Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TiO2 Thin Film Preparation
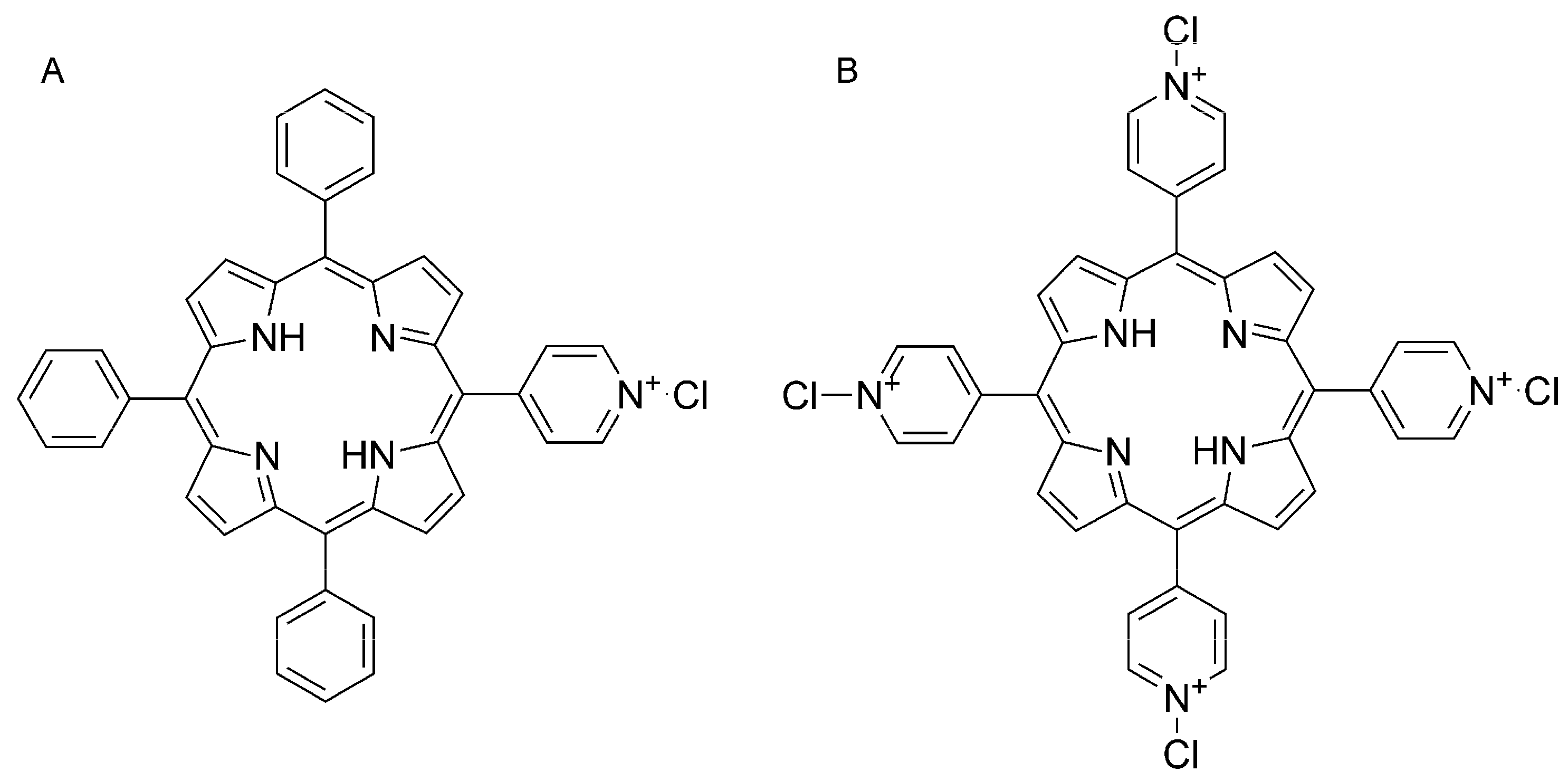
2.2. Porphyrins and Reagents
2.3. Composite Thin Film Preparation and Characterisation
2.4. Gas Sensing System
3. Results and Discussion
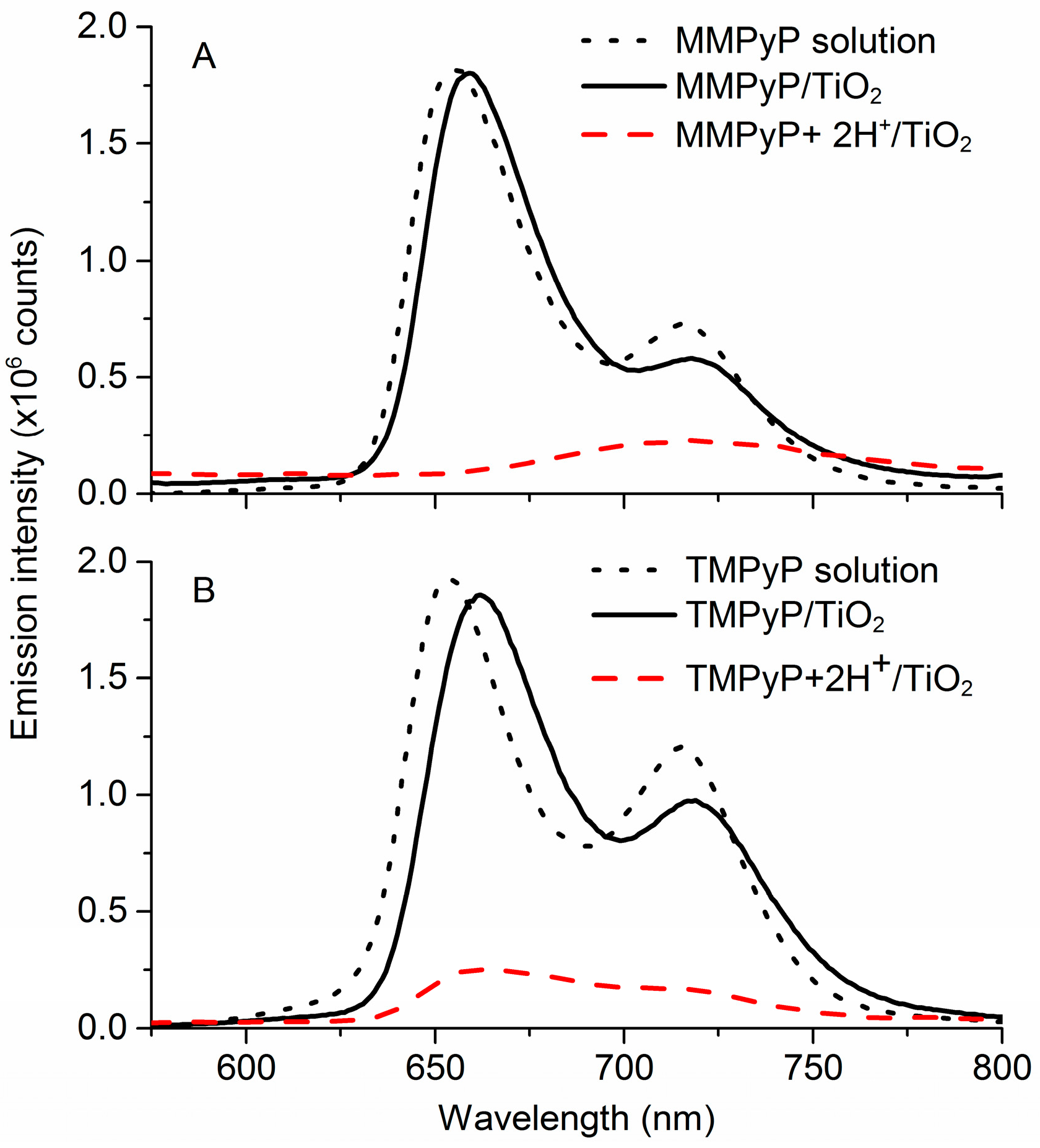
3.1. Optical Properties of MMPyP and TMPyP before and after Protonation
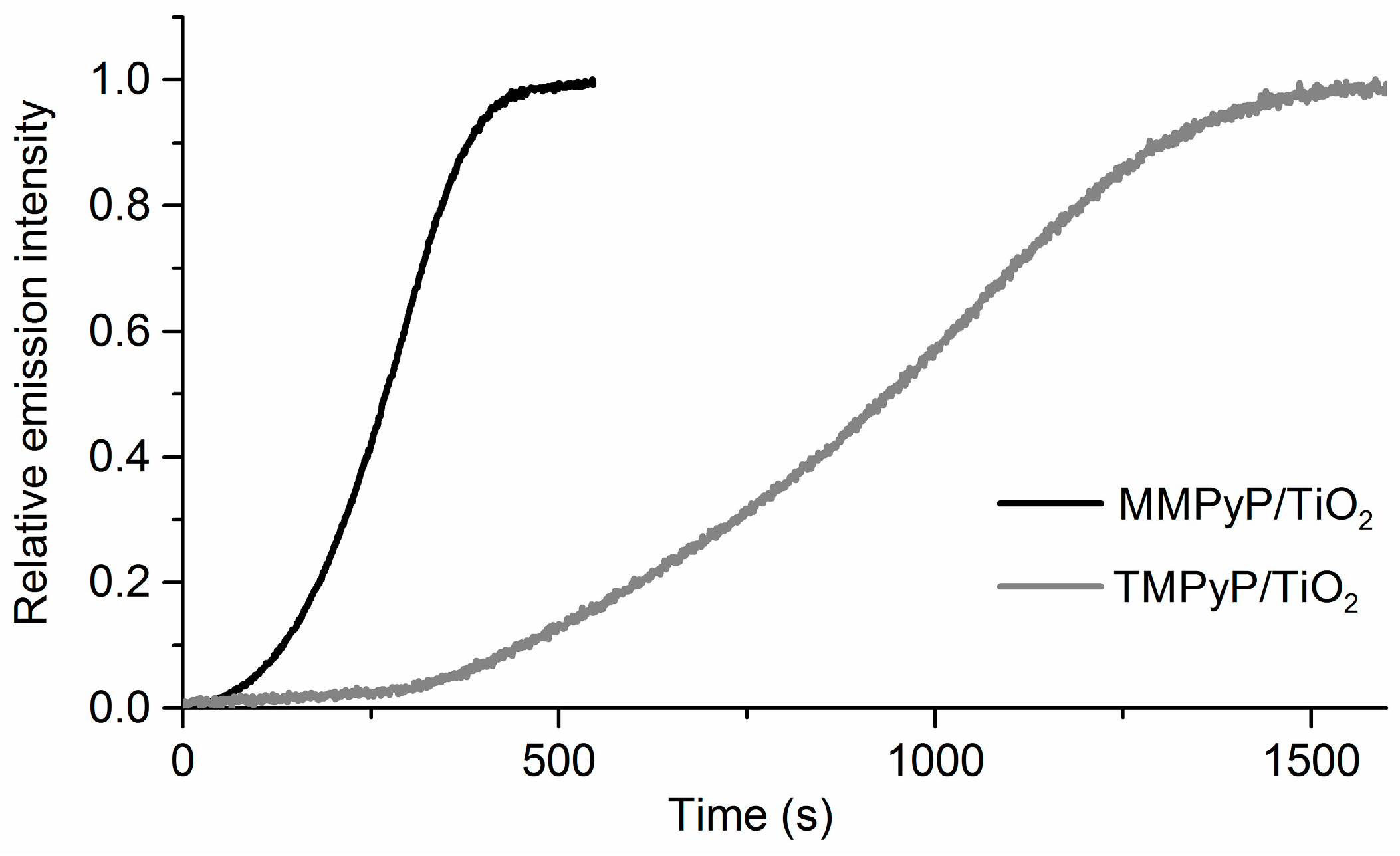
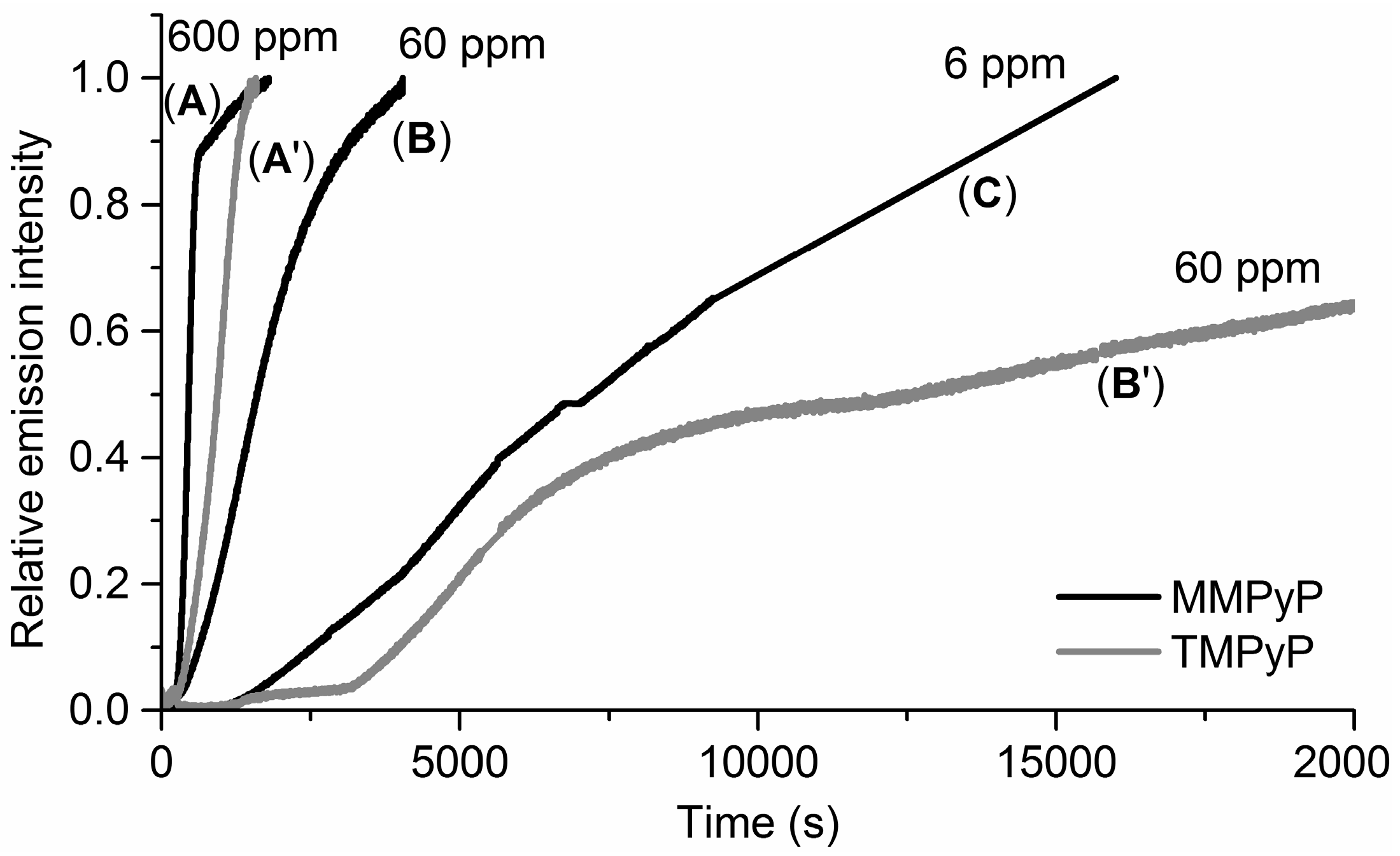
3.2. Response to Ammonia
3.3. Selectivity and Repeatability of the Sensing System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erisman, J.W.; Otjes, R.; Hensen, A.; Jongejan, P.; Van Den Bulk, P.; Khlystov, A.; Möls, H.; Slanina, S. Instrument development and application in studies and monitoring of ambient ammonia. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ament, W.; Huizenga, J.R.; Kort, E.; Van Der Mark, T.W.; Grevink, R.G.; Verkerke, G.J. Respiratory ammonia output and blood ammonia concentration during incremental exercise. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999, 20, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearney, D.J.; Hubbard, T.; Putnam, D. Breath ammonia measurement in Helicobacter pylori infection. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002, 47, 2523–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbioni, G.; Richter, E. Aromatic Amines, Nitroarenes, and Heterocyclic Aromatic Amines. In Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 729–741. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, M.H.S. Biogenic amines: Their importance in foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 29, 213–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, V. Biosensors in fish production and quality control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prester, L. Biogenic amines in fish, fish products and shellfish: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2011, 28, 1547–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacquit, A.; Lau, K.T.; McLaughlin, H.; Frisby, J.; Quilty, B.; Diamond, D. Development of a volatile amine sensor for the monitoring of fish spoilage. Talanta 2006, 69, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewska, K. Mixed oxides as gas sensors. Thin Solid Films 2001, 391, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanan, S.M.; El-Kadri, O.M.; Abu-Yousef, I.A.; Kanan, M.C. Semiconducting metal oxide based sensors for selective gas pollutant detection. Sensors 2009, 9, 8158–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, G.F.; Cavanagh, L.M.; Afonja, A.; Binions, R. Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 5469–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Tillman, E.S.; Lewis, N.S. Detection and classification of volatile organic amines and carboxylic acids using arrays of carbon black-dendrimer composite vapor detectors. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2904–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobnik, A.; Špela, K.U.; Turel, M.; Frančič, N. Sol-gel based optical chemical sensors. SPIE Proc. 2011, 8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Applications and advances in electronic-nose technologies. Sensors 2009, 9, 5099–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sotzing, G.A.; Weiss, R.A. Conductive polymer foams as sensors for volatile amines. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpel, J.E.; Wouters, C.; Herzer, N.; Ziegler, J.; Broer, D.J.; Bastiaansen, C.W.M.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. An Optical Sensor for Volatile Amines Based on an Inkjet-Printed, Hydrogen-Bonded, Cholesteric Liquid Crystalline Film. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sberveglieri, G. Recent developments in semiconducting thin-film gas sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 1995, 23, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imawan, C.; Solzbacher, F.; Steffes, H.; Obermeier, E. Gas-sensing characteristics of modified-MoO3 thin films using Ti-overlayers for NH3 gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 64, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, P.K.; Tuma, D.T. Characteristics of semiconductor gas sensors I. Steady state gas response. Sens. Actuators 1982, 3, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.N.; Miura, N.; Ishida, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Yamazoe, N. Selective detection of NH3 over NO in combustion exhausts by using Au and MoO3 doubly promoted WO3 element. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 65, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.M.; Dooling, C.M.; Richardson, T.H.; Hyde, R.K.; Hunter, C.A.; Martín, M.T.; Camacho, L. The optical gas-sensing properties of an asymmetrically substituted porphyrin. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-S.; Lo, Y.-L.; Sung, T.-W. Review on recent developments of fluorescent oxygen and carbon dioxide optical fiber sensors. Photonic Sens. 2011, 1, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakow, N.A.; Suslick, K.S. A colorimetric sensor array for odour visualization. Nature 2000, 406, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Castillero, P.; Cano, M.; Richardson, T.H.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Selective Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds by Spectral Imaging of Porphyrin Derivatives Bound to TiO2 Porous Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5147–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Guillén, M.G.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Pinto, S.M.A.; Calvete, M.J.F.; Pereira, M.M. Optical detection of amine vapors using ZnTriad porphyrin thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brittle, S.; Richardson, T.H.; Dunbar, A.D.F.; Turega, S.; Hunter, C.A. Alkylamine sensing using langmuir-blodgett films of n-alkyl-N-phenylamide-substituted zinc porphyrins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 11278–11283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, M. Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) in the process industries—A review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2007, 23, 65–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.M.; Dooling, C.M.; Richardson, T.H.; Hyde, R.K.; Hunter, C.A.; Martín, M.T.; Camacho, L. Characterization and fast optical response to NO2 of porphyrin LB films. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 22, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Castillero, P.; Cano, M.; Richardson, T.H. Optimization of mixed Langmuir-Blodgett films of a water insoluble porphyrin in a calixarene matrix for optical gas sensing. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, N.H.; Salleh, M.M.; Yahaya, M. Room Temperature Fluorescence Gas Sensor Based on Coated TiO2 Nanoparticles. Key Eng. Mater. 2013, 543, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, L.R. The Colours of Life; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, N.; Akins, D.L. Dye-doped inorganic/organic composite films as fluorescence sensors for methanol vapor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, M.E.; Knapp, M.J. Optical explosives detection: From color changes to fluorescence turn-on. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillero, P.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Cano, M.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Roales, J.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Active and optically transparent tetracationic porphyrin/TiO2 composite thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, M.; Castillero, P.; Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Brittle, S.; Richardson, T.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Barranco, A. A transparent TMPyP/TiO2 composite thin film as an HCl sensitive optochemical gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 150, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, V.; Borrás, A.; Yubero, F.; Espinós, J.P.; Frutos, F.; González-Elipe, A.R. Wetting angles on illuminated Ta2O5 thin films with controlled nanostructure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 3775–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Borrás, A.; Barranco, A.; Rico, V.J.; Espinós, J.P.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Borrás, A.; Espinos, J.P.; González-Elipe, A.R. Preillumination of TiO2 and Ta2O5 photoactive thin films as a tool to tailor the synthesis of composite materials. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9460–9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barranco, A.; Borras, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R.; Palmero, A. Perspectives on oblique angle deposition of thin films: From fundamentals to devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 76, 59–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcrae, E.G.; Kasha, M. Enhancement of phosphorescence ability upon aggregation of dye molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1958, 28, 721–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czikklely, V.; Forsterling, H.D.; Kuhn, H. Extended dipole model for aggregates of dye molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1970, 6, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H.; Foersterling, H.-D. Principles of Physical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Czikkely, V.; Försterling, H.D.; Kuhn, H. Light absorption and structure of aggregates of dye molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1970, 6, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.E.; Song, Q.; Bohn, P.W. Influence of molecular orientation and proximity on spectroscopic line shape in organic monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 12302–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, H. π-Electron systems - Building blocks of supramolecular machines. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 171, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.M.; Dooling, C.M.; Richardson, T.H.; Hyde, R.K.; Hunter, C.A.; Martín, M.T.; Camacho, L. Influence of molecular organization of asymmetrically substituted porphyrins on their response to NO2 gas. Langmuir 2002, 18, 7594–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šišková, K.; Vlčková, B.; Mojzeš, P. Spectral detection of J-aggregates of cationic porphyrin and investigation of conditions of their formation. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, J.M.; Martín, M.T.; Camacho, L.; Prieto, I.; Möbius, D. Determination of porphyrin dimer in a mixed monolayer of porphyrin/phospholipid transferred on ITO electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2000, 2, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Guillén, M.G.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Castillero, P.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R. Free-Base Carboxyphenyl Porphyrin Films Using a TiO2 Columnar Matrix: Characterization and Application as NO2 Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 11118–11132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, R.; Al-Karadaghi, S.; Ferreira, G.C. Resonance Raman spectroscopic examination of ferrochelatase-induced porphyrin distortion. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2011, 15, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spellane, P.J.; Gouterman, M.; Antipas, A.; Kim, S.; Liu, Y.C. Porphyrins. 40. Electronic spectra and four-orbital energies of free-base, zinc, copper, and palladium tetrakis(perfluorophenyl)porphyrins. Inorg. Chem. 1980, 19, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalimuthu, P.; Abraham John, S. Optochemical sensing of hydrogen chloride gas using meso-tetramesitylporphyrin deposited glass plate. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; A Imam, S.; T Beg, M. A Novel Method for Evaluation of Band Width of MEMS-Based Embedded Gas Sensor. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 2, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roales, J.; Pedrosa, J.M.; Cano, M.; Guillén, M.G.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Castillero, P.; Barranco, A.; Gonzalez-Elipe, A.R. Anchoring effect on (tetra)carboxyphenyl porphyrin/TiO2 composite films for VOC optical detection. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Max, J.-J.; Chapados, C. Aqueous ammonia and ammonium chloride hydrates: Principal infrared spectra. J. Mol. Struct. 2013, 1046, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

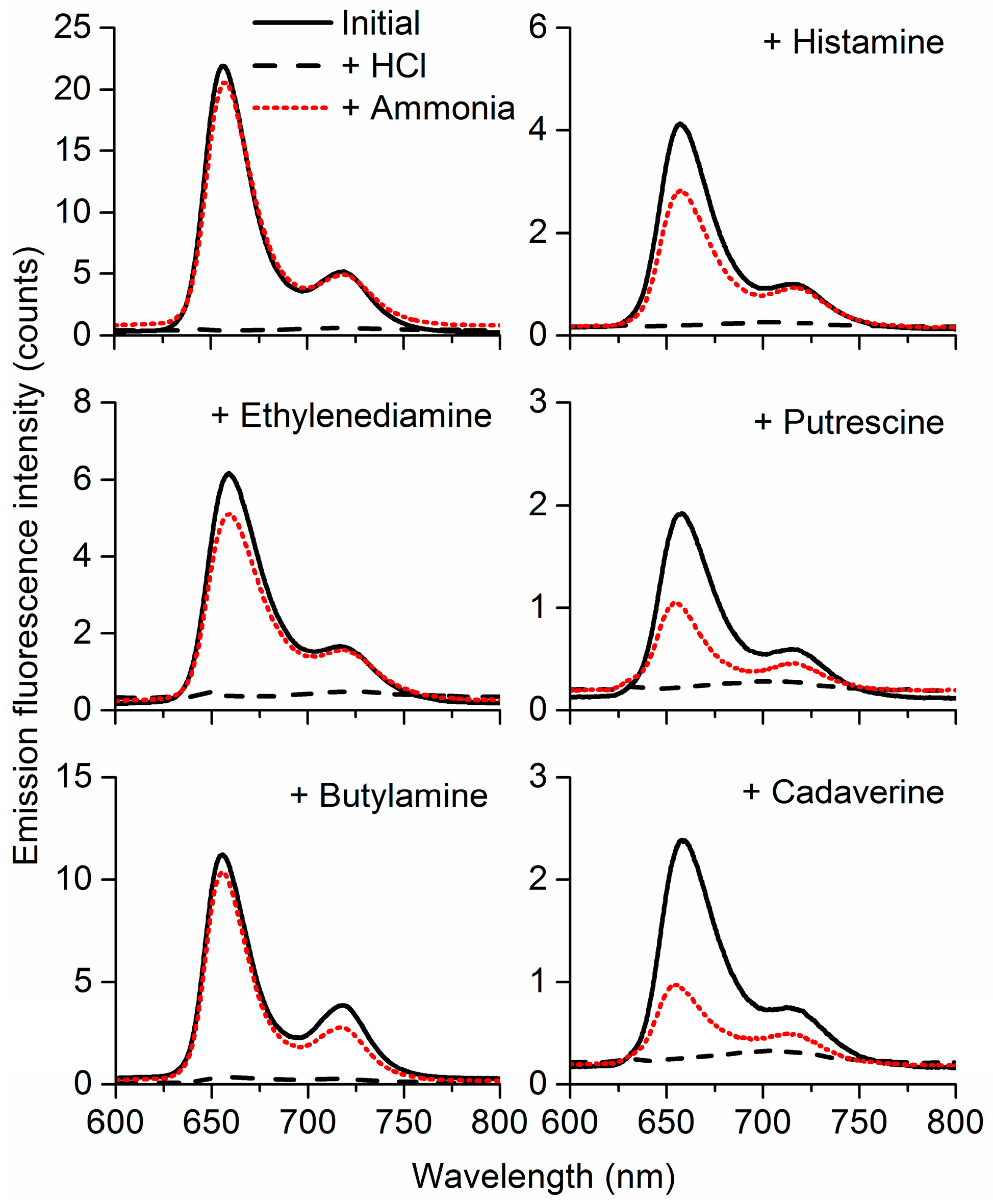

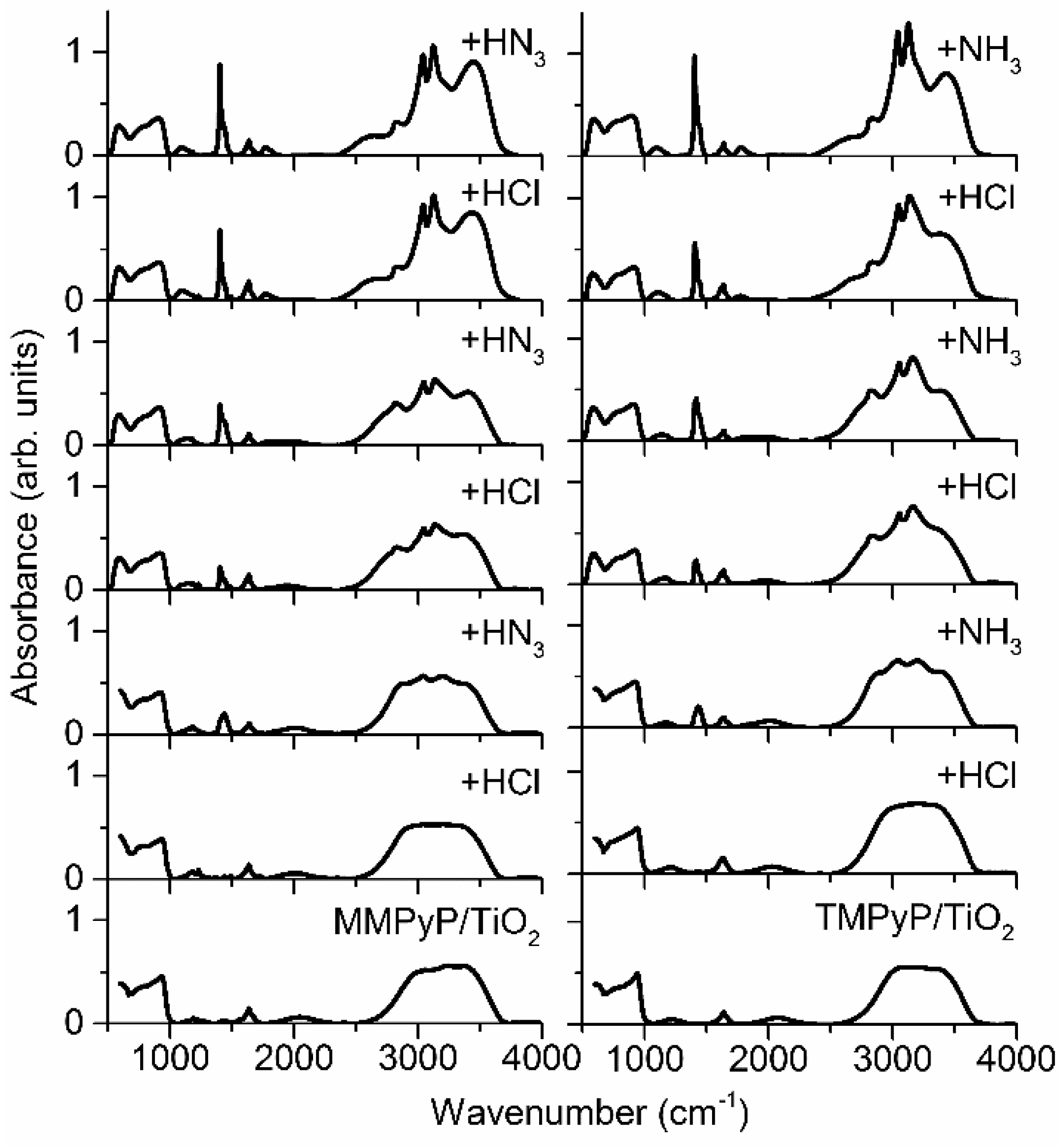
| Absorbance Peaks | Fluorescence Peaks | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B(0,0) | Qy(1,0) | Qy(0,0) | Qx(1,0) | Qy(0,0) | Isosbestic Point | Q(0,0) | Q(0,1) | |
| MMPyP solution | 415 | 515 | 554 | 591 | 648 | 434 | 653 | 715 |
| MMPyP+2H+ solution | 448 | 556 | 608 | 659 | 434 | |||
| MMPyP/TiO2 | 426 | 518 | 558 | 596 | 649 | 431 | 657 | 718 |
| MMPyP+2H+/TiO2 | 440 | 611 | 670 | 431 | 718 | |||
| TMPyP solution | 425 | 516 | 551 | 590 | 647 | 438 | 653 | 714 |
| TMPyP+2H+ solution | 453 | 551 | 600 | 652 | 438 | |||
| TMPyP/TiO2 | 427 | 523 | 560 | 600 | 651 | 443 | 662 | 717 |
| TMPyP+2H+/TiO2 | 458 | 612 | 654 | 443 | 662 | 717 | ||
| MMPyP/TiO2 | TMPyP/TiO2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Intercept (counts × 104) | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 9.7 ± 1.2 |
| Slope (counts/ppm × 102) | 10.4 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 0.4 |
| Regression coefficient (r) | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Standard deviation of residuals (Sy/x) | 14.1 | 17.6 |
| Limit of detection (ppm) | 0.05 | 0.16 |
| Relative standard deviation (%) | 2.3 | 3.7 |
| Measurement wavelength (nm) | 660 | 660 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castillero, P.; Roales, J.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Sánchez-Valencia, J.R.; Barranco, A.; González-Elipe, A.R.; Pedrosa, J.M. Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films. Sensors 2017, 17, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010024
Castillero P, Roales J, Lopes-Costa T, Sánchez-Valencia JR, Barranco A, González-Elipe AR, Pedrosa JM. Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films. Sensors. 2017; 17(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastillero, Pedro, Javier Roales, Tânia Lopes-Costa, Juan R. Sánchez-Valencia, Angel Barranco, Agustín R. González-Elipe, and José M. Pedrosa. 2017. "Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films" Sensors 17, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010024
APA StyleCastillero, P., Roales, J., Lopes-Costa, T., Sánchez-Valencia, J. R., Barranco, A., González-Elipe, A. R., & Pedrosa, J. M. (2017). Optical Gas Sensing of Ammonia and Amines Based on Protonated Porphyrin/TiO2 Composite Thin Films. Sensors, 17(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17010024








