Infrared LED Enhanced Spectroscopic CdZnTe Detector Working under High Fluxes of X-rays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
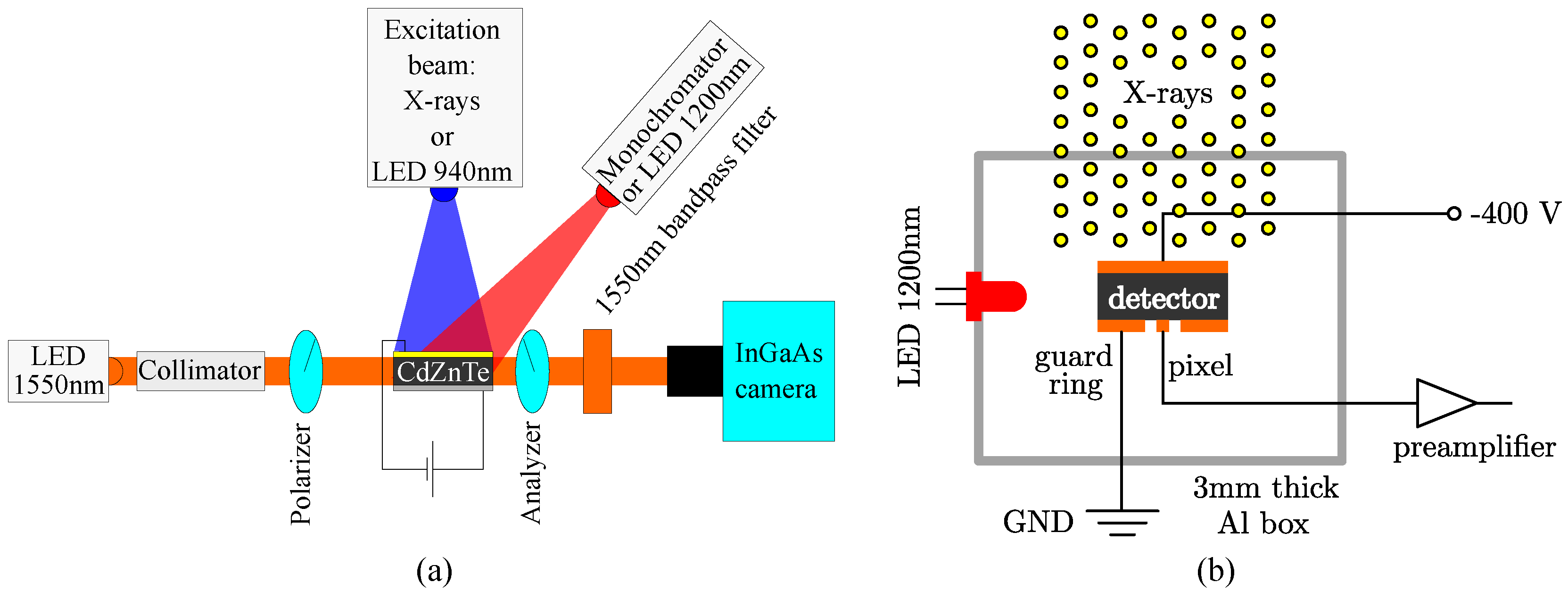
2. Experimental Section
3. Results and Discussion
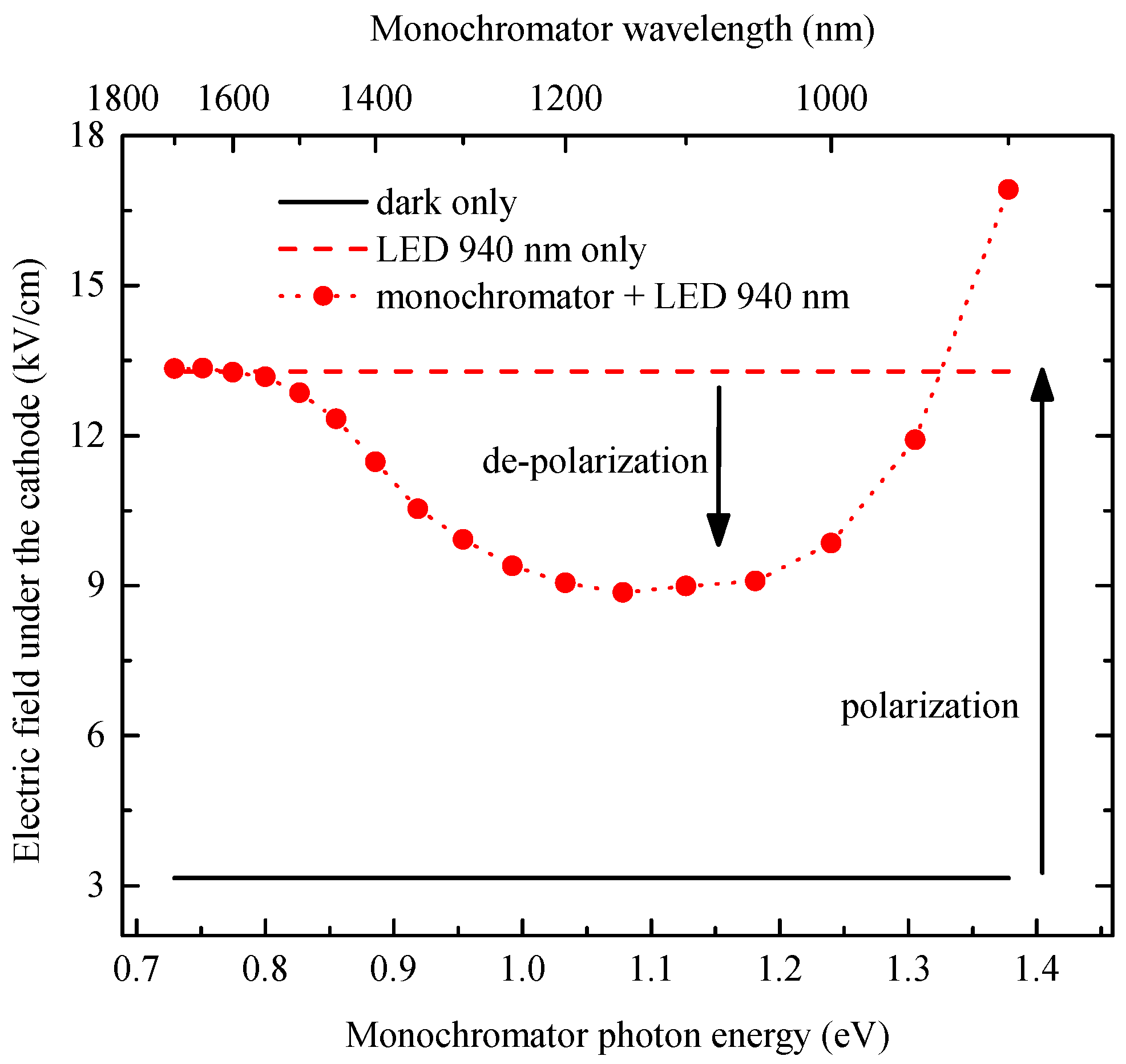
3.1. Polarization and IR De-Polarization
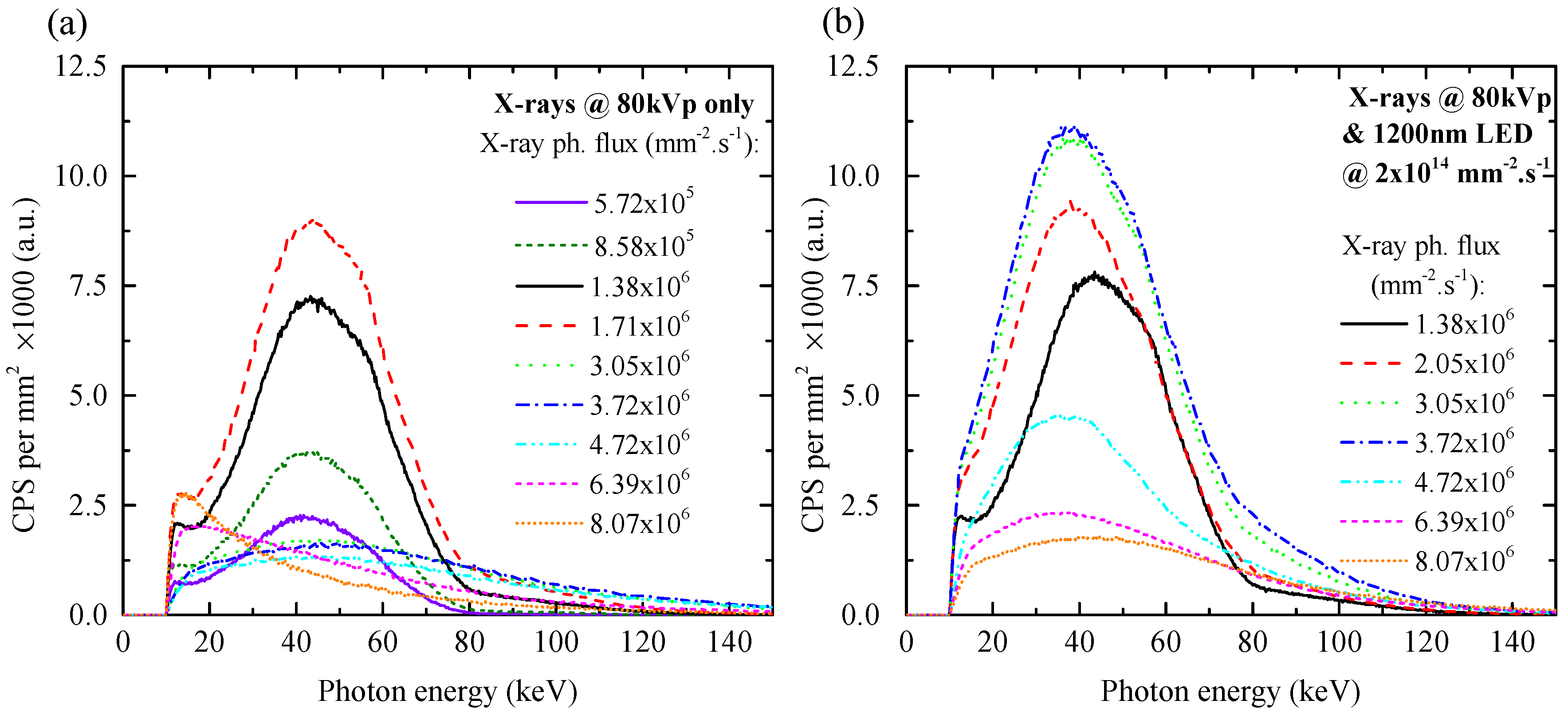
3.2. IR De-Polarization in Spectroscopic Mode: X-rays
3.3. Energy Resolution: Gamma-rays
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCE | Charge collection efficiency |
| CZT | CdZnTe |
| IR | Infrared |
| IRSS | Infrared spectral scanning method |
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
References
- Sordo, S.D.; Abbene, L.; Caroli, E.; Mancini, A.M.; Zappettini, A.; Ubertini, P. Progress in the development of CdTe and CdZnTe semiconductor radiation detectors for astrophysical and medical applications. Sensors 2009, 9, 3491–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, D.S.; Szeles, C. Nature of polarization in wide-bandgap semiconductor detectors under high-flux irradiation: Application to semi-insulating Cd1-xZnxTe. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2008, 77, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, M.; Schroeter, C.; Hackenschmied, P. CdTe/CZT under high flux irradiation. J. Instrum. 2011, 6, C01055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, J.; Dědič, V.; Sellin, P.J.; Grill, R.; Veeramani, P. Radiation induced control of electric field in Au/CdTe/In structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 232115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cola, A.; Farella, I. Electric field and current transport mechanisms in Schottky CdTe X-ray detectors under perturbing optical radiation. Sensors 2013, 13, 9414–9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokesch, M.; Bale, D.S.; Szeles, C. Fast High-Flux Response of CdZnTe X-ray Detectors by Optical Manipulation of Deep Level Defect Occupations. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2010, 57, 2397–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dědič, V.; Franc, J.; Sellin, P.J.; Grill, R.; Perumal, V. Study on electric field in Au/CdZnTe/In detectors under high fluxes of X-ray and laser irradiation. J. Instrum. 2012, 7, P02011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dědič, V.; Franc, J.; Rejhon, M.; Grill, R.; Zázvorka, J.; Sellin, P.J. De-polarization of a CdZnTe radiation detector by pulsed infrared light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 032105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, J.; Dědič, V.; Zázvorka, J.; Hakl, M.; Grill, R.; Sellin, P.J. Flux-dependent electric field changes in semi-insulating CdZnTe. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 235306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franc, J.; Dědič, V.; Rejhon, M.; Zázvorka, J.; Praus, P.; Touš, J.; Sellin, P.J. Control of electric field in CdZnTe radiation detectors by above-bandgap light. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 165702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Antonis, P.; Morton, E.J.; Podd, F.J.W. Infra-red microscopy of Cd(Zn)Te radiation detectors revealing their internal electric field structure under bias. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1996, 43, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zumbiehl, A.; Fougeres, P.; Koebel, J.M.; Regal, R.; Siffert, P. Electric field distribution in CdTe and Cd1-xZnxTe nuclear detectors. J. Cryst. Growth 1999, 197, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.; Groza, M.; Cui, Y.; Hillman, D.; Brewer, E.; Bilikiss, A.; Wright, G.W.; Li, L.; Lu, F.; James, R.B. Characterization of large single-crystal gamma-ray detectors of cadmium zinc telluride. J. Electron. Mater. 2003, 32, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cola, A.; Farella, I.; Auricchio, N.; Caroli, E. Investigation of the electric field distribution in x-ray detectors by Pockels effect. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2006, 8, S467–S472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellin, P.J.; Prekas, G.; Franc, J.; Grill, R. Electric field distributions in CdZnTe due to reduced temperature and x-ray irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washington, A.L.; Teague, L.C.; Duff, M.C.; Burger, A.; Groza, M.; Buliga, V. Response of the internal electric field in cdznte to illumination at multiple optical powers. J. Electron. Mater. 2012, 41, 2874–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolotnikov, A.E.; Camarda, G.S.; Chen, E.; Cheng, S.; Cui, Y.; Gul, R.; Gallagher, R.; Dedic, V.; De Geronimo, G.; Giraldo, L.O.; et al. CdZnTe position-sensitive drift detectors with thicknesses up to 5 cm. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 093504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zázvorka, J.; Franc, J.; Dědič, V.; Hakl, M. Electric field response to infrared illumination in CdTe/CdZnTe detectors. J. Instrum. 2014, 9, C04038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverria, R.; Vicent, A.; Joshi, N. Photoquenching effect and its consequence in p type gallium arsenide. Sol. State Commun. 1984, 52, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosyachenko, L.A.; Sklyarchuk, V.M.; Sklyarchuk, O.F.; Maslyanchuk, O.L.; Gnatyuk, V.A.; Aoki, T. Higher voltage Ni/CdTe schottky diodes with low leakage current. IEEE Trans. Nuc. Sci. 2009, 56, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pekárek, J.; Dědič, V.; Franc, J.; Belas, E.; Rejhon, M.; Moravec, P.; Touš, J.; Voltr, J. Infrared LED Enhanced Spectroscopic CdZnTe Detector Working under High Fluxes of X-rays. Sensors 2016, 16, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101591
Pekárek J, Dědič V, Franc J, Belas E, Rejhon M, Moravec P, Touš J, Voltr J. Infrared LED Enhanced Spectroscopic CdZnTe Detector Working under High Fluxes of X-rays. Sensors. 2016; 16(10):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101591
Chicago/Turabian StylePekárek, Jakub, Václav Dědič, Jan Franc, Eduard Belas, Martin Rejhon, Pavel Moravec, Jan Touš, and Josef Voltr. 2016. "Infrared LED Enhanced Spectroscopic CdZnTe Detector Working under High Fluxes of X-rays" Sensors 16, no. 10: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101591
APA StylePekárek, J., Dědič, V., Franc, J., Belas, E., Rejhon, M., Moravec, P., Touš, J., & Voltr, J. (2016). Infrared LED Enhanced Spectroscopic CdZnTe Detector Working under High Fluxes of X-rays. Sensors, 16(10), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16101591




