Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design of a Textile Electrode for Electrical Stimulation
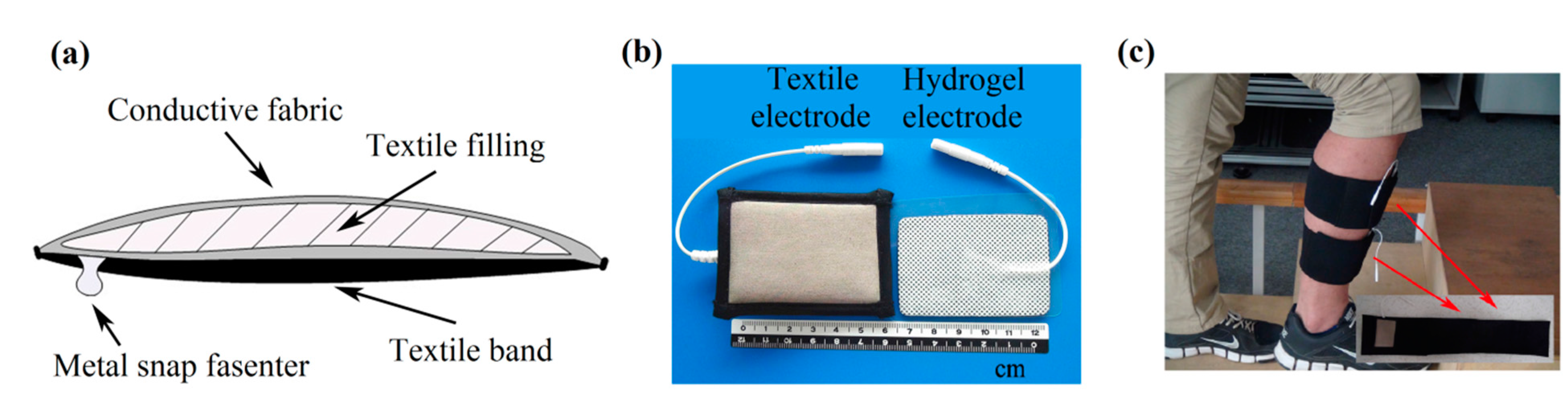
2.2. Impedance Spectroscopy Measurement of the Textile Electrode

2.3. Stimulation Thresholds and Comfort Evaluation
2.4. Modeling of Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation

| Layer | Electrical Conductivity (S/m) | Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|
| Stratum corneum | 2 × 10−5 [22,23] | 29 [24,25] |
| Epidermis | Horizontal:0.95, vertical:0.15 [20,22] | 60 [24,25] |
| Dermis | Horizontal:2.57, vertical:1.62 [20,22] | 1300 [26,27] |
| Fat | 0.04 [28] | 2500 [29] |
| Muscle | Horizontal:0.25, vertical:0.75 [28] | 10000 [29] |
| Textile electrode sheet | 1.4 × 105 | Thickness: 400, line width:150 |
| Wet textile electrode | 1.4 [30] | 5800 |
| Hydrogel | 4.6 × 10−3 | 1000 |
| Foil electrode | 6.67 × 105 [20] | 50 |
3. Results
3.1. Electrode Impedance Spectroscopy

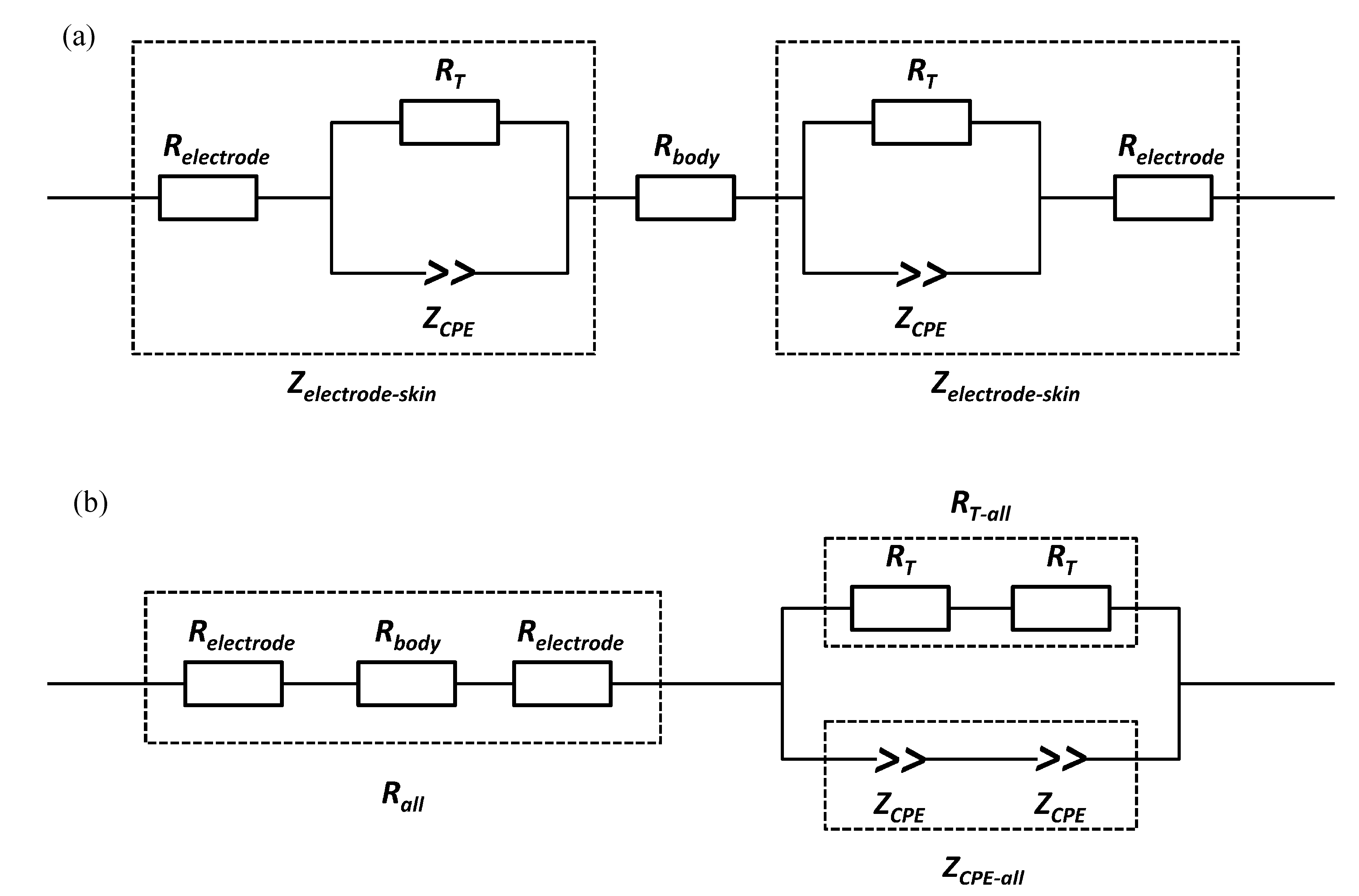

| Parameters | Unit | Hydrogel | Textile | w-Textile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z (at 1 kHz) | Ω | 1572.3 ± 83.78 | 4716.7 ± 815.60 | 947.5 ± 53.65 |
| Rall | Ω | 269.2 ± 9.13 | 97.1 ± 21.5 | 80.18 ± 4.73 |
| RT-all | kΩ | 304.1 ± 109.79 | 477.0 ± 141.69 | 79.3 ± 24.17 |
| CPE-q | μFn-1 | 0.98 ± 0.11 | 1.04 ± 0.12 | 1.52 ± 0.14 |
| CPE-n | 0 ≤ n ≤ 1 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.70 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.01 |
| Relectrode | Ω | 90.98 ± 1.44 | 1.33 ± 0.35 | 0.80 ± 0.02 |
| Rbody | Ω | 87.24 | 94.44 | 78.58 |
3.2. Stimulation Thresholds
| Threshold (mA) | Hydrogel | Wet Textile | Dry Textile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensory | 6.3 ± 0.59 *1 | 5.9 ± 0.65 *2 | 2.35 ± 0.30 |
| Motor | 19.9 ± 1.29 † | 21.6 ± 1.42 | NA |
| Pain | 33.15 ± 2.01 ‡1 | 31.90 ± 2.01 ‡2 | 3.2 ± 0.53 |
3.3. Comfort Evaluation
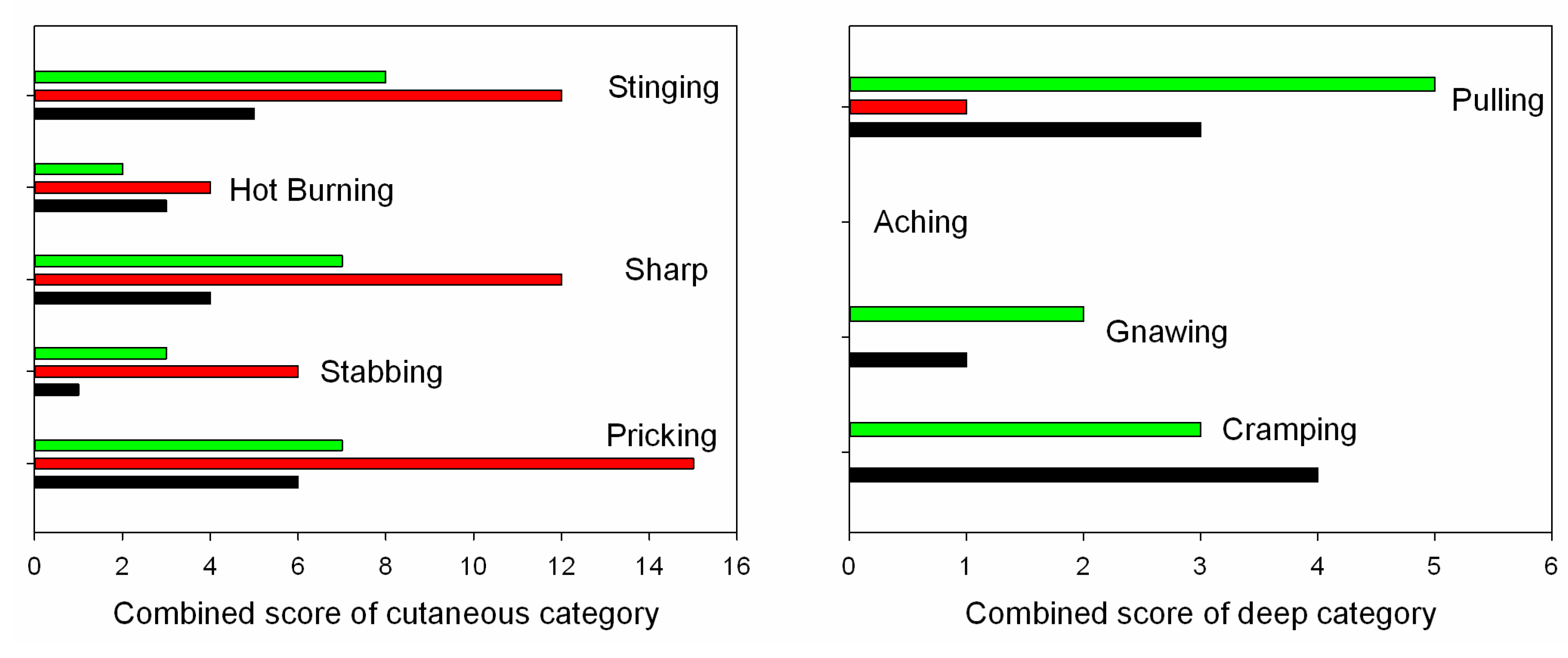
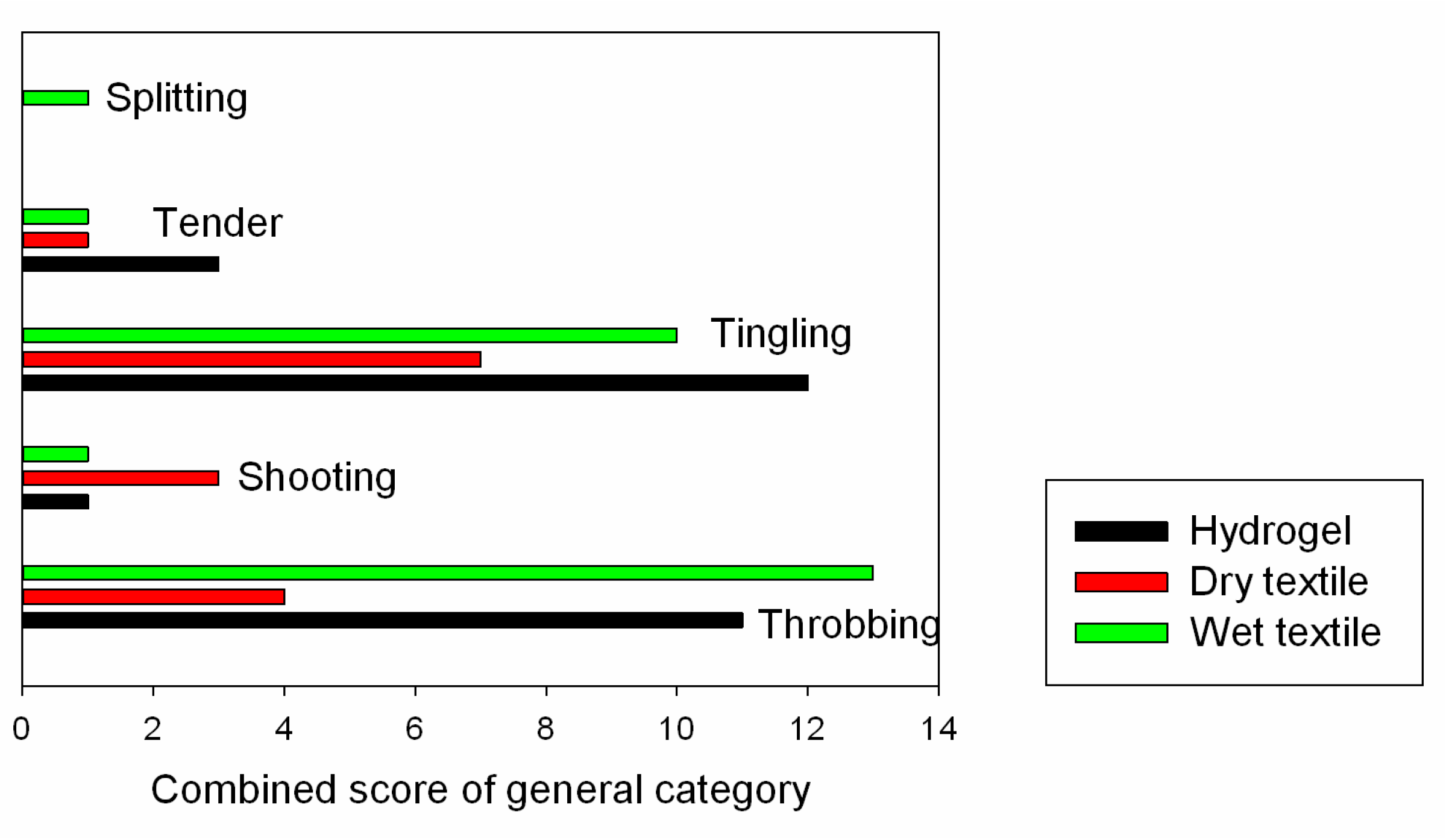
| Electrode Type | Cutaneous Pain | Deep Pain | General Pain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogel | 19 | 8 | 27 |
| Dry textile | 49 | 1 | 15 |
| Wet textile | 27 | 10 | 26 |
3.4. Finite Element Analysis
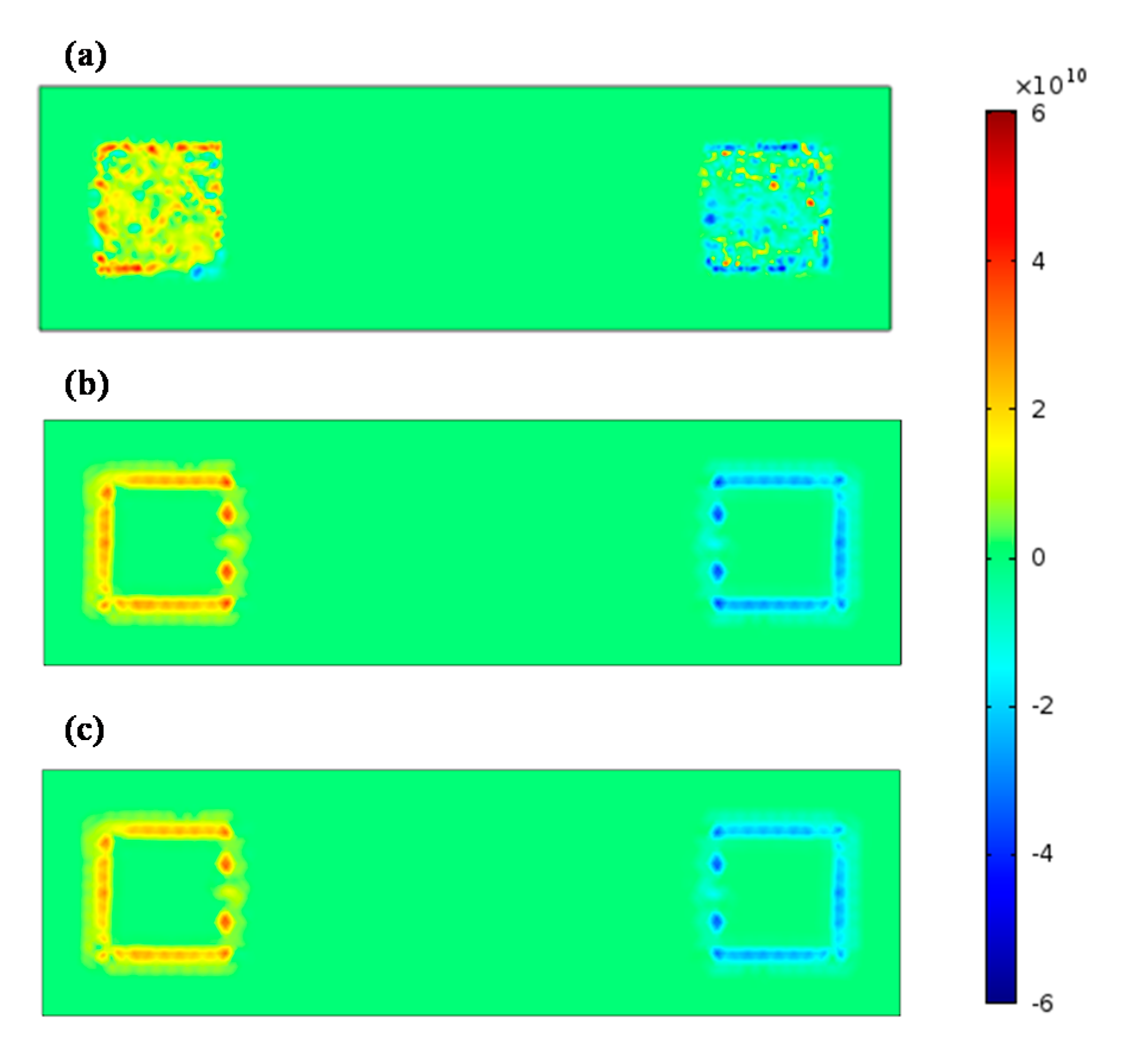
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popović, D.B. Advances in functional electrical stimulation (FES). J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2014, 24, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley, G.J.; Breen, P.P.; Bîrlea, S.I.; Serrador, J.M.; Grace, P.A.; ÓLaighin, G. Hemodynamic effects of habituation to a week-long program of neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2012, 34, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, M.J.; Wei, S.H.; Chang, Y.J. Effect of Neuromuscular Electrical Muscle Stimulation on Energy Expenditure in Healthy Adults. Sensors 2011, 11, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devrimsel, G.; Turkyilmaz, A.K.; Yildirim, M.; Beyazal, M.S. The effects of whirlpool bath and neuromuscular electrical stimulation on complex regional pain syndrome. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.E.; Shivdasani, M.N.; Leuenberger, J.; Fallon, J.B.; Shepherd, R.K.; Millard, R.E.; Rathbone, G.D.; Williams, C.E. An automated system for rapid evaluation of high-density electrode arrays in neural prostheses. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.; Barker, A.T.; Heller, B.W.; Good, T.; Kenney, L.P.J.; Howard, D. The use of hydrogel as an electrode-skin interface for electrode array FES applications. Med. Eng. Phys. 2011, 33, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meziane, N.; Webster, J.G.; Attari, M.; Nimunkar, A.J. Dry electrodes for electrocardiography. Physiol. Meas. 2013, 34, R47–R69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.J.; Zhang, H.; Tao, X.M. Textile-structured electrodes for electrocardiogram. Text. Prog. 2008, 40, 183–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marozas, V.; Petrenas, A.; Daukantas, S.; Lukosevicius, A. A comparison of conductive textile-based and silver/silver chloride gel electrodes in exercise electrocardiogram recordings. J. Electrocardiol. 2011, 44, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, G.; Jeong, K.; Paik, M.J.; Kwun, Y.; Sung, M. Performance Evaluation of Textile-Based Electrodes and Motion Sensors for Smart Clothing. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3183–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, Y.; Tao, D.; Zhou, P. Performance of electromyography recorded using textile electrodes in classifying arm movements. In Proceeding of 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 4243–4246.
- Finni, T.; Hu, M.; Kettunen, P.; Vilavuo, T.; Cheng, S. Measurement of EMG activity with textile electrodes embedded into clothing. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfhede, J.; Seoane, F.; Thordstein, M. Textile Electrodes for EEG Recording—A Pilot Study. Sensors 2012, 12, 16907–16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, G. Using textile electrode EMG for prosthetic movement identification in transradial amputees. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Cambridge, MA, USA, 6-9 May 2013; pp. 1–5.
- Keller, T.; Kuhn, A. Electrodes for transcutaneous (surface) electrical stimulation. J. Autom. Control 2008, 18, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gniotek, K.; Frydrysiak, M.; Zieba, J.; Tokarska, M.; Stempien, Z. Innovative textile electrodes for muscles electrostimulation. In Proceeding of 2011 IEEE International Workshop on Medical Measurements and Applications Proceedings (MeMeA), Bari, Italy, 30–31 May 2011; pp. 305–310.
- Li, L.; Au, W.M.; Li, Y.; Wan, K.M.; Wan, S.H.; Wong, K.S. Design of Intelligent Garment with Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Function Based on the Intarsia Knitting Technique. Text. Res. J. 2009, 80, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Freeman, C.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Screen printed fabric electrode array for wearable functional electrical stimulation. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2014, 213, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M. Transcutaneous Electrode Technology for Neuroprostheses. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, N.; Kenney, L.P.J.; Heller, B.W.; Barker, A.T.; Howard, D.; Moatamedi, M. A Finite Element Model to Identify Electrode Influence on Current Distribution in the Skin. Artif. Organs 2008, 32, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mørch, C.D.; Hennings, K.; Andersen, O.K. Estimating nerve excitation thresholds to cutaneous electrical stimulation by finite element modeling combined with a stochastic branching nerve fiber model. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2011, 49, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Electrical properties of the epidermal stratum corneum. Med. Biol. Eng. 1976, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neerken, S.; Lucassen, G.W.; Bisschop, M.A.; Lenderink, E.; Nuijs, T.A. Characterization of age-related effects in human skin: a comparative study that applies confocal laser scanning microscopy and optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2004, 9, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, J.S.; Poulsen, T.; Wulf, H.C. Epidermal Thickness at Different Body Sites: Relationship to Age, Gender, Pigmentation, Blood Content, Skin Type and Smoking Habits. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2003, 83, 410–413. [Google Scholar]
- Fornage, B.D.; McGavran, M.H.; Duvic, M.; Waldron, C.A. Imaging of the skin with 20-MHz US. Radiology 1993, 189, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krackowizer, P.; Brenner, E. Thickness of the human skin-24 points of measurement. Phlebologie 2008, 37, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Doheny, E.P.; Caulfield, B.M.; Minogue, C.M.; Lowery, M.M. Effect of subcutaneous fat thickness and surface electrode configuration during neuromuscular electrical stimulation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2010, 32, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A. Modeling Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yufera, A.; Leger, G.; Rodriguez-Villegas, E.O.; Muñoz, J.M.; Rueda, A.; Ivorra, A.; Gomez, R.; Noguera, N.; Aguiló, J. An integrated circuit for tissue impedance measure. In Proceeding of Microtechnologies in Medicine & Biology 2nd Annual International IEEE-EMB Special Topic Conference on, 2–4 May 2002; pp. 88–93.
- Bioness L300 Electrodes and Bases. Available online: https://www.bioness.com/Documents/TechSupport/L300_Plus/l300_plus_accessories.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2015).
- Weder, M.; Hegemann, D.; Amberg, M.; Hess, M.; Boesel, L.; Abächerli, R.; Meyer, V.; Rossi, R. Embroidered Electrode with Silver/Titanium Coating for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Keller, T.; Lawrence, M.; Morari, M. A model for transcutaneous current stimulation: simulations and experiments. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2009, 47, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahm, K.S.; Mørch, C.D.; Grill, W.M.; Lubock, N.B.; Hennings, K.; Andersen, O.K.E. Activation of peripheral nerve fibers by electrical stimulation in the sole of the foot. BMC Neurosci. 2013, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H.; Krundel, L.; Li, G. Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation. Sensors 2015, 15, 17241-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150717241
Zhou H, Lu Y, Chen W, Wu Z, Zou H, Krundel L, Li G. Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation. Sensors. 2015; 15(7):17241-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150717241
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hui, Yi Lu, Wanzhen Chen, Zhen Wu, Haiqing Zou, Ludovic Krundel, and Guanglin Li. 2015. "Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation" Sensors 15, no. 7: 17241-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150717241
APA StyleZhou, H., Lu, Y., Chen, W., Wu, Z., Zou, H., Krundel, L., & Li, G. (2015). Stimulating the Comfort of Textile Electrodes in Wearable Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation. Sensors, 15(7), 17241-17257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150717241





