Thermal Frequency Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Absorber Using Phase Change Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
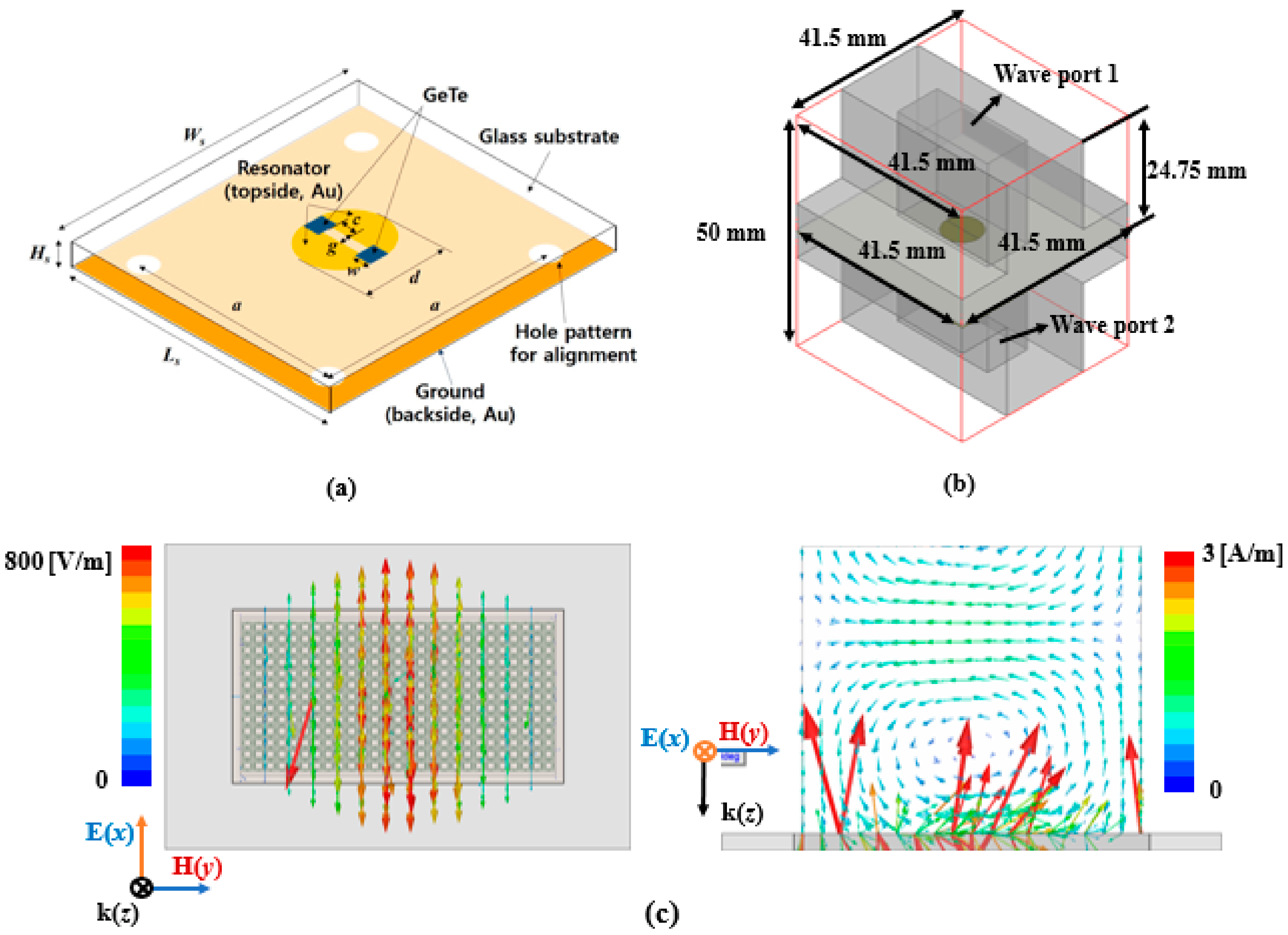
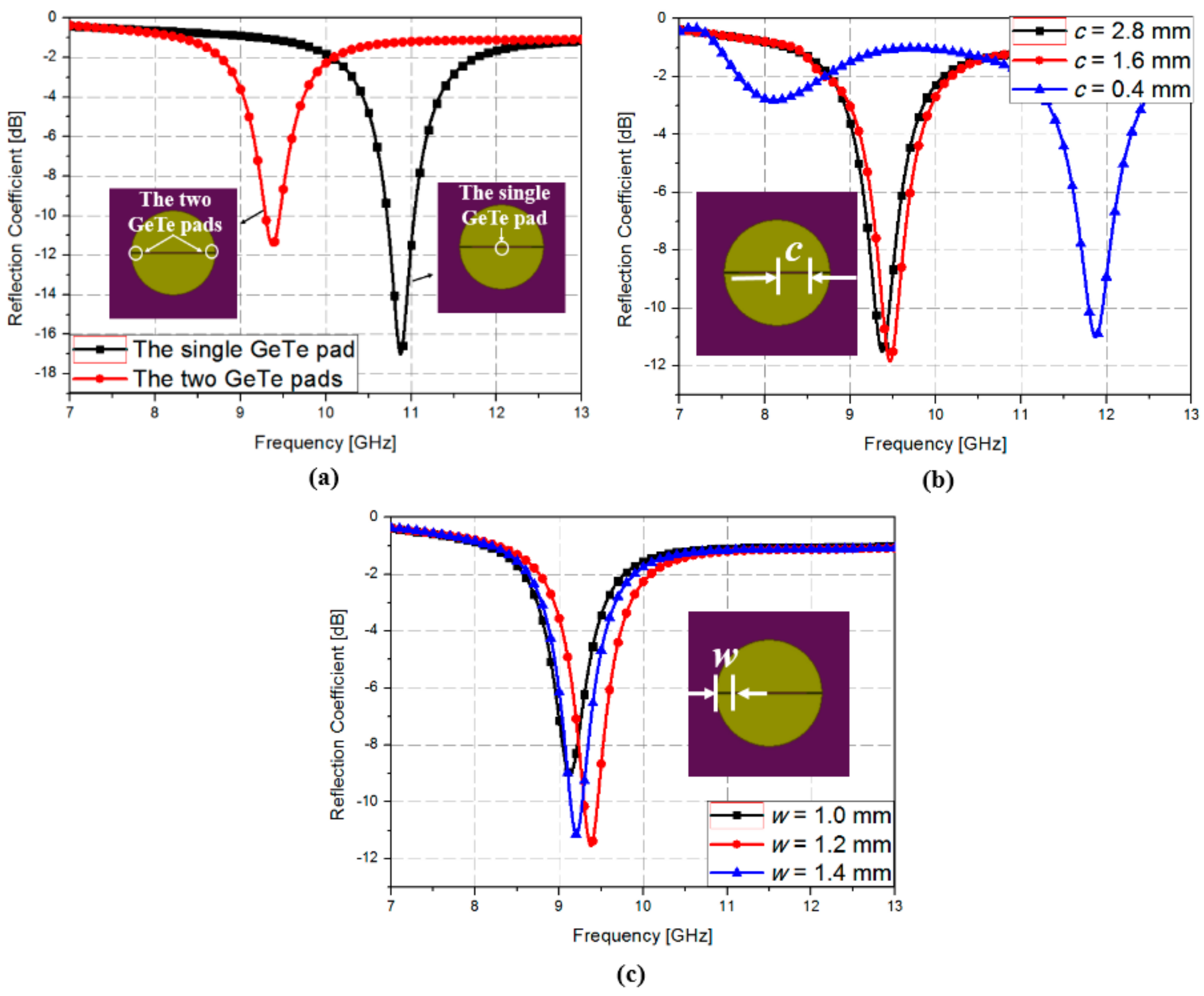
2. Numerical Simulation
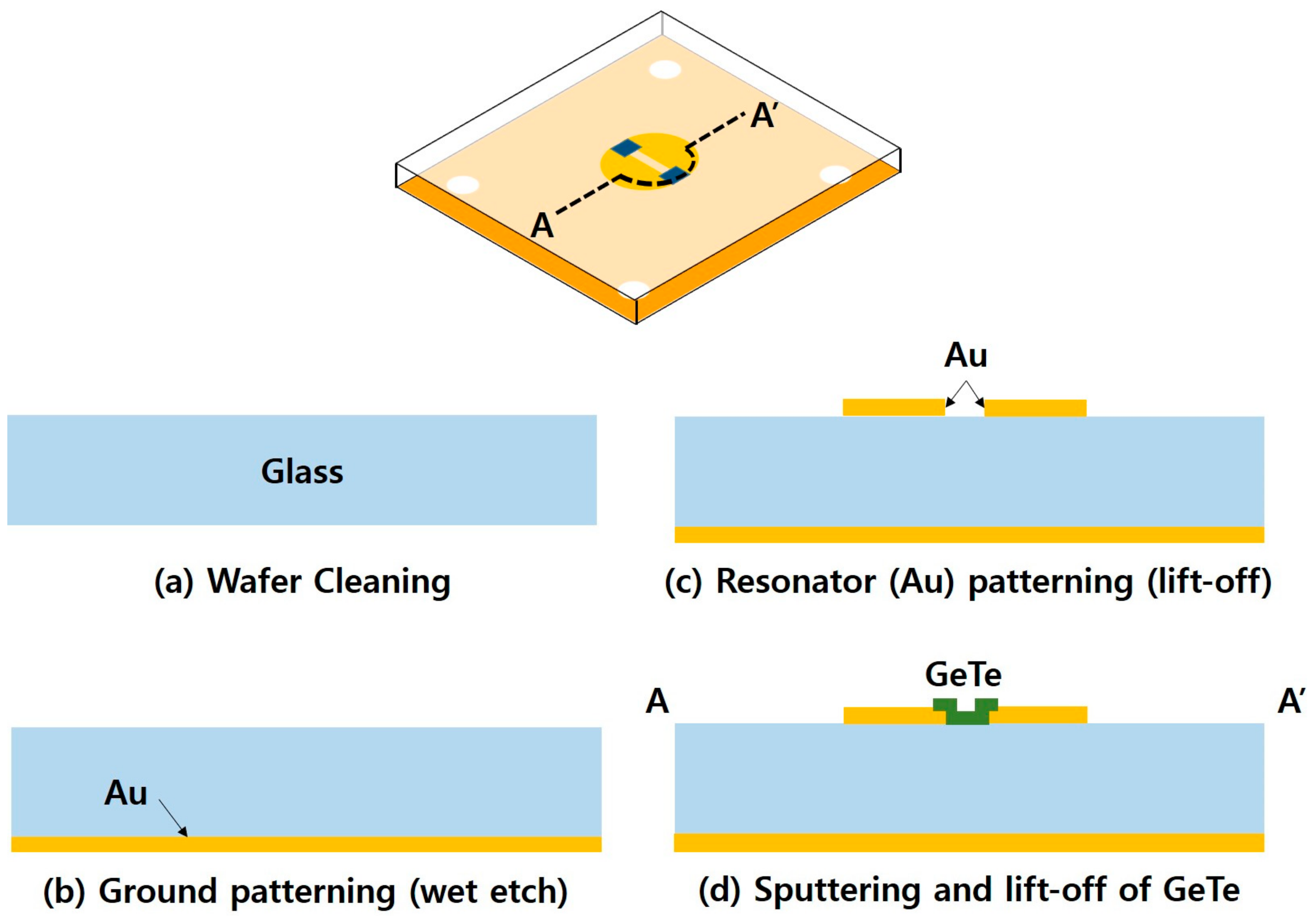
3. Fabrication Process
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahparnia, S.; Ramahi, O.M. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) reduction from printed circuit boards (PCB) using electromagnetic bandgap strctures. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2004, 46, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Hanai, K.; Takano, K.; Nishida, T.; Miyamaru, F.; Nakajima, M.; Hangyo, M. Trapping waves with terahertz metamaterial absorber based on isotropic Mie resonators. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3197–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Sung, H.; Lim, S. Flexible subterahertz metamaterial absorber fabrication using inkjet printing technology. Appl. Phys. B-Lasers Opt. 2016, 122, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, N.; Bingham, C.; Tyler, T.; Jokerst, N.; Smith, D.; Padilla, W. Design, theory, and measurement of a polarization-insensitive absorber for terahertz imaging. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurig, D.; Mock, J.J.; Justice, B.J.; Cummer, S.A.; Pendry, J.B.; Starr, A.F.; Smith, D.R. Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies. Science 2006, 314, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaszczuk, K.; Strikwerda, A.C.; Fan, K.; Zhang, X.; Averitt, R.D.; Jepsen, P.U. Flexible metamaterial absorbers for stealth applications at terahertz frequencies. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.W.; Gong, S.X.; Zhang, S.; Mu, X.; Hong, T. RCS reduction of array antennas with radar absorbing structures. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2011, 25, 2487–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, H.M.; Chan, N.H.; Ma, G.C.; Sheng, P. Acoustic metamaterial panels for sound attenuation in the 50–1000 Hz regime. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 041906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenneau, S.; Movchan, A.; Petursson, G.; Ramakrishna, S.A. Acoustic metamaterials for sound focusing and confinement. New J. Phys. 2007, 9, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Zhu, X.; Cheng, J. Fine manipulation of sound via lossy metamaterials with independent and arbitrary reflection amplitude and phase. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1632. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, S. Analysis of Absorption Loss by a Human Body in On-to-off Body Communication at 2.45 GHz. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2015, 15, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Choi, J.; Kim, S.S. Wide bandwidth pyramidal absorbers of granular ferrite and carbonyl iron powders. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 3272–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Oh, J.H. The microwave absorbing phenomena of ferrite microwave absorbers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1993, 29, 3437–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Jo, K.-J.; Jung, G.-B.; An, C.-C. Effects of sheet thickness on the electromagnetic wave absorbing characterization of Li0.375Ni0.375Zn0.25-ferrite composite as a radiation absorbent material. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2016, 16, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, L.J. The design of Jauman absorbers. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1994, 36, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhao, C.Y.; Bao, H. Design and analysis of Salisbury screens and Jaumann absorbers for solar radiation absorption. Front. Energy 2018, 12, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, N.I.; Sajuyigbe, S.; Mock, J.J.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 207402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Lim, S. Wide Incidence Angle-Insensitive Metamaterial Absorber for Both TE and TM Polarization Using Eight-Circular-Sector. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3204. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Kim, H.K.; Lim, S. Textile Metamaterial Absorber using Screen Printed Chanel Logo. Microwave Opt. Technol. Lett. 2017, 59, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-B.; Zhou, P.-H.; Lu, H.-P.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Liang, D.-F.; Deng, L.-J. Resistance selection of high impedance surface absorbers for perfect and broadband absorption. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Monorchio, A. A frequency selective radome with wideband absorbing properties. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2012, 60, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Ouslimani, H.H. Broadband polarization-independent wide-angle and reconfigurable phase transition hybrid metamaterial absorber. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 093104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Hu, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhou, P. Design of a wide-band nearly perfect absorber based on multi-resonance with square patch. Solid State Commun. 2014, 188, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Tuong, P.V.; Rhee, J.Y.; Kim, K.W.; Jang, W.H.; Choi, E.H.; Chen, L.Y.; Lee, Y. Multi-band metamaterial absorber based on the arrangement of donut-type resonators. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9691–9702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.-Y.; Wang, B.; Lai, S.; Zhang, D.H.; Teng, J.-H. Ultrathin multi-band planar metamaterial absorber based on standing wave resonances. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 27756–27765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mias, C.; Yap, J.H. A varactor-tunable high impedance surface with a resistvie-lumped-element biasing grid. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.; Monorchio, A.; Manara, G. Analysis and design of ultra thin electromagnetic absorbers comprising resistively loaded high impedance surfaces. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 1551–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Gong, R.Z.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X. Design, fabrication and measurement of a broadband polarization-insensitive metamaterial absorber based on lumped elements. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 044902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Jeong, H.; Lim, S. Electronically Switchable Broadband Metamaterial Absorber. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennant, A.; Chambers, B. Adaptive radar absorbing structure with PIN diode controlled active frequency selective surface. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Sonkusale, S. Microwave diode switchable metamaterial reflector/absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 03192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. Frequency-Tunable Metamtaerial Absorber Using a Varactor-Loaded Fishnet-Like Resonator. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 4113–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isić, G.; Vasić, B.; Zografopoulos, D.C.; Beccherelli, R.; Gajić, R. Electrically Tunable Critically Coupled Terahertz Metamaterial Absorber Based on Nematic Liquid Crystals. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 064007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrekenhamer, D.; Chen, W.-C.; Padilla, W.J. Liquid crystal tunable metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 177403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Lee, D.; Lim, S. A Fluidically Tunable Metasurface Absorber for Flexible Large-Scale Wireless Ethanol Sensor Applications. Sensors 2016, 16, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, K.; Kim, H.K.; Yoo, M.; Lim, S. Frequency-Switchable Metamaterial Absorber Injecting Eutectic Gallium-Indium (EGaIn) Liquid Metal Alloy. Sensors 2015, 15, 28154–28165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, D.; Eom, S.; Lim, S. Stretchable Metamaterial Absorber Using Liquid Metal-Filled Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). Sensors 2016, 16, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Lim, S. A Stretchable Electromagnetic Absorber Fabricated Using Screen Printing Technology. Sensors 2017, 17, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Feng, S.; Qiu, K.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, J. Mechanically stretchable and tunable metamaterial absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 106, 091907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shah, C.M.; Withayachumnankul, W.; Ung, B.S.; Mitchell, A.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Chang, S.; Abbott, D. Mechanically tunable terahertz metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankhorst, M.; Ketelaars, B.; Wolters, R. Low-cost and nanoscale non-volatile memory concept for future silicon chips. Nat. Mater. 2005, 4, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.N.; Krusin-Elbaum, L.; Newns, D.M.; Elmegreen, B.G.; Cheek, R.; Rana, N.; Young, A.M.; Koester, S.J.; Lam, C. Programmable via using indirectly heated phase-change switch for reconfigurable logic applications. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2008, 29, 131–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.-Y.; Zhang, H.-W.; Yang, Q.-H.; Chen, Z.; Long, Y.; Jing, Y.-L.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, P.-X. A tunable hybrid metamaterial absorber based on vanadium oxide films. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 235106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.R. Metamaterials based on the phase transition of VO2. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, E.K.; Shi, L.P.; Zhao, R.; Lim, K.G.; Chong, T.C.; Schlesinger, T.E.; Bain, J.A. Low resistance, high dynamic range reconfigurable phase change switch for radio frequency applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 183506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shim, Y.; Rais-Zadeh, M. A low-loss directly heated two-port RF phase change switch. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2014, 35, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hinnawy, N.; Borodulin, P.; Wagner, B.; King, M.; Jones, E.; Howell, R.; Lee, M.; Young, R. Low-loss latching microwave switch using thermally pulsed non-volatile chalcogenide phase change materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 013501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Reference Paper | Tuning Technology | Lowest Frequency (flow) [GHz] | Highest Frequency (fhigh) [GHz] | TR (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [45] | Vanadium Oxide | 9.0 | 9.6 | 1.06 |
| [44] | Vanadium Oxide | 9.36 | 9.98 | 1.06 |
| Proposed work | Germanium Telluride | 9.4 | 10.51 | 1.11 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, H.; Park, J.-H.; Moon, Y.-H.; Baek, C.-W.; Lim, S. Thermal Frequency Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Absorber Using Phase Change Material. Sensors 2018, 18, 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103506
Jeong H, Park J-H, Moon Y-H, Baek C-W, Lim S. Thermal Frequency Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Absorber Using Phase Change Material. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103506
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Heijun, Jeong-Heum Park, You-Hwan Moon, Chang-Wook Baek, and Sungjoon Lim. 2018. "Thermal Frequency Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Absorber Using Phase Change Material" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103506
APA StyleJeong, H., Park, J.-H., Moon, Y.-H., Baek, C.-W., & Lim, S. (2018). Thermal Frequency Reconfigurable Electromagnetic Absorber Using Phase Change Material. Sensors, 18(10), 3506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103506






