Abstract
Recorded neural data are frequently corrupted by large amplitude artifacts that are triggered by a variety of sources, such as subject movements, organ motions, electromagnetic interferences and discharges at the electrode surface. To prevent the system from saturating and the electronics from malfunctioning due to these large artifacts, a wide dynamic range for data acquisition is demanded, which is quite challenging to achieve and would require excessive circuit area and power for implementation. In this paper, we present a high performance Delta-Sigma modulator along with several design techniques and enabling blocks to reduce circuit area and power. The modulator was fabricated in a 0.18-μm CMOS process. Powered by a 1.0-V supply, the chip can achieve an 85-dB peak signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio (SNDR) and an 87-dB dynamic range when integrated over a 10-kHz bandwidth. The total power consumption of the modulator is 13 μW, which corresponds to a figure-of-merit (FOM) of 45 fJ/conversion step. These competitive circuit specifications make this design a good candidate for building high precision neurosensors.
1. Introduction
Growing concerns for human health have stimulated the development of biomedical devices [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], such as biosensors for recording neural spikes, field potentials, electroencephalography (EEG), electrocardiography (ECG), electromyography (EMG), and so on. Figure 1 shows the block diagram in a wireless neural recording microsystem [1], where an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is used for digitizing neural data recorded at each electrode. These neural data include several components, like local field potentials (LFPs), extracellular spikes and motion artifacts [18,19,20,21,22]. To record these neural data without saturating from large artifacts, it requires a wide dynamic range for data acquisition. The requirement is further pushed by the need to support more sophisticated neuroscience experiments and clinical applications, where motion artifacts tend to be more frequent and severe [23]. In this regard, it is important to integrate a high precision ADC in the recording microsystem.
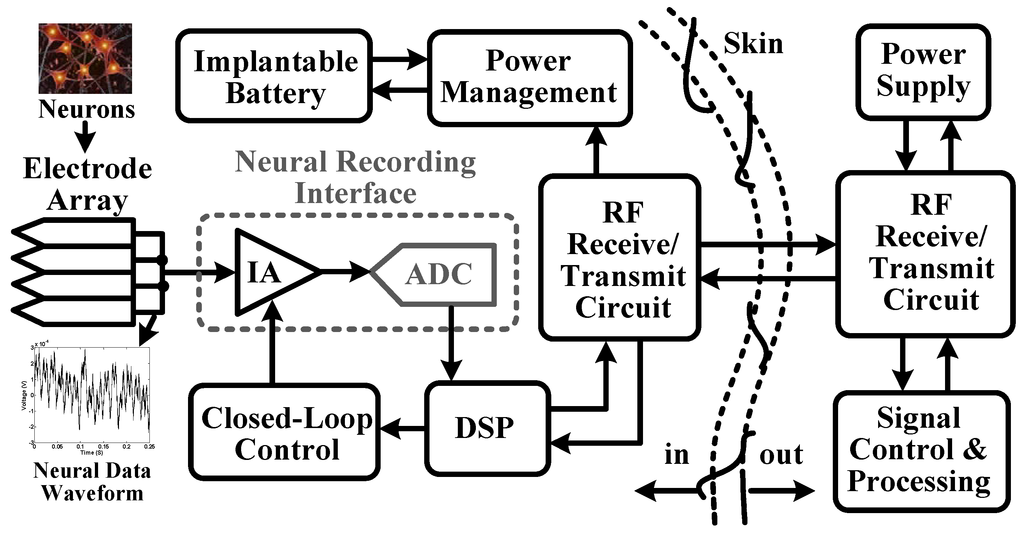
Figure 1.
Block diagram of a wireless neural recording system.
In this paper, we present a Delta-Sigma ADC for building high precision recording microsystems. Compared to recent Delta-Sigma ADC designs [24,25,26,27,28,29], several techniques are used to improve circuit performance in terms of power, precision, area and FOM. (1) We have used high density metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) capacitors to replace metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitors for reducing circuit area [30]. As detailed in Section 4 and Section 5, circuit bias and integrator output swing are carefully designed, such that the distortion caused by MOS capacitors can be negligible. (2) We have adopted a multi-bit switched op-amp (MBSO)-based modulator architecture. Compared to those non-op-amp-based designs reported previously [25], our design offers a competitive performance in terms of power and area, maintaining less design complexity and restriction on precision [31].
To implement the proposed MBSO-based architecture, several circuit techniques have been incorporated as summarized below. First, we have performed careful characterization with each type of MOS capacitor. Based on the simulation results, we have chosen the optimal type of capacitor for each integrator. Second, a switched op-amp technique has been used where amplifiers are automatically turned off when they are not in use. Realizing such high performance switched op-amp depends on the bias circuits. In this design, novel bias circuits have been proposed to reduce switching power loss. Third, the static power of the quantizer has been removed through an elegant circuit arrangement. Finally, a new half-cycle operating resonator scheme has been designed for reducing in-band quantization noise. These techniques together boost the performance of the modulator and make it a competitive candidate for building high precision recording microsystems.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 analyzes the dynamic range of neural data using different sequences recorded from in vivo preparations and epilepsy patients. Section 3 gives a brief overview of different ADC structures. Section 4 presents the design analysis for the proposed Delta-Sigma modulator. The circuit implementation is shown in Section 5, followed by measurement results in Section 6. Section 7 gives the concluding remarks of this paper.
2. In Vivo Neural Data Dynamic Range Analysis
In vivo neural data recorded from extracellular space consist of both LFPs and extracellular spikes. The amplitude of extracellular spikes is inversely proportional to the distance between the recording site and neuron [32]. Neural spikes are from a few μV (the recording site is about 300 μm away from the neuron) to several hundred μV (the recording site is closest to the neuron), and LFPs are from tens of μV to several mV [32]. However, as shown in Figure 2, motion artifacts can be much larger, which would cause misinterpretation of the signals and sometimes saturate the recording electronics.
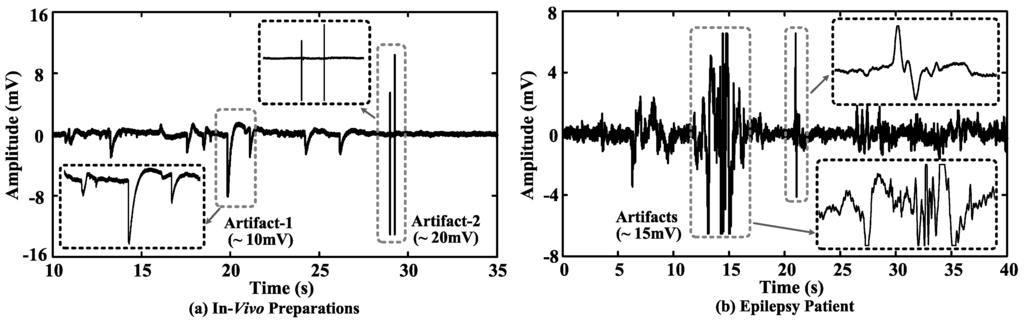
Figure 2.
(a) In vivo neural recording from a rat preparation and (b) an intracortical recording from an epilepsy patient.
To study the required system dynamic range to accommodate both neural activities and artifacts, we have analyzed data sequences obtained from different setups: (1) in vivo preparations sampled at 40 kHz; (2) full-spectrum recordings from epilepsy patients sampled at 32 kHz. Table 1 summarizes the averaged data dynamic range with/without artifacts from different sequences, where the artifacts and spikes are manually labeled by a domain expert.
The formula to estimate the data dynamic range is shown below:
where is dynamic range in dB, is the data amplitude and is the root mean-square (RMS) amplitude of a labeled spike template. The effective number of bits (ENOB) of dynamic range can be calculated as . A few example spike templates extracted from four in vivo data sequences are shown in Figure 3. We assume that the spike template is digitalized at 16 levels, thus having sufficient resolution for neural signal processing. As shown in Table 1, the estimated data dynamic range based on the recordings from in vivo preparations and epilepsy patients are (12.06–13.58)-bit and (11.73–13.09)-bit, respectively.

Table 1.
Averaged data dynamic range of in vivo neural activities.
| Parameter | In Vivo Neural Data (1 Hz–10 kHz) | Epilepsy Patient Data (0.5 Hz–9 kHz) |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic range without artifacts | (10.57 ± 0.32)-bit | (9.55 ± 0.31)-bit |
| Dynamic range with artifacts | (12.82 ± 0.76)-bit | (12.41 ± 0.68)-bit |
| Increase in dynamic range | 2.25-bit | 2.86-bit |
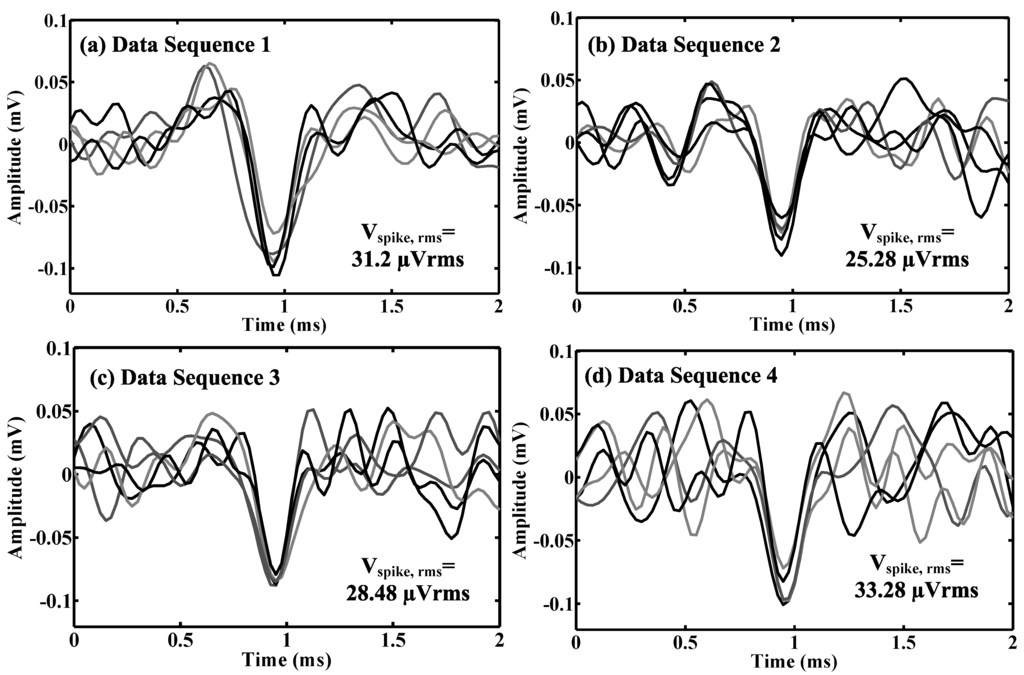
Figure 3.
Exampled spike templates extracted from four in vivo data sequences (a–d).
3. ADC Architecture Comparison and Selection
Figure 4 shows a survey of ADC designs published in the literature [33], including successive approximation register (SAR) ADC, flash ADC, pipelined ADC and Delta-Sigma ADC. Among the surveyed designs, the power consumption and power ratio (ADC power divided by the total power consumption) of neurosensors are shown in Figure 5 [2,5,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41], where the maximum power ratio is less than 10%, and the total power consumption includes the power of instrumentation amplifier (IA), ADC, digital signal processor, power management circuits, and so on. The low power ratio suggests that there is some power budget trade-off for precision. Among the surveyed ADCs, flash and pipelined ADCs tend to have better performance in high speed (>20 MS/s) and medium resolution ((4–10)-bit) applications. The SAR ADCs typically provide an (8–10)-bit resolution [2,5,34,35,36,37,38], which is not enough to simultaneously record LFPs, extracellular spikes and artifacts without causing system saturation. Delta-Sigma ADCs can provide higher precision, thus avoiding saturation by using small gain in the IA. However, the costs are extra circuit power and area. In Section 4 and Section 5, we will focus on circuit design techniques for optimizing Delta-Sigma ADC to make it suitable for neural recordings.
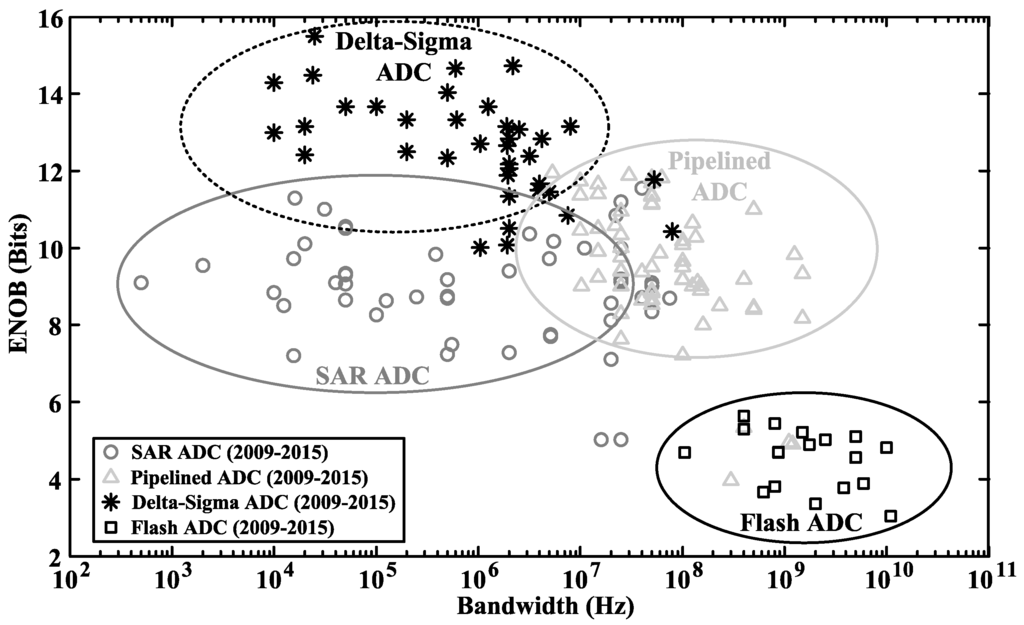
Figure 4.
Performance comparison of ADC works published in the literature [33].
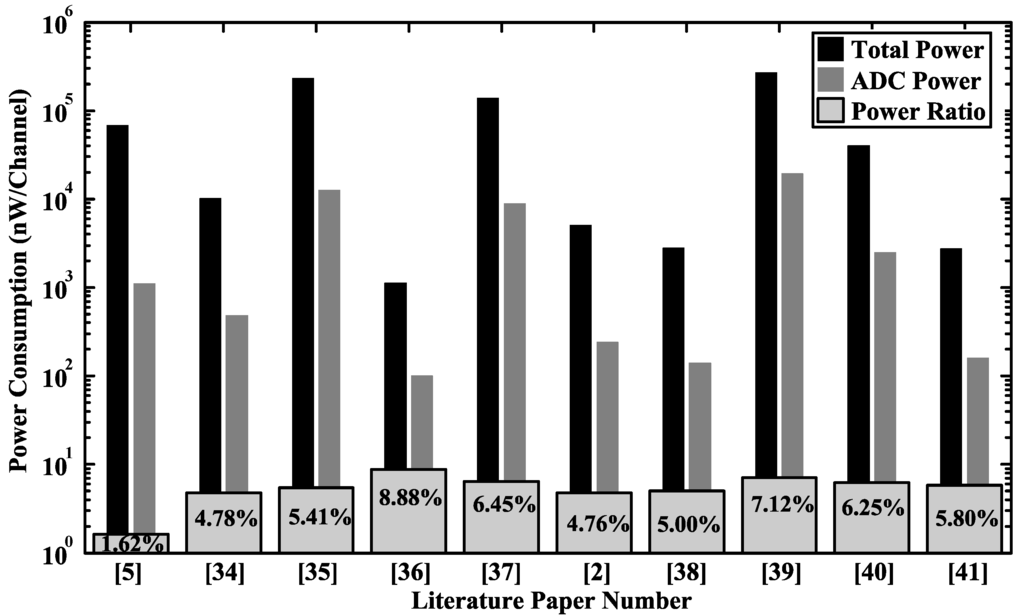
Figure 5.
The total power consumption of the ADC block and its power ratio [2,5,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41]. The power ratio is referred to as the ADC power divided by the total sensor power.
4. Multi-Bit Switched Op-Amp-Based Delta-Sigma Modulator Design
4.1. Delta-Sigma Modulator Topology
The proposed Delta-Sigma modulator topology is shown in Figure 6, where a number of design choices are made for improving circuit performance. First, we have used a fully-feed-forward loop filter instead of a feedback one, because it gives extra signal paths from the outputs of integrators to the quantizer, so most of the signal energy is prevented from leaking into the modulator loop. Second, a multi-bit quantization technique and a local resonator with a coefficient of 1/50 are used for reducing in-band quantization noise, which in turn increases the ADC precision. Third, the switched-capacitor (SC) integrator is powered off during the sampling phase and powered back on during the integration phase. Hence, it can reduce the amplifier power consumption by half. Fourth, to suppress harmonic distortions caused by capacitor mismatches in the feedback digital-to-analog converter (DAC), a pseudo data weighted averaging (DWA) block is used to provide several dB boosting in dynamic range [42]. Fifth, the gain coefficient of the feed-forward summation block is scaled down by half to reduce its output swing, which can effectively allow one to adopt high-density MOS capacitors to simultaneously achieve a small circuit area and good linearity. Last, substantial processing time has been reserved for key blocks through clock scheduling. Due to these circuit design techniques, the proposed modulator topology is supposed to be suitable for ultra-low power high-precision applications [31].
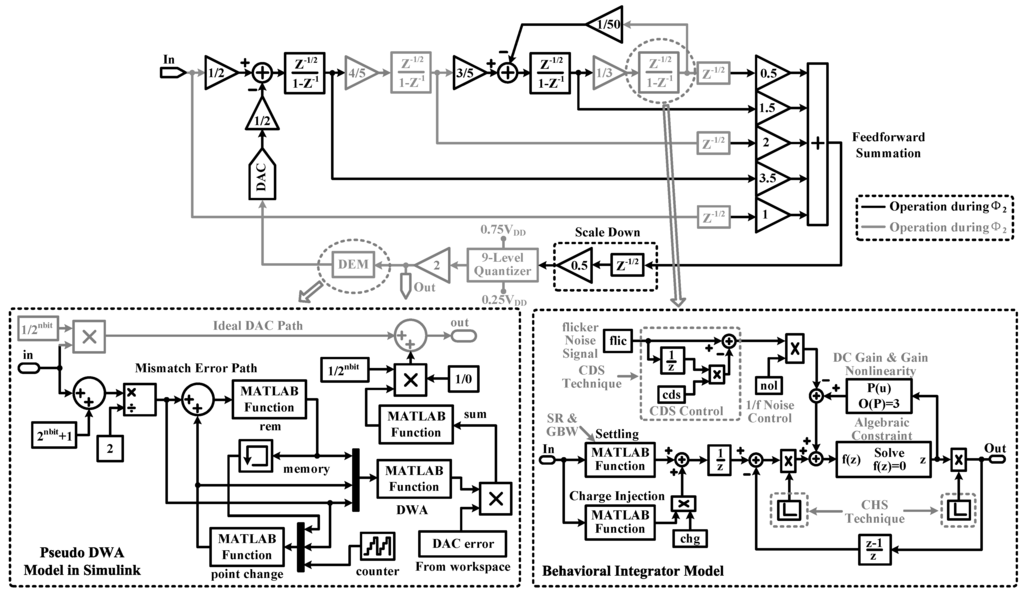
Figure 6.
Block diagram of the proposed Delta-Sigma modulator with the behavioral integrator model [43,44] and the pseudo data weighted averaging (DWA) model.
4.2. Design Analysis on Non-Ideal Factors
This section gives the detailed analyses of the proposed modulator. A number of circuit design issues, including slew rate (SR), gain bandwidth (GBW), voltage gain, nonlinearity, charge injection, noise and noise, are presented for discussion.
4.2.1. Finite Amplifier Gain
The noise transfer function (NTF) of the proposed modulator can be calculated as:
When considering the finite amplifier gain in each integrator, the NTF becomes:
where , and is the finite voltage gain of the i-th integrator ().
Figure 7a shows the normalized RMS gains of the NTF with different amplifier gains. For the solid curve, the voltage gain of each operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) is set to be equal and scanned from 0 dB–120 dB. For the dotted line with “*”, the voltage gains of the first two stage OTAs are scanned from 0 dB–120 dB, while the gains of the third and fourth stage OTAs are fixed at 60 dB. For the dotted curve with “∘”, the voltage gains of the third- and fourth-stage OTAs are scanned from 0 dB–120 dB, while the gains in the first two stages are fixed at 60 dB. According to the simulation results, the OTA gains in the first two stages can be reduced to 40 dB, while the OTA gains in the third and fourth stages should be more than 60 dB.
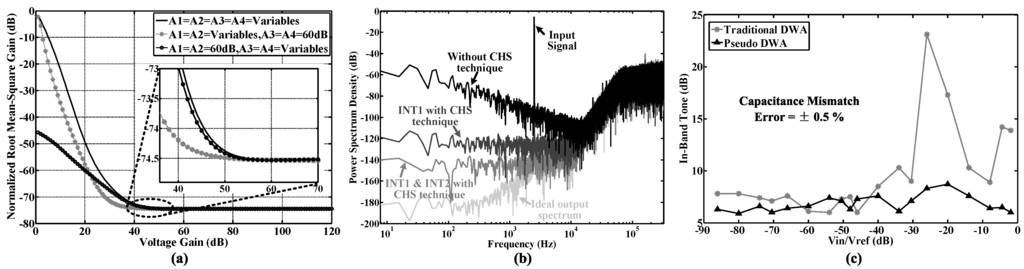
Figure 7.
Simulation results of the proposed Delta-Sigma modulator. (a) The normalized RMS gain of the proposed noise transfer function (NTF) versus different voltage gains; (b) The modulator output spectrum with/without the chopper stabilization (CHS) technique in each integrator; (c) In-band tone performance with pseudo/traditional DWA. The capacitor mismatch error of the feedback digital-to-analog converter (DAC) is set to be ±0.5%.
4.2.2. Chopper Stabilization
As shown in Figure 7b, low frequency noise can compromise ADC precision if not removed, especially for noise. Among different methods to remove low frequency noise, chopper stabilization (CHS) and correlated double sampling (CDS) techniques are popularly used [45,46,47]. In this design, we choose CHS, because CDS requires the amplifier to be constantly powered on, thus consuming more power. Figure 6 gives the integrator model with parameters, including finite gain, gain nonlinearity, finite SR, finite GBW, noise, switch-on resistance, charge injection, CDS, CHS, etc. Figure 7b shows the power spectrum at the modulator output. Through simulation, it is found that CHS is required in the first stage for achieving a 14-bit conversion precision, while this technique will be required for every stage when the target is to achieve a higher precision.
4.2.3. Pseudo Data Weighted Averaging
A pseudo DWA behavioral block as shown in Figure 6 is added to analyze the effect of capacitor mismatch. The model can be explained as follows.
where and are the actual and ideal output of the feedback DAC, respectively; is capacitor mismatch error, which has been processed by the pseudo DWA algorithm.
Figure Figure 7c gives the in-band tone performance with a capacitor mismatch error of ±0.5% in the feedback DAC. Compared to the traditional DWA, pseudo DWA can effectively suppress in-band harmonic distortions (<8 dB) to optimize the SNDR performance over the required bandwidth.
5. Circuit Design and Implementation
5.1. High Density MOS Capacitors
Considering efficiency in terms of area, MOS capacitors are preferred due to their higher capacitance density [30]. Figure 8 illustrates three MOS capacitor circuits: (a) the parallel p-channel MOS (PMOS) type in the depletion region; (b) the single-PMOS type in the accumulation region and (c) the series-PMOS type in the accumulation region. The equivalent capacitances of the three MOS capacitors are shown as follows.
where is equivalent capacitance and and are the gate-oxide capacitance and depletion capacitance of a transistor, respectively.
For circuit analysis, can be analytically approximated as:
where , and are periodic time, instantaneous AC current and instantaneous AC voltage of the input sinusoid waveform, respectively.
Figure 8 shows the simulated capacitance-voltage (C-V) curves of the three MOS capacitors in a 0.18-μm complementary MOS (CMOS) process. The single-PMOS type is able to provide a high density (8.45 fF/μm2) at a moderate bias voltage range (0.4 V–1.4 V) and poor linearity (<4.1%). The parallel-PMOS type gives a moderate density (2.35 fF/μm2) at a narrow bias voltage range (±0.2 V) and moderate linearity (<3.5%). The series-PMOS type has a moderate density (2.05 fF/μm2) with a wide bias voltage range (0.2 V–1.4 V) and good linearity (<2.8%). The density of the MIM capacitor is only 0.97 fF/μm2, though it allows a wide bias voltage range (−0.4 V–1.4 V) and good linearity (<0.1%).
Figure 9 shows the normalized output swings of several circuit blocks in the proposed modulator when the input is supplied with a −3.0 dB sinusoid input. It shows that the largest output swing in the feed-forward summation block is about 0.5 (0.25 V–0.75 V), while the output of the integrators is less than 0.3 (0.35 V–0.65 V). The simulation results suggest that the proposed MOS capacitor structures can be used without causing major distortions.
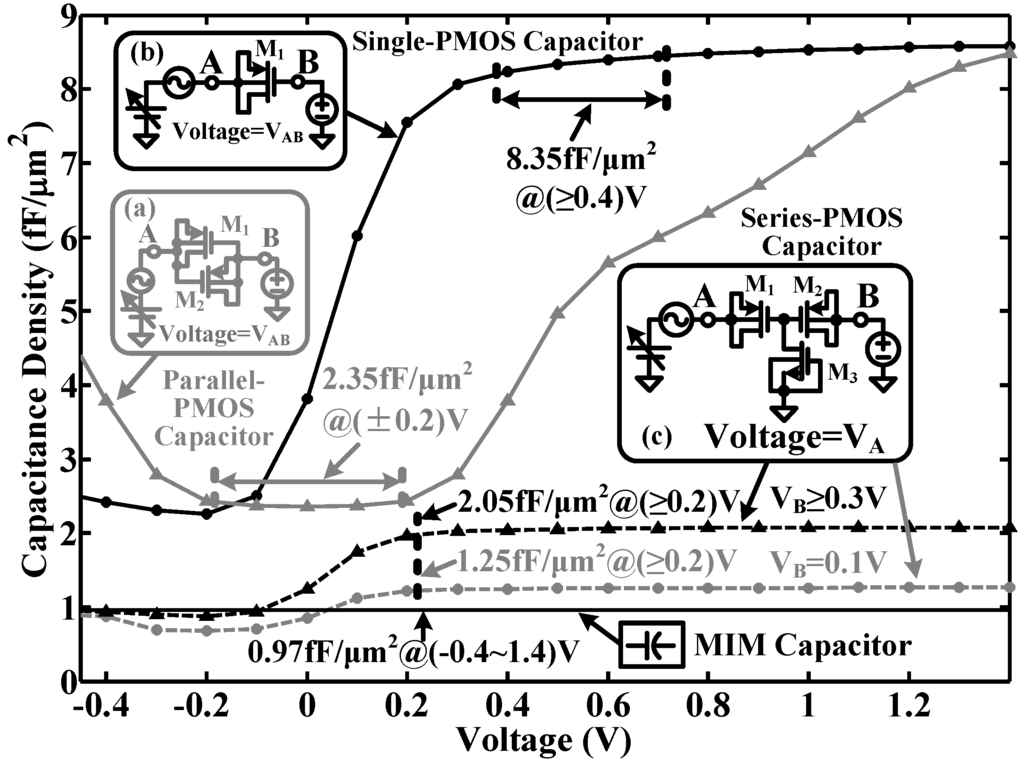
Figure 8.
Simulated capacitance-voltage (C-V) curves of the proposed MOS capacitors in a 0.18-μm CMOS process: (a) parallel-PMOS type in the depletion region; (b) single-PMOS type and (c) series-PMOS type in the accumulation region.
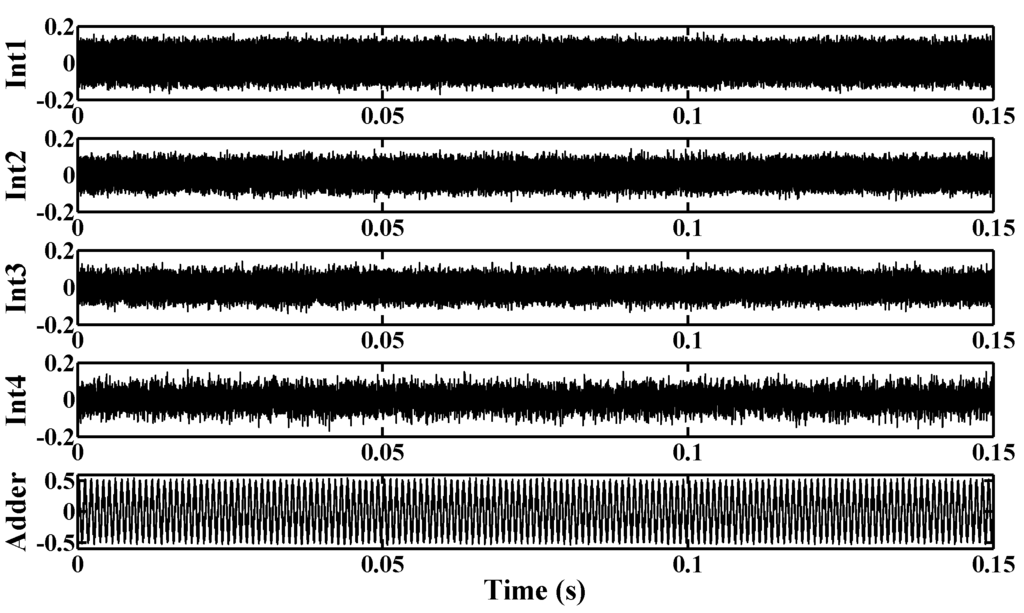
Figure 9.
Simulated output swings of several circuit blocks in the proposed modulator.
5.2. Fully-Clocked Power-Efficient Switched Op-Amp
Figure 10 shows the circuit schematics of the proposed fully-clocked current-mirror switched op-amps (NMOS input-pair type and PMOS input-pair type). It is a load-compensated single-stage OTA with a Class-AB output stage. A cross-coupling structure (–) is built in to achieve a large voltage gain and fast recovery from the off state. To save power, switches and are added to fully turn off the switched op-amp during the sampling phase. With a traditional bias circuit (highlighted in gray color, as shown in Figure 10), would be pulled to either (NMOS input-pair switched op-amp) or ground (PMOS input-pair switched op-amp) during the off state. When the switched op-amp is turned on, there could be large instantaneous current and power consumption, which can be prevented by adding a series switch to reduce the voltage fluctuation of (<100 mV). With the proposed bias circuit, the power consumption of the switched op-amps can be reduced by 24% (2.4 μA).
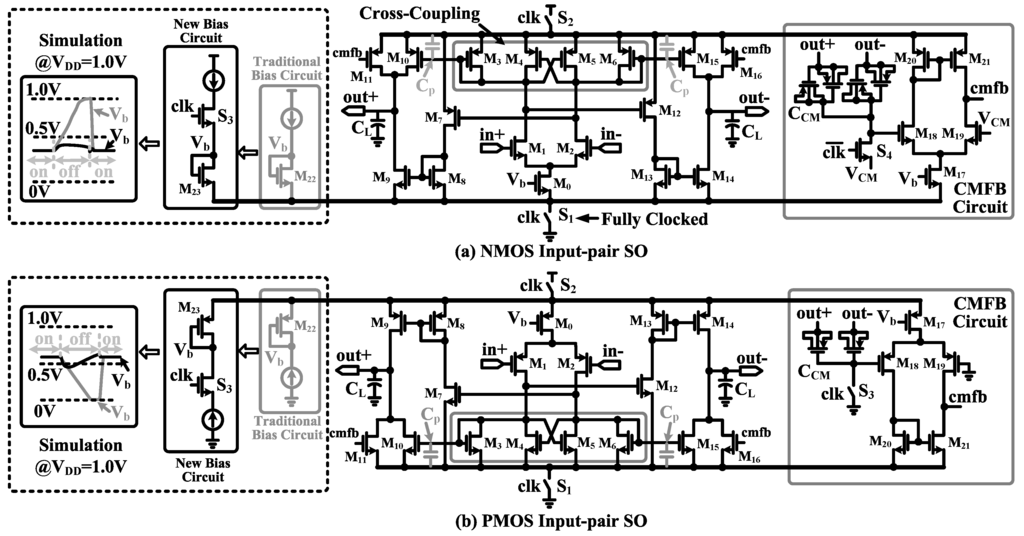
Figure 10.
Fully-clocked power-efficient switched op-amps with the corresponding common mode feedback (CMFB) circuit: (a) NMOS input pair and (b) PMOS input pair.
To reduce circuit power and noise, it is important to select an appropriate switched op-amp for each integrator. The simulation results of both NMOS input-pair switched op-amp and PMOS input-pair switched op-amp are shown in Table 2, where the amplifier gain A, , total current power consumption and amplifier input-referred noise are shown.

Table 2.
Simulation results of the proposed switched op-amps.
| Parameter | NMOS Input-Pair Switched Op-Amp | PMOS Input-Pair Switched Op-Amp |
|---|---|---|
| Gain A | 61.1 dB | 57.7 dB |
| Phase Margin | 58.0∘ | 50.8∘ |
| 5.1 MHz | 4.9 MHz | |
| 4 pF | 4 pF | |
| Current Power | 3.0 μA at 1.0 V | 3.4 μA at 1.0 V |
| Noise Power | 17.8 μV at (1–10 k) Hz | 70.8 μV at (1–10 k) Hz |
| 5.0 μV at (150 k–160 k) Hz | 15.8 μV at (150 k–160 k) Hz | |
| FOM | 6800 MHz·pF/mA | 5765 MHz·pF/mA |
The drain current () of input-pair transistors ( and ) is calculated as:
where I is the reference current, is the voltage difference between the gate terminal and the source terminal and W and L are the transistor width and length; and are the transistor threshold voltage; and are the electron mobility and hole mobility, respectively. As is larger than , needs to be smaller than to achieve the same drain current .
The voltage gain A and gain bandwidth can be calculated as:
where is load capacitance, B is the current mirror ratio, r is the current starving ratio in the cross-coupling structure and and are the channel length modulation coefficients.
Given < , it is found from Equations (8) and (9) that both and are larger than and , respectively.
The input-referred noise of the proposed switched op-amps, including noise and thermal noise, can be approximately written as:
where K is a process-dependent constant on the order of ; k is a Boltzmann constant with a value of 1.38 × . Given the same ratio of (), Equation (10) suggests that the NMOS input-pair switched op-amp has lower input-referred noise.
The total current power consumption of the proposed switched op-amps is calculated as:
where is source current in the common mode feedback (CMFB) circuit and is bias current.
The FOM of an amplifier based on , load capacitance and total current power consumption is shown below.
The typical FOM of a power-efficient OTA [28,30] is 4000–4500 MHz·pF/mA. As a comparison, the FOM of the proposed switched op-amp reaches 6800 MHz·pF/mA, corresponding to 50% increment.
5.3. Static Power-Less Area-Efficient Quantizer
As shown in Figure 11a, a flash ADC consisting of a resistor ladder and comparators with pre-amps is a popular choice for implementing a quantizer, but its drawbacks are large circuit power and area caused by the resistor ladder and pre-amps. A dynamic comparator without pre-amps, as shown in Figure 11b, can be used to remove the static power. However, due to the effect of clock kick-back, large glitches appear at the reference-input terminals, which may give incorrect comparison results and degrade system performance. Instead of a resistor ladder, MIM capacitor strings in Figure 11c can be a remedy to eliminate the glitches and generate the required voltage references. In this case, the static power consumed by both the comparators and resistor ladder is removed. Two non-overlapping clock signals ( and ) with their corresponding delayed versions ( and ) are used to stabilize the voltage references generated by the MIM capacitor strings before the comparators give the comparison results. To further reduce the circuit area, the MIM capacitor is replaced by the high density series-PMOS structure, as shown in Figure 11d. After optimizing the reference circuit, the number of unit capacitors in the MOS capacitor strings is reduced, as shown in Figure 11e.
Figure 12a shows the simulated power and circuit area of the quantizers in Figure 11a–e. Compared to the traditional structure in Figure 11a, the proposed quantizer saves power consumption by 96% and reduces circuit area by 69%. Figure 12b gives the effect of random comparator offset. To achieve a 85-dB signal-to-quantization noise ratio (SQNR), the random offset with a standard deviation of up to 0.4 LSB (equal to 50 mV) can be easily accommodated in the proposed modulator.
5.4. Novel Power- and Area-Efficient Resonator
A local resonator scheme with a coefficient of 1/50 is applied to reduce in-band quantization noise power. Figure 13a–c show the resonator schematics, and their corresponding transfer functions are listed below.
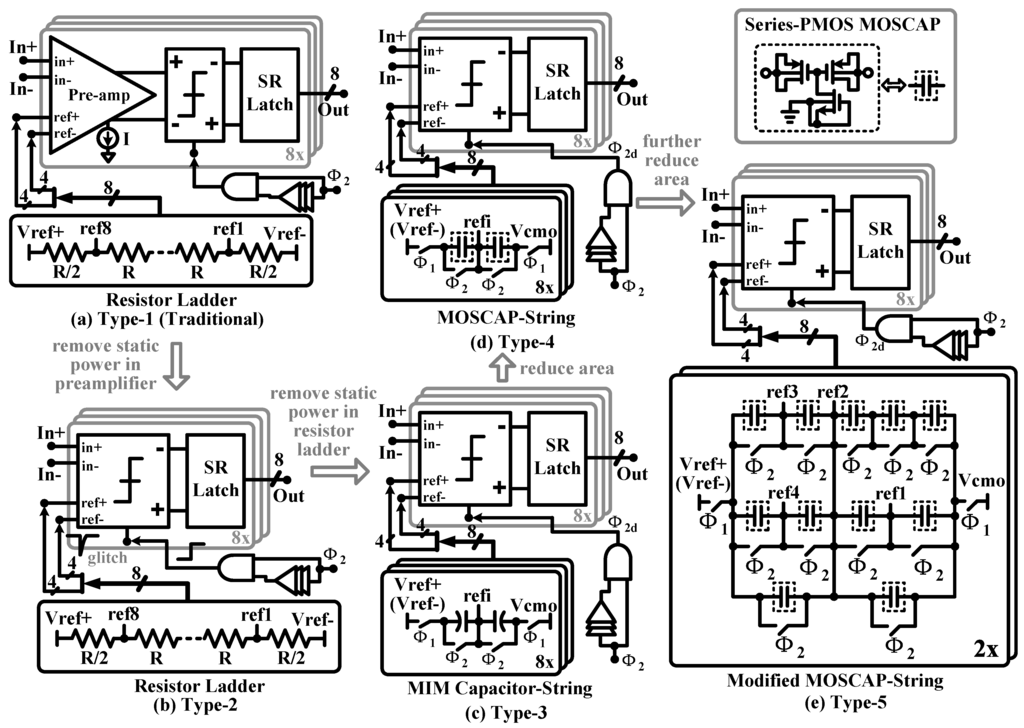
Figure 11.
Circuit schematics of five nine-level quantizer structures. (a) Type 1: one resistor ladder and eight comparators with pre-amps; (b) Type 2: one resistor ladder and eight comparators without pre-amps; (c) Type 3: eight metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitor strings and eight comparators without pre-amps. (d) Type 4: eight MOS capacitor strings and eight comparators without pre-amps. (e) Type 5: two MOS capacitor strings and eight comparators without pre-amps.
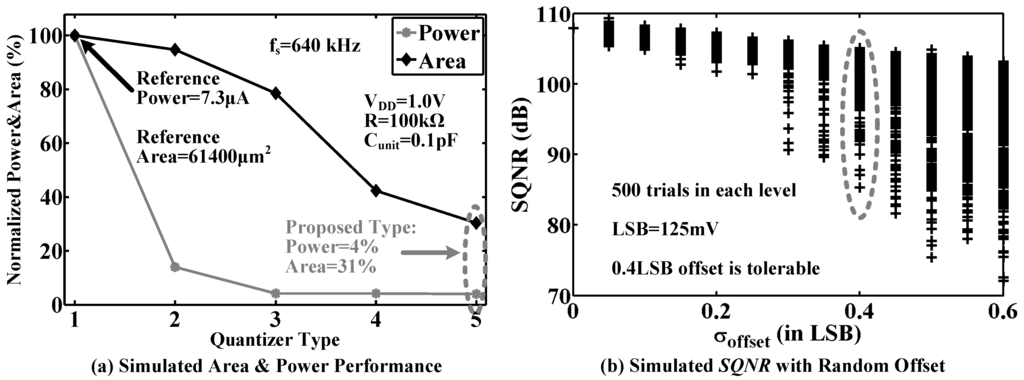
Figure 12.
(a) Simulated area and power performance of the introduced five nine-level quantizers; (b) Simulated signal-to-quantization noise ratio (SQNR) with random comparator offset, where there are 500 trials at each level.
The traditional resonator as shown in Figure 13a can be used to realize a coefficient larger than 1/20, where the amplifier can be turned off during . To implement a smaller coefficient, the traditional resonator will take severe penalties in power and area. Figure 13b shows a modified resonator that was reported in [48] for implementing a notch filter. This modified resonator can achieve small coefficients without requiring much extra circuit area. However, it is not applicable to the switched op-amp technique, because the amplifier has to be constantly turned on. As a comparison, we propose a novel design as shown in Figure 13c, which can implement a wide range of coefficients, yet achieve good efficiency in terms of power and area.
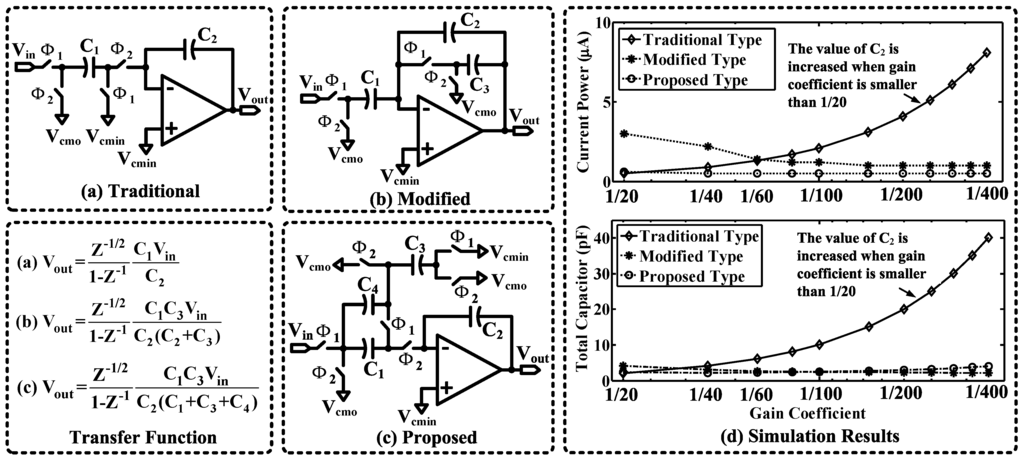
Figure 13.
The circuit schematics and simulation results of three resonator structures ((a) traditional, (b) modified and (c) proposed). (d) Simulated power and area performance of the resonators. For a fair comparison, the integration capacitance and the unit capacitance are assumed to be 2 pF and 0.1 pF, respectively. Furthermore, the slew rate (SR) of the operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) is assumed to be 2 V/μs.
5.5. Complete Modulator Circuit
Figure 14 shows the circuit implementation of the proposed fourth-order feed-forward Delta-Sigma modulator. We have done a careful selection of appropriate switched op-amp structure and MOS capacitor type for each integrator. (1) Because the input-referred noise of the first-stage integrator is directly transferred to the modulator output with a closed-loop gain of near 1 V/V, the NMOS input-pair switched op-amp (low noise), the MIM capacitor (perfect linearity) and the parallel-PMOS capacitor (moderate density) are used. These allow a lower noise floor, a smaller distortion and a higher area efficiency. (2) The NMOS input-pair switched op-amp and series-PMOS capacitor (wide bias voltage range) are adopted in the feed-forward signal summation block to meet the requirement of near full-scale input range inp or inn. In order to suppress the harmonic distortions caused by the series-PMOS capacitor, the output signal swing of this block is scaled down by 50%. (3) For other integrators, a single-PMOS capacitor (high density) is employed to improve the area efficiency effectively. To make sure that the single-PMOS capacitor operates in the saturation region and has good linearity, PMOS input-pair switched op-amp is used, and the input common mode voltage is set to be 0 V. (4) To improve the SQNR, a novel area- and power-efficient resonator scheme using a parallel-PMOS capacitor is proposed to realize a small coefficient of 1/50. Compared to a modulator using only an MIM capacitor, 55% capacitor area is saved in the proposed modulator design.
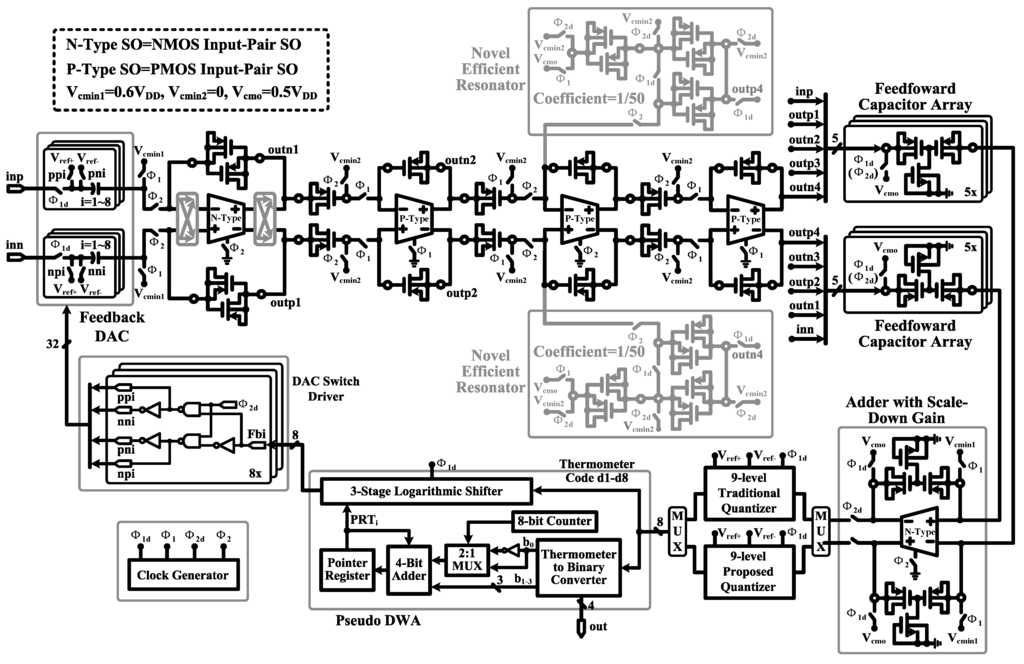
Figure 14.
Circuit schematic of the proposed modulator. The amplifiers in the first-stage integrator and feed-forward signal summation block are designed with NMOS input-pair switched op-amp, while other amplifiers are designed with PMOS input-pair switched op-amp. A DAC switch driver is adopted to reduce the number of the feedback signalsfrom pseudo DWA.
6. Measurement Results
The proposed modulator was fabricated in a 0.18-μm CMOS process. The chip micrograph and circuit testing setup are shown in Figure 15, where the core area is 0.4 mm × 0.6 mm. The traditional quantizer and proposed quantizer occupy an area of 280 μm × 415 μm and 110 μm × 190 μm, respectively. The input is provided by an Audio Precision signal generator, and the output is captured by a logical analyzer. There are two designs on this chip: Modulator A with the traditional quantizer and Modulator B with the proposed quantizer. Figure 16, Figure 17 and Figure 18 show the measurement results with a 1.0-V supply and a 640-kHz clock. Figure 16 demonstrates that the proposed modulator has an 87 dB dynamic range (14-bit) for digitizing biomedical signals and artifacts. Figure 17 shows that the pseudo DWA technique can noticeably suppress in-band harmonic distortions. Figure 18a gives the measured SNDR versus different input amplitudes. For Modulator A, the measured peak SNDR and dynamic range are 80 dB and 87 dB, respectively, while the total power consumption is 20 μW with an FOM of 122 fJ/conversion step. For Modulator B, the measured peak SNDR and dynamic range are 85 dB and 87 dB, respectively, while the total power consumption is 13 μW. These specifications correspond to an FOM of 45 fJ/conversion step. Figure 18b shows the measured peak SNDR at different signal frequencies and power supplies. Table 3 gives a performance summary in comparisonto other publications.
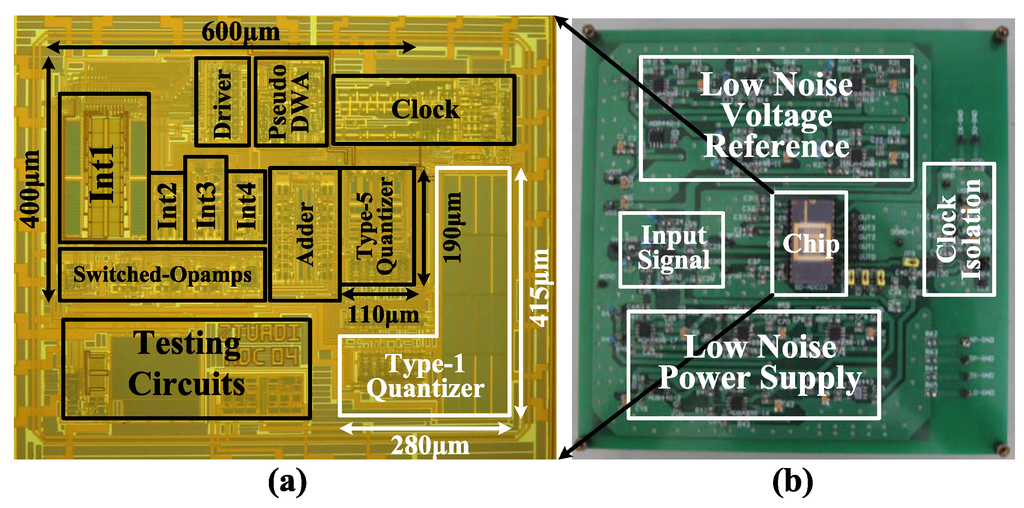
Figure 15.
(a) Chip photo of the proposed Delta-Sigma modulator; (b) Circuit testing board.
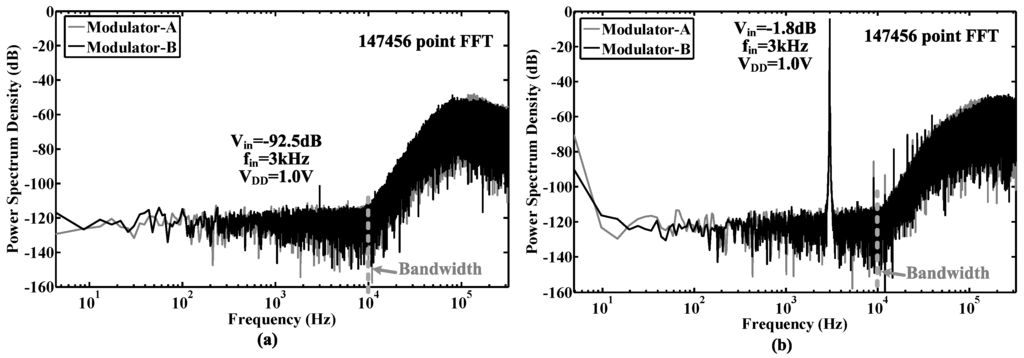
Figure 16.
Measured output spectrums of the modulators versus different input amplitudes. (a) The input is a -dB, 3-kHz sinusoidal waveform with respect to a 1.0-V reference; (b) The input is a -dB, 3-kHz sinusoidal waveform with respect to a 1.0-V reference.
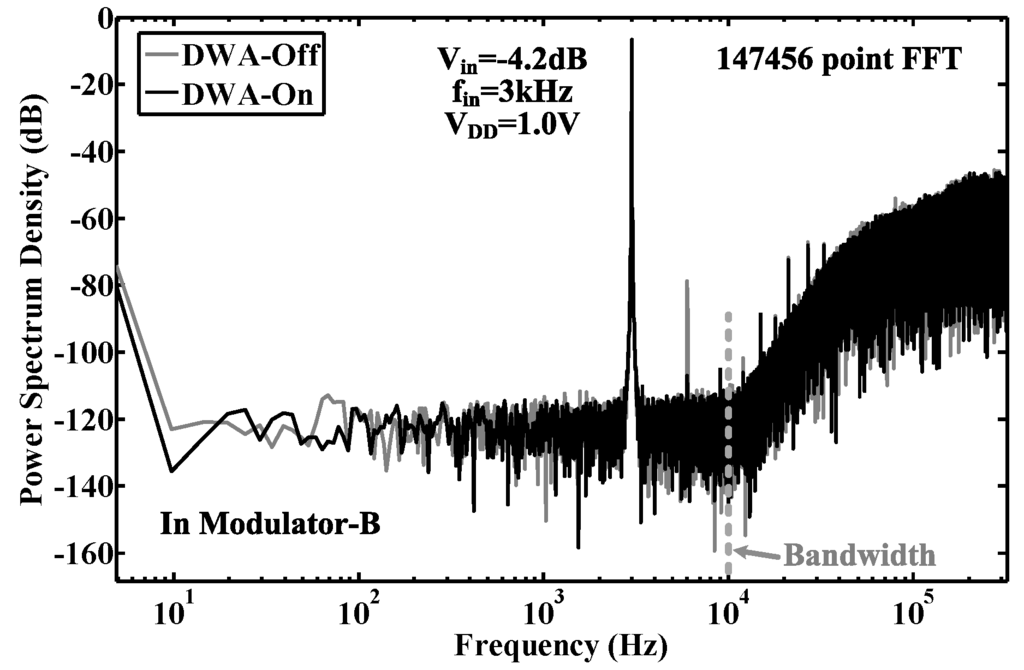
Figure 17.
Measured output spectrum of Modulator B with/without pseudo DWA. The input is a -dB, 3-kHz sinusoidal waveform with respect to a 1.0-V reference.
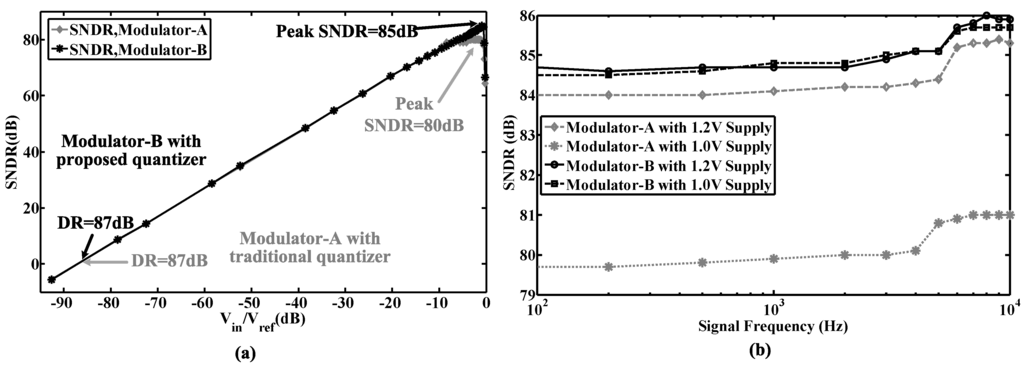
Figure 18.
(a) Measured SNDR at different input amplitudes; (b) Measured peak SNDR at different frequencies and supply voltages.

Table 3.
Performance summary and comparison.
| Modulator | [49] | [50] | [26] | [30] | [51] | [28] | [25] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process (nm) | 130 | 65 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 |
| Integrator Type | Inverter | Comp. | SO | OTA | OTA | OTA | Inverter | SO |
| (V) | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| (MHz) | 1.28 | 40 | 5 | 1.024 | 6.144 | 4 | 4 | 0.64 |
| Bandwidth (kHz) | 20 | 2500 | 25 | 8 | 24 | 20 | 20 | 10 |
| Power (μW) | 165 | 3730 | 870 | 80 | 110 | 140 | 36 | 13 |
| Dynamic Range (dB) | 83.0 | 71.3 | 100 | 75 | 92.5 | 88 | 85 | 87 |
| SNDR (dB) | 72.5 | 70.4 | 95 | 67 | 88 | 81 | 81 | 85 |
| FOM (fJ/conversion step) | 1197 | 276 | 378.5 | 2733 | 111.6 | 381.7 | 98.1 | 45 |
Comp., comparator; SO, switched op-amp; OTA, operational transconductance amplifier.
7. Conclusions
Data analysis on recorded sequences from both in vivo preparations and epileptic patients suggests that a wide system dynamic range is required to simultaneously record both neural activities and artifacts. To meet the required dynamic range, yet low power operation, this paper presents design analyses, circuit implementation and measurement of a Delta-Sigma modulator chip. Powered by a 1.0-V supply, the chip can achieve an 85-dB peak SNDR and an 87-dB dynamic range when integrated over a 10-kHz bandwidth. The total power consumption of the modulator is 13 μW, which corresponds to an FOM of 45 fJ/conversion step. The competitive circuit specifications make this design a good candidate for building high precision neurosensors.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Kuldeep Singh Rajput for proof reading and paper editing. Furthermore, the comments and suggestions by the reviewers that enhance the content and clarity of this paper are greatly appreciated.
Author Contributions
Jian Xu conceived and designed the circuit implementation; Jian Xu and Menglian Zhao performed the experiments; Md. Kafiul Islam analyzed the data; Menglian Zhao, Xiaobo Wu and Zhi Yang contributed technique discussions and analysis tools; Jian Xu and Zhi Yang wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Kiani, M.; Jow, U.; Ghovanloo, M. An inductively powered scalable 32-channel wireless neural recording system-on-a-chip for neuroscience applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2010, 4, 360–371. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, R.; Gambini, S.; Rabaey, J. A 0.013 mm2, 5 μW, DC-coupled neural signal acquisition IC with 0.5 V supply. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 232–243. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, I.; Kording, K. How advances in neural recording affect data analysis. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, T.; Qian, X.; Kumar, G.; Hwan, Y.; Haridas, K.; Pang, C.; Cha, H.; Je, M. A 700-μW wireless sensor node SoC for continuous real-time health monitoring. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Walker, R.; Nuyujukian, P.; Makinwa, K.; Shenoy, K.; Murmannn, B.; Meng, T. HermesE: A 96-channel full data rate direct neural interface in 0.13 μm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Holleman, J.; Otis, B. Design of ultra-low power biopotential amplifiers for biosignal acquisition applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yuan, J.; Huang, J.; Law, J.; Yeung, C.; Chan, M. 32.9 nV/rt Hz—60.6 dB THD dual-band micro-electrode array signal acquisition IC. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Xu, X.; Yao, L.; Lian, Y. A 1-V 450-nW fully integrated programmable biomedical sensor interface chip. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kiani, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Gosselin, B.; Ghovanloo, M. A wireless magnetoresistive sensing system for an intraoral tongue-computer interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrokhi, F.; Abdelhalim, K.; Serletis, S.; Carlen, P.; Genov, R. The 128-channel fully differential digital integrated neural recording and stimulation interface. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2010, 4, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.; Sawan, M.; Dang, K.N. A novel low-power-implantable epileptic seizure-onset detector. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger, R.; Taylor, J. A switched-capacitor front-end for velocity-selective eng recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roham, M.; Covey, D.; Daberkow, D.; Ramsson, E.; Howard, C.; Heidenreich, B.; Garris, P.; Mohseni, P. A wireless IC for time-share chemical and electrical neural recording. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 3645–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, R.; Deng, S. Double-differential recording and AGC using microcontrolled variable gain ASIC. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2013, 21, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapolli, A.; Coppa, B.; Heliot, R. Low-power hardware for neural spike compression in BMIs. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Socirty, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2156–2159.
- Huang, W.; Hung, S.; Chung, J.; Chang, M.; Van, L.; Lin, C.T. FPGA implementation of 4-channel ICA for on-line EEG signal separation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20–22 November 2008; pp. 65–68.
- Clements, M.; Vichienchom, K.; Liu, W.; Hughes, C.; McGucken, E.; DeMarco, C.; Mueller, J.; Humayun, M.; de Juan, E.; Weiland, J.; et al. An implantable neuro-stimulator device for a retinal prosthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17 February 1999; pp. 216–217.
- Mollazadeh, M.; Murari, K.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Thakor, N. Micropower CMOS integrated low-noise amplification, filtering, and digitization of multimodal neuropotentials. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2009, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, B. Recent advances in neural recording microsystems. Sensors 2011, 11, 4572–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Shi, J.; Parramon, J.; Sanchez-Sinencio, E. A low-power configurable neural recording system for epileptic seizure detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.; Ross, J.; Blum, R.; Nam, Y.; Wheeler, B.; DeWeerth, S. Stimulus-artifact elimination in a multi-electrode system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2008, 2, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Van, H.C.; Yazicioglu, R. A 160 μA biopotential acquisition IC with fully integrated IA and motion artifact suppression. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 552–561. [Google Scholar]
- Gnadt, J.; Echols, S.; Yildirim, A.; Zhang, H.; Paul, K. Spectral cancellation of microstimulation artifact for simultaneous neural recording in situ. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Theogarajan, L. A micro power delta-sigma modulator based on a self-biased super inverter for neural recording systems. In Porceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–22 September 2010; pp. 1–4.
- Chae, Y.; Lee, I.; Han, G. A 0.7 V 36 μW 85 dB-DR audio ΣΔ modulator using class-c inverter. In Porceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 February 2008; pp. 490–491.
- Park, H.; Nam, K.; Su, D.; Vleugels, K.; Wooley, B. A 0.7-V 100-dB 870-μW digital audio ΣΔ modulator. In Porceedings of the IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–20 June 2008; pp. 178–179.
- Goes, J.; Vaz, B.; Monteiro, R.; Paulino, N. A 0.9 V ΔΣ modulator with 80 dB SNDR and 83 dB DR using a single-phase technique. In Porceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2006; pp. 191–200.
- Yao, L.; Steyaert, M.; Sansen, W. A 1-V 140-μW 88-dB audio sigma-delta modulator in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Theogarajan, L. An 18 μW 79 dB-DR 20 KHz-BW MASH sigma-delta modulator utilizing self-biased amplifiers for biomedical applications. In Porceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2011; pp. 1–4.
- Sauerbrey, J.; Tille, T.; Schmitt-Landsiedel, D.; Thewes, R. A 0.7-V MOSFET-only switched-op-amp ΣΔ modulator in standard digital CMOS technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M.; Fan, R.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; Liu, B. Ultra low-FOM high-precision ΔΣ modulators with fully-clocked SO and zero static power quantizers. In Porceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 19–21 September 2011; pp. 1–4.
- Buzsaki, G.; Anastassiou, C.; Koch, C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents-EEG, ECoG, LFP and spikes. Nat. Rev. Neuronsci. 2012, 13, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murmann, B. ADC Performance Survey 1997–2015. Available online: http://web.stanford.edu/murmann/adcsurvey.html (accessed on 14 June 2015).
- Wattanapanitch, R.; Sarpeshkar, R. A low-power 32-channel digitally programmable neural recording integrated circuit. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2011, 5, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Prodanov, D.; Braeken, D.; Gligorijevic, I.; Eberle, W.; Bartic, C.; Puers, R.; Gielen, G. A multichannel integrated circuit for electrical recording of neural activity, with independent channel programmability. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liew, W.; Yao, L.; Lian, Y. A 1 V 22 μW 32-channel implantable EEG recording IC. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 February 2010; pp. 122–123.
- Gosselin, B.; Ayoub, A.; Roy, J.; Sawan, M.; Lepore, F.; Chaudhuri, A.; Guitton, D. A mixed-signal multichip neural recording interface with bandwidth reduction. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2009, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberto, R.; Jesus, R.; Manuel, D.; Angel, R. A low-power programmable neural spike detection channel with embedded calibration and data compression. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2012, 6, 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bonfanti, A.; Ceravolo, M.; Zambra, G.; Gusmeroli, R.; Borghi, T.; Spinelli, A.; Lacaita, A. A 0.7-V 100-dB 870-μW digital audio ΣΔ modulator. In Proceedings of the IEEE European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), Seville, Spain, 14–16 September 2010; pp. 330–333.
- Lo, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, K.; Tsai, M.; Hsueh, F. A 64-channel neuron recording system. In Proceedings of the 33th Annual International Conferenceof the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 2862–2865.
- Do, A.; Tan, Y.; Lam, C.; Je, M.; Yeo, K. Low power implantable neural recording front-end. In Proceedings of the IEEE International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Jeju Island, Korea, 4–7 November 2012; pp. 387–390.
- Hamoui, A.; Martin, K. High-order multibit modulators and pseudo data-weighted-averaging in low-oversampling ΔΣ ADCs for broad-band applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2004, 51, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M.; Shen, J. A 20 μW 95 dB dynamic range 4th-order Delta-Sigma modulator with novel power efficient operational transconductance amplifier and resonator. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2011, 12, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Xu, J.; Wu, X. Dual cycle shift data-weighted averaging technique for multi-bit sigma-delta modulators. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits Conference (EDSSC), Xi’an, China, 25–27 December 2009; pp. 174–177.
- Denison, T.; Consoer, K.; Kelly, A.; Hachenburg, A.; Santa, W. A 2.2 μW 94 , chopper-stabilized instrumentation amplifier for EEG detection in chronic implants. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2007; pp. 162–163.
- Chen, H.; Chen, P.; Chiang, J. A low-offset low-noise sigma-delta modulator with pseudorandom chopper-stabilization technique. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 2009, 56, 2533–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, C.; Temes, G. Circuit techniques for reducing the effects of op-amp imperfections: Autozeroing, correlated double sampling, and chopper stabilization. IEEE Proc. 1996, 84, 1584–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, K. A parasitic-insensitive area-efficient approach to realizing very large time constants in switched-capacitor circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I 1989, 36, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, J.; Goes, J.; Paulino, N.; Oliveira, J.; Bruun, E. A 1.2-V 165-μW 0.29-mm2 multibit Sigma-Delta ADC for hearing aids using nonlinear DACs and with over 91 dB dynamic-range. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2013, 7, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, K.; Carusone, A. A 1-1-1-1 MASH Delta-Sigma modulator with dynamic comparator-based OTAs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1866–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, S.; Sankar, P. An 110 μW single bit audio continuous-time oversampled converter with 92.5 dB dynamic range. In Proceedings of the IEEE European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), Athens, Greece, 14–18 September 2009; pp. 320–323.
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).