Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Materials
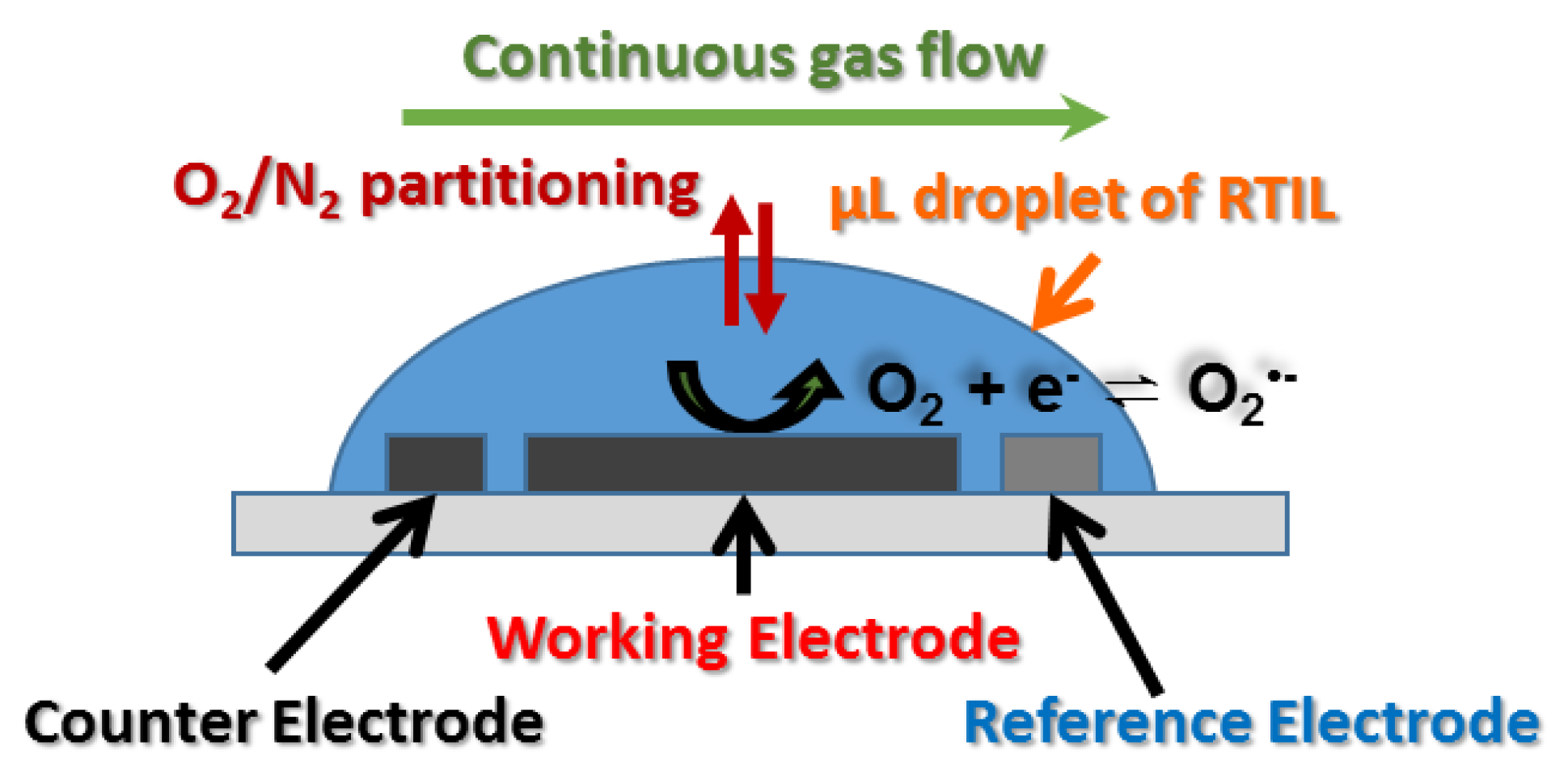
2.3. Electrochemical Experiments
2.4. Gas Mixing Setup
3. Results and Discussion
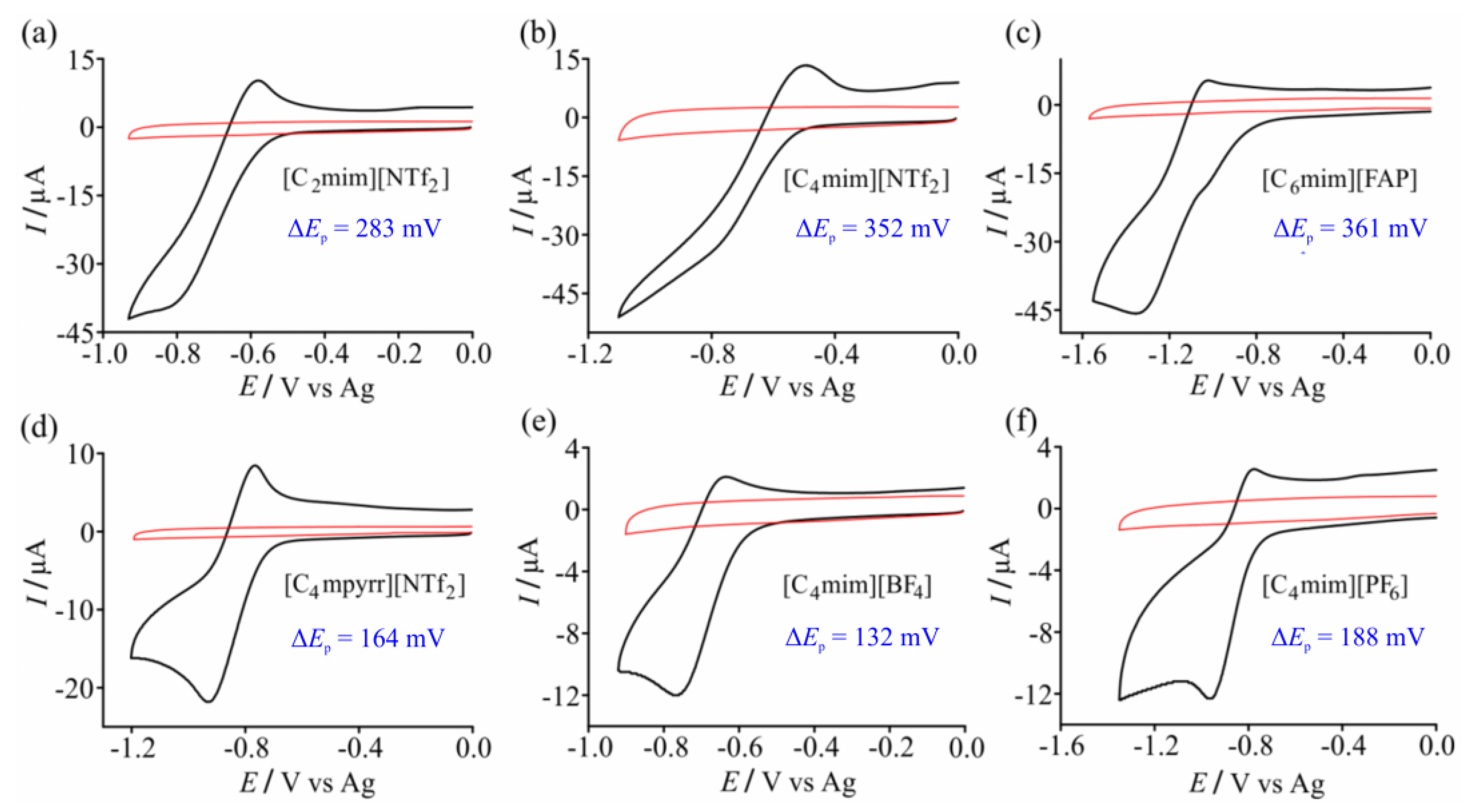
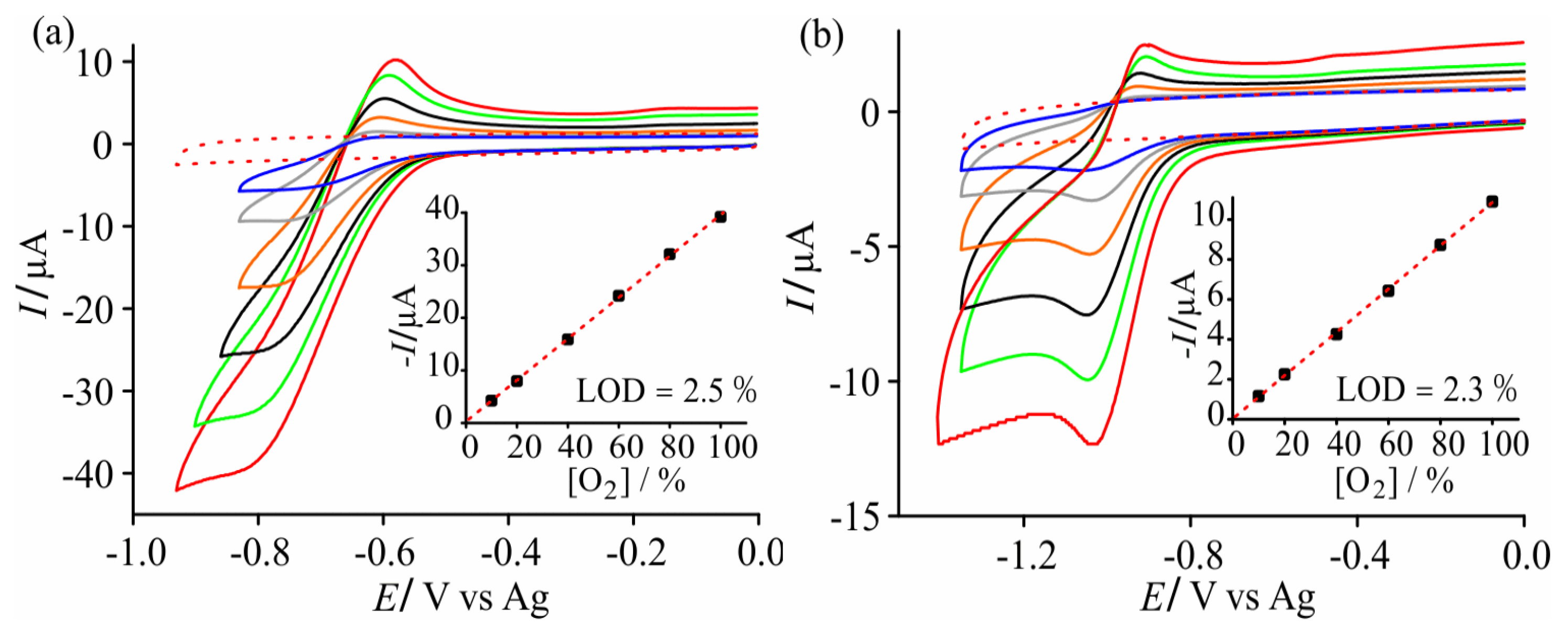
3.1. Cyclic Voltammetry
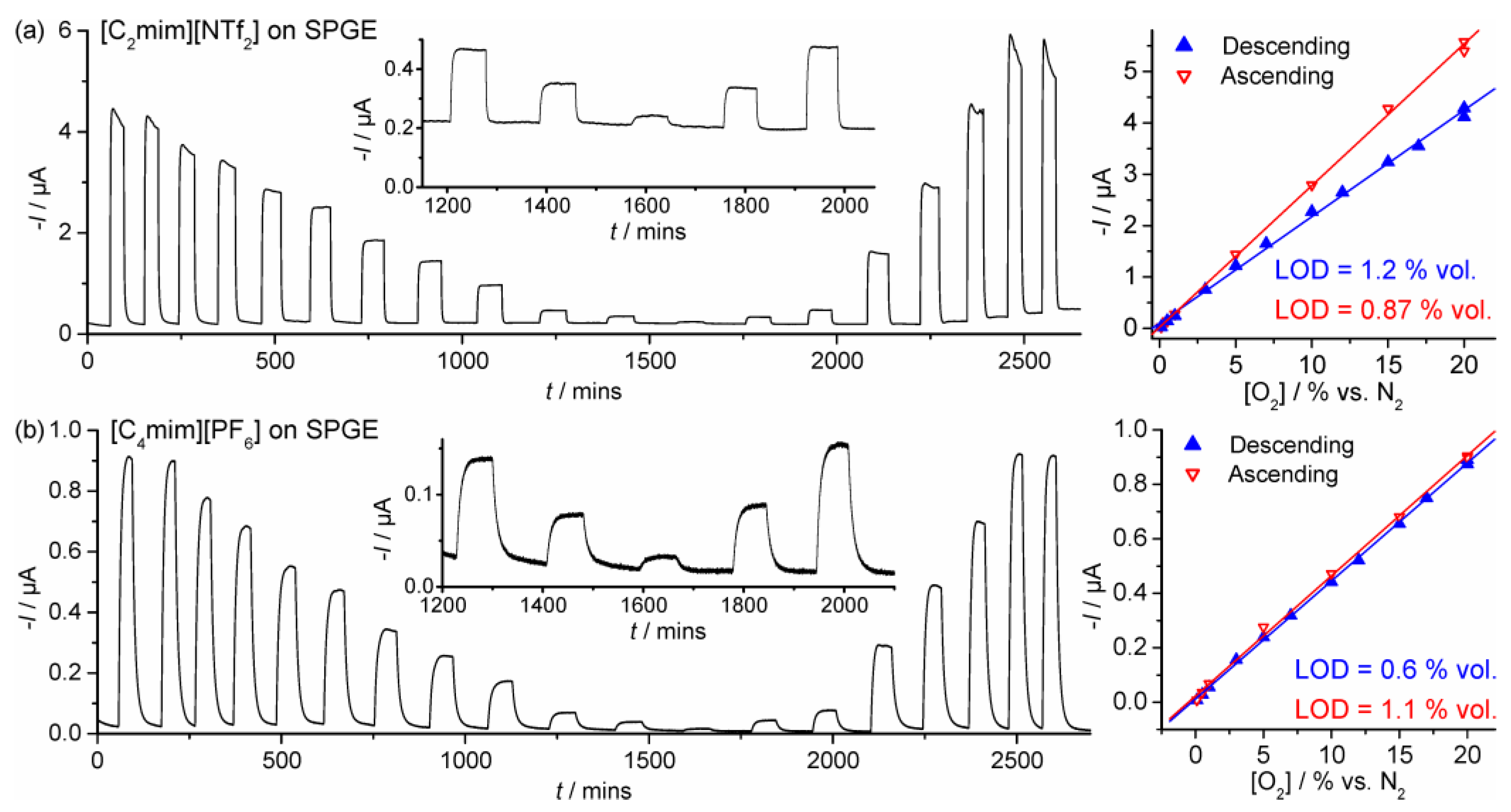
3.2. Chronoamperometry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Mu, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Zeng, X.; Mason, A.J. Room Temperature Ionic-Liquid Electrochemical Gas Sensor Array System for Real-Time Mine Safety Monitoring. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- O’Driscoll, B.R.; Howard, L.S.; Davison, A.G. BTS guideline for emergency oxygen use in adult patients. Thorax 2008, 63, vi1–vi68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hempel, A.W.; Papkovsky, D.B.; Kerry, J.P. Use of Optical Oxygen Sensors in Non-Destructively Determining the Levels of Oxygen Present in Combined Vacuum and Modified Atmosphere Packaged Pre-Cooked Convenience-Style Foods and the Use of Ethanol Emitters to Extend Product Shelf-Life. Foods 2013, 2, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tengberg, A.; Hovdenes, J.; Andersson, H.J.; Brocandel, O.; Diaz, R.; Hebert, D.; Arnerich, T.; Huber, C.; Körtzinger, A.; Khripounoff, A.; et al. Evaluation of a lifetime-based optode to measure oxygen in aquatic systems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2006, 4, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, E.M. Apollo Expeditions to the Moon; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1975.
- Reduced Oxygen Atmospheres: Resulting from the Use of Cryogens or Compressed Gases in the Workplace. In HSD053C (rev3); Occupational Health and Safety Service, University of Cambridge: Cambridge, UK, 2016.
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Dutta, P.K.; Akbar, S.A. Oxygen sensors: Materials, methods, designs and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 4271–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sorensen, O.T. Oxygen sensors based on semiconducting metal oxides: An overview. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2000, 65, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Compton, R.G. Amperometric Gas detection: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 7152–7181. [Google Scholar]
- Buzzeo, M.C.; Hardacre, C.; Compton, R.G. Use of Room Temperature Ionic Liquids in Gas Sensor Design. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrosse-Antle, L.E.; Bond, A.M.; Compton, R.G.; O’Mahony, A.M.; Rogers, E.I.; Silvester, D.S. Voltammetry in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids: Comparisons and Contrasts with Conventional Electrochemical Solvents. Chem. Asian J. 2010, 5, 202–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzeo, M.C.; Evans, R.G.; Compton, R.G. Non-Haloaluminate Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids in Electrochemistry—A Review. ChemPhysChem 2004, 5, 1106–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugappan, K.; Lee, J.; Silvester, D.S. Comparative study of screen printed electrodes for ammonia gas sensing in ionic liquids. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvester, D.S.; Aldous, L. Chapter 10: Electrochemical detection using ionic liquids. In Electrochemical Strategies in Detection Science; Arrigan, D.W.M., Ed.; RSC: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kadara, R.O.; Jenkinson, N.; Banks, C.E. Characterisation of commercially available electrochemical sensing platforms. Sens. Act. B Chem. 2009, 138, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metters, J.P.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. New directions in screen printed electroanalytical sensors: An overview of recent developments. Analyst 2011, 136, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, J.; González García, M.B.; Hernández Santos, D.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Ribotti, A.; McCaul, M.; Diamond, D.; Magni, P. Screen-printed electrodes for environmental monitoring of heavy metal ions: A review. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez Renedo, O.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Arcos Martínez, M.J. Recent developments in the field of screen-printed electrodes and their related applications. Talanta 2007, 73, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, R.A.S.; Lima, J.L.F.C.; Quinaz, M.B. Recent developments, characteristics and potential applications of screen-printed electrodes in pharmaceutical and biological analysis. Talanta 2016, 146, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Randviir, E.P.; Banks, C.E. Detection of theophylline utilising portable electrochemical sensors. Analyst 2014, 139, 2000–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Arrigan, D.W.M.; Silvester, D.S. Mechanical polishing as an improved surface treatment for platinum screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2016, 9, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Foster, C.W.; Cumba, L.R.; do Carmo, D.R.; Banks, C.E. Can solvent induced surface modifications applied to screen-printed platforms enhance their electroanalytical performance? Analyst 2016, 141, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Washe, A.P.; Lozano-Sanchez, P.; Bejarano-Nosas, D.; Katakis, I. Facile and versatile approaches to enhancing electrochemical performance of screen printed electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Sun, J.-J.; Xie, Y.; Lin, C.-G.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yin, W.-H.; Chen, G.-N. Enhanced electrochemical performance at screen-printed carbon electrodes by a new pretreating procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 588, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-L.; Tai, C.-Y.; Zen, J.-M. A Simple Method to Tune Up Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes Applicable to the Design of Disposable Electrochemical Sensors. Electroanalysis 2013, 11, 2539–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamouss, F.; Luais, E.; Thobie-Gautier, C.; Tessier, P.-Y.; Boujtita, M. Argon plasma treatment to enhance the electrochemical reactivity of screen-printed carbon surfaces. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 3026–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Chang, K.S.; Yuan, C.J. Enhancement of electrochemical properties of screen-printed carbon electrodes by oxygen plasma treatment. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4937–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumba, L.R.; Foster, C.W.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Smith, J.P.; Iniesta, J.; Thakur, B.; do Carmo, D.R.; Banks, C.E. Can the mechanical activation (polishing) of screen-printed electrodes enhance their electroanalytical response? Analyst 2016, 141, 2791–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Arrigan, D.W.M.; Silvester, D.S. Achievement of Prolonged Oxygen Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids on Mechanically Polished Platinum Screen-Printed Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5104–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravda, M.; O’Meara, C.; Guilbault, G.G. Polishing of screen-printed electrodes improves IgG adsorption. Talanta 2001, 54, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossi, N.; Toniolo, R.; Pizzariello, A.; Carrilho, E.; Piccin, E.; Battiston, S.; Bontempelia, G. An electrochemical gas sensor based on paper supported room temperature ionic liquids. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis-Berenguer, A.; Gómez-Mingot, M.; Montiel, V.; Canals, A.; Thiemann, T.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E.; Iniesta, J. Exploring the electrochemical behavior of screen printed graphite electrodes in a room temperature ionic liquid. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7735–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Murugappan, K.; Arrigan, D.W.M.; Silvester, D.S. Oxygen reduction voltammetry on platinum macrodisk and screen-printed electrodes in ionic liquids: Reaction of the electrogenerated superoxide species with compounds used in the paste of Pt screen-printed electrodes? Electrochim. Acta 2013, 101, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, K.; Arrigan, D.W.M.; Silvester, D.S. Electrochemical Behavior of Chlorine on Platinum Microdisk and Screen-Printed Electrodes in a Room Temperature Ionic Liquid. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 23572–23579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugappan, K.; Silvester, D.S. Sensors for Highly Toxic Gases: Methylamine and Hydrogen Chloride Detection at Low Concentrations in an Ionic Liquid on Pt Screen Printed Electrodes. Sensors 2015, 15, 26866–26876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.-Q.; Wei, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.-H.; Huang, X.-J. Toward Membrane-Free Amperometric Gas Sensors: An Ionic Liquid–Nanoparticle Composite Approach. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17471–17478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebicki, J.; Kloskowski, A.; Chrzanowski, W. Effect of oxygenation time on signal of a sensor based on ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9910–9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Silvester, D.S. Detection of sub-ppm Concentrations of Ammonia in an Ionic Liquid: Enhanced Current Density Using ‘Filled’ Recessed Microarrays. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12453–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudry, N.A.; Kampouris, D.K.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. Disposable highly ordered pyrolytic graphite-like electrodes: Tailoring the electrochemical reactivity of screen printed electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumba, L.R.; Smith, J.P.; Brownson, D.A.C.; Iniesta, J.; Metters, J.P.; do Carmo, D.R.; Banks, C.E. Electroanalytical detection of pindolol: Comparison of unmodified and reduced graphene oxide modified screen-printed graphite electrodes. Analyst 2015, 140, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.W.; Pillay, J.; Metters, J.P.; Banks, C.E. Cobalt Phthalocyanine Modified Electrodes Utilised in Electroanalysis: Nano-Structured Modified Electrodes vs. Bulk Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sensors 2014, 14, 21905–21922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Silvester, D.S. Low-cost microarray thin-film electrodes with ionic liquid gel-polymer electrolytes for miniaturised oxygen sensing. Analyst 2016, 141, 3705–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayyan, M.; Hashim, M.A.; AlNashef, I.M. Superoxide Ion: Generation and Chemical Implications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3029–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlNashef, I.M.; Leonard, M.L.; Kittle, M.C.; Matthews, M.A.; Weidner, J.W. Electrochemical Generation of Superoxide in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, D16–D18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Gunawan, C.A.; Zhao, C. Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Ionic Liquids: Fundamentals and Applications in Energy and Sensors. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3698–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-J.; Rogers, E.I.; Hardacre, C.; Compton, R.G. The Reduction of Oxygen in Various Room Temperature Ionic Liquids in the Temperature Range 293–318 K: Exploring the Applicability of the Stokes-Einstein Relationship in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 8953–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Lee, J.; Silvester, D.S. Electroreduction of 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids: Evidence of an EC2 Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 10997–11005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuberský, P.; Altšmíd, J.; Hamáček, A.; Nešpůrek, S.; Zmeškal, O. An Electrochemical NO2 Sensor Based on Ionic Liquid: Influence of the Morphology of the Polymer Electrolyte on Sensor Sensitivity. Sensors 2015, 15, 28421–28434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, A.M.; Silvester, D.S.; Aldous, L.; Hardacre, C.; Compton, R.G. Effect of water on the electrochemical window and potential limits of room-temperature ionic liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2008, 53, 2884–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Compton, R.G. Electrochemical High Concentration Oxygen Sensing Using a Phosphonium Cation Based Room Temperature Ionic Liquid: Analytical Studies. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 1550–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
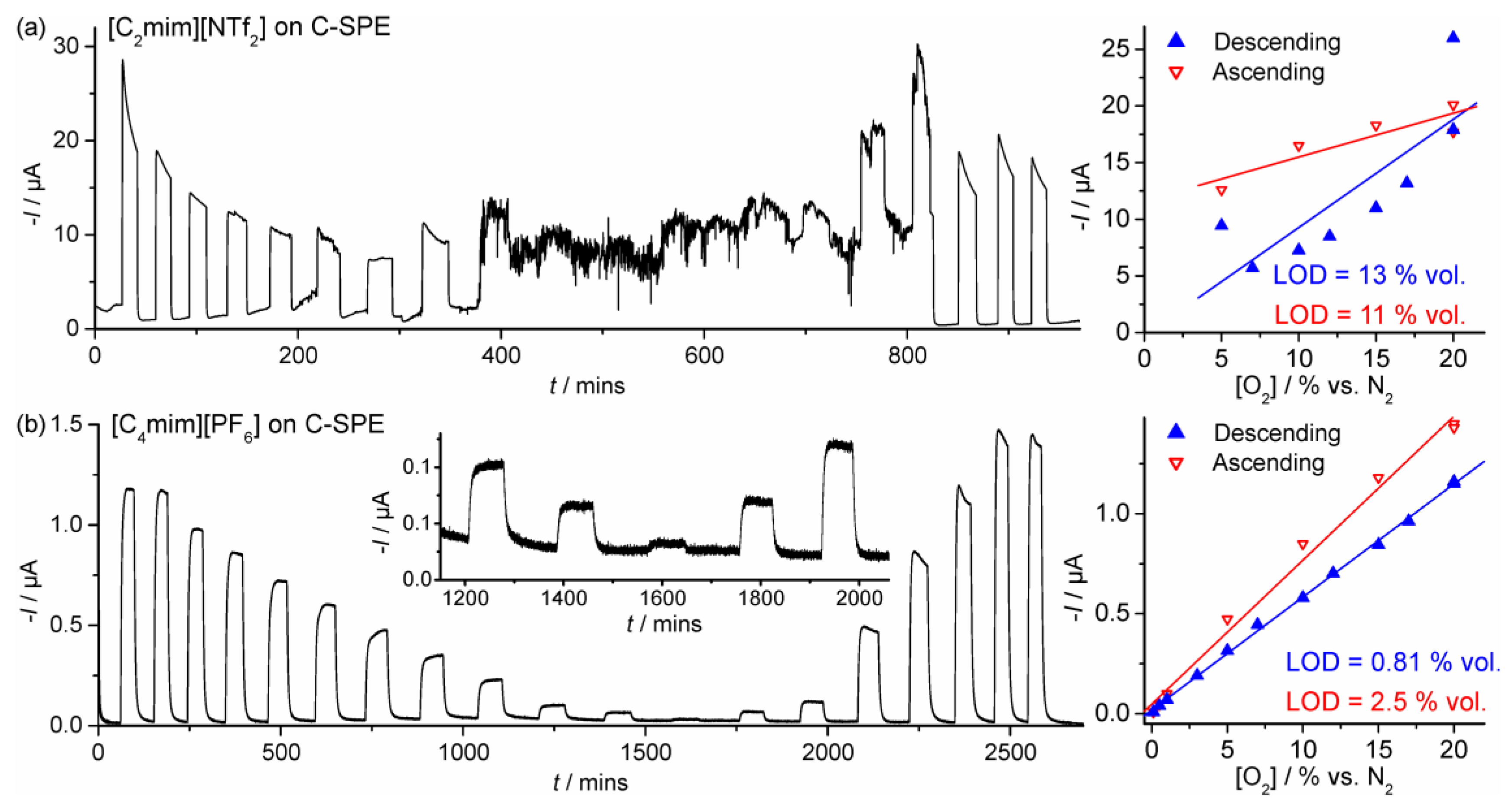
| Electrode | RTIL | [O2] Range | Order | Equation of Linear Best Fit | LOD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /% vol. | I/A, [O2]/% vol. | /% vol. | ||||
| SPGE | [C2mim][NTf2] | 0.1–20 | Descending | I = 2.07 × 10−7[O2] + 1.02 × 10−7 | 1.2 | 0.997 |
| C-SPE | Descending | I = 9.55 × 10−7[O2] − 2.72 × 10−7 | 13 | 0.663 | ||
| SPGE | [C4mim][PF6] | 0.1–20 | Descending | I = 4.33 × 10−8[O2] + 1.22 × 10−8 | 0.60 | 0.999 |
| C-SPE | Descending | I = 5.65 × 10−8[O2] + 1.85 × 10−8 | 0.81 | 0.999 |
| Electrode | RTIL | Comments on Short-Term Stability (After CV Experiments) | Comments on Long-Term Stability (after LTCA Experiments) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPGE | [C2mim][NTf2] | Stable, no deterioration observed | Working electrode broke off in a large chunk |
| C-SPE | [C2mim][NTf2] | Stable, no deterioration observed. Some darkening of RTIL | Significant darkening of RTIL, and working and reference electrodes tarnished. |
| SPGE | [C4mim][PF6] | Stable, no deterioration observed | Stable, no deterioration observed |
| C-SPE | [C4mim][PF6] | Stable, no deterioration observed | Darkening of RTIL observed |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Hussain, G.; Banks, C.E.; Silvester, D.S. Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Sensors 2017, 17, 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122734
Lee J, Hussain G, Banks CE, Silvester DS. Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Sensors. 2017; 17(12):2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122734
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Junqiao, Ghulam Hussain, Craig E. Banks, and Debbie S. Silvester. 2017. "Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids" Sensors 17, no. 12: 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122734
APA StyleLee, J., Hussain, G., Banks, C. E., & Silvester, D. S. (2017). Screen-Printed Graphite Electrodes as Low-Cost Devices for Oxygen Gas Detection in Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Sensors, 17(12), 2734. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122734






