Quencher-Free Fluorescence Method for the Detection of Mercury(II) Based on Polymerase-Aided Photoinduced Electron Transfer Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Feasibility of the Strategy
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Hg2+
3. Results and Discussion
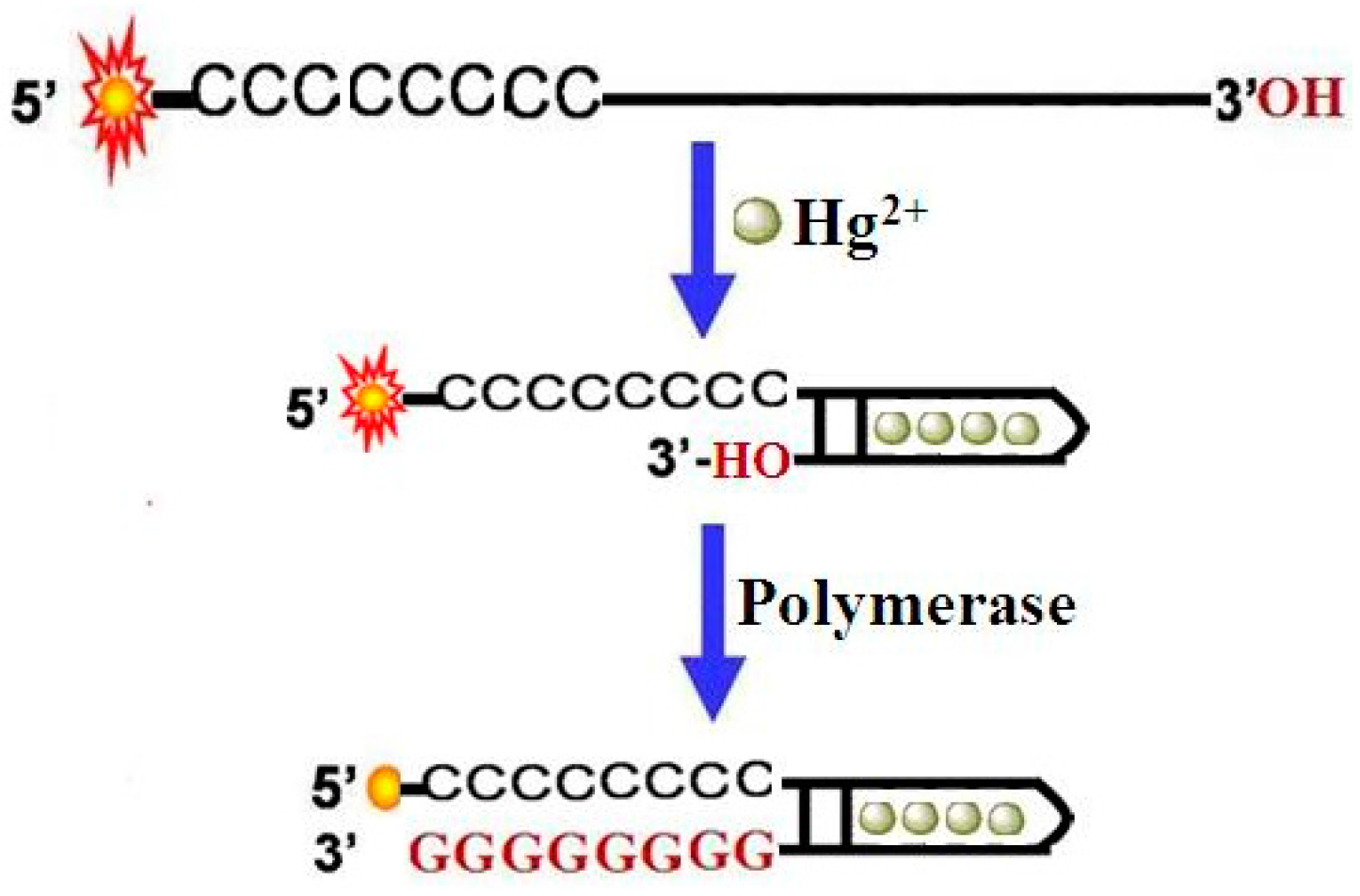
3.1. Sensing Strategy
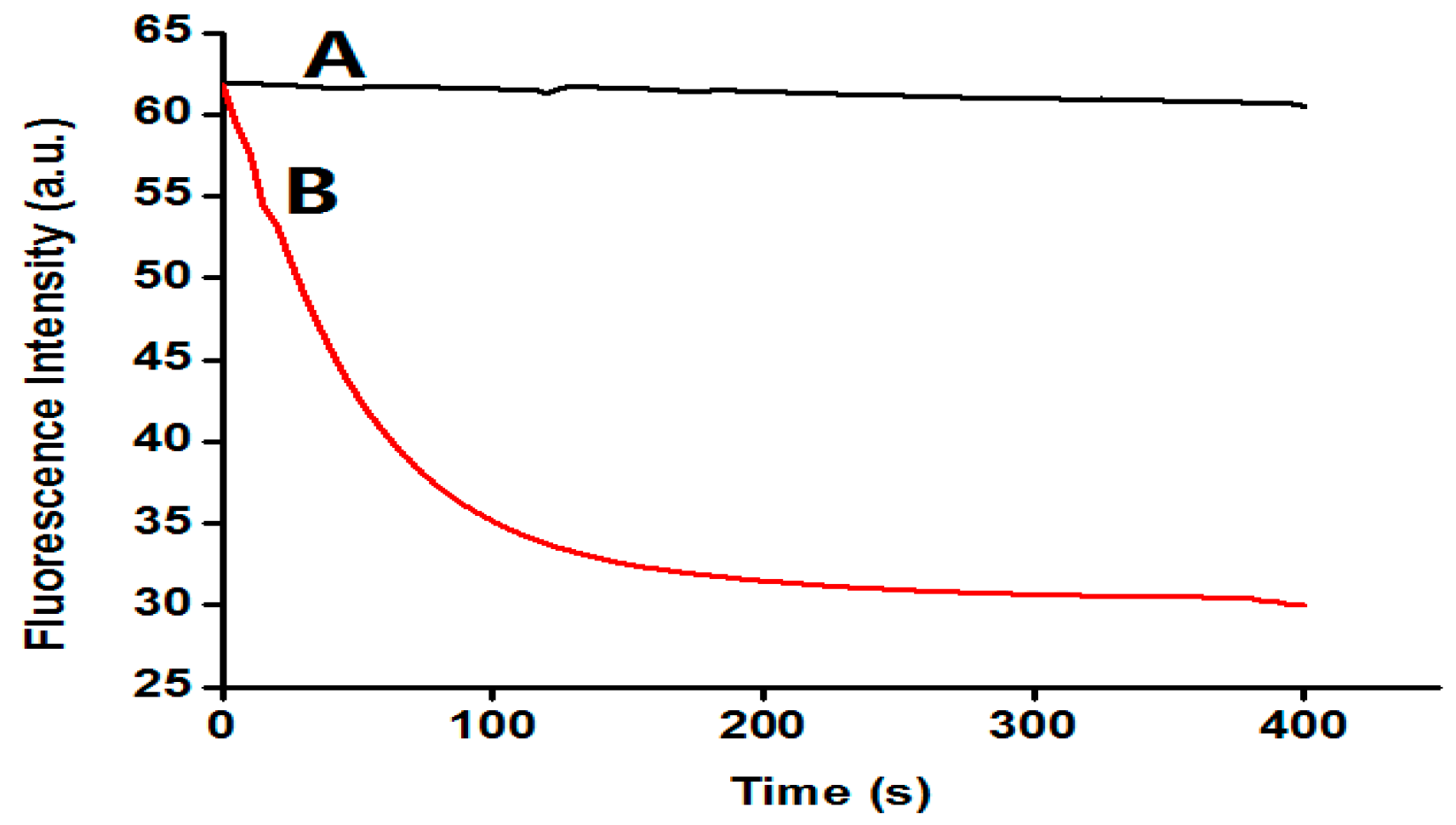
3.2. The Feasibility of the Assay
3.3. Optimization of the Reaction Conditions
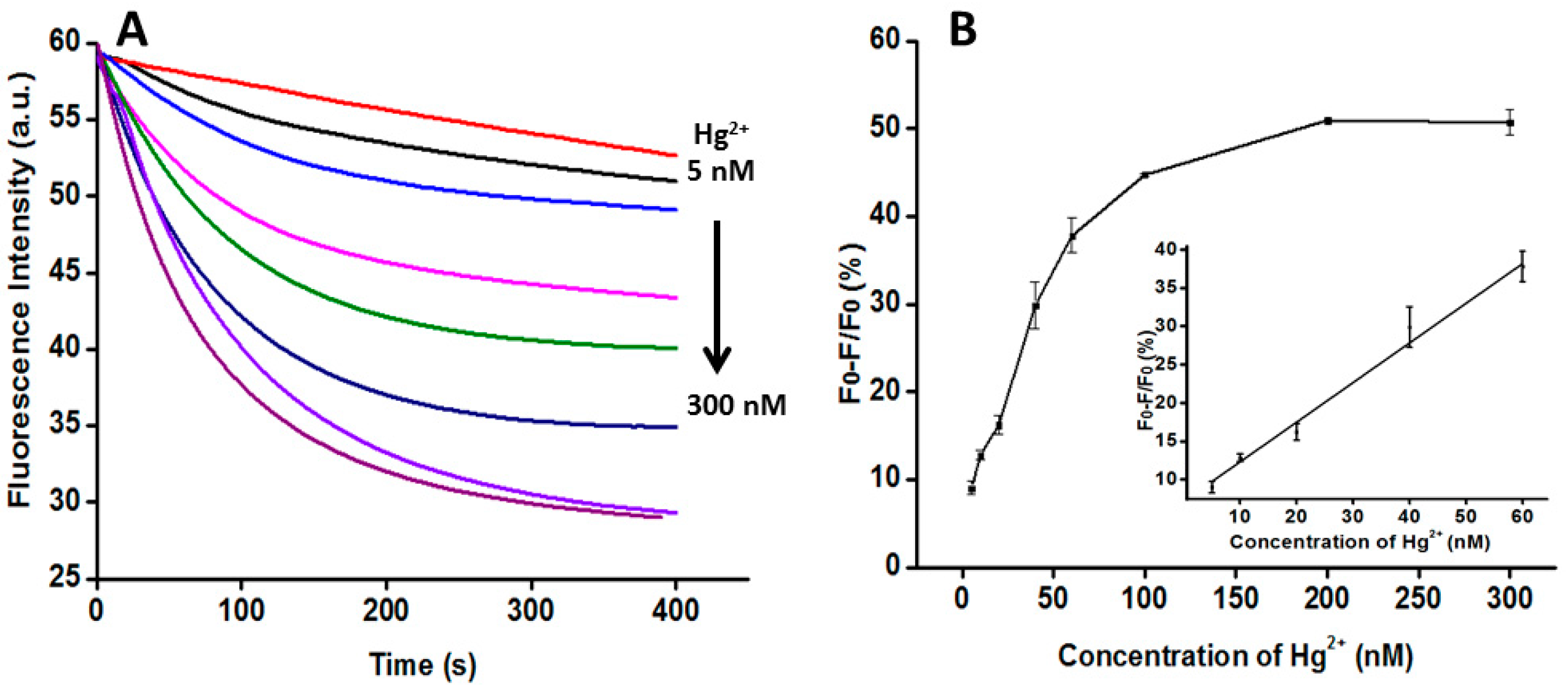
3.4. Quantitative Analysis of Hg2+
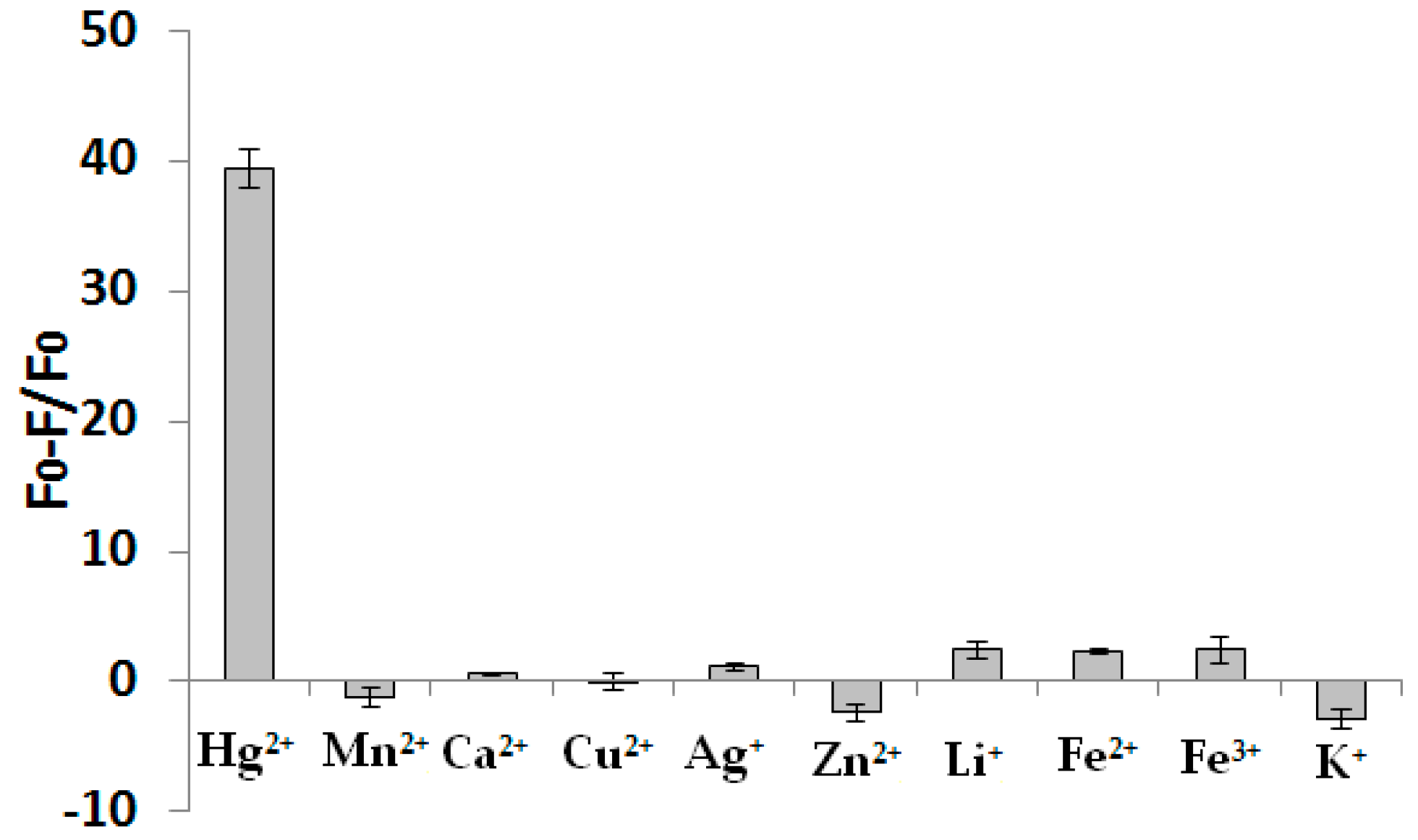
3.5. The Selectivity of this Assay
3.6. Detection of Hg2+ in Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodson, M. Heavy metals-geochemical bogey men? Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, M. Cytidine-stabilized gold nanocluster as a fluorescence turn-on and turn-off probe for dual functional detection of Ag+ and Hg2+. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 870, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, T.; Cui, Z.; Li, X. A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent sensor for the rapid detection of Hg2+ based on phenylamine-oligothiophene derivative. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2016, 153, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, F. Highly sensitive label-free fluorescent detection of Hg2+ ions by DNA molecular machine-based Ag nanoclusters. Analyst 2013, 138, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sun, L.; Ding, T. Multiplexed sensing of mercury (II) and silver (I) ions: A new class of DNA electrochemiluminescent-molecular logic gates. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3570–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, X.; Yu, F.; Xue, L.; Hu, B.; Fan, P.; Dong, Y. A highly selective and sensitive fluorescent probe for quantitative detection of Hg2+ based on aggregation-induced emission features. Talanta 2015, 132, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Highly sensitive and selective voltammetric detection of mercury (II) using an ITO electrode modified with 5-methyl-2-thiouracil, graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wen, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, Q.; Song, S.; Zuo, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, G. Development of mercury (II) ion biosensors based on mercury-specific oligonucleotide probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Ling, J.; Zhang, X.; Bai, H.; Zheng, L.; Cao, Q.; Ding, Z. Sensitive detection of mercury and copper ions by fluorescent DNA/Ag nanoclusters in guanine-rich DNA hybridization. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 137, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, H.; Lan, M. A novel electrochemical biosensor for Hg2+ determination based on Hg2+-induced DNA hybridization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 158, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bings, N.; Bogaerts, A. Atomic spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3917–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaedi, M.; Fathi, M.; Shokrollahi, A.; Shajarat, F. Highly Selective and Sensitive Preconcentration of Mercury Ion and Determination by Cold Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy. Anal. Lett. 2006, 39, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoori, J.; Sorouraddin, M.; Shabani, A. Determination of mercury by cold vapour atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration with dithizone immobilized on surfactant-coated alumina. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1998, 13, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, K.; Foulkes, M.; Worsfold, P. Methods for the determination and speciation of mercury in natural waters—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Feng, W.; Shi, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Zhu, M.; Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Chai, F. Development of a mild mercaptoethanol extraction method for determination of mercury species in biological samples by HPLC-ICP-MS. Talanta 2007, 71, 2034–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Tong, P.; Lin, Y.; Lu, W.; He, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. Highly sensitive fluorescent sensor for mercury based on hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Analyst 2015, 140, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Jin, Y.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y.; Li, Z. A new colorimetric platform for ultrasensitive detection of protein and cancer cells based on the assembly of nucleic acids and proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 871, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, J.; Yu, L.; Feng, G.; Lei, L.; Qun, L.; Bing, L. A regenerative electrochemical biosensor for mercury (II) by using the insertion approach and dual-hairpin-based amplification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 295, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhou, X.; Xing, D. Ultrasensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) in aqueous solution by polymerase assisted fluorescence amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, A.; Togashi, H. Highly selective oligonucleotide-based sensor for mercury (II) in aqueous solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 4300–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Zhao, M. Real-Time Monitoring of the activity and kinetics of T4 polynucleotide kinase by a singly labeled DNA-hairpin smart probe coupled with λ exonuclease cleavage. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohr, K.; Hafner, B.; Nolte, O.; Wolfrum, J.; Sauer, M.; Herten, D. Species-specific identification of mycobacterial 16S rRNA PCR amplicons using smart probes. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7195–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knemeyer, J.; Marme, N.; Sauer, M. Probes for detection of specific DNA sequences at the single-molecule level. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhang, C. Single-labeled hairpin probe for highly specific and sensitive detection of lead (II) based on the fluorescence quenching of deoxyguanosine and G-quartet. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 41, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| River Sample | Added (nM) | Mean Found a (nM) | Mean Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.00 | 18.10 ± 0.50 | 90.50 |
| 2 | 60.00 | 59.80 ± 1.80 | 99.80 |
| 3 | 100.00 | 103.10 ± 2.75 | 103.10 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Ma, C.; Du, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, K. Quencher-Free Fluorescence Method for the Detection of Mercury(II) Based on Polymerase-Aided Photoinduced Electron Transfer Strategy. Sensors 2016, 16, 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111945
Liu H, Ma L, Ma C, Du J, Wang M, Wang K. Quencher-Free Fluorescence Method for the Detection of Mercury(II) Based on Polymerase-Aided Photoinduced Electron Transfer Strategy. Sensors. 2016; 16(11):1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111945
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haisheng, Linbin Ma, Changbei Ma, Junyan Du, Meilan Wang, and Kemin Wang. 2016. "Quencher-Free Fluorescence Method for the Detection of Mercury(II) Based on Polymerase-Aided Photoinduced Electron Transfer Strategy" Sensors 16, no. 11: 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111945
APA StyleLiu, H., Ma, L., Ma, C., Du, J., Wang, M., & Wang, K. (2016). Quencher-Free Fluorescence Method for the Detection of Mercury(II) Based on Polymerase-Aided Photoinduced Electron Transfer Strategy. Sensors, 16(11), 1945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16111945





