Integrated 3D Hydrogel Waveguide Out-Coupler by Step-and-Repeat Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography: A Promising Sensor Device for Water and pH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
2.1. Material Formulation
2.2. Substrate Preparation
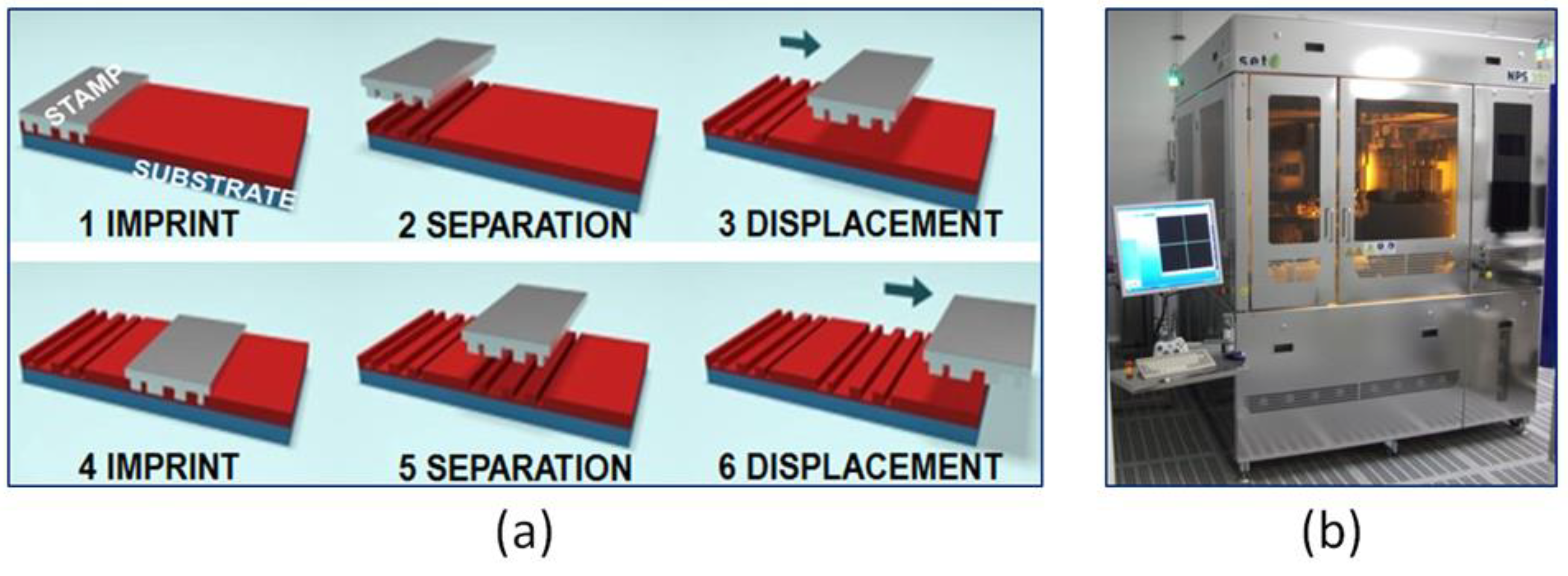
2.3. Stamp Manufacturing
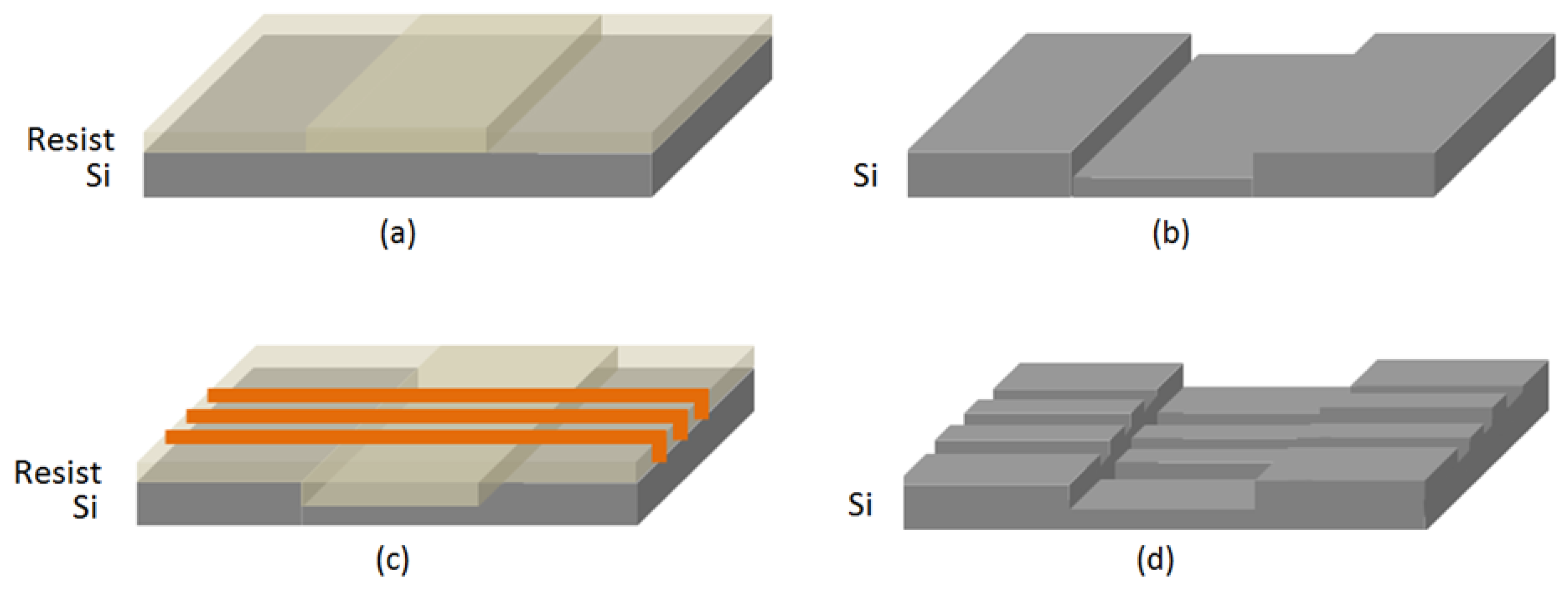
2.4. Patterning Method
2.5. Sensor Evaluation Setup
3. Results and Discussion
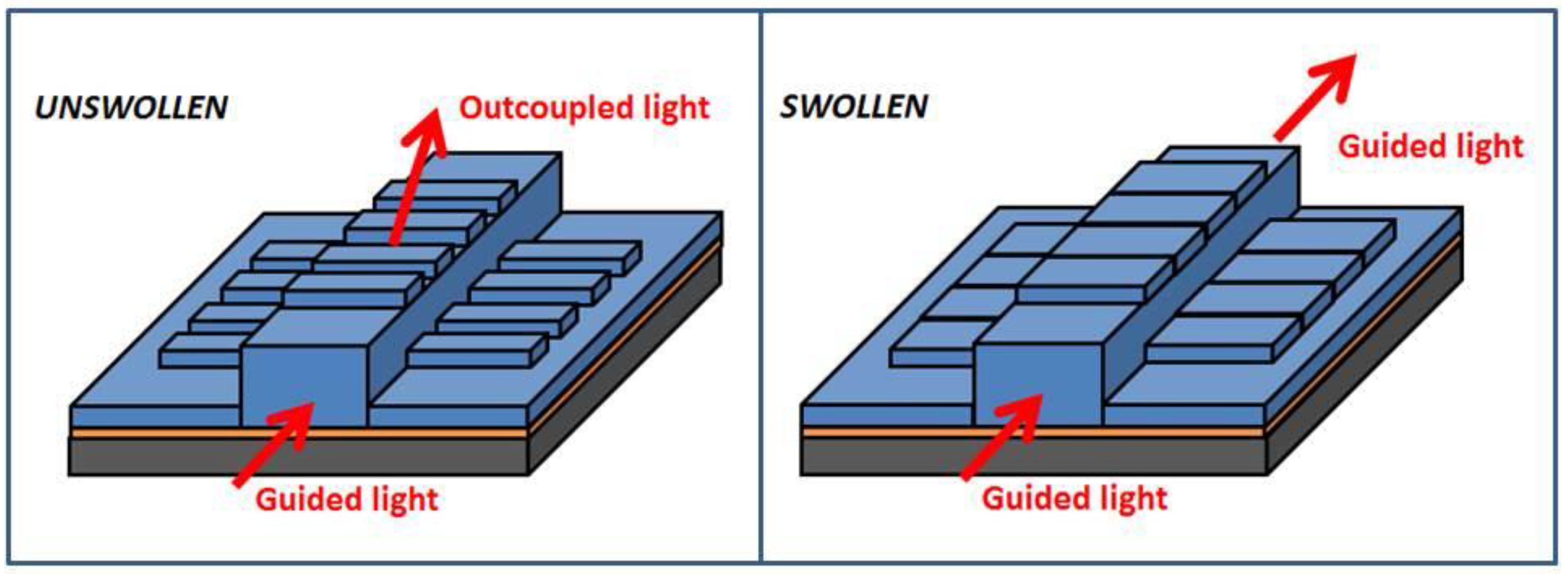
3.1. Device Concept
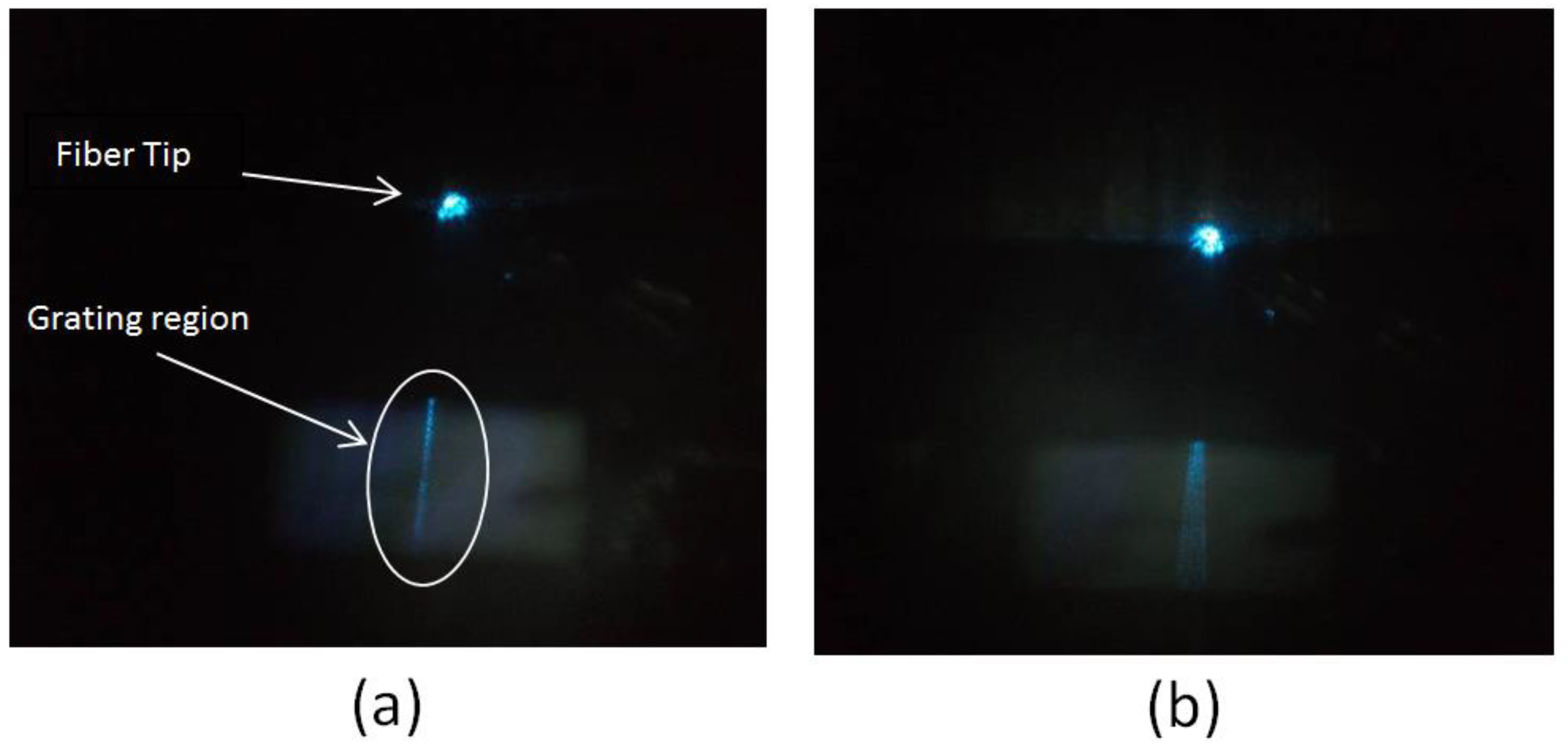
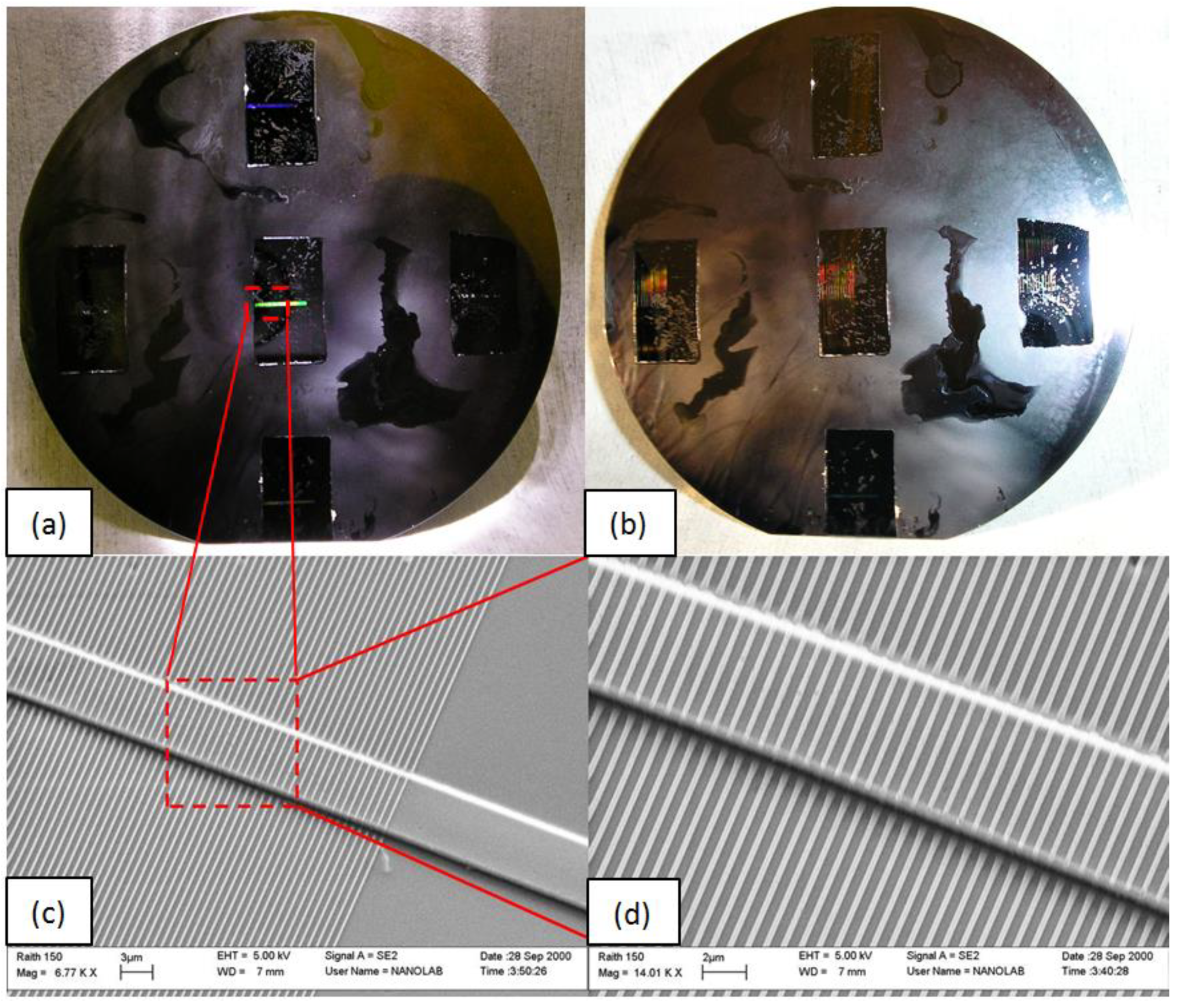
3.2. Device Fabrication
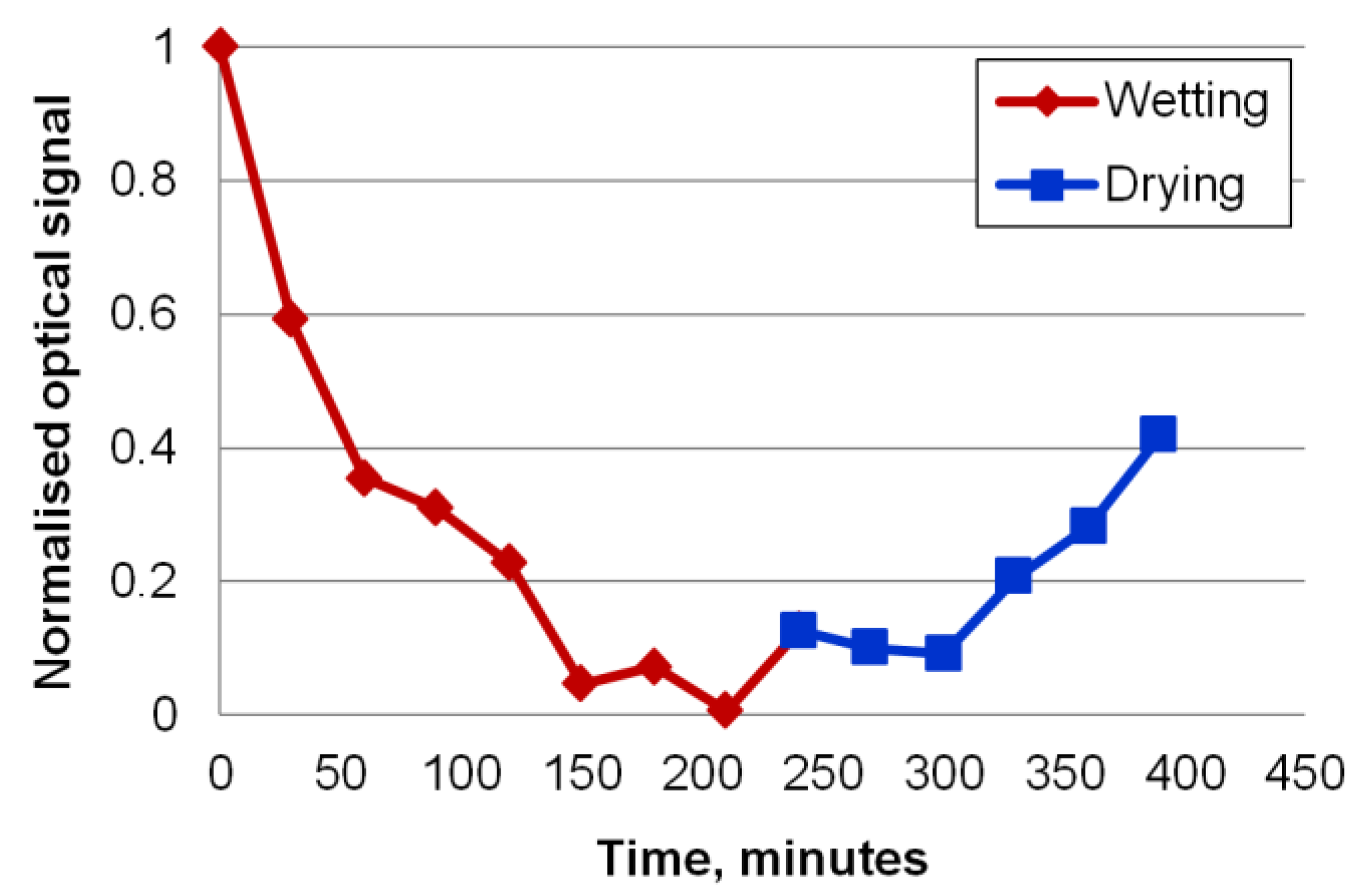
3.3. How Water Affects the Sensor
3.4. How pH Affects the Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahinroosta, M.; Farsangi, Z.J.; Allahverdi, A.; Shakoori, Z. Hydrogels as intelligent materials: A brief review of synthesis, properties and applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 8, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Bae, Y.H.; Okano, T. Hydrogels: Swelling, drug loading, and release. Pharm. Res. 1992, 9, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Hydrogel Based Sensors for Biomedical Applications: An Updated Review. Polymers 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.J.R.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogel scaffolds to study cell biology in four dimensions. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnoni, M.; Scotti, A.; Rudov, A.A.; Gelissen, A.P.H.; Caumanns, T.; Radulescu, A.; Eckert, T.; Pich, A.; Potemkin, I.I.; Richtering, W. Swelling of a responsive network within different constraints in multi-thermosensitive microgels. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2662–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew Lyon, L. “Smart Nanoparticles” Stimuli Sensitive Hydrogel Particles. Available online: http://nanoparticles.org/pdf/40-Lyon.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Gerlach, G.; Arndt, K.-F. Hydrogel Sensors and Actuators, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 165–195. ISBN 978-3-540-75645-3. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G.; Klatt, S.; Lienig, J.; Arndt, K.F.; Adler, H.J.P. Review on Hydrogel-based pH Sensors and Microsensors. Sensors 2008, 8, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Diffraction grating of hydrogel functionalized with glucose oxidase for glucose detection. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3872–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Liu, P.; Dong, L. Multichannel detection using transmissive diffraction grating sensor. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Moshe, M.; Alexeev, V.L.; Asher, S.A. Fast responsive crystalline colloidal array photonic crystal glucose sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y. Tunable Multiresponsive Methacrylic Acid Based Inverse Opal Hydrogels Prepared by Controlling the Synthesis Conditions. Langmuir 2009, 25, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, A.J.; Blyth, J.; Davidson, C.A.B.; Lowe, C.R. pH-Sensitive Holographic Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diemeer, M.B.J. Integrated Optical Waveguide Evanescent Field Sensor. WO Patent 2011157767A1, 22 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Foerster, T.; Strohhoefer, C. Fiber Optic Core and Biosensor. EP Patent 2088423A1, 12 August 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cong, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, K. Demonstration of etched cladding fiber Bragg grating-based sensors with hydrogel coating. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 96, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Wang, X. Polymer diffraction gratings on stimuli-responsive hydrogel surfaces: Soft-lithographic fabrication and optical sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 147, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, S.V. Nanoimprint lithography steppers for volume fabrication of leading-edge semiconductor integrated circuits. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 17075–17093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, A.; Khokhar, A.Z.; Bilbao, L.; Sáez-Martínez, V.; Corres, A.; Obieta, I.; Gadegaard, N. Nanopatterned UV curable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboud, V.; Obieta, I.; Bilbao, L.; Saez-Martinez, V.; Brun, M.; Laulagnet, F.; Landis, S. Imprinted hydrogels for tunable hemispherical microlenses. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 111, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- “Thermal Oxide Wafer” Product Specification. Available online: http://www.semiwafer.com/thermal%20oxide%20wafer.html (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Beines, P.W.; Klosterkamp, I.; Menges, B.; Jonas, U.; Knoll, W. Responsive Thin Hydrogel Layers from Photo-Cross-Linkable Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Terpolymers. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revzin, A.; Russel, R.J.; Yadavalli, W.K.; Koh, W.-G.; Deister, C.; Hile, D.D.; Mellott, M.B.; Pishko, M.V. Fabrication of Poly(ethylene glycol) Hydrogel Microstructures Using Photolithography. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5440–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.Y.; Krauss, P.R.; Renstrom, P.J. Imprint of sub-25 nm vias and trenches in polymers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1995, 67, 3114–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-W.; Shen, Y.-K.; Chuang, S.-Y.; Wei, C. Anti-adhesive effects of diverse self-assembled monolayers in nanoimprint lithography. Sens. Actuators A 2007, 139, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.; Graczyk, M.; Maximov, I.; Sarwe, E.L.; Ling, T.G.I.; Keil, M.; Montelius, L. Improving stamps for 10 nm level wafer scale nanoimprint lithography. Microelectron. Eng. 2002, 61–62, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francone, A. Materials and Anti-Adhesive Issues in UV-NIL. Ph.D. Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Grenoble-INPG, Grenoble, France, 9 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Peppas, N.A. Equilibrium swelling behavior of pH-sensitive hydrogels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Waveguide Width | Waveguide Height | Grating Height | Grating Line Width | Grating Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 1–5 μm | 0.5–1.0 μm | 100–150 nm | 400–500 nm | 700–800 nm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francone, A.; Kehoe, T.; Obieta, I.; Saez-Martinez, V.; Bilbao, L.; Khokhar, A.Z.; Gadegaard, N.; Simao, C.D.; Kehagias, N.; Sotomayor Torres, C.M. Integrated 3D Hydrogel Waveguide Out-Coupler by Step-and-Repeat Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography: A Promising Sensor Device for Water and pH. Sensors 2018, 18, 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103240
Francone A, Kehoe T, Obieta I, Saez-Martinez V, Bilbao L, Khokhar AZ, Gadegaard N, Simao CD, Kehagias N, Sotomayor Torres CM. Integrated 3D Hydrogel Waveguide Out-Coupler by Step-and-Repeat Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography: A Promising Sensor Device for Water and pH. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103240
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancone, Achille, Timothy Kehoe, Isabel Obieta, Virginia Saez-Martinez, Leire Bilbao, Ali Z. Khokhar, Nikolaj Gadegaard, Claudia Delgado Simao, Nikolaos Kehagias, and Clivia M. Sotomayor Torres. 2018. "Integrated 3D Hydrogel Waveguide Out-Coupler by Step-and-Repeat Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography: A Promising Sensor Device for Water and pH" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103240
APA StyleFrancone, A., Kehoe, T., Obieta, I., Saez-Martinez, V., Bilbao, L., Khokhar, A. Z., Gadegaard, N., Simao, C. D., Kehagias, N., & Sotomayor Torres, C. M. (2018). Integrated 3D Hydrogel Waveguide Out-Coupler by Step-and-Repeat Thermal Nanoimprint Lithography: A Promising Sensor Device for Water and pH. Sensors, 18(10), 3240. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103240





