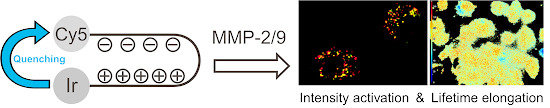
MMP-2/9-Specific Activatable Lifetime Imaging Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. General
2.2. Synthesis of Peptide-Cy5 (1)
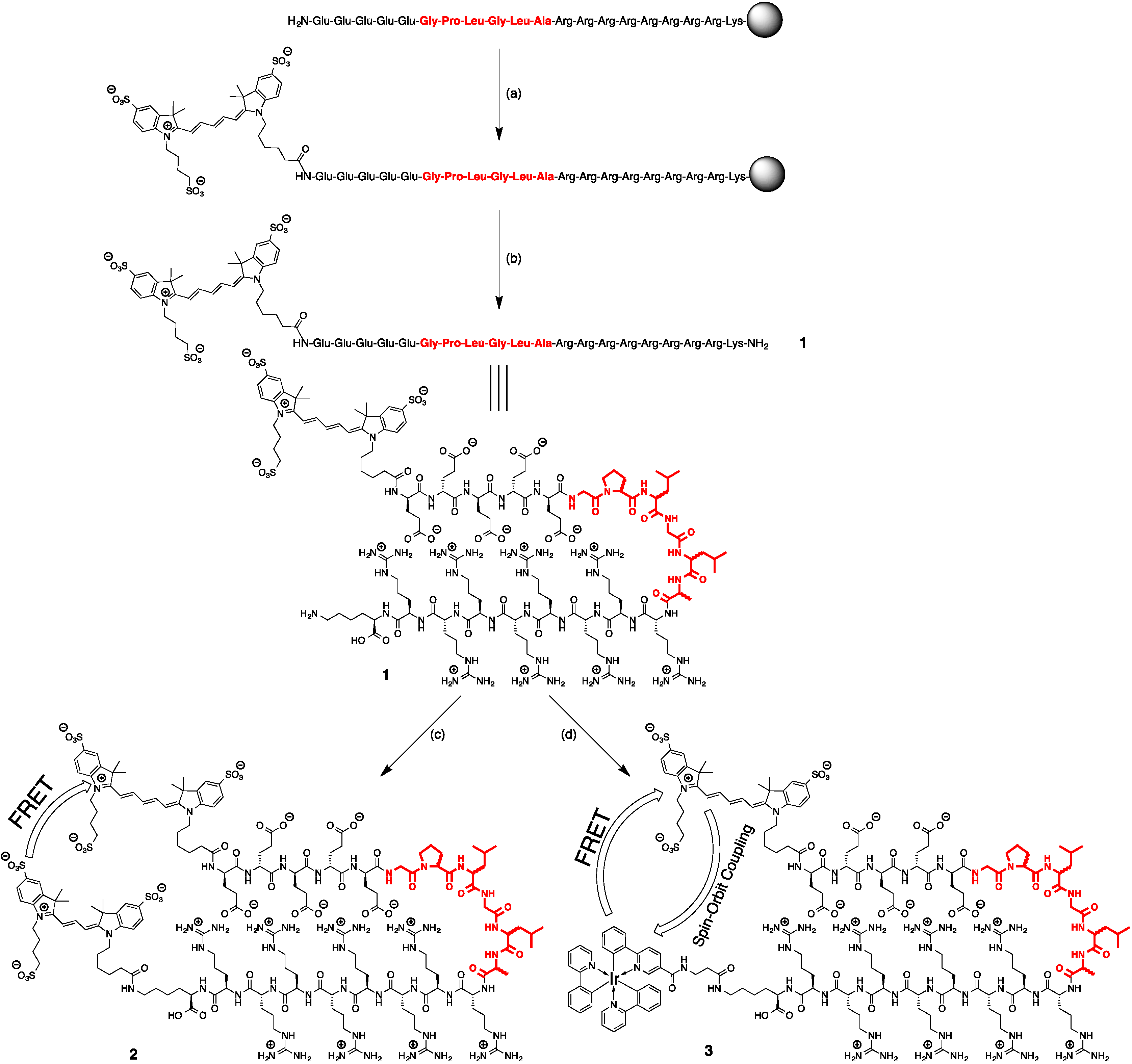
2.3. Synthesis of Cy3-Cy5 Peptides (2L and 2D)
2.4. Synthesis of Ir(ppy)3-Cy5 Peptides (3L and 3D)
2.5. Spectroscopic Measurements
2.6. Calculation of Distances between Luminophores
2.7. Enzymatic Peptide Cleavage by Cells in Suspension
2.8. Enzymatic Peptide Cleavage by Adherent Cells
2.9. Confocal Imaging
2.10. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Synthesis of the Imaging Agents

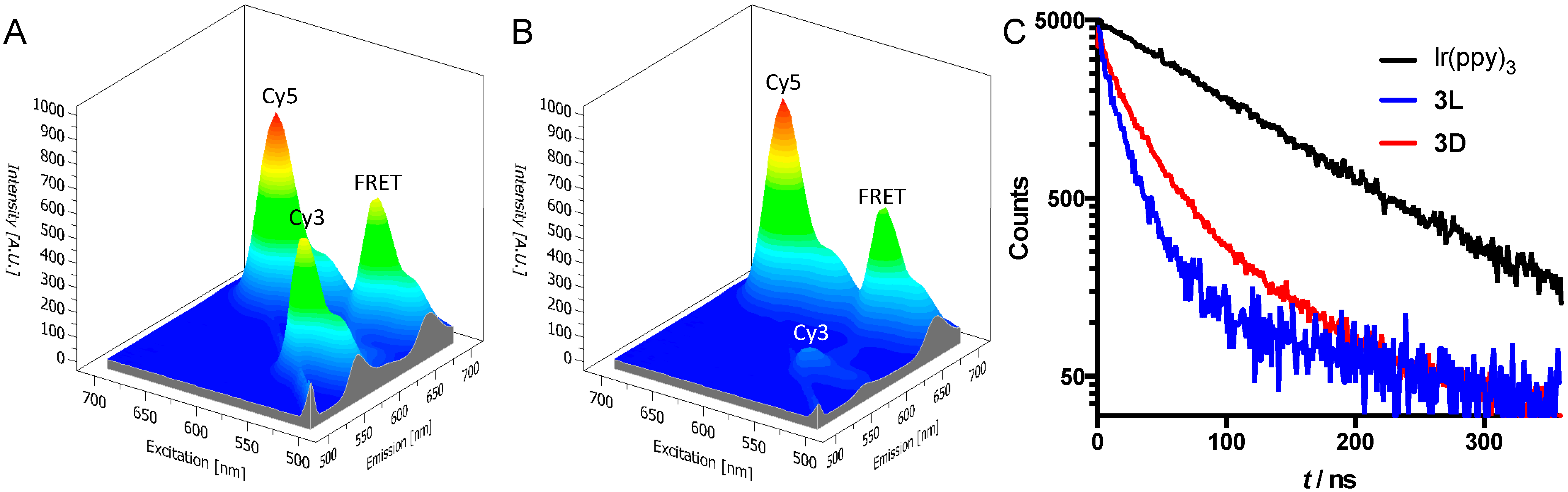
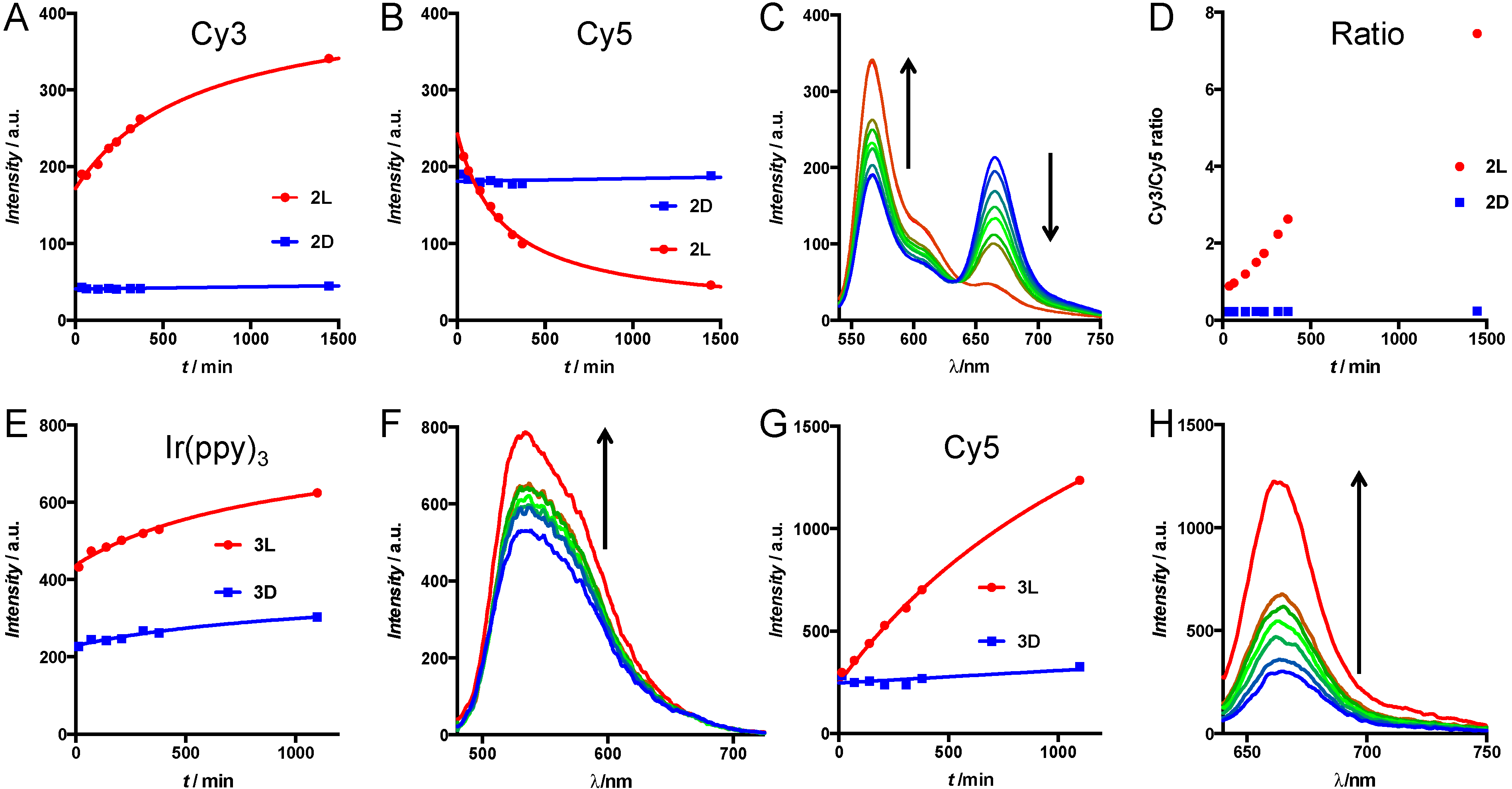
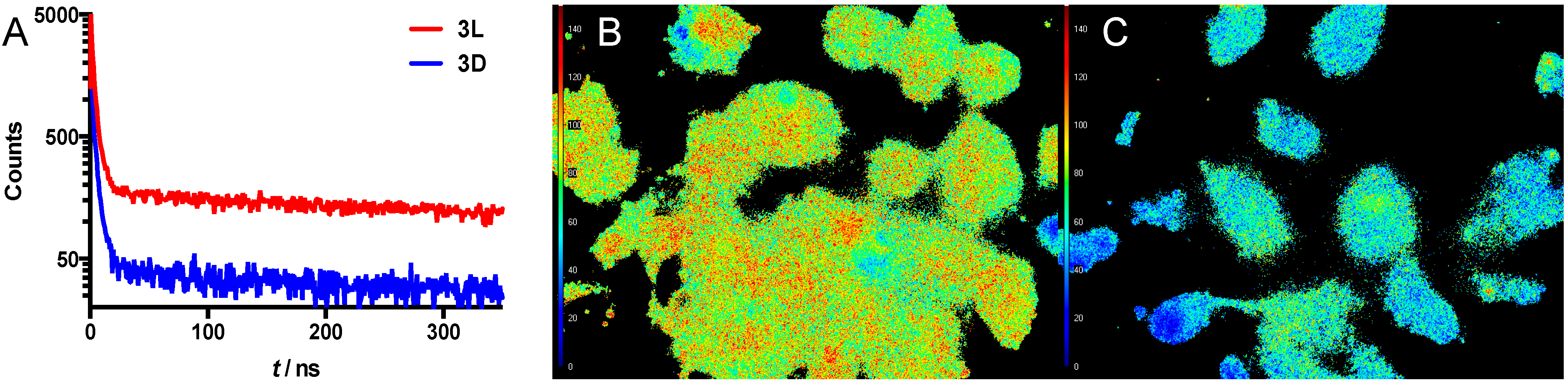
3.2. Photophysical Analysis of the Imaging Agents
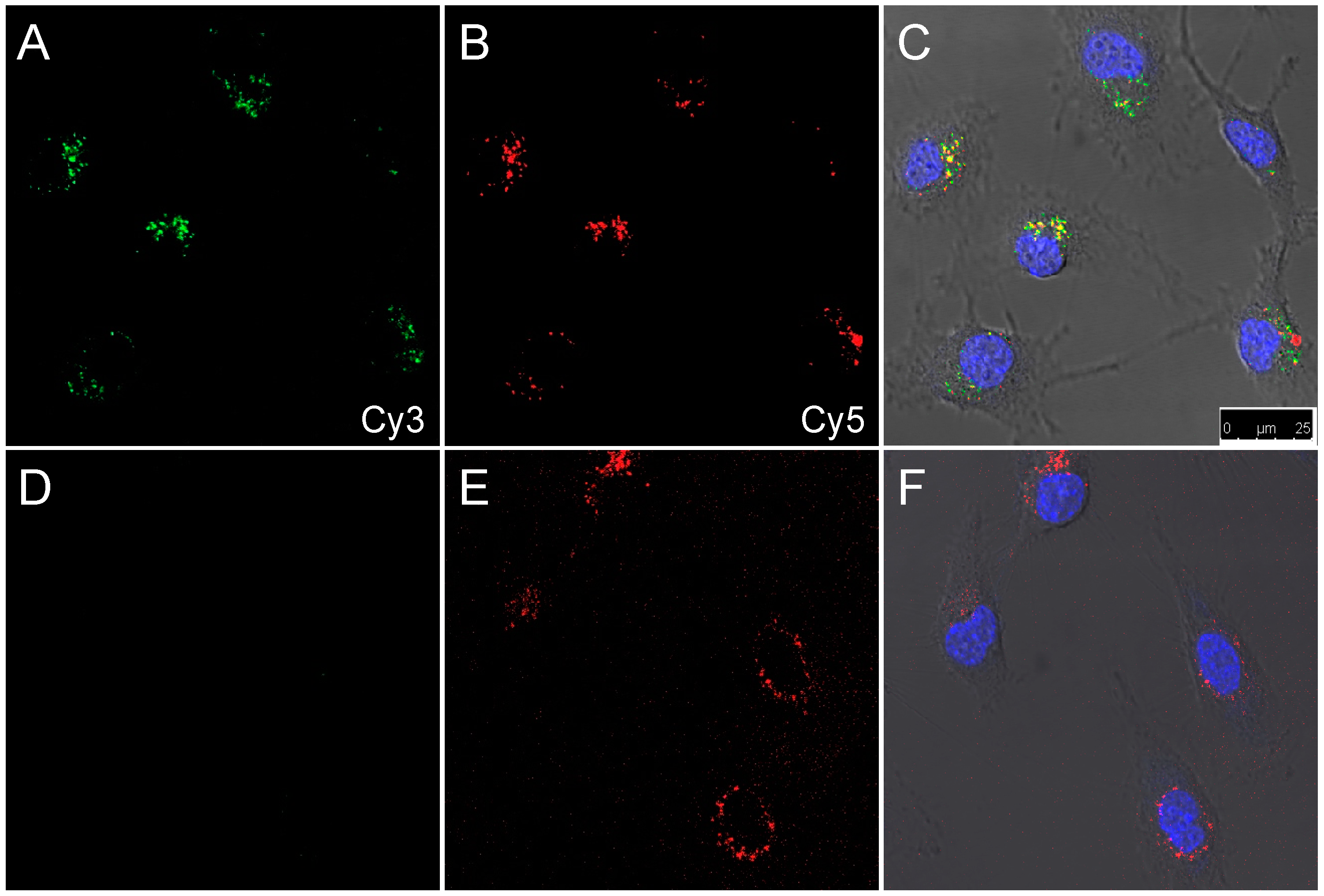
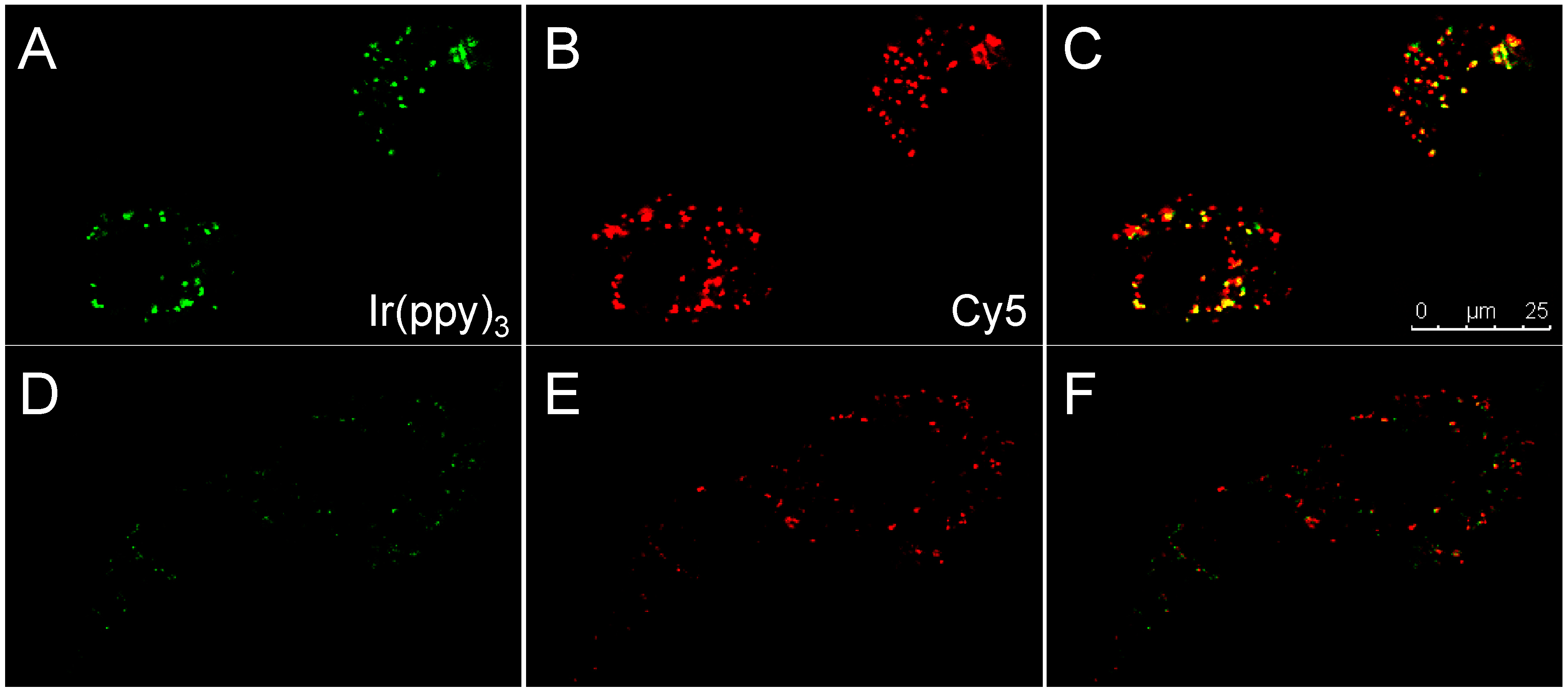
3.3. Enzymatic Cleavage Assay by Cells in Suspension
3.4. Enzymatic Cleavage Assay Followed by Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, J.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Yao, H.; Yao, H. Fluorescence imaging in vivo: Recent advances. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monici, M. Cell and tissue autofluorescence research and diagnostic applications. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2005, 11, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Billinton, N.; Knight, A.W. Seeing the wood through the trees: A review of techniques for distinguishing green fluorescent protein from endogenous autofluorescence. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 291, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezin, M.Y.; Achilefu, S. Fluorescence lifetime measurements and biological imaging. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2641–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, A.; Roth, D.; Enderle, T.; Nau, W.M. Nanosecond time-resolved fluorescence protease assays. Chembiochem 2006, 7, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maliwal, B.P.; Fudala, R.; Raut, S.; Kokate, R.; Sorensen, T.J.; Laursen, B.W.; Gryczynski, Z.; Gryczynski, I. Long-lived bright red emitting azaoxa-triangulenium fluorophores. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, R.M.; Stankowska, D.L.; Maliwal, B.P.; Sorensen, T.J.; Laursen, B.W.; Krishnamoorthy, R.R.; Gryczynski, Z.; Borejdo, J.; Gryczynski, I.; Fudala, R. Elimination of autofluorescence background from fluorescence tissue images by use of time-gated detection and the azadioxatriangulenium (adota) fluorophore. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggi, A.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Velders, A.H. Interaction of dioxygen with the electronic excited state of Ir(iii) and Ru(ii) complexes: Principles and biomedical applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2542–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggi, A.; Beekman, C.; Wasserberg, D.; Subramaniam, V.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Velders, A.H. Dendritic ruthenium(ii)-based dyes tuneable for diagnostic or therapeutic applications. Chemistry 2011, 17, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuil, J.; Steunenberg, P.; Chin, P.T.K.; Oldenburg, J.; Jalink, K.; Velders, A.H.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B. Peptide-functionalized luminescent iridium complexes for lifetime imaging of cxcr4 expression. Chembiochem 2011, 12, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Longmire, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clearance properties of nano-sized particles and molecules as imaging agents: Considerations and caveats. Nanomedicine 2008, 3, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, J.F.; Zheng, G. Activatable smart probes for molecular optical imaging and therapy. J. Innov. Opt. Health Sci. 2008, 1, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Kocher, B.; Barnett, E.M.; Marasa, J.; Piwnica-Worms, D. Caspase-activated cell-penetrating peptides reveal temporal coupling between endosomal release and apoptosis in an rgc-5 cell model. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, Y.; Sakabe, M.; Kosaka, N.; Ogawa, M.; Mitsunaga, M.; Asanuma, D.; Kamiya, M.; Young, M.R.; Nagano, T.; Choyke, P.L.; et al. Rapid cancer detection by topically spraying a gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase-activated fluorescent probe. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 110ra119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Olson, E.S.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Roy, M.; Jennings, P.A.; Tsien, R.Y. Tumor imaging by means of proteolytic activation of cell-penetrating peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17867–17872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, W.J.; Xu, B.; Lee, H.; Sudlow, G.P.; Fields, G.B.; Achilefu, S.; Edwards, W.B. Detection of mmp-2 and mmp-9 activity in vivo with a triple-helical peptide optical probe. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, K.; Kim, K.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C. Activatable imaging probes with amplified fluorescent signals. Chem. Commun. 2008, 4250–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlokarnik, G.; Negulescu, P.A.; Knapp, T.E.; Mere, L.; Burres, N.; Feng, L.X.; Whitney, M.; Roemer, K.; Tsien, R.Y. Quantitation of transcription and clonal selection of single living cells with beta-lactamase as reporter. Science 1998, 279, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorokhin, D.; Hsu, S.H.; Tomczak, N.; Blum, C.; Subramaniam, V.; Huskens, J.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Velders, A.H.; Vancso, G.J. Visualizing resonance energy transfer in supramolecular surface patterns of beta-cd-functionalized quantum dot hosts and organic dye guests by fluorescence lifetime imaging. Small 2010, 6, 2870–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Choyke, P.L. Target-cancer-cell-specific activatable fluorescence imaging probes: Rational design and in vivo applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorokhin, D.; Hsu, S.H.; Tomczak, N.; Reinhoudt, D.N.; Huskens, J.; Velders, A.H.; Vancso, G.J. Fabrication and luminescence of designer surface patterns with beta-cyclodextrin functionalized quantum dots via multivalent supramolecular coupling. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, M.E.; Roy, B.; Ahn, K.H. “Turn-on” fluorescent sensing with “reactive” probes. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 7583–7601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, O.; Mena, N.; Berrios, T.A.; Castro, E.A.; Cassels, B.K.; Nunez, M.T.; Aliaga, M.E. A selective fluorescent probe for the detection of mercury (ii) in aqueous media and its applications in living cells. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6598–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, C.R.; Miller, D.C.; Jones, E.F. Activatable optical probes for the detection of enzymes. Curr. Org. Synth. 2011, 8, 498–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, T.A.; Olson, E.S.; Timmers, M.M.; Jiang, T.; Tsien, R.Y. Systemic in vivo distribution of activatable cell penetrating peptides is superior to that of cell penetrating peptides. Integr. Biol. 2009, 1, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westermarck, J.; Kahari, V.M. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in turner invasion. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.R.; Fingleton, B.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinases: Biologic activity and clinical implications. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rood, M.T.M.; Oikonomou, M.; Buckle, T.; Raspe, M.; Urano, Y.; Jalink, K.; Velders, A.H.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B. An activatable, polarity dependent, dual-luminescent imaging agent with a long luminescence lifetime. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9733–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.; Guo, K.; Sudlow, G.P.; Berezin, M.Y.; Edwards, W.B.; Achilefu, S.; Akers, W.J. Detection of enzyme activity in orthotopic murine breast cancer by fluorescence lifetime imaging using a fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based molecular probe. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goergen, C.J.; Chen, H.H.; Bogdanov, A.; Sosnovik, D.E.; Kumar, A.T.N. In vivo fluorescence lifetime detection of an activatable probe in infarcted myocardium. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steunenberg, P.; Ruggi, A.; van den Berg, N.S.; Buckle, T.; Kuil, J.; van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Velders, A.H. Phosphorescence imaging of living cells with amino acid-functionalized tris(2-phenylpyridine)iridium(iii) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Funatsu, T.; Wazawa, T.; Yanagida, T. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between single fluorophores attached to a coiled-coil protein in aqueous solution. Chem. Phys. 1999, 247, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, A.; Medina, L.; Piura, B.; Segal, S.; Huleihel, M. Regulation of ovarian carcinoma skov-3 cell proliferation and secretion of mmps by autocrine il-6. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whitney, M.; Savariar, E.N.; Friedman, B.; Levin, R.A.; Crisp, J.L.; Glasgow, H.L.; Lefkowitz, R.; Adams, S.R.; Steinbach, P.; Nashi, N.; et al. Ratiometric activatable cell-penetrating peptides provide rapid in vivo readout of thrombin activation. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savariar, E.N.; Felsen, C.N.; Nashi, N.; Jiang, T.; Ellies, L.G.; Steinbach, P.; Tsien, R.Y.; Nguyen, Q.T. Real-time in vivo molecular detection of primary tumors and metastases with ratiometric activatable cell-penetrating peptides. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Hohng, S. Single-molecule three-color fret with both negligible spectral overlap and long observation time. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rae, M.; Fedorov, A.; Berberan-Santos, M.N. Fluorescence quenching with exponential distance dependence: Application to the external heavy-atom effect. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 119, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doose, S.; Neuweiler, H.; Sauer, M. Fluorescence quenching by photoinduced electron transfer: A reporter for conformational dynamics of macromolecules. Chemphyschem 2009, 10, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadran, S.; Standley, S.; Wong, K.; Otiniano, E.; Amighi, A.; Baudry, M. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (fret)-based biosensors: Visualizing cellular dynamics and bioenergetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Leeuwen, F.W.B.; Hardwick, J.C.; van Erkel, A.R. Luminescence-based imaging approaches in the field of interventional (molecular) imaging. Radiology 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rood, M.T.M.; Raspe, M.; Hove, J.B.t.; Jalink, K.; Velders, A.H.; Van Leeuwen, F.W.B. MMP-2/9-Specific Activatable Lifetime Imaging Agent. Sensors 2015, 15, 11076-11091. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150511076
Rood MTM, Raspe M, Hove JBt, Jalink K, Velders AH, Van Leeuwen FWB. MMP-2/9-Specific Activatable Lifetime Imaging Agent. Sensors. 2015; 15(5):11076-11091. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150511076
Chicago/Turabian StyleRood, Marcus T.M., Marcel Raspe, Jan Bart ten Hove, Kees Jalink, Aldrik H. Velders, and Fijs W.B. Van Leeuwen. 2015. "MMP-2/9-Specific Activatable Lifetime Imaging Agent" Sensors 15, no. 5: 11076-11091. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150511076
APA StyleRood, M. T. M., Raspe, M., Hove, J. B. t., Jalink, K., Velders, A. H., & Van Leeuwen, F. W. B. (2015). MMP-2/9-Specific Activatable Lifetime Imaging Agent. Sensors, 15(5), 11076-11091. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150511076