An Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibodies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
2.3.1. Preparation of a Large Phage Displayed Single-Chain Fragment Variable (scFv) Antibody Library
2.3.2. Screening of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
2.3.3. Characterization of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody Positive Clones by ELISA
2.3.4. DNA Sequencing and Binding Affinity of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
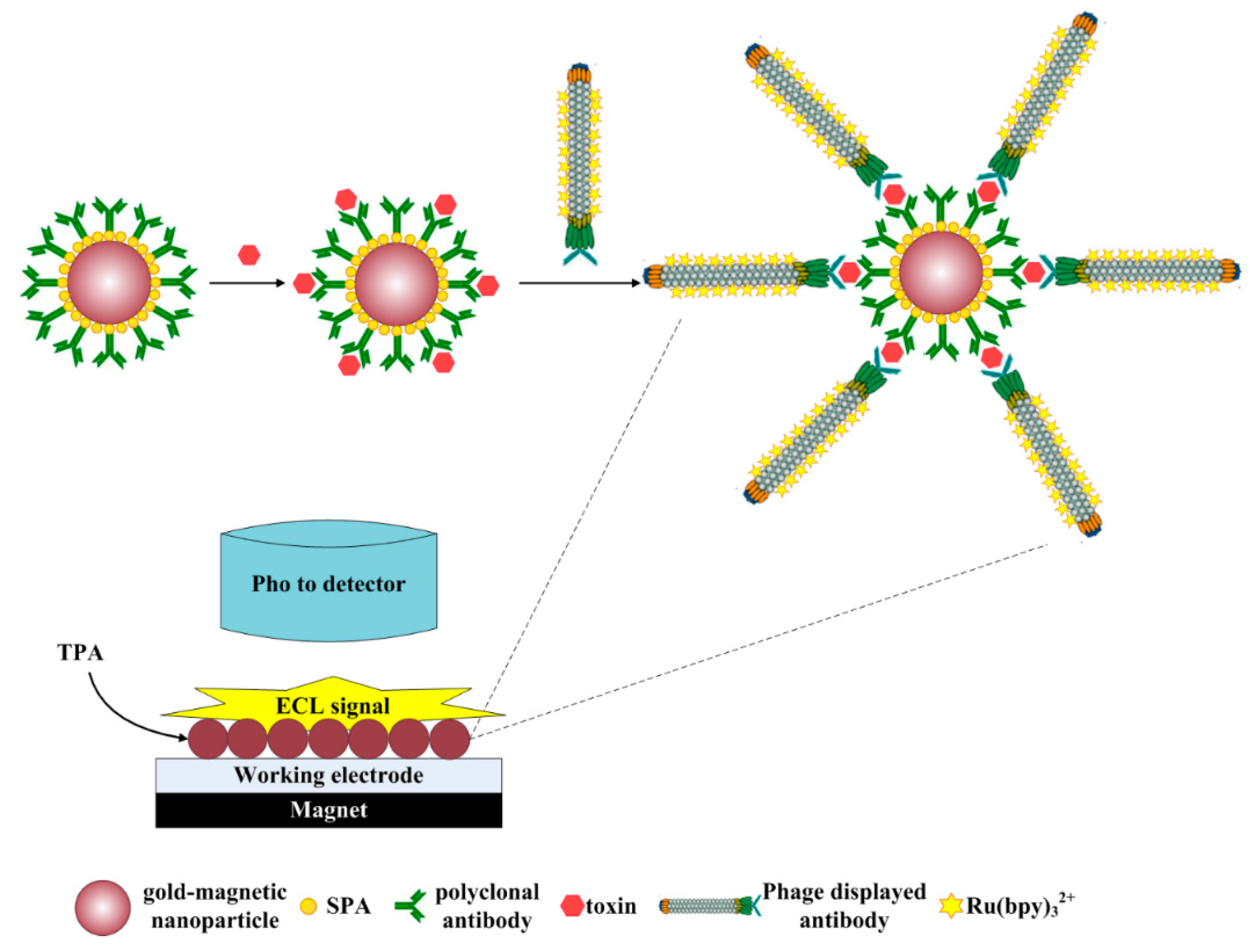
2.4. Preparation of the SPA-Coated Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized Capturing Probes
2.5. Preparation of ECL Probes
2.6. Establishment of the ECL Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibody
2.7. Regeneration of the Electrodes Surface of ECL Immunosensor
2.8. Limit of Detection, Linear Range and Specificity
2.9. Measurement of Simulated Ricin Samples
3. Results
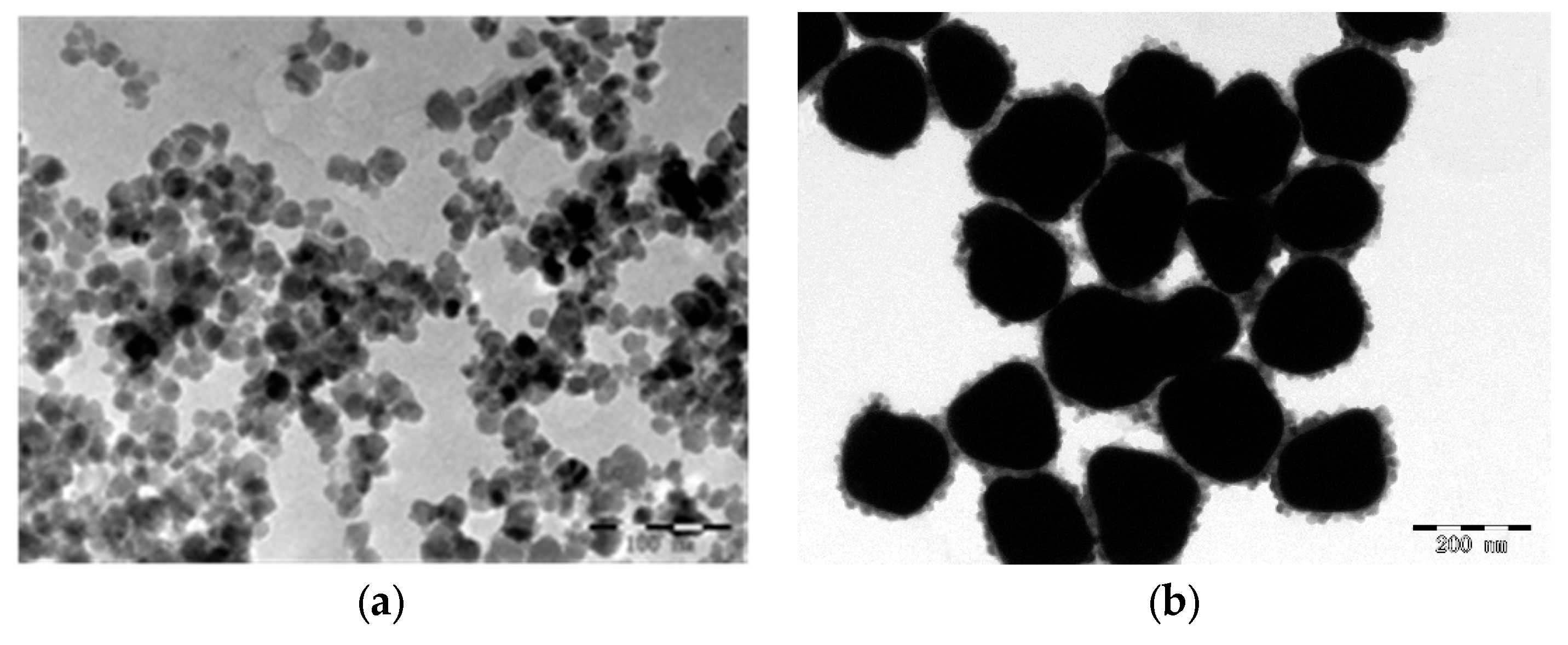
3.1. Preparation of Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.2. Preparation of Magnetic Ricin-Capturing Probe
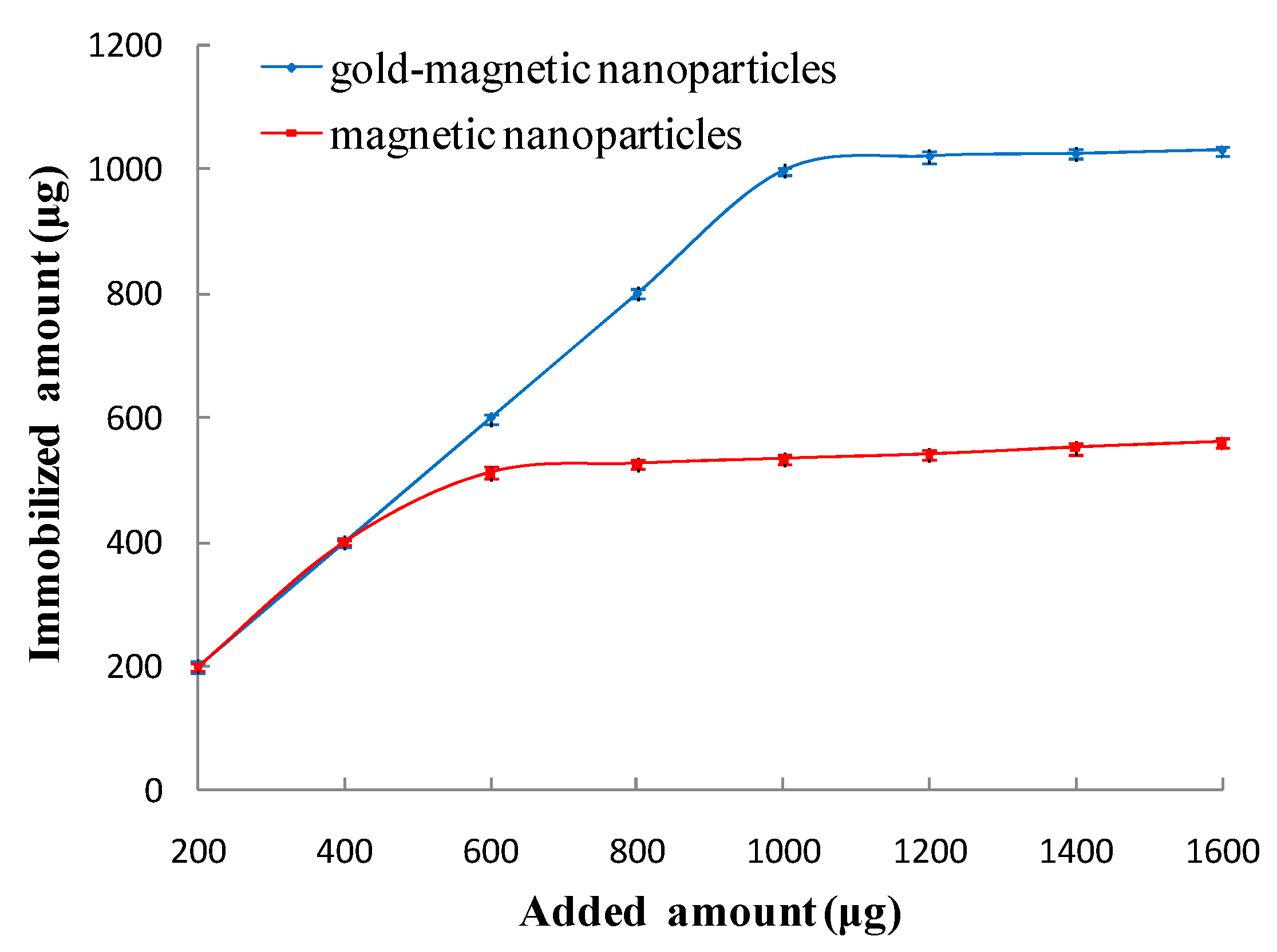
3.2.1. Optimal Amount of Immobilized Anti-Ricin Polyclonal Antibody
3.2.2. Qualification of the SPA-Coated Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized Capturing Probe
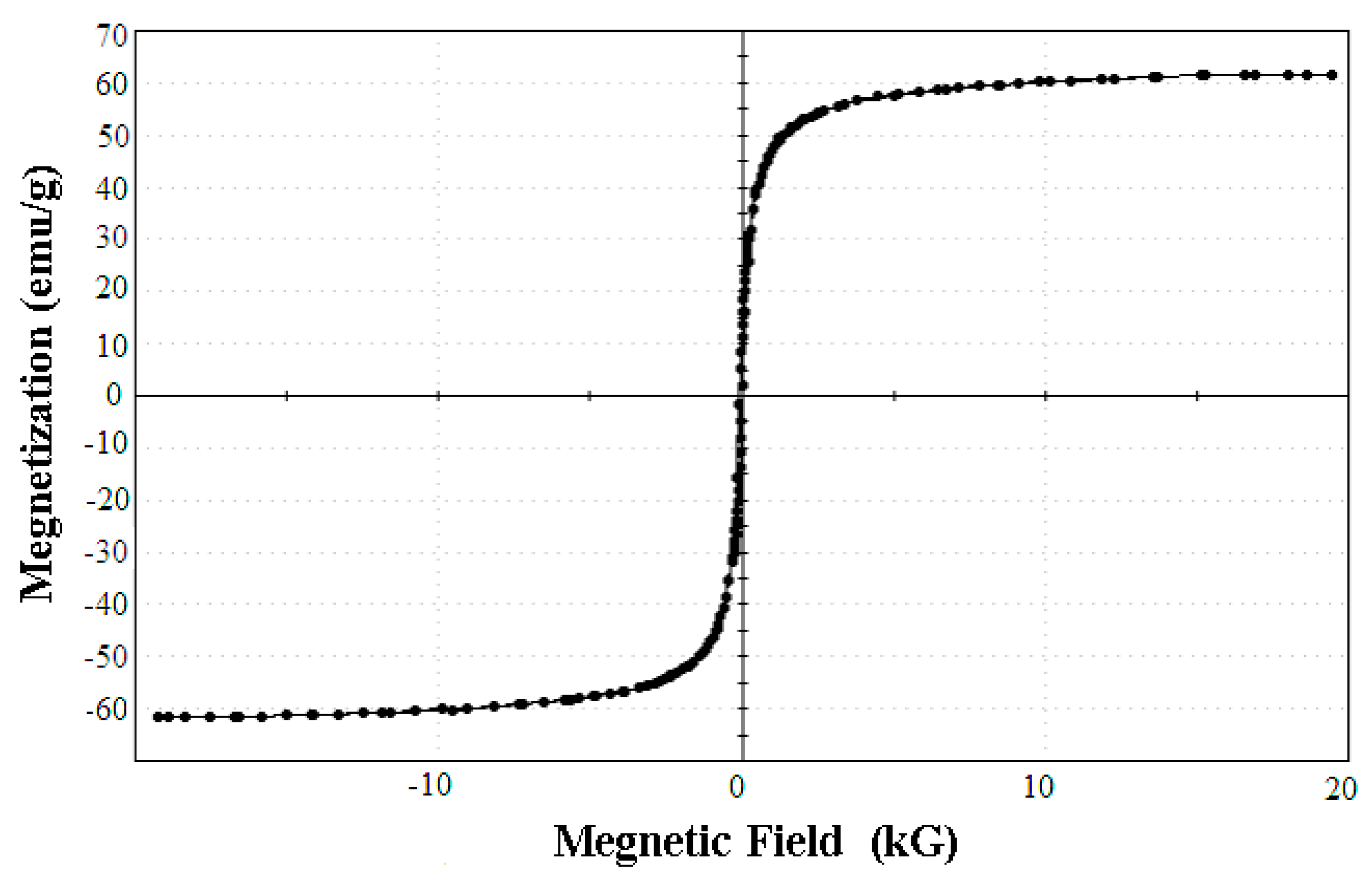
The Magnetic Features of the SPA-Coated Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized Capturing Probe
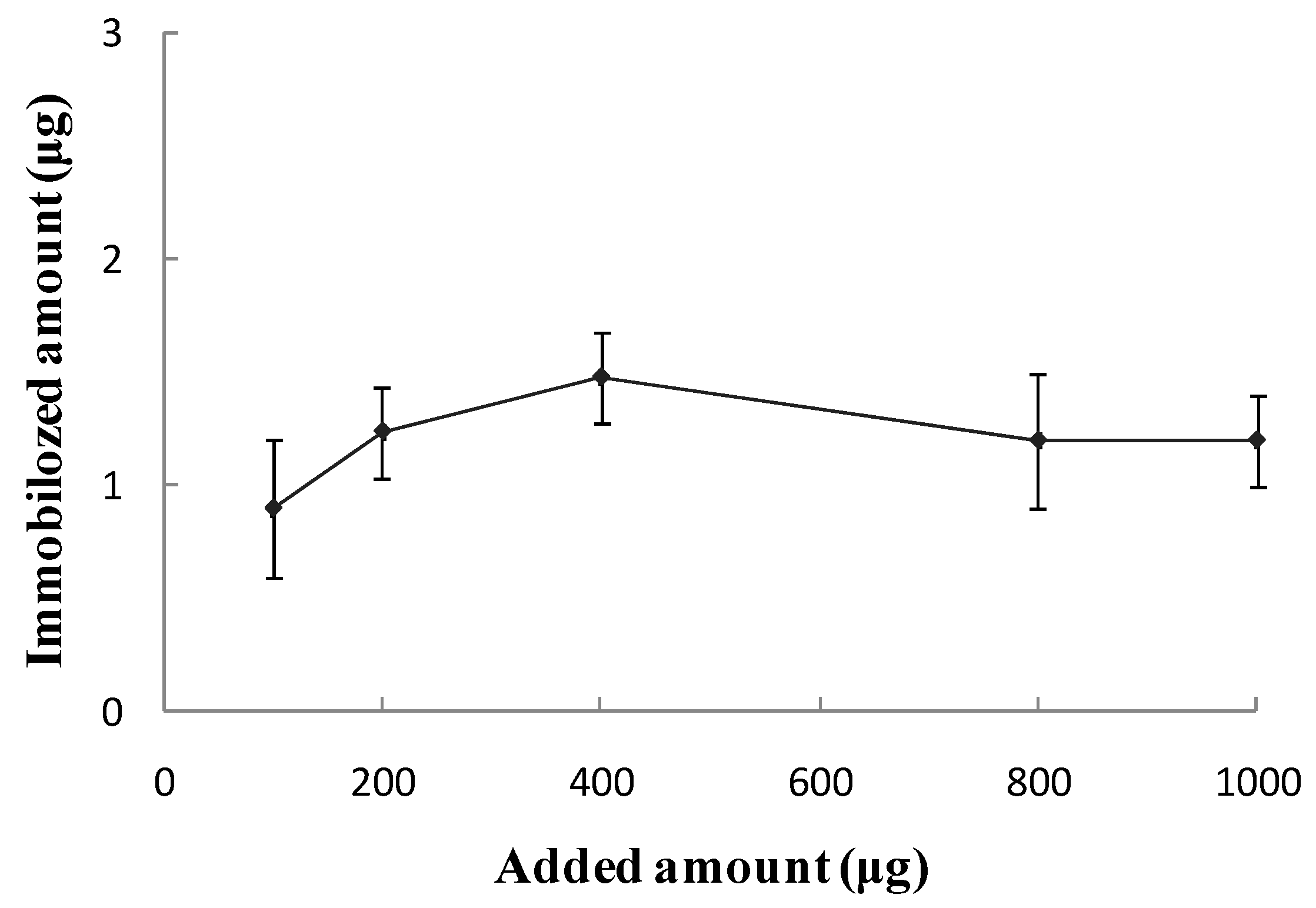
Biological Activity of the SPA-Coated Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles Functionalized Capturing Probe
3.3. The Preparation and Characterization of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
3.3.1. Screening of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
3.3.2. Characterization of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody Positive Clones by ELISA
3.3.3. DNA Sequencing and Binding Affinity of Anti-Ricin Phage Displayed Antibody
3.4. The Qualification Feature of ECL Probe
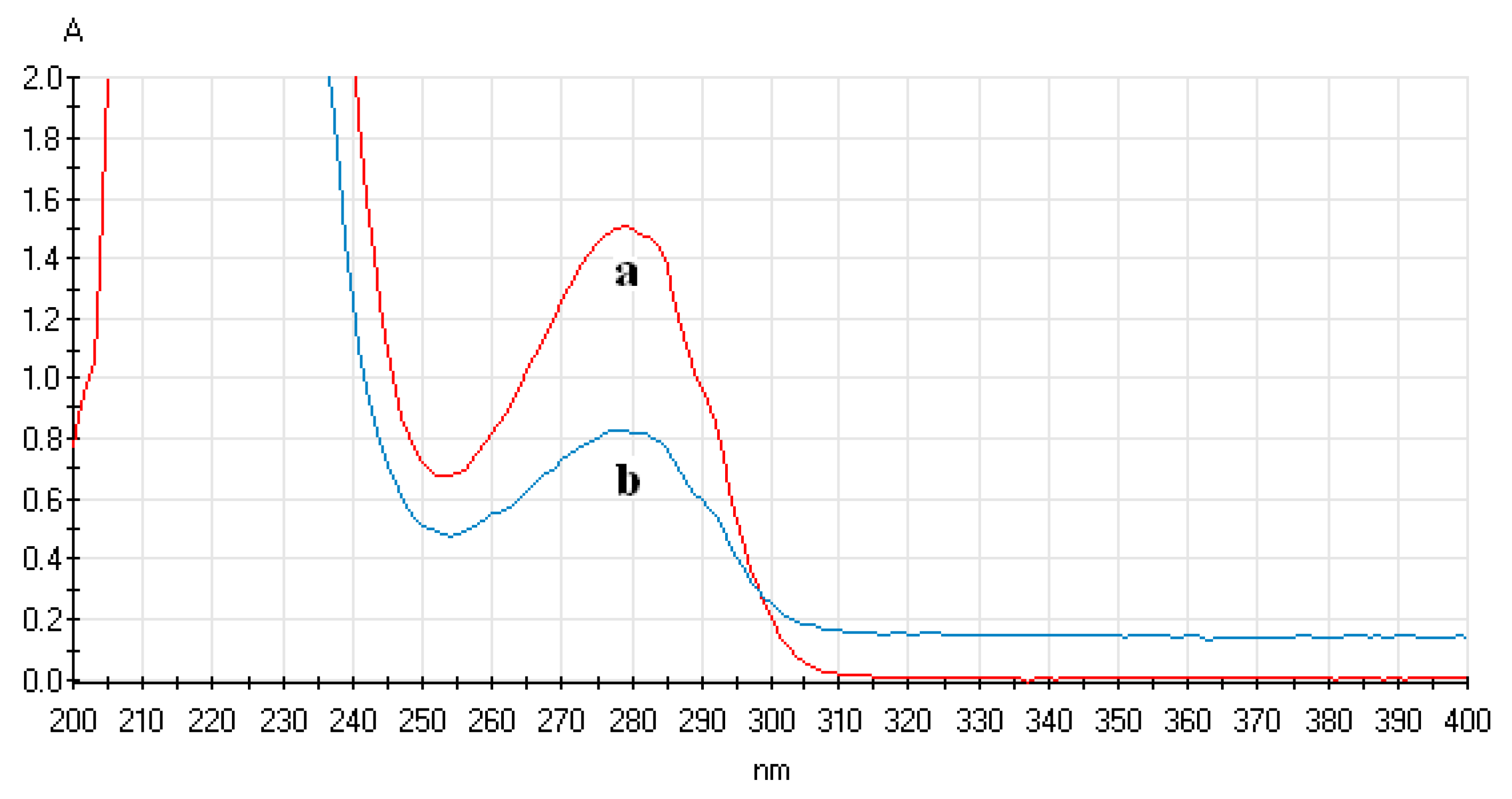
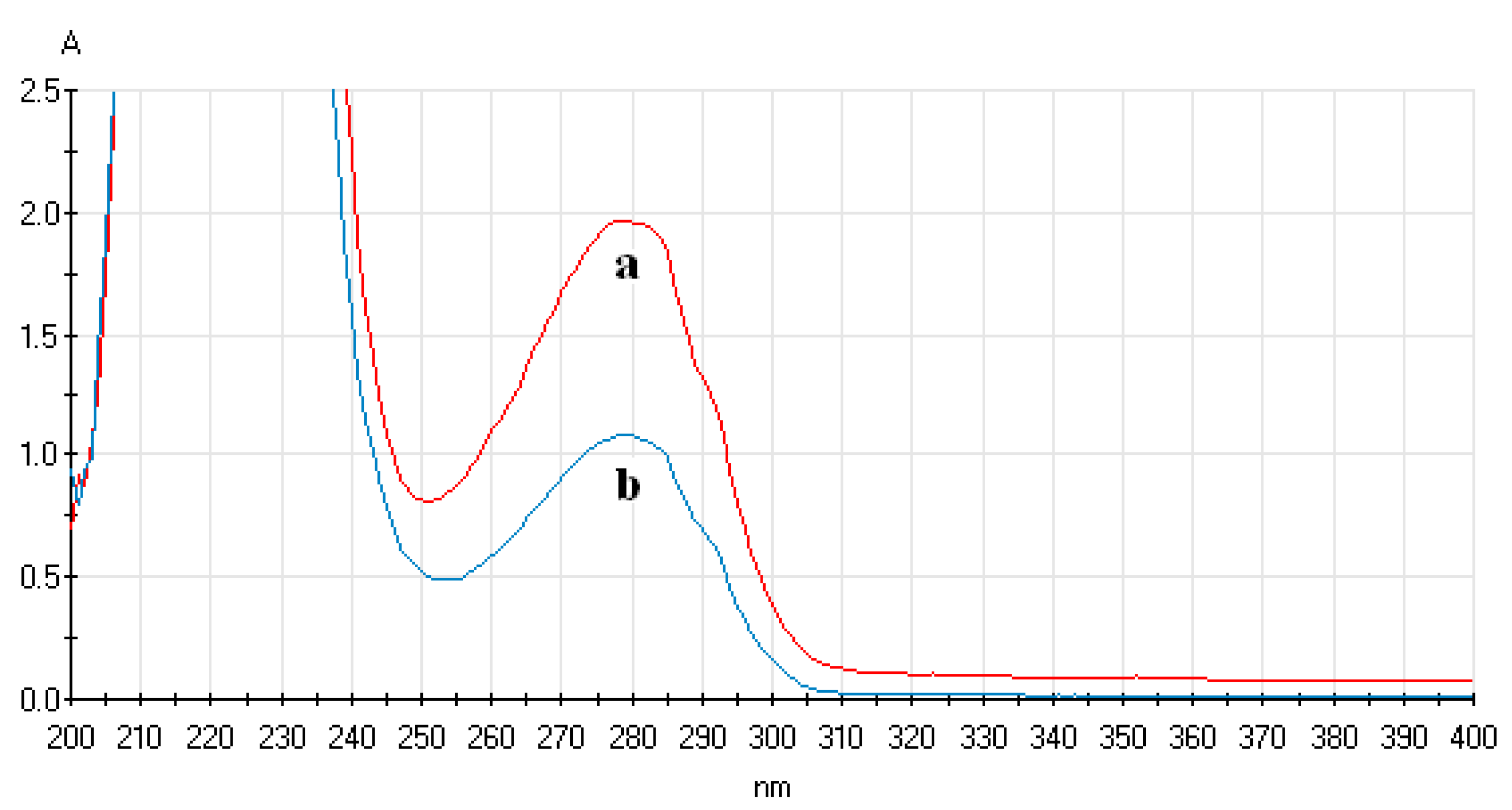
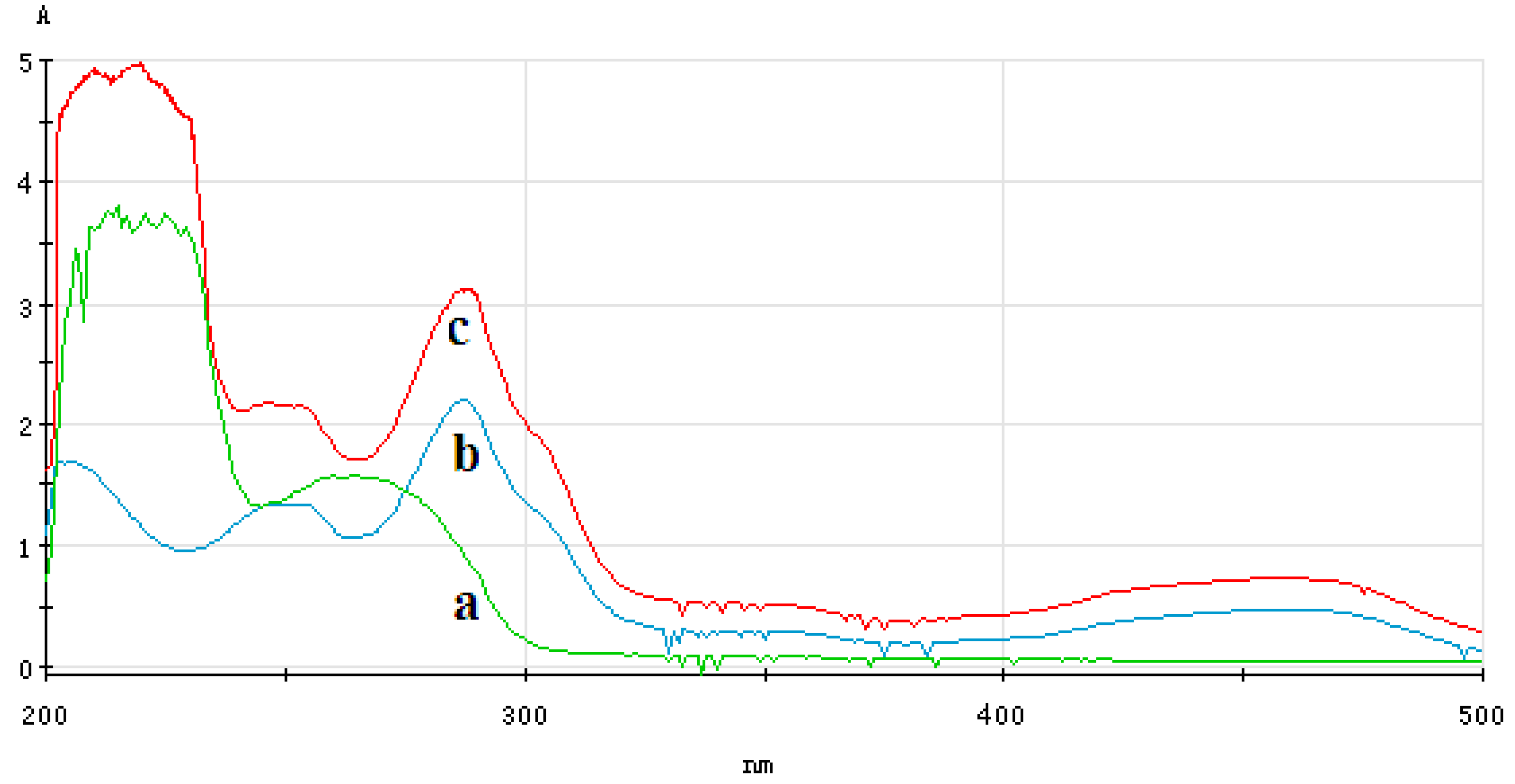
3.4.1. Analysis of UV-Vis Spectrum of ECL Probe
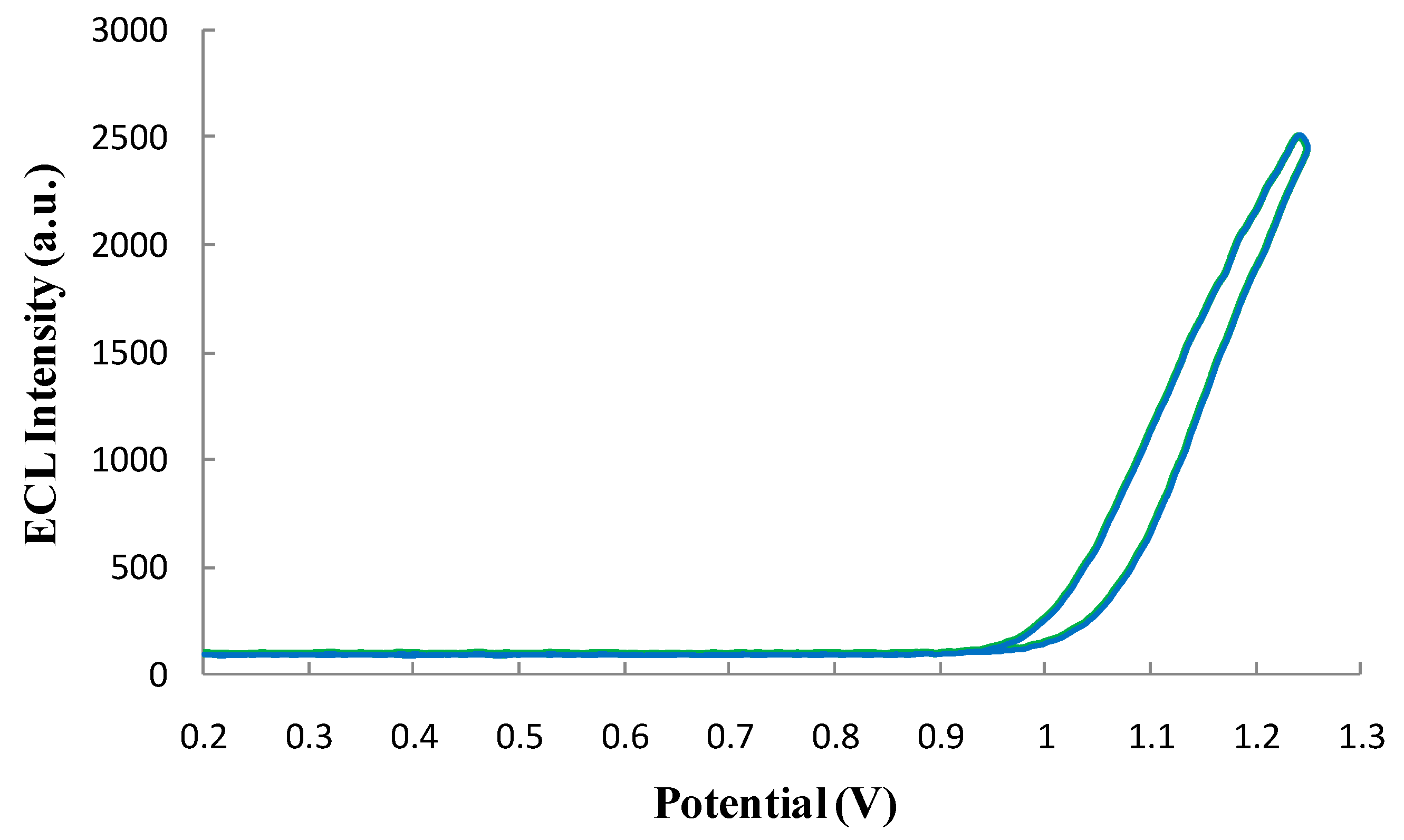
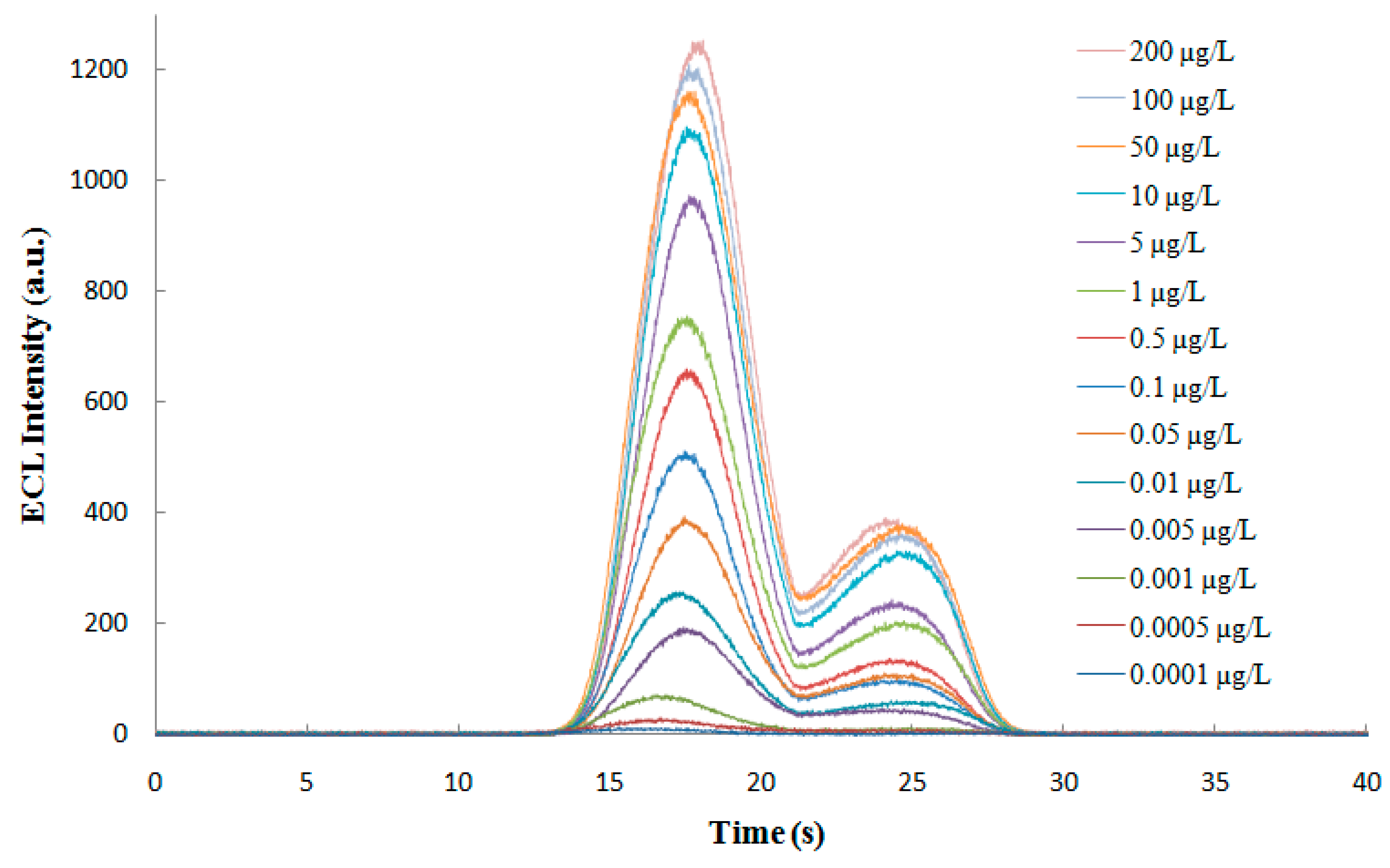
3.4.2. Qualification of the ECL Profile of the ECL Probe
3.5. The Performance of ECL Immunosensor
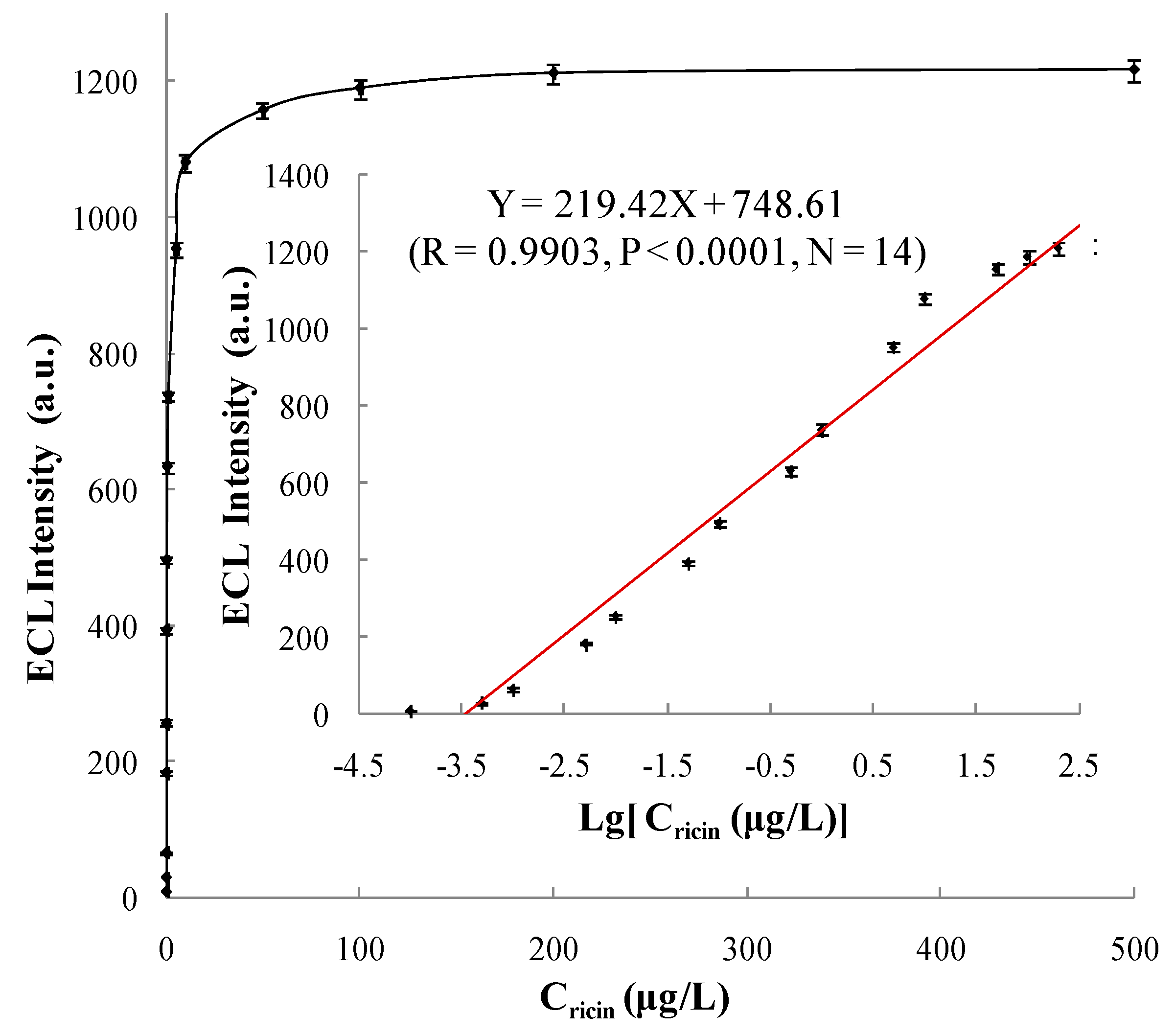
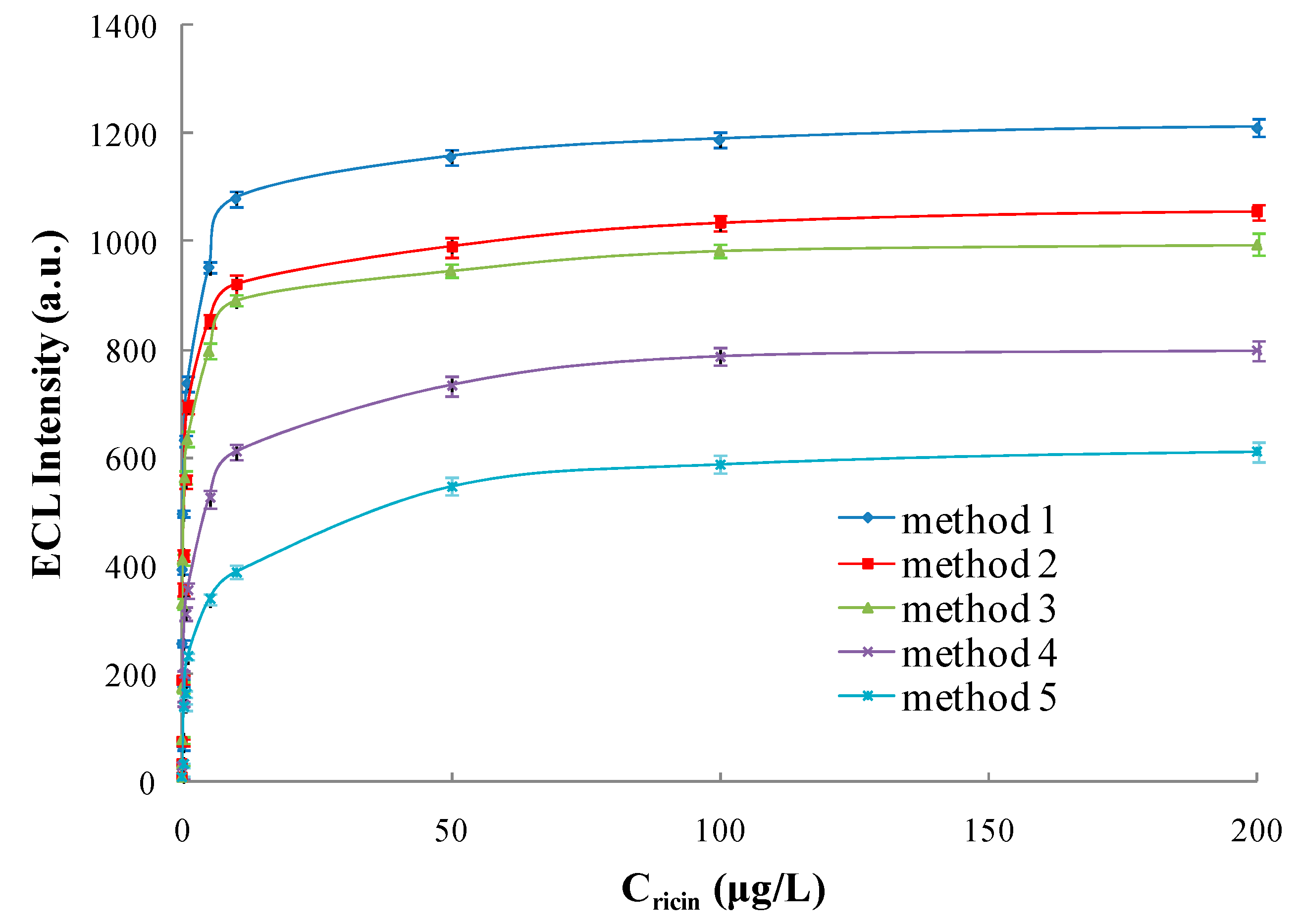
3.5.1. Linear Range and Limit of Detection
3.5.2. Accuracy and Specificity
3.5.3. Detection of Ricin in Simulated Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muzyka, K. Current trends in the development of the electrochemiluminescent mmunosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncello, P.; Forster, R.J. Nanostructured materials for electrochemiluminescence (ECL)-based detection methods: Recent advances and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.P. Filamentous fusion phage: Novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Science 1985, 228, 1315–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCafferty, J.; Griffiths, A.D.; Winter, G.; Chisweu, D.J. Phage antibodies: Filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature 1990, 348, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boel, E.; Verlaan, S.; Poppelier, M.J.J.G.; Westerdaal, N.A.C.; van Strijp, J.A.G.; Logtenberg, T. Functional human monoclonal antibodies of all isotypes constructed from phage display library-derived single-chain Fv antibody fragments. J. Immunol. Methods 2000, 239, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, A.; Ricci, C.; Bracci, L. Phage display and colony filter screening for high-throughput selection of antibody libraries. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2002, 5, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, M.; De Haard, H. Properties, production, and applications of camelid single-domain antibody fragments. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Ahn, K.C.; González-Techera, A.; González-Sapienza, G.G.; Gee, S.J.; Hammock, B.D. Magnetic bead-based phage anti-immunocomplex assay (PHAIA) for the detection of the urinary biomarker 3-phenoxybenzoic acid to assess human exposure to pyrethroid insecticides. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 386, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Tong, Z.Y.; Liu, W.; Hao, L.Q.; Mu, X.H.; Huang, Q.B. Determination of Abrin by Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Phage-displayed Antibody. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 41, 1449–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.B.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.W.; Hao, L.Q.; Zhang, J.P. Magnetic Affinity Immunoassay Based Enzyme-labeled Phage Displayed Antibody. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 42, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Huang, Q.B.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.W.; Hao, L.Q.; Zhang, J.P.; Gao, C.; Wang, F.W. Nano-magnetic Immunosensor Based on Staphylococcus Protein A and the Amplification Effect of HRP-conjugated Phage Antibody. Sensors 2015, 15, 3896–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, Y.; Usami, M.; Suzuki, O. Highly Sensitive Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay Using the Ruthenium Chelate Labeled Antibody Bound on the Magnetic Micro Beads. Anal. Sci. 1999, 15, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. 80. C-reactive protein determination at high amplification with [Ru(bpy)3]2+-containing microspheres. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 7109–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Zou, G.Z.; Zhang, X.L. Ultrasensitive eletrogenerated chemiluminescence immunoassay by magnetic nanobead amplification. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.H.; Xing, D. Rapid and sensitive immunomagnetic-electrochemiluminescent detection of p53 antibodies in human serum. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 288, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.V.; Messina, G.A.; Raba, J. Integrated microfluidic magnetic immunosensor for quantification of human serum IgG antibodies to Helicobacter pylori. J. Chromatogr. B 2010, 878, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Raymonda, J.W.; McMahon, T.M. Detection of biological threat agents by immunomagnetic microsphere-based solid phase fluorogenic and electro-chemiluminescence. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 14, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, K.H.; Chen, H.C.; Hu, Y.G. Magnetic beads-based electrochemical immunosensor for detection of pseudorabies virus antibody in swine serum. Talanta 2011, 87, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Tong, Z.Y.; Liu, W.; Hao, L.Q.; Mu, X.H.; Huang, Q.B. An Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay Based on GoldMag Particles. Chin. J. Instrum. Anal. 2013, 32, 998–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.J.; Lee, J.W.; Park, T.J.; Lee, S.J.; Parkd, J.Y.; Lee, J.B. Ultrasensitive DNA monitoring by Au-Fe3O4 nanocomplex. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 163, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoomi, L.L.; Sadeghi, O.; Banitaba, M.H.; Shahrjerdi, A.; Davarani, S.S.H. A non-enzymatic nanomagnetic electro-immunosensor for determination of Aflatoxin B1 as a model antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.P.; Liang, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, J.D. Facile preparation of novel core-shell enzyme-Au-polydopamine-Fe3O4 magnetic bionanoparticles for glucose sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parshetti, G.K.; Lin, F.H.; Doong, R.A. Sensitive amperometric immunosensor for α-fetoprotein detection based on multifunctional dumbbell-like Au-Fe3O4 heterostructures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 186, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Bi, S.; Jia, X.Q.; He, P. Aptamer-conjugated bio-bar-code Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles as amplification station for electrochemiluminescence detection of tumor cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 837, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi, S.A.; David, T.M.; Jayashainy, J.; Nathan, D.M.; Sagayaraj, P. A convenient two-step bottom-up approach for developing Au/Fe3O4 nanocomposites with useful optical and magnetic properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 606, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Huang, S.R.; Ge, F. 3D antibody immobilization on a planar matrix surface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Hata, Y.; Ninomiya, K.I. Oriented immobilization of antibodies on a silicon wafer using Si-tagged protein A. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 385, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.Y.; Cai, C.B.; Wang, K.; Lu, J.L. Improvement of antibody immobilization using hyperbranched polymer and protein A. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 409, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Tang, J.J.; Hao, L.Q.; Mu, X.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Yan, Y.; Dong, Z.H. A new purification method for ricin toxin. Chin. J. Biotechnology. 2005, 15, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Mu, D.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Mu, X.H.; Hao, L.Q. Determination of Ricin by double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2007, 35, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Y.; Mu, D.H.; Tong, Z.Y.; Mu, X.H.; Hao, L.Q. Rapid determination of ricin by indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chin.J. Instrum. Anal. 2007, 26, 533–536. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.H.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Tong, Z.Y.; Liu, B.; Hao, L.Q. Detection of abrin by piezoelectric immunosensor based on biotin-avidin system. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 37, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, Y.L.; Hui, W.L.; Wang, H.R.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, C. The preparation conditions and properties research of Fe3O4/Au composite particles. Sci. China Ser. B 2003, 33, 482–488. [Google Scholar]
- Molek, P.; Vodnik, M.; Štrukelj, B.; Bratkovic, T. Screening of synthetic phage display scFv libraries yields competitive ligands of human leptin receptor. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2014, 452, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, X.L.; Mao, H.W.; Gao, T.T.; Hu, Z.G.; He, L.F.; Pan, F.Y.; Guo, Z.G. Selection and characterization of human PCSK9 antibody from phage displayed antibody library. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Co. 2015, 463, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.J.; Choi, J.P.; Bard, A.J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence 69: The Tris(2,2′-bipy-ridine) ruthenium(II), (Ru(bpy)32+)/Tri-n-pro-pylamine (TPrA) system revisited-a new route involving TPrA·+ cation radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14478–14485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, E.A.; Thole, J. Application of microwave irradiation and heat to improve gliadin detection and ricin ELISA throughput with food samples. Toxins 2015, 7, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, E.R.; Liu, J.L.; Bernstein, R.D.; Swain, M.D.; Mitchell, S.Q.; Anderson, G.P. Ricin detection using phage displayed single domain antibodies. Sensors 2009, 9, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenigsberg, J.D.; Bertocchi, A.; Garber, E.A.E. Rapid detection of ricin in cosmetics and elimination of artifacts associated with wheat lectin. J. Immunol. Methods 2008, 336, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shyu, R.H.; Shyu, H.F.; Liu, H.W.; Tang, S.S. Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for detection of ricin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo-Viret, V.; Thullier, P. Comparison of an electrochemiluminescence assay in plate format over a colorimetric ELISA, for the detection of ricin B chain (RCA-B). J. Immunol. Methods 2007, 328, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, K.; Zeng, K.; Ruan, C.; Grimes, C.A. Quantification of ricin concentrations in aqueous media. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 107, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shia, W.W.; Bailey, R.C. Single domain antibodies for the detection of ricin using silicon photonic microring resonator arrays. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.P.; Glaven, R.H.; Algar, W.R.; Susumu, K.; Stewart, M.H.; Medintz, I.L.; Goldman, E.R. Single domain antibody–quantum dot conjugates for ricin detection by both fluoroimmunoassay and surface plasmon resonance. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 786, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, D.; Pauly, D.; Zydek, M.; Müller, C.; Avondet, M.A.; Worbs, S.; Lisdat, F.; Dorner, M.B.; Dorner, B.G. Simultaneous differentiation and quantification of ricin and agglutinin by an antibody-sandwich surface plasmon resonance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 78, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Yu, J.H.; Zhao, H.F.; Tong, C.Y.; Wang, P.H. A novel method for label-free detection of ricin using liquid crystals supported on chemically functionalized surfaces. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, L.; Richards, J.; Daniel, J.; Roon, L.; Rowland, T.J.; Bonham, A.J. Electrochemical aptamer scaffold biosensors for detection of botulism and ricin toxins. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15137–15140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periyakaruppan, A.; Arumugam, P.U.; Meyyappan, M.; Koehne, J.E. Detection of ricin using a carbon nanofiber based biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamont, E.A.; He, L.L.; Warriner, K.; Labuza, T.P.; Sreevatsan, S. A single DNA aptamer functions as a biosensor for ricin. Analyst 2011, 136, 3884–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; McMahon, S.; McKeon, T.A.; Brandon, D.L. Development of a novel immuno-PCR assay for detection of ricin in ground beef, liquid chicken egg, and milk. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.Q.; Jia, M.X.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.G. A nanoparticle-based bio-barcode assay for ultrasensitive detection of ricin toxin. Toxicon 2012, 59, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori-Kataoka, M.; Kato, H.; Uzawa, H.; Ohta, S.; Takei, Y.; Furuno, M.; Seto, Y. Determination of ricin by nano liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry after extraction using lactose-immobilized monolithic silica spin column. J. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 46, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
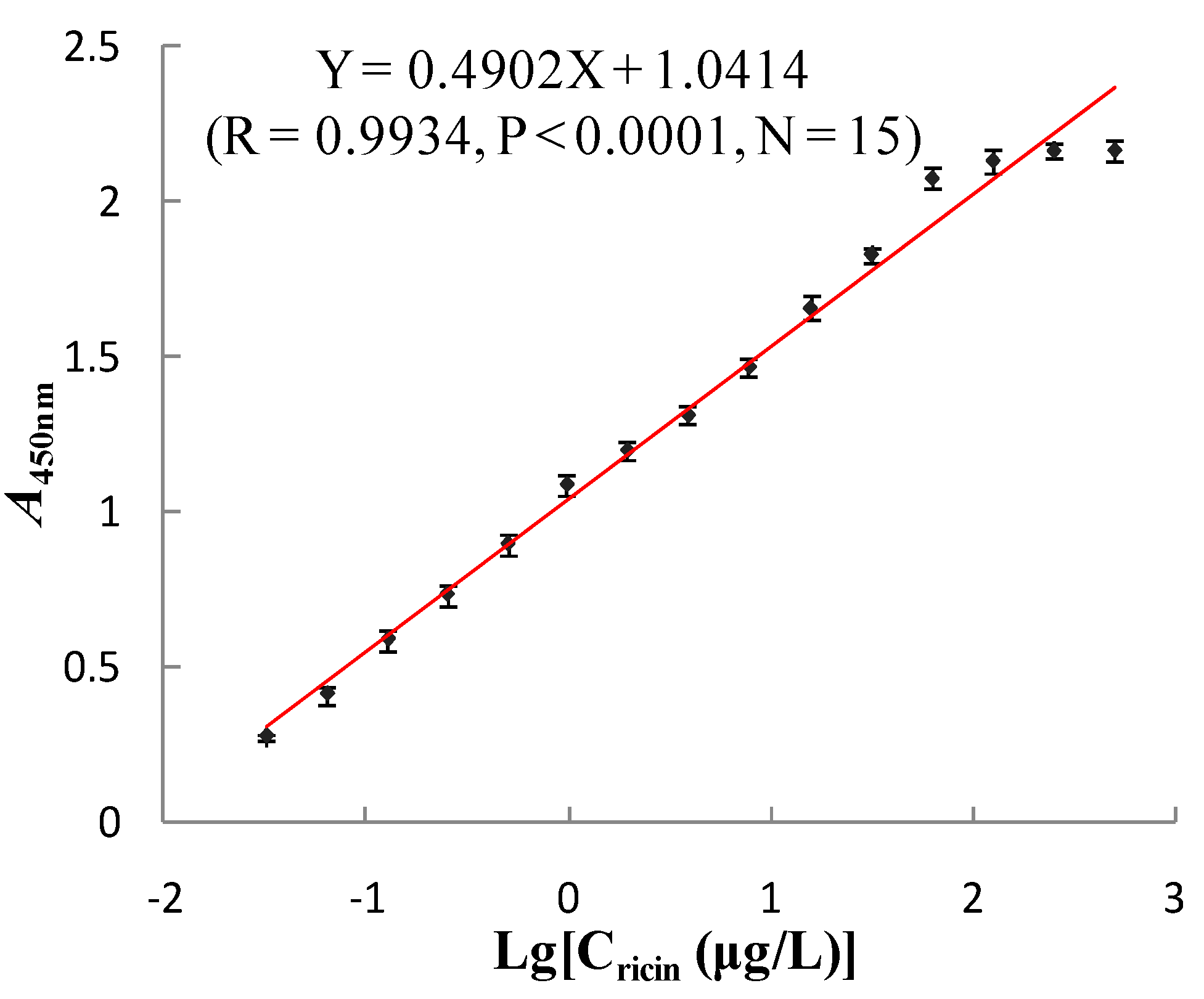
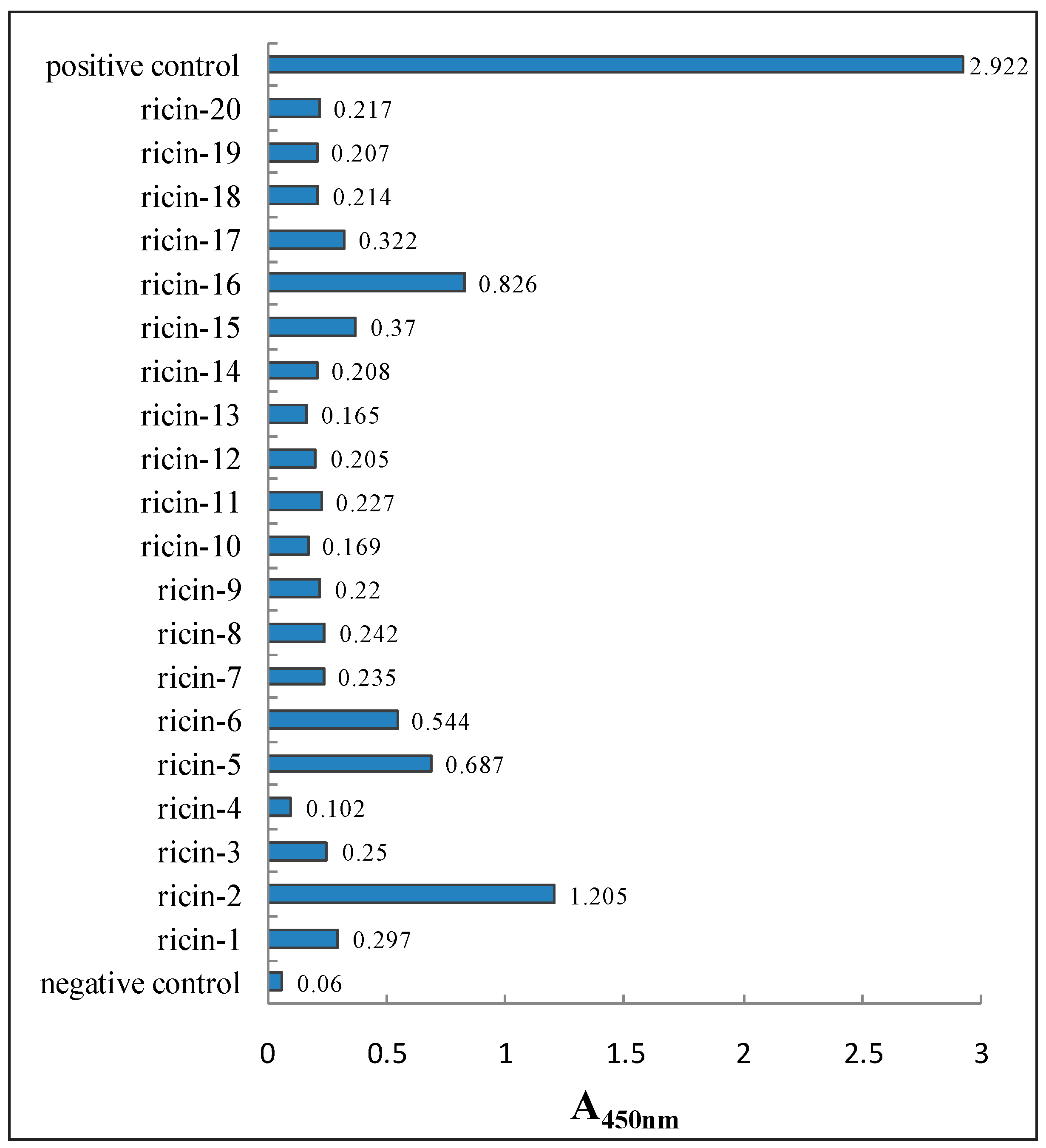
| Added Amount (µg) | A280nm before | A280nm after | Binding Ratio (%) | Immobilized Amount (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0.428 ± 0.005 | 0.043 ± 0.003 | 75.0 | 30 |
| 80 | 0.773 ± 0.007 | 0.106 ± 0.006 | 72.5 | 58 |
| 160 | 1.077 ± 0.008 | 0.249 ± 0.005 | 63.8 | 102 |
| 240 | 1.498 ± 0.007 | 0.530 ± 0.008 | 46.3 | 111 |
| 320 | 1.959 ± 0.009 | 0.931 ± 0.008 | 35.3 | 113 |
| 400 | 2.443 ± 0.008 | 1.404 ± 0.009 | 29.3 | 117 |
| 500 | 3.037 ± 0.009 | 1.998 ± 0.008 | 24.0 | 120 |
| Added Amount (µg) | A280nm before | A280nm after | Binding Ratio (%) | Immobilized Amount (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0.428 ± 0.006 | 0.107 ± 0.004 | 90.0 | 36 |
| 80 | 0.773 ± 0.008 | 0.213 ± 0.006 | 86.3 | 69 |
| 160 | 1.077 ± 0.007 | 0.390 ± 0.006 | 76.9 | 123 |
| 240 | 1.498 ± 0.008 | 0.800 ± 0.007 | 64.6 | 155 |
| 320 | 1.959 ± 0.009 | 1.267 ± 0.008 | 52.5 | 168 |
| 400 | 2.443 ± 0.008 | 1.720 ± 0.007 | 42.3 | 169 |
| 500 | 3.037 ± 0.009 | 2.308 ± 0.009 | 34.2 | 171 |
| Added Amount (µg) | A280nm before | A280nm after | Binding Ratio (%) | Immobilized Amount (µg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0.434 ± 0.008 | 0.043 ± 0.006 | 90.0 | 36 |
| 80 | 0.795 ± 0.009 | 0.099 ± 0.007 | 87.5 | 70 |
| 160 | 1.094 ± 0.008 | 0.219 ± 0.008 | 80.0 | 128 |
| 240 | 1.518 ± 0.009 | 0.411 ± 0.006 | 72.9 | 175 |
| 320 | 1.923 ± 0.007 | 0.600 ± 0.009 | 68.8 | 220 |
| 400 | 2.446 ± 0.009 | 0.824 ± 0.008 | 66.3 | 265 |
| 480 | 2.956 ± 0.010 | 1.318 ± 0.009 | 55.4 | 266 |
| 560 | 3.550 ± 0.010 | 1.864 ± 0.010 | 47.5 | 266 |
| Round | Phage Input (PFU) | Phage Output (PFU) | Recovery Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3 × 1012 | 6.2 × 105 | 1.9 × 10−7 |
| 2 | 9.6 × 1011 | 9.7 × 105 | 1.0 × 10−6 |
| 3 | 1.4 ×1012 | 2.2 × 106 | 1.6 × 10−6 |
| Detecting Scheme | Linear Range (μg/L) | Regression Equation | Correlation Coefficient (R) | Limit of Detection (μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1 | 0.0001~200 | Y = 219.42X + 748.61 | 0.9903 | 0.0001 |
| Method 2 | 0.0003~200 | Y = 204.83X + 643.88 | 0.9918 | 0.0003 |
| Method 3 | 0.0003~200 | Y = 194.17X + 613.61 | 0.9919 | 0.0003 |
| Method 4 | 0.002~500 | Y = 171.42X + 398.51 | 0.9905 | 0.002 |
| Method 5 | 0.018~500 | Y = 158.86X + 236.21 | 0.9913 | 0.018 |
| Method 6 | 0.25~250 | Y = 0.5415X + 0.6196 | 0.9945 | 0.25 |
| Detection Method | Ricin Enrichment Method | Sample Matrix | LOD | Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sandwich-type ELISA based on microwave irradiation and heat | Antibody conjugated to 96-well plate | Food Samples | 10 ppb | 2 h | [37] |
| ELISA and Luminex fluid array assays | sdAb conjugated to 96-well plate | Buffer | 1 ng/mL and 64 pg/mL | Not reported | [38] |
| Lateral flow devices | Antibody conjugated nitrocellulose membrane | Cosmetics | 0.01 μg/mL | Not reported | [39] |
| Colloidal immunochromatographic assay | Antibody conjugated nitrocellulose membrane | Buffer | 0.1~50 ng/mL | 10 min | [40] |
| Electrochemiluminescence assay | Antibody conjugated to 96-well plate | Buffer | 50 pg/mL | 2.5 h | [41] |
| Magnetoelastic sensor | Antibody conjugated to sensor surface | Water, blood and serum | 5 ng/mL | 3.5 h | [42] |
| Microring resonator array | sdAb conjugated to microring resonator array | Buffer | 300 pM | 15 min | [43] |
| Surface plasmon resonance based on sdAb-QD | sdAb conjugated to SPR chip | Buffer | 1 ng/mL and 0.7 ng/mL | 2~6 min | [44] |
| Antibody-sandwich surface plasmon resonance sensor | Antibody conjugated to SPR chip | Buffer | 3 ng/mL | <30 min | [45] |
| Liquid-crystal based sensor | Antibody conjugated to liquid crystals supported surfaces | Buffer | 10 μg/mL | 1–2 h | [46] |
| Electrochemical aptamer scaffold biosensors | Aptamer conjugated to gold electrode surface | Buffer | 0.3~0.1 nM | Not reported | [47] |
| Nanoelectrode array biosensor based on carbon nanofiber | Antibody or aptamer conjugated to the carbon nanofibers chips | Buffer | <1 pM | 4 h | [48] |
| DNA aptamer and Raman scattering technique | Aptamer conjugated to magnetic particles | Buffer and beverages | 25 ng/mL | Not reported | [49] |
| Immuno-PCR | Antibody conjugated to microtitration plate | Ground beef, milk, and egg | 0.01~0.1 ng/mL | Not reported | [50] |
| Real-time fluorescence PCR of nanoparticle-based bio-barcode | Antibody conjugated to magnetic nanoparticle | Buffer | 1 fg/mL | Not reported | [51] |
| Nano LC–MS | Lactose-immobilized monolithic spin column | High protein solution | 8 ng/mL | 5 h | [52] |
| Object | ECL Intensity (a.u.) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Ricin | 737.8 ± 13.5 | 1.8 |
| Abrin | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 8.6 |
| SEB | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 9.8 |
| BSA | 5.6 ± 0.5 | 9.8 |
| River water | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 9.3 |
| Fertilized soil | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 8.6 |
| Butter biscuit | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 8.6 |
| Whole rabbit blood | 5.6± 0.5 | 9.8 |
| PBS buffer | 5.2 ± 0.4 | 8.6 |
| Sample | Added (μg/L) | Found (μg/L) | Recovery Ratio (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 5 | 4.71 ± 0.15 | 94.2 | 3.08 |
| Fertilized soil | 5 | 4.58 ± 0.07 | 91.6 | 1.46 |
| Butter biscuit | 5 | 4.55 ± 0.14 | 91.1 | 2.97 |
| Whole rabbit blood | 5 | 4.54 ± 0.11 | 90.8 | 2.38 |
| Sample | Added (μg/L) | Found (μg/L) | Recovery Ratio (%) | Relative Standard Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| River water | 5 | 4.61 ± 0.12 | 92.2 | 2.60 |
| Fertilized soil | 5 | 5.77 ± 0.11 | 115.4 | 1.91 |
| Butter biscuit | 5 | 4.55 ± 0.09 | 91.0 | 1.98 |
| Whole rabbit blood | 5 | 5.96 ± 0.14 | 119.2 | 2.35 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, X.; Tong, Z.; Huang, Q.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Hao, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C. An Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibodies. Sensors 2016, 16, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030308
Mu X, Tong Z, Huang Q, Liu B, Liu Z, Hao L, Dong H, Zhang J, Gao C. An Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibodies. Sensors. 2016; 16(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Xihui, Zhaoyang Tong, Qibin Huang, Bing Liu, Zhiwei Liu, Lanqun Hao, Hua Dong, Jinping Zhang, and Chuan Gao. 2016. "An Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibodies" Sensors 16, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030308
APA StyleMu, X., Tong, Z., Huang, Q., Liu, B., Liu, Z., Hao, L., Dong, H., Zhang, J., & Gao, C. (2016). An Electrochemiluminescence Immunosensor Based on Gold-Magnetic Nanoparticles and Phage Displayed Antibodies. Sensors, 16(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16030308





