Quantitative Evaluation System of Soft Neurological Signs for Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Systems Design Section
2.1. System Configuration and Procedure of Experiment
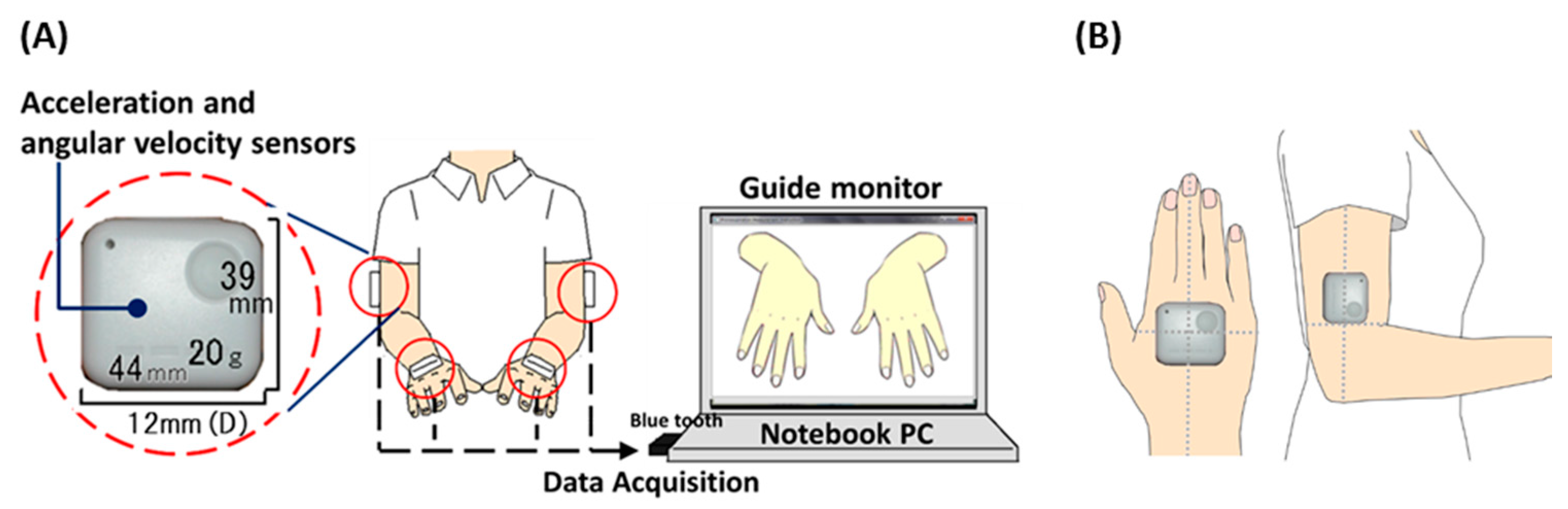
2.2. Participants
| TD Group | ADHD Group | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Male/Female | Total | Age | Male/Female | Total | IQ | |
| 4 | 6/3 | 9 | |||||
| 5 | 9/5 | 14 | |||||
| 6 | 4/7 | 11 | |||||
| 7 | 13/19 | 32 | 7 | 4/2 | 6 | 110.8 (10.9) | |
| 8 | 22/14 | 36 | 8 | 3/1 | 4 | 101.8 (20.7) | |
| 9 | 19/21 | 40 | 9 | 8/2 | 10 | 94.0 (9.0) | |
| 10 | 17/20 | 37 | 10 | 5/1 | 6 | 99.4 (6.2) | |
| 11 | 8/18 | 26 | 11 | 7/0 | 7 | 103.9 (10.4) | |
| 12 | 9/9 | 18 | |||||
| 21–29 | 19/6 | 25 | |||||
| Total | 126/122 | 248 | Total | 27/6 | 33 | 101.3 (12.9) | |
3. Analysis Design
3.1. Evaluation Indices and Analyzed Parameters
3.2. Score and Statistics for Evaluation Indices
4. Results
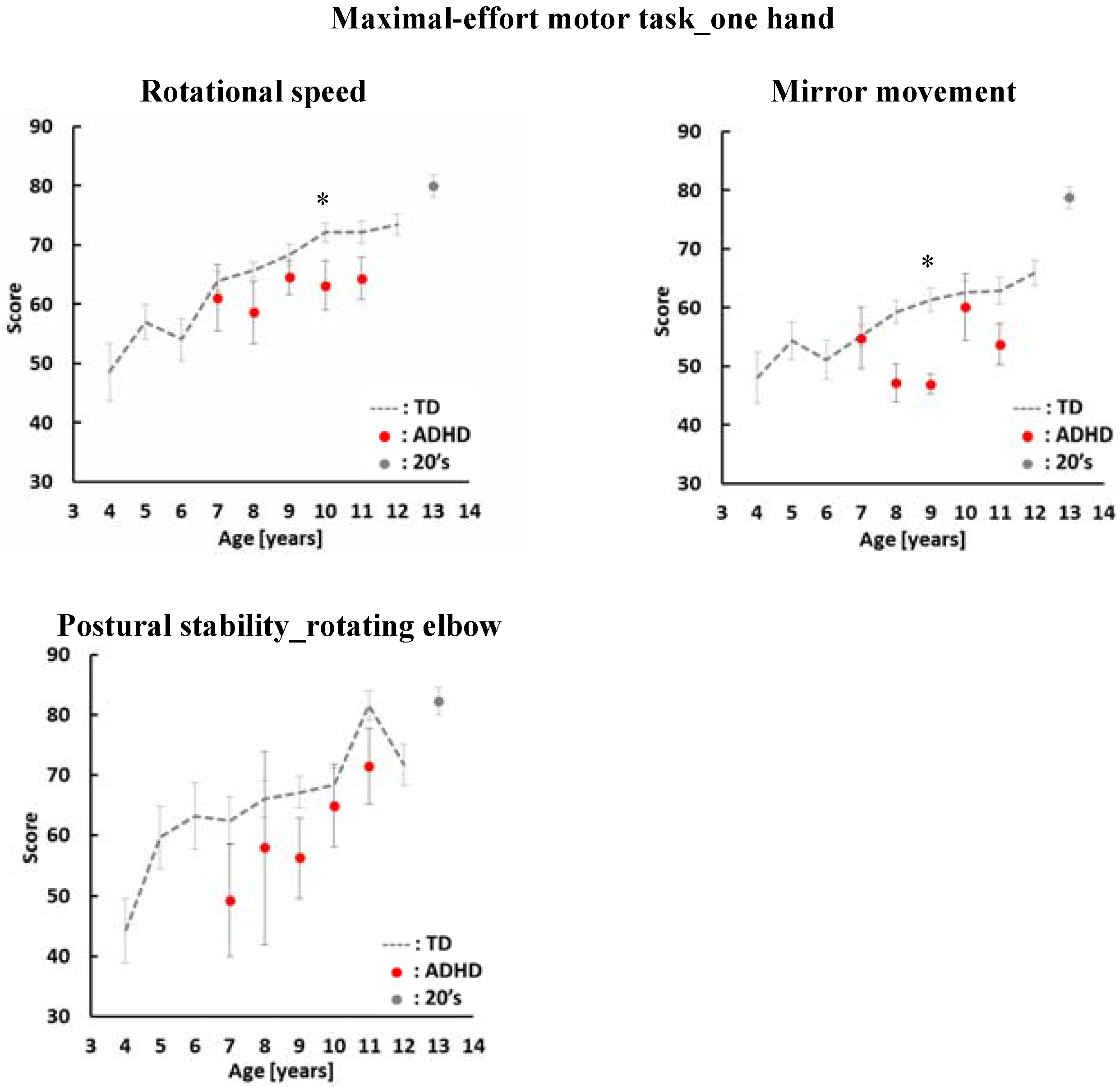
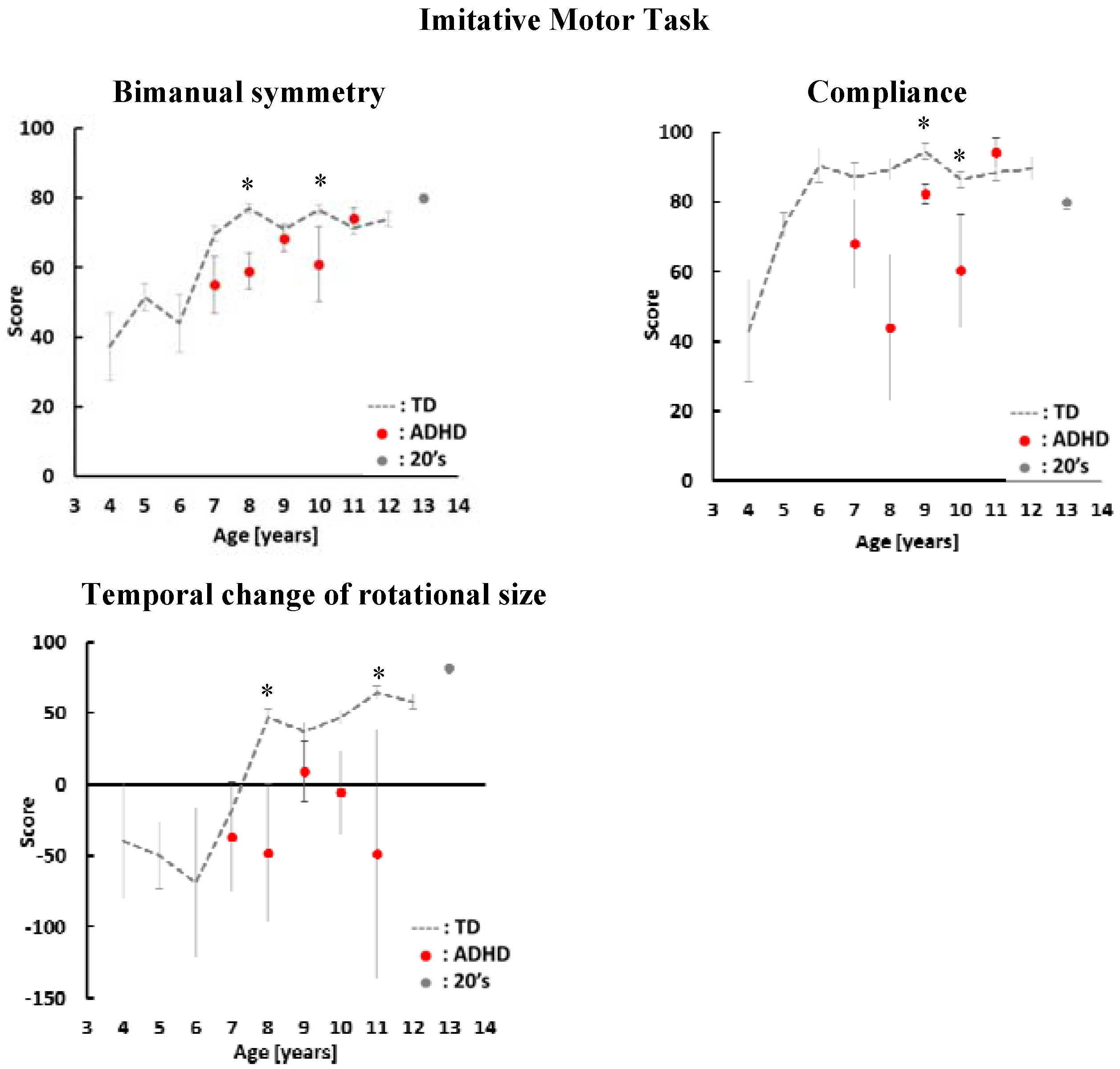
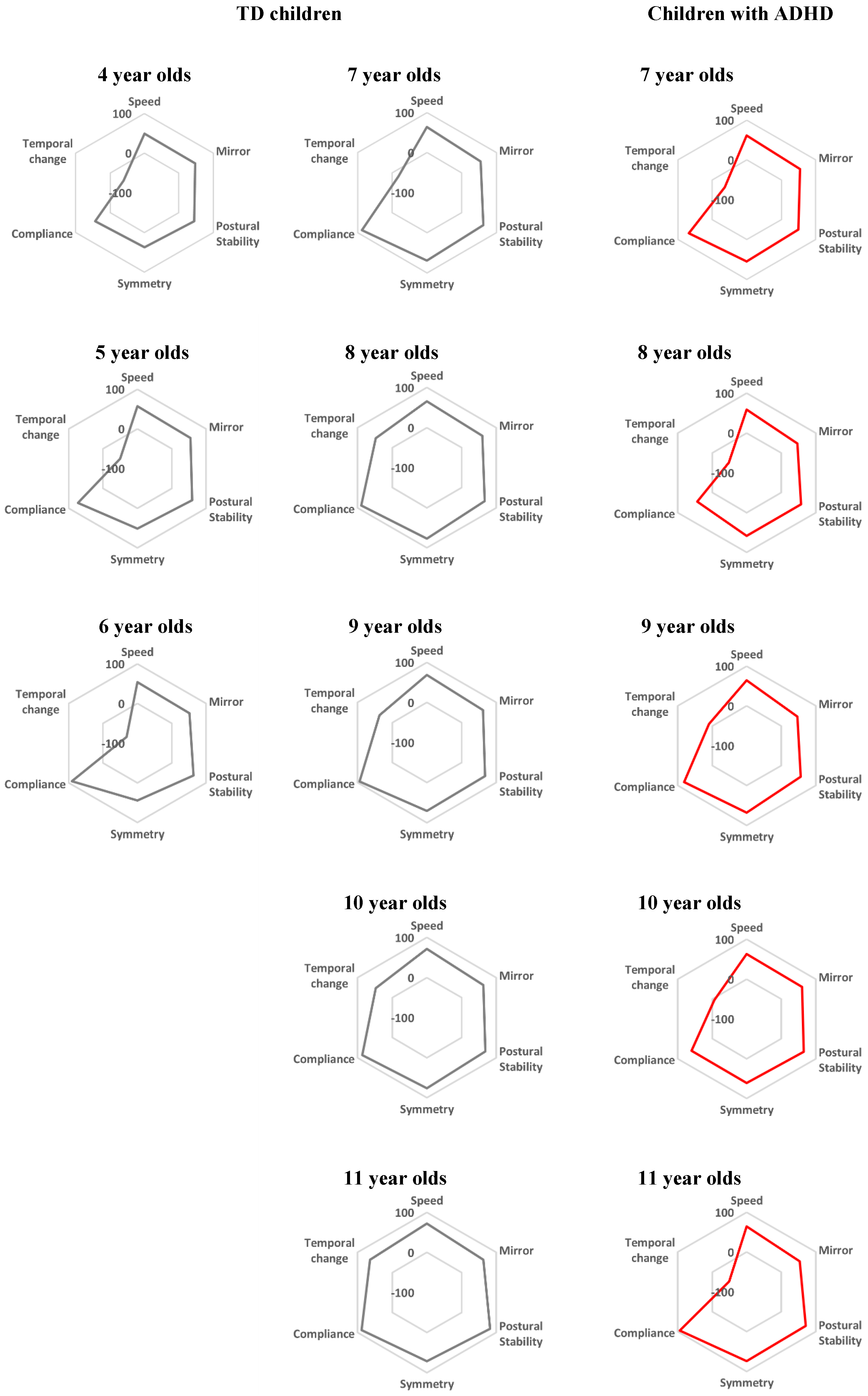
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mijna, H.A. The Neurological Examination of the Child with Minor Neurological Dysfunction, 3rd ed.; Mac Keith Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Touwen, B.C.L.; Prechtl, H.F.R. The Neurological Examination of the Child with Minor Neurological Dysfunction; William Heinemann Medical Books: London, UK, 1970; pp. 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Patankar, C.V.; Sangle, J.P.; Shah, R.H.; Dave, M.; Kamath, M.R. Neurological soft signs in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Indian J. Psychiatry 2012, 54, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fewell, R.R. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder in Very Young Children: Early Signs and Interventons. Inf. Young Child. 2002, 14, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, R.; Kapci, G.E.; Oztop, D. Neurological soft signs in comorbid learning and attention deficit hyperactivity disorders. Turk. J. Pediatr. 2007, 49, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pineda, D.; Ardila, A.; Rosselli, M.; Arias, E.B.; Henao, C.G.; Gomez, F.L.; Mejia, E.S.; Miranda, L.M. Prevalence of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in 4- to 17-Year-Old Children in the General Population. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 1999, 27, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonga, J.; Xie, J.; Chenb, G.; Zhanga, Y.; Wang, S. Neurological soft signs in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Their relationship to executive function and parental neurological soft signs. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroes, M.; Kessels, A.G.H.; Kalff, A.C.; Feron, F.J.M.; Vissers, Y.L.J.; Jolles, J.; Vles, J.S.H. Quality of movement as predictor of ADHD: Results from a prospective population study in 5- and 6-year-old children. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Omizzolo, C.; Galea, M.P.; Vance, A. Motor imagery skills of children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Developmental Coordination Disorder. Hum.s Mov. Sci. 2013, 32, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.M.; Kocsis, J.J.; Estes, R.E. Soft neurological signs in learning- disabled children and controls. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1974, 128, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, M.; Punt, M.; de Groot, E.; Minderaa, R.B.; Hadders-Algra, M. Minor neurological dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorder. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2011, 53, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, J.; Thomas, P.R.; Maruff, P.; Butson, M.; Wilson, P.H. Motor, visual and egocentric transformations in children with Developmental Coordination Disorder. Child Care Health Dev. 2006, 32, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmut, K.; Wann, J.P.; Brown, J.H. Problems in the coupling of eye and hand in the sequential movements of children with Developmental Coordination Disorder. Child Care Health Dev. 2006, 32, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, C.M.; Kleser, C.; Schneider, M.; Gontard, A.V. Quantitative Assessment of Neuromotor Function in Adolescents with High Functioning Autism and Asperger Syndrome. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2007, 37, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreulen, M.; Smeulders, M.J.C.; Veeger, H.E.J.; Hage, J.J.; Vanderhorst, C.M.M. Three-dimensional video analysis of forearm rotation before and after combined pronator teres rerouting and flexor carpi ulnaris tendon transfer surgery in patients with cerebral palsy. J. Hand Surg. Br. Eur. 2004, 29, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Okada, M. A method for quantification of alternate pronation and supination for forearms. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1983, 16, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsdorfer, J. Comparative analysis of diadochokinetic movements. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1999, 9, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iramina, K.; Kamei, Y.; Katayama, Y. Evaluation System for Minor Nervous Dysfunction by Pronation and Supination of Forearm using Wireless Acceleration and Angular Velocity Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 7364–7367.
- Kaneko, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Inomoto, O.; Iramina, K. Soft Neurological Signs in Childhood by Measurement of Arm Movements Using Acceleration and Angular Velocity Sensors. Sensors 2015, 15, 25793–25808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largo, R.H.; Caflish, J.A.; Hug, F.; Muggli, K.; Monar, A.A. Neuromotor development from 5 to 18 years. Part 2: Associated movements. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2001, 43, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landgren, M.; Kjellman, B.; Gillberg, C. Deficits in attention, motor control and perception (DAMP): A simplified school entry examination. Acta Paediatr. 2000, 89, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracy, J.I.; Faro, S.S.; Mohammed, F.B.; Pinus, A.B.; Madi, S.M.; Laskas, J.W. Cerebellar mediation of the complexity of bimanual compared to unimanual movement. Neurology 2001, 57, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoppenbrouwers, S.S.; Schutter, D.J.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Chen, R.; Daskalakis, S.K. The role of the cerebellum in the pathophysiology and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders: A review. Brain Res. Rev. 2008, 59, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, B.N.; Kaplan, J.B.; Crawford, G.S.; Campbell, A.; Dewey, D. Reliability and Validity of a Parent Questionnaire on Childhood Motor Skills. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2000, 54, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaneko, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Iramina, K. Quantitative Evaluation System of Soft Neurological Signs for Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Sensors 2016, 16, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010116
Kaneko M, Yamashita Y, Iramina K. Quantitative Evaluation System of Soft Neurological Signs for Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Sensors. 2016; 16(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaneko, Miki, Yushiro Yamashita, and Keiji Iramina. 2016. "Quantitative Evaluation System of Soft Neurological Signs for Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder" Sensors 16, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010116
APA StyleKaneko, M., Yamashita, Y., & Iramina, K. (2016). Quantitative Evaluation System of Soft Neurological Signs for Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Sensors, 16(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010116





