Robust Dehaze Algorithm for Degraded Image of CMOS Image Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Degradation Model
3. Local Consistent Markov Random Fields
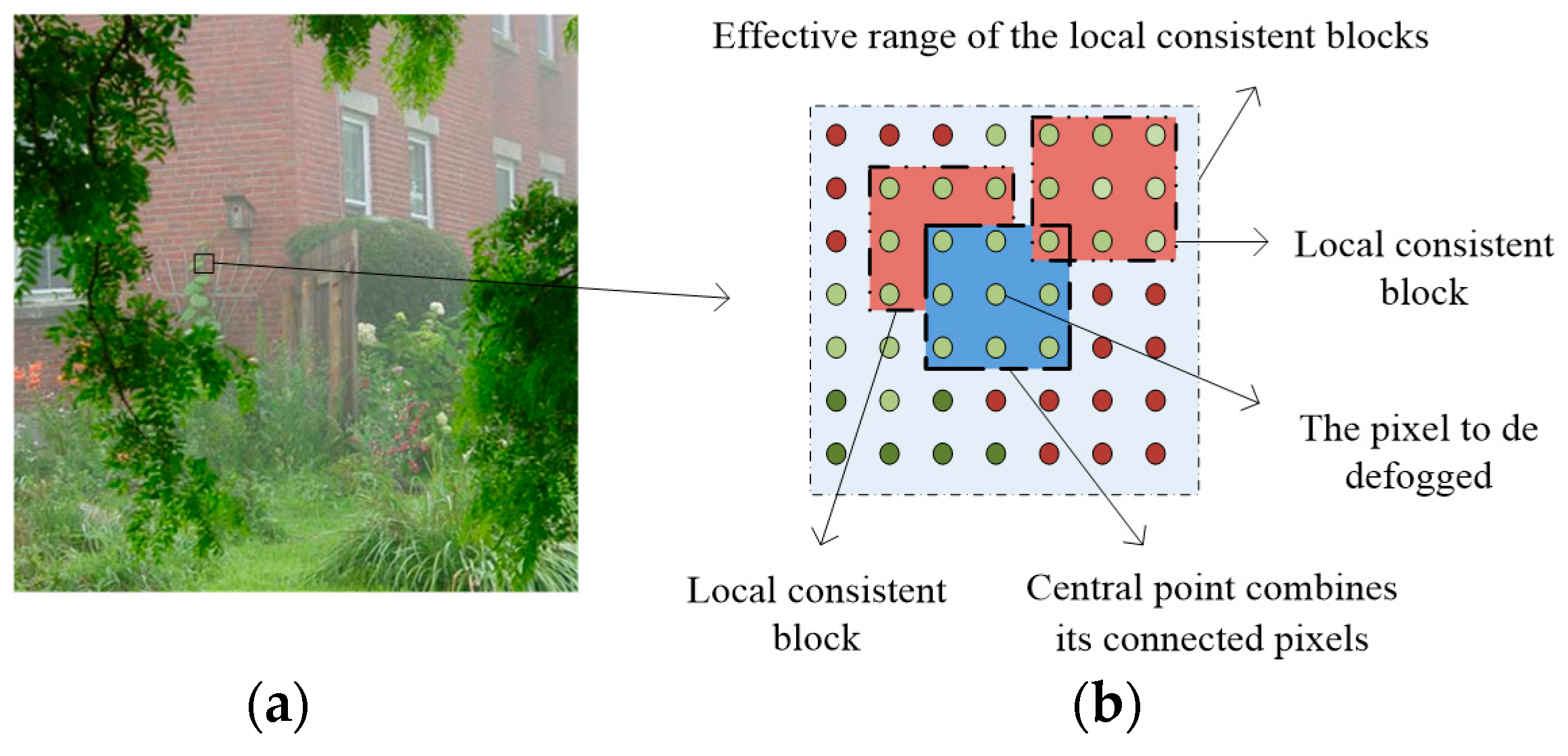
3.1. Basic Definition
3.2. Formulation of Local Consistent MRF Model
4. The Solution of Local Consistent MRF
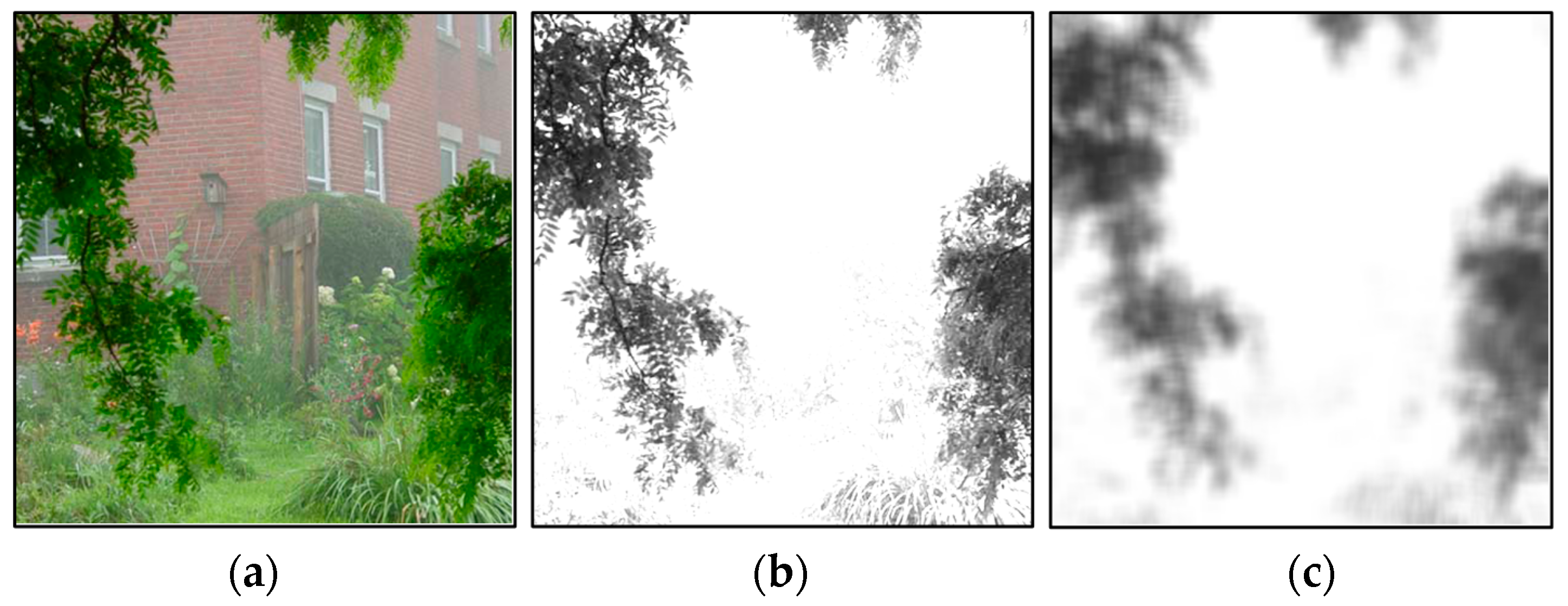
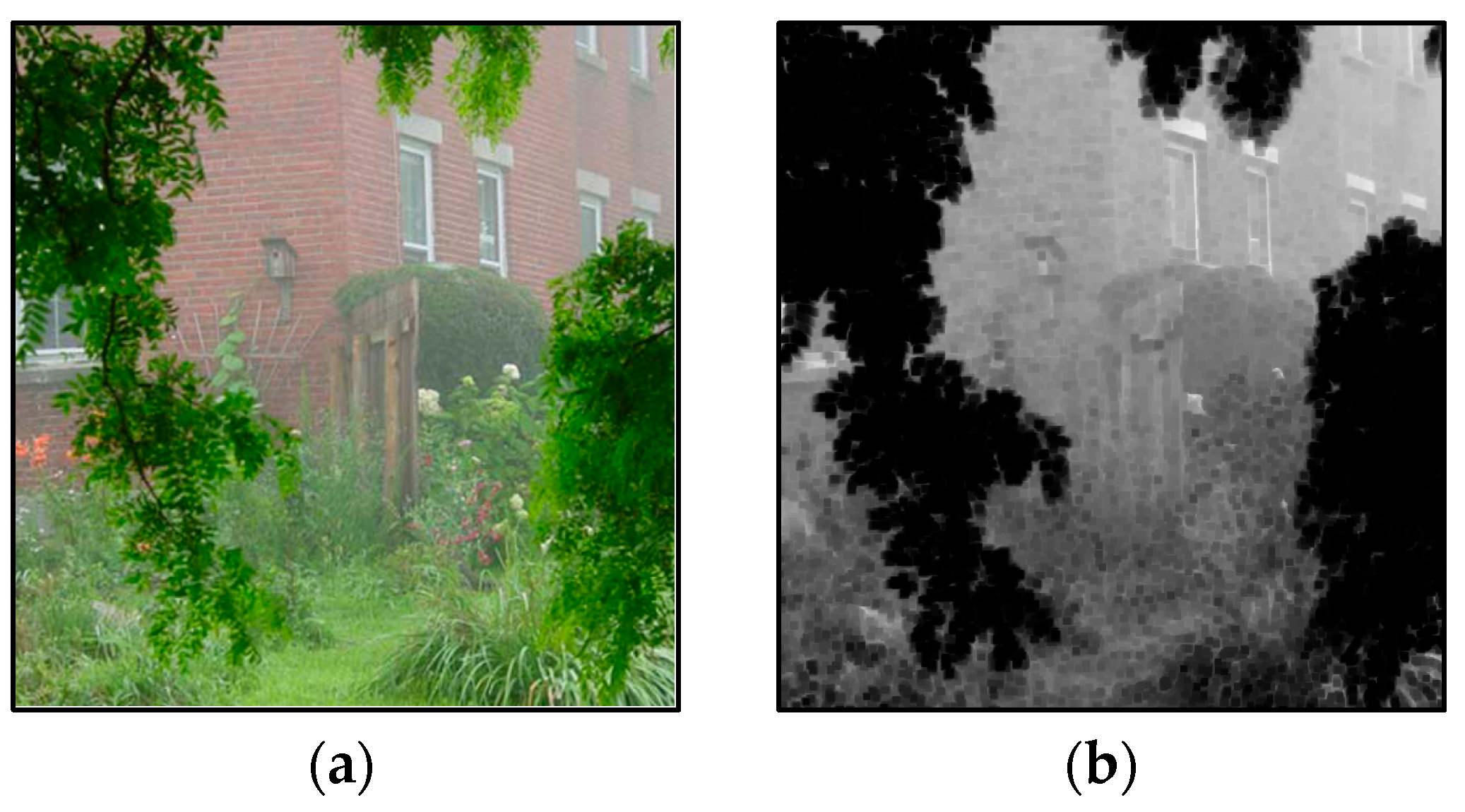
- The input images degraded by haze are normally taken from outdoor natural scenes. Therefore, the scene depth change is usually gradual and the correct depth values of neighboring pixels tend to the same and, hence, the medium transmission map t(x) can be considered as a constant in a small patch, regardless of their scattering coefficient β(x).
- The value variations of A(x) are dependent on the scene depth, that is, objects with the same depth have the same values of A(x). So, the values of A(x) tend to be the same in local except for the pixels at depth discontinuities, whose number is relatively small.
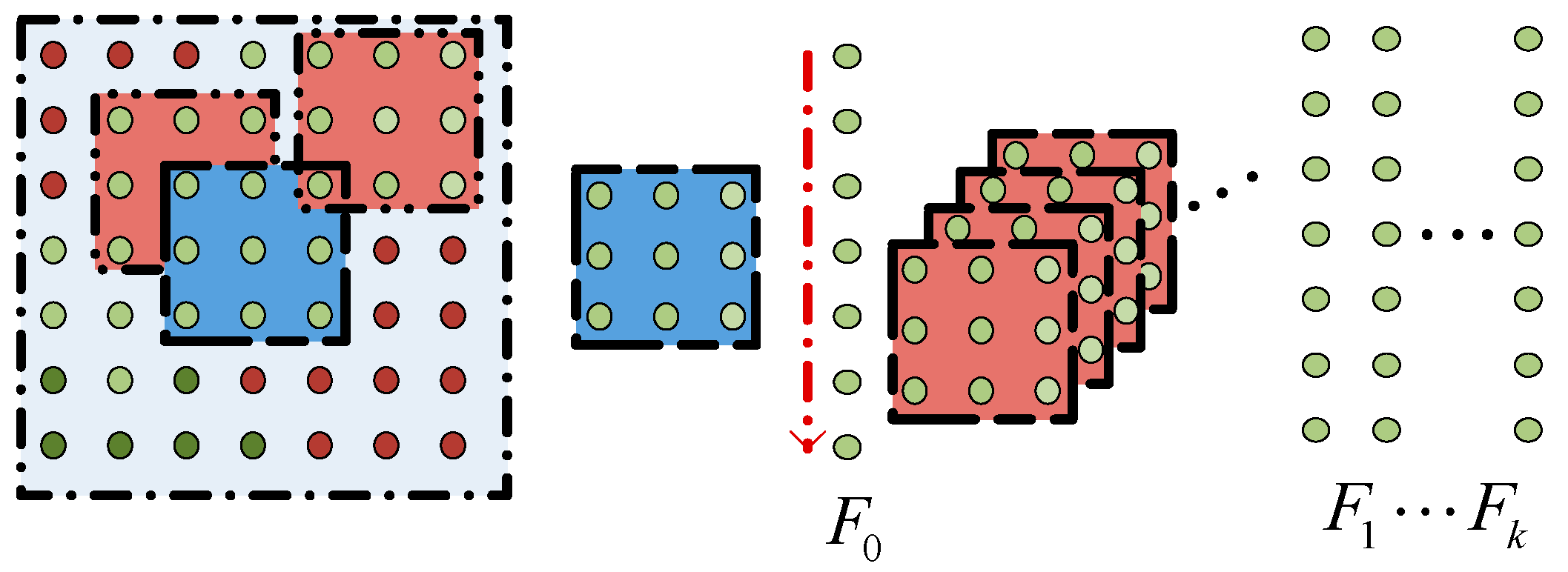
4.1. Construction of Local Consistent MRF Model
4.2. Label Candidates and Initialization
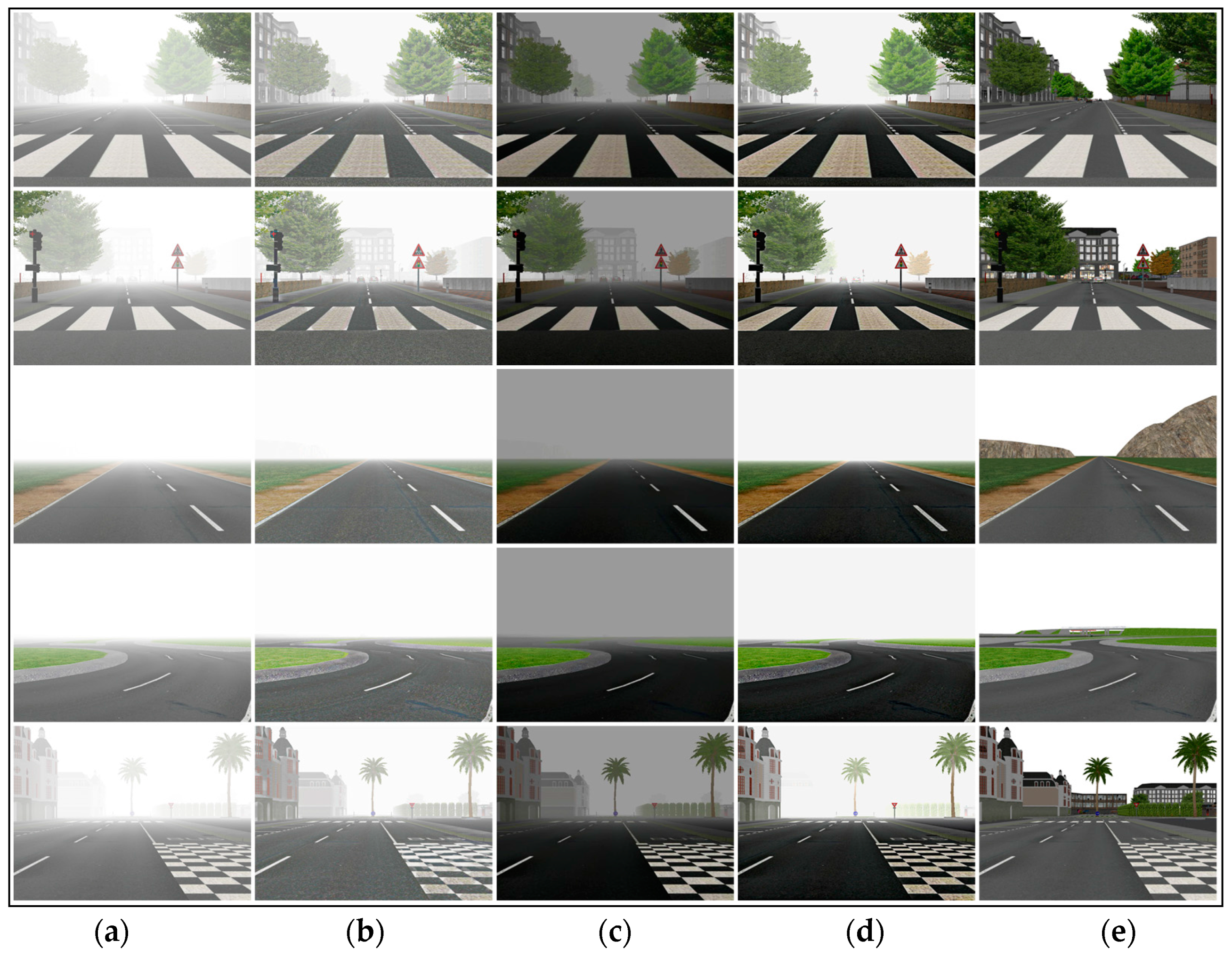
5. Experimental Results
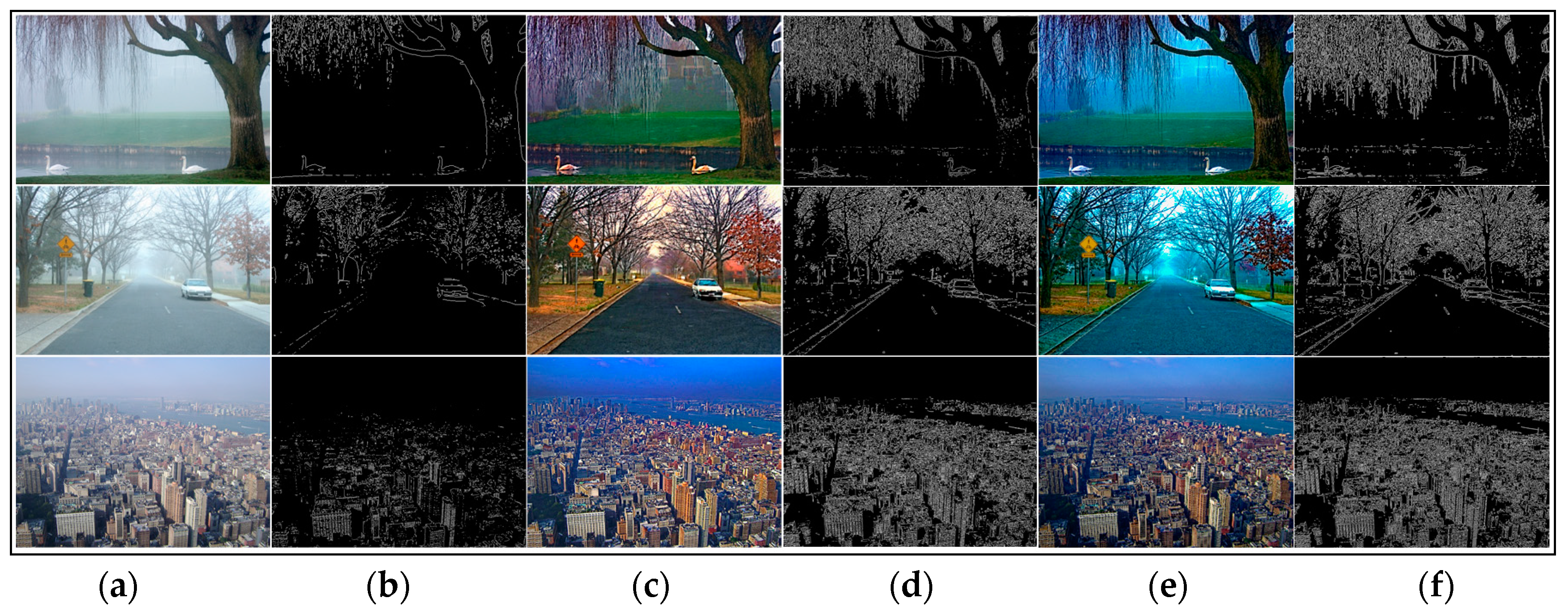
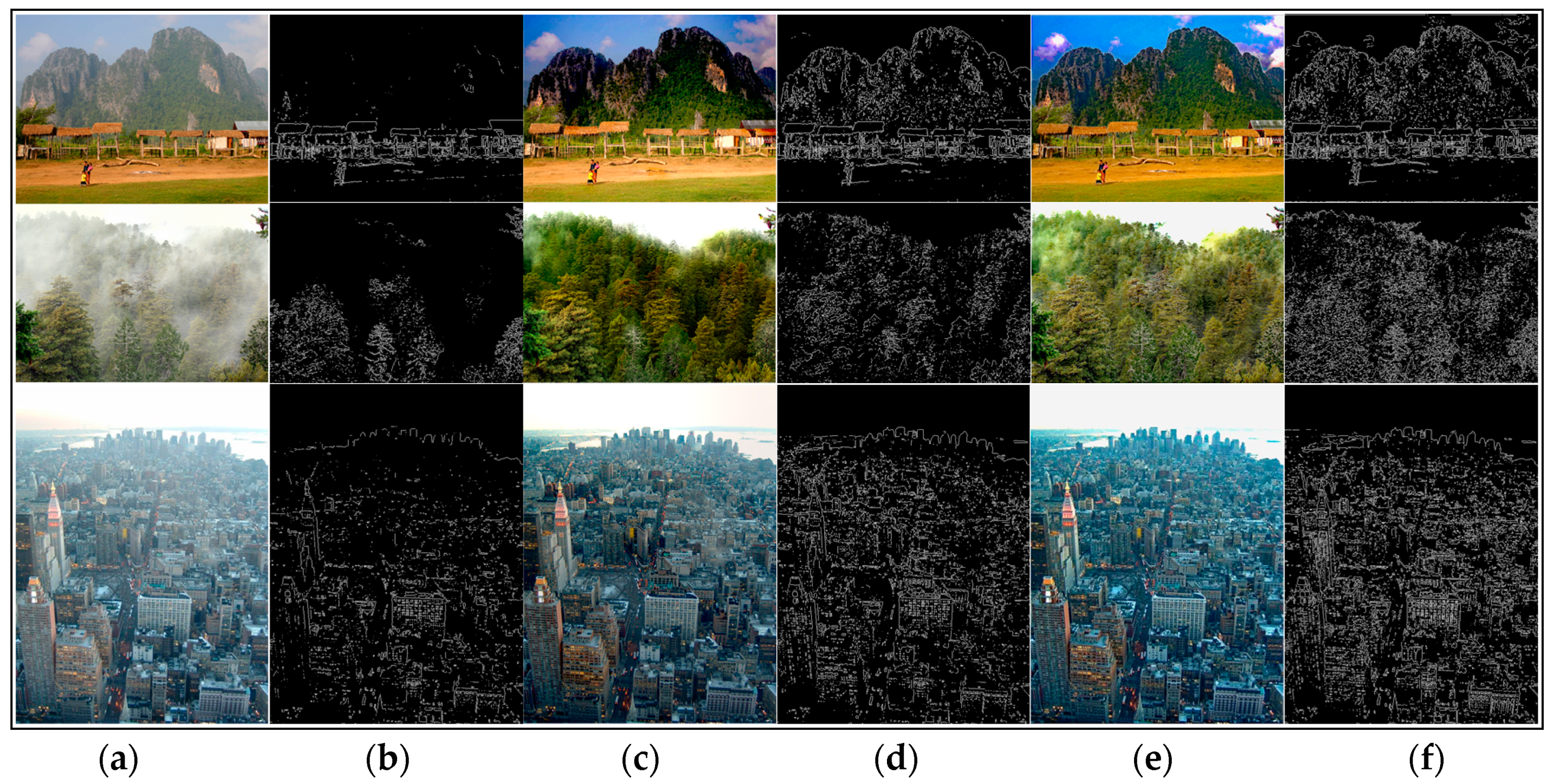
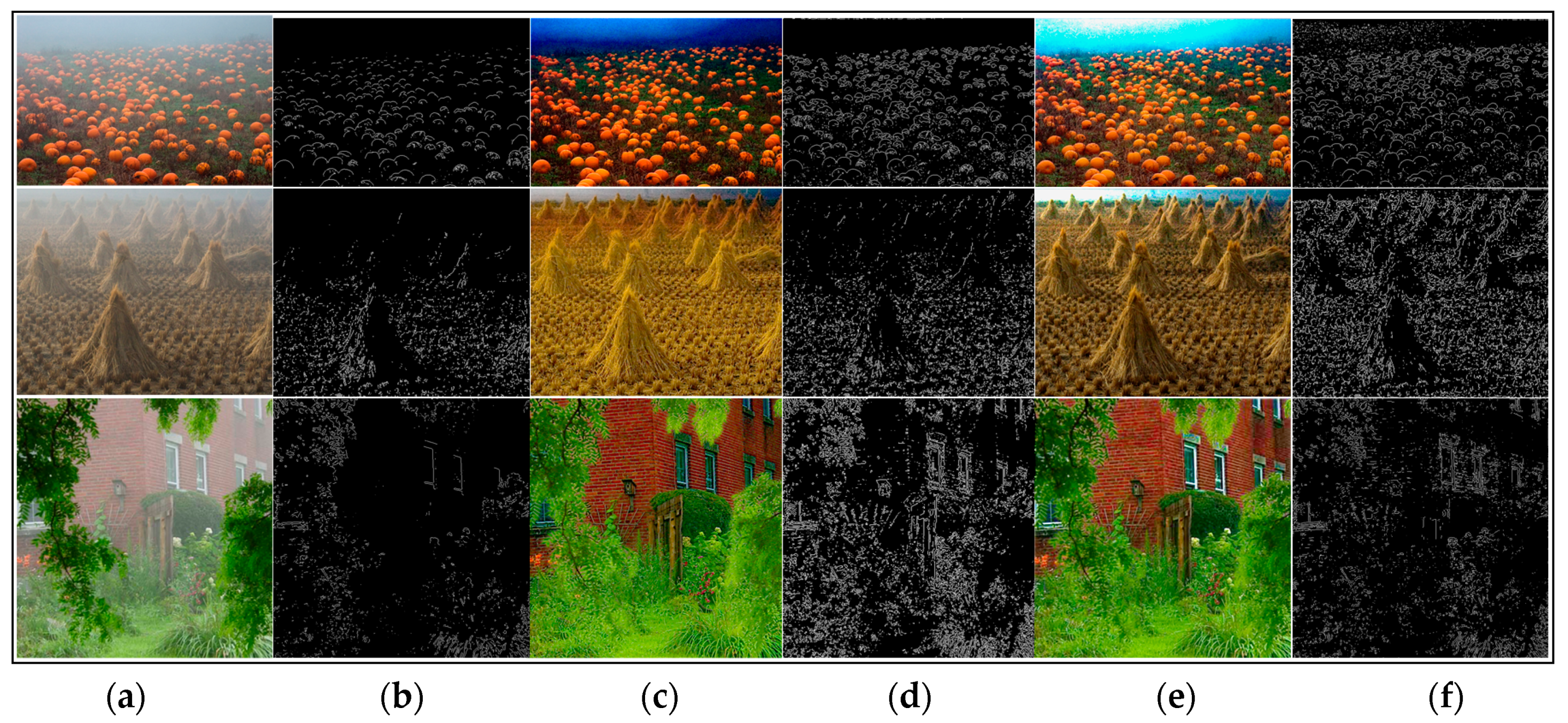
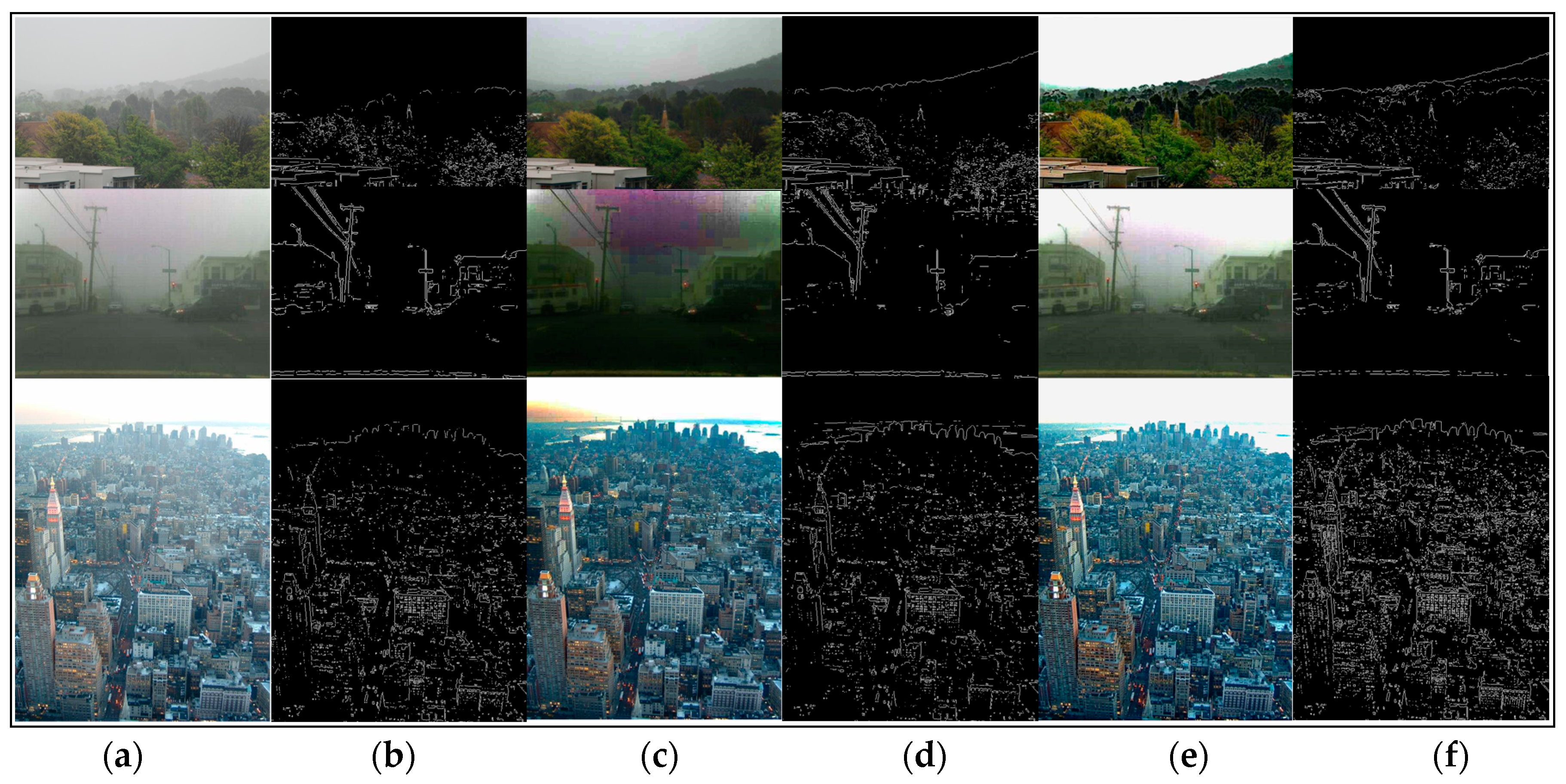
5.1. Qualitative Comparison among Real-World Hazy Images
5.2. Quantitative Comparison
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.; Song, M.; Choe, B.; Kim, S. A Multi-Resolution Mode CMOS Image Sensor with a Novel Two-Step Single-Slope ADC for Intelligent Surveillance Systems. Sensors 2017, 17, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Bello, D.S.S.; Chris, V.H.; Albert, J.P.T. Biologically inspired autonomous agent navigation using an integrated polarization analyzing CMOS image sensor. Procedia Eng. 2010, 5, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Lee, A.B.; Simoncelli, E.P.; Zhu, S.C. On advances in statistical modeling of natural images. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2003, 18, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Simoncelli, E.P. Modeling multiscale subbands of photographic images with fields of Gaussian scale mixtures. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2009, 31, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, O.J.; Rother, C.L.; Kolmogorov, V. A Global Perspective on Map Inference for Low-level Vision. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009; pp. 2319–2326. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Zheng, N.N.; Shum, H.Y. Stereo matching using belief propagation. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2003, 25, 787–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, A.; Zhu, S.C. Generalizing Swendsen-Wang to sampling arbitrary posterior probabilities. IEEE Trans. PAMI 2005, 27, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samucl, K.G.G.; Tappen, M.F. Learning Optimized MAP Estimates in Continuously-valued MRF Models. In Proceedings of the 2009 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 20–26 June 2009; pp. 477–484. [Google Scholar]
- Barbu, A. Training an active random field for real-time image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tappen, M.F.; Liu, C.; Adelson, E.H.; Freeman, W.T. Learning Gaussian Conditional Random Fields for Low-level Vision. In Proceedings of the 2007 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Black, M.J. Steerable Random Field. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–20 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fattal, R. Single image dehazing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.T. Visibility in Bad Weather from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the 2008 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, K.; Kratz, L.; Lombardi, S. Bayesian defogging. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 98, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraffa, L.; Tarel, J.P. Markov Random Field Model for Single Image Defogging. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Gold Coast, Australia, 23–26 June 2013; pp. 994–999. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Sun, J.; Tang, X. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J. Local albedo-insensitive single image dehazing. Vis. Comput. 2010, 26, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.; Hartley, R. Improved Single Image Dehazing Using Geometry. In Proceedings of the 2009 Digital Image Computing Techniques and Applications, Melbourne, Australia, 1–3 December 2009; pp. 103–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kopf, J.; Neubert, B.; Chen, B.; Cohen, M.F.; Cohenor, D.; Deussen, O.; Uyttendaele, M.; Lischinski, D. Deep photo: Model-based photograph enhancement and viewing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, S.G.; Nayar, S.K. Contrast restoration of weather degraded images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, P. Markov random fields in statistics. In Disorder in Physical Systems: A Volume in Honour of John M. Hammersly; Grimmett, G., Welsh, D., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1990; pp. 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Black, M.J. Fields of experts. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 82, 205–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, Y.W.; Welling, M.; Osindero, S.; Hinton, G.E. Energy-based models for sparse overcomplete representations. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 41235–41260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besag, J. On the statistical analysis of dirty pictures. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1986, 48, 259–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geman, S.; Geman, D. Stochastic relaxation, Gibbs distributions, and the Bayesian restoration of images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1984, 6, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Mumford, D. Statistics of Natural Images and Models. In Proceedings of the 1999 Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Ft. Collins, CO, USA, 23–25 June 1999; pp. 541–547. [Google Scholar]
- Portilla, J.; Strela, V.; Wainwright, M.J.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image denoising using scale mixtures of Gaussians in the wavelet domain. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2003, 12, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Image | Entropy | PSNR | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Tan | Ours | Tan | Ours | ||
| Figure 6 | Image (1) | 7.0079 | 7.2235 | 7.6043 | 9.9862 | 10.9585 |
| Image (2) | 7.0079 | 7.3420 | 7.0079 | 9.3524 | 9.7479 | |
| Image (3) | 7.0955 | 7.6129 | 7.7114 | 10.6062 | 12.5667 | |
| Image | Input | Nishino | Ours | Nishino | Ours | |
| Figure 7 | Image (1) | 7.1143 | 7.6770 | 7.7742 | 10.1835 | 16.3444 |
| Image (2) | 7.1578 | 6.9343 | 7.2157 | 15.8571 | 15.9809 | |
| Image (3) | 6.5114 | 7.0954 | 7.4754 | 12.1857 | 14.7134 | |
| Image | Input | Fattal | Ours | Fattal | Ours | |
| Figure 8 | Image (1) | 7.0878 | 7.3270 | 7.4739 | 12.6795 | 15.2639 |
| Image (2) | 6.7272 | 6.9164 | 7.6595 | 9.3204 | 12.5983 | |
| Image (3) | 7.1773 | 7.2793 | 7.1832 | 16.1457 | 17.5572 | |
| Image | Input | He | Ours | He | Ours | |
| Figure 9 | Image (1) | 5.6610 | 6.8479 | 7.1597 | 14.4612 | 12.5766 |
| Image (2) | 6.4788 | 6.9625 | 6.9819 | 10.6480 | 18.4398 | |
| Image (3) | 7.1773 | 7.2793 | 7.1832 | 16.1457 | 17.5572 | |
| Image | Size | Tan | Ours | |
| Figure 6 | Image (1) | 624 × 416 | 21.9913 | 30.5733 |
| Image (2) | 596 × 396 | 18.4131 | 25.8991 | |
| Image (3) | 1024 × 768 | 53.9185 | 71.4230 | |
| Image | Size | Nishino | Ours | |
| Figure 7 | Image (1) | 600 × 400 | 29.7421 | 33.8257 |
| Image (2) | 465 × 384 | 21.8739 | 26.1618 | |
| Image (3) | 440 × 448 | 25.8193 | 29.8271 | |
| Image | Size | Fattal | Ours | |
| Figure 8 | Image (1) | 512 × 348 | 18.9123 | 25.2018 |
| Image (2) | 351 × 244 | 8.0125 | 12.9139 | |
| Image (3) | 576 × 768 | 36.9777 | 43.5120 | |
| Image | Size | He | Ours | |
| Figure 9 | Image (1) | 660 × 440 | 107.9991 | 39.8194 |
| Image (2) | 480 × 360 | 84.3372 | 23.7916 | |
| Image (3) | 576 × 768 | 181.0391 | 43.5120 | |
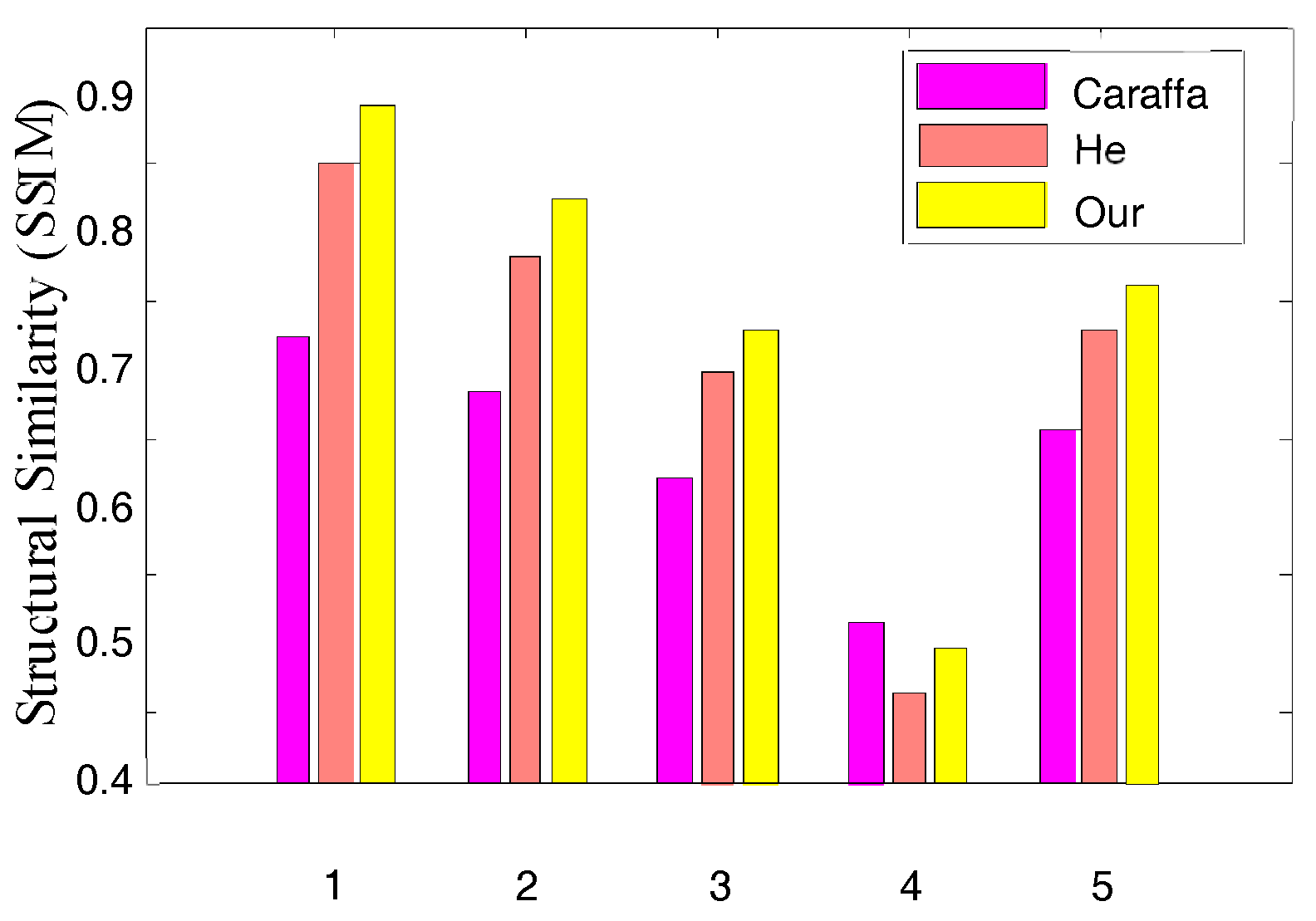
| Input | Size | Caraffa | He | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Figure 10 Image (1) | 640 × 480 | 36.8444 | 102.3404 | 42.4456 |
| Figure 10 Image (2) | 1376 × 1032 | 113.3376 | 387.5691 | 125.9364 |
| Figure 10 Image (3) | 512 × 384 | 18.9124 | 59.4183 | 24.7468 |
| Figure 10 Image (4) | 960 × 720 | 57.1672 | 197.8565 | 69.8188 |
| Figure 10 Image (5) | 736 × 552 | 42.3516 | 173.0013 | 58.8756 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, C.; Bi, D.-Y.; Sui, P.; Chao, A.-N.; Wang, Y.-F. Robust Dehaze Algorithm for Degraded Image of CMOS Image Sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102175
Qu C, Bi D-Y, Sui P, Chao A-N, Wang Y-F. Robust Dehaze Algorithm for Degraded Image of CMOS Image Sensors. Sensors. 2017; 17(10):2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102175
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Chen, Du-Yan Bi, Ping Sui, Ai-Nong Chao, and Yun-Fei Wang. 2017. "Robust Dehaze Algorithm for Degraded Image of CMOS Image Sensors" Sensors 17, no. 10: 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102175
APA StyleQu, C., Bi, D.-Y., Sui, P., Chao, A.-N., & Wang, Y.-F. (2017). Robust Dehaze Algorithm for Degraded Image of CMOS Image Sensors. Sensors, 17(10), 2175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17102175





