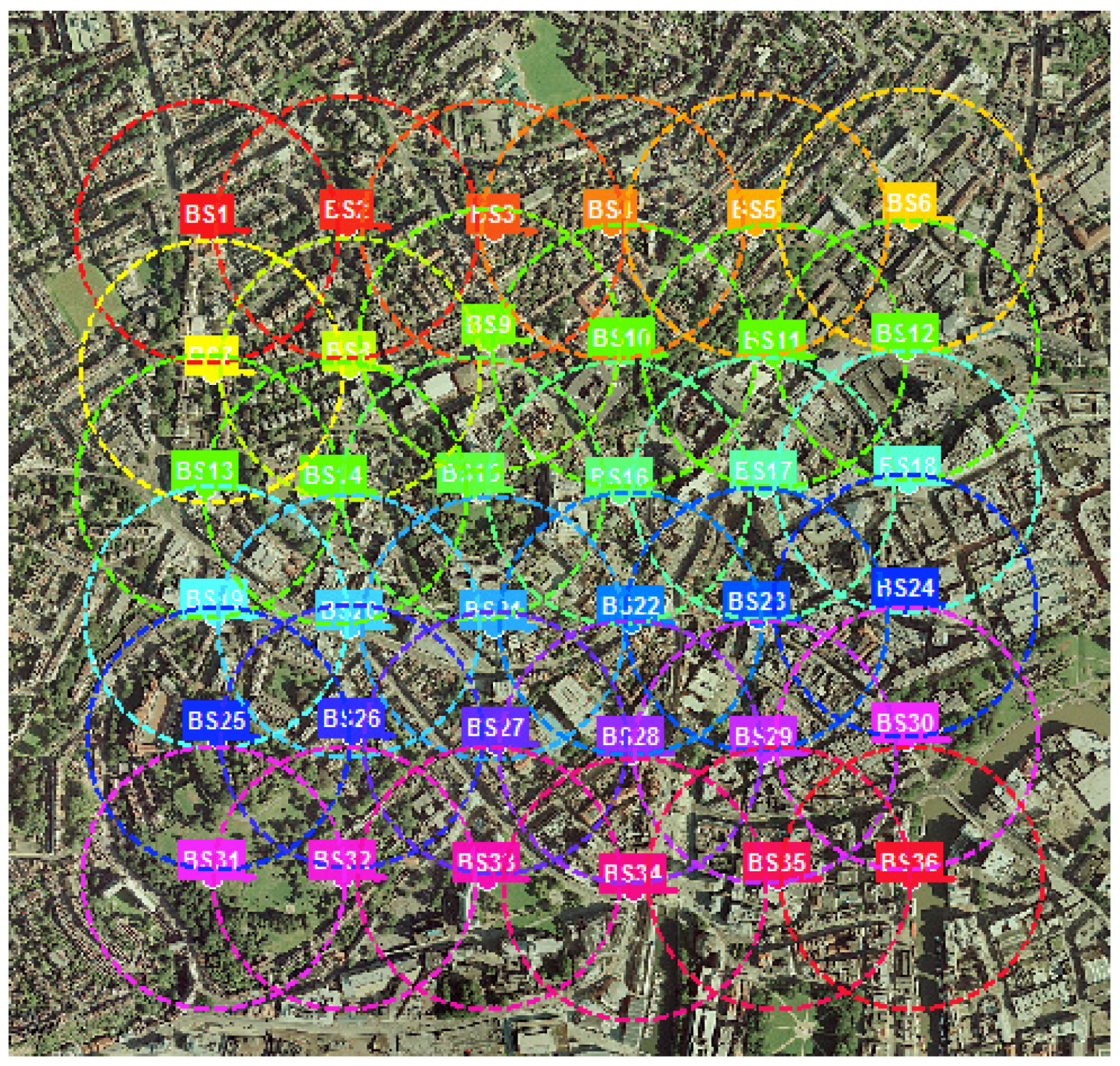
2.8. Environments Considered
2.9. Performance Comparisons
3. Results
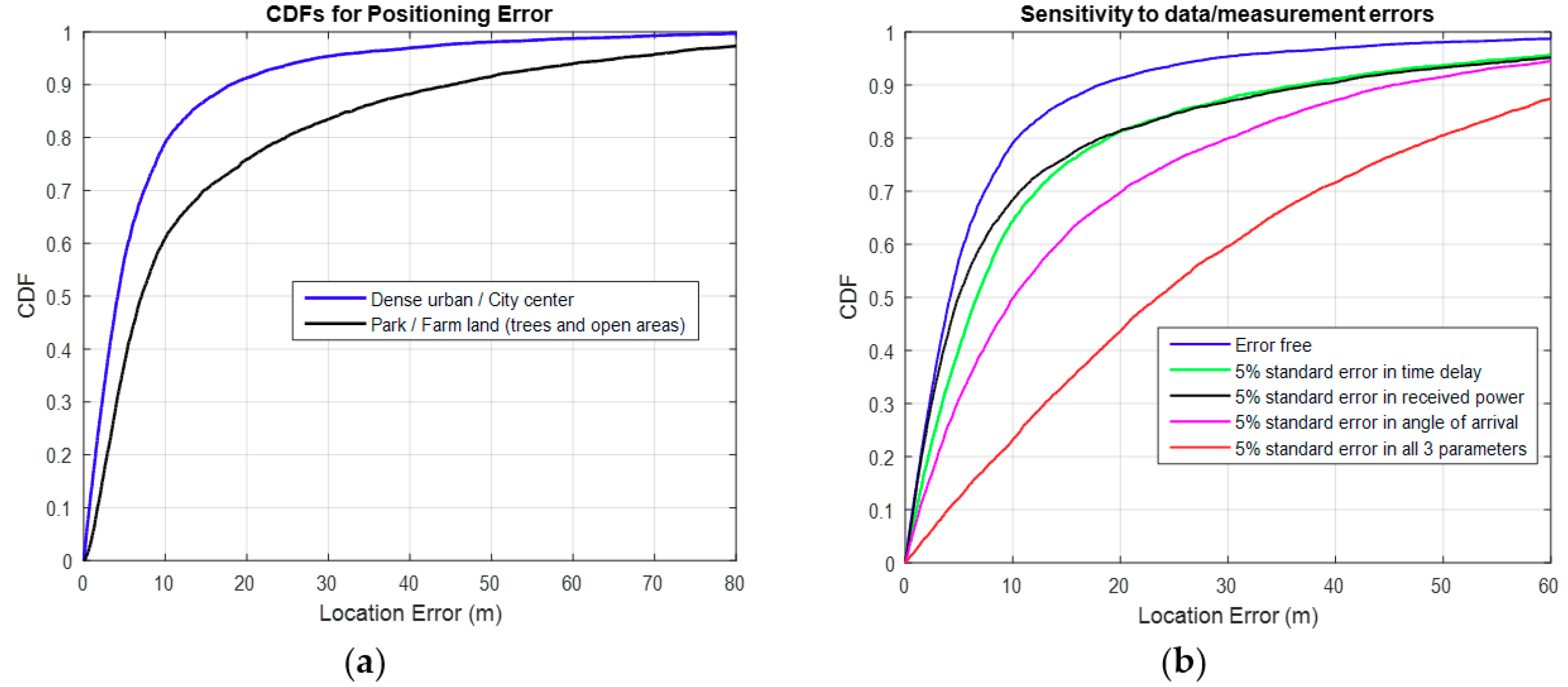
3.1. Results for the Direct Method
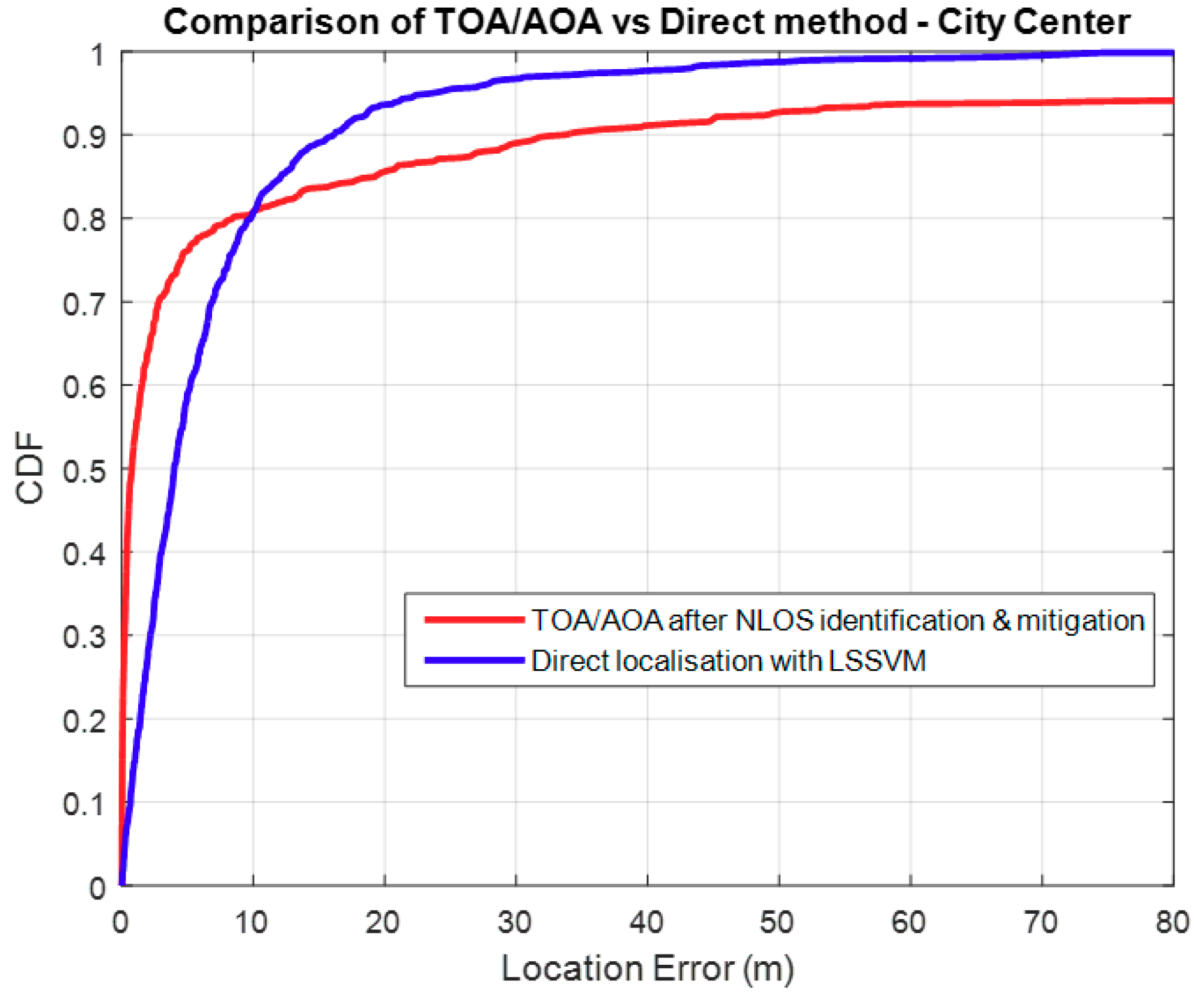
3.2. Comparison with TOA/AOA
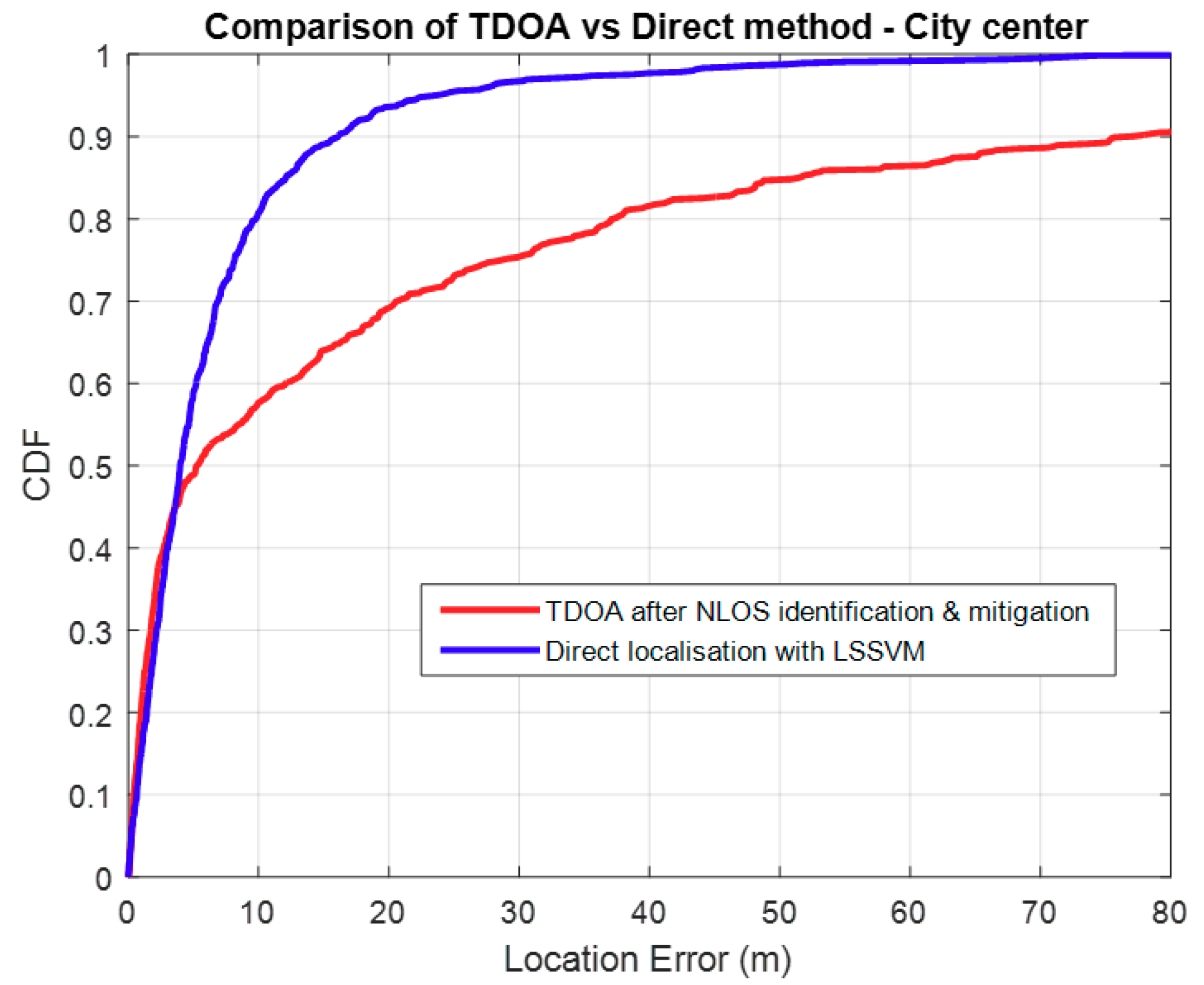
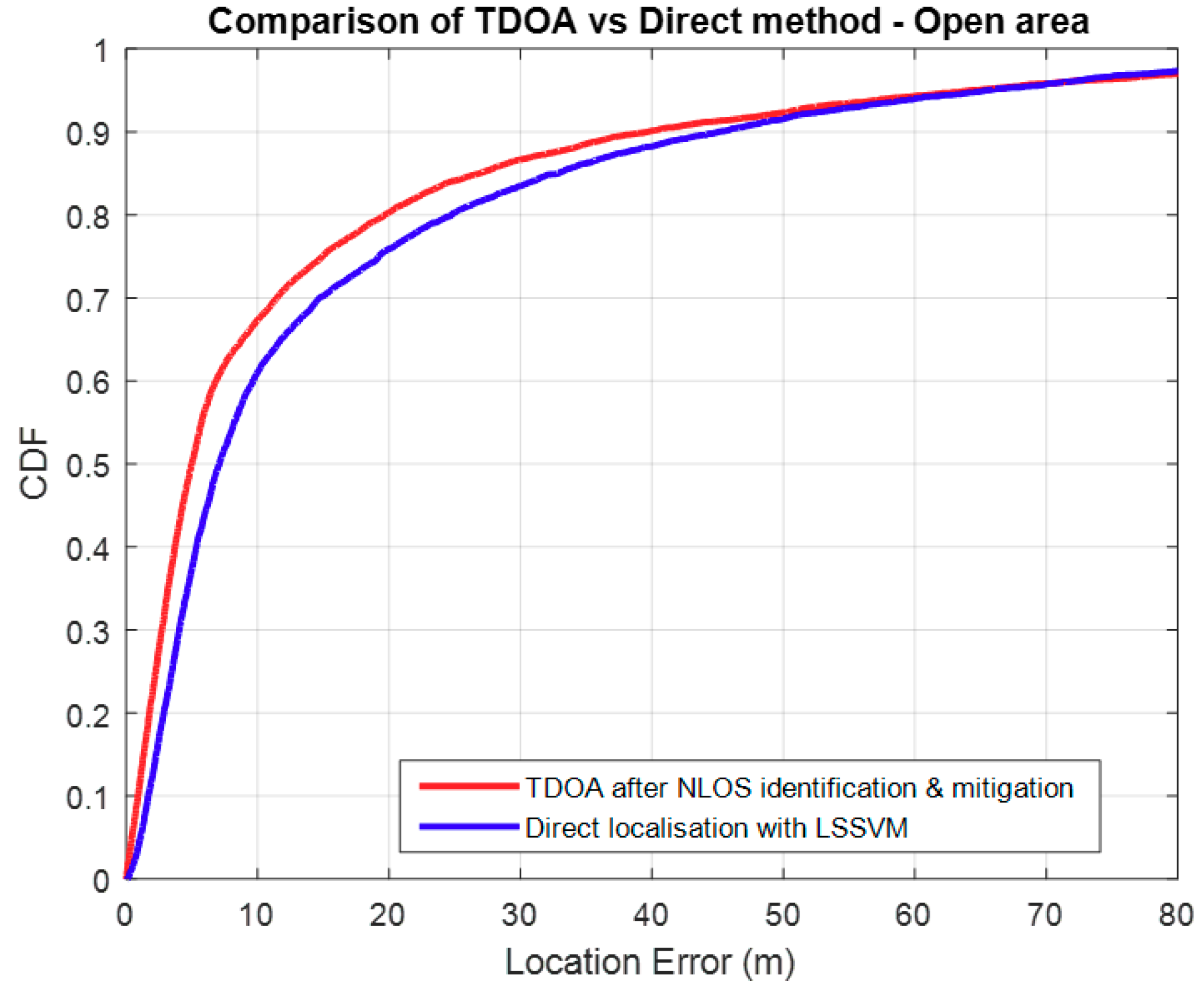
3.3. Comparison with TDOA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GSA. Available online: https://www.gsa.europa.eu/newsroom/news/results-are-galileo-increases-accuracy-location-based-services (accessed on 11 November 2018).
- Chitambira, B.; Armour, S.; Wales, S.; Beach, M. NLOS Identification and Mitigation for Geolocation Using Least-squares Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (IEEE WCNC 2017), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chitambira, B.; Armour, S.; Wales, S.; Beach, M. Direct Localisation Using Ray-tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Guimaraes, Portugal, 26–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodjaev, J.; Park, Y.; Saeed-Malik, A. Survey of NLOS identification and error mitigation problems in UWB-based positioning algorithms for dense environments. Ann. Telecommun. J. 2010, 65, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J. A 3D Fingerprinting Positioning Method Based on Cellular Networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2014, 10, 248981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, M.N.; Thomä, R.S. Mobile Station Localization Emitter in Urban NLoS using Multipath Ray Tracing Fingerprints and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Conference on Localization and GNSS (ICL-GNSS), Guimaraes, Portugal, 26–28 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, J.; Schröder, F.; Mathar, R. TDOA fingerprinting for localization in non-line-of-sight and multipath environments. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (ISAP), Hobart, Australia, 9–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, S.; Sano, A.; Tsuji, H. Blind Mobile Positioning in Urban Environment Based on Ray-Tracing Analysis. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal. Process. 2006, 2006, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.H.; Tameh, E.K.; Doufexi, A.; Hunukumbure, M.; Nix, A.R. Efficient multi-element Ray Tracing with site-specific comparisons using measured MIMO channel data. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2007, 56, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tameh, E.K.; Nix, A.R. The use of measurement data to analyse the performance of rooftop diffraction and foliage loss algorithms in a 3-D integrated urban/rural propagation model. In Proceedings of the Vehicular Technology Conference Spring 1998, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 21 May 1998; pp. 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, T.A.; Vook, F.W.; Mellios, E.; Hilton, G.S.; Nix, A.R.; Visotsky, E. 3D extension of the 3GPP/ITU channel model. In Proceedings of the 77th IEEE Vehicular Technologies Conference (VTC-Spring), Dresden, Germany, 2–5 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, P.; Hassan, W.B.; Brice, H.; Chitambira, B.; Beach, M.A.; Mellios, E.; Nix, A.R.; Armour, S.; Doufexi, A. An Overview of Massive MIMO Research at the University of Bristol. In Proceedings of the Radio Propagation and Technologies for 5G (2016), Durham, UK, 3 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dardari, D.; Chong, C.-C.; Win, M.Z. Improved lower bounds on Time-of-Arrival estimation error in realistic UWB Channels. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Ultra-Wide-Band, Waltham, MA, USA, 24–27 September 2006; pp. 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landron, O.; Feuerstein, M.J.; Rappaport, T.S. A comparison of theoretical and empirical reflection coefficients for typical exterior wall surfaces in a mobile radio environment. IEEE Trans. Antennas. Propagat. 1996, 44, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Vandewalle, J. Least Squares Support Vector Machine Classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, S.; Gifford, W.M.; Wymeersch, H.; Win, M.Z. NLOS identification and mitigation for localization based on UWB experimental data. IEEE J. Sel. Area. Commun. 2010, 28, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gestel, T.; Suykens, J.A.; Baesens, B.; Viaene, S.; Vanthienen, J.; Dedene, G.; de Moor, B.; Vandewalle, J. Benchmarking Least Squares Support Vector Machine Classifiers. Mach. Learn. 2004, 54, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]


| Ray-Tracer Output Data |
|---|
|
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chitambira, B.; Armour, S.; Wales, S.; Beach, M. Employing Ray-Tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines for Localisation. Sensors 2018, 18, 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114059
Chitambira B, Armour S, Wales S, Beach M. Employing Ray-Tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines for Localisation. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114059
Chicago/Turabian StyleChitambira, Benny, Simon Armour, Stephen Wales, and Mark Beach. 2018. "Employing Ray-Tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines for Localisation" Sensors 18, no. 11: 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114059
APA StyleChitambira, B., Armour, S., Wales, S., & Beach, M. (2018). Employing Ray-Tracing and Least-Squares Support Vector Machines for Localisation. Sensors, 18(11), 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114059





