Initial Results from SQUID Sensor: Analysis and Modeling for the ELF/VLF Atmospheric Noise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
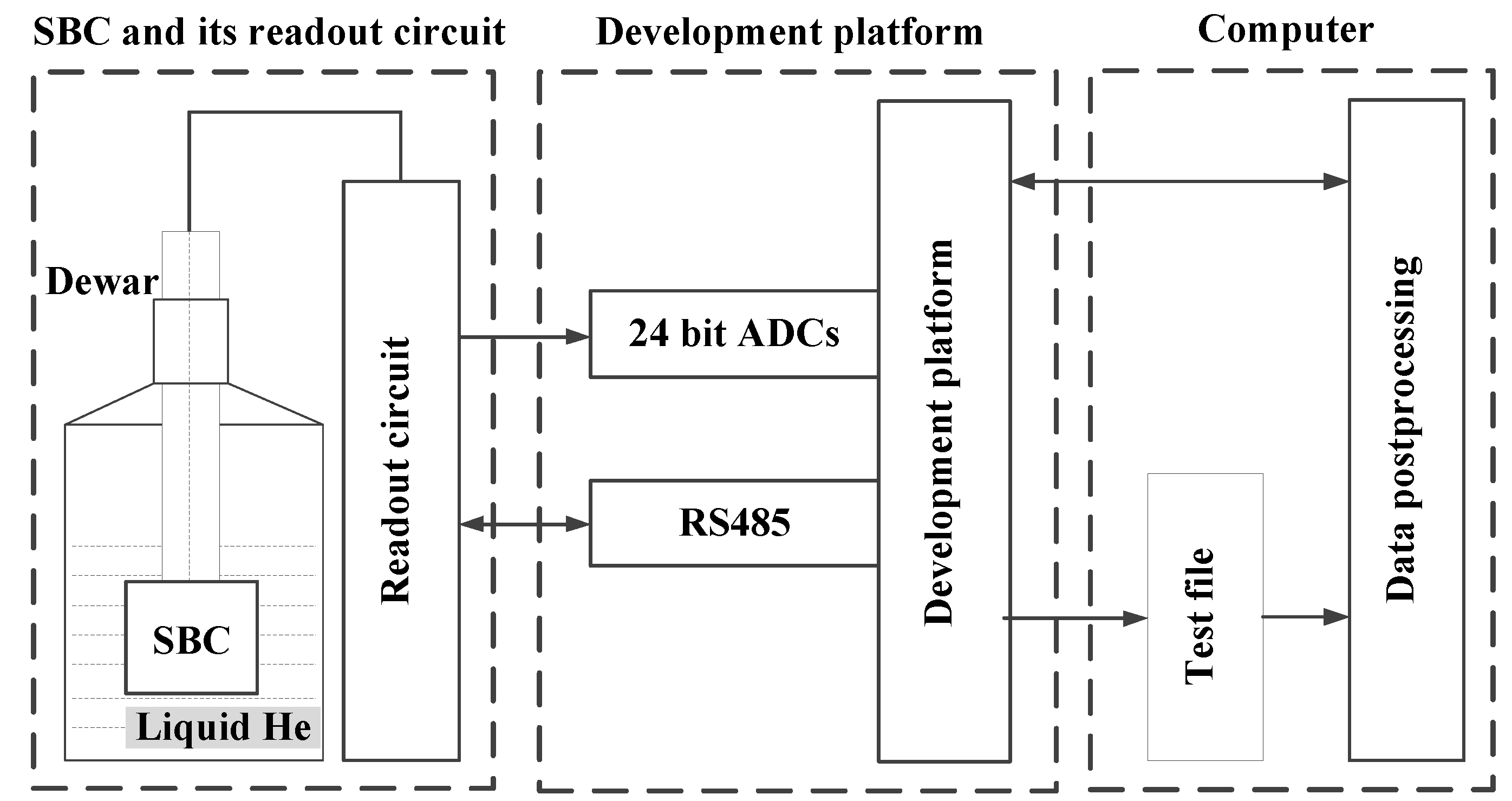
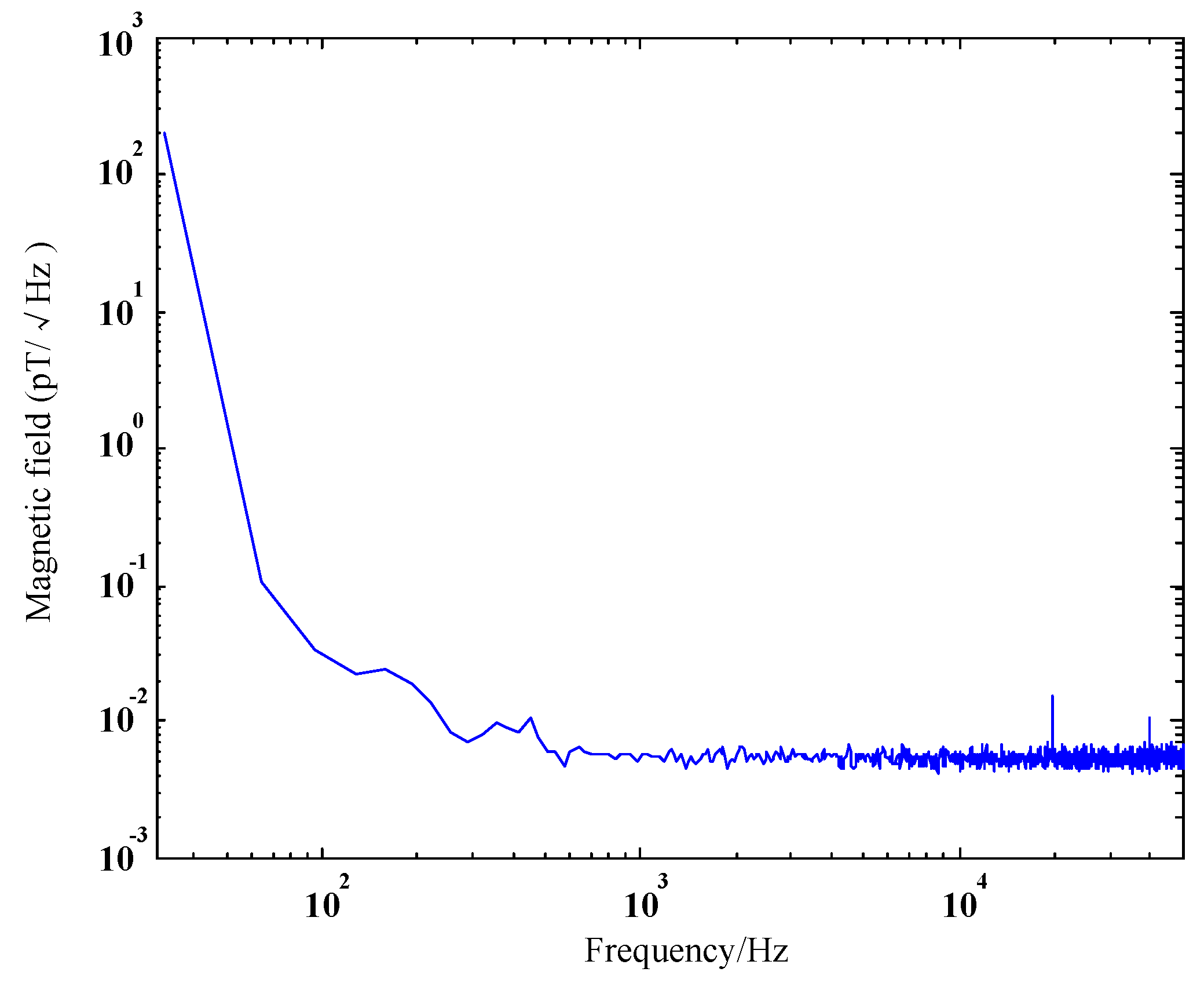
2. System Description
3. Data Preprocessing
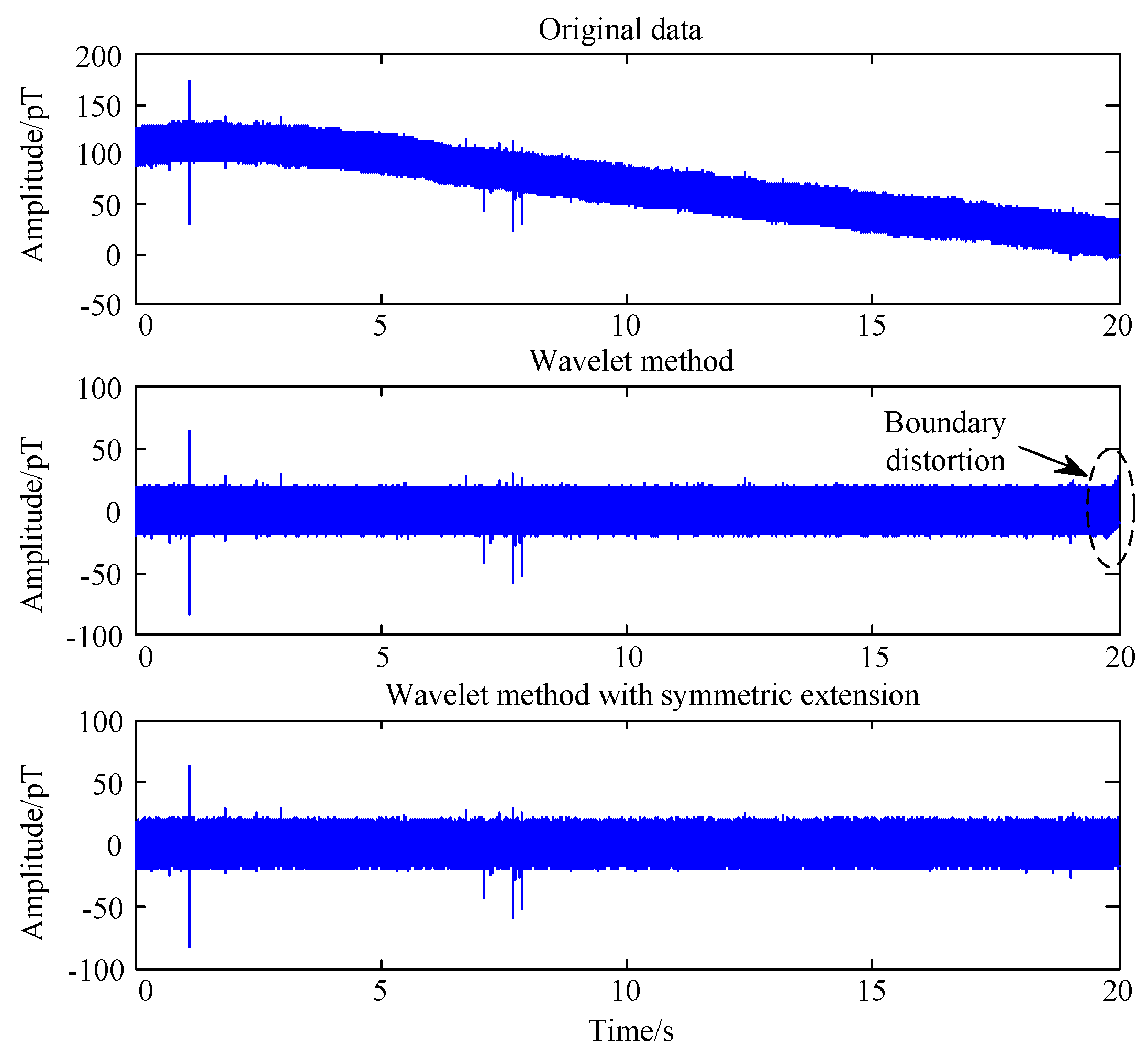
3.1. Baseline Correction
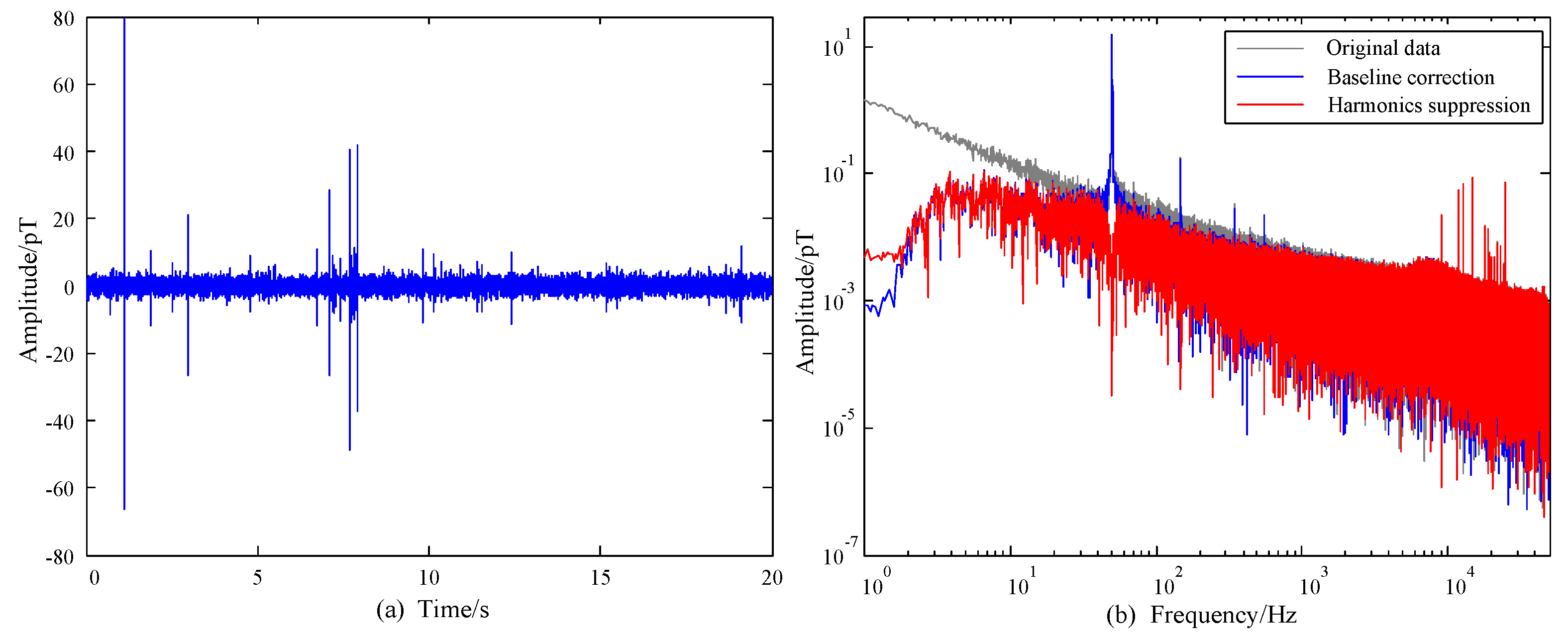
3.2. Harmonic Suppression
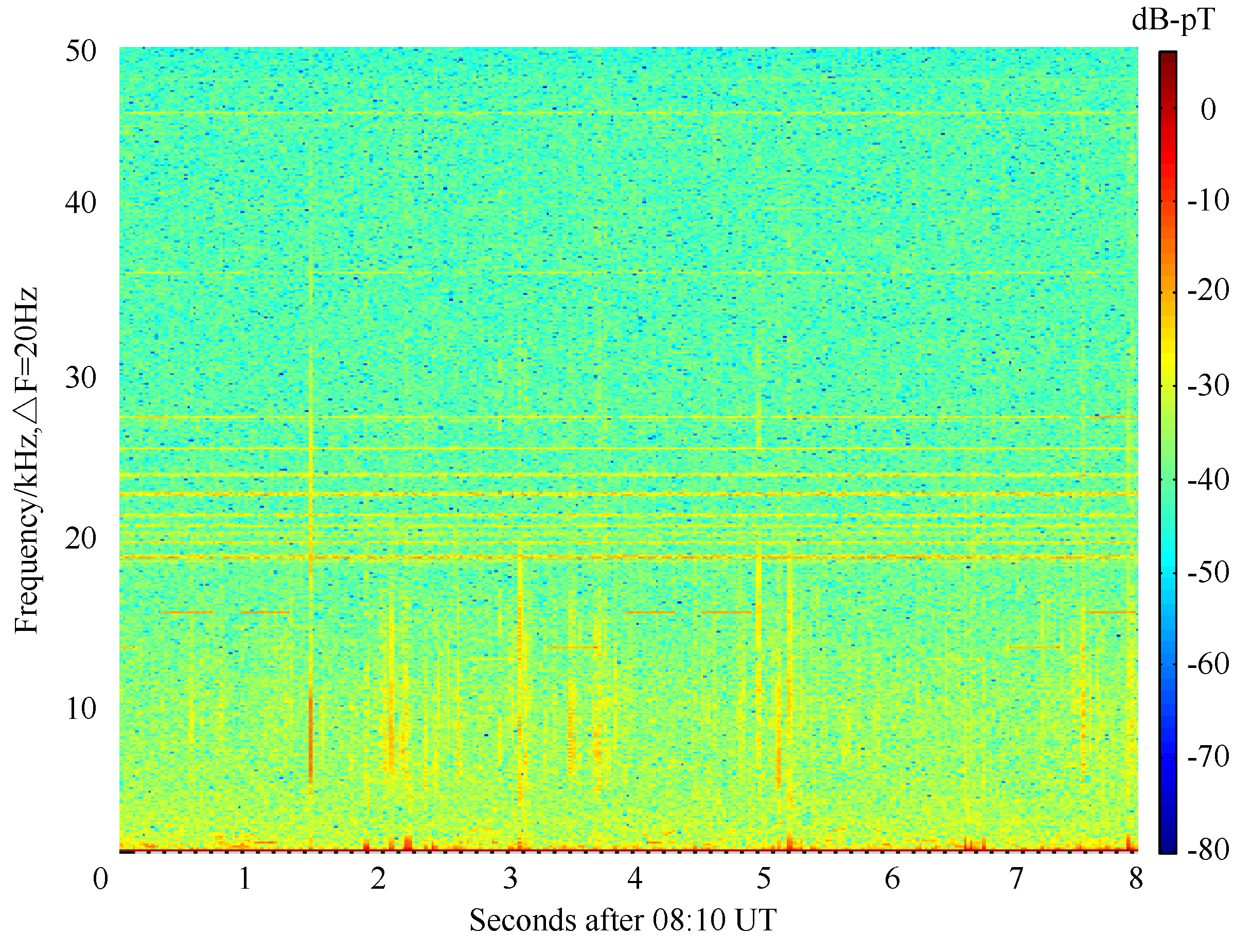
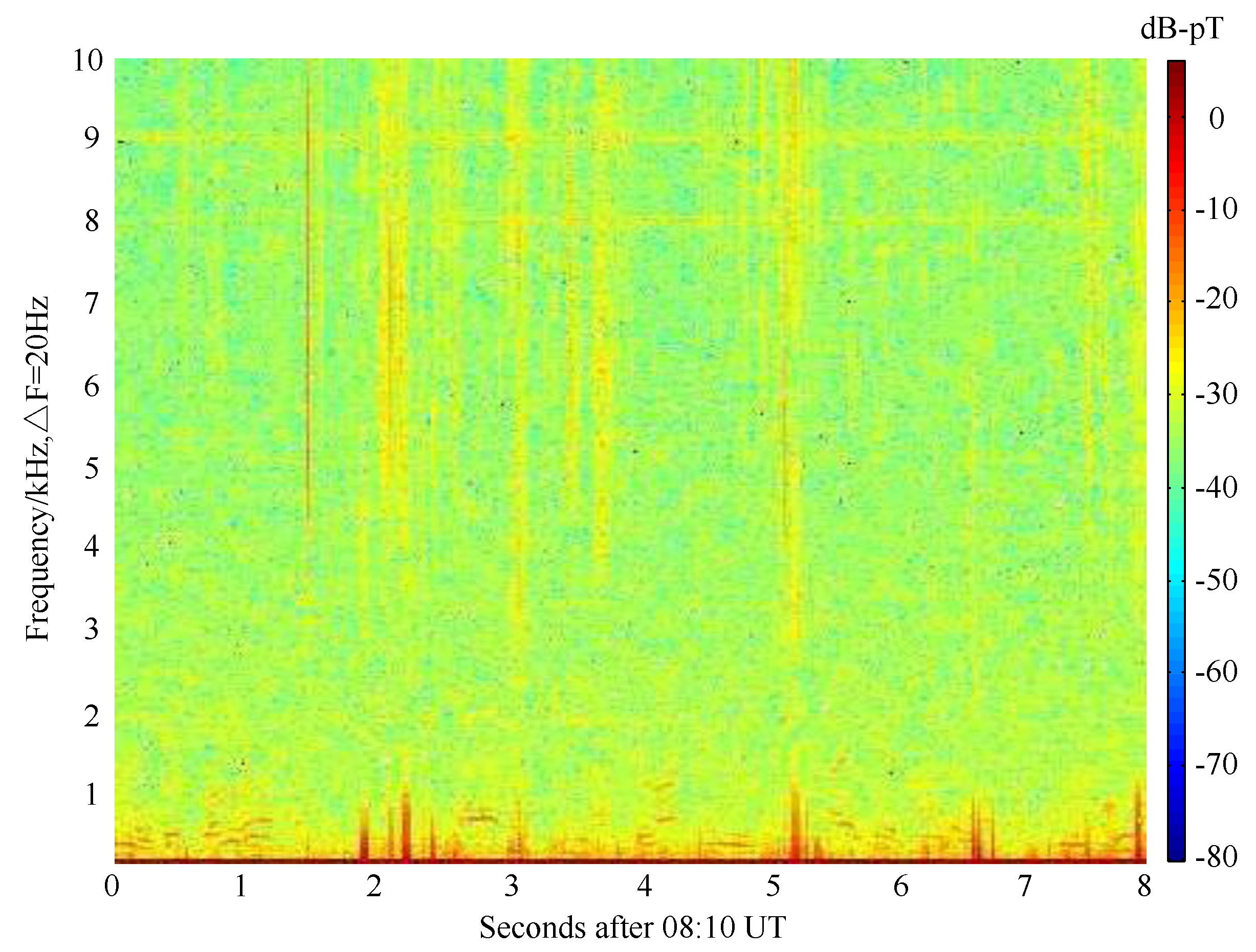
4. Statistical Analysis and Modeling for the Atmospheric Noise
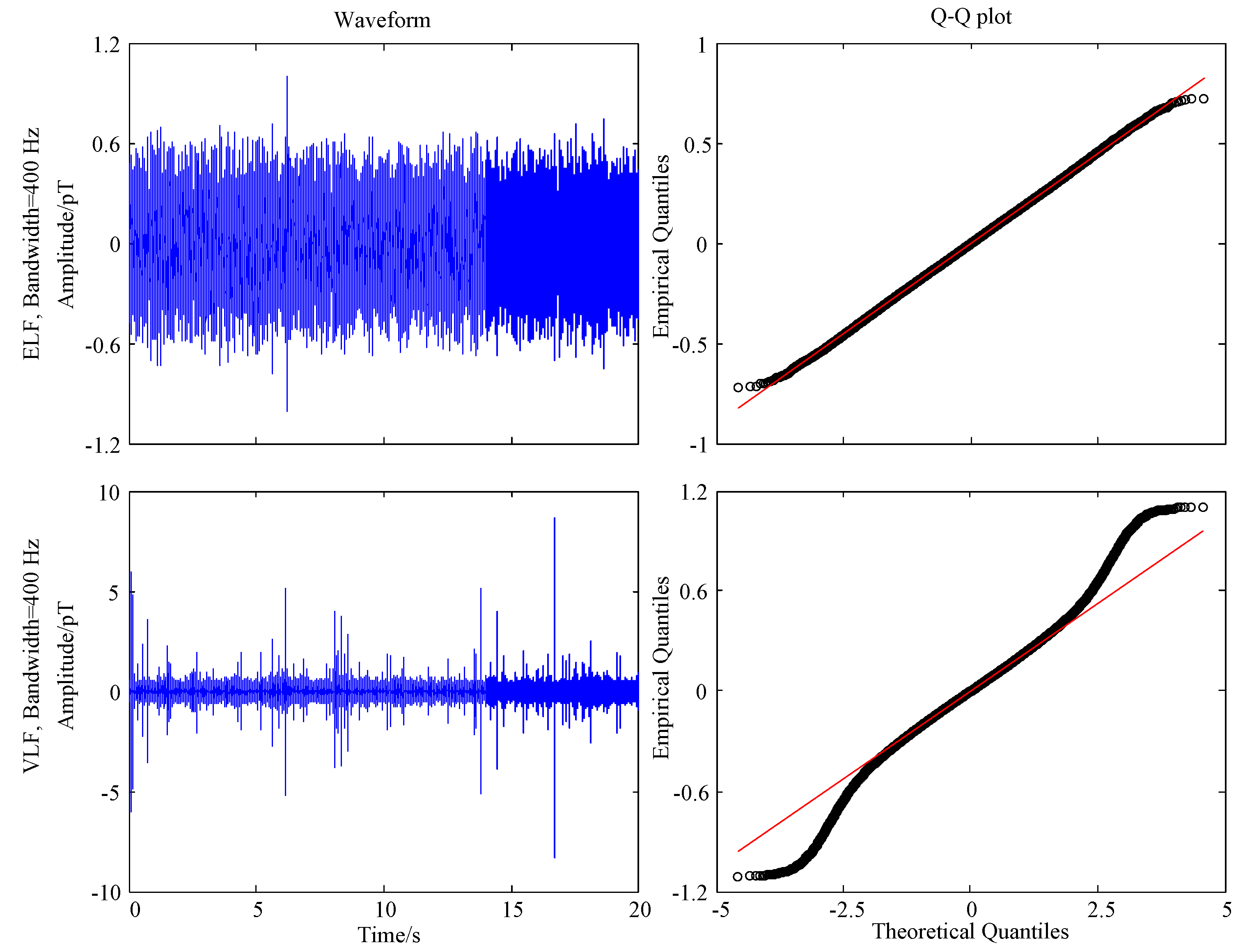
4.1. Normality Test for the Narrow Band Noise
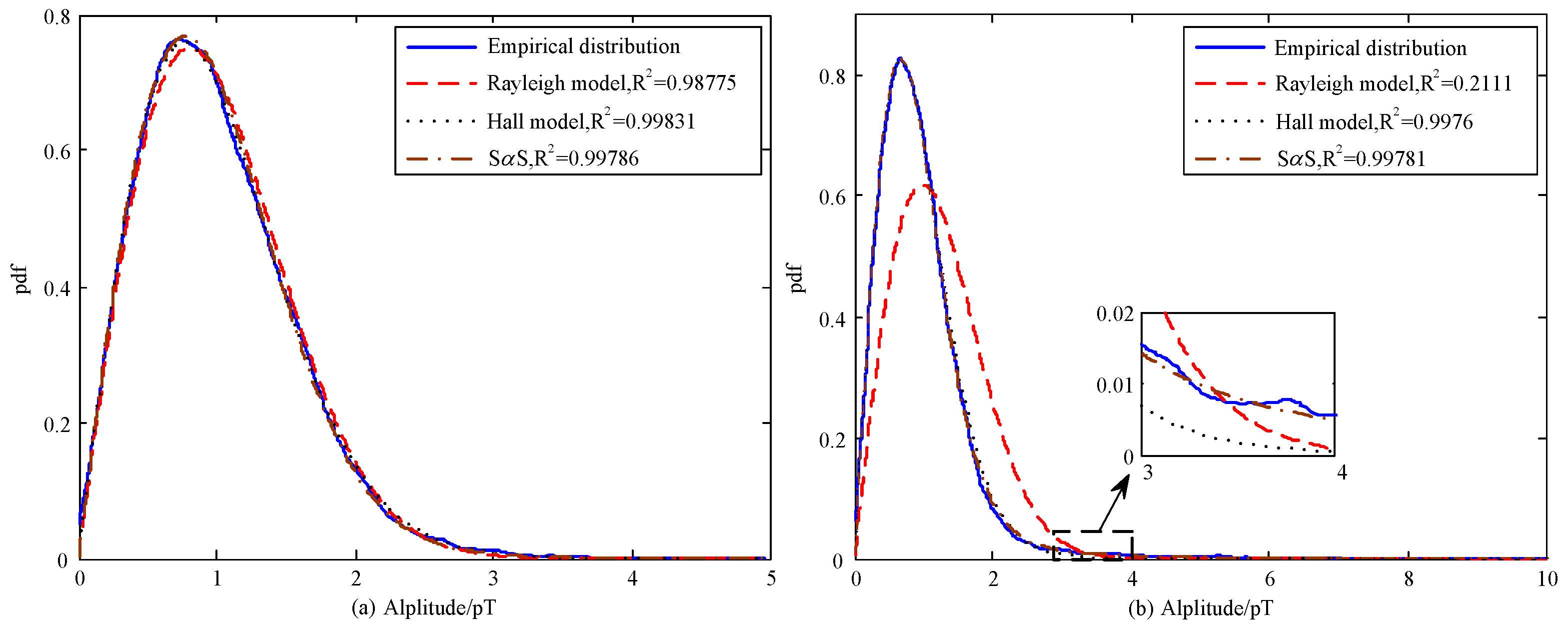
4.2. Amplitude Probability Distribution of the Narrow Band Noise Envelope
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shvets, A.; Hayakawa, M. Global lightning activity on the basis of inversions of natural ELF electromagnetic data observed at multiple stations around the world. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 6, 705–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.; Davis, J.; Nisenoff, M. Superconducting extremely low frequency (ELF) magnetic field sensors for submarine communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1974, 4, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.B.; Said, R.K.; Inan, U.S. Mitigation of 50–60 Hz power line interference in geophysical data. Radio Sci. 2010, 6, RS6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffbauer, W.H.; Brune, J.F. Coal Mine Communications. Available online: http://www.wvminesafety.org/PDFs/AdditionalInformationTable/Coal_Mine_Communications.pdf (accessed on 14 February 2016).
- Chrissan, D.A.; Fraser-Smith, A.C. A comparison of low-frequency radio noise amplitude probability distribution models. Radio Sci. 2000, 1, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.B.; Inan, U.S.; Gołkowski, M.; McCarrick, M.J. ELF/VLF wave generation via ionospheric HF heating: Experimental comparison of amplitude modulation, beam painting, and geometric modulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, A02302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Spasojevic, M.; Cohen, M.B.; Inan, U.S. Utilizing nonlinear ELF generation in modulated ionospheric heating experiments for communications applications. Radio Sci. 2013, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriman, S.K. Custom Integrated Amplifier Chip for VLF Magnetic Receiver. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; He, Q.; Lin, F.; Lu, Y. Design and characterization of a low-cost self-oscillating fluxgate transducer for precision measurement of high-current. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 9, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, J.; Edelstein, A.S. Magnetic sensors and their applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 3, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.; Han, Y. A Missile-Borne Angular Velocity Sensor Based on Triaxial Electromagnetic Induction Coils. Sensors 2016, 10, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Tang, M.; Gao, F.; Zhu, B.; Fu, S.; Ouyang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, H.; Li, J.; Shum, P.; Liu, D. An ultra-sensitive magnetic field sensor based on extrinsic fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometer and terfenol-D. J. Lightwave Technol. 2015, 15, 3332–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.B.; Inan, U.S.; Paschal, E.W. Sensitive broadband ELF/VLF radio reception with the AWESOME instrument. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote 2010, 1, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.; Braginski, A.I. Fundamentals and Technology of SQUID and SQUID Systems. In The SQUID Handbook; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rombetto, S.; Granata, C.; Vettoliere, A.; Russo, M. Multichannel System Based on a High Sensitivity Superconductive Sensor for Magnetoencephalography. Sensors 2014, 7, 12114–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.; Dinger, R.; Goldstein, J. Development of a superconducting ELF receiving antenna. IEEE Trans. Antenn. Propag. 1977, 2, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagor, D.; Fan, Y.; Mombourquette, C.; Jia, Q.; Stolarczyk, L. A high-temperature superconducting receiver for low-frequency radio waves. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercon. 1997, 4, 3845–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, P. HTcSQUID low frequency receiver and through-wall receving experiments. Chin. Acta Phys. Sin. 2014, 19, 198501. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchedda, A.; Chouteau, M.; Keating, P.; Smith, R. Sferics noise reduction in timedomain electromagnetic systems: Application to MegaTEMII signal enhancement. Explor. Geophys. 2010, 41, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Lin, J.; Yang, G.H.; Tian, P.P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.B.; Ji, Y.J. Ground-airborne electromagnetic signals de-noising using a combined wavelet transform algorithm. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 9, 3145–3152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, S.; Lin, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, G. A wavelet-based baseline drift correction method for grounded electrical source airborne transient electromagnetic signals. Explor. Geophys. 2013, 44, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.F.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, Y.L.; Dong, H.; Xie, X.M.; Muck, M.; Krause, H.J.; Braginski, A.I.; Offenhausser, A.; Jiang, M.H. Comparison of noise performance of dc SQUID bootstrap circuit with that of the standard flux modulation dc SQUID readout scheme. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercon. 2011, 3, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyappa, N.; Sengottuvel, S.; Parasakthi, C.; Gireesan, K.; Janawadkar, M.P.; Radhakrishnan, T.S.; Sundar, C.S. Baseline drift removal and denoising of MCG data using EEMD: Role ofnoise amplitude and the thresholding effect. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 1266–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Analysis and modeling for the ELF atmospheric noise using a low-temperature superconducting receiver. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), Guilin, China, 12–15 June 2016; pp. 19–23.
- Chrissan, D.A. Statistical Analysis and Modeling of Low-Frequency Radio Noise and Improvement of Low-Frequency Communications. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, X. BER analysis for digital modulation schemes under symmetric alpha-stable noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–8 October 2014; pp. 350–355.
- Lilliefors, H.W. On the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normality with mean and variance unknown. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1967, 318, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, M.B.; Gnanadesikan, R. Probability plotting methods for the analysis of data. Biometrika 1968, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambike, S.; Ilow, J.; Hatzinakos, D. Detection for binary transmission in a mixture of Gaussian noise and impulsive noise modeled as an alpha-stable process. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 1994, 3, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Wiklundh, K. Evaluation of Impact on Digital Radio Systems by Measuring Amplitude Probability Distribution of Interfering Noise. IEICE Trans. Commun. 2015, 7, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boashash, B. Estimating and interpreting the instantaneous frequency of a signal. Proc. IEEE 1992, 4, 520–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklundh, K.; Fors, K.; Holm, P. A log-likelihood ratio for improved receiver performance for VLF/LF communication in atmospheric noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, Tampa, FL, USA, 26–28 October 2015; pp. 1120–1125.
- Ying, W.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y. A multidimensional Class B noise model based on physical and mathematical analysis. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 2012, 11, 3519–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruoglu, E.E.; Zerubia, J. Modeling SAR images with a generalization of the Rayleigh distribution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 4, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, M. A central limit theorem and a strong mixing condition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1956, 1, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Frequency Band | Length | Data1 | Data2 | Data3 | Data4 | Data5 | Data6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELF | 20 ms | 0.42 | 0.361 | 0.377 | 0.395 | 0.382 | 0.386 |
| 5 ms | 0.872 | 0.866 | 0.866 | 0.868 | 0.868 | 0.864 | |
| 2.5 ms | 0.974 | 0.971 | 0.973 | 0.973 | 0.974 | 0.971 | |
| VLF | 20 ms | 0.309 | 0.357 | 0.363 | 0.348 | 0.324 | 0.324 |
| 5 ms | 0.747 | 0.753 | 0.756 | 0.789 | 0.771 | 0.761 | |
| 2.5 ms | 0.892 | 0.9 | 0.912 | 0.923 | 0.921 | 0.914 |
| Noise | Model | 50 Hz | 200 Hz | 400 Hz | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | MSLE | Parameters | MSLE | Parameters | MSLE | ||
| ELF | Rayleigh | σ = 0.823 | 8.59 | σ = 0.809 | 1.82 | σ = 0.807 | 2.04 |
| Hall | m = 19.68 | 2.15 | m = 40.43 | 4.67 | m = 30.18 | 4.65 | |
| γ = 3.349 | γ = 4.939 | γ = 4.212 | |||||
| SαS | α = 1.833 | 5.89 | α = 1.945 | 6.75 | α = 1.96 | 6.55 | |
| γ = 0.317 | γ = 0.316 | γ = 0.316 | |||||
| VLF | Rayleigh | σ = 0.91 | 1.32 | σ = 0.959 | 1.81 | σ = 0.978 | 1.86 |
| Hall | m = 8.303 | 2.09 | m = 12.76 | 3.48 | m = 15.68 | 3.41 | |
| γ = 1.823 | γ = 2.356 | γ = 2.681 | |||||
| SαS | α = 1.736 | 1.04 | α = 1.776 | 8.04 | α = 1.803 | 6.15 | |
| γ = 0.297 | γ = 0.293 | γ = 0.292 | |||||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Qiu, L.; Rong, L. Initial Results from SQUID Sensor: Analysis and Modeling for the ELF/VLF Atmospheric Noise. Sensors 2017, 17, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020371
Hao H, Wang H, Chen L, Wu J, Qiu L, Rong L. Initial Results from SQUID Sensor: Analysis and Modeling for the ELF/VLF Atmospheric Noise. Sensors. 2017; 17(2):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Huan, Huali Wang, Liang Chen, Jun Wu, Longqing Qiu, and Liangliang Rong. 2017. "Initial Results from SQUID Sensor: Analysis and Modeling for the ELF/VLF Atmospheric Noise" Sensors 17, no. 2: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020371
APA StyleHao, H., Wang, H., Chen, L., Wu, J., Qiu, L., & Rong, L. (2017). Initial Results from SQUID Sensor: Analysis and Modeling for the ELF/VLF Atmospheric Noise. Sensors, 17(2), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020371





