The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Electronic Components
2.3. Equipment
2.4. Enzymatic Assay for Glucose Detection
2.5. RGB Colorimeter Design
2.6. Test with Saliva Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of Colorimeter and Analytical Performance
3.2. Test with Saliva Specimen
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rohit; Kanwar, L.; Rao, K.K. Development of a low-cost portable colorimeter for the estimation of fluoride in drinking water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 149, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, Y.; Rao, G. Low-cost optical instrumentation for biomedical measurements. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.-K.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, G.-D.; Rhee, H.-I. Rapid determination of capsaicinoids by colorimetric method. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, H.D.; Mishra, R.K.; Muñoz, R.; Marty, J.L. Low cost optical device for detection of fluorescence from Ochratoxin A using a CMOS sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Rodríguez Nũ Ez, J.; Maxwell, E.J.; Algar, W.R. Build Your Own Photometer: A Guided-Inquiry Experiment to Introduce Analytical Instrumentation. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, G.; Glover, A.; Pearce, J. Open-Source Colorimeter. Sensors 2013, 13, 5338–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.D.; Hostetler, D.M.; Nettey, H.; Swamidoss, I.; Ranieri, N.; Newton, P.N. Integration of novel low-cost colorimetric, laser photometric, and visual fluorescent techniques for rapid identification of falsified medicines in resource-poor areas: Application to artemether-lumefantrine. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asheim, J.; Kvittingen, E.V.; Kvittingen, L.; Verley, R. A Simple, Small-Scale Lego Colorimeter with a Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Used as Detector. J. Chem. Educ. 2014, 91, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntzleman, T.S.; Jacobson, E.C. Teaching Beer’s Law and Absorption Spectrophotometry with a Smart Phone: A Substantially Simplified Protocol. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasse, E.K.; Torcasio, M.H.; Smith, A.W. Teaching UV-Vis Spectroscopy with a 3D-Printable Smartphone Spectrophotometer. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvittingen, E.V.; Kvittingen, L.; Sjursnes, B.J.; Verley, R. Simple and Inexpensive UV-Photometer Using LEDs as Both Light Source and Detector. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1814–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, L.A.; Washer, B.M.; Hakim, M.H.; Dallinger, R.F. User-Friendly 3D Printed Colorimeter Models for Student Exploration of Instrument Design and Performance. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macka, M.; Piasecki, T.; Dasgupta, P.K. Light-Emitting Diodes for Analytical Chemistry. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 7, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, D.A.; Hauser, P.C. Analytical devices based on light-emitting diodes—A review of the state-of-the-art. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anh Bui, D.; Hauser, P.C. Absorbance measurements with light-emitting diodes as sources: Silicon photodiodes or light-emitting diodes as detectors? Talanta 2013, 116, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, A.; Jha, S.K. A paper strip based non-invasive glucose biosensor for salivary analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oncescu, V.; O’Dell, D.; Erickson, D. Smartphone based health accessory for colorimetric detection of biomarkers in sweat and saliva. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler-Llorens, J.L.; Galiana-Merino, J.J.; Giner-Caturla, J.; Jauregui-Eslava, P.; Rosa-Cintas, S.; Rosa-Herranz, J. Development and programming of Geophonino: A low cost Arduino-based seismic recorder for vertical geophones. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, J.M.; Anzalone, N.C.; Heldt, C.L. Open-Source Wax RepRap 3-D Printer for Rapid Prototyping Paper-Based Microfluidics. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wijnen, B.; Pearce, J.M. Open-Source 3-D Platform for Low-Cost Scientific Instrument Ecosystem. J. Lab. Autom. 2016, 21, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinder, P. Determination of Glucose in Blood Using Glucose Oxidase with an Alternative Oxygen Acceptor. Ann. Clin. Biochem. Ann. Int. J. Biochem. Lab. Med. 1969, 6, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Report on Diabetes; WHO Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Solal, A.; Beauvais, F.; Logeart, D. Heart Failure and Diabetes Mellitus: Epidemiology and Management of an Alarming Association. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasznicki, J.; Drzewoski, J. Heart failure in the diabetic population—Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management. Arch. Med. Sci. 2014, 10, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K. Non-invasive glucose monitoring technology in diabetes management: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 750, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vashist, S.K.; Luong, J.H. Point-of-Care Glucose Detection for Diabetic Monitoring and Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781498788755. [Google Scholar]
- Makaram, P.; Owens, D.; Aceros, J. Trends in Nanomaterial-Based Non-Invasive Diabetes Sensing Technologies. Diagnostics 2014, 4, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malon, R.S.P.; Sadir, S.; Balakrishnan, M.; Córcoles, E.P. Saliva-Based Biosensors: Noninvasive Monitoring Tool for Clinical Diagnostics. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowska Nery, E.; Kundys, M.; Jeleń, P.S.; Jönsson-Niedziółka, M. Electrochemical Glucose Sensing: Is There Still Room for Improvement? Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11271–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.; Rani, A.; Singh, V.; Murari, B.M. Prospects and limitations of non-invasive blood glucose monitoring using near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2015, 18, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.; Yousuf, M.; Siddiqui, P.Q.R.; Alam, J. Salivary Glucose Concentration in Patients with Diabetes mellitus—A minimally invasive technique for monitoring blood glucose levels. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balan, P.; Babu, S.G.; Sucheta, K.N.; Shetty, S.R.; Rangare, A.L.; Castelino, R.L.; Fazil, A.K. Can saliva offer an advantage in monitoring of diabetes mellitus?—A case control study. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2014, 6, e335–e338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurysta, C.; Bulur, N.; Oguzhan, B.; Satman, I.; Yilmaz, T.M.; Malaisse, W.J.; Sener, A. Salivary glucose concentration and excretion in normal and diabetic subjects. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 430426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, M.L.; Leggio, A.; Le Pera, A.; Liguori, A.; Napoli, A.; Siciliano, C.; Sindona, G. Quantitative analysis of human salivary glucose by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 801, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, P.; Fatela, B.; Barahona, I. Effect of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 on Salivary Glucose—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchbhai, A.S. Correlation of salivary glucose level with blood glucose level in diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2012, 3, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, A.; De Icaza, E. Costos de la Diabetes en Ameŕica Latina: Evidencias del Caso Mexicano. Value Health 2011, 14, S85–S88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Brown, J.; Vistisen, D.; Sicree, R.; Shaw, J.; Nichols, G. Global healthcare expenditure on diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abikshyeet, P.; Ramesh, V.; Oza, N. Glucose estimation in the salivary secretion of diabetes mellitus patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2012, 5, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrici, A.; Foca, G.; Seeber, R. Algorithms and Strategies for Extracting Optimal Information from Chemical Sensing Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Foca, G.; Masino, F.; Antonelli, A.; Ulrici, A. Prediction of compositional and sensory characteristics using RGB digital images and multivariate calibration techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 706, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, S.B.; Chidambar, S.; Brinda, B.R.; Kumar, M.A.; Sarada, R.; Ravishankar, G.A. Digital image processing—an alternate tool for monitoring of pigment levels in cultured cells with special reference to green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 21, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida, P.D.V.; Grégio, A.M.T.; Machado, M.Â.N.; De Lima, A.A.S.; Azevedo, L.R. Saliva composition and functions: A comprehensive review. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2008, 9, 72–80. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, A.B.; Birkhed, D.; Berntorp, K.; Lindgarde, F.; Matsson, L. Glucose concentration in parotid saliva after glucose/food intake in individuals with glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

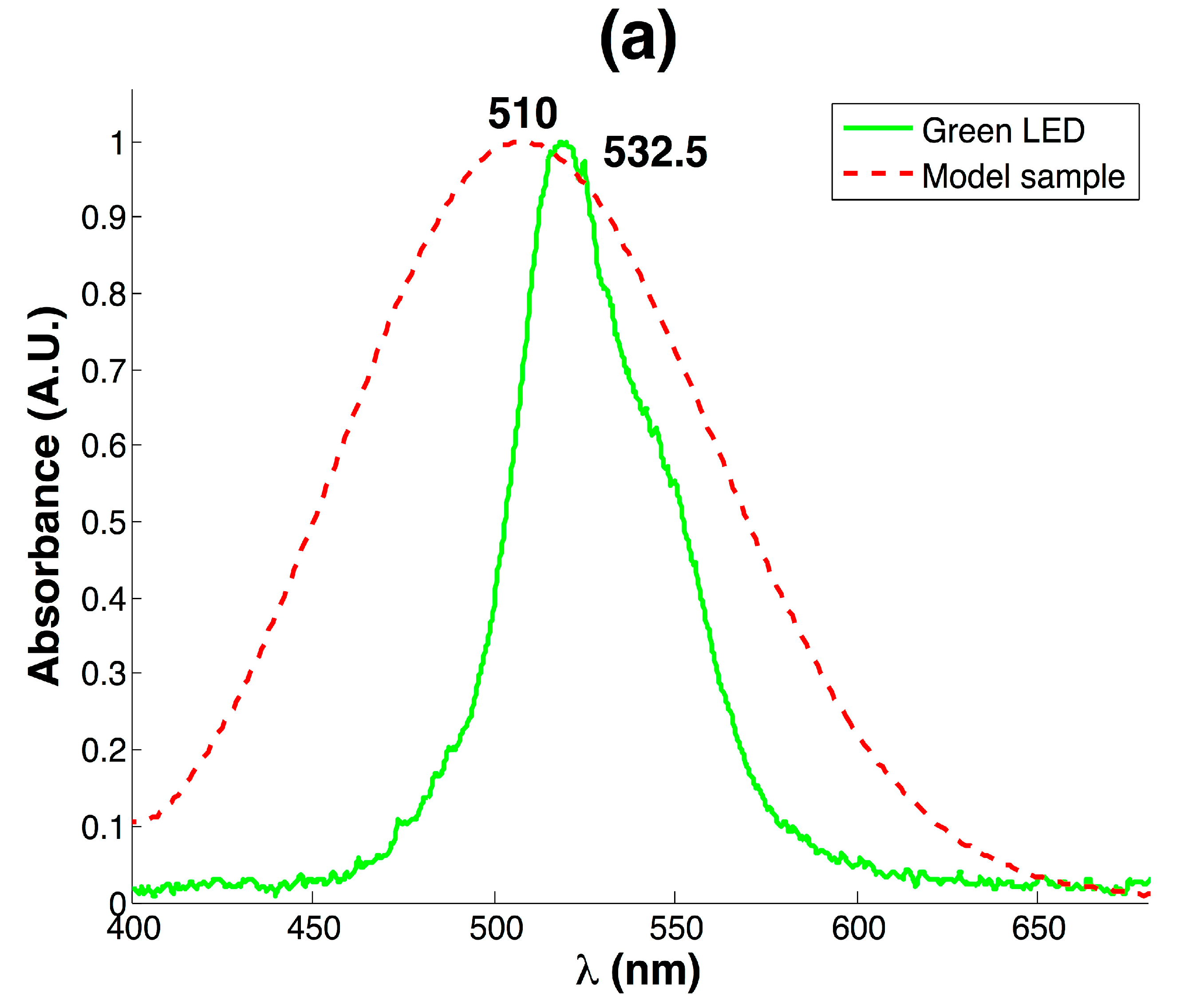
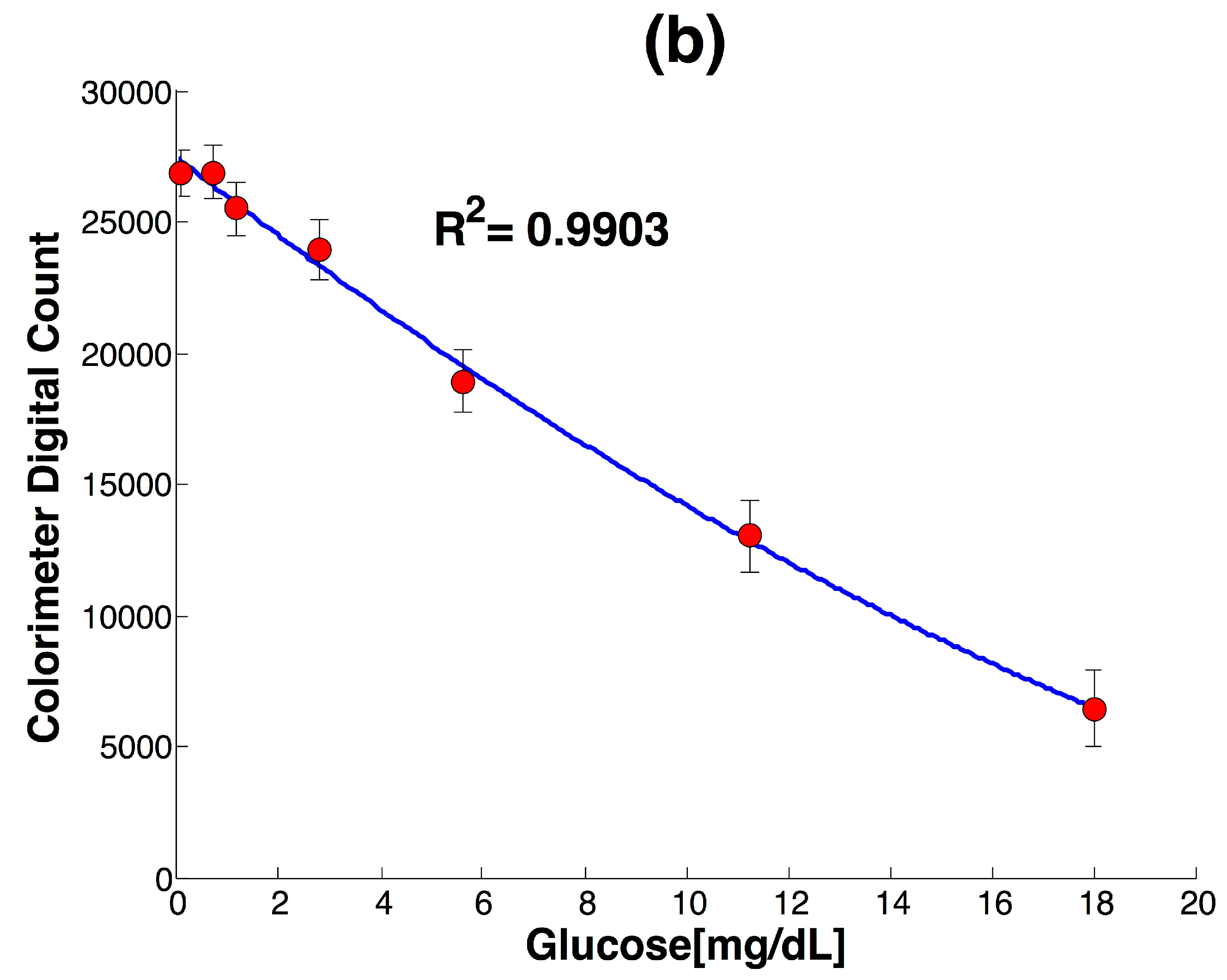
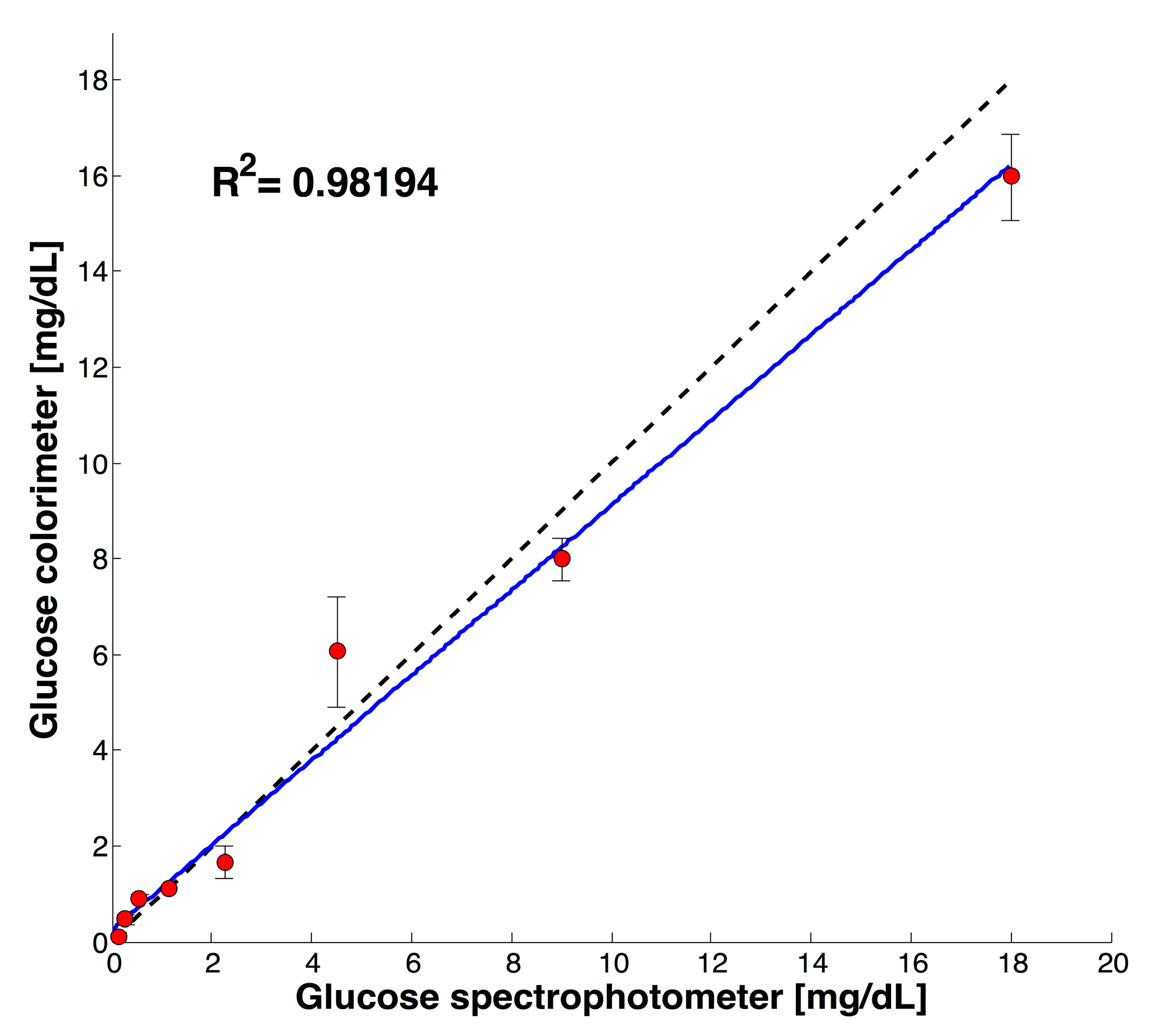
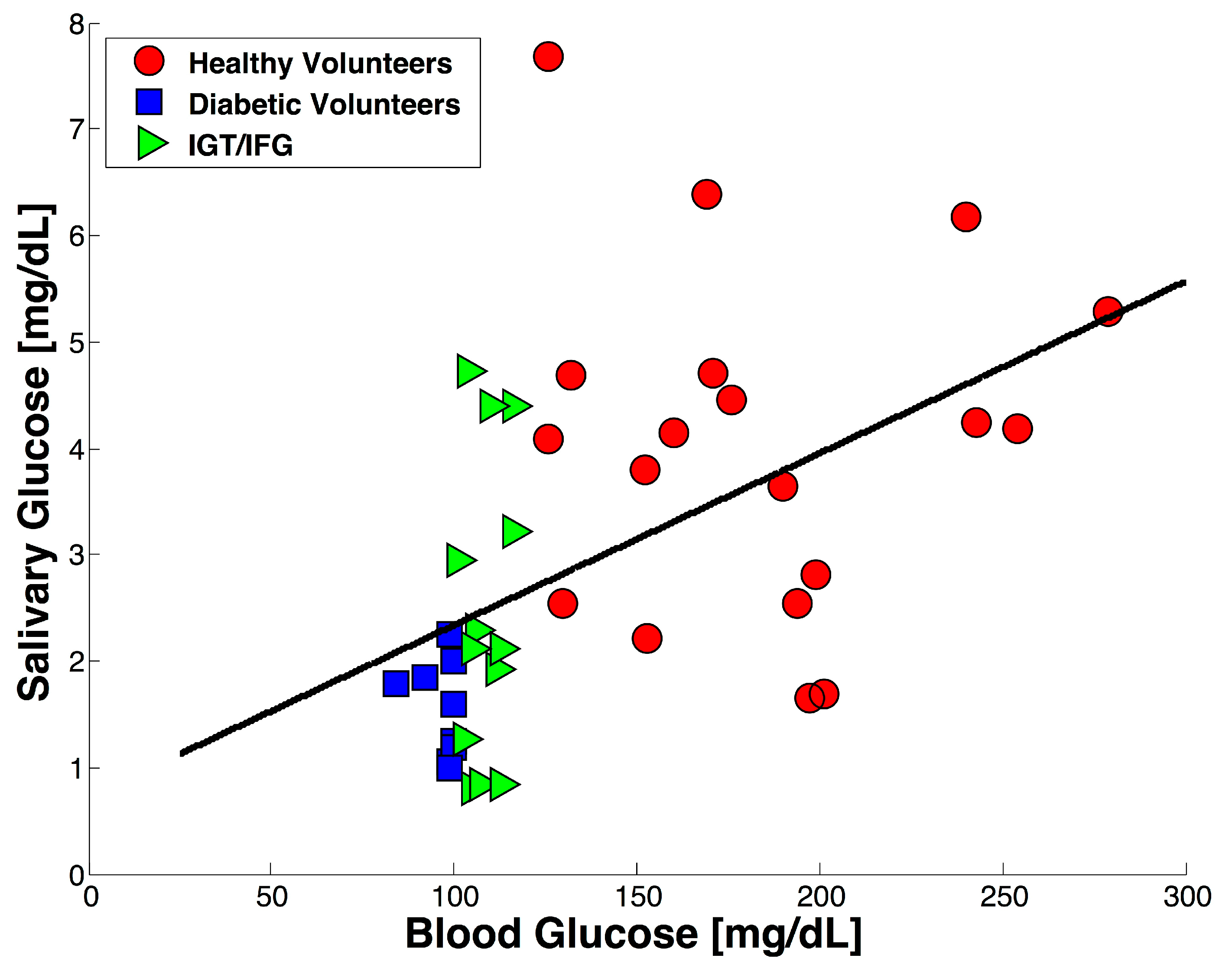
| LOD | R2 | STD (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.17 mg/dL | 0.9903 | 5% |
| UV-Vis-NIR [mg/dL] | Colorimeter [mg/dL] | CV (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.56 | 0.66 | 4.7% |
| 2.25 | 2.26 | 3.8% |
| 9 | 8.67 | 4.06% |
| 1.91 | 1.65 | 4% |
| Element | Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| ISL29125 RGB module | 7.95 |
| Green LED | 0.30 |
| Arduino UNO | 10.00 |
| RTC module | 8.95 |
| Touch screen | 30 |
| Micro SD | 7.50 |
| ABS filament | 0.4 |
| Total | 65.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dominguez, R.B.; Orozco, M.A.; Chávez, G.; Márquez-Lucero, A. The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples. Sensors 2017, 17, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112495
Dominguez RB, Orozco MA, Chávez G, Márquez-Lucero A. The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples. Sensors. 2017; 17(11):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112495
Chicago/Turabian StyleDominguez, Rocio B., Miguel A. Orozco, Giovanny Chávez, and Alfredo Márquez-Lucero. 2017. "The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples" Sensors 17, no. 11: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112495
APA StyleDominguez, R. B., Orozco, M. A., Chávez, G., & Márquez-Lucero, A. (2017). The Evaluation of a Low-Cost Colorimeter for Glucose Detection in Salivary Samples. Sensors, 17(11), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112495




