Fabrication of a Novel Highly Sensitive and Selective Immunosensor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Based on an Effective Platform of Electrosynthesized Gold Nanodendrites/Chitosan Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Apparatus
2.2. Preparation of the Antibody and Antigen
2.3. Preparation of CSNPs
2.4. Preparation of Proposed Immunosensor
2.5. Preparation of Real Sample
3. Results
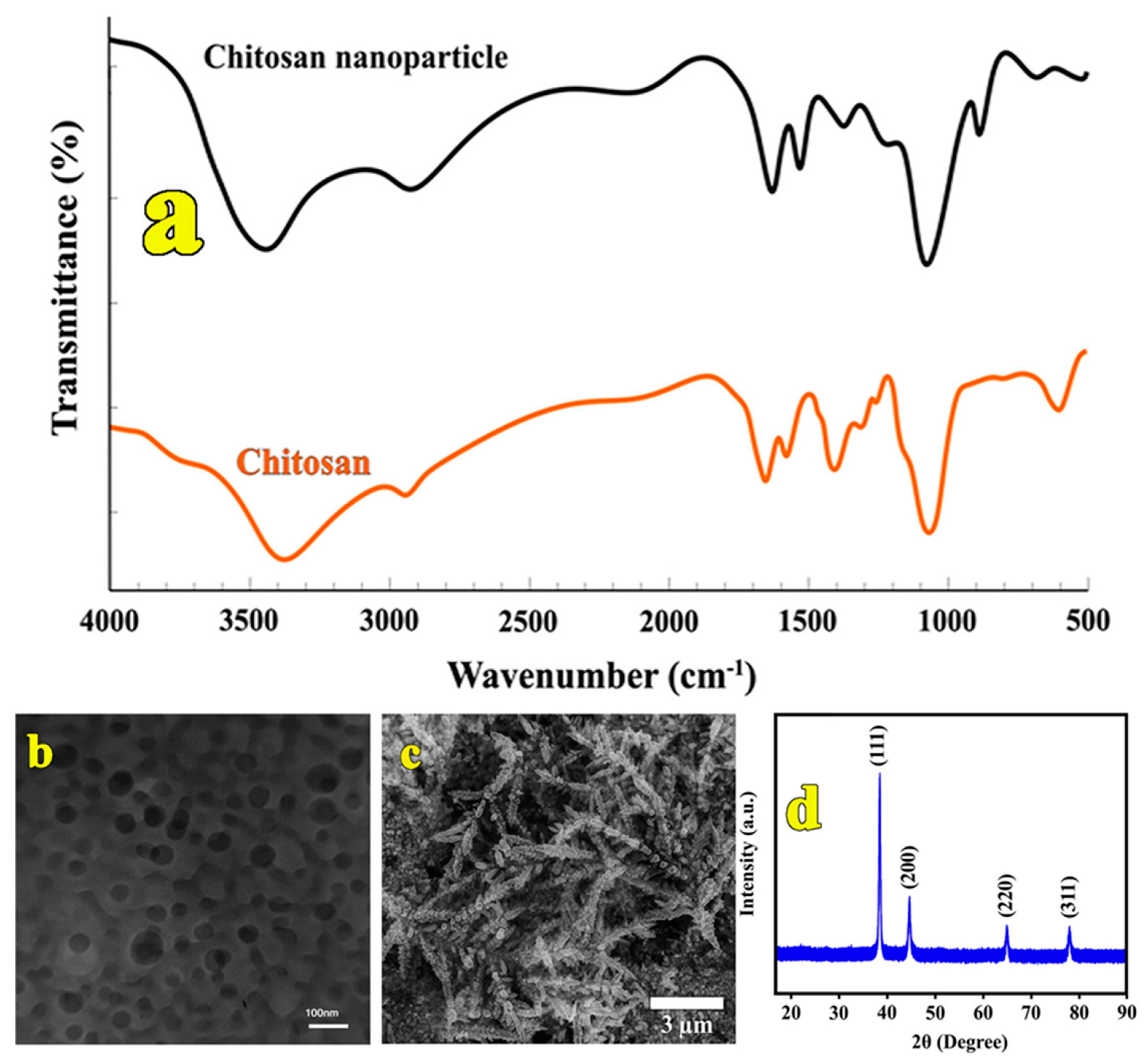
3.1. Characterization of Synthesized CS Nanocomposite
3.2. Characterization of the Immunosensor (CV and EIS)
3.3. Optimization of the Antibody Immobilization Conditions
3.4. Optimization of Assay Conditions
3.5. Analytical Performance of the Immunosensor
3.6. Application of the Immunosensor in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koh, C.-Y.; Schaff, U.Y.; Piccini, M.E.; Stanker, L.H.; Cheng, L.W.; Ravichandran, E.; Singh, B.-R.; Sommer, G.J.; Singh, A.K. Centrifugal microfluidic platform for ultrasensitive detection of botulinum toxin. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, A.L.; Hoard-Fruchey, H.M. A capillary electrophoresis method to assay catalytic activity of botulinum neurotoxin serotypes: Implications for substrate specificity. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 366, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oordt, T.; Stevens, G.B.; Vashist, S.K.; Zengerle, R.; Von Stetten, F. Rapid and highly sensitive luciferase reporter assay for the automated detection of botulinum toxin in the centrifugal microfluidic LabDisk platform. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22046–22052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Kang, L.; Liu, Y. Avian eyelid assay, a new diagnostic method for detecting botulinum neurotoxin serotypes A, B and E. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Song, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, C. Development of highly sensitive chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay based on the anti-recombinant HC subunit of botulinum neurotoxin type A monoclonal antibodies. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 735, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grate, J.W.; Ozanich, R.M.; Warner, M.G.; Bruckner-Lea, C.J.; Marks, J.D. Advances in assays and analytical approaches for botulinum-toxin detection. Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1137–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruge, D.R.; Dunning, F.M.; Piazza, T.M.; Molles, B.E.; Adler, M.; Zeytin, F.N.; Tucker, W.C. Detection of six serotypes of botulinum neurotoxin using fluorogenic reporters. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 411, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, S.; Korampally, V.; Darr, C.M.; Folk, W.R.; Polo-Parada, L.; Gangopadhyay, K.; Gangopadhyay, S. Femtogram-level detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin type A by sandwich immunoassay using nanoporous substrate and ultra-bright fluorescent suprananoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, S.; Ferracci, G.; Berthomieu, M.; Kozaki, S.; Miquelis, R.; Boucraut, J.; Seagar, M.; Lévêque, C. A protein chip membrane-capture assay for botulinum neurotoxin activity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, B.; Kim, Y.; Janda, K.D. A cyclic peptide-polymer probe for the detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. Toxicon 2006, 47, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Baudys, J.; Kalb, S.R.; Barr, J.R. Improved detection of botulinum neurotoxin type A in stool by mass spectRometry. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 412, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Baudys, J.; Ye, Y.M.; Rees, J.C.; Barr, J.R.; Pirkle, J.L.; Kalb, S.R. Improved Detection of Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A by Endopep-MS through Peptide Substrate Modification. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 15, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, B.; Schmidt, J.J.; Smith, L.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Rapid product analysis and increased sensitivity for quantitative determinations of botulinum neurotoxin proteolytic activity. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 396, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Khoshsafar, H.; Afkhami, A.; Amidi, S. Sensitive and simple simultaneous determination of morphine and codeine using a Zn2SnO4 nanoparticle/graphene composite modified electrochemical sensor. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 7102–7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Hashemi, P.; Bagheri, H.; Salimian, J.; Ahmadi, A.; Madrakian, T. Impedimetric immunosensor for the label-free and direct detection of botulinum neurotoxin serotype A using Au nanoparticles/graphene-chitosan composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Wright, J.D.; Millner, P.A. Novel impedimetric immunosensor for detection of pathogenic bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes in human saliva. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 12118–12125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Mitra, C.K. Simple and sensitive electrochemical impedimetric approach towards analysis of biophysical interaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Ranjbari, E.; Amiri-Aref, M.; Hajian, A.; Ardakani, Y.H.; Amidi, S. Modified fractal iron oxide magnetic nanostructure: A novel and high performance platform for redox protein immobilization, direct electrochemistry and bioelectrocatalysis application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Afkhami, A.; Khoshsafar, H.; Hajian, A.; Shahriyari, A. Protein capped Cu nanoclusters-SWCNT nanocomposite as a novel candidate of high performance platform for organophosphates enzymeless biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, H.; Talemi, R.P.; Afkhami, A. Gold nanoparticles deposited on fluorine-doped tin oxide surface as an effective platform for fabricating a highly sensitive and specific digoxin aptasensor. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 58491–58498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Wei, S.; Cai, C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, J.M. One-Step Electrodeposition of Polyallylamine-Functionalized Gold Nanodendrites and Their Application in Sensing. ChemPlusChem 2015, 80, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racoviţă, S.; Vasiliu, S.; Popa, M.; Luca, C. Polysaccharides based on micro-and nanoparticles obtained by ionic gelation and their applications as drug delivery systems. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2009, 54, 709–718. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, A.C.; Buckley, N.; Halliwell, J.; Gwenin, C. Botulinum neurotoxin serotypes detected by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Toxins 2015, 7, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KoUKaras, E.N.; Papadimitriou, S.A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; Froudakis, G.E. Insight on the formation of chitosan nanoparticles through ionotropic gelation with tripolyphosphate. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2856–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.K.; Samdani, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.H. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide assisted direct electrodeposition of gold nanodendrites and its electrochemical applications. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, V.R.; Gamez, F.J.; Keener, W.K.; White, J.A.; Poli, M.A. Rapid detection of Clostridium botulinum toxins A, B, E, and F in clinical samples, selected food matrices, and buffer using paramagnetic bead-based electrochemiluminescence detection. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 353, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Zou, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Fu, S. Chitosan nanoparticles as a novel delivery system for ammonium glycyrrhizinate. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 295, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Du, Y. Effect of molecular structure of chitosan on protein delivery properties of chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Blasi, P.; Bellich, B.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, size evolution and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, K.A.; Fresneau, M.P.; Marazuela, A.; Fabra, A.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan nanoparticles as delivery systems for doxorubicin. J. Control. Release 2001, 73, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vais, R.D.; Sattarahmady, N.; Karimian, K.; Heli, H. Green electrodeposition of gold hierarchical dendrites of pyramidal nanoparticles and determination of azathioprine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromidis, M.I. Impedimetric immunosensors-A review. Electrochim. Acta. 2010, 55, 4227–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Arab, S.M.; Khoshsafar, H.; Afkhami, A. A novel sensor for sensitive determination of atropine based on a Co3O4-reduced graphene oxide modified carbon paste electrode. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 3875–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.J.; Yang, G.J.; Shao, H.X.; Qin, A.J. A novel label-free impedimetric immunosensor for detection of semicarbazide residue based on gold nanoparticles-functional chitosan composite membrane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, D.B.; Stevens, R.C. Sequence homology and structural analysis of the clostridial neurotoxins. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 291, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W. Covalent functionalization of gold nanoparticles as electronic bridges and signal amplifiers towards an electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type A. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Ponmariappan, S.; Shaik, M.; Upadhyay, S. Electrochemical immunosensor for botulinum neurotoxin type-E using covalently ordered graphene nanosheets modified electrodes and gold nanoparticles-enzyme conjugate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 69, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, C.; Tsang, M.K.; Tian, F.; Hao, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, M. A reduced graphene oxide-Au based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxin A. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ferreira, J.; Eblen, B.; Whiting, R. Detection of type A, B, E, and F neurotoxins in foods by using an amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with digoxigenin-labeled antibodies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, J.; Webb, M.D.; Peck, M.W. Rapid affinity immunochromatography column-based tests for sensitive detection of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxins and Escherichia coli O157. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4143–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, S.R.; Baudys, J.; Webb, R.P.; Wright, P.; Smith, T.J.; Smith, L.A.; Fernández, R.; Raphael, B.H.; Maslanka, S.E.; Pirkle, J.L. Discovery of a novel enzymatic cleavage site for botulinum neurotoxin F5. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Electrode | Ipa (µA) | ∆Ep (mV) | RCT (Ω) | Rs (Ω) | W (Mho) | Q | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0 (µMho) | N | ||||||
| SPCE | 74.4 | 210 | 401 | 291 | 2.39 | 2.81 | 0.883 |
| SPCE/AuNDs | 138 | 180 | 244 | 289 | 1.76 | 3.35 | 0.858 |
| SPCE/AuNDs/CSNPs | 84.5 | 271 | 339 | 290 | 1.66 | 2.80 | 0.882 |
| SPCE/AuNDs/CSNPs/Glu | 76.85 | 322 | 526 | 293 | 1.41 | 2.20 | 0.914 |
| SPCE/AuNDs/CSNPs/Glu/Ab | 43.9 | 384 | 1100 | 294 | 1.48 | 2.07 | 0.922 |
| SPCE/AuNDs/CSNPs/Glu/Ab/BSA | 27.8 | 428 | 1210 | 304 | 1.56 | 2.24 | 0.914 |
| Samples | Added (pg·mL−1) | Found (pg·mL−1) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) (N = 3) | ELISA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | 0.00 | - | - | - | N. D. * |
| 1.00 | 0.984 | 98.4 | 4.33 | N. D. | |
| 10.0 | 10.31 | 103.1 | 3.8 | N. D. | |
| 100.0 | 97.4 | 97.4 | 2.32 | 102.9 | |
| Milk | 0.00 | - | - | - | N. D. |
| 1.00 | 1.022 | 102.2 | 4.49 | N. D. | |
| 10.0 | 9.88 | 98.8 | 4.06 | N. D. | |
| 100.0 | 101.9 | 101.9 | 2.53 | 102.2 |
| Detection Method | Dynamic Range | Analysis Time | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence | 15–800 ng·mL−1 | 20 h | 10 ng·mL−1 | [7] |
| Fluorescence | 20–300 pg·mL−1 | 4 h | 21.3 fg·mL−1 | [8] |
| Au nanoparticles/graphene-chitosan/EIS 1 | 0.27–268 pg·mL−1 | 60 min | 0.11 pg·mL−1 | [15] |
| EIS | 25–125 fg·mL−1 | 30 min | 25 fg·mL−1 | [23] |
| CV 2 | 4–35 pg·mL−1 | - | 1 pg·mL−1 | [38] |
| LSV 3 | 10 pg·mL−1–10 ng· mL−1 | 65 min | 5 pg·mL−1 | [39] |
| DPV 4 | 1 pg·mL−1–1 ng·mL−1 | - | 1 pg·mL−1 | [40] |
| Enzyme linked Immunosorbent assay | - | 5 h | 163 pg·mL−1 | [41] |
| Immunochromatographic method | - | 15–30 min | 5 ng·mL−1 | [42] |
| Mass spectrometry | - | - | 50 ng·mL−1 | [43] |
| Gold nanodendrites/chitosan/EIS | 0.2–230 pg·mL−1 | 60 min | 0.15 pg·mL−1 | This work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorouri, R.; Bagheri, H.; Afkhami, A.; Salimian, J. Fabrication of a Novel Highly Sensitive and Selective Immunosensor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Based on an Effective Platform of Electrosynthesized Gold Nanodendrites/Chitosan Nanoparticles. Sensors 2017, 17, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051074
Sorouri R, Bagheri H, Afkhami A, Salimian J. Fabrication of a Novel Highly Sensitive and Selective Immunosensor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Based on an Effective Platform of Electrosynthesized Gold Nanodendrites/Chitosan Nanoparticles. Sensors. 2017; 17(5):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051074
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorouri, Rahim, Hasan Bagheri, Abbas Afkhami, and Jafar Salimian. 2017. "Fabrication of a Novel Highly Sensitive and Selective Immunosensor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Based on an Effective Platform of Electrosynthesized Gold Nanodendrites/Chitosan Nanoparticles" Sensors 17, no. 5: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051074
APA StyleSorouri, R., Bagheri, H., Afkhami, A., & Salimian, J. (2017). Fabrication of a Novel Highly Sensitive and Selective Immunosensor for Botulinum Neurotoxin Serotype A Based on an Effective Platform of Electrosynthesized Gold Nanodendrites/Chitosan Nanoparticles. Sensors, 17(5), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17051074





