A Novel Fiber Optic Based Surveillance System for Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Motivation and Organization of the Paper
- Incorporating feature-level contextual information in an intelligent way, adapting the so-called tandem approach widely used in speech recognition [42] to enhance the feature vector of the baseline system.
- Combining the outputs of different pattern classification processes, each of them using a combination of frequency-based and tandem features, exploiting different temporal ranges of contextual information.
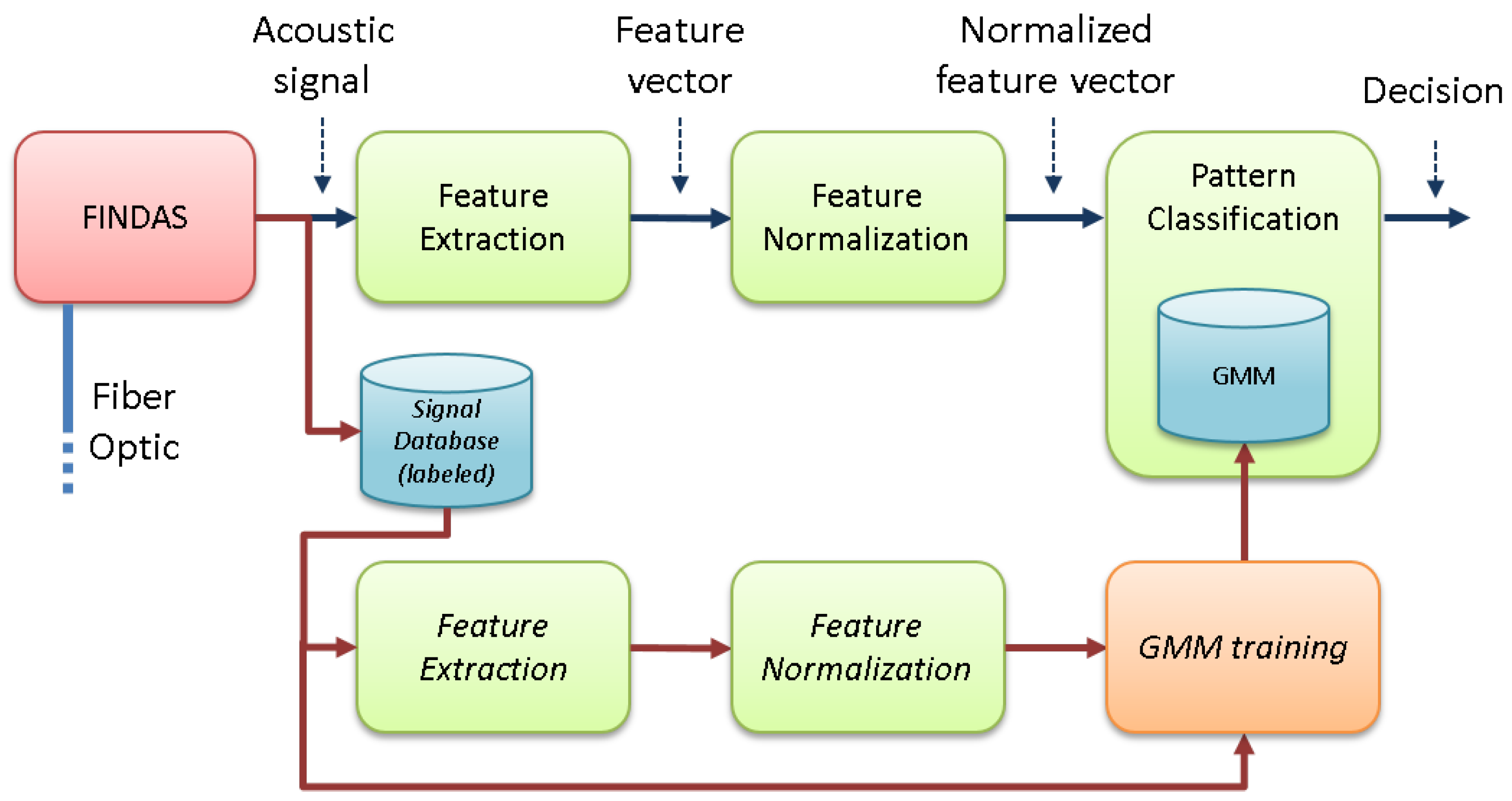
2. Baseline System
2.1. Sensing System
2.2. Pattern Recognition System
- The machine + activity identification mode identifies the machine and the activity that the machine is conducting along the pipeline.
- The threat detection mode directly identifies if the activity is an actual threat for the pipeline or not.
- Feature extraction, which reduces the high-dimensionality of the signals acquired with the DAS system to a more informative and discriminative set of features.
- Feature vector normalization, which compensates for variabilities in the signal acquisition process and the sensed locations.
- Pattern classification, which classifies the acoustic signal into a set of predefined classes (using a set of signal models, GMMs, previously trained from a labeled signal database).
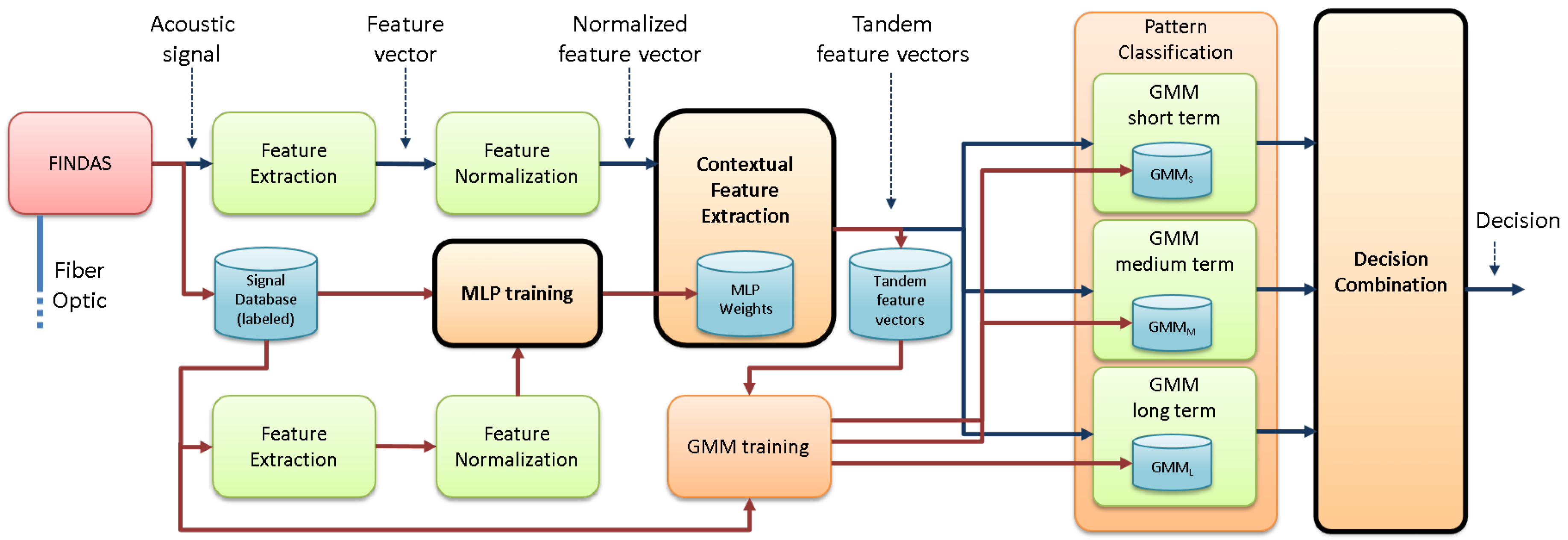
3. Novel Pipeline Integrity Threat Detection System
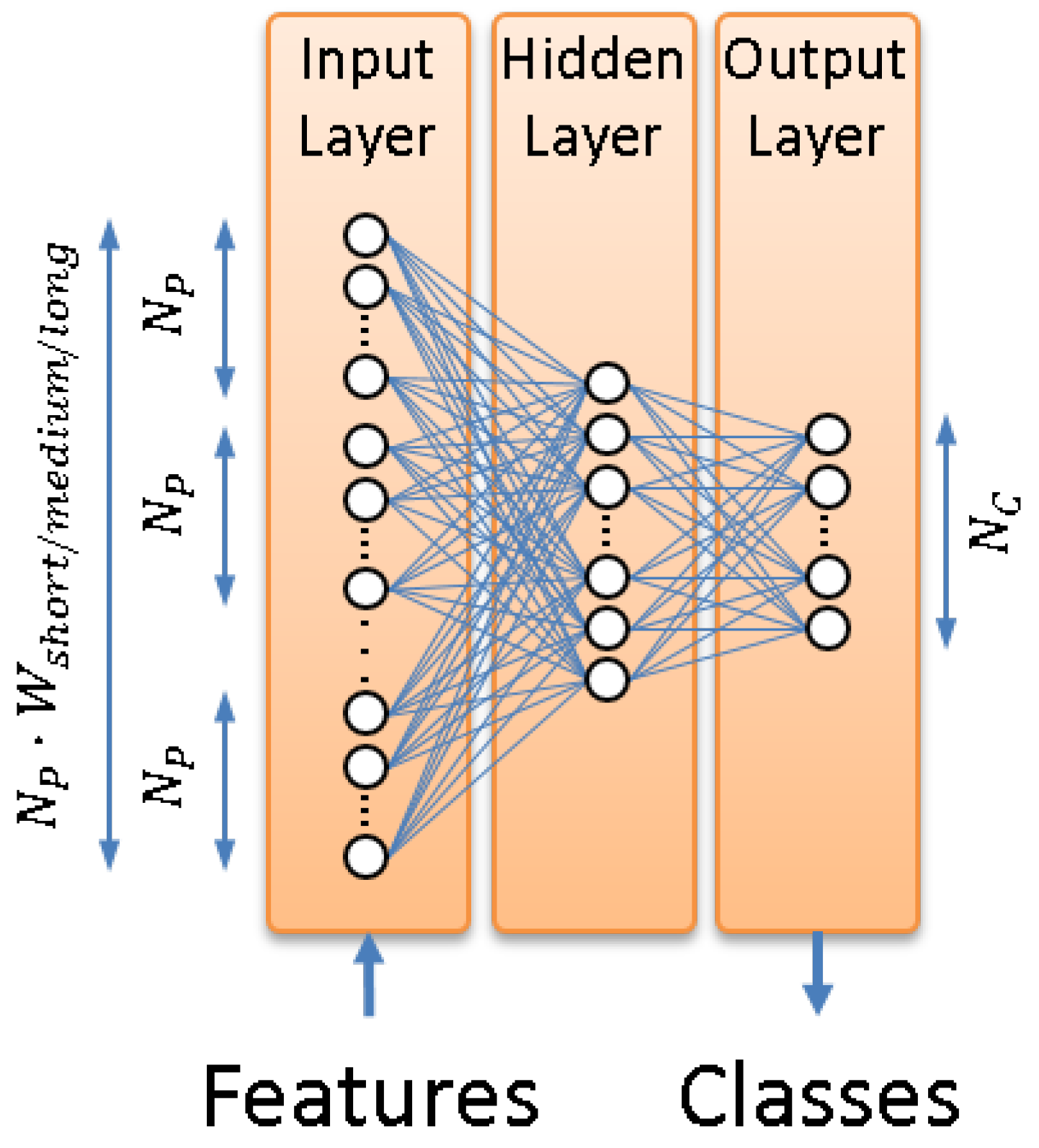
3.1. Contextual Feature Extraction
3.1.1. Posterior Probability Vector Computation
3.1.2. Tandem Feature Vector Building
3.2. Decision Combination
3.2.1. Sum Method
3.2.2. Product Method
3.2.3. Maximum Method
4. Experimental Procedure
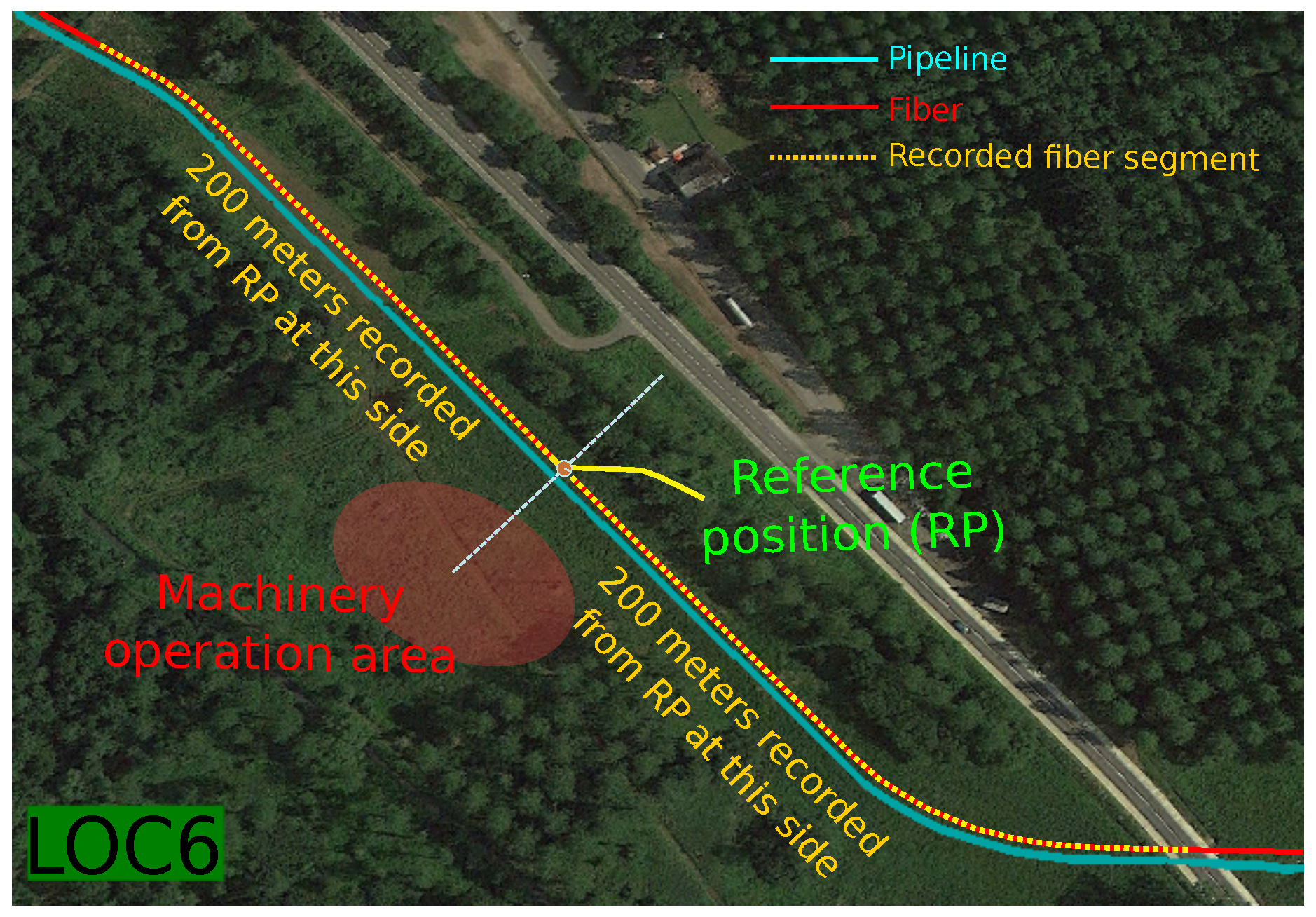
4.1. Database Description
4.2. System Configuration
4.3. Evaluation Strategy
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Preliminary Experiments
5.2. Contextual Feature Extraction
5.3. Decision Combination
5.3.1. Machine + Activity Identification Mode
5.3.2. Threat Detection Mode
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, K.N.; Juarez, J.C.; Taylor, H.F. Distributed fiber optic pressure/seismic sensor for low-cost monitoring of long perimeters. Proc. SPIE 2003, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, J.C.; Maier, E.W.; Choi, K.N.; Taylor, H.F. Distributed Fiber-Optic Intrusion Sensor System. J. Lightwave Technol. 2005, 23, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, J.C.; Taylor, H.F. Field test of a distributed fiber-optic intrusion sensor system for long perimeters. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1968–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.J.; Luo, J.; Ran, Z.L.; Yue, J.F.; Luo, X.D.; Zhou, Z. Long-distance fiber-optic ψ-OTDR intrusion sensing system. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Optical Fibre Sensors, Edinburgh, UK, 5–14 October 2009; Volume 7503, pp. 75031O-1–75031O-4.
- Juarez, J.C.; Taylor, H.F. Polarization discrimination in a phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometer intrusion-sensor system. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 3284–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, P.; Hui, Z.; Bin, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Xiahoan, S. Distributed optical-fiber vibration sensing system based on differential detection of differential coherent-OTDR. In Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Sensors, Taipei, Taiwan, 28–31 October 2012; pp. 1–3.
- Quin, Z.G.; Chen, L.; Bao, X.Y. Wavelet denoising method for improving detection performance of distributed vibration sensor. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 542–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.N.; Li, J.; Fan, M.Q.; Zhang, L.; Peng, F.; Wu, H.; Zeng, J.J.; Zhou, Y.; Rao, Y.J. Phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry with Brillouin amplification. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 4313–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, H.F.; Martín-López, S.; Corredera, P.; Filograno, M.L.; Frazão, O.; González-Herráez, M. Phase-sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometer Assisted by First-order Raman Amplification for Distributed Vibration Sensing Over >100 km. J. Lightwave Technol. 2014, 32, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wu, H.; Jia, X.H.; Rao, Y.J.; Wang, Z.N.; Peng, Z.P. Ultra-long high-sensitivity ϕ-OTDR for high spatial resolution intrusion detection of pipelines. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 13804–13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Peng, F.; Xiao, S.; Wu, H.; Rao, Y. 124 km Phase-sensitive OTDR with Brillouin Amplification. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9157, 91575Z-1–91575Z-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Peng, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, H.; Rao, Y. 175 km Phase-sensitive OTDR with Hybrid Distributed Amplification. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9157, 9157D5-1–9157D5-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Q.; Cai, H.; Qu, R.; Fang, Z. High sampling rate multi-pulse phase-sensitive OTDR employing frequency division multiplexing. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9157, 91576X-1–91576X-4. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Feng, H.; Zeng, Z. A Long Distance Phase-Sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometer with Simple Structure and High Locating Accuracy. Sensors 2015, 15, 21957–21970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Pan, C.; Sun, X. Vibration Pattern Recognition and Classification in OTDR Based Distributed Optical-Fiber Vibration Sensing System. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9062, 906205-1–906205-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, C.; Mondanos, M. An introduction to fibre optic Intelligent Distributed Acoustic Sensing (iDAS) technology for power industry applications. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Insulated Power Cables, Versailles, France, 21–25 June 2015; Volume A3.4, pp. 1–6.
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Peng, F.; Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Rao, Y. Field test of a fully distributed fiber optic intrusion detection system for long-distance security monitoring of national borderline. Proc. SPIE 2014, 91579, 915790-1–915790-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Peng, Z.; Rao, Y. A novel intrusion signal processing method for phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (ϕ-OTDR). Proc. SPIE 2014, 9157, 9157O-1–9157O-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Fan, X.Y.; Liu, Q.W.; He, Z.Y. Practical Pattern Recognition System for Distributed Optical Fiber Intrusion Monitoring System Based on Phase-Sensitive Coherent OTDR. In Proceedings of the Asia Communications and Photonics Conference, Hong Kong, China, 19–23 November 2015; pp. 145:1–145:3.
- Sun, Q.; Feng, H.; Yan, X.; Zeng, Z. Recognition of a Phase-Sensitivity OTDR Sensing System Based on Morphologic Feature Extraction. Sensors 2015, 15, 15179–15197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Rao, Y. Separation and Determination of the Disturbing Signals in Phase-Sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (ϕ-OTDR). J. Lightwave Technol. 2015, 33, 3156–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejedor, J.; Martins, H.F.; Piote, D.; Macias-Guarasa, J.; Pastor-Graells, J.; Martin-Lopez, S.; Corredera, P.; Smet, F.D.; Postvoll, W.; Gonzalez-Herraez, M. Towards Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats using a Smart Fiber Optic Surveillance System. J. Lightwave Technol. 2016, 34, 4445–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, G.T. The use of context in pattern recognition. Pattern Recognit. 1978, 10, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, C.; Balakrishnan, K. Development & evaluation of different acoustic models for Malayalam continuous speech recognition. Procedia Eng. 2012, 30, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, F.; Li, J.; Luo, C.; Zhang, G. Improved Context-Dependent Acoustic Modeling for Continuous Chinese Speech Recognition. Proc. Eurospeech 2001, 3, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Laface, P.; Mori, R.D. Speech Recognition and Understanding: Recent Advances, Trends, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.B.; Abu-Mostafa, Y.; Sill, J.; Kasdan, H.; Pavel, M. Robust image recognition by fusion of contextual information. Inf. Fusion 2002, 3, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, M.A.; Ramírez, J.A.; Thévenaz, L. Intensifying the response of distributed optical fibre sensors using 2D and 3D image restoration. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, M.A.; Ramírez, J.A.; Thévenaz, L. Reaching millikelvin resolution in Raman distributed temperature sensing using image processing. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9916, 99162A-1–99162A-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Spontaneous Speech with Microphone Arrays. Ph.D. Thesis, Ottawa-Carleton Institute for Physics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y. Action recognition with multiscale spatio-temporal contexts. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3185–3192.
- Bianne-Bernard, A.L.; Menasri, F.; Mohamad, R.A.H.; Mokbel, C.; Kermorvant, C.; Likforman-Sulem, L. Dynamic and Contextual Information in HMM Modeling for Handwritten Word Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Robinovitch, S.N.; Mori, G. Discriminative Latent Models for Recognizing Contextual Group Activities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ji, Q. A Hierarchical Context Model for Event Recognition in Surveillance Video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2561–2568.
- Kittler, J.; Hatef, M.; Duin, R.P.; Matas, J. On Combining Classifiers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klautau, A.; Jevtic, N.; Orlitsky, A. Combined Binary Classifiers With Applications To Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP2002)—INTERSPEECH 2002, Denver, CO, USA, 16–20 September 2002; pp. 2469–2472.
- Tulyakov, S.; Jaeger, S.; Govindaraju, V.; Doermann, D. Review of Classifier Combination Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.K.; Hull, J.H.; Srihari, S.N. Decision combination in multiple classifier systems. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Prampero, P.S.; de Carvalho, A.C.P.L.F. Classifier combination for vehicle silhouettes recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Processing and its Applications, London, UK, 13–15 July 1999; pp. 67–71.
- Madsen, C.; Baea, T.; Snider, T. Intruder Signature Analysis from a Phase-sensitive Distributed Fiber-optic Perimeter Sensor. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6770, 67700K-1–67700K-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, H.F.; Piote, D.; Tejedor, J.; Macias-Guarasa, J.; Pastor-Graells, J.; Martin-Lopez, S.; Corredera, P.; Smet, F.D.; Postvoll, W.; Ahlen, C.H.; et al. Early Detection of Pipeline Integrity Threats using a SmarT Fiber-OPtic Surveillance System: The PIT-STOP Project. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9634, 96347X-1–96347X-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, B.; Morgan, N.; Stolcke, A. On using MLP in LVCSR. In Proceedings of the of ICSLP, Jeju, Korea, 4–8 October 2004; pp. 921–924.
- FOCUS S.L. FIber Network Distributed Acoustic Sensor (FINDAS). 2015. Available online: http://www.focustech.eu/docs/FINDAS-MR-datasheet.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- Martins, H.F.; Martín-López, S.; Corredera, P.; Filograno, M.L.; Frazão, O.; González-Herráez, M. Coherent noise reduction in high visibility phase sensitive optical time domain reflectometer for distributed sensing of ultrasonic waves. J. Lightwave Technol. 2013, 31, 3631–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, B.; Grezl, F.; Morgan, N. Improved MLP structures for data-driven feature extraction for ASR. In Proceedings of the INTERSPEECH 2005—Eurospeech, 9th European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, Lisbon, Portugal, 4–8 September 2005; pp. 2129–2131.
- Morgan, N.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Q.; Stolcke, A. Trapping conversational speech: Extending TRAP/TANDEM approaches to conversational speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004; pp. 537–540.
- Faria, A.; Morgan, N. Corrected tandem features for acoustic model training. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008; pp. 4737–4740.
- Bishop, C.M. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D. ICSI Quicknet Software Package. 2004. Available online: http://www.icsi.berkeley.edu/Speech/qn.html (accessed on 12 February 2017).
- Al-ani, A.; Deriche, M. A New Technique for Combining Multiple Classifiers using The Dempster-Shafer Theory of Evidence. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 17, 333–361. [Google Scholar]
- Breukelen, M.V.; Duin, R.P.W.; Tax, D.M.J.; Hartog, J.E.D. Handwritten digit recognition by combined classifiers. Kybernetika 1998, 34, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, T.T. Performance evaluation of classification algorithms by k-fold and leave-one-out cross validation. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2839–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H.A.; Gunnink, J.L. The Paired t Test Under Artificial Pairing. Am. Stat. 1997, 51, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Machine | Activity | Duration (in Seconds) | Threat/Non-Threat | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC1 | LOC2 | LOC3 | LOC4 | LOC5 | LOC6 | Total | |||
| Big excavator | Moving along the ground | 1100 | 1100 | 3540 | 1740 | 1620 | 4160 | 13,260 | Non-threat |
| Hitting the ground | 120 | 140 | 240 | 220 | 80 | 260 | 1060 | Threat | |
| Scrapping the ground | 460 | 460 | 920 | 620 | 200 | 580 | 3240 | Threat | |
| Small excavator | Moving along the ground | 600 | 500 | 1700 | 820 | 820 | 1660 | 6100 | Non-threat |
| Hitting the ground | 200 | 180 | 220 | 220 | 80 | 240 | 1140 | Threat | |
| Scrapping the ground | 420 | 340 | 780 | 360 | 180 | 520 | 2600 | Threat | |
| Pneumatic hammer | Compacting ground | 660 | 0 | 580 | 1320 | 0 | 1320 | 3880 | Non-threat |
| Plate compactor | Compacting ground | 740 | 0 | 740 | 1240 | 0 | 1680 | 4400 | Non-threat |
| Window Size | Machine + Activity Identification | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Excavator | Small Excavator | Pneumatic Hammer | Plate Compactor | Acc. | |||||
| Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Compact. | Compact. | ||
| Baseline [22] | |||||||||
| Short | |||||||||
| Medium | |||||||||
| Long | |||||||||
| Window Size | Machine + Activity Identification | Threat Detection | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Excavator | Small Excavator | Pneumatic Hammer | Plate Compactor | Acc. | TDR | FAR | Acc. | |||||
| Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Compact. | Compact. | |||||
| Baseline [22] | ||||||||||||
| Short | ||||||||||||
| Medium | ||||||||||||
| Long | ||||||||||||
| Method | Machine + Activity Identification | Threat Detection | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Big Excavator | Small Excavator | Pneumatic Hammer | Plate Compactor | Acc. | TDR | FAR | Acc. | ||||||
| Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Mov. | Hit. | Scrap. | Compact. | Compact. | ||||||
| Baseline [22] | |||||||||||||
| Prod | S-M | 59.9% | 19.4% | 36.3% | 60.4% | 13.0% | 33.8% | 75.8% | 44.4% | 53.06% | 76.8% | 33.2% | 69.10% |
| S-L | 64.3% | 23.7% | 32.1% | 57.7% | 18.0% | 31.1% | 80.4% | 40.1% | 53.91% | 74.9% | 33.7% | 68.25% | |
| M-L | 66.1% | 22.2% | 33.7% | 57.9% | 14.3% | 36.6% | 78.4% | 41.3% | 54.92% | 73.9% | 32.0% | 69.32% | |
| S-M-L | 61.5% | 24.0% | 34.0% | 57.6% | 15.0% | 36.9% | 78.2% | 39.8% | 53.09% | 75.0% | 33.2% | 68.68% | |
| Max | S-M | 67.3% | 17.3% | 36.9% | 64.2% | 9.7% | 27.2% | 79.5% | 56.6% | 57.75% | 81.0% | 36.2% | 67.66% |
| S-L | 76.8% | 17.2% | 32.1% | 62.9% | 10.9% | 29.4% | 81.1% | 50.0% | 60.20% | 79.7% | 35.0% | 68.29% | |
| M-L | 76.6% | 14.8% | 34.2% | 64.1% | 11.5% | 29.2% | 80.1% | 49.9% | 60.33% | 78.4% | 33.4% | 69.24% | |
| S-M-L | 77.0% | 14.5% | 34.0% | 65.0% | 10.0% | 27.8% | 81.7% | 51.4% | 60.82% | 81.1% | 35.4% | 68.34% | |
| Recognized Class | ||||||||||||
| Big Excavator | Small Excavator | Pneumatic Hammer | Plate Compactor |  | ||||||||
Moving | Hitting | Scrapping | Moving | Hitting | Scrapping | Compacting | Compacting | |||||
| Real class | Big excavator | Moving | 66.09 | |||||||||
| Hitting | 30.60 | 22.15 | 19.21 | |||||||||
| Scrapping | 24.64 | 33.74 | 18.39 | |||||||||
| Small excavator | Moving | 57.91 | 16.92 | |||||||||
| Hitting | 17.03 | 14.01 | 14.32 | 29.55 | ||||||||
| Scrapping | 15.55 | 12.62 | 36.57 | |||||||||
| Pneumatic hammer | Compacting | 78.38 | ||||||||||
| Plate Compactor | Compacting | 14.24 | 16.29 | 41.28 | ||||||||
| Big Excavator | Small Excavator | Pneumatic Hammer | Plate Compactor | Averages | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving | Hitting | Scrapping | Moving | Hitting | Scrapping | Compacting | Compacting | ||
| Baseline | |||||||||
| Novel | |||||||||
| Relative improvement | 34.74% | 10.14% | 29.62% | 12.89% | 3.92% | 21.01% | 9.10% | 4.48% | 21.30% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tejedor, J.; Macias-Guarasa, J.; Martins, H.F.; Piote, D.; Pastor-Graells, J.; Martin-Lopez, S.; Corredera, P.; Gonzalez-Herraez, M. A Novel Fiber Optic Based Surveillance System for Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats. Sensors 2017, 17, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020355
Tejedor J, Macias-Guarasa J, Martins HF, Piote D, Pastor-Graells J, Martin-Lopez S, Corredera P, Gonzalez-Herraez M. A Novel Fiber Optic Based Surveillance System for Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats. Sensors. 2017; 17(2):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020355
Chicago/Turabian StyleTejedor, Javier, Javier Macias-Guarasa, Hugo F. Martins, Daniel Piote, Juan Pastor-Graells, Sonia Martin-Lopez, Pedro Corredera, and Miguel Gonzalez-Herraez. 2017. "A Novel Fiber Optic Based Surveillance System for Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats" Sensors 17, no. 2: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020355
APA StyleTejedor, J., Macias-Guarasa, J., Martins, H. F., Piote, D., Pastor-Graells, J., Martin-Lopez, S., Corredera, P., & Gonzalez-Herraez, M. (2017). A Novel Fiber Optic Based Surveillance System for Prevention of Pipeline Integrity Threats. Sensors, 17(2), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17020355






