Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Target Images Classification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multiple Features Extraction and Representation Learning Classifier
2.1. Multiple Features Extraction
2.1.1. PCA Features Extraction
2.1.2. Wavelet Transform Feature Extraction
2.1.3. 2DSZM Feature Extraction
2.2. Sparse Representation Classifier
2.3. Collaborative Representation Classifier
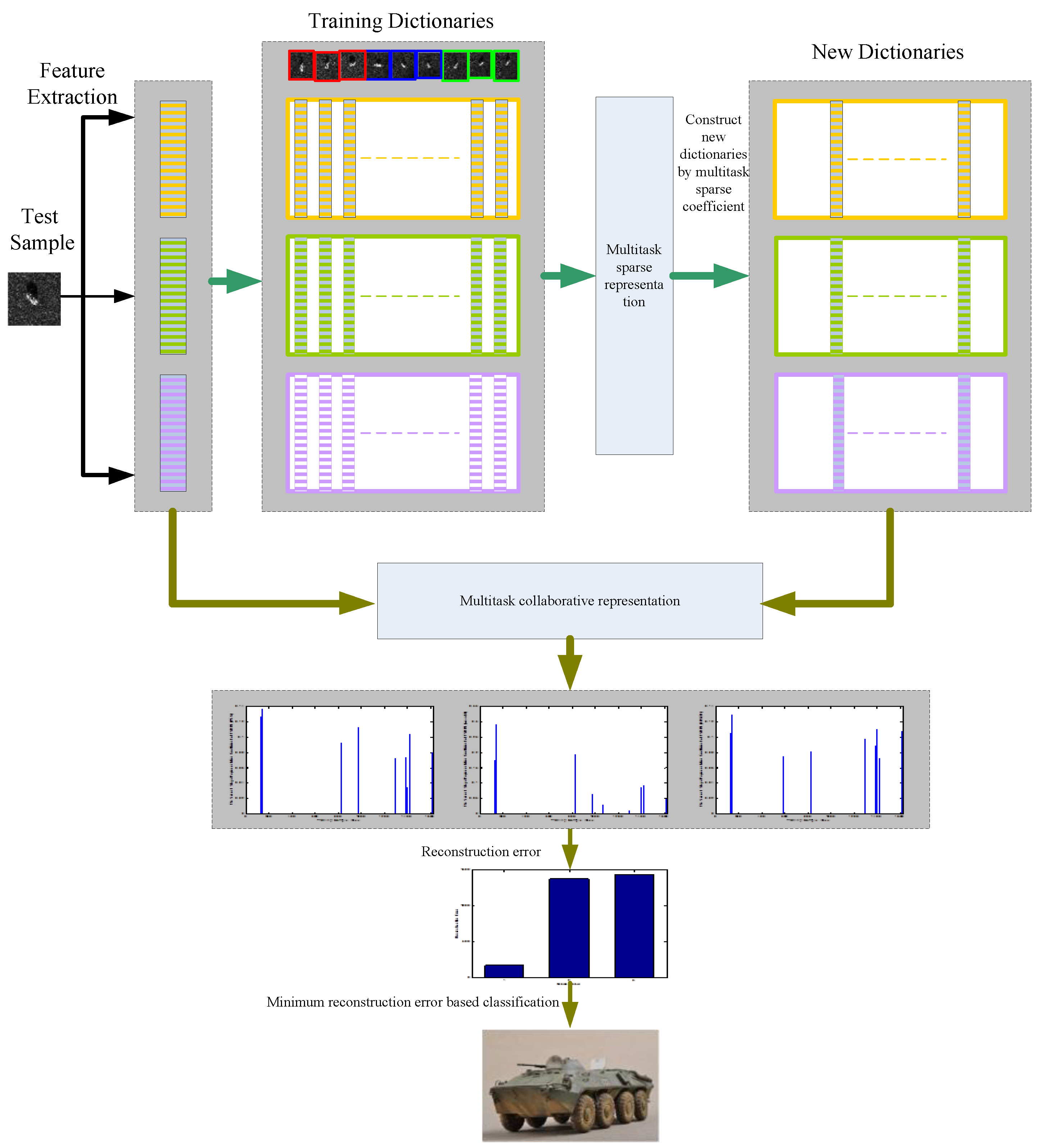
3. Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning
3.1. The First Stage: -Norm Regularized Multi-Task Sparse Representation Learning
3.2. The Second Stage: Multi-Task Collaborative Representation Learning
| Algorithm 1 Two-stage multi-task representation learning for SAR target images classification |
| Input: |
| All training samples |
| : All test samples |
| Output: the identity of Steps:
|
|
|
|
4. Experimental Results
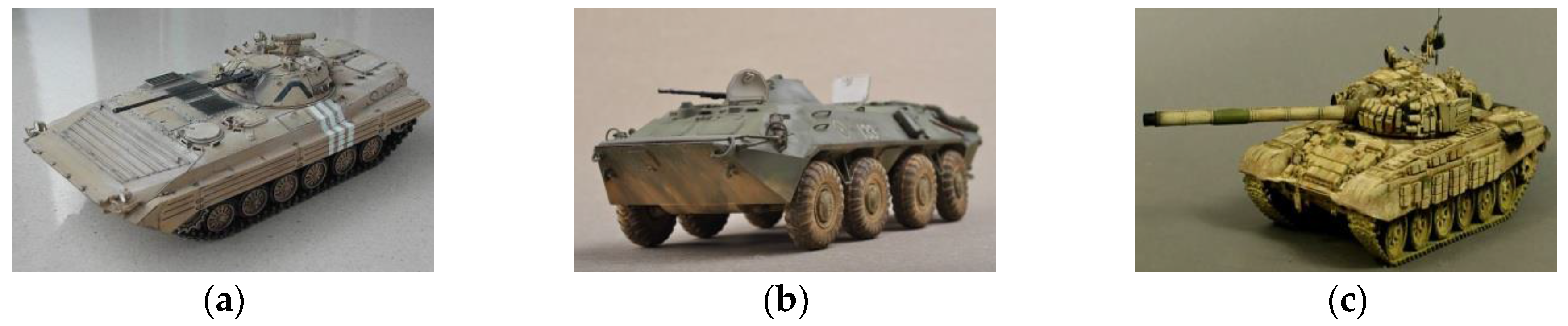
4.1. Experimental Data Set
4.2. Classification Results and Analysis
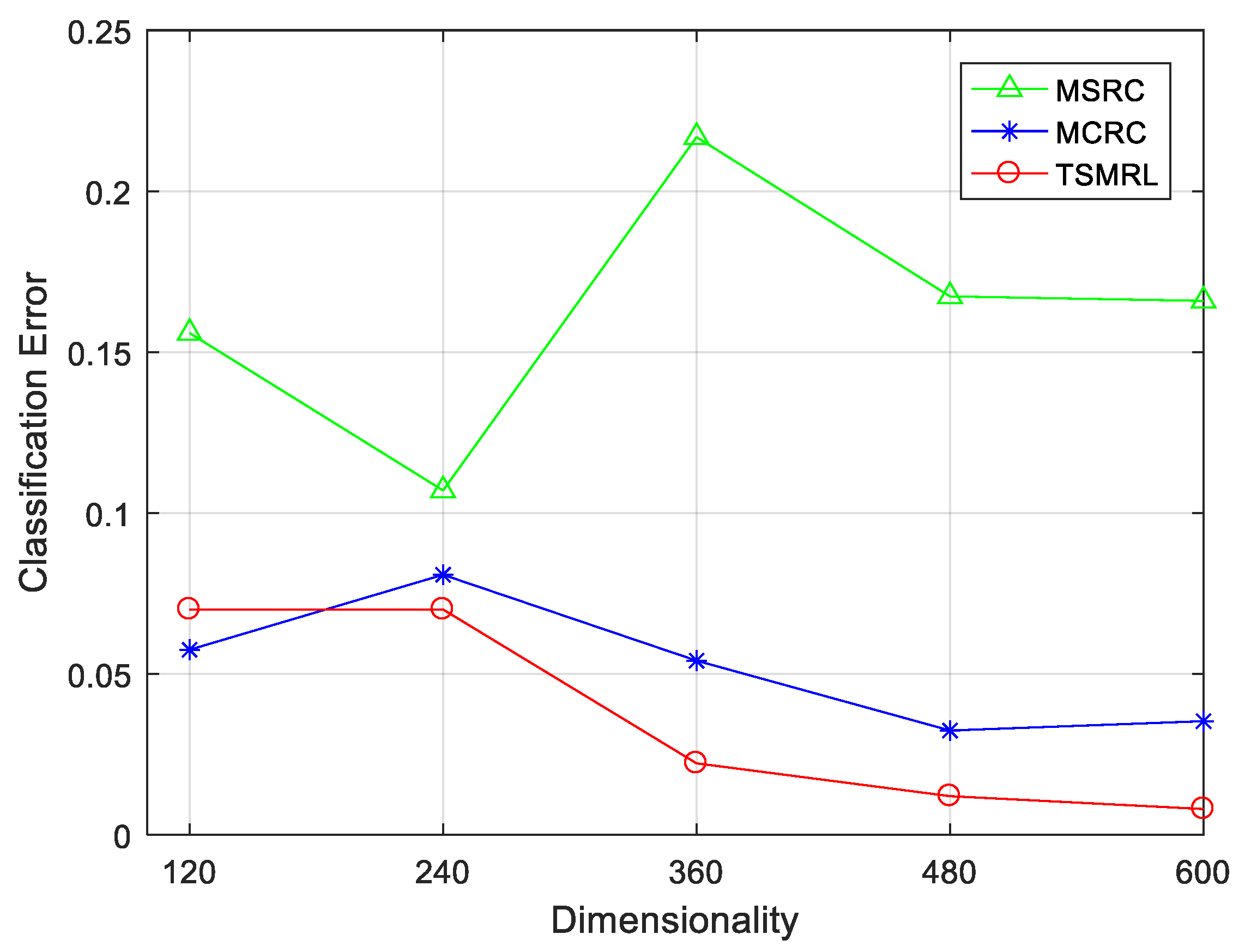
4.2.1. Classification Performance under Different Feature Dimensions
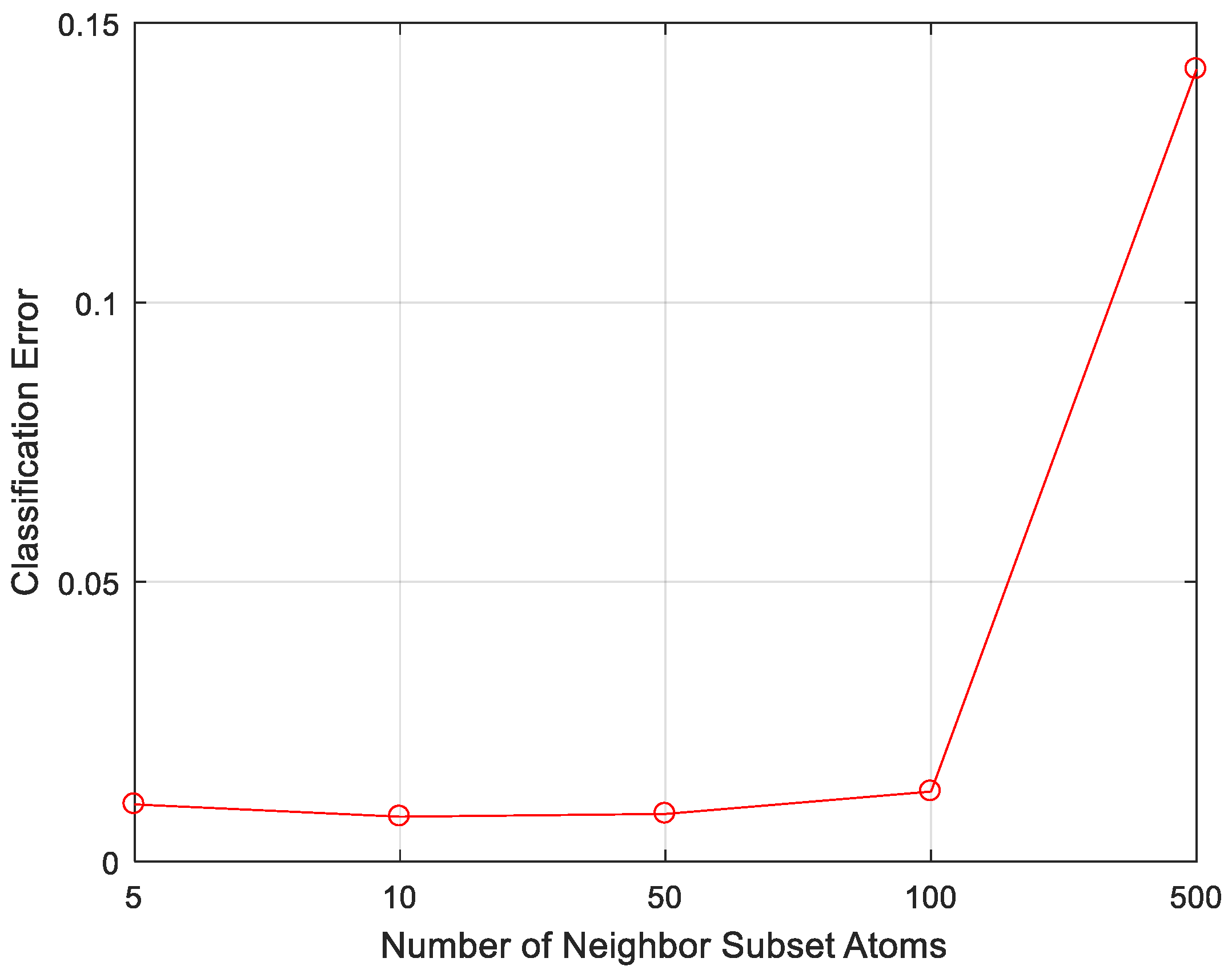
4.2.2. Classification Performance under Different Number of Neighbor Atoms
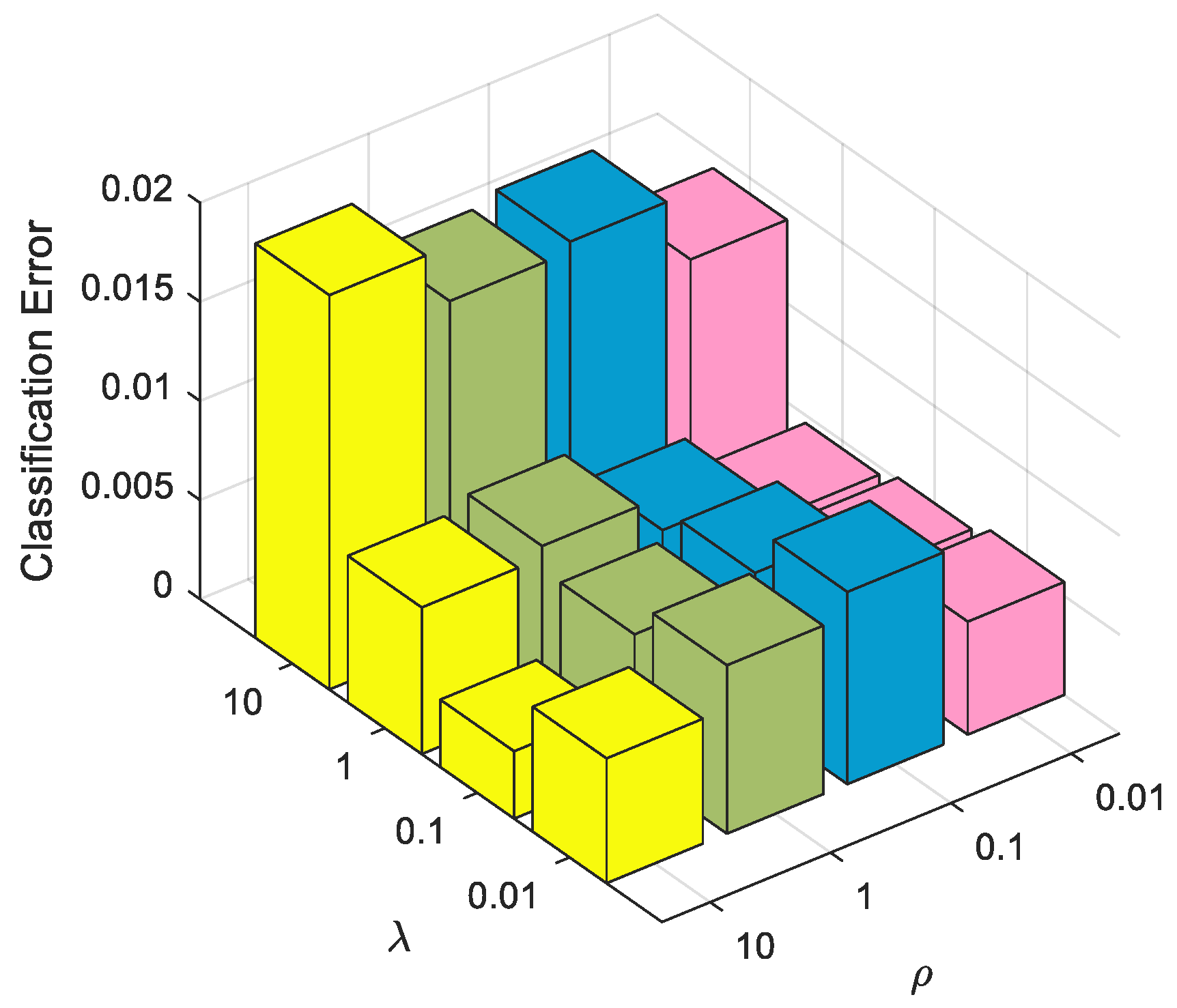
4.2.3. Classification Performance with Regularization Parameter Value Change
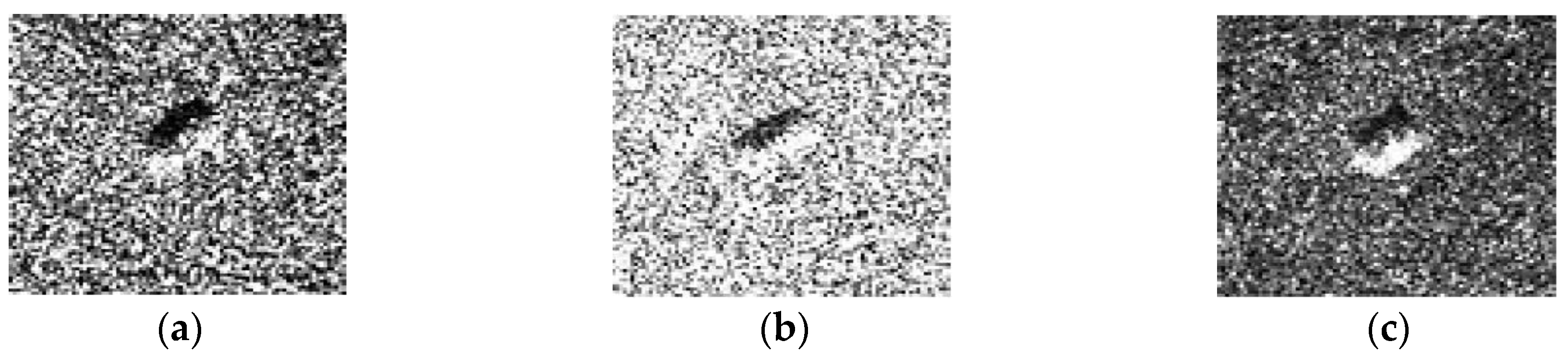
4.2.4. Robustess to Noise
4.2.5. Experiments Conducted with Depression Angle Variations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, S. Preliminary research of low-RCS moving target detection based on Ka-band video SAR. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Clausi, D.A. SAR sea-ice analysis based on iterative region growing using semantics. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 12, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velotto, D.; Bentes, C.; Tings, B.; Lehner, S. First comparison of Sentine-1 and TerraSAR-X data in the framework of maritime targets detection: South Italy Case. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 4, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Darymli, K.; Gill, E.W.; Mcguire, P.; Power, D.; Moloney, C. Automatic target recognition in synthetic aperture radar imagery: A state-of-the-art review. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 6014–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.M.; Owirka, G.J.; Netishen, C.M. Performance of a high-resolution polarimetric SAR automatic target recognition system. Lincoln Lab. J. 1993, 6, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Wen, G.J.; Ding, B.Y.; Zhong, J.R.; Yang, X. Three-dimensional electromagnetic model-based scattering center matching method for synthetic aperture radar automatic target recognition by combining spatial and attributed information. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.A. SAR ATR by a combination of convolutional neural network and support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2016, 52, 2861–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Kang, Z.; Cheng, Q. Integrating feature and graph learning with low-rank representation. Neurocomputing 2017, 249, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. A survey of sparse representation: Algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 2017, 3, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.K.; Zhu, G.; Shen, J.; Yan, S. Robust image analysis with sparse representation on quantized visual features. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Yang, A.Y.; Ganesh, A.; Sastry, S.S.; Ma, Y. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2009, 31, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawazuddin, S.; Sinha, R. Sparse coding over redundant dictionaries for fast adaptation of speech recognition system. Comput. Speech Lang. 2016, 43, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Benediktsson, J. Hyperspectral image classification via multiple-feature-based adaptive sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2017, 66, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.S. Multi-view automatic target recognition using joint sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2012, 48, 2481–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Wang, F. SAR target recognition based on improved joint sparse representation. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2014, 2014, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Kuang, G.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Lu, J. SAR target recognition via joint sparse representation of monogenic signal. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 3316–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Kuang, G. SAR target recognition via sparse representation of monogenic signal on grassmann manifolds. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Liao, G. Dempster-Shafer fusion of multiple sparse representation and statistical property for SAR target configuration recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J. SAR automatic target recognition based on dictionary learning and joint dynamic sparse representation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xu, B.; Yang, J. SAR target recognition via supervised discriminative dictionary learning and sparse representation of the SAR-HOG feature. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiu, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Y. Attributed scattering center extraction algorithm based on sparse representation with dictionary refinement. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2017, 65, 2604–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Porikli, F. Classification and boosting with multiple collaborative representations. IEEE Comput. Sci. 2014, 36, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Du, Q.; Zhang, F.; Hu, W. Collaborative-representation-based nearest neighbor classifier for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva-Murillo, J.M.; Gomez-Chova, L.; Camps-Valls, G. Multitask remote sensing data classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 51, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.T.; Yan, S. Visual classification with multitask joint sparse representation. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3493–3500. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Li, S. Face recognition by exploiting local Gabor features with multitask adaptive sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L. Joint collaborative representation with multitask learning for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 5923–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Tao, D.C.; Geng, B.; Xu, C.; Maybank, S.J. Manifold regularized multitask learning for semi-supervised multilabel image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 22, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Wen, Y.G.; Tao, D.C.; Gui, J.; Xu, C. Large margin multi-modal multi-task feature extraction for image classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, M. Convolutional neural network with data augmentation for SAR target recognition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, D.; Jia, Y.; Huang, P. Sparse coding of 2D-slice Zernike moments for SAR ATR. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, K.; Yao, L. Multi-feature kernel discriminant dictionary learning for face recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 66, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Elad, M. Optimal sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via ℓ1 minimization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2197–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candes, E.J.; Tao, T. Near-optimal signal recovery from random projections: Universal encoding strategies? IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 5406–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Yu, B. On model selection consistency of Lasso. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 2541–2563. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Feng, X. Sparse representation or collaborative representation: Which helps face recognition? In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Chiu, K.C.; Xu, L. Improved system for object detection and star/galaxy classification via local subspace analysis. Neural Netw. 2003, 16, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, V.; Fung, G.; Krishnapuram, B.; Dy, J.G.; Rao, B. Using local dependencies within batches to improve large margin classifiers. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 183–206. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.Y. A two-phase test sample sparse representation method for use with face recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2011, 21, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A.; Evgeniou, T.; Pontil, M. Multitask Feature Learning. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’06), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]

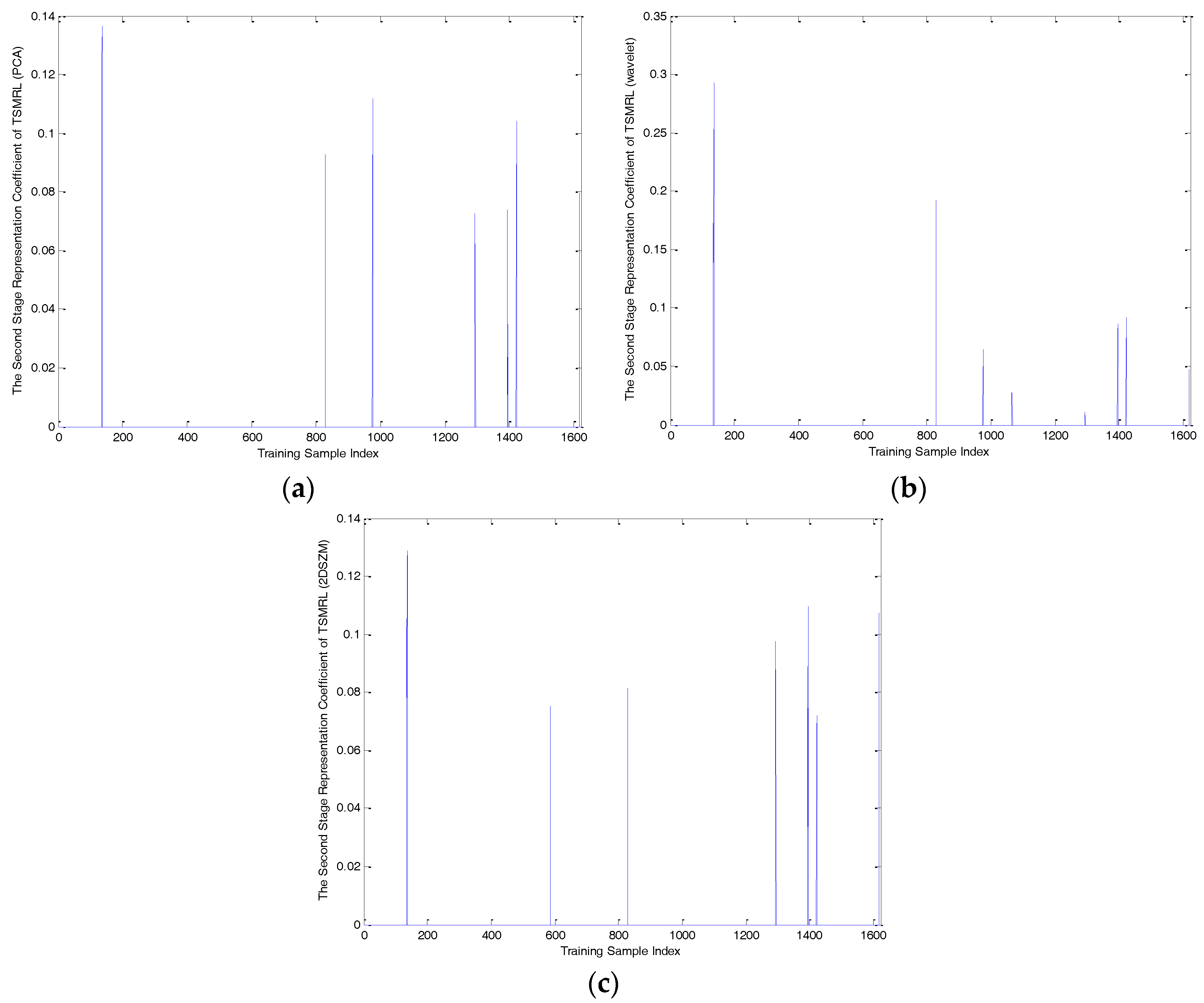
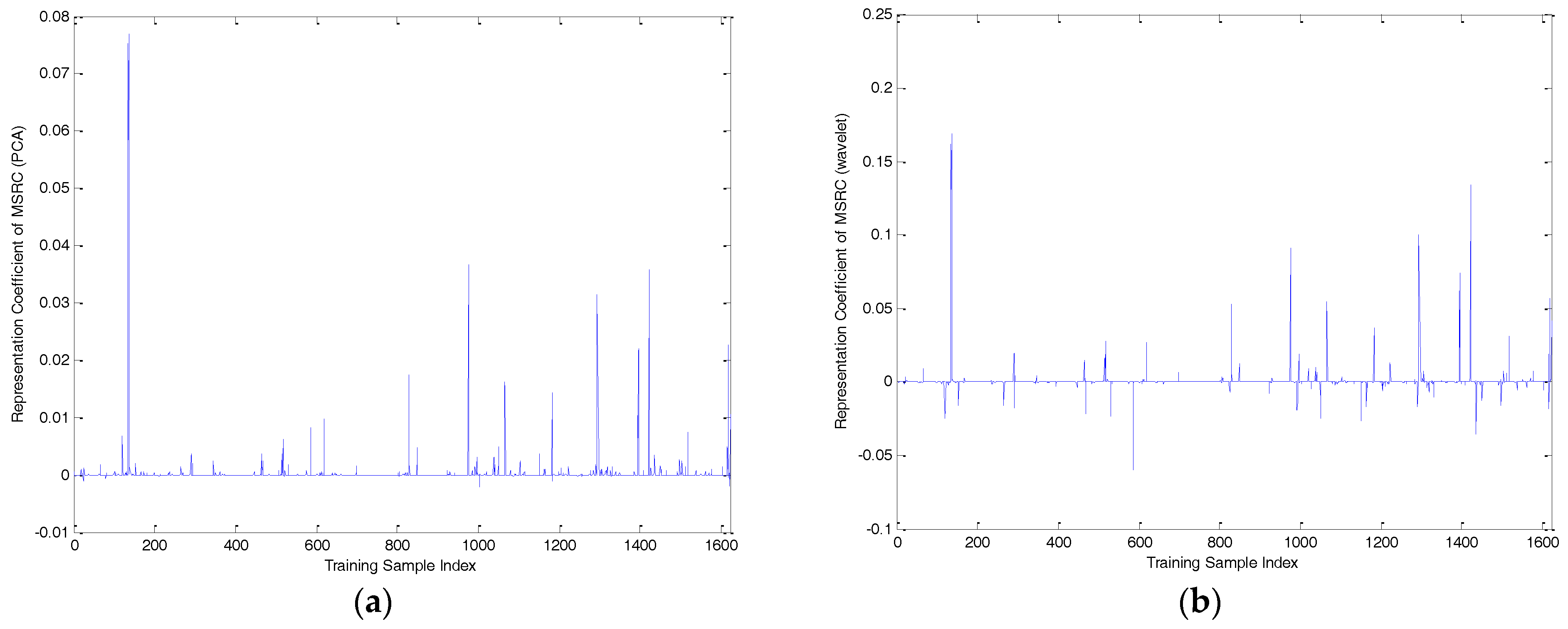
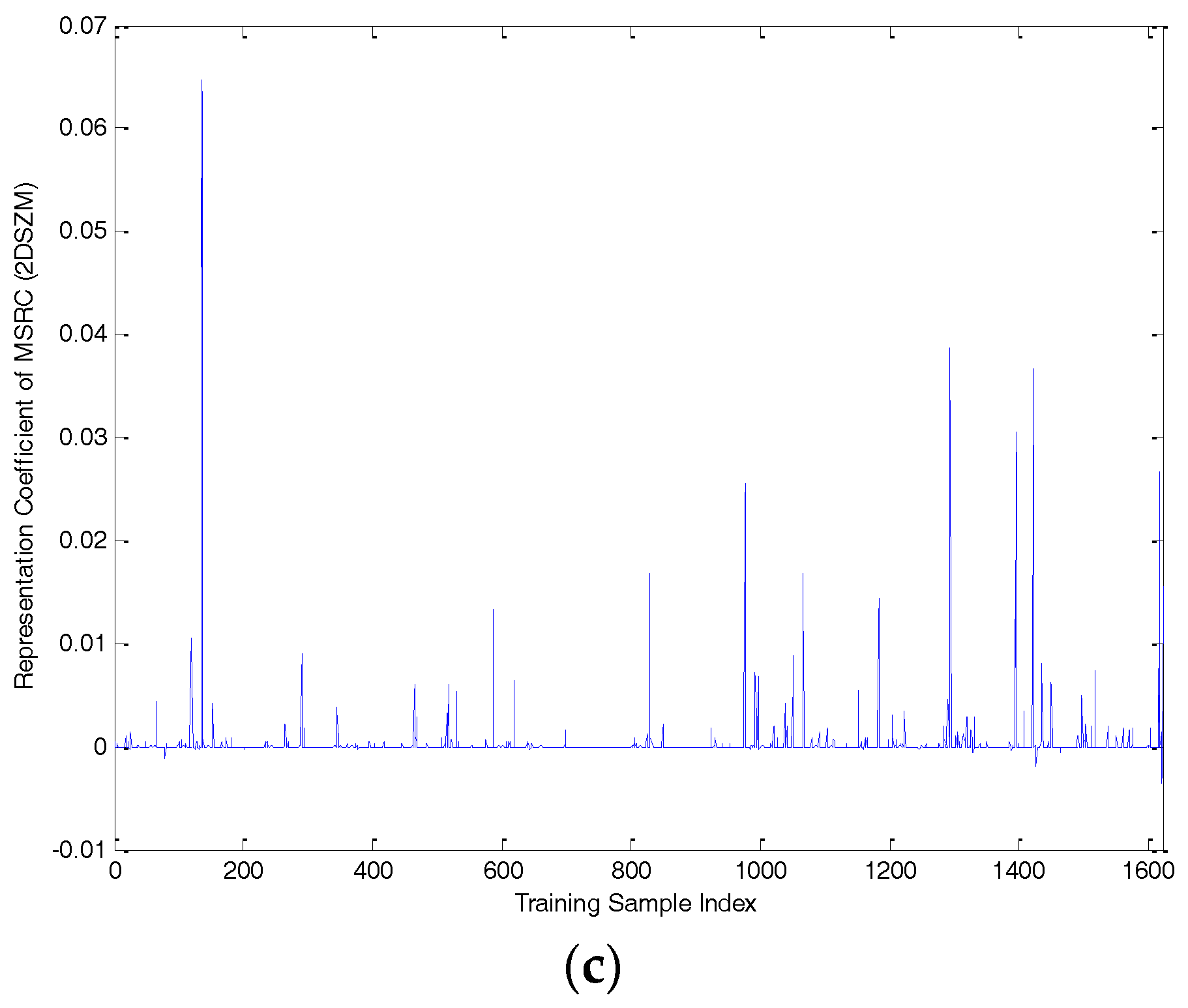
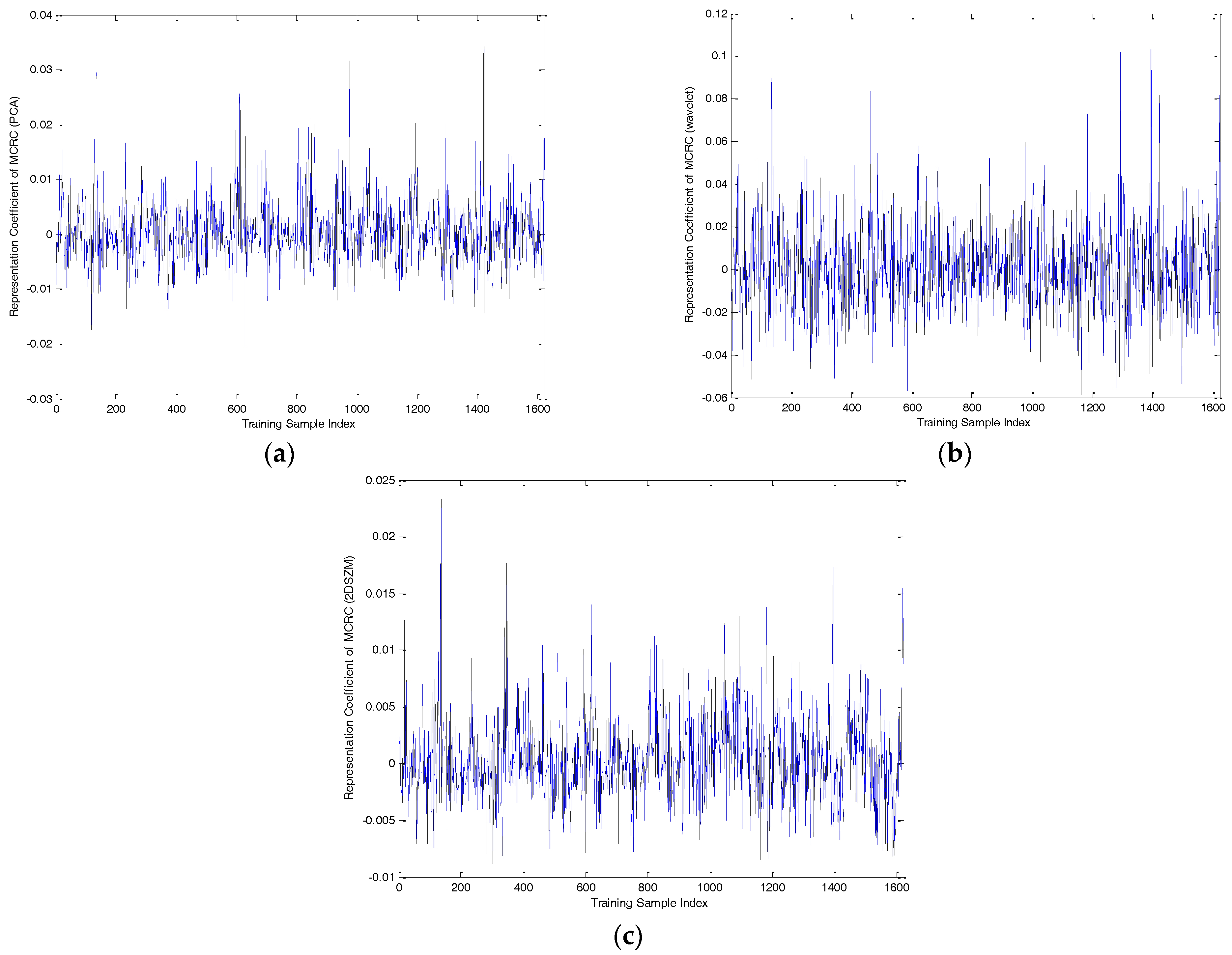
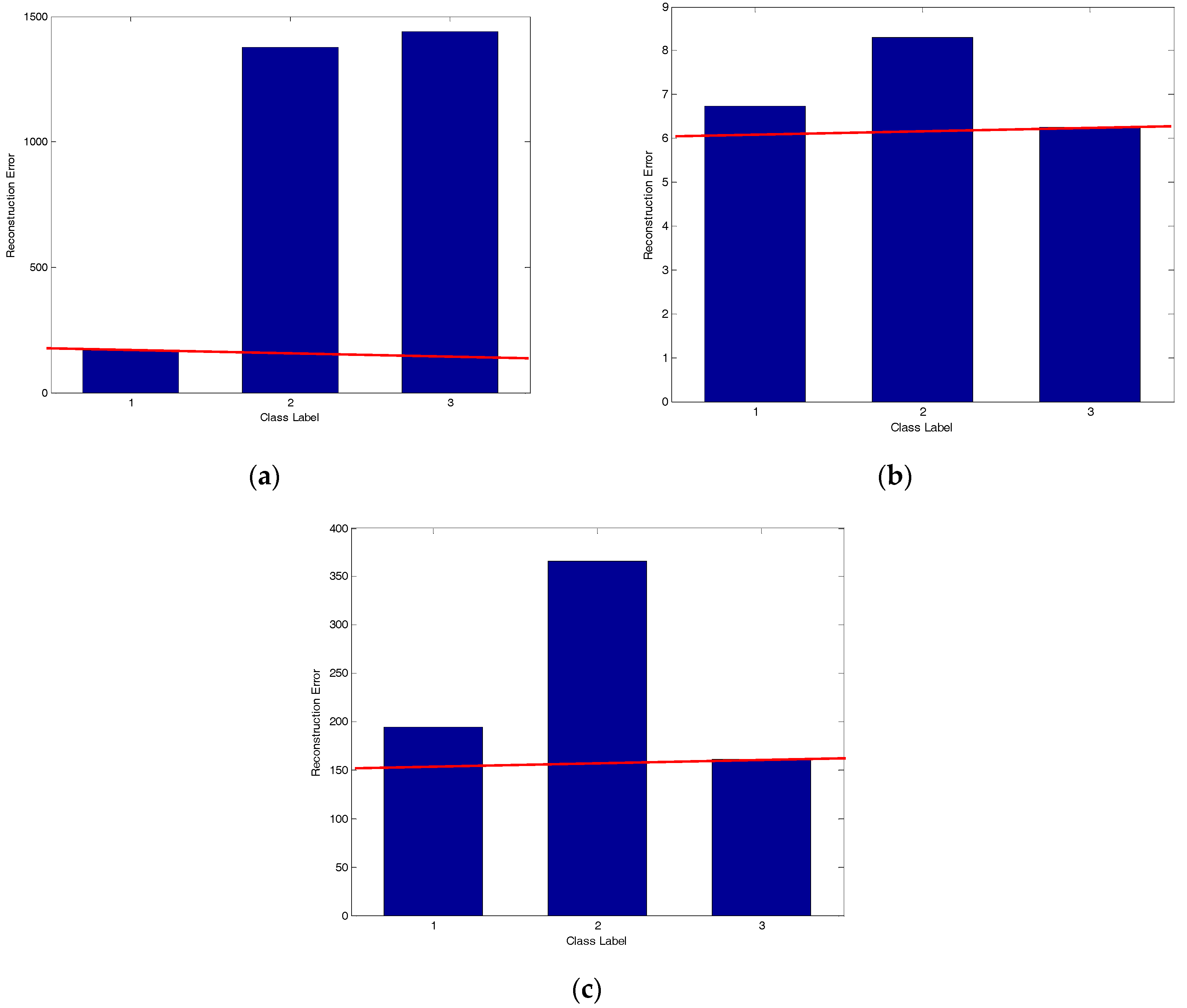



| Number of Objects | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training sample type (17°) | BMP2 sn-9563 | BMP2 sn-9566 | BMP2 sn-c21 | BTR70 sn-c71 | T72 sn-132 | T72 sn-812 | T72 sn-s7 |
| Number | 233 | 232 | 233 | 233 | 232 | 231 | 228 |
| Testing sample type (15°) | BMP2 sn-9563 | BMP2 sn-9566 | BMP2 sn-c21 | BTR70 sn-c71 | T72 sn-132 | T72 sn-812 | T72 sn-s7 |
| Number | 195 | 196 | 196 | 196 | 196 | 195 | 191 |
| Dimensionality | Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TSMRL | MSRC | MCRC | |
| 120 | 7.00% | 15.59% | 5.75% |
| 240 | 7.00% | 10.70% | 8.08% |
| 360 | 2.22% | 21.68% | 5.41% |
| 480 | 1.20% | 16.73% | 3.24% |
| 600 | 0.80% | 16.56% | 3.53% |
| Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| TSMRL | MSRC | MCRC | |
| 10−3 | 0.68% | 22.03% | 20.43% |
| 10−2 | 0.57% | 21.51% | 17.70% |
| 0.1 | 0.74% | 20.26% | 11.27% |
| 1 | 0.80% | 16.56% | 3.53% |
| 5 | 1.25% | 11.61% | 2.45% |
| 10 | 1.99% | 16.56% | 2.96% |
| Method | Ground Truth | = 10−3 | = 10−2 | ||||
| BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | ||
| TSMRL | BMP2 | 585 | 0 | 2 | 586 | 0 | 1 |
| BTR70 | 5 | 579 | 4 | 4 | 581 | 3 | |
| T72 | 1 | 1 | 580 | 1 | 1 | 580 | |
| MSRC | BMP2 | 433 | 91 | 63 | 439 | 86 | 62 |
| BTR70 | 66 | 487 | 35 | 64 | 495 | 29 | |
| T72 | 56 | 76 | 450 | 57 | 80 | 445 | |
| MCRC | BMP2 | 548 | 0 | 39 | 552 | 0 | 35 |
| BTR70 | 168 | 274 | 146 | 145 | 317 | 126 | |
| T72 | 6 | 0 | 576 | 5 | 0 | 577 | |
| Method | Ground Truth | = 0.1 | = 1 | ||||
| BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | ||
| TSMRL | BMP2 | 583 | 0 | 4 | 583 | 1 | 3 |
| BTR70 | 6 | 580 | 2 | 8 | 578 | 2 | |
| T72 | 1 | 0 | 581 | 0 | 0 | 582 | |
| MSRC | BMP2 | 453 | 73 | 61 | 484 | 64 | 39 |
| BTR70 | 53 | 510 | 25 | 54 | 510 | 24 | |
| T72 | 65 | 79 | 438 | 55 | 55 | 472 | |
| MCRC | BMP2 | 560 | 0 | 27 | 562 | 2 | 23 |
| BTR70 | 96 | 421 | 71 | 15 | 552 | 21 | |
| T72 | 4 | 0 | 578 | 1 | 0 | 581 | |
| Method | Ground Truth | = 5 | = 10 | ||||
| BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | BMP2 | BTR70 | T72 | ||
| TSMRL | BMP2 | 581 | 1 | 5 | 579 | 1 | 7 |
| BTR70 | 6 | 574 | 8 | 17 | 563 | 16 | |
| T72 | 1 | 1 | 580 | 2 | 0 | 580 | |
| MSRC | BMP2 | 536 | 32 | 19 | 539 | 9 | 39 |
| BTR70 | 53 | 505 | 30 | 122 | 381 | 85 | |
| T72 | 28 | 42 | 512 | 14 | 22 | 546 | |
| MCRC | BMP2 | 554 | 7 | 26 | 542 | 11 | 34 |
| BTR70 | 0 | 580 | 8 | 0 | 585 | 3 | |
| T72 | 0 | 2 | 580 | 1 | 3 | 578 | |
| BRDM2 | 2S1 | ZSU23/4 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Training Set (17°) | 298 | 299 | 299 |
| Testing Set (30°) | 287 | 288 | 288 |
| Testing Set (45°) | 303 | 303 | 303 |
| Depression | Method | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TSMRL | MSRC | MCRC | |
| 30° | 5.33% | 28.85% | 8.11% |
| 45° | 44.11% | 63.81% | 59.52% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Target Images Classification. Sensors 2017, 17, 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112506
Zhang X, Wang Y, Tan Z, Li D, Liu S, Wang T, Li Y. Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Target Images Classification. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112506
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinzheng, Yijian Wang, Zhiying Tan, Dong Li, Shujun Liu, Tao Wang, and Yongming Li. 2017. "Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Target Images Classification" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112506
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, Y., Tan, Z., Li, D., Liu, S., Wang, T., & Li, Y. (2017). Two-Stage Multi-Task Representation Learning for Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Target Images Classification. Sensors, 17(11), 2506. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112506





