Label-Free Detection of Human Glycoprotein (CgA) Using an Extended-Gated Organic Transistor-Based Immunosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
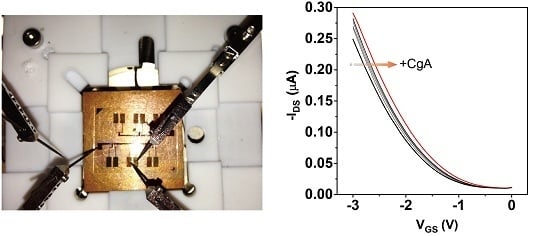
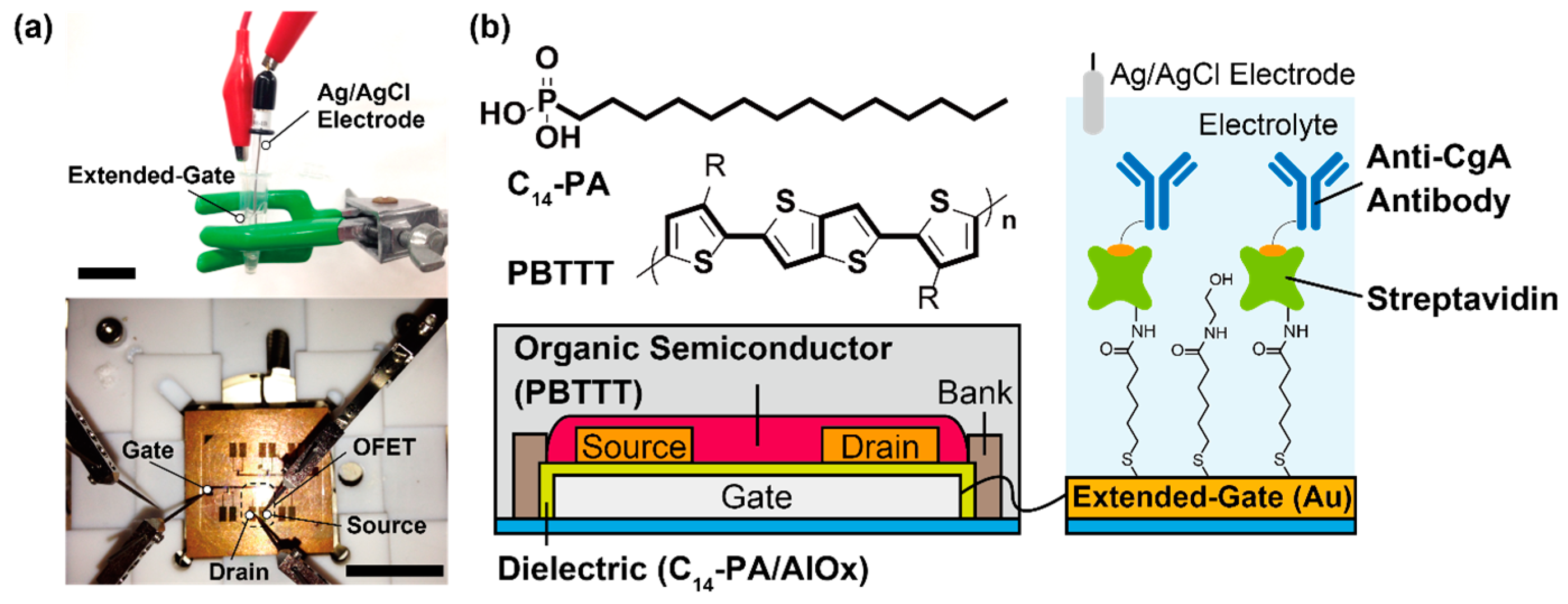
3.1. Characterization of the Fabricated Device
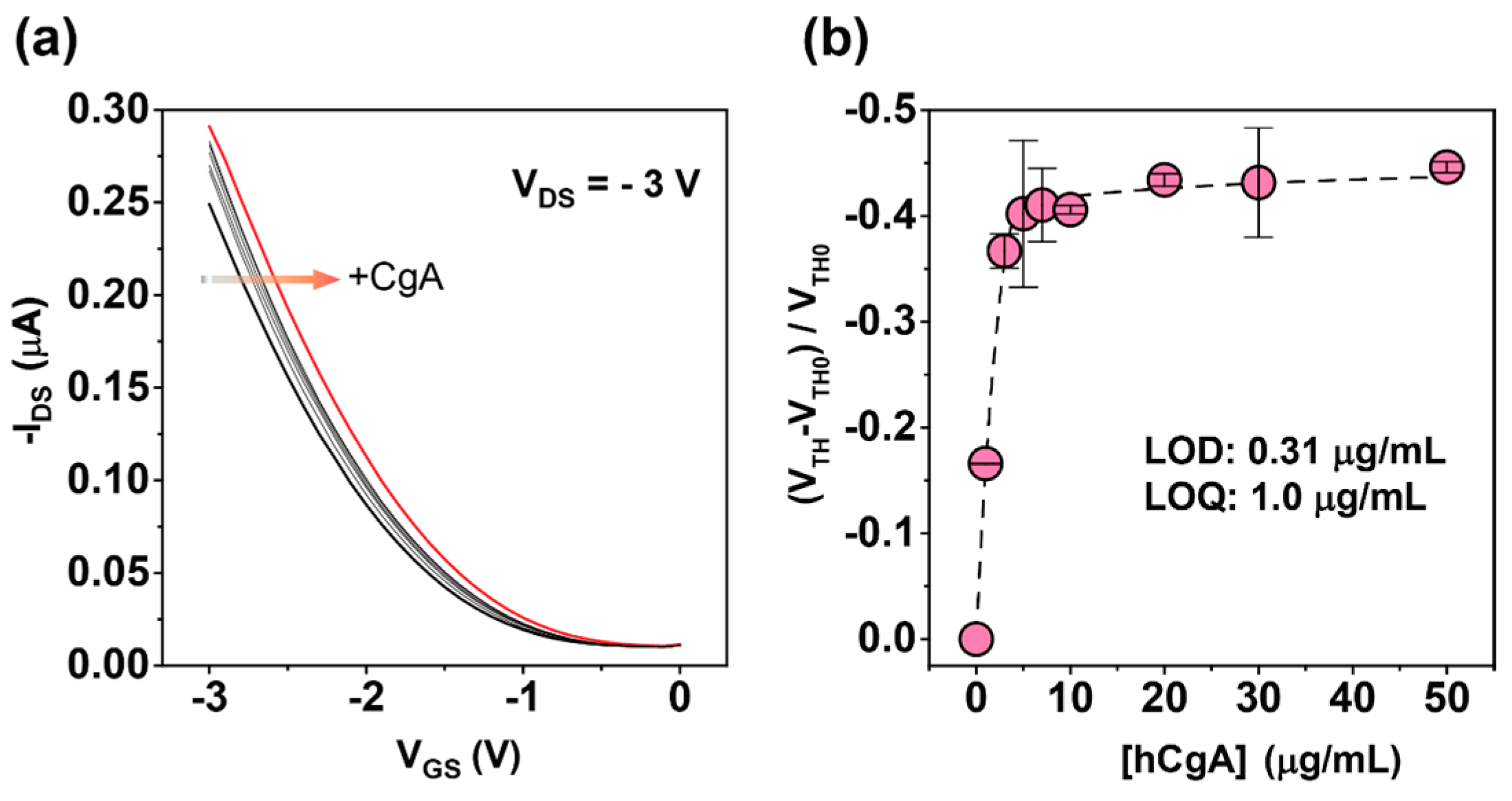
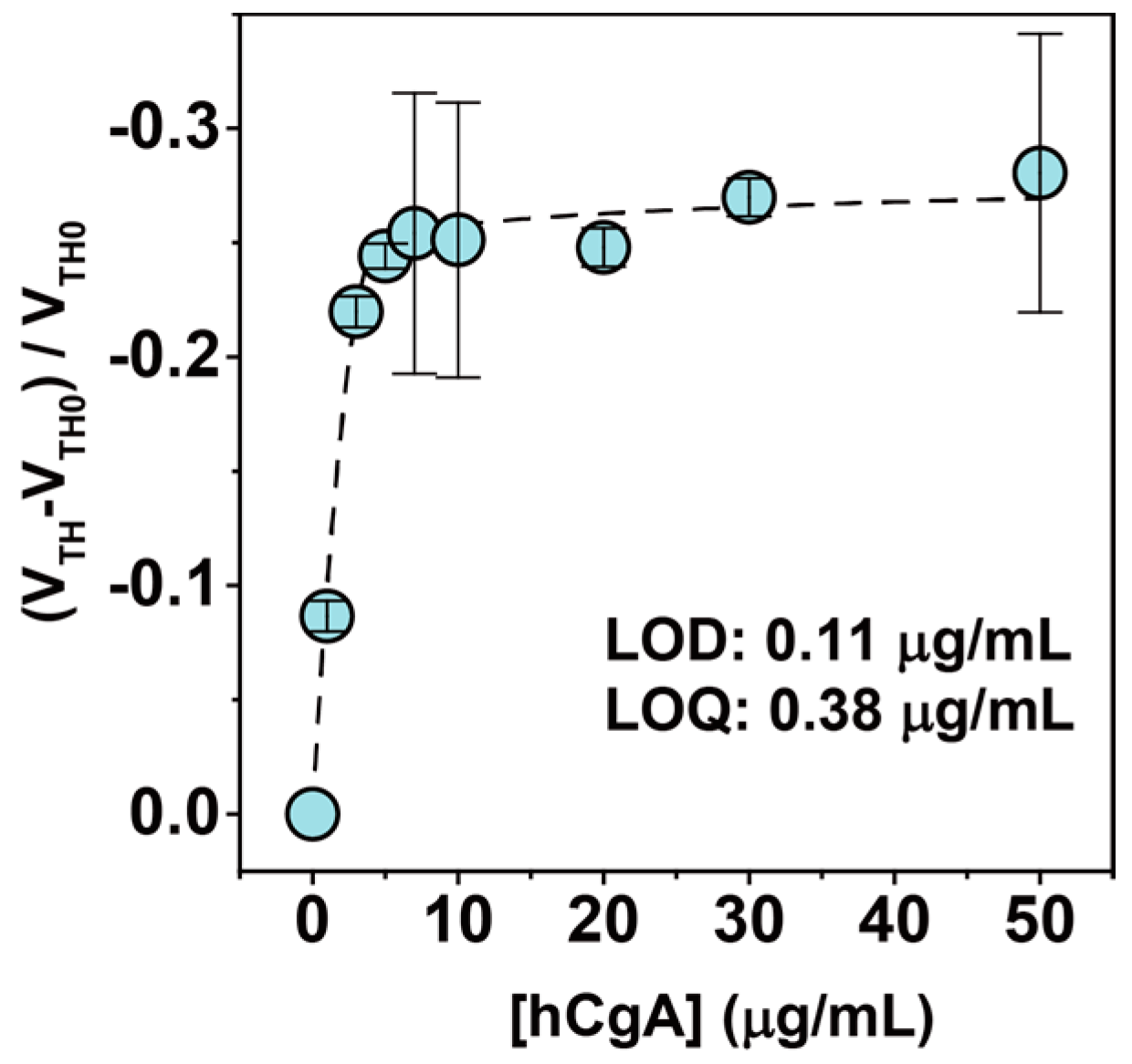
3.2. Label-Free Electrical Detection of hCgA
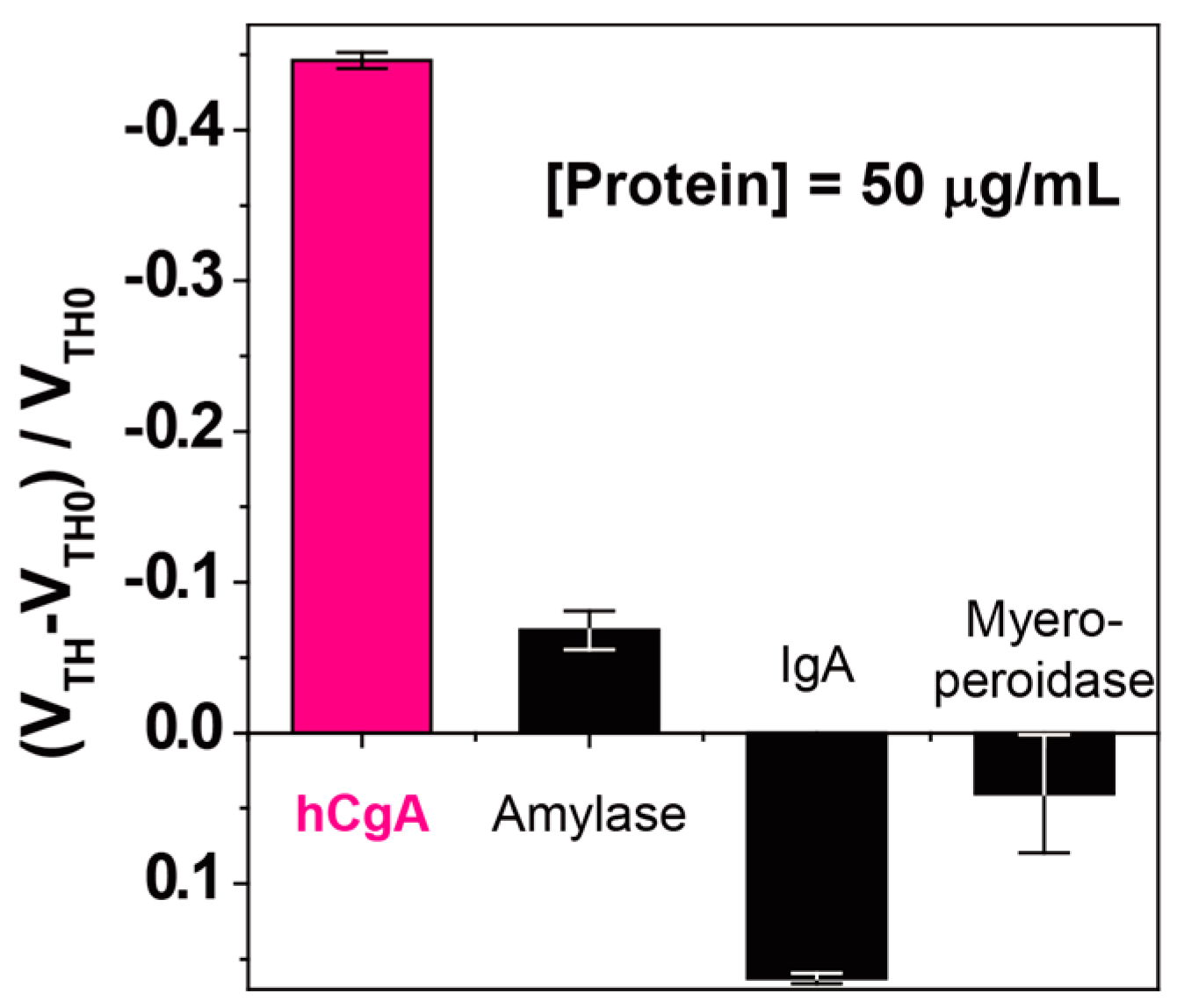
3.3. Selectivity
3.4. CgA Detection in Artificial Saliva
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’amico, M.A.; Ghinassi, B.; Izzicupo, P.; Manzoli, L.; Baldassarre, A.D. Biological function and clinical relevance of chromogranin A and derived peptides. Endocr. Connect. 2014, 3, R45–R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasciotto, B.H.; Denny, J.C.; Greeley, G.H., Jr.; Cohn, D.V. Processing of chromogranin A in the parathyroid: generation of parastatin-related peptides. Peptides 2000, 21, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomarkers Definition Working Group. Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Conlon, J.M. Granin-derived peptides as diagnostic and prognostic markers for endocrine tumors. Regul. Pept. 2010, 165, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Toole, D.; Grossman, A.; Gross, D.; Delle-Fave, G.; Barkmanova, J.; O’Connor, J.; Pape, U.F.; Plöckinger, U. ENETS consensus guidelines for the standards of care in neuroendocrine tumors: Biochemical markers. Neuroendocrinology 2009, 90, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bartolomucci, A.; Pasinetti, G.M.; Salton, S.R.J. Granins as disease-biomarkers: translational potential for psychiatric and neurological disorders. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allgrove, J.E.; Gomes, E.; Hough, J.; Gleeson, M. Effects of exercise intensity on salivary antimicrobial proteins and markers of stress in active men. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, S.; Fukusaki, C.; Ohtani, M.; Kobayashi, K. Effects of hyperoxic inhalation on psychological stress-induced salivary biomarkers. Biomed. Res. 2009, 30, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, B.; Kaur, J. Salivary stress markers and psychological stress in simulated microgravity: 21 days in 6o head-down tilt. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 53, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, M.; Hinode, D.; Yokoyama, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Kataoka, K.; Ito, H. Levels of salivary stress markers in patients with anxiety about halitosis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2010, 55, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.; Cik, M.; Marth, E.; Santner, B.I.; Gallasch, E.; Lackner, A.; Raggam, R.B. Feasibility of testing three salivary stress biomarkers in relation to naturalistic traffic noise exposure. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuura, S.; Kamezaki, Y.; Yamagishi, N.; Kuwano, Y.; Nishida, K.; Masuda, K.; Tanahashi, T.; Kawai, T.; Arisawa, K.; Rokutan, K. Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor is independently and negatively associated with trait anxiety and depressive mood in healthy Japanese university students. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2011, 81, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubouchi, H.; Nakai, Y.; Toda, M.; Morimoto, K.; Chang, Y.S.; Ushioda, N.; Kaku, S.; Nakamura, T.; Kimura, T.; Shimoya, K. Change of salivary stress marker concentrations during pregnancy: maternal depressive status suppress changes of those levels. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2011, 37, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, D.S. Immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 294R–304R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.W.; Pan, C.Y.; Wu, H.C.; Shih, P.Y.; Tsai, C.C.; Liao, K.T.; Lu, L.L.; Hsieh, W.H.; Chen, C.D.; Chen, Y.T. In Situ Detection of Chromogranin A Released from Living Neurons with a Single-Walled Carbon-Nanotube Field-Effect Transistor. Small 2007, 3, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoli, K.; Magliulo, M.; Mulla, M.Y.; Singh, M.; Sabbatini, L.; Palazzo, G.; Torsi, L. Printable Bioelectronics To Investigate Functional Biological Interfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12562–12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammock, M.L.; Knopfmacher, O.; Ng, T.N.; Tok, J.B.H.; Bao, Z. Electronic Readout Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay with Organic Field-Effect Transistors as a Preeclampsia Prognostic. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6138–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzo, G.; De Tullio, D.; Magliulo, M.; Mallardi, A.; Intranuovo, F.; Mulla, M.Y.; Favia, P.; Vikholm-Lundin, I.; Torsi, L. Detection Beyond Debye’s length with an Electrolyte-Gated Organic Field-Effect Transistor. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Kurita, R.; Niwa, O.; Wakida, S.; Fukuda, K.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. A Label-Free Immunosensor for IgG Based on an Extended-Gate Type Organic Field Effect Transistor. Materials 2014, 7, 6843–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Kurita, R.; Niwa, O.; Wakida, S.; Tokito, S. An Organic Field-effect Transistor with an Extended-gate Electrode Capable of Detecting Human Immunoglobulin A. Anal. Sci. 2015, 31, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, T.; Minamiki, T.; Hashima, Y.; Yokoyama, D.; Sekine, T.; Fukuda, K.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. An extended-gate type organic field effect transistor functionalised by phenylboronic acid for saccharide detection in water. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15613–15615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Kurita, R.; Niwa, O.; Wakida, S.; Fukuda, K.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Accurate and reproducible detection of proteins in water using an extended-gate type organic transistor biosensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 243703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, I.; Heeney, M.; Bailey, C.; Genevicius, K.; MacDonald, I.; Shkunov, M.; Sparrowe, D.; Tierney, S.; Wagner, R.; Zhang, W.; et al. Liquid-crystalline semiconducting polymers with high charge-carrier mobility. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauk, H.; Zschieschang, U.; Pflaum, J.; Halik, M. Ultralow-power organic complementary circuits. Nature 2007, 445, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, G. Organic Field-Effect Transistors. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedaa, A.; Burkhardt, M.; Zschieschang, U.; Klauk, H.; Habich, D.; Schmid, G.; Halik, M. The impact of self-assembled monolayer thickness in hybrid gate dielectrics for organic thin-film transistors. Org. Electron. 2009, 10, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, T.; Fukuda, R. Simultaneous Biosensing with Quartz Crystal Microbalance with a Dissipation Coupled-Gate Semiconductor Device. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5796–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, T.; Miyahara, Y. Interpretation of Protein Adsorption through Its Intrinsic Electric Charges: A Comparative Study Using a Field-Effect Transistor, Surface Plasmon Resonance, and Quartz Crystal Microbalance. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14730–14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergveld, P. Thirty years of ISFETOLOGY: What happened in the past 30 years and what may happen in the next 30 years. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 88, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.P.; Ganguly, A.; Lu, C.Y.; Chen, T.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Chen, R.S.; Tu, W.H.; Fischer, W.B.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, L.C. Ultrasensitive in Situ Label-Free DNA Detection Using a GaN Nanowire-Based Extended-Gate Field-Effect-Transistor Sensor. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1938–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakata, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakajima, Y.; Miyahara, Y. Potential Behavior of Biochemically Modified Gold Electrode for Extended-Gate Field-Effect Transistor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 2860–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson: Harlow, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zitella, A.; Berruti, A.; Destefanis, P.; Mengozzi, G.; Torta, M.; Ceruti, C.; Casetta, G.; Mosca, A.; Greco, A.; Rolle, L.; et al. Comparison between two commercially available chromogranin A assays in detecting neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stridsberg, M.; Eriksson, B.; Öberg, K.; Janson, E.T. A comparison between three commercial kits for chromogranin A measurements. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 177, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, K.; Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Watanabe, M.; Fukuda, T.; Kumaki, D.; Tokito, S. Printed Organic Transistors with Uniform Electrical Performance and Their Application to Amplifiers in Biosensors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1400052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagarasan, S.; Honjo, T. Intestinal IgA synthesis: regulation of front-line body defences. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakowski, J.J.; Bruns, D.E. Biochemistry of human alpha amylase isoenzymes. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 1985, 21, 283–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nater, U.M.; Rohleder, N.; Gaab, J.; Berger, S.; Jud, A.; Kirschbaum, C.; Ehlert, U. Human salivary alpha-amylase reactivity in a psychosocial stress paradigm. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2005, 55, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.L.; Jefferson, M.M.; Joyner, R.E.; Cook, G.S.; King, C.C. Leukocyte Myeloperoxidase and Salivary Lactoperoxidase: Identification and Quantitation in Human Mixed Saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 73, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.S.; Lloyd, R.V. Detection of chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells with a monoclonal antibody. Am. J. Pathol. 1984, 115, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Jun, L.; Futai, Y.; Yanaihara, N.; Iguchi, K.; Mochizuki, T.; Hoshino, M.; Yanaihara, C. Region-Specific Radioimmunoassay for Human Chromogranin A. Biomed. Res. 1998, 19, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-C.; Chou, J.-C.; Sun, T.-P.; Hsiung, S.-K. Portable urea biosensor based on the extended-gate field effect transistor. Sens. Actuators B 2003, 91, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Koutnik, P.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr.; Tokito, S. Antibody- and Label-Free Phosphoprotein Sensor Device Based on an Organic Transistor. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minamiki, T.; Minami, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Wakida, S.-i.; Kurita, R.; Niwa, O.; Tokito, S. Label-Free Detection of Human Glycoprotein (CgA) Using an Extended-Gated Organic Transistor-Based Immunosensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122033
Minamiki T, Minami T, Sasaki Y, Wakida S-i, Kurita R, Niwa O, Tokito S. Label-Free Detection of Human Glycoprotein (CgA) Using an Extended-Gated Organic Transistor-Based Immunosensor. Sensors. 2016; 16(12):2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122033
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinamiki, Tsukuru, Tsuyoshi Minami, Yui Sasaki, Shin-ichi Wakida, Ryoji Kurita, Osamu Niwa, and Shizuo Tokito. 2016. "Label-Free Detection of Human Glycoprotein (CgA) Using an Extended-Gated Organic Transistor-Based Immunosensor" Sensors 16, no. 12: 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122033
APA StyleMinamiki, T., Minami, T., Sasaki, Y., Wakida, S.-i., Kurita, R., Niwa, O., & Tokito, S. (2016). Label-Free Detection of Human Glycoprotein (CgA) Using an Extended-Gated Organic Transistor-Based Immunosensor. Sensors, 16(12), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122033