A Spray-On Carbon Nanotube Artificial Neuron Strain Sensor for Composite Structural Health Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
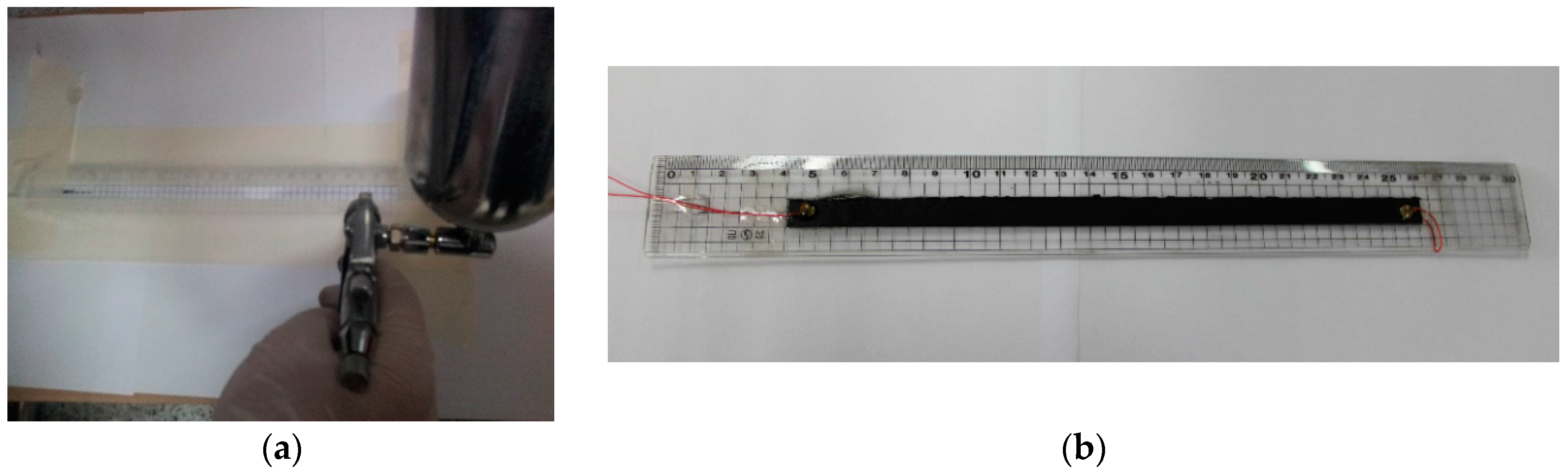
2. Fabrication of the Neuron
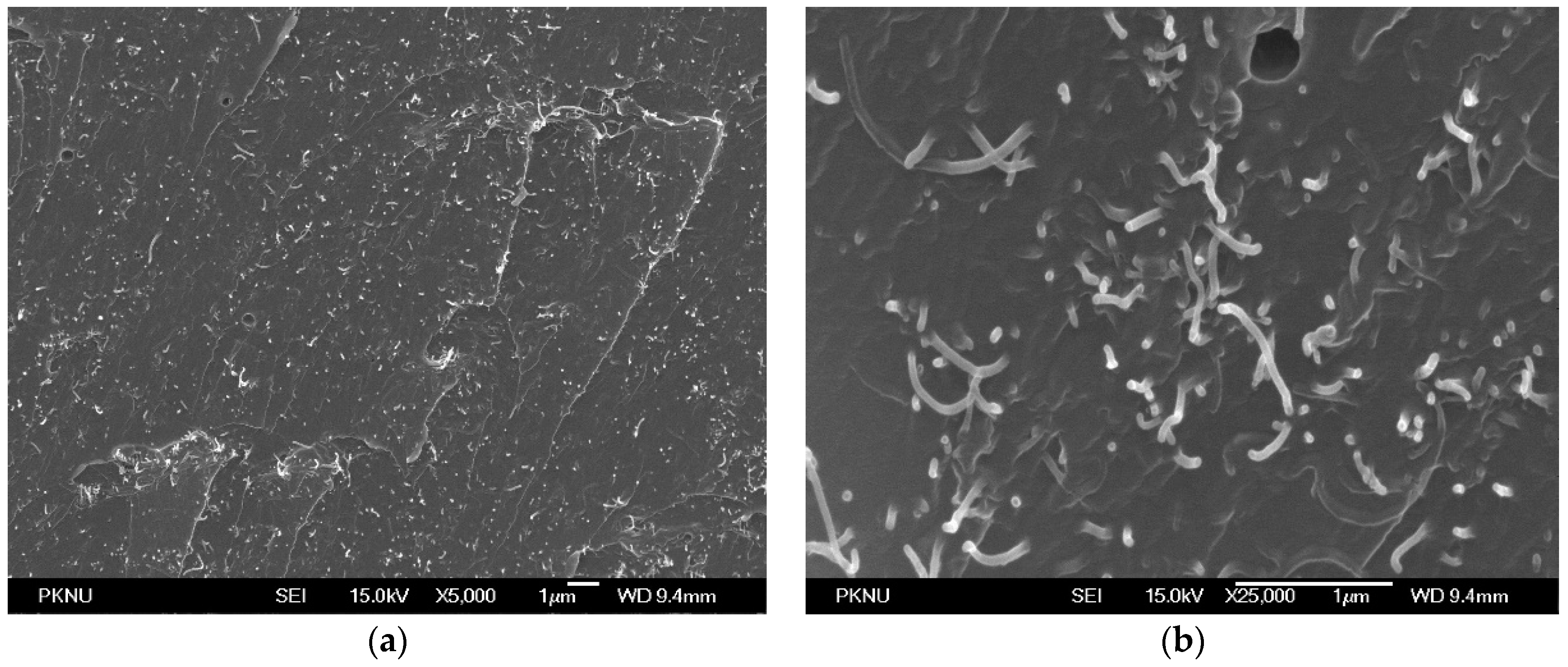
3. Characteristics of the MWCNT/Epoxy Strain Sensor
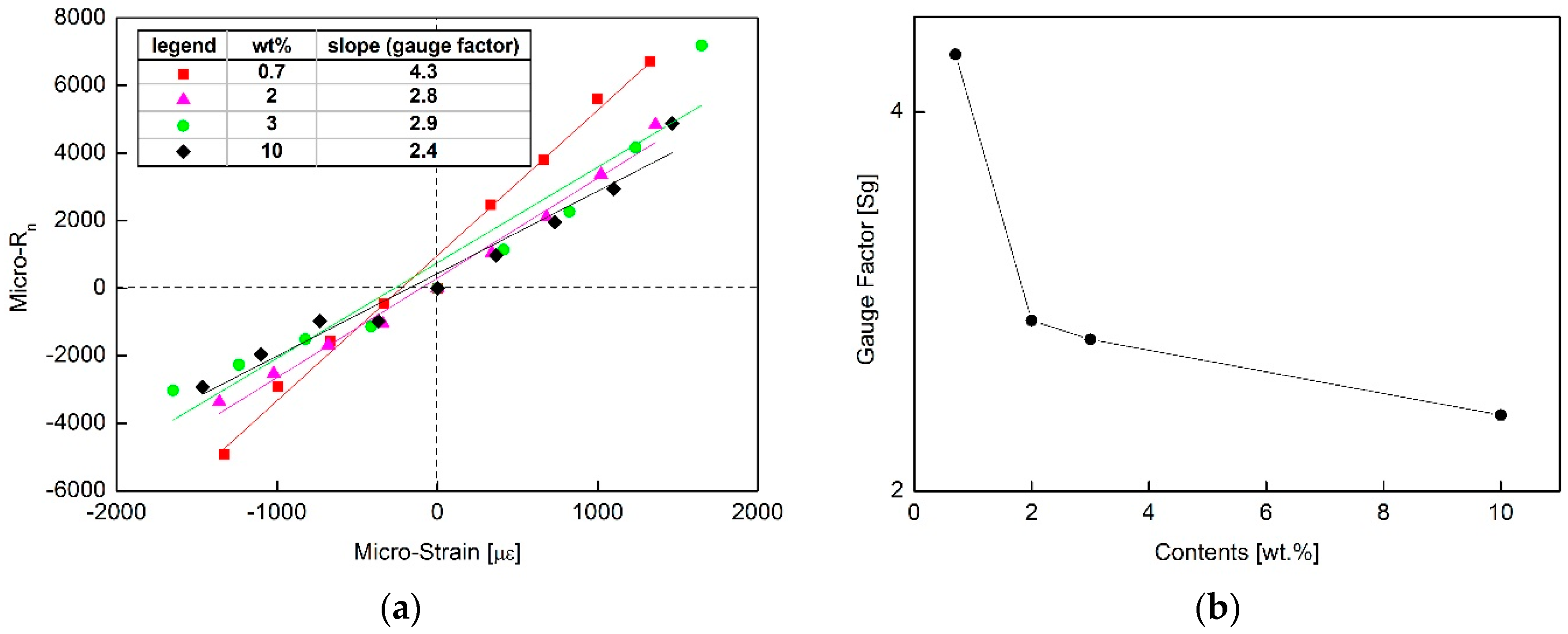
3.1. Piezoresistive Characteristics of the MWCNT/Epoxy Composites
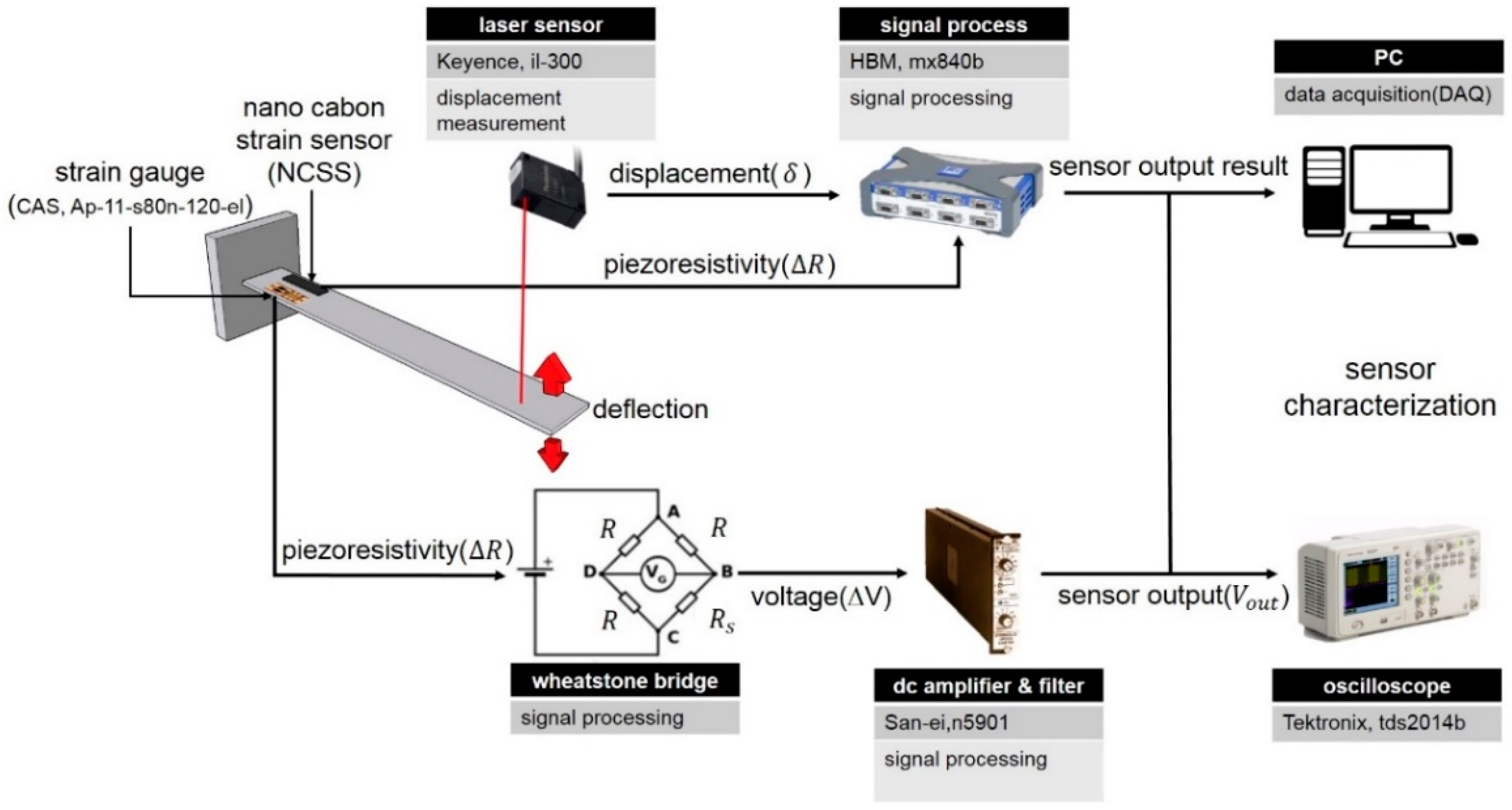
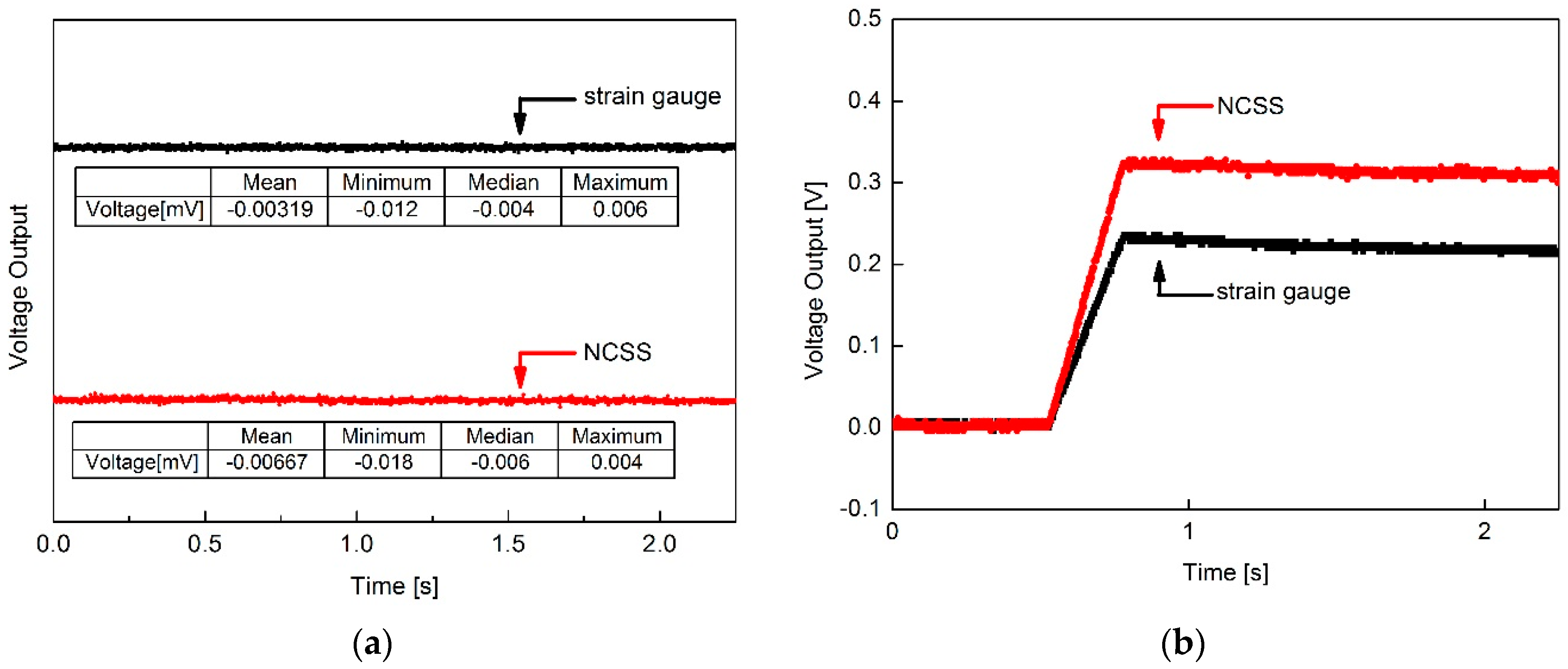
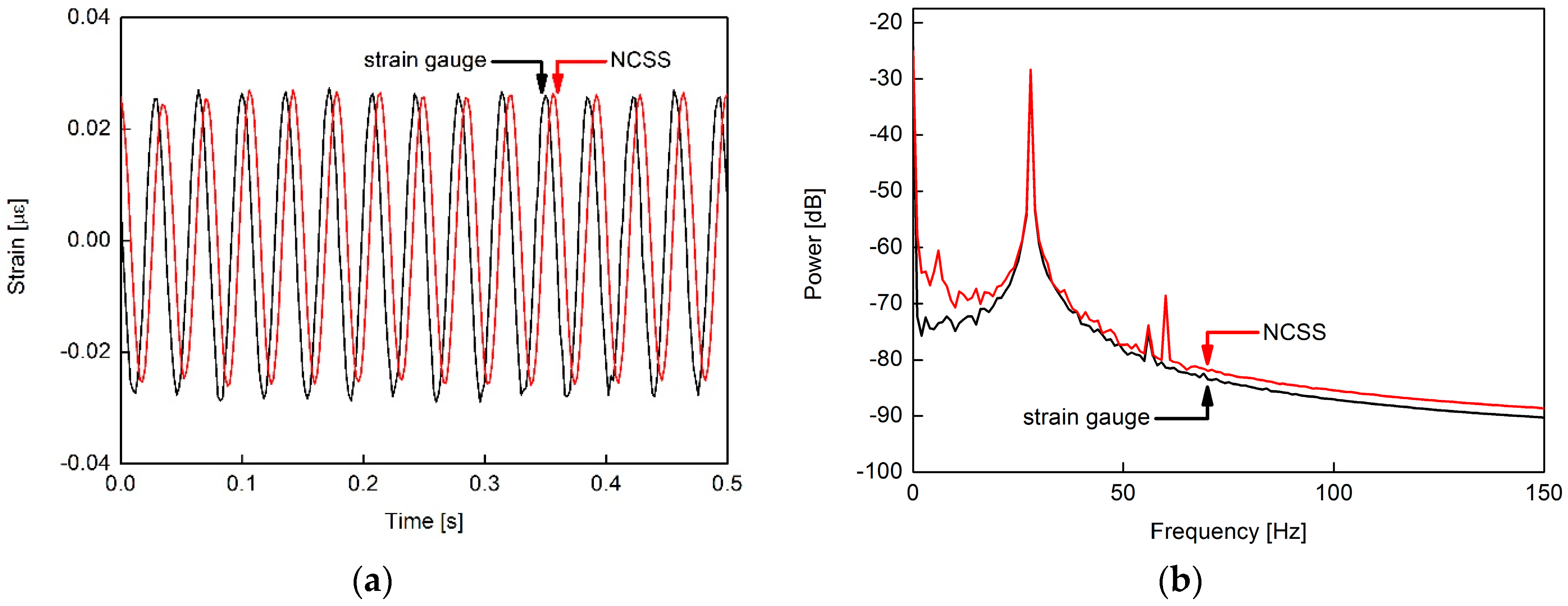
3.2. Strain Sensing Characteristics of the MWCNT/Epoxy NCSS
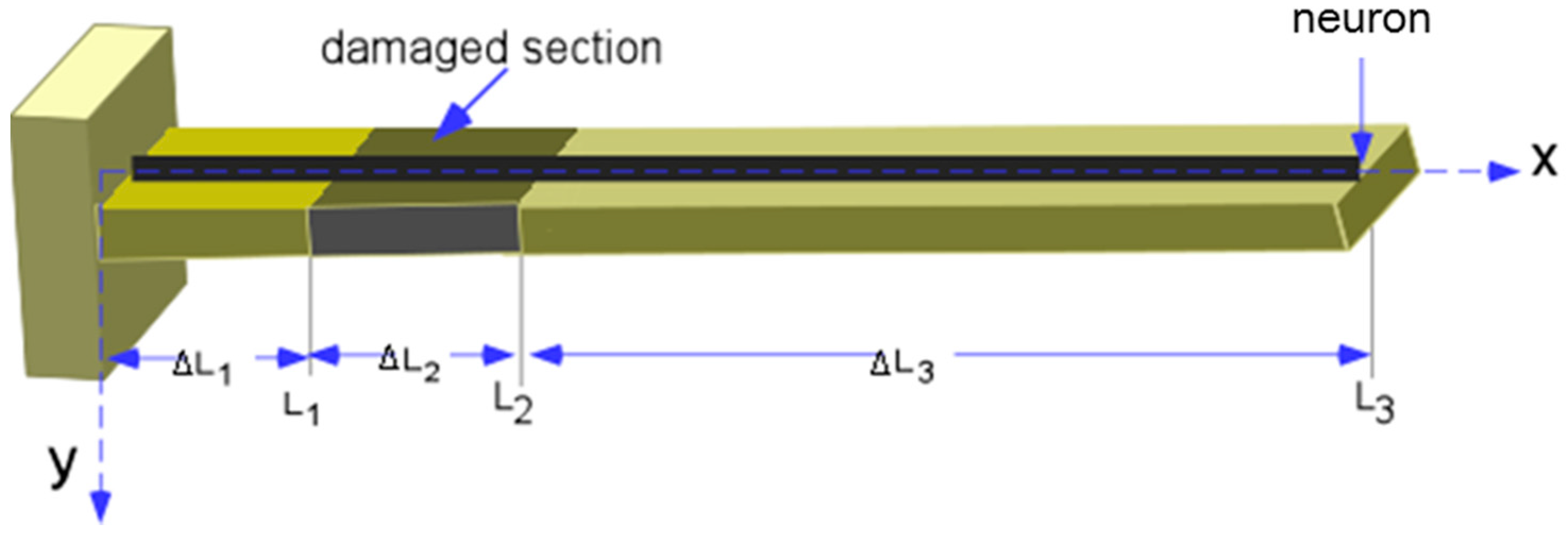
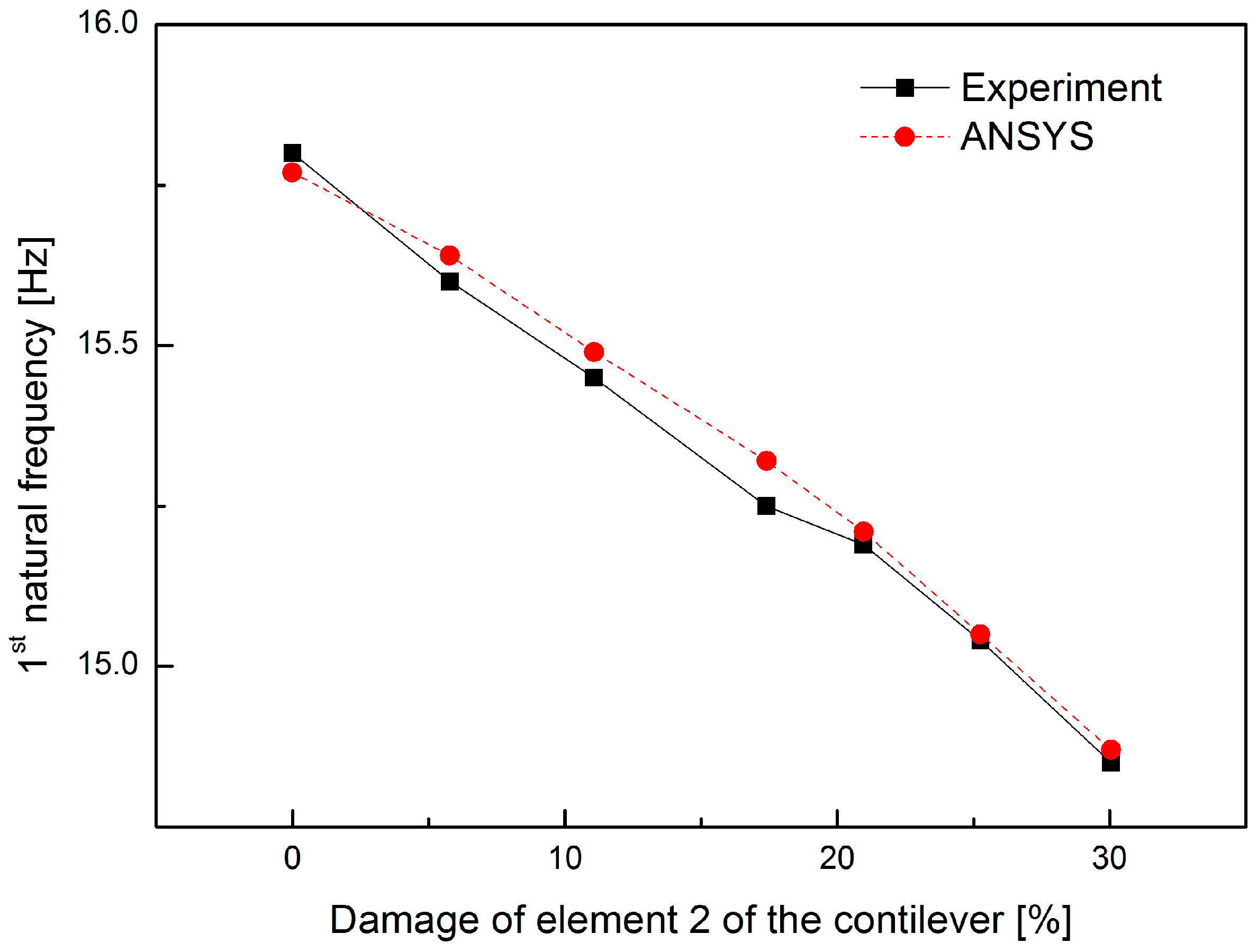
4. Cross-Sectional Damage Detection in a Vibrating Cantilever
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hale, J. Boeing 787 from the Ground Up. Available online: www.boeing.com (accessed on 16 February 2016).
- Cawley, P.; Woolfrey, A.M.; Adams, R.D. Natural frequency measurements for production quality control of fibre composites. Composites 1985, 16, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti, K.; Soutis, C. Structural health monitoring techniques for aircraft composite structures. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2010, 46, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Dujardin, E.; Ebbesen, T.W.; Yianilos, P.N.; Treacy, M.M.J. Young’s modulus of single-walled nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 14013–14019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Sakhidov, A.A.; de Heer, W.A. Carbon Nanotubes—the Route toward Applications. Science 2002, 297, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.; Schulz, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shanov, V.; Shi, D. A Carbon Nanotube Strain Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knite, M.; Tupureina, V.; Fuith, A.; Zavickis, J.; Teteris, V. Polyisoprene-Multi-wall carbon nanotube composites for sensing strain. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2006, 27, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.J.; Kim, J.; Lynch, J.P.; Kam, N.W.S.; Kotov, N.A. Multifunctional layer-by-layer carbon nanotube-polyelectrolyte thin films for strain and corrosion sensing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyola, B.R.; Zhao, Y.; Loh, K.J.; Saponara, V.L. The electrical response of carbon nanotube-based thin film sensors subjected to mechanical and environmental effects. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.S.; Song, S.A.; Kim, J.H.; Han, C.S. Fabrication of Carbon Nanotube Strain Sensors. KSME 2009, 33, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Yoon, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.W.; Gollapudi, R.; Subramaniam, S.; Narsimhadevara, S.; Hurd, D.; Kirikera, G.R.; Shanov, V.; et al. Introduction to carbon nanotube and nanofiber smart materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2005, 37, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, I.; Joung, K.Y.; Choi, G.R.; Schulz, M.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, S.H.; Ko, H.S. The Bulk Piezoresistive Characteristics of Carbon Nanotube Composites for Strain Sensing of Structures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 3736–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Yao, G.; Liao, F.; Gao, M.; Huang, Z.; Li, K.; Lin, Y. Highly stretchable, sensitive, and flexible strain sensors based on silver nanoparticles/carbon nanotubes composites. J. Alloys Compds. 2015, 652, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, J.; Schehl, N.; Bouchard, M.; Boehle, M. Health monitoring of structural composites with embedded carbon nanotube coated glass fiber sensors. Carbon 2014, 66, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgousis, G.; Pandis, C.; Kalamiotis, A.; Georgiopoulos, P.; Kyritsis, A.; Kontou, E.; Pissis, P.; Micusik, M.; Czanikova, K.; Kulicek, J.; et al. Strain sensing in polymer/carbon nanotube composites by electrical resistance measurement. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 68, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusay, S.; Iwasawaz, N. Piezoelectric paints as one approach to smart structural materials with health-monitoring capabilities. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, Y.; Aldraihem, O.; Baz, A. Smart paint sensor for monitoring structural vibrations. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capsal, J.F.; David, C.; Dantras, E.; Lacabanne, C. Piezoelectric sensing coating for real time impact detection and location on aircraft structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 2012, 21, 055021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutham, R.K.; Shinde, V.; Schulz, M.J.; Ghoshal, A.; Sundaresan, M.; Allemang, R. Damage localisation in composite and metallic structures using a structural neural system and simulated acoustic emissions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2007, 21, 280–297. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, R.B. Vibration-Based Condition Monitoring; Wiley: West Sussex, UK, 2011; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.K.; Biswas, M.; Samman, M.M. Damage detection from changes in curvature mode shapes. J. Sound Vib. 1991, 145, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebling, S.W.; Farrar, C.R.; Prime, M.B. A Review of Damage Identification Methods that Examine Changes in Dynamic Properties. Shock Vib. Dig. 1998, 30, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauhofer, W.; Kovacs, J.Z. A review and analysis of electrical percolation in carbon nanotube polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordas, K.; Mustonen, T.; Toth, G.; Jantunen, H.; Lajunen, M.; Soldano, C.; Talapatra, S.; Kar, S.; Vajtai, R.; Ajayan, P.M. Inkjet printing of electrically conductive patterns of carbon nanotubes. Small 2006, 2, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Foil Strain Gauge | Nano Composite Strain Sensor (NCSS) | |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance [Ω] | 120 | 2.7 k |
| Gauge factor | 2.1 | 2.8 |
| Size [mm] w × l × t | 6 × 40 × 0.07 | 9.15 × 51.76 × 2.85 |
| Thickness t (m) | Beam width B (m) | Estimated E E (Gpa) | Density D (kg/m3) | Length 1 L1 (m) | Length 2 L2 (m) | Length 3 L3 (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00346 | 0.024 | 25.1 | 1806 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.28 |
| Damage to Element 2 (%) | Experimental (Hz) | ANSYS (Hz) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy | 0 | 15.80 | 15.77 |
| Case 1 | 5.78 | 15.60 | 15.64 |
| Case 2 | 11.08 | 15.45 | 15.49 |
| Case 3 | 17.40 | 15.25 | 15.32 |
| Case 4 | 20.96 | 15.19 | 15.21 |
| Case 5 | 25.26 | 15.04 | 15.05 |
| Case 6 | 30.05 | 14.85 | 14.87 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, G.; Lee, J.W.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.-S.; Schulz, M.J.; Moon, C.K.; Lim, K.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Kang, I. A Spray-On Carbon Nanotube Artificial Neuron Strain Sensor for Composite Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081171
Choi G, Lee JW, Cha JY, Kim Y-J, Choi Y-S, Schulz MJ, Moon CK, Lim KT, Kim SY, Kang I. A Spray-On Carbon Nanotube Artificial Neuron Strain Sensor for Composite Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors. 2016; 16(8):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081171
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Gyeongrak, Jong Won Lee, Ju Young Cha, Young-Ju Kim, Yeon-Sun Choi, Mark J. Schulz, Chang Kwon Moon, Kwon Tack Lim, Sung Yong Kim, and Inpil Kang. 2016. "A Spray-On Carbon Nanotube Artificial Neuron Strain Sensor for Composite Structural Health Monitoring" Sensors 16, no. 8: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081171
APA StyleChoi, G., Lee, J. W., Cha, J. Y., Kim, Y.-J., Choi, Y.-S., Schulz, M. J., Moon, C. K., Lim, K. T., Kim, S. Y., & Kang, I. (2016). A Spray-On Carbon Nanotube Artificial Neuron Strain Sensor for Composite Structural Health Monitoring. Sensors, 16(8), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16081171






