A Tapered Aluminium Microelectrode Array for Improvement of Dielectrophoresis-Based Particle Manipulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background of FDEP
3. Experiments and Methods
3.1. Microelectrode Fabrication

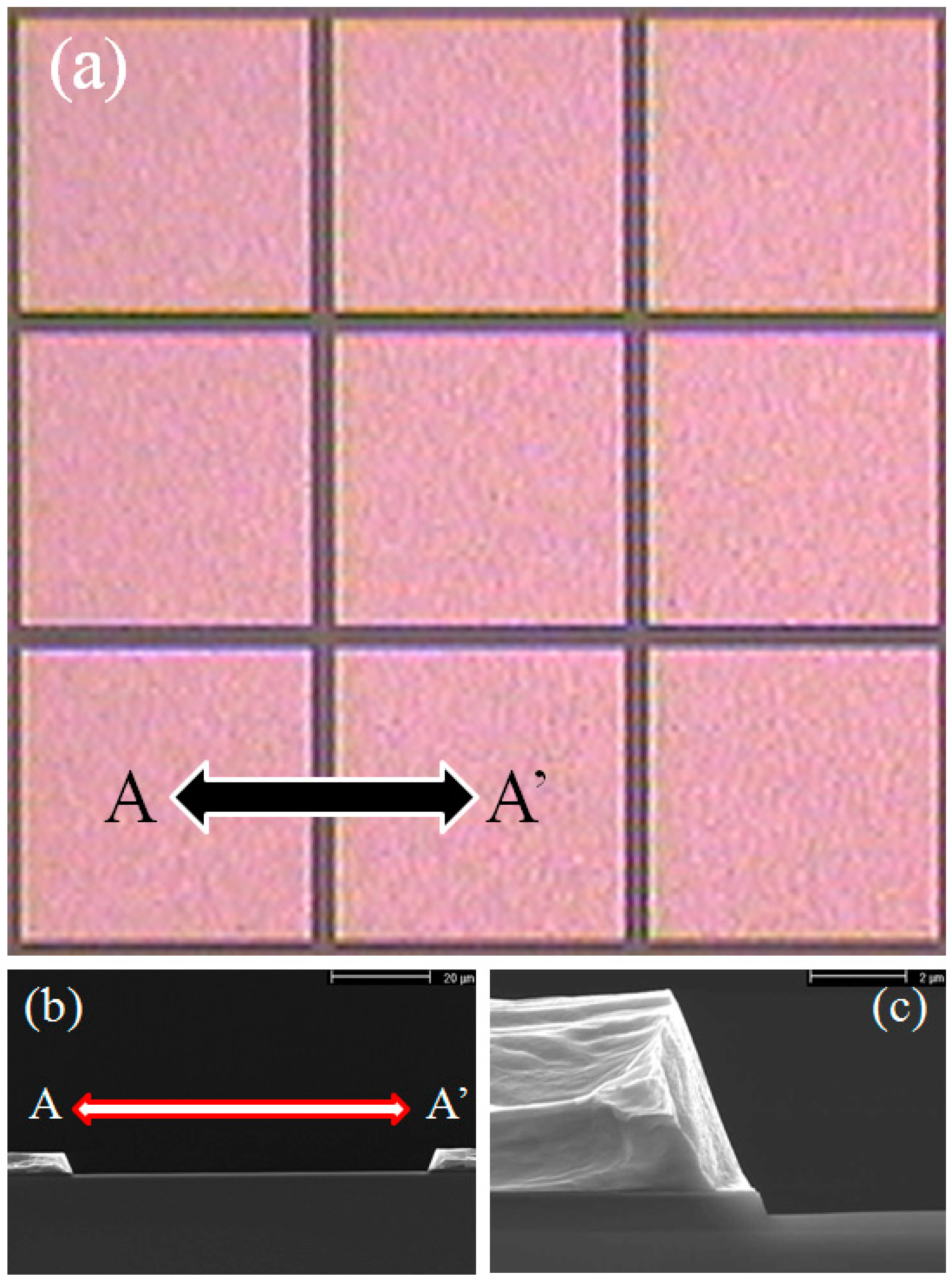
3.2. Measurement Equipment and Methods
3.2.1. Particle Preparation

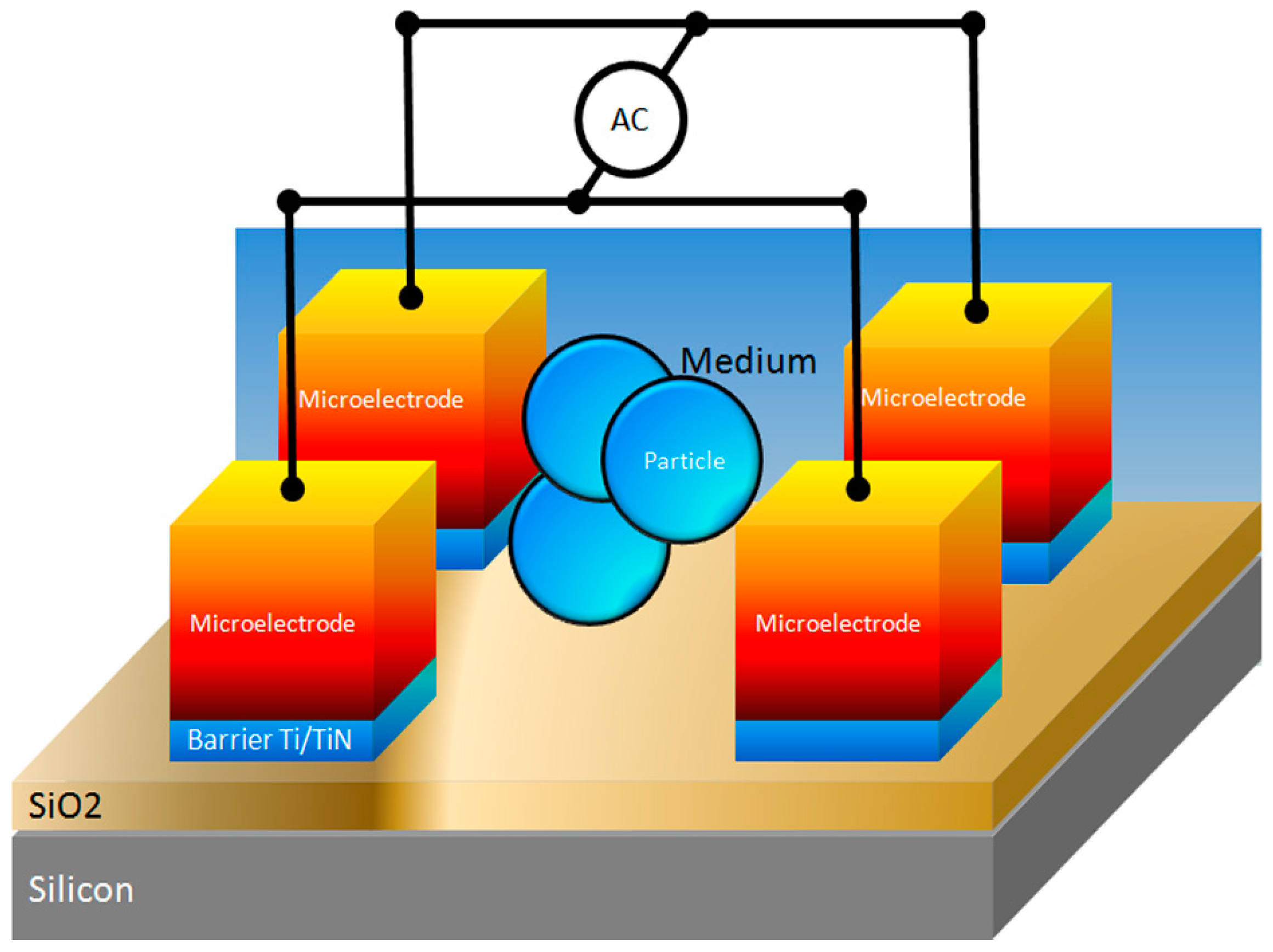
3.2.2. Experimental Setup

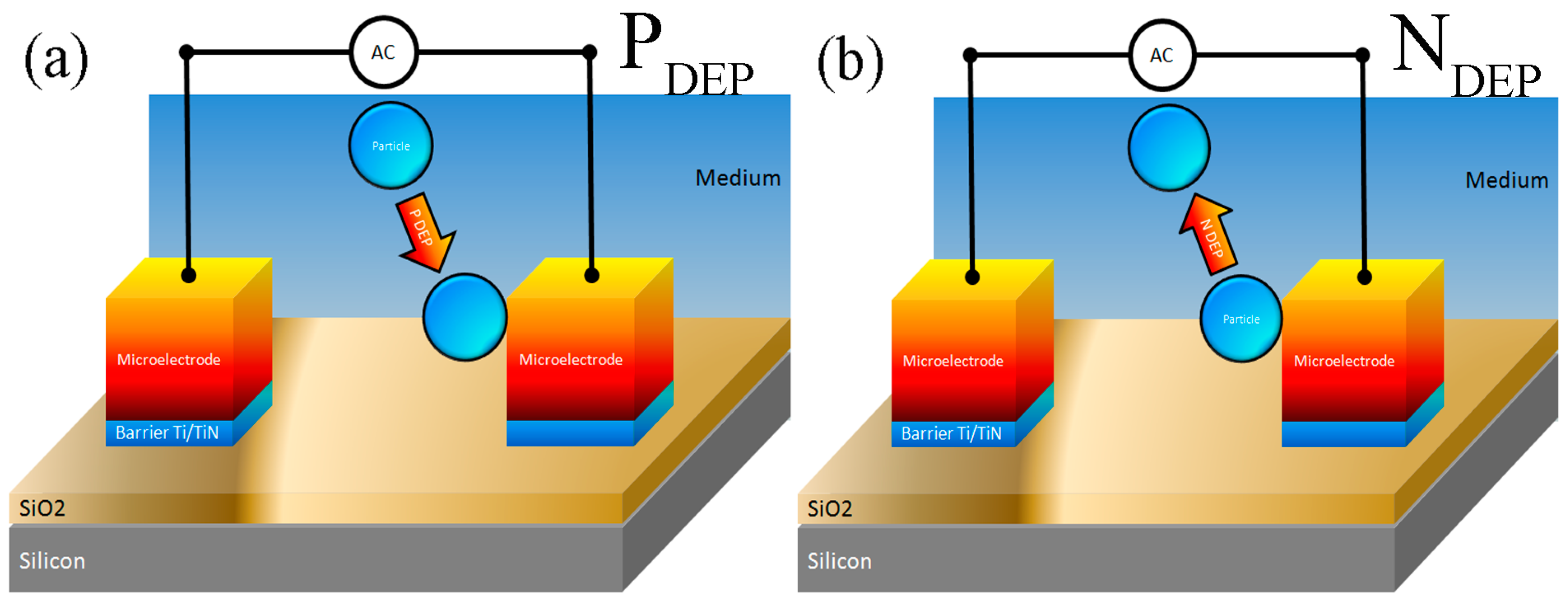
3.2.3. Determination of CMF
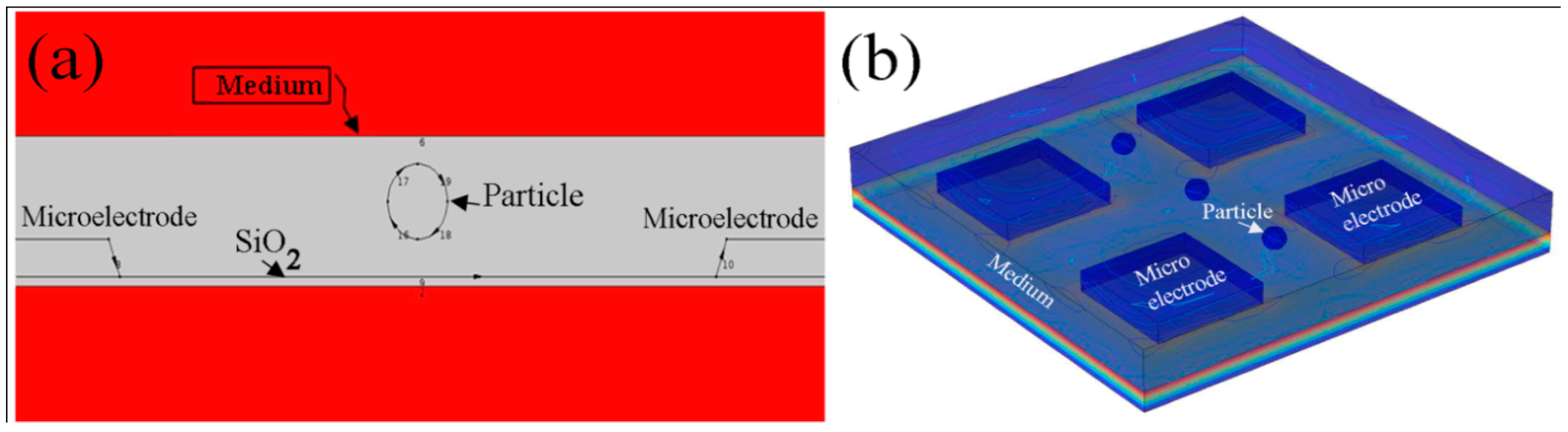
3.2.4. Numerical Simulation
4. Results and Discussion
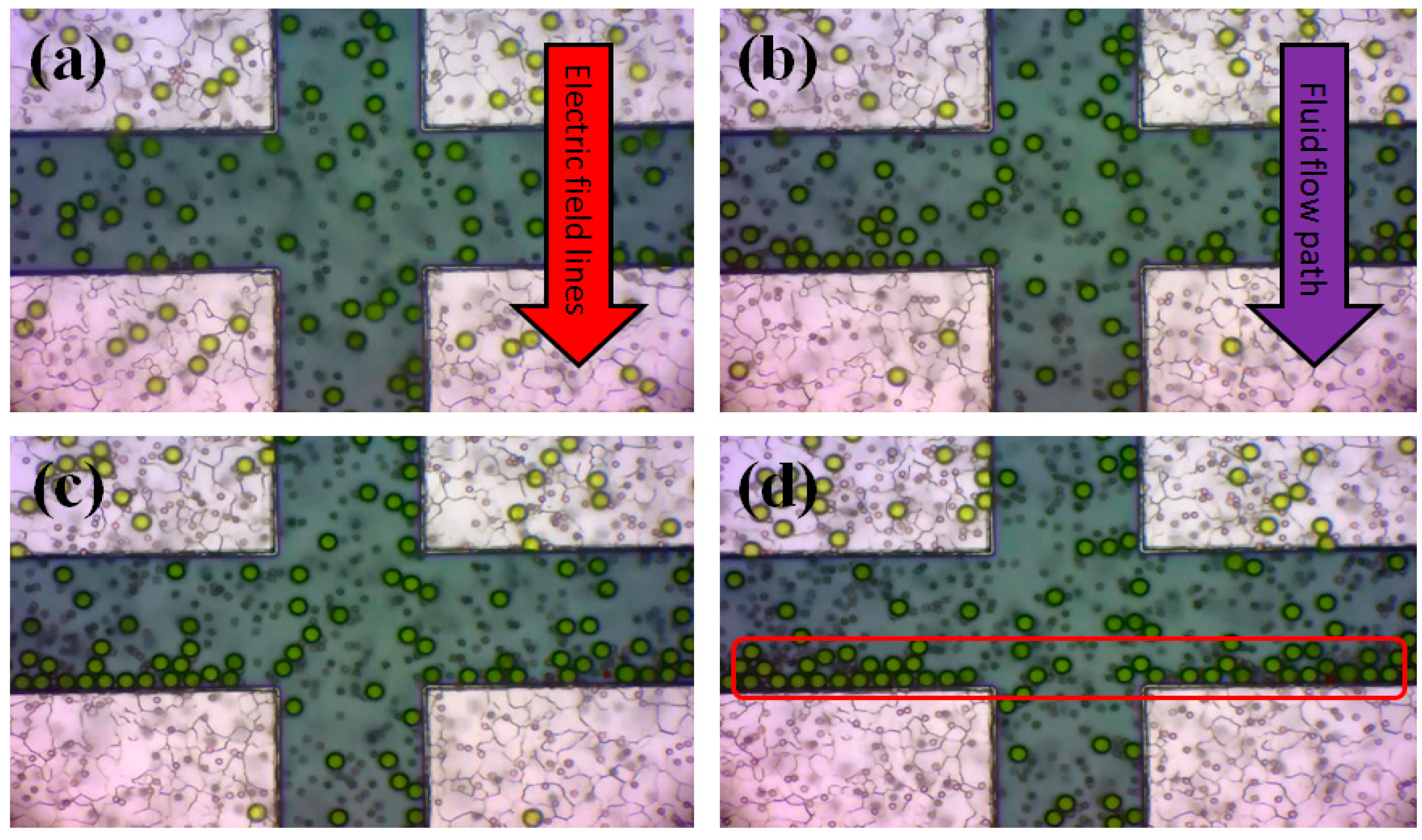
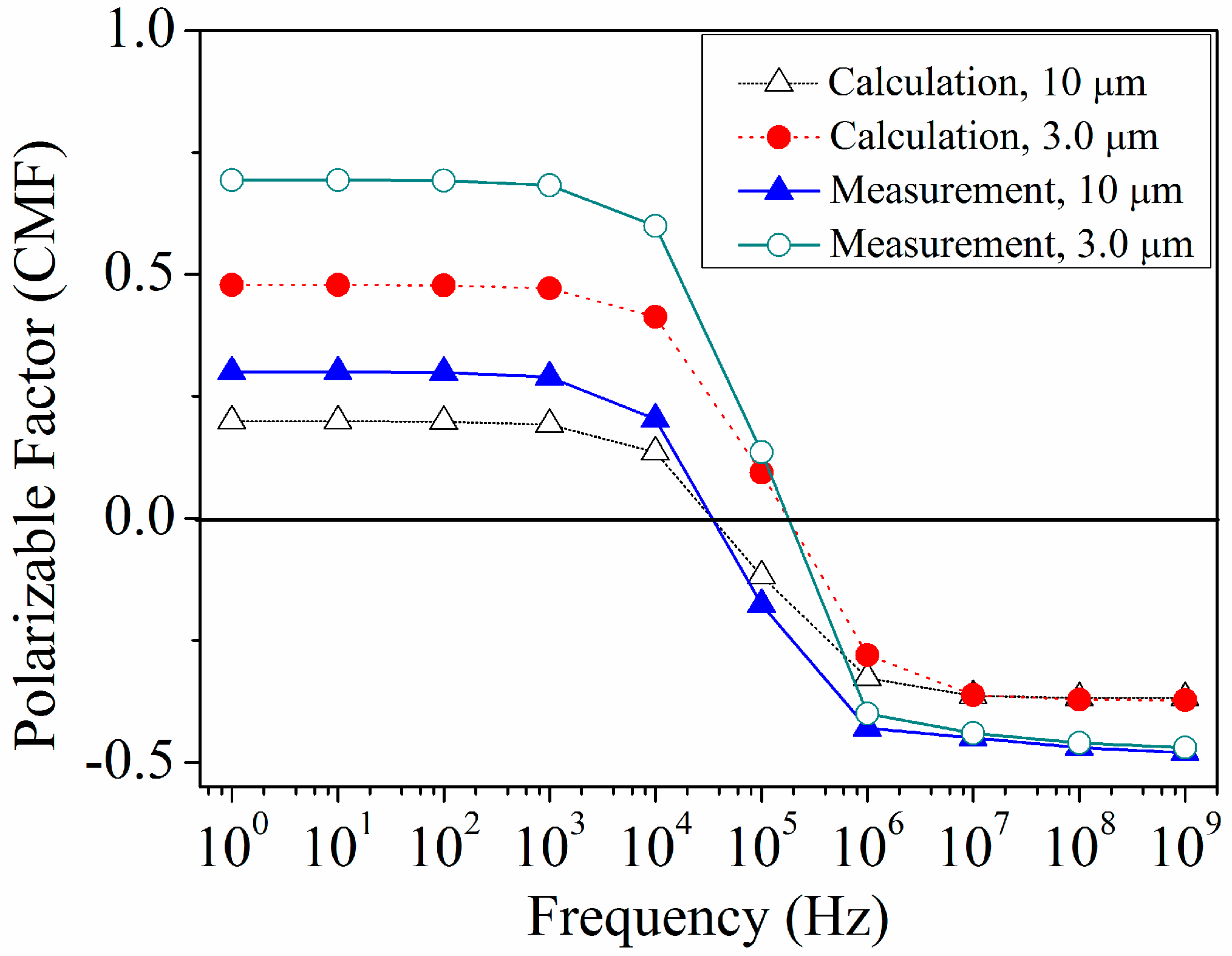



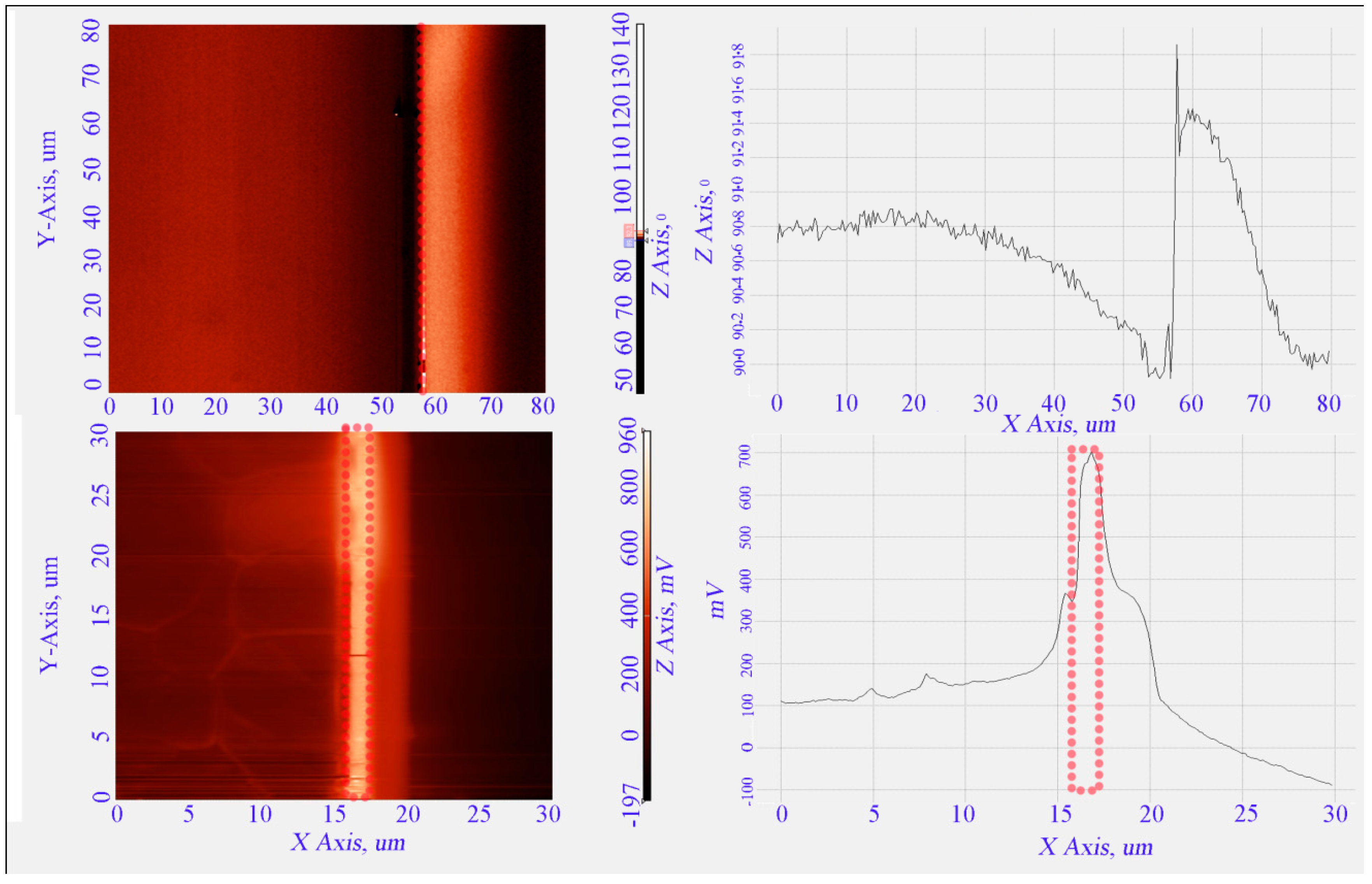
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pohl, H.A. Some effects of nonuniform fields on dielectrics. J. Appl. Phys. 1958, 29, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, H.A.; Pohl, H. Dielectrophoresis: The Behavior of Neutral Matter in Nonuniform Electric Fields; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1978; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Cetin, B. Microfluidic Continuous Separation of Particles and Cells by AC-Dielectrophoresis; Vanderbilt University: Nashville, TN, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gascoyne, P.R.; Vykoukal, J. Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Dielectrophoretic platforms for bio-microfluidic systems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Jafferji, I.; Garza, M.; Melnikova, V.O.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Pethig, R.; Davis, D.W. Apostream™, a new dielectrophoretic device for antibody independent isolation and recovery of viable cancer cells from blood. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 024133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Noshari, J.; Becker, F.F.; Gascoyne, P.R. Dielectrophoresis has broad applicability to marker-free isolation of tumor cells from blood by microfluidic systems. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, T.; Peyrade, D. Comprehensive analysis of alternating current electrokinetics induced motion of colloidal particles in a three-dimensional microfluidic chip. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 194702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Barrett, M.J.; Oliver, P.M.; Cetin, D.; Vezenov, D. Dielectrophoretic tweezers as a platform for molecular force spectroscopy in a highly parallel format. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4248–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-W.; Wu, Y.-T. System-level biochip for impedance sensing and programmable manipulation of bladder cancer cells. Sensors 2011, 11, 11021–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yafouz, B.; Kadri, N.A.; Ibrahim, F. Microarray dot electrodes utilizing dielectrophoresis for cell characterization. Sensors 2013, 13, 9029–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, W.N.W.; Kadri, N.A.; Ibrahim, F. Cell patterning for liver tissue engineering via dielectrophoretic mechanisms. Sensors 2014, 14, 11714–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, A.; Aziz, N.A.; Majlis, B.Y.; Yunas, J.; Dee, C.; Bais, B. Optimization of hna etching parameters to produce high aspect ratio solid silicon microneedles. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 095017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.Y.; Spence, C.; Scherer, A.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. A microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergent-Tanguy, S.; Chagneau, C.; Neveu, I.; Naveilhan, P. Fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS): A rapid and reliable method to estimate the number of neurons in a mixed population. J. Neurosci. Methods 2003, 129, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smistrup, K.; Kjeldsen, B.; Reimers, J.; Dufva, M.; Petersen, J.; Hansen, M.F. On-chip magnetic bead microarray using hydrodynamic focusing in a passive magnetic separator. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furlani, E.; Sahoo, Y. Analytical model for the magnetic field and force in a magnetophoretic microsystem. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, B.; Zattoni, A.; Reschiglian, P.; Moon, M.H.; Mirasoli, M.; Michelini, E.; Roda, A. Field-flow fractionation in bioanalysis: A review of recent trends. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 635, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascoyne, P.R.; Shim, S.; Noshari, J.; Becker, F.F.; Stemke-Hale, K. Correlations between the dielectric properties and exterior morphology of cells revealed by dielectrophoretic field-flow fractionation. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.; Holzschuh, S.; Traeger, A.; Fahr, A.; Schubert, U.S. Asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation in the field of nanomedicine. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5201–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethig, R. Dielectrophoresis: An assessment of its potential to aid the research and practice of drug discovery and delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Banada, P.P.; Chatni, M.R.; Lim, K.S.; Bhunia, A.K.; Ladisch, M.; Bashir, R. A multifunctional micro-fluidic system for dielectrophoretic concentration coupled with immuno-capture of low numbers of listeria monocytogenes. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, N.; Darabi, J.; Voglewede, P.; Guo, F.; Bayoumi, A. An analysis of interdigitated electrode geometry for dielectrophoretic particle transport in micro-fluidics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Lee, K.-K.; Koo, D.-B.; Park, J.-K. Dielectrophoretic oocyte selection chip for in vitro fertilization. Biomed. Microdevices 2008, 10, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Khoshmanesh, K.; Tovar-Lopez, F.; Mitchell, A.; Wlodarski, W.; Klantar-Zadeh, K. Dielectrophoretic separation of carbon nanotubes and polystyrene microparticles. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 7, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Qian, J.; Kenrick, S.A.; Daugherty, P.S.; Soh, H.T. Multitarget dielectrophoresis activated cell sorter. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8656–8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Zhang, C.; Tovar-Lopez, F.J.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Kalantar-zadeh, K.; Mitchell, A. Dielectrophoretic manipulation and separation of microparticles using curved microelectrodes. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshmanesh, K.; Zhang, C.; Tovar-Lopez, F.J.; Nahavandi, S.; Baratchi, S.; Mitchell, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Dielectrophoretic-activated cell sorter based on curved microelectrodes. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2010, 9, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grom, F.; Kentsch, J.; Müller, T.; Schnelle, T.; Stelzle, M. Accumulation and trapping of hepatitis a virus particles by electrohydrodynamic flow and dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, L.-S.; Huang, P.-H.; Lan, K.-C. Single-cell trapping utilizing negative dielectrophoretic quadrupole and microwell electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3637–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, N.; Rosenthal, A.; Voldman, J. nDEP microwells for single-cell patterning in physiological media. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.S.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. Negative dep traps for single cell immobilisation. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, T.P.; Issadore, D.; Westervelt, R.M. Integrated circuit/microfluidic chip to programmably trap and move cells and droplets with dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliescu, C.; Yu, L.; Tay, F.E.; Chen, B. Bidirectional field-flow particle separation method in a dielectrophoretic chip with 3d electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Du, H.; Li, W. Bioparticle separation and manipulation using dielectrophoresis. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 133, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Du, H.; Li, W. A 3D paired microelectrode array for accumulation and separation of microparticles. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Park, C.; Lee, J.G.; Ko, C. Bacteria concentration using a membrane type insulator-based dielectrophoresis in a plastic chip. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3153–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, H.; Caldwell, J.L.; Sano, M.B.; Davalos, R.V. Contactless dielectrophoresis: A new technique for cell manipulation. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, H.; Caldwell, J.L.; Davalos, R.V. A microfluidic system for biological particle enrichment using contactless dielectrophoresis. J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2010, 15, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, A.A.; Majlis, B.Y.; Ahmad, I. HF etching of sacrificial spin-on glass in straight and junctioned microchannels for MEMS microstructure release. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, D376–D382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. Ac electrokinetics: Colloids and nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Baldock, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pethig, R.; Talary, M.S.; Lee, R.S. Enhancing traveling-wave dielectrophoresis with signal superposition. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 22, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.P.; Hoettges, K.F. Microengineering in Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Honegger, T.; Berton, K.; Picard, E.; Peyrade, D. Determination of clausius–mossotti factors and surface capacitances for colloidal particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 181906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honegger, T.; Peyrade, D. Dielectrophoretic properties of engineered protein patterned colloidal particles. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 044115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buyong, M.R.; Larki, F.; Faiz, M.S.; Hamzah, A.A.; Yunas, J.; Majlis, B.Y. A Tapered Aluminium Microelectrode Array for Improvement of Dielectrophoresis-Based Particle Manipulation. Sensors 2015, 15, 10973-10990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150510973
Buyong MR, Larki F, Faiz MS, Hamzah AA, Yunas J, Majlis BY. A Tapered Aluminium Microelectrode Array for Improvement of Dielectrophoresis-Based Particle Manipulation. Sensors. 2015; 15(5):10973-10990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150510973
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuyong, Muhamad Ramdzan, Farhad Larki, Mohd Syafiq Faiz, Azrul Azlan Hamzah, Jumrail Yunas, and Burhanuddin Yeop Majlis. 2015. "A Tapered Aluminium Microelectrode Array for Improvement of Dielectrophoresis-Based Particle Manipulation" Sensors 15, no. 5: 10973-10990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150510973
APA StyleBuyong, M. R., Larki, F., Faiz, M. S., Hamzah, A. A., Yunas, J., & Majlis, B. Y. (2015). A Tapered Aluminium Microelectrode Array for Improvement of Dielectrophoresis-Based Particle Manipulation. Sensors, 15(5), 10973-10990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s150510973








