Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Low Back 3D Accelerometer in Post-Stroke Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition
2.2. Gait Symmetry Assessment with Two Feet Sensors
2.2.1. Symmetry of Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters
2.2.2. Symmetry of Foot Pitch Angular Velocity
2.3. Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Single 3D Accelerometer at the Low Back
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
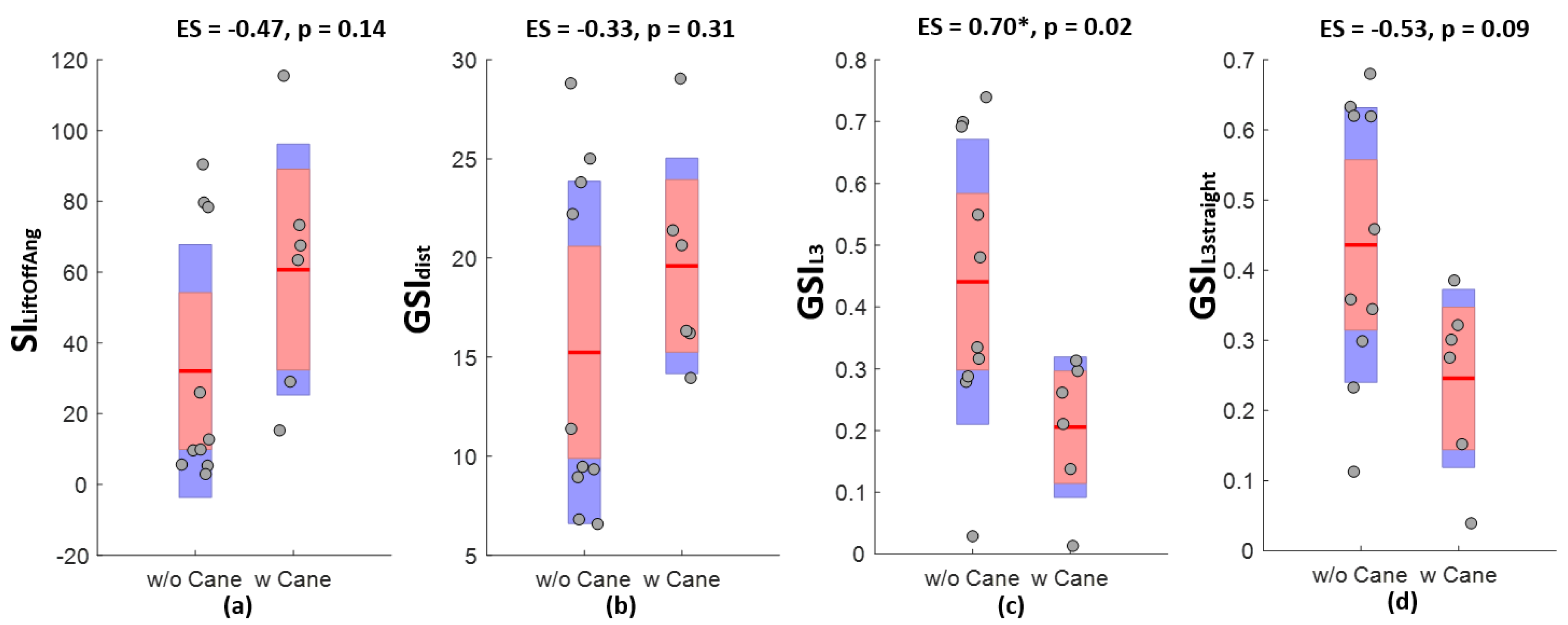
3.1. Discriminative Power of Gait Symmetry as Measured by Various Indices
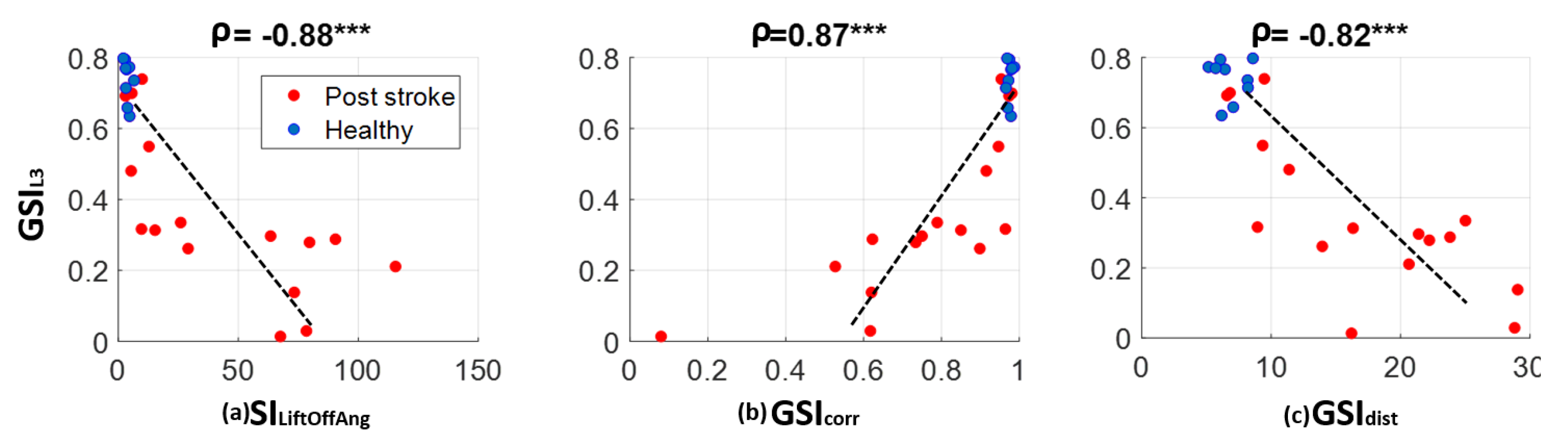
3.2. Correlations between Gait Symmetry Measured with Low Back Accelerometry and That Measured with Two Feet Sensors
4. Discussion
4.1. Advantages in Technical Implementation
4.2. Advantages in Clinical Practice
4.3. Limitations
4.4. Future Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mobility after Stroke. Available online: http://www.stroke.org/stroke-resources/library/mobility-after-stroke (accessed on 7 February 2018).
- Patterson, K.K.; Parafianowicz, I.; Danells, C.J.; Closson, V.; Verrier, M.C.; Staines, W.R.; Black, S.E.; McIlroy, W.E. Gait asymmetry in community-ambulating stroke survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olney, S.J.; Richards, C. Hemiparetic gait following stroke. Part I: Characteristics. Gait Posture 1996, 4, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, A.-L.; Tang, P.-F.; Jan, M.-H. Analysis of impairments influencing gait velocity and asymmetry of hemiplegic patients after mild to moderate stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.-T.; Novak, A.C.; Brouwer, B.; Li, Q. Estimation of spatio-temporal parameters for post-stroke hemiparetic gait using inertial sensors. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.K.; Gage, W.H.; Brooks, D.; Black, S.E.; McIlroy, W.E. Evaluation of gait symmetry after stroke: A comparison of current methods and recommendations for standardization. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna, A.S.; Wickström, N.; Eklund, H.; Zügner, R.; Tranberg, R. Assessment of Gait Symmetry and Gait Normality Using Inertial Sensors: In-Lab and In-Situ Evaluation. In Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 239–254. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-38256-7_16 (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Sung, P.S.; Danial, P. A Kinematic Symmetry Index of Gait Pattern Between Older Adults with and without Low Back Pain. Spine. 10 November 2017. Publish Ahead of Print. Available online: http://journals.lww.com/spinejournal/Abstract/publishahead/A_Kinematic_Symmetry_Index_of_Gait_Pattern_Between.95621.aspx (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Moevus, A.; Mignotte, M.; de Guise, J.A.; Meunier, J. A perceptual map for gait symmetry quantification and pathology detection. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2015, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewar, M.E.; Judge, G. Temporal asymmetry as a gait quality indicator. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1980, 18, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüest, S.; Massé, F.; Aminian, K.; Gonzenbach, R.; de Bruin, E.D. Reliability and validity of the inertial sensor-based Timed “Up and Go” test in individuals affected by stroke. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2016, 53, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodt-Billington, C.; Helbostad, J.L.; Moe-Nilssen, R. Should trunk movement or footfall parameters quantify gait asymmetry in chronic stroke patients? Gait Posture 2008, 27, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Anna, A.; Wickström, N. A Symbol-Based Approach to Gait Analysis from Acceleration Signals: Identification and Detection of Gait Events and a New Measure of Gait Symmetry. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Smuck, M.; Legault, C.; Ith, M.A.; Muaremi, A.; Aminian, K. Simple Gait Symmetry Measures Based on Foot Angular Velocity: Analysis in Post Stroke Patients. Honolulu, HI, USA, 2018. Available online: http://embc.embs.org/2018/wp-content/uploads/sites/35/2018/08/99118-EMBC-Final-Program.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Stroke Impact Scale (SIS). Stroke Engine. Available online: https://www.strokengine.ca/en/assess/sis/ (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Kosak, M.; Smith, T. Comparison of the 2-, 6-, and 12-minute walk tests in patients with stroke. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2005, 42, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MTw Awinda—Products. Xsens 3D Motion Tracking. Available online: https://www.xsens.com/products/mtw-awinda/ (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Mariani, B.; Hoskovec, C.; Rochat, S.; Büla, C.; Penders, J.; Aminian, K. 3D gait assessment in young and elderly subjects using foot-worn inertial sensors. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, B.; Rouhani, H.; Crevoisier, X.; Aminian, K. Quantitative estimation of foot-flat and stance phase of gait using foot-worn inertial sensors. Gait Posture 2013, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, B.; Jiménez, M.C.; Vingerhoets, F.J.G.; Aminian, K. On-Shoe Wearable Sensors for Gait and Turning Assessment of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, B.; Rochat, S.; Büla, C.J.; Aminian, K. Heel and Toe Clearance Estimation for Gait Analysis Using Wireless Inertial Sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3162–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashi, F.; Mariani, B.; Rochat, S.; Büla, C.J.; Santos-Eggimann, B.; Aminian, K. Gait and Foot Clearance Parameters Obtained Using Shoe-Worn Inertial Sensors in a Large-Population Sample of Older Adults. Sensors 2013, 14, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe-Nilssen, R.; Helbostad, J.L. Estimation of gait cycle characteristics by trunk accelerometry. J. Biomech. 2004, 37, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Schroeder, H.P.; Coutts, R.D.; Lyden, P.D.; Billings, E.; Nickel, V.L. Gait parameters following stroke: A practical assessment. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 1995, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Macbeth, G.; Razumiejczyk, E.; Ledesma, R.D. Cliff’s Delta Calculator: A non-parametric effect size program for two groups of observations. Univ. Psychol. 2011, 10, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, J.; Kromrey, J.D.; Coraggio, J.; Skowronek, J.; Devine, L. Appropriate Statistics for Ordinal Level Data: Should We Really Be Using t-Test and Cohen’sd for Evaluating Group Differences on the NSSE and Other Surveys? BibSonomy: Arlington, Virginia, 2006. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.595.6157&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Moufawad el Achkar, C.; Lenoble-Hoskovec, C.; Paraschiv-Ionescu, A.; Major, K.; Büla, C.; Aminian, K. Physical Behavior in Older Persons during Daily Life: Insights from Instrumented Shoes. Sensors 2016, 16, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, U.-X.; Veluvolu, K.C.; Latt, W.T.; Shee, C.Y.; Riviere, C.N.; Ang, W.T. Estimating Displacement of Periodic Motion with Inertial Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 8, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesse, S.; Jahnke, M.; Schreiner, C.; Mauritz, K.-H. Gait symmetry and functional walking performance in hemiparetic patients prior to and after a 4-week rehabilitation programme. Gait Posture 1993, 1, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter [Unit] | Description |
|---|---|
| Spatial | |
| PathLength [% stride length] | Ratio between the length of the real path of the foot in 3D space (including both stride length and width) and stride length of one cycle. |
| StrikeAng [deg] | Angle between the foot and the ground at heel strike in sagittal plane. |
| LiftOffAng [deg] | Angle between the foot and the ground at toe off in sagittal plane. |
| MaxAngVel [deg/s] | Maximum pitch foot angular velocity during swing phase. |
| Temporal | |
| StanceRatio [%] | Percentage of the gait cycle during which the foot is in stance phase. |
| LoadRatio [%] | Percentage of the stance corresponding to loading phase defined as the time between heel strike and toe strike |
| FootFlatRatio [%] | Percentage of the stance corresponding to the foot-flat phase |
| PushRatio [%] | Percentage of the stance corresponding to push phase defined as the time between heel off and toe off. |
| Symmetry Index (SI) | Control Group | Post-stroke | ES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gait symmetry based on spatiotemporal gait parameter | |||
| PathLength | 0.54 ± 0.07 | 4.30 ± 5.69 | −0.85 *** |
| StrikeAng | 8.50 ± 4.53 | 35.78 ± 30.85 | −0.79 ** |
| LiftOffAng | 3.78 ± 1.33 | 42.80 ± 37.27 | −0.88 *** |
| MaxAngVel | 6.31 ± 3.78 | 44.86 ± 39.23 | −0.81 ** |
| StanceRatio | 3.06 ± 2.27 | 12.19 ± 8.06 | −0.79 ** |
| LoadRatio | 22.36 ± 9.42 | 32.36 ± 22.06 | −0.22 |
| FootFlatRatio | 5.99 ± 2.28 | 7.18 ± 4.98 | −0.13 |
| PushRatio | 6.88 ± 3.67 | 25.76 ± 25.57 | −0.71 ** |
| Gait symmetry based on feet angular velocity signal profile | |||
| 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.76 ± 0.24 | 0.85 *** | |
| 6.84 ± 1.23 | 16.87 ± 7.70 | −0.89 *** | |
| Gait symmetry based on low back accelerometry | |||
| 0.74 ± 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.22 | 0.89 *** | |
| 0.69 ± 0.09 | 0.36 ± 0.19 | 0.89 *** | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Smuck, M.; Legault, C.; Ith, M.A.; Muaremi, A.; Aminian, K. Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Low Back 3D Accelerometer in Post-Stroke Patients. Sensors 2018, 18, 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103322
Zhang W, Smuck M, Legault C, Ith MA, Muaremi A, Aminian K. Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Low Back 3D Accelerometer in Post-Stroke Patients. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103322
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Matthew Smuck, Catherine Legault, Ma A. Ith, Amir Muaremi, and Kamiar Aminian. 2018. "Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Low Back 3D Accelerometer in Post-Stroke Patients" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103322
APA StyleZhang, W., Smuck, M., Legault, C., Ith, M. A., Muaremi, A., & Aminian, K. (2018). Gait Symmetry Assessment with a Low Back 3D Accelerometer in Post-Stroke Patients. Sensors, 18(10), 3322. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103322






