Non-Contact Measurement of the Spectral Emissivity through Active/Passive Synergy of CO2 Laser at 10.6 µm and 102F FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Spectrometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
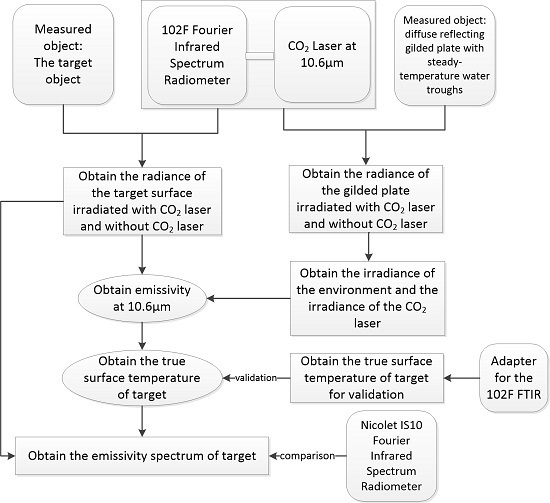
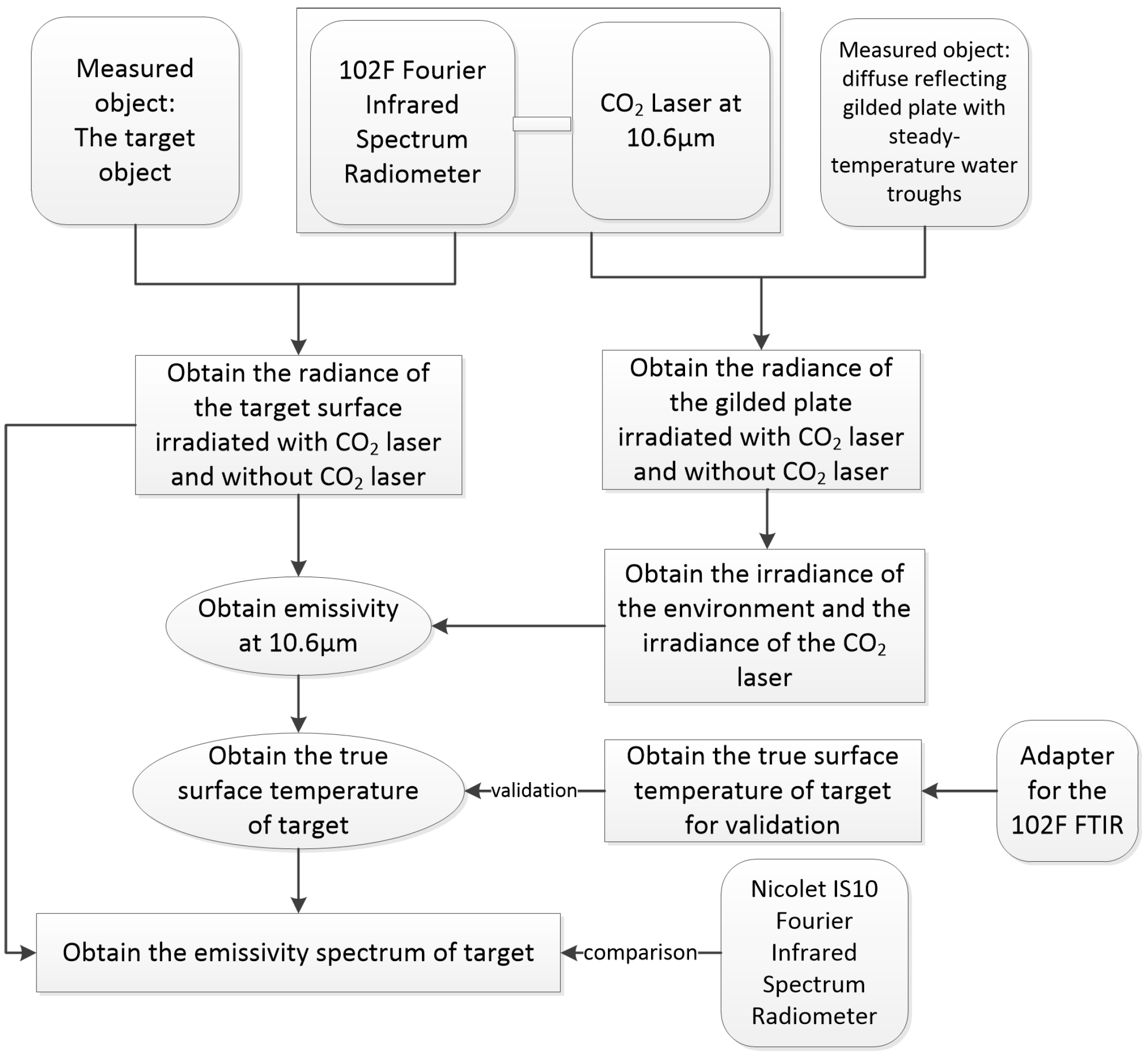
2.1. Measuring Concepts
2.2. Measuring Procedures and Algorithm Derivation
2.2.1. The Determination of the Emissivity at 10.6 µm ()
2.2.2. The Determination of the Irradiance of the CO2 Laser ()
2.2.3. The Determination of the Irradiance of the Environment ()
2.2.4. The Calculation of the True Temperature of the Target Surface (Ts)
2.2.5. The Determination of the Emissivity Spectrum of the Target Surface
3. Measuring Instruments
3.1. 102F FTIR Spectrometer
3.2. The CO2 Laser
3.3. Diffuse Reflecting Gilded Plate with Steady-Temperature Water Troughs
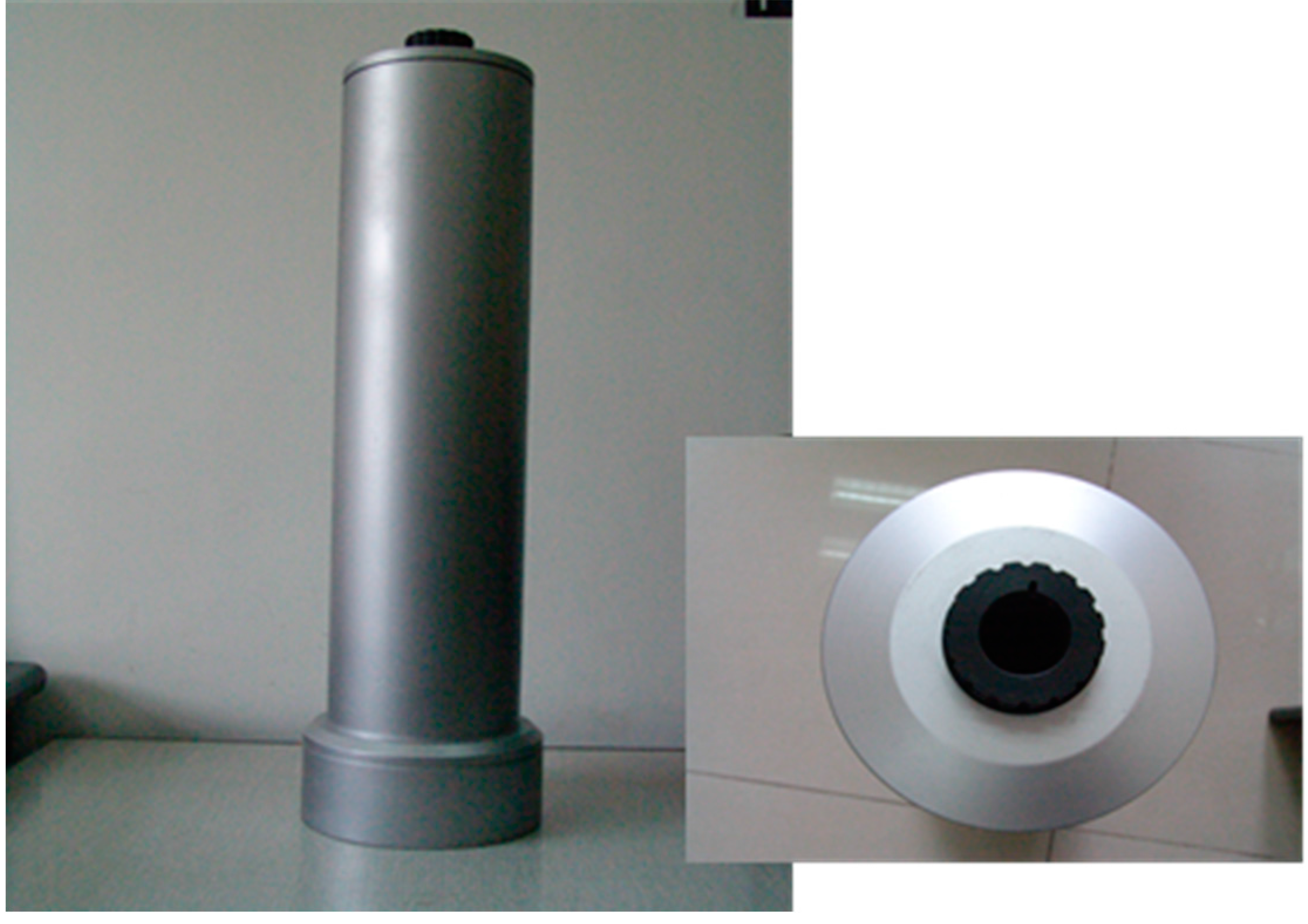
3.4. The Adapter of the 102F FTIR Spectrometer
3.5. Nicolet IS10 FTIR Spectrometer
4. Experiment and Validation
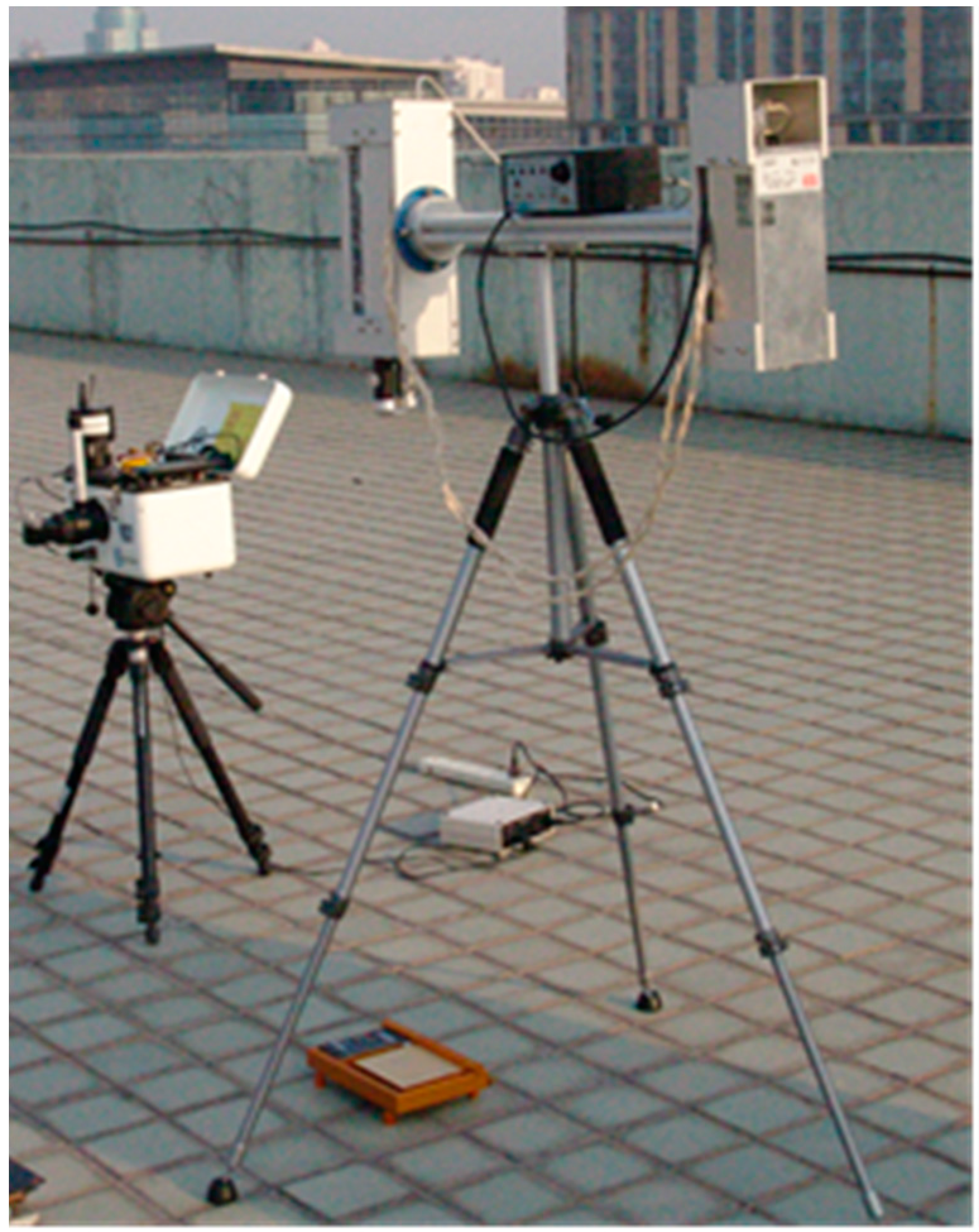
4.1. Experiment Description
4.2. Validation of the Retrievals of the True Temperature of the Sample
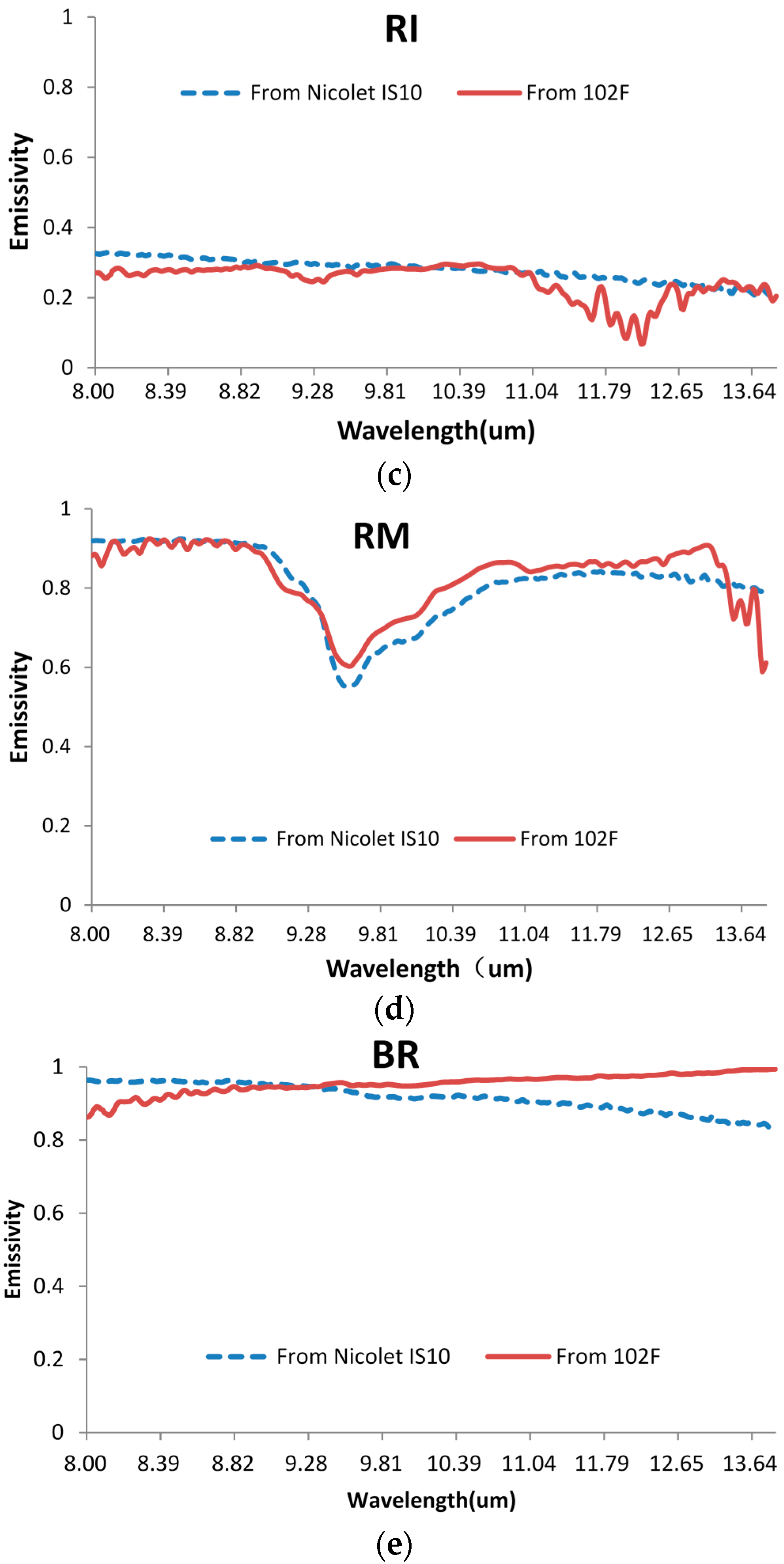
4.3. The Comparison of the Emissivities Retrieved by the Nicolet FTIR Spectrometer and by the CO2 Laser and 102F FTIR Spectrometer
5. Conclusions and Discussions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahle, A.B.; Madura, D.P.; Soha, J.M. Middle infrared multispectral aircraft scanner data: Analysis for geologic applications. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 2279–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, K. Spectral ratio method for measuring emissivity. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K. Two-temperature method for measuring emissivity. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Rokugawa, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Cothern, J.S.; Hook, S.; Kahle, A.B. A temperature and emissivity separation algorithm for Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kealy, P.S.; Gabell, A.R. Estimation of Emissivity and Temperature Using Alpha Coefficients; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Hook, S.J.; Gabell, A.R.; Green, A.A.; Kealy, P.S. A comparison of Techniques for Extracting Emissivity Information from Thermal Infrared Data for Geologic Studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 42, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, F.; Li, Z.L. Temperature-independent spectral indices in thermal infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 32, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Becker, F. Feasibility of land surface temperature and emissivity determination from AVHRR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 43, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-L.; Becker, F.; Stoll, M.P. Evaluation of six methods for extracting relative emissivity spectra from thermal infrared images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 69, 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-L.; Petitcolin, F.; Zhang, R.H. A physically based algorithm for land surface emissivity retrieval from combined mid-infrared and thermal infrared data. Sci. China Ser. E Technol. Sci. 2000, 43, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Stoll, M.P.; Zhang, R.H.; Jia, L.; Su, Z.B. On the separate retrieval off soil and vegetation temperatures from ATSR data. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2001, 44, 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Ren, H.; Yan, G.; Wan, Z.; Trigo, I.F.; Sobrino, J.A. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: Current status and perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 131, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.M.; Li, Z.L. A physics-based algorithm for retrieving land surface emissivity and temperature from EOS/MODIS data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 980–996. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z. MODIS Land-Surface Temperature Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Barducci, A.; Pippi, I. Temperature and emissivity retrieval from remotelysensed images using the “grey body emissivity” method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R. Lithologic mapping of silicate rocks using TIMS. In The TIMS Data Users’ Workshop; JPL Publication: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Abbott, E.A.; Gilson, L.; Hulley, G.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. Residual errors in ASTER temperature and emissivity standard products AST08 and AST05. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3681–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.R.; Rokugawa, S.; Hook, S.J.; Matsunaga, T.; Kahle, A.B. Temperature/Emissivity Separation Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document, Version 2.4; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Borel, C. Iterative retrieval of surface emissivity and temperature for a hyperspectral sensor. In Proceedings of the First JPL Workshop on Remote Sensing of Land Surface Emissivity, Pasadena, CA, USA, 6–8 May 1997; pp. 1–5.
- Borel, C. Surface emissivity and temperature retrieval for a hyperspectral sensor. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seattle, Washington, DC, USA, 6–10 July 1998; pp. 546–549.
- Borel, C. Error analysis for a temperature and emissivity retrieval algorithm for hyperspectral imaging data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5029–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, H.; Nerry, F.; Li, C.R.; Li, Z.-L. Temperature and emissivity retrievals from hyperspectral thermal infrared data using linear spectral emissivity constraint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Chédin, A.; Scott, N.A.; Rossow, W.B. A regularized neural net approach for retrieval of atmospheric and surface temperatures with the IASI instrument. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2002, 41, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Prigent, C.; Rossow, W.B.; Rothstein, M. A new neural network approach including first guess for retrieval of atmospheric water vapor, cloud liquid water path, surface temperature, and emissivities over land from satellite microwave observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 106, 14887–14907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, F.; Rossow, W.B.; Scott, N.A.; Chédin, A. Remote sensing from the infrared atmospheric sounding interferometer instrument 2. Simultaneous retrieval of temperature, water vapor, and ozone atmospheric profiles. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Weisz, E.; Zhou, D.K. Physical retrieval of surface emissivity spectrum from hyperspectral infrared radiances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Wan, Z.; Moeller, C.C.; Menzel, W.P.; Gumley, L.E. Simultaneous retrieval of atmospheric profiles, land-surface temperature, and surface emissivity from moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer thermal infrared data: Extension of a two-step physical algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.L.; Wan, Z.; Moeller, C.C.; Menzel, W.P.; Gumley, L.E.; Zhang, Y. Retrieval of geophysical parameters from Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer thermal infrared data: Evaluation of a two-step physical algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 3537–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, P.; Kochendorfer, J.; Dumas, E.J.; Guillevic, P.C.; Baker, B.B.; Meyers, T.P.; Martos, B. Comparison of in-situ, aircraft, and satellite Land Surface Temperature measurements over a NOAA Climate Reference Network Site. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 165, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Munoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A. A generalized single-channel method for retrieving land surface temperature from remote sensing data. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.H.; Karnieli, A.; Berliner, P. A mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from Landsat TM data and its application to the Israel-Egypt border region. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3719–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, E.; Caselles, V.; Badenas, C. Emissivity measurements of several soils and vegetation types in the 8–14 μm wave band: Analysis of two field methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 490–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mira, M.; Valor, E.; Boluda, R.; Caselles, V.; Coll, C. Influence of soil water content on the thermal infrared emissivity of bare soils: Implication for land surface temperature determination. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrino, J.A.; Mattar, C.; Pardo, P.; Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Hook, S.J.; Baldridge, A.; Ibañez, R. Soil emissivity and reflectance spectra measurements. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 3664–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.H. Emissivity measurements for long distance using CO2 laser. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1985, 23, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H. Far Distance Emissivity Measurement of Object by CO2-Laser. Chin. Sci. Bull. 1987, 32, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H. A proposed approach to determine the emissivities of territorial surface from airborne and space borne. Int. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 9, 591–595. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.H.; Sun, X.M.; Zhu, Z.L. Feasibility of measuring directly distribution of the emissivities for territorial surface on sensing platforms. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Remote Sensing A Scientific Vision for Sustainable Development, Singapore, 3–8 August 1997.
- Nerry, F.; Stoll, M.P.; Kologo, N. Scattering of a CO2 laser beam at 10.6 µm by bare soils: Experimental study of the polarized bi-directional scattering coeffcient; model and comparison with directional emissivity measurements. Appl. Opt. 1991, 30, 3984–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kologo, N.; Stoll, M.P. CO2 laser light scattering by bare soil for emissivity measurement: Absolute calibration and correlation with backscattering and composition. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zallat, J.; Stoll, M.P. Polarized bidirectional scattering by bare soils. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opy. 2000, 2, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korb, A.R.; Dybwad, P.; Wadsworth, W.; Salisbury, J.W. Spectroradiometer for field measurements of radiance and emissivity. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 1679–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulley, G.C.; Hook, S.J.; Baldridge, A.M. Investigating the effects of soil moisture on thermal infrared land surface temperature and emissivity using satellite retrievals and laboratory measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Spectral range | 2 to 16 mircon meter |
| Spectral resolution | 4 cm−1, 8 cm−1, and 16 cm−1 (adjustable), 2 cm−1 can be chosen |
| Spectral precision | ±1 cm−1 covers the whole spectral range |
| Scanning speed | 1 scan/s, 4 cm−1 resolution |
| Sampling frequency | 5 kHz |
| Signal bandwidth | 2 kHz |
| Type: C-20A | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Output power | 20 W |
| Waveband | 10.55~10.63 μm |
| PC-1 controller | Controller component: PC-1 24 KHz |
| Cooling mode | Air cooling |
| Power | C-20A power adapter |
| Samples | Rough Surface of Marble Plate (RM) | Polished Surface of Aluminum Plate (PA) | Oxidized Surface of Copper Plate (OC) | Rusty Iron Plate (RI) | Black Rubber Sheet (BR) | Paper Board (PB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emissivity at 10.6µm | 0.844 | 0.102 | 0.362 | 0.239 | 0.964 | 0.871 |
| Measured Ts (TS_m, K) | 301.8 | 300.6 | 301.1 | 301.5 | 301.2 | 301.3 |
| Retrieved Ts (TS_e, K) | 301.2 | 301.5 | 301.8 | 300.8 | 301.7 | 301.5 |
| Difference (K) | 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Objects | RM | RI | BR | OC | PA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE of the Spectral Emissivity | 0.046 | 0.049 | 0.073 | 0.077 | 0.122 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.-H.; Su, H.-B.; Tian, J.; Mi, S.-J.; Li, Z.-L. Non-Contact Measurement of the Spectral Emissivity through Active/Passive Synergy of CO2 Laser at 10.6 µm and 102F FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Spectrometer. Sensors 2016, 16, 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070970
Zhang R-H, Su H-B, Tian J, Mi S-J, Li Z-L. Non-Contact Measurement of the Spectral Emissivity through Active/Passive Synergy of CO2 Laser at 10.6 µm and 102F FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Spectrometer. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070970
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ren-Hua, Hong-Bo Su, Jing Tian, Su-Juan Mi, and Zhao-Liang Li. 2016. "Non-Contact Measurement of the Spectral Emissivity through Active/Passive Synergy of CO2 Laser at 10.6 µm and 102F FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Spectrometer" Sensors 16, no. 7: 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070970
APA StyleZhang, R.-H., Su, H.-B., Tian, J., Mi, S.-J., & Li, Z.-L. (2016). Non-Contact Measurement of the Spectral Emissivity through Active/Passive Synergy of CO2 Laser at 10.6 µm and 102F FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Spectrometer. Sensors, 16(7), 970. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070970