In Vivo Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Rabbit Brain within 10 Hz–1 MHz
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Preparation of Animals
2.3. Surgery
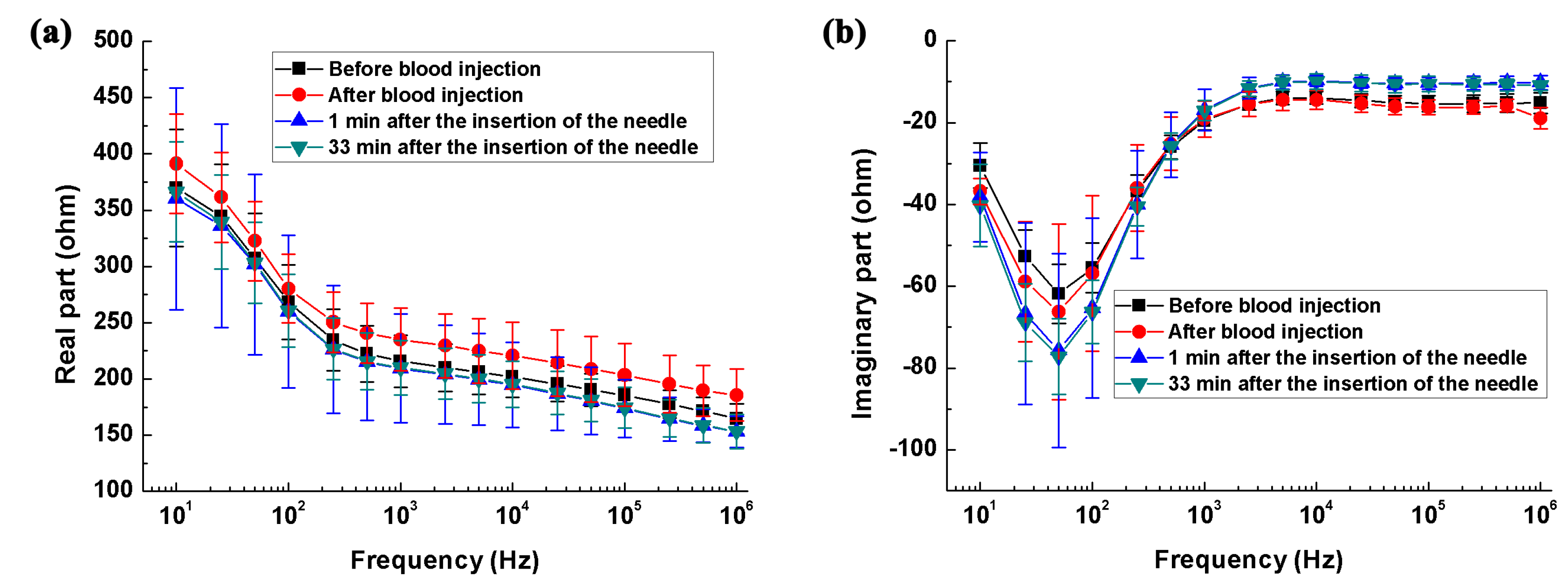
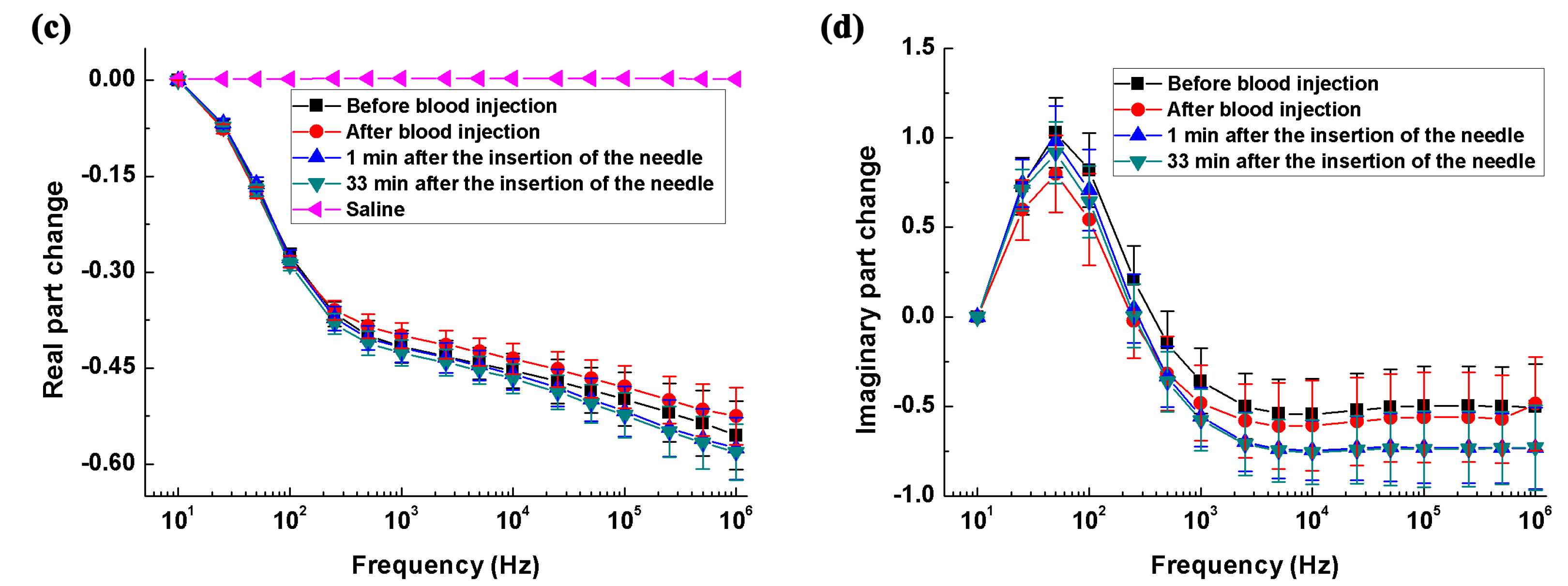
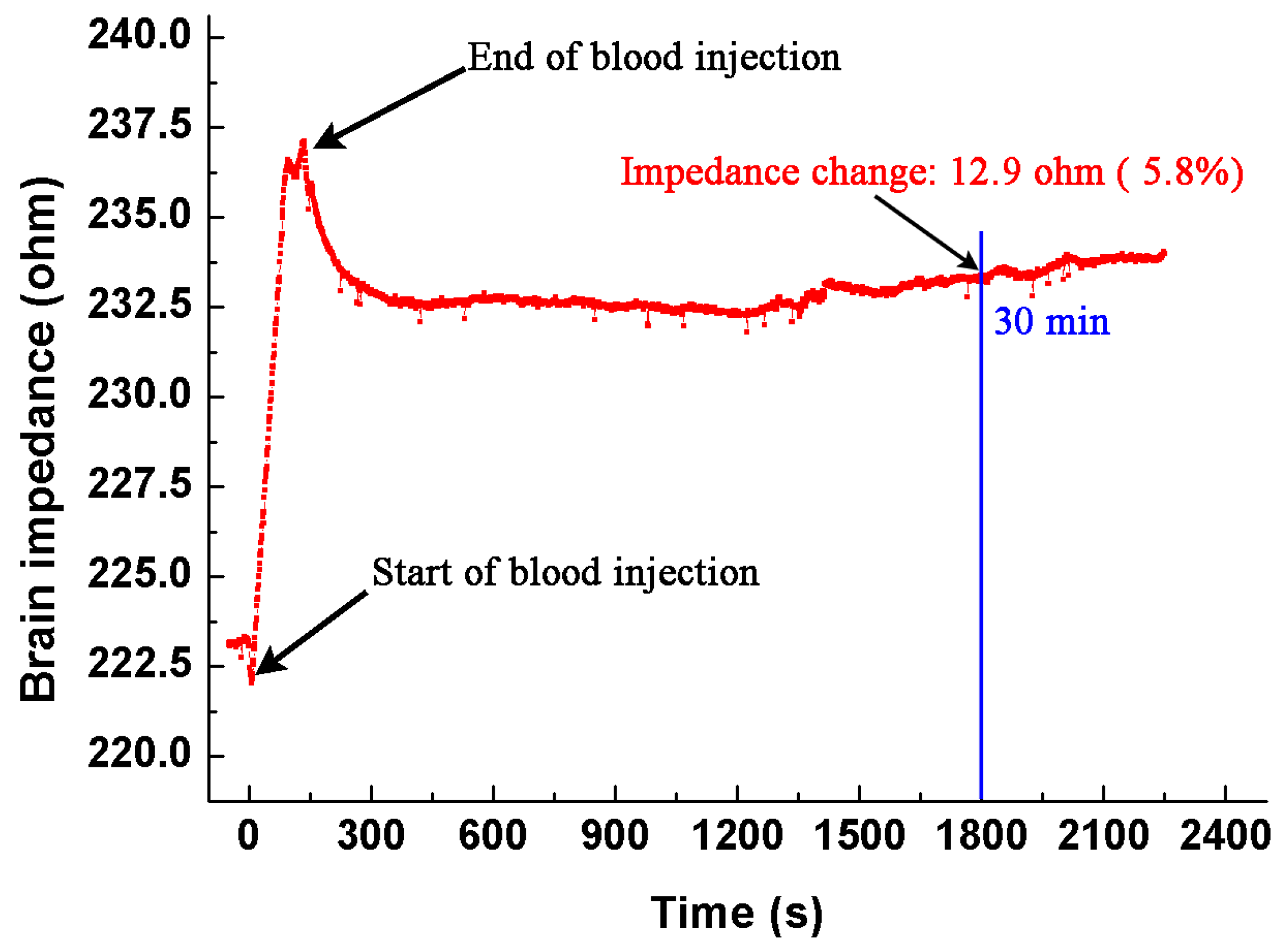
2.3.1. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Model
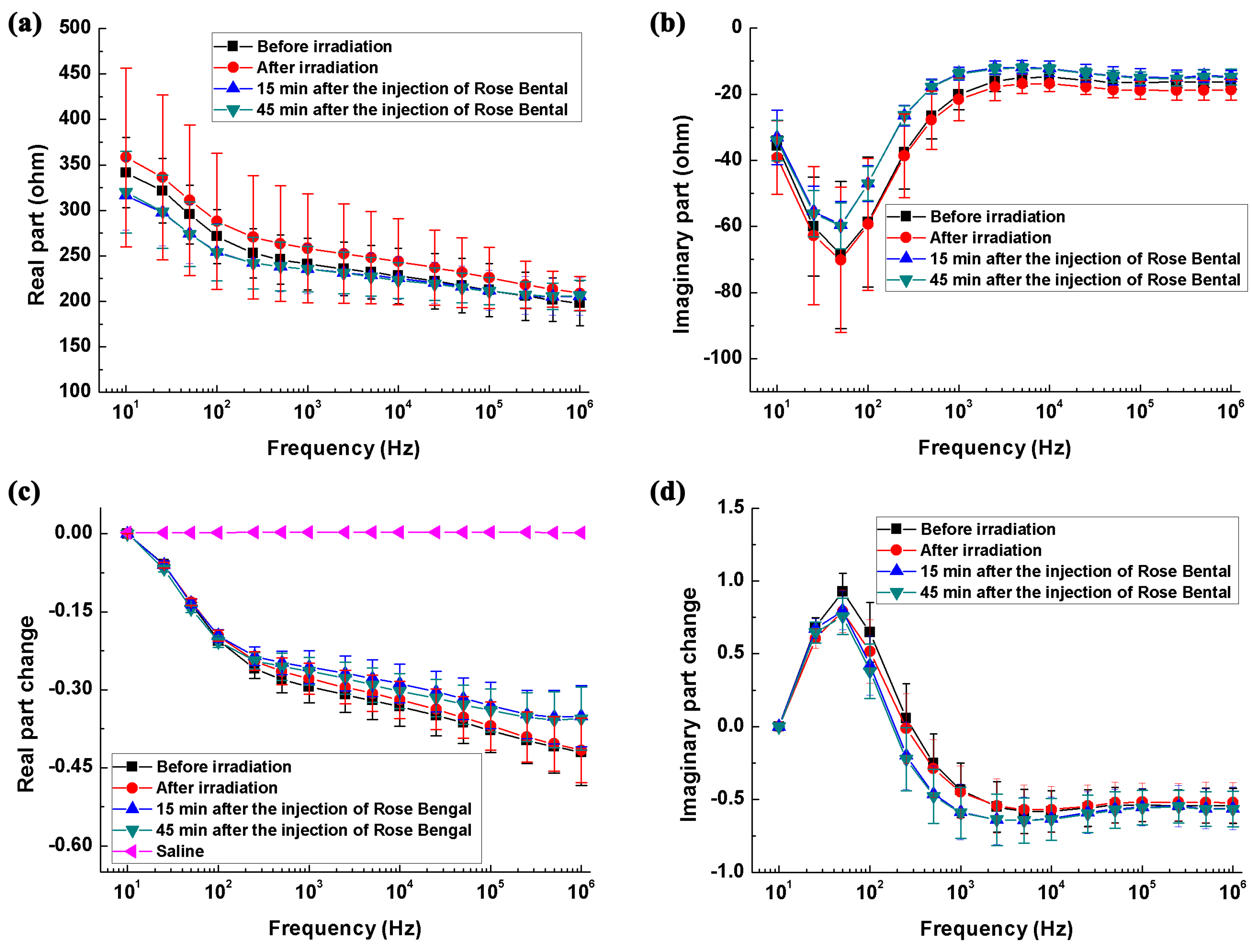
2.3.2. Ischemic Model
2.4. In Vivo Measurement of Brain Impedance Spectra
2.4.1. Measurement: Protocol and Hardware
2.4.2. Measurement in Saline Solution
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Measurement of the Impedance Spectra of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Brain
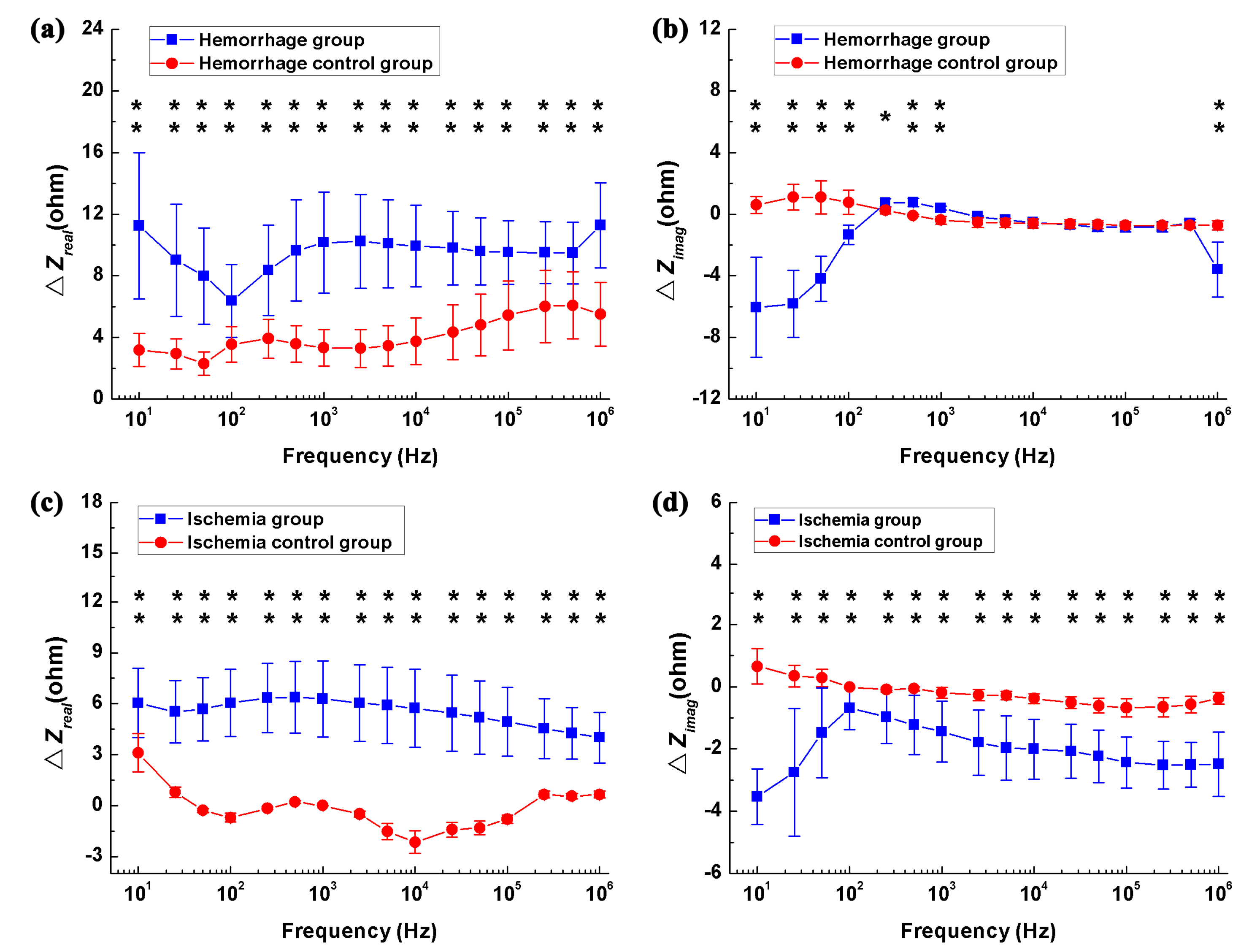
3.2. Difference in Impedance Spectra between Healthy and Stroke-Affected Brains (Hemorrhagic or Ischemic Brain)
3.3. Difference in the Rate of Change in Brain Impedance with Frequency between Ischemic and Hemorrhagic Stroke
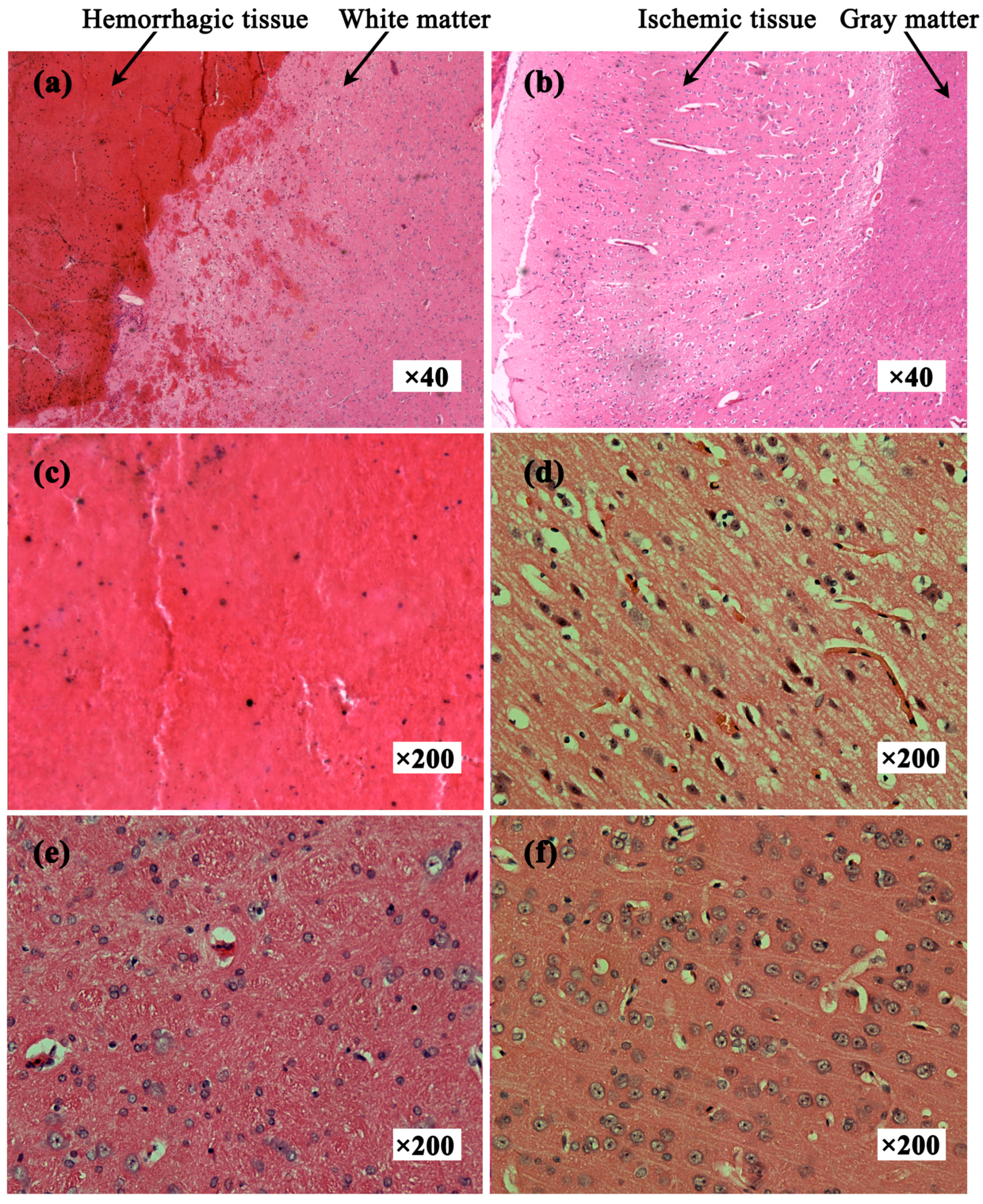
3.4. Histopathology
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of the Results and Comparative Analysis of the Literature
4.1.1. The Impedance Spectra of the Healthy Brain
4.1.2. The Impedance Spectra of the Hemorrhagic Brain
4.1.3. The Impedance Spectra of the Ischemic Brain
4.2. Optimal Frequency Ranges for Stroke Detection Using MFEIT
4.3. Limitaions of This Study
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bamford, J.; Sandercock, P.; Dennis, M.; Warlow, C.; Burn, J. Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 1991, 337, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadah, A.; Franklin, G.M.; Benson, R.T. Global disparities in stroke and why we should care. Neurology 2016, 87, 450–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morihara, R.; Kono, S.; Sato, K.; Hishikawa, N.; Ohta, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Deguchi, K.; Manabe, Y.; Takao, Y.; Kashihara, K.; et al. Thrombolysis with low-dose tissue plasminogen activator 3–4.5 h after acute ischemic stroke in five hospital groups in Japan. Transl. Stroke Res. 2016, 7, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwan, A.; Romsauerova, A.; Yerworth, R.; Horesh, L.; Bayford, R.; Holder, D. Design and calibration of a compact multi-frequency EIT system for acute stroke imaging. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S199–S210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romsauerova, A.; McEwan, A.; Horesh, L.; Yerworth, R.; Bayford, R.H.; Holder, D.S. Multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography (EIT) of the adult human head: Initial findings in brain tumours, arteriovenous malformations and chronic stroke, development of an analysis method and calibration. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, S147–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.; Jehl, M.; Arridge, S.; Betcke, T.; Holder, D. Stroke type differentiation using spectrally constrained multifrequency EIT: Evaluation of feasibility in a realistic head model. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.W.; Zribi, H.; Woo, E.J. Frequency-difference electrical impedance tomography (fdEIT): Algorithm development and feasibility study. Physiol. Meas. 2008, 29, 929–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, G.; Song, J.; Dai, M.; Xu, C.; Dong, X.; Fu, F. Ex Vivo characterization of bioimpedance spectroscopy of normal, ischemic and hemorrhagic rabbit brain tissue at frequencies from 10 Hz to 1 MHz. Sensors 2016, 16, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Dowrick, T.; Malone, E.; Avery, J.; Li, N.; Sun, Z.; Xu, H.; Holder, D. Multifrequency electrical impedance tomography with total variation regularization. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1943–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.; dos Santos, G.S.; Holder, D.; Arridge, S. Multifrequency electrical impedance tomography using spectral constraints. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xu, C.; Dai, M.; Fu, F.; Shi, X.; Dong, X. A novel multi-frequency electrical impedance tomography spectral imaging algorithm for early stroke detection. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Seo, J.K. Detection of admittivity anomaly on high-contrast heterogeneous backgrounds using frequency difference EIT. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packham, B.; Koo, H.; Romsauerova, A.; Ahn, S.; McEwan, A.; Jun, S.C.; Holder, D.S. Comparison of frequency difference reconstruction algorithms for the detection of acute stroke using EIT in a realistic head-shaped tank. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 767–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingwood, B.E.; Dunster, K.R.; Healy, G.N.; Ward, L.C.; Colditz, P.B. Cerebral impedance and neurological outcome following a mild or severe hypoxic/ischemic episode in neonatal piglets. Brain Res. 2003, 969, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranck, J.B., Jr. Analysis of specific impedance of rabbit cerebral cortex. Exp. Neurol. 1963, 7, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowrick, T.; Blochet, C.; Holder, D. In vivo bioimpedance measurement of healthy and ischaemic rat brain: Implications for stroke imaging using electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 1273–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atefi, S.R.; Seoane, F.; Thorlin, T.; Lindecrantz, K. Stroke damage detection using classification trees on electrical bioimpedance cerebral spectroscopy measurements. Sensors 2013, 13, 10074–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, F.; Lindecrantz, K.; Olsson, T.; Kjellmer, I.; Flisberg, A.; Bagenholm, R. Brain electrical impedance at various frequencies: The effect of hypoxia. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 September 2004; pp. 2322–2325. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Dong, X.; Qin, M.; Fu, F.; Wang, Y.; You, F.; Xiang, H.; Liu, R.; Shi, X. In vivo measurement of rabbits brain impedance frequency response and the elementary imaging of EIT. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 2003, 20, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dowrick, T.; Blochet, C.; Holder, D. In vivo bioimpedance changes during haemorrhagic and ischaemic stroke in rats: Towards 3d stroke imaging using electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 765–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Shi, X.T.; Dai, M.; Xu, C.H.; You, F.S.; Fu, F.; Liu, R.G.; Dong, X.Z. Real-time imaging of cerebral infarction in rabbits using electrical impedance tomography. J. Int. Med. Res. 2014, 42, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Yan, Q.G.; You, F.S.; Fu, F.; Dong, X.Z.; Shi, X.T.; Yang, M. Correlation between the dielectric properties and biological activities of human ex vivo hepatic tissue. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Wand, L.; Xu, C.; Li, L.; Gao, G.; Dong, X. Real-time imaging of subarachnoid hemorrhage in piglets with electrical impedance tomography. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manwaring, P.K.; Moodie, K.L.; Hartov, A.; Manwaring, K.H.; Halter, R.J. Intracranial electrical impedance tomography: A method of continuous monitoring in an animal model of head trauma. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 117, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seoane, F.; Reza Atefi, S.; Tomner, J.; Kostulas, K.; Lindecrantz, K. Electrical bioimpedance spectroscopy on acute unilateral stroke patients: Initial observations regarding differences between sides. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 613247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluri, F.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kleinschnitz, C. Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar]
- Peyman, A.; Gabriel, C.; Grant, E.H. Complex permittivity of sodium chloride solutions at microwave frequencies. Bioelectromagnetics 2007, 28, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Dai, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Fu, F.; Shi, X.; Dong, X. The frequency spectral properties of electrode-skin contact impedance on human head and its frequency-dependent effects on frequency-difference EIT in stroke detection from 10 Hz to 1 MHz. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170563. [Google Scholar]
- Schwan, H.P.; Ferris, C.D. Four-electrode null techniques for impedance measurement with high resolution. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1968, 39, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuetao, S.; Fusheng, Y.; Feng, F.; Ruigang, L.; Xiuzhen, D. High precision multifrequency electrical impedance tomography system and preliminary imaging results on saline tank. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 1492–1495. [Google Scholar]
- Mokri, B. The monro-kellie hypothesis: Applications in CSF volume depletion. Neurology 2001, 56, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horesh, L. Some Novel Approaches in Modelling and Image Reconstruction for Multi-Frequency Electrical Impedance Tomography of the Human Brain. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, W.D.; Busto, R.; Watson, B.D.; Scheinberg, P.; Ginsberg, M.D. Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 72, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Liu, W.; Chen, R.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Fu, F.; Dong, X. In Vivo Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Rabbit Brain within 10 Hz–1 MHz. Sensors 2017, 17, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040791
Yang L, Liu W, Chen R, Zhang G, Li W, Fu F, Dong X. In Vivo Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Rabbit Brain within 10 Hz–1 MHz. Sensors. 2017; 17(4):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040791
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lin, Wenbo Liu, Rongqing Chen, Ge Zhang, Weichen Li, Feng Fu, and Xiuzhen Dong. 2017. "In Vivo Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Rabbit Brain within 10 Hz–1 MHz" Sensors 17, no. 4: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040791
APA StyleYang, L., Liu, W., Chen, R., Zhang, G., Li, W., Fu, F., & Dong, X. (2017). In Vivo Bioimpedance Spectroscopy Characterization of Healthy, Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Rabbit Brain within 10 Hz–1 MHz. Sensors, 17(4), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17040791






