A Microflow Cytometer with a Rectangular Quasi-Flat-Top Laser Spot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design
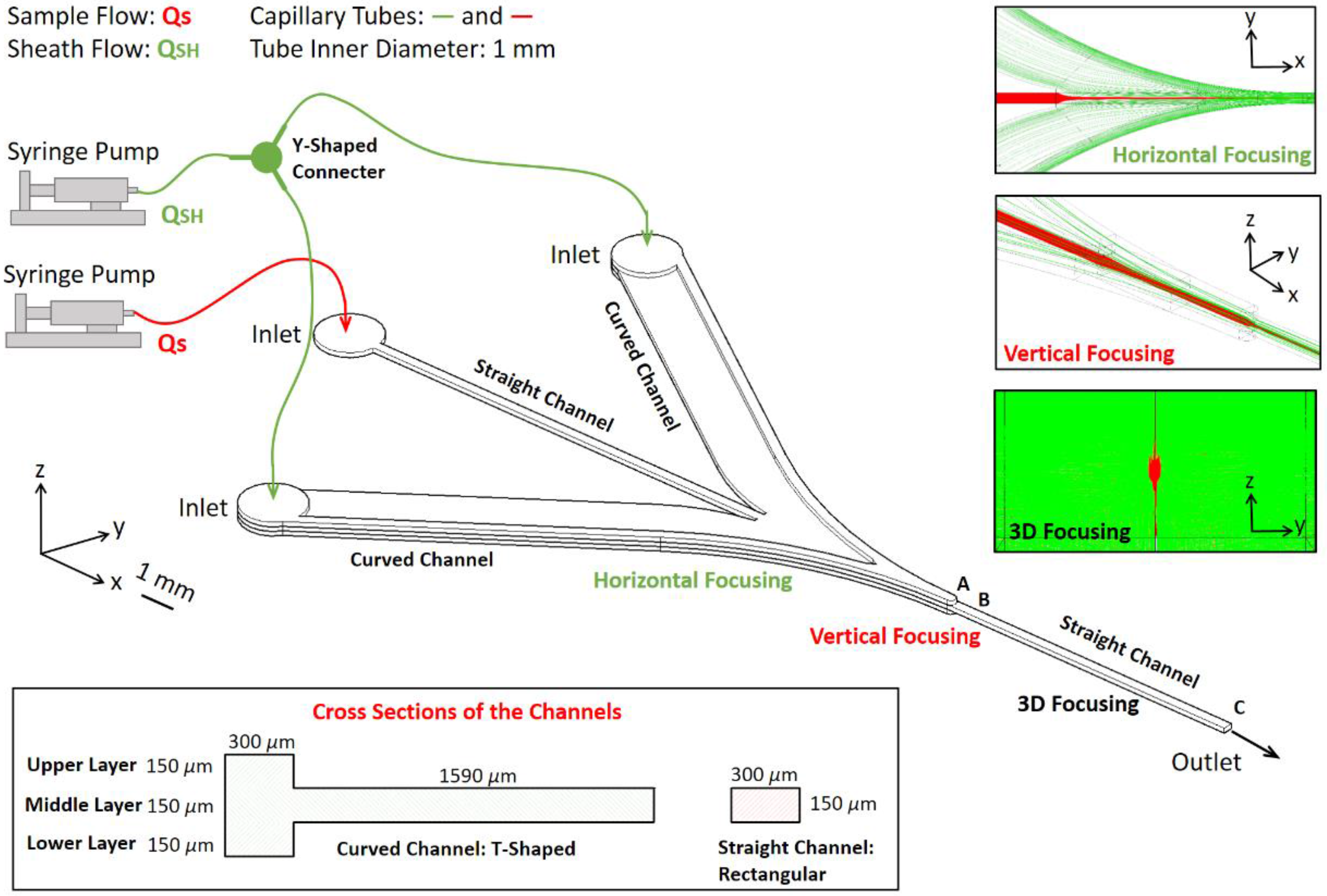
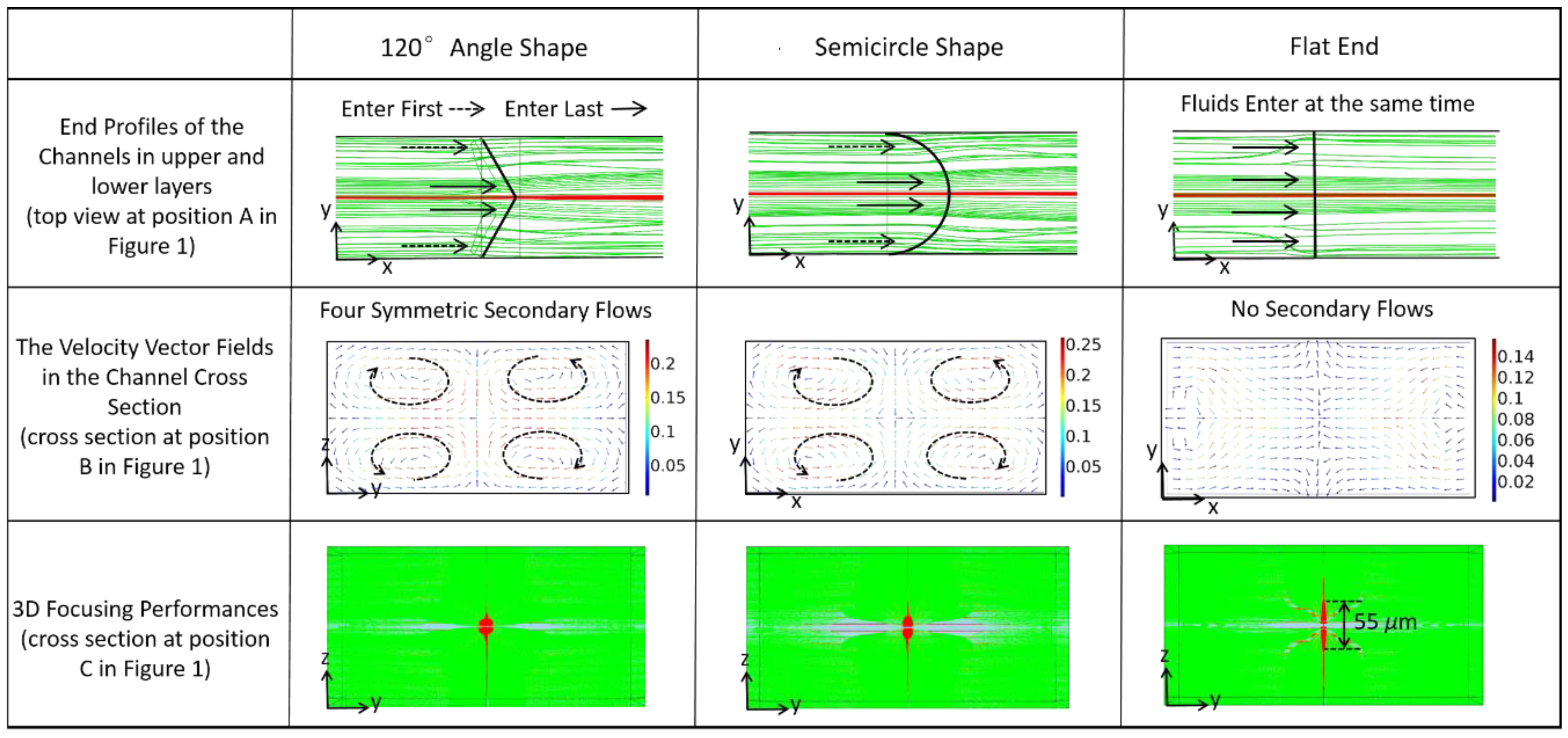
2.1. Microfluidic Chip for 3D Hydrodynamic Focusing
2.2. BOE for Laser Beam Shaping and Homogenization
3. Experimental Setup
3.1. Microfluidic Chip
3.2. BOE
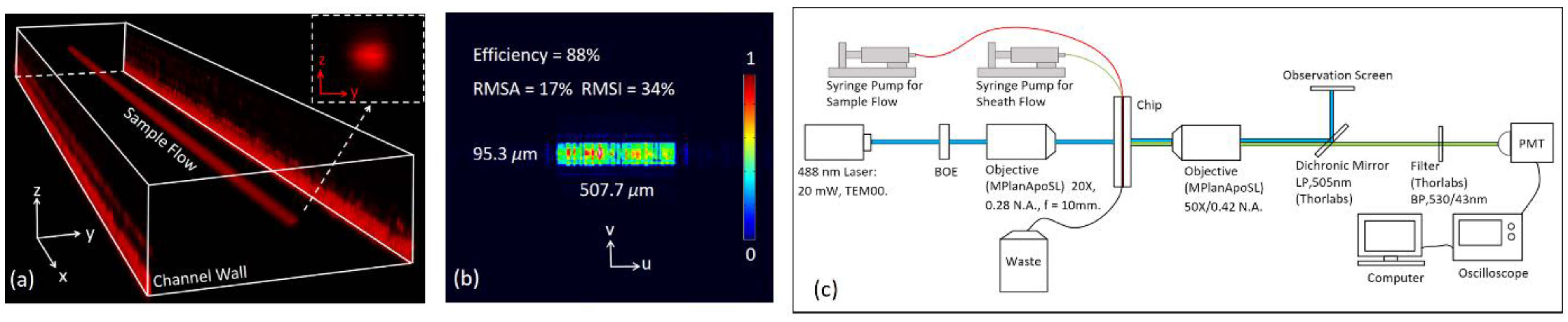
3.3. Microflow Cytometer
4. Results and Discussions
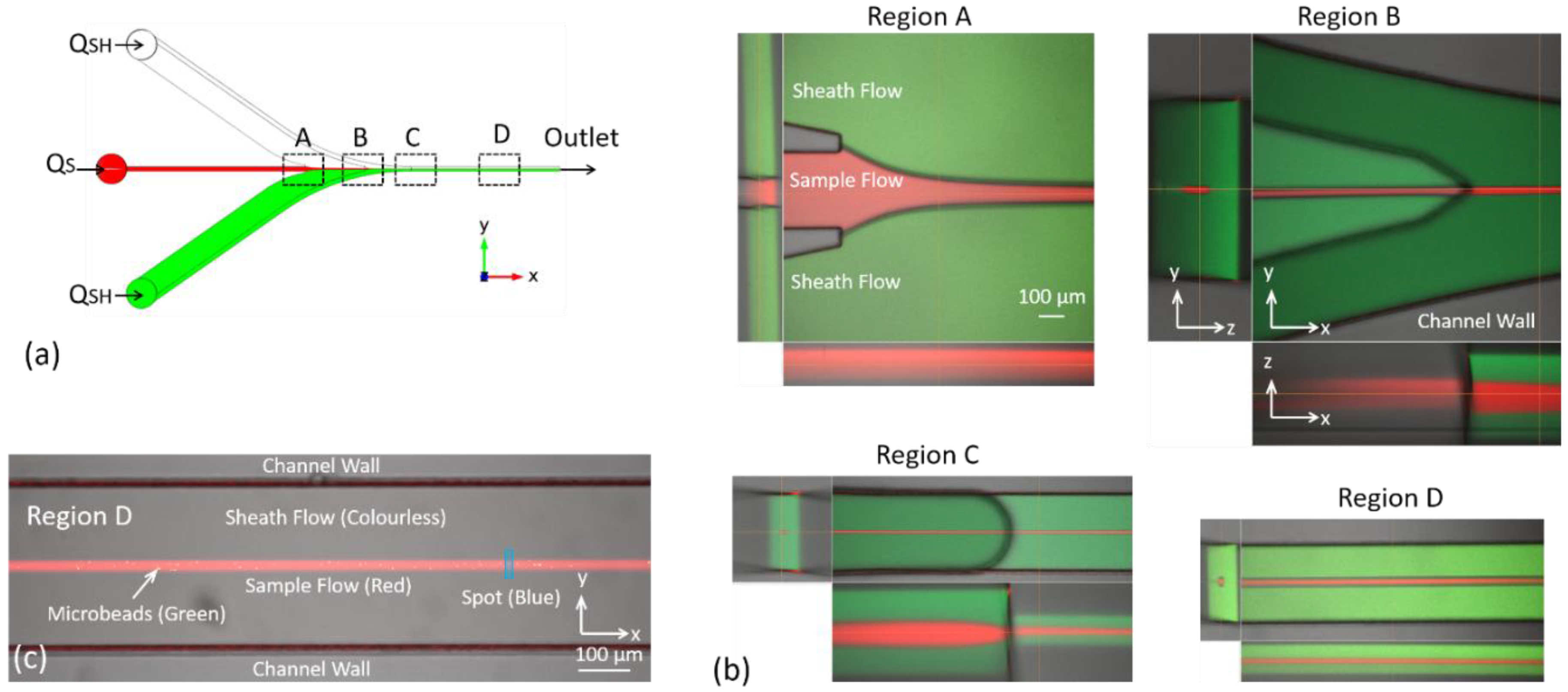
4.1. Flow Configuration in Key Regions of the Microfluidic Chip
4.2. Characteristics of the Focusing Chip
4.3. Characteristics of the Fluorescence Signals
4.4. CVs of Microbeads under Different Sample Flow Rates
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McClain, M.A.; Culbertson, C.T.; Jacobson, S.C.; Ramsey, J.M. Flow cytometry of Escherichia coli on microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5334–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Weng, X.; Li, D. A novel microfluidic flow focusing method. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 054120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Tzeng, T.R.J.; Xuan, X. Electrokinetic focusing and filtration of cells in a serpentine. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 044109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.H.; Soh, H.T. Acoustophoretic sorting of viable mammalian cells in a microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10756–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burguillos, M.A.; Magnusson, C.; Nordin, M.; Lenshof, A.; Augustsson, P.; Hansson, M.J.; Deierborg, T. Microchannel acoustophoresis does not impact survival or function of microglia, leukocytes or tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, Y.B.V.; Agrawal, A. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic flow focusing of dye, particles and cells in a microfluidic device by employing two bends of opposite curvature. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2016, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Wu, C.; Nam, S.; Di Carlo, D.; Lee, W. Inertial focusing in non-rectangular cross-section microchannels and manipulation of accessible focusing positions. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zandi, M.; Ho, C.C.; Kaval, N.; Papautsky, I. Single stream inertial focusing in a straight microchannel. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, I.D.; McDonnell, M.B.; Tan, C.K.L.; McCluskey, D.K.; Davies, M.J.; Tracey, M.C. Dean flow focusing and separation of small microspheres within a narrow size range. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.H.; Lee, K.S.; Jung, J.H.; Sung, H.J. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic flow and particle focusing using four vortices Dean flow. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.J.; Pulido, D.; Oka, J.C.; Amini, H.; Masaeli, M.; Di Carlo, D. Microstructure-induced helical vortices allow single-stream and long-term inertial focusing. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2942–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.L.; He, X.K.; Han, Y.; Zhe, J.; Zhao, L. Continuous 3D particle focusing in a microchannel with curved and symmetric sharp corner structures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 035020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, J.P.; Kim, J.S.; Erickson, J.S.; Hilliard, L.R.; Howell, P.B.; Anderson, G.P.; Ligler, F.S. Multi-wavelength microflow cytometer using groove-generated sheath flow. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1942–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Park, J.K. Sheathless hydrophoretic particle focusing in a microchannel with exponentially increasing obstacle arrays. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3035–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, A.J.; Gossett, D.R.; Di Carlo, D. Three dimensional, sheathless, and high-throughput microparticle inertial focusing through geometry-induced secondary flows. Small 2013, 9, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, H.M. Chapter 4 How Flow Cytometers Work. In Practical Flow Cytometry, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken. NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gambin, Y.; Simonnet, C.; VanDelinder, V.; Deniz, A.; Groisman, A. Ultrafast microfluidic mixer with three-dimensional flow focusing for studies of biochemical kinetics. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hairer, G.; Pärr, G.S.; Svasek, P.; Jachimowicz, A.; Vellekoop, M.J. Investigations of micrometer sample stream profiles in a three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing device. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 132, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, R.; Ohki, H.; Yamazaki, I.; Takagi, T. Investigation of Sheath Flow Chambers for Flow Cytometers (Micro Machined Flow Chamber with Low Pressure Loss). JSME Int. J. Ser. B 1997, 40, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.J.; Cho, S.H.; Mei, Z.; Lien, V.; Wu, T.F.; Lo, Y.H. Universally applicable three-dimensional hydrodynamic microfluidic flow focusing. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiè, P.; Bragheri, F.; Vazquez, R.M.; Osellame, R. Straightforward 2D hydrodynamic focusing in femtosecond laser fabricated microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummrow, A.; Theisen, J.; Frankowski, M.; Tuchscheerer, A.; Yildirim, H.; Brattke, K.; Neukammer, J. Microfluidic structures for flow cytometric analysis of hydrodynamically focused blood cells fabricated by ultraprecision micromachining. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, H.M. Chapter 1 Overture. In Practical Flow Cytometry, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons. Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, H.; Hyun, K.A.; Kwon, M.H.; Ha, K.S.; Joo, C.; Jung, H.I. Microfluidic sorting of fluorescently activated cells depending on gene expression level. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 3103–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirasaki, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Makazu, H.; Tashiro, K.; Shoji, S.; Tsukita, S.; Funatsu, T. On-chip cell sorting system using laser-induced heating of a thermoreversible gelation polymer to control flow. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, H.; Arakawa, T.; Nara, Y.; Shirasaki, Y.; Ozaki, K.; Shoji, S.; Funatsu, T. Integration in a multilayer microfluidic chip of 8 parallel cell sorters with flow control by sol-gel transition of thermoreversible gelation polymer. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.H.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, F.S.; Godin, J.M.; Lo, Y.H. Human mammalian cell sorting using a highly integrated micro-fabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter (μFACS). Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Sugino, H.; Shirasaki, Y.; Aoki, T.; Arakawa, T.; Funatsu, T.; Shoji, S. Microfluidic cell sorter with flow switching triggered by a sol–gel transition of a thermo-reversible gelation polymer. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 150, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneoka, M.; Shirasaki, Y.; Sugino, H.; Aoki, T.; Arakawa, T.; Ozaki, K.; Funatsu, T. Microfluidic active sorting of DNA molecules labeled with single quantum dots using flow switching by a hydrogel sol-gel transition. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 159, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, M.; Theisen, J.; Kummrow, A.; Simon, P.; Ragusch, H.; Bock, N.; Neukammer, J. Microflow cytometers with integrated hydrodynamic focusing. Sensors 2013, 13, 4674–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Nawaz, A.A.; Lin, S.C.S.; Lapsley, M.I.; Zhao, Y.; McCoy, J.P.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Huang, T.J. An integrated, multiparametric flow cytometry chip using “microfluidic drifting” based three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 024113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Stelick, S.J.; Sayam, L.G.; Yen, A.; Erickson, D.; Batt, C.A. Hydrodynamic optical alignment for microflow cytometry. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, G.; Persichetti, G.; Bernini, R. Micro flow cytometer with self-aligned 3D hydrodynamic focusing. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 6, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, B.R.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.Q.; Cao, X.; Lin, M. Integration of optical components on-chip for scattering and fluorescence detection in an optofluidic device. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 2784–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schonbrun, E.; Steinvurzel, P.E.; Crozier, K.B. A microfluidic fluorescence measurement system using an astigmatic diffractive microlens array. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marre, S.; Jensen, K.F. Synthesis of micro and nanostructures in microfluidic systems. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1183–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majedi, F.S.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Emami, S.H.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; VanDersarl, J.J.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P. Microfluidic assisted self-assembly of chitosan based nanoparticles as drug delivery agents. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliescu, C.; Tresset, G. Microfluidics-Driven Strategy for Size-Controlled DNA Compaction by Slow Diffusion through Water Stream. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8193–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, Z. Microfluidic hydrodynamic focusing for high-throughput applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 125006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, H.P. Chapter 1 Design of Refractive and Diffractive Micro-optics. In Micro-Optics: Elements, Systems and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gerchberg, R.W.; Saxton, W.O. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures. Optik 1972, 35, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Ruli, W. Optics diffraction transform pair and its application to design of diffractive phase elements. Acta Photonica Sin. 1997, 11, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Tonin, M.; Descharmes, N.; Houdré, R. Hybrid PDMS/glass microfluidics for high resolution imaging and application to sub-wavelength particle trapping. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, R.J. Flow in a pipe of rectangular cross-section. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1928, 120, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


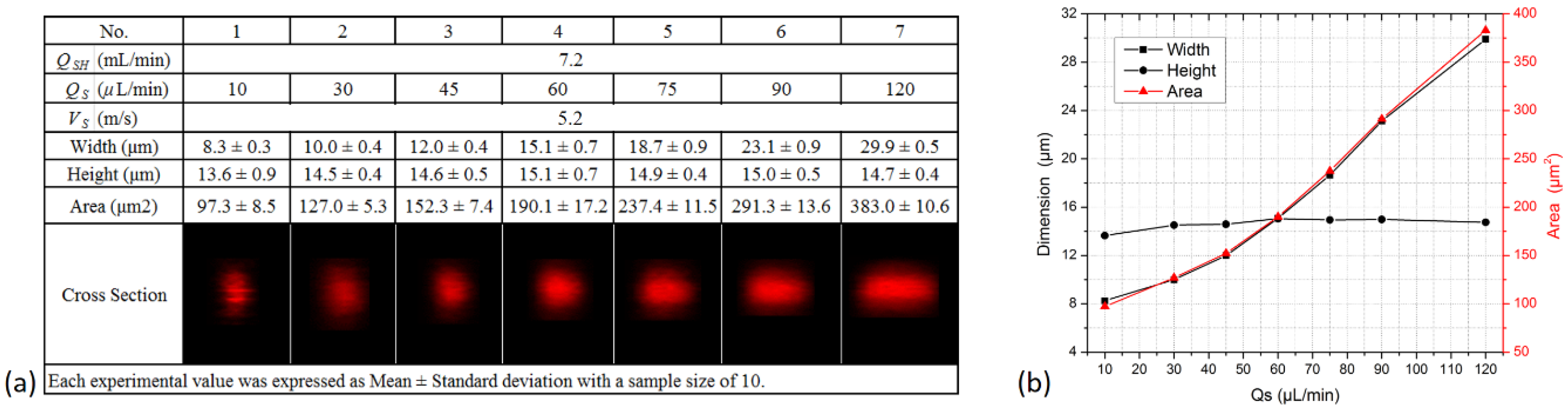

| Flow Cytometer | Microflow Cytometer | BD Accuri C6 | BD LSR Fortessa | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
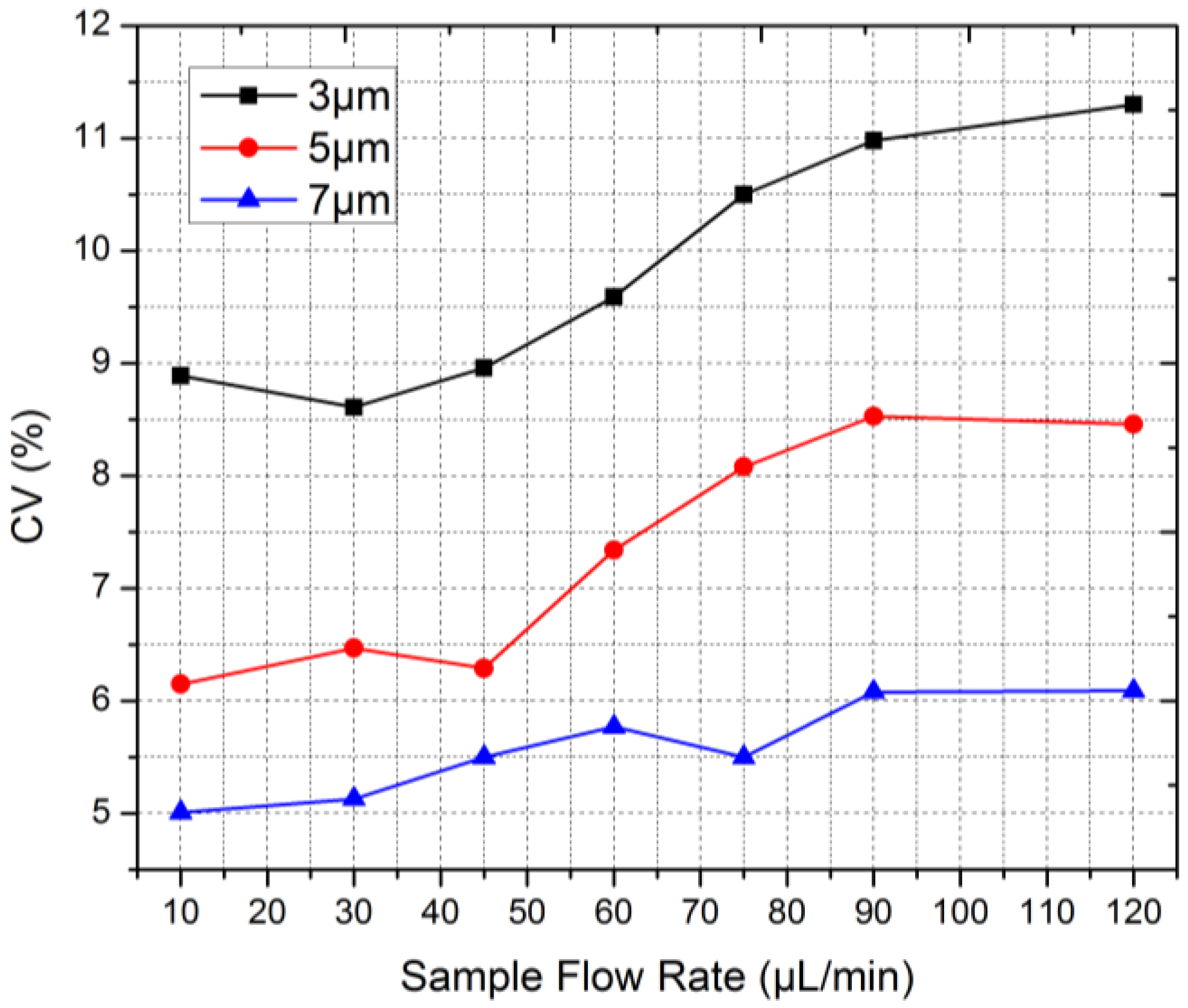
| Sample Flow Rate (μL/min) | 10 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 120 | 14 | 35 | 66 | 12 | 35 | 60 |
| 3 μm Beads | 8.9 | 8.6 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.3 | 12.1 | 13.0 | 13.7 | 5.6 | 5.8 | 5.9 |
| 5 μm Beads | 6.2 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 8.8 | 9.1 | 6.8 | 6.9 | 6.8 |
| 7 μm Beads | 5.0 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 5.5 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 13.4 | 14.7 | 14.8 | 9.7 | 9.2 | 9.9 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; You, Z. A Microflow Cytometer with a Rectangular Quasi-Flat-Top Laser Spot. Sensors 2016, 16, 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091474
Zhao J, You Z. A Microflow Cytometer with a Rectangular Quasi-Flat-Top Laser Spot. Sensors. 2016; 16(9):1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091474
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Jingjing, and Zheng You. 2016. "A Microflow Cytometer with a Rectangular Quasi-Flat-Top Laser Spot" Sensors 16, no. 9: 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091474
APA StyleZhao, J., & You, Z. (2016). A Microflow Cytometer with a Rectangular Quasi-Flat-Top Laser Spot. Sensors, 16(9), 1474. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091474





