Characterization of Textile-Insulated Capacitive Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
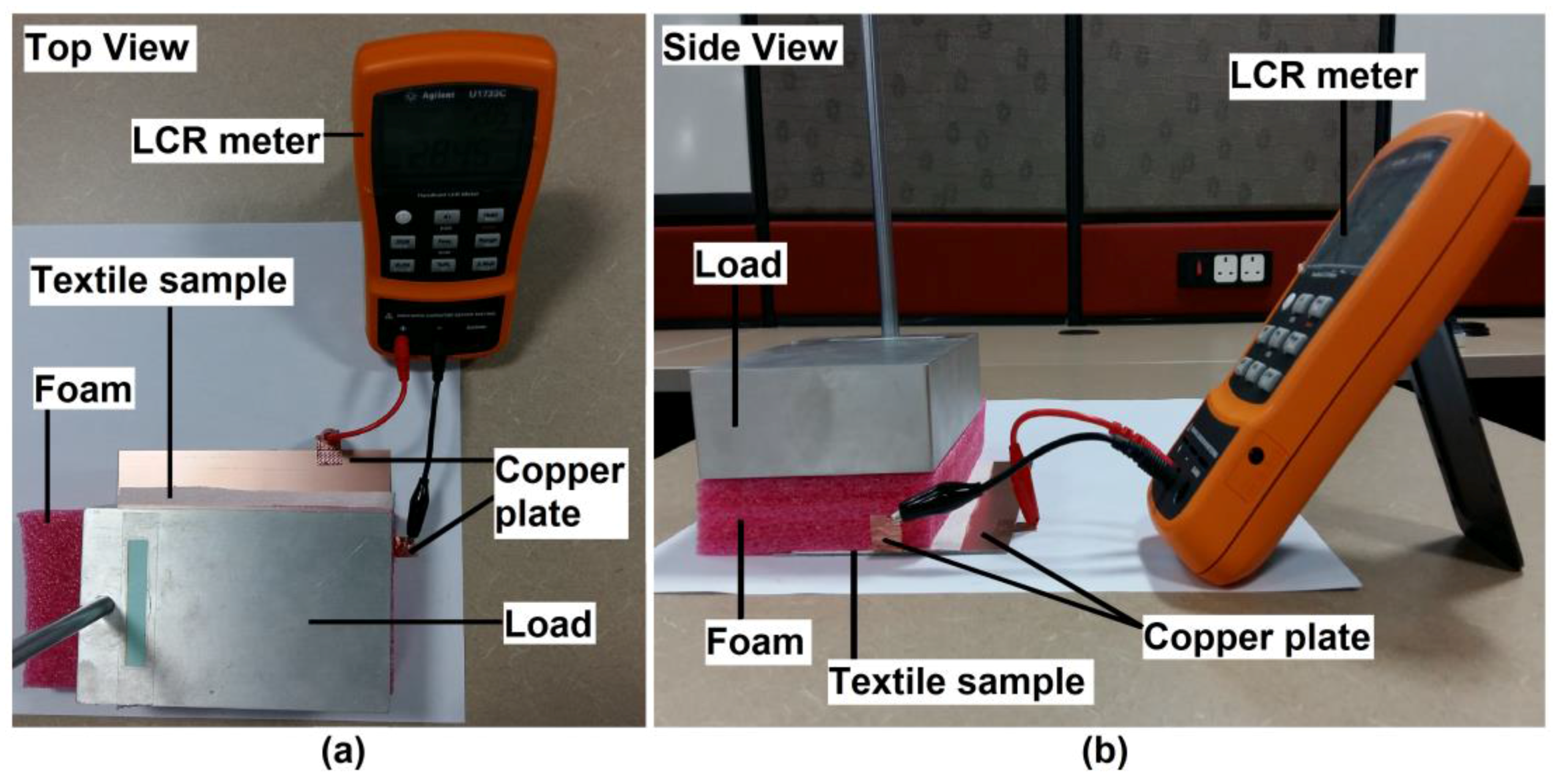
2.1. Textile Properties and Characteristic
- εo is the constant value of the vacuum permittivity, 8.854 × 10−12 F/m;
- Cm is the capacitance measured by the LCR meter;
- At is the area size of the top copper plate which is 875 mm2;
- dt is the thickness of the textile material.
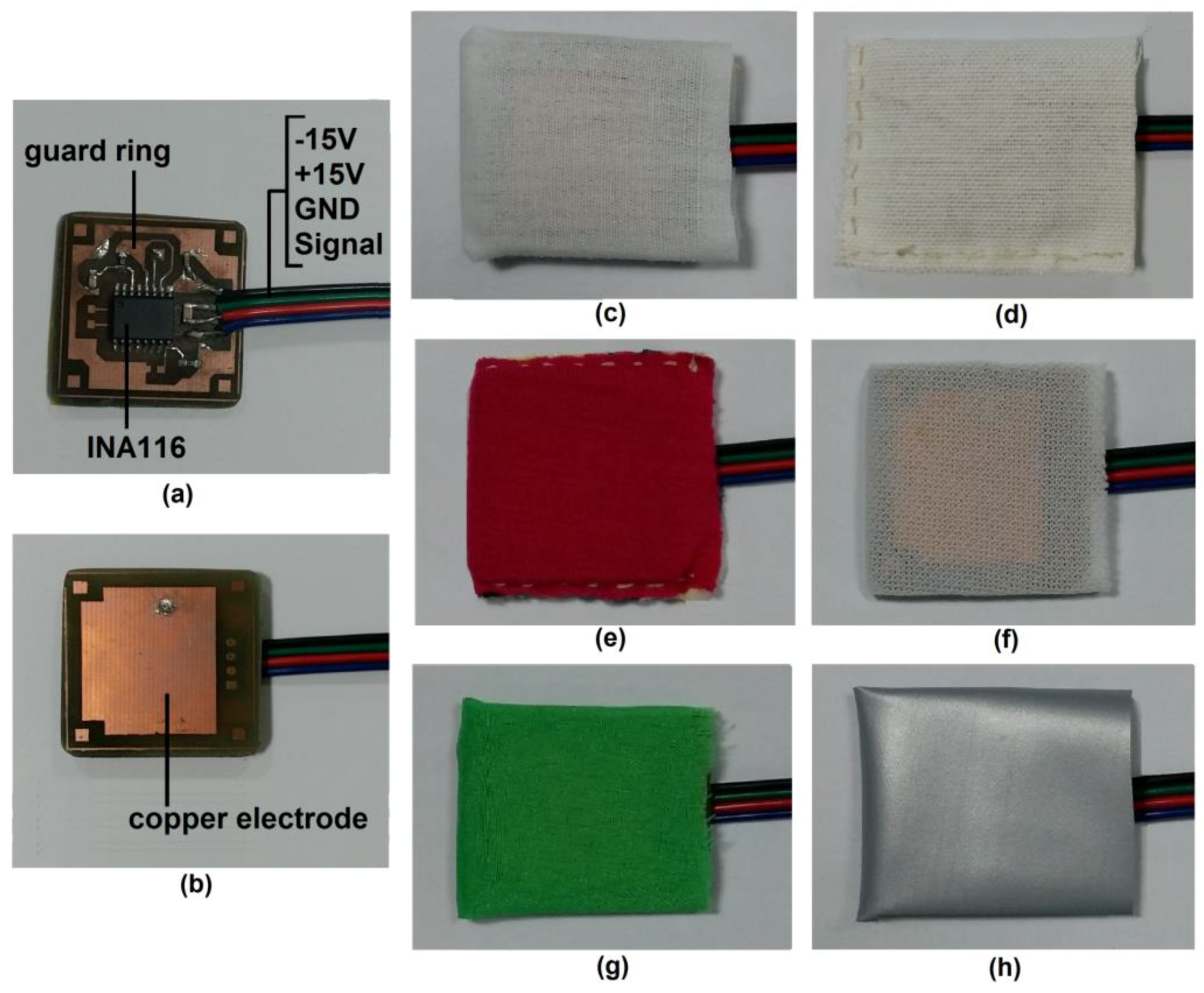
2.2. TEX-C Biosensor
- εo is the constant value of the vacuum permittivity, 8.854 × 10−12 F/m;
- εr is the relative permittivity of the textile material;
- A is the copper electrode’s area size, 510 mm2;
- d is the thickness of textile which control the distance between skin and electrode.
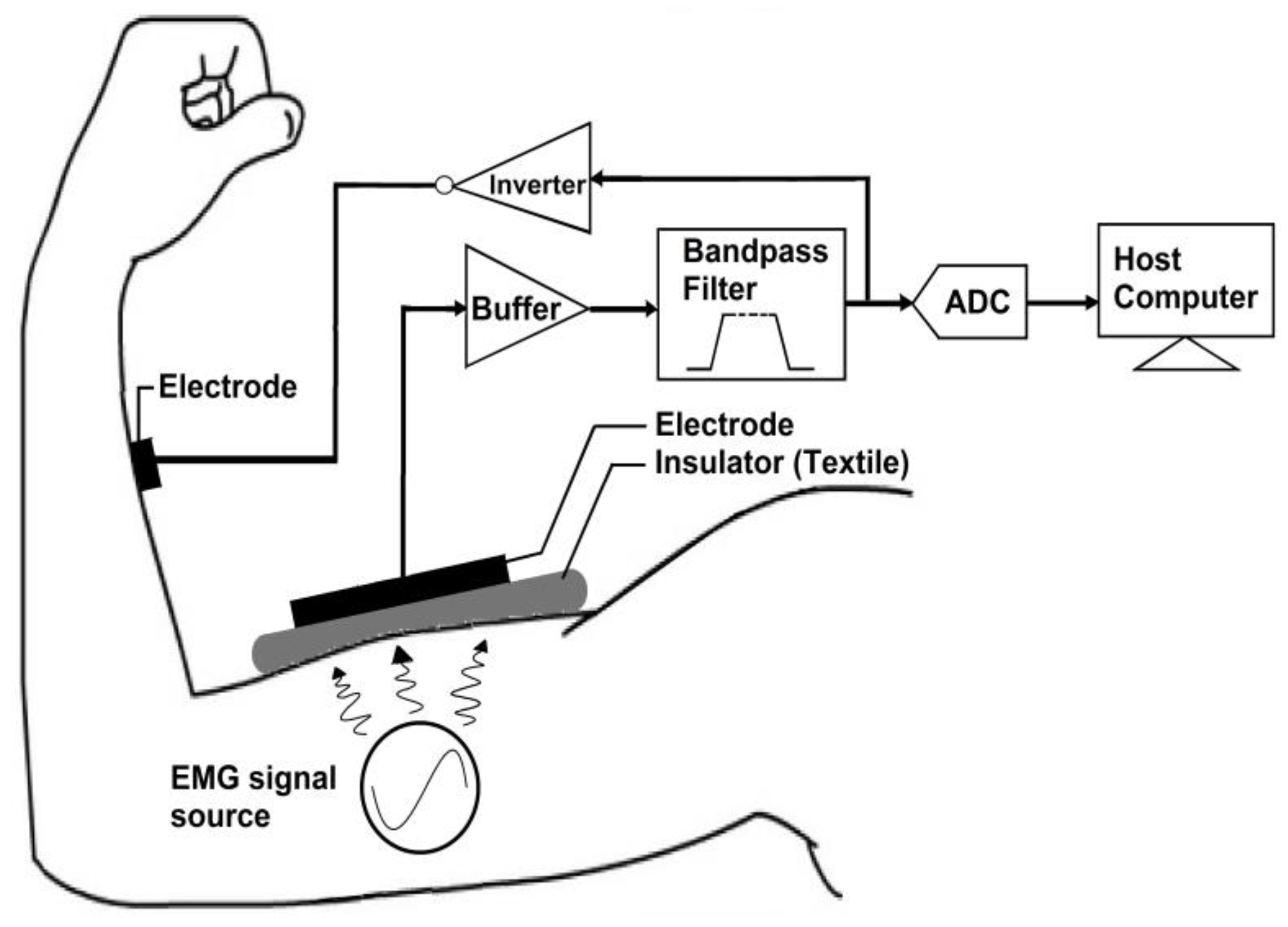
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Noise Floor and Characterization
- ICM is the induced current from the human body;
- ZC is the impedance between the skin and the TEX-C biosensor.
- kB is the Boltzmann’s constant, 1.38 × 10−23 J/K;
- T is the temperature of the system in Kelvin;
- R is the resistance value of a resistor;
- ∆f is the bandwidth which the noise is measured.
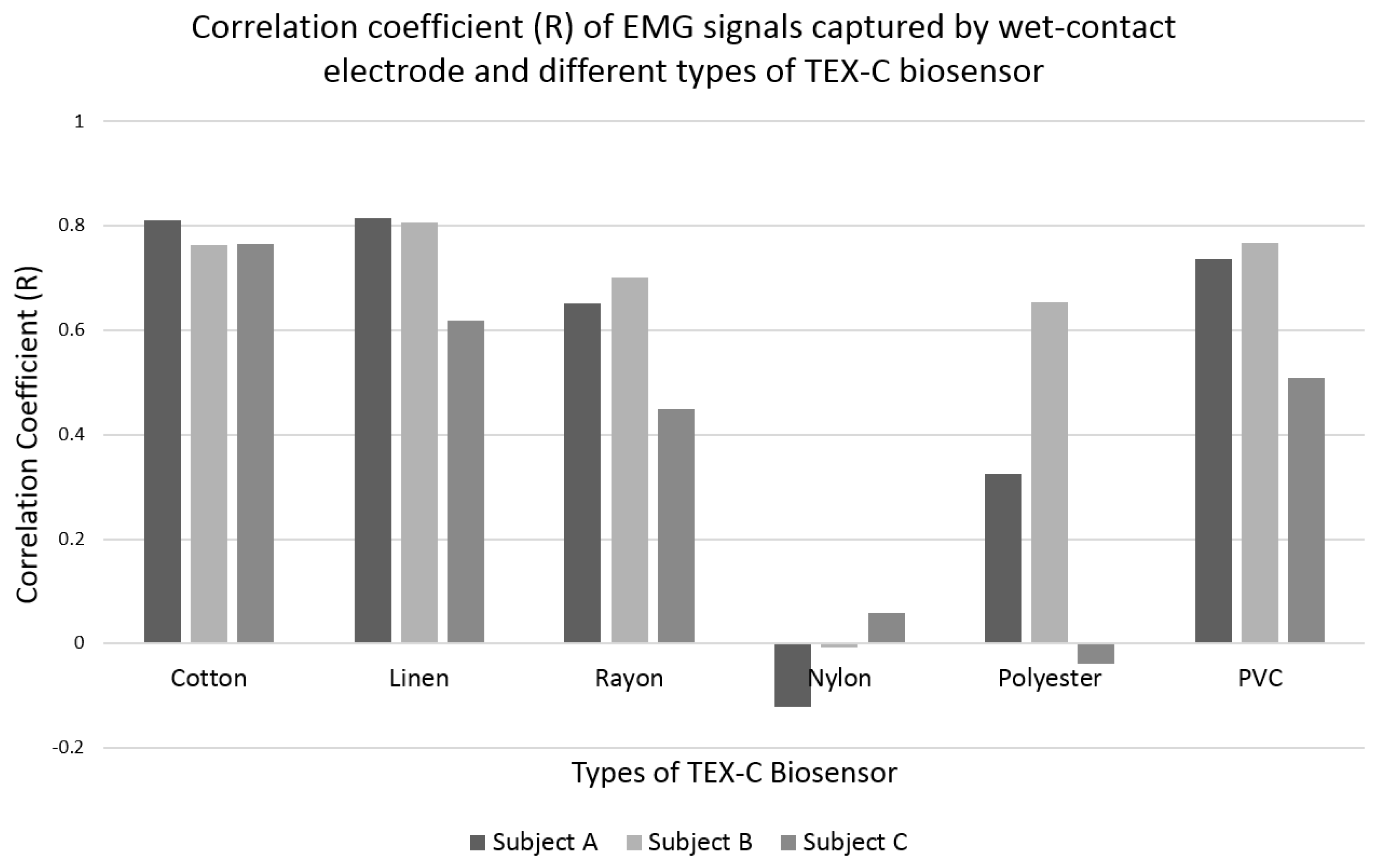
3.2. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castano, L.M.; Flatau, A.B. Smart fabric sensors and e-textile technologies: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Wearable sensors for human activity monitoring: A review. IEEE Sensors J. 2014, 15, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundt, C.W.; Montgomery, K.N.; Udoh, U.E.; Barker, V.N.; Thonier, G.C.; Tellier, A.M.; Ricks, R.D.; Darling, R.B.; Cagle, Y.D.; Cabrol, N.A.; et al. A multiparameter wearable physiological monitoring system for space and terrestrial applications. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradiso, R.; Loriga, G.; Taccini, N. A wearable health care system based on knitted integral sensors. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Rienzo, M.; Rizzo, F.; Parati, G.; Brambilla, G.; Ferratini, M.; Castiglioni, P. MagIC system: A new textile-based wearable device for biological signal monitoring applicability in daily life and clinical setting. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International Conference Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 7167–7169.
- Heilman, K.J.; Porges, S.W. Accuracy of the LifeshirtR (Vivometrics) in the detection of cardiac rhythms. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 3, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelopoulos, A.; Bourbakis, N.G. A survey on wearable sensor-based systems for health monitoring and prognosis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 2010, 40, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.M.; Jung, T.-P.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-Contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes: Methodology review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, X.B. Capacitive Biopotential Measurement for Electrophysiological Signal Acquisition: A Review. IEEE Sensors J. 2016, 16, 2832–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, A.; Akabane, Y.; Kato, T.; Hoshino, H.; Kataoka, S.; Ishiyama, Y. Capacitive sensing of electrocardiographic potential through cloth from the dorsal surface of the body in a supine position: A preliminary study. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linz, T.; Gourmelon, L.; Langereis, G. Contactless EMG sensors embroidered onto textile. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN 2007), Aachen, Germany, 26–28 March 2007; pp. 29–34.
- Gourmelon, L.; Langereis, G. Contactless sensors for surface electromyography. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society: Engineering Revolution in BioMedicine, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 2514–2517.
- Langereis, G.; de Voogd-Claessen, L.; Spaepen, A.; Siplia, A.; Rotsch, C.; Linz, T. ConText: Contactless sensors for body monitoring incorporated in textiles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Portable Information Devices, Orlando, FL, USA, 25–29 May 2007; pp. 1–5.
- Nemati, E.; Deen, M.J.; Mondal, T. A wireless wearable ECG sensor for long-term application. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yu, C.; Dong, Y. Capacitively coupled electrocardiogram measuring system and noise reduction by singular spectrum analysis. IEEE Sensors J. 2016, 16, 3802–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvado, R.; Loss, C.; Goncalves, R.; Pinho, P. Textile materials for the design of wearable antennas: A survey. Sensors 2012, 12, 15841–15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilinskas, P.J.; Lozovski, T.; Jankauskas, V.; Jurksus, J. Electrostatic Properties and Characterization of Textile Materials Affected by Ion Flux. Mater. Sci. 2013, 19, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kang, Y.K.; Im, S.S. Biodegradability of cellulose fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 95, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschle-Diller, G.; Zeronian, S.H.; Pan, N.; Yoon, M.Y. Enzymatic hydrolysis of cotton, linen, ramie, and viscose rayon fabric. Texile Res. J. 1994, 64, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S. Tensile Deformation of Fiber Used in Textile Industry. Available online: http://cp.literature.agilent.com/litweb/pdf/5991–0274EN.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2016).
- Zhang, W.; Wu, C.W.; Tan, Y.Y.; Silva, S.R.P. Functionalisation of nylon with carbon nanotubes to make thermally stable fabric and wearable capacitor. Micro Nano Lett. 2012, 7, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaralingam, S.; Gupta, B. Determination of Dielectric Constant of Fabric Materials and Their Use as Substrates for Design and Development of Antennas for Wearable Applications. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2010, 59, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, M.; Paunovic, V.; Prijic, Z.; Prijic, A.; Dankovic, D.; Mitic, V. One the measurement methods for dielectric constant determination in Nb/BaTiO3 ceramics. In Proceedings of the X International Symposium on Industrial Electrinics (INDEL), Banja Luka, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 6–8 November 2014; pp. 38–41.
- Jilani, M.T.; Rehman, M.Z.; Khan, A.M.; Khan, M.T.; Ali, S.M. A brief review of measuring techniques for characterization of dielectric materials. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Electr. Eng. 2012, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Tereshchenko, O.V.; Buesink, F.J.K.; Leferink, F.B.J. An overview of the techniques for measuring the dielectric properties of materials. In Proceedings of the General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–20 August 2011; pp. 1–4.
- Grove, T.T.; Masters, M.F.; Miers, R.E. Determining dielectric constants using a parallel plate capacitor. Am. J. Phys. 2005, 73, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.K.; Lim, Y.K.; Park, K.S. Common mode noise cancellation for electrically non-contact ECG measurement system on a chair. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 1–4 September 2005; pp. 5881–5883.
- Beck, T.W.; Housh, T.J.; Cramer, J.T.; Weir, J.P.; Coburn, J.W.; Malek, M.H. Electromyographic instantaneous amplitude and instantaneous mean power frequency patterns across a range of motion during a concentric isokinetic muscle action of the biceps brachii. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2006, 16, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huigen, E.; Peper, A.; Grimbergen, C.A. Investigation into the origin of the noise of surface electrodes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Textile Types | Category | Thickness (mm) | Resistance (Ω) | Relative Permittivity (εr) at 1 kHz | Physical Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Natural | 0.23 | >40.0 M | 3.004 | Absorbent, Breathable |
| Linen | Natural | 0.40 | >40.0 M | 4.007 | Absorbent, Breathable |
| Rayon | Synthetic | 0.58 | >40.0 M | 5.082 | Breathable, Elasticity * |
| Nylon | Synthetic | 0.48 | >40.0 M | 1.222 | Breathable, Elasticity * |
| Polyester | Synthetic | 0.16 | >40.0 M | 1.178 | Breathable |
| PVC-textile | Synthetic | 0.24 | >40.0 M | 3.118 | Waterproof, Non-breathable |
| Insulators of TEX-C Biosensor | Electrode Surface Area, A (mm2) | Relative Permittivity, εr at 1 kHz | Thickness, d (mm) | Skin-Electrode Capacitance, Cs (pF) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 510 | 3.004 | 0.23 | 58.96 |
| Linen | 510 | 4.007 | 0.40 | 45.22 |
| Rayon | 510 | 5.082 | 0.58 | 39.56 |
| Nylon | 510 | 1.222 | 0.48 | 11.49 |
| Polyester | 510 | 1.178 | 0.16 | 33.24 |
| PVC-textile | 510 | 3.118 | 0.24 | 58.65 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, C.L.; Reaz, M.B.I. Characterization of Textile-Insulated Capacitive Biosensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030574
Ng CL, Reaz MBI. Characterization of Textile-Insulated Capacitive Biosensors. Sensors. 2017; 17(3):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030574
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Charn Loong, and Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz. 2017. "Characterization of Textile-Insulated Capacitive Biosensors" Sensors 17, no. 3: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030574
APA StyleNg, C. L., & Reaz, M. B. I. (2017). Characterization of Textile-Insulated Capacitive Biosensors. Sensors, 17(3), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17030574






