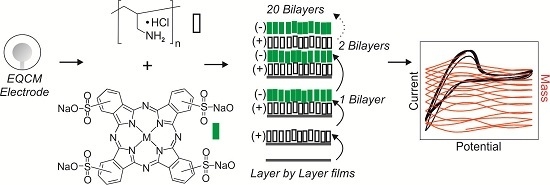
An Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Multisensor System Based on Phthalocyanine Nanostructured Films: Discrimination of Musts
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Grape Samples
| Grape Variety | Sugar Content (g/L) | Brix Degree | Total Polyphenol Index. TPI | Degree 16.8 | Polyphenol Content. Folin-Ciocalteau Method (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prieto Picudo | 224.1 | 22.89 | 19 | 13.31 | 0.46 |
| Garnacha | 187.4 | 19.68 | 15 | 11.13 | 0.38 |
| Cabernet-Sauvignon | 246.4 | 24.75 | 28 | 14.64 | 0.62 |
| Tempranillo | 209.1 | 21.53 | 28 | 12.42 | 0.52 |
| Juan García | 216.0 | 22.18 | 29 | 12.83 | 0.69 |
| Mencía Regadio | 203.3 | 21.05 | 23 | 12.08 | 0.54 |
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Calibration of the Quartz Crystal
2.4. Sensor Preparation
2.5. UV-Visible Characterization
2.6. Multisensor System Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
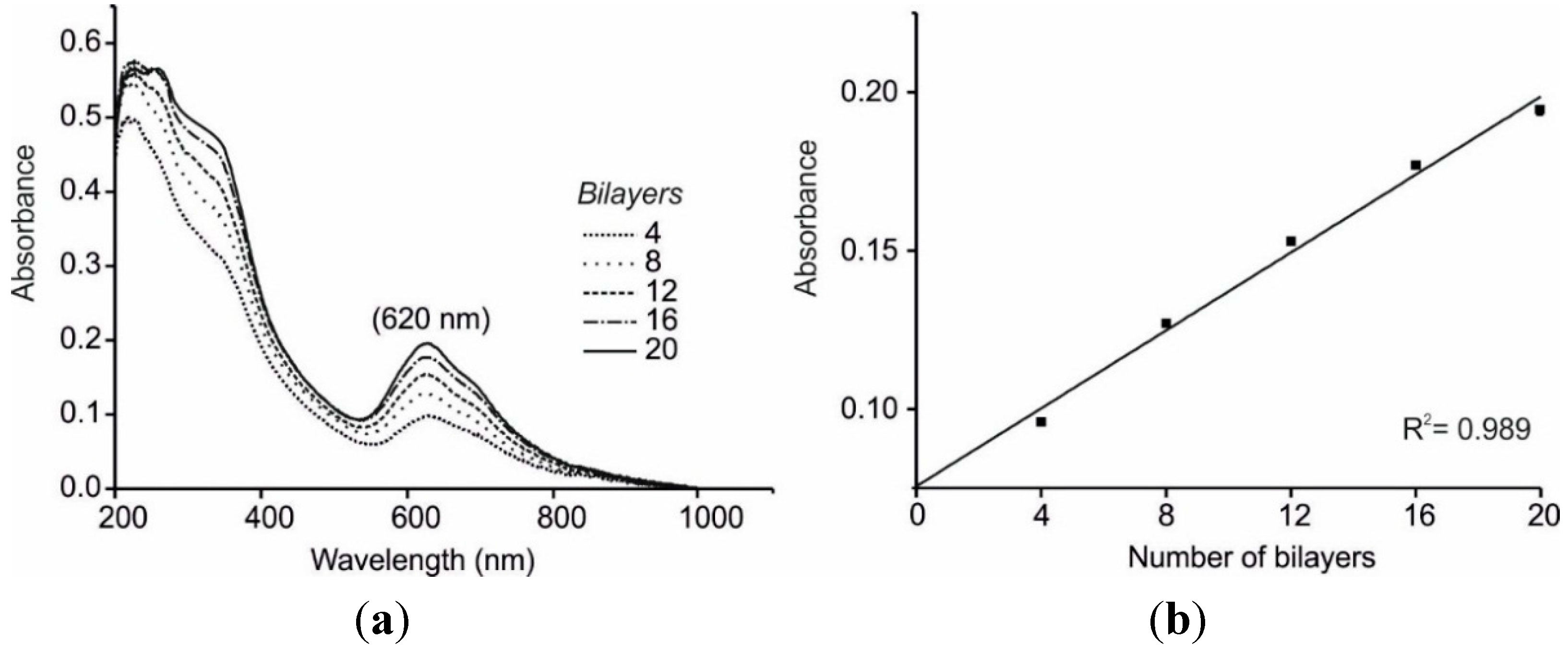
3.1. UV-Visible characterization
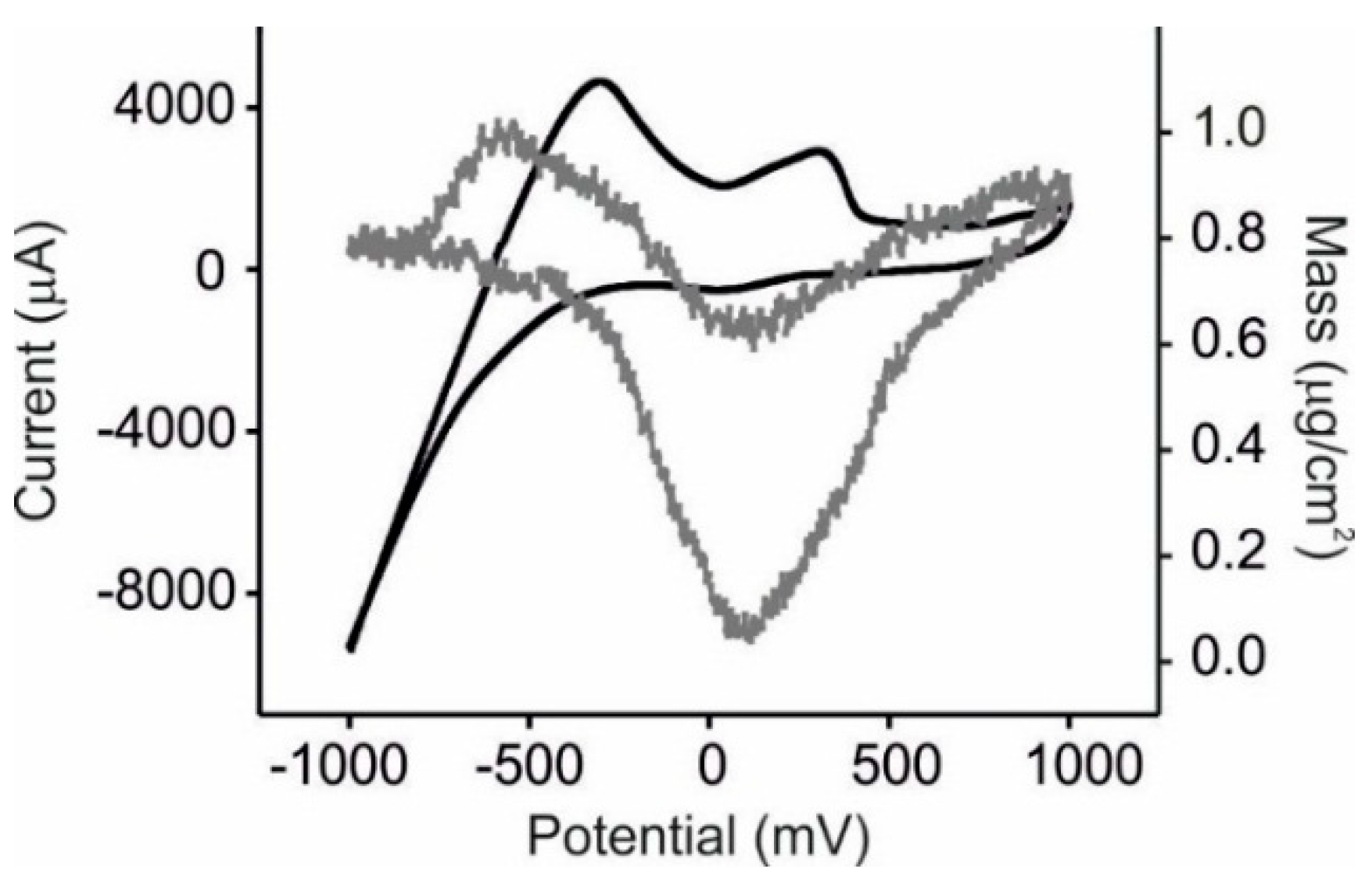
3.2. EQCM Measurements in Glucose and Catechol
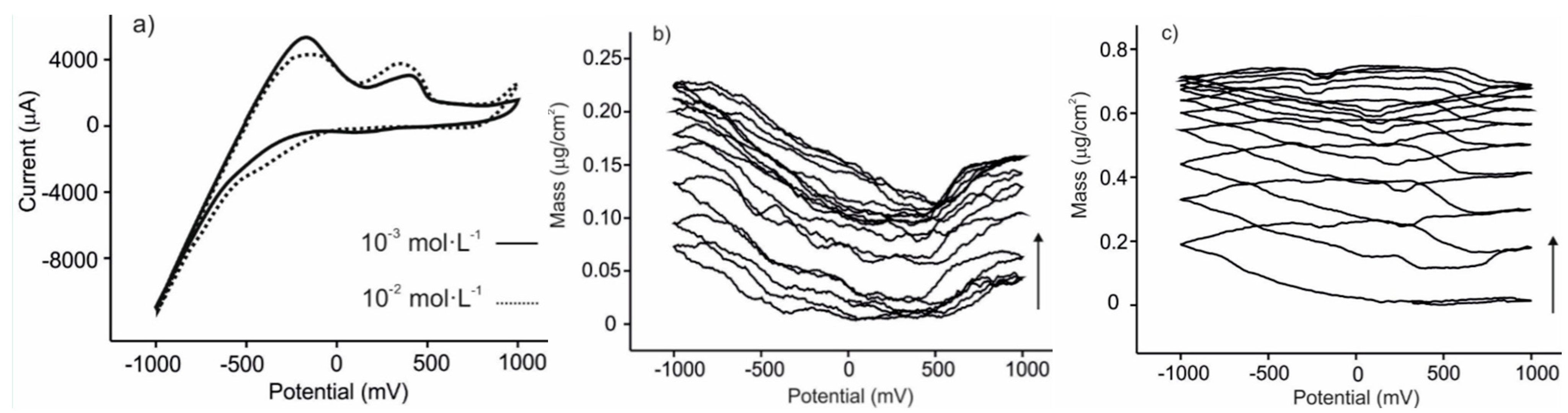
3.3. Analysis of Grape Juices
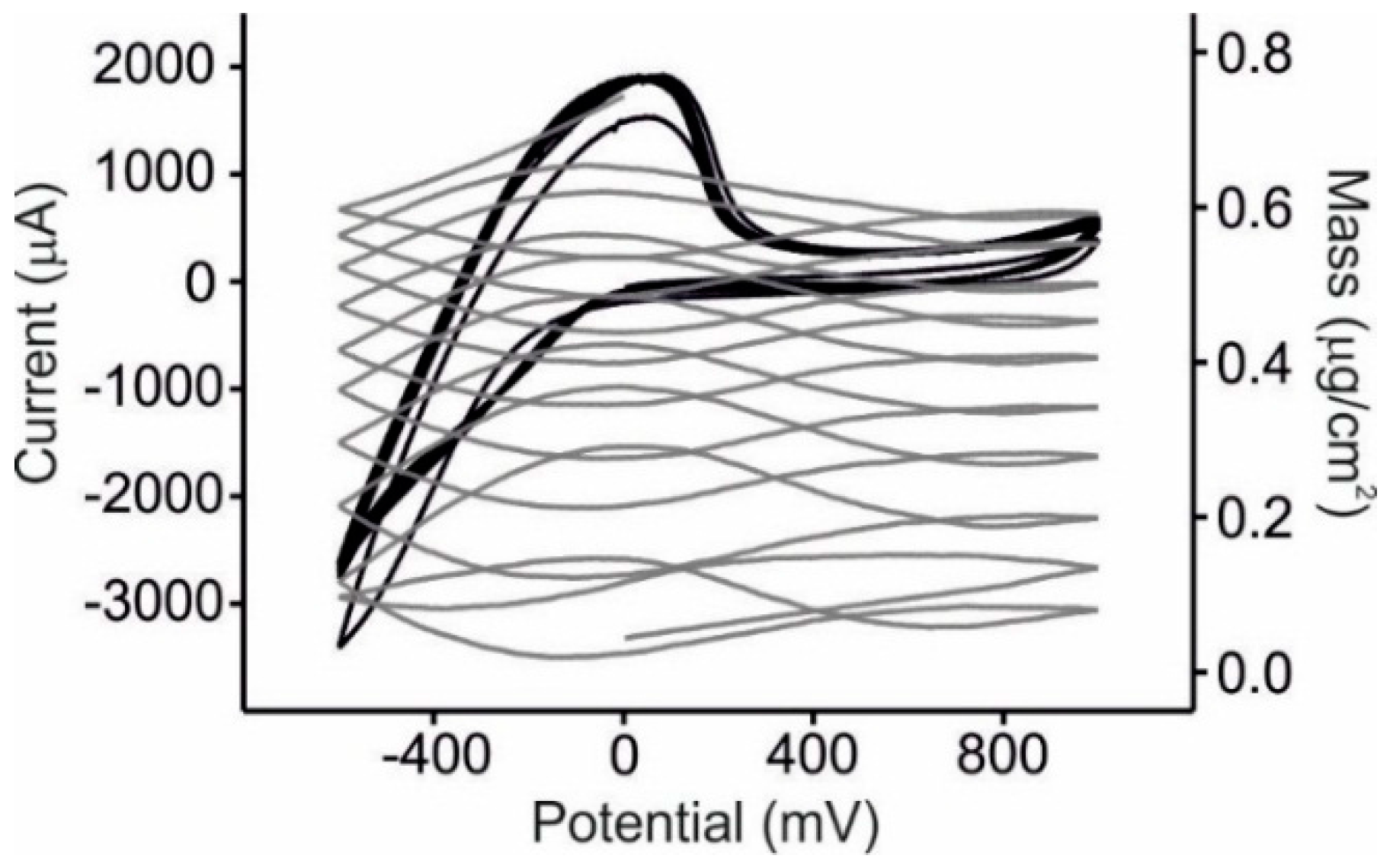
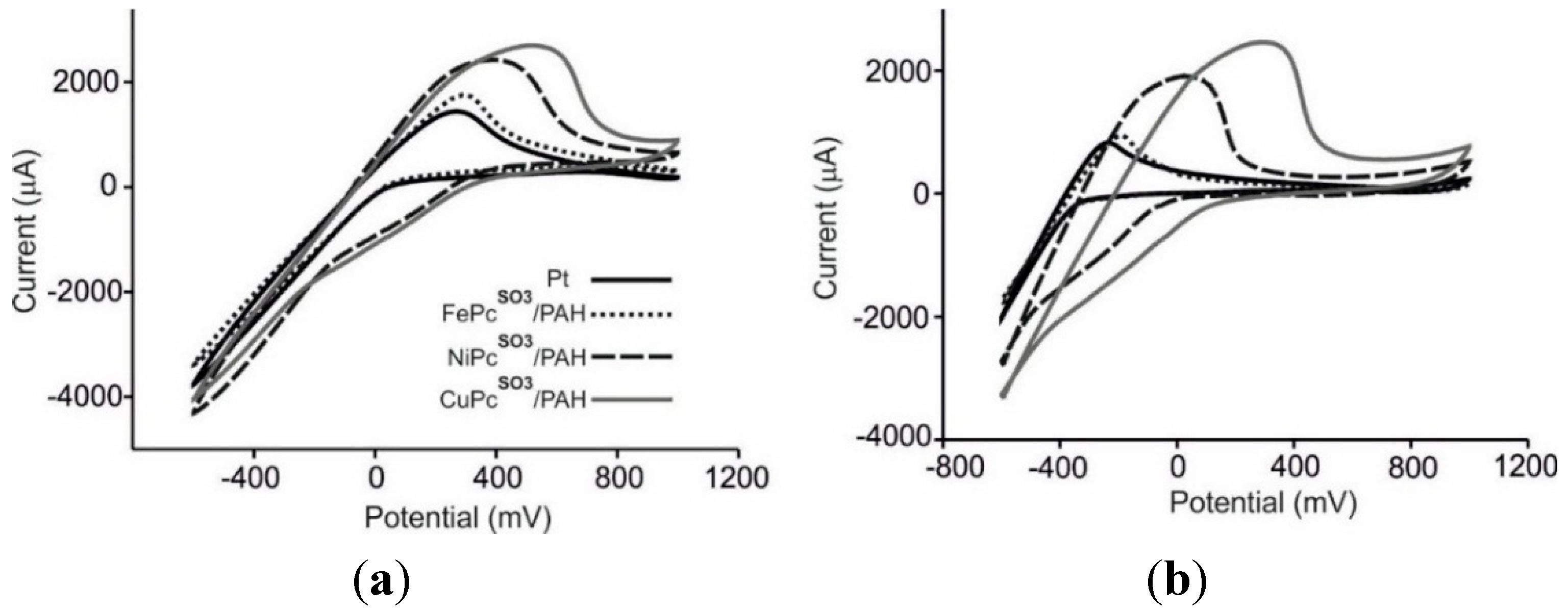
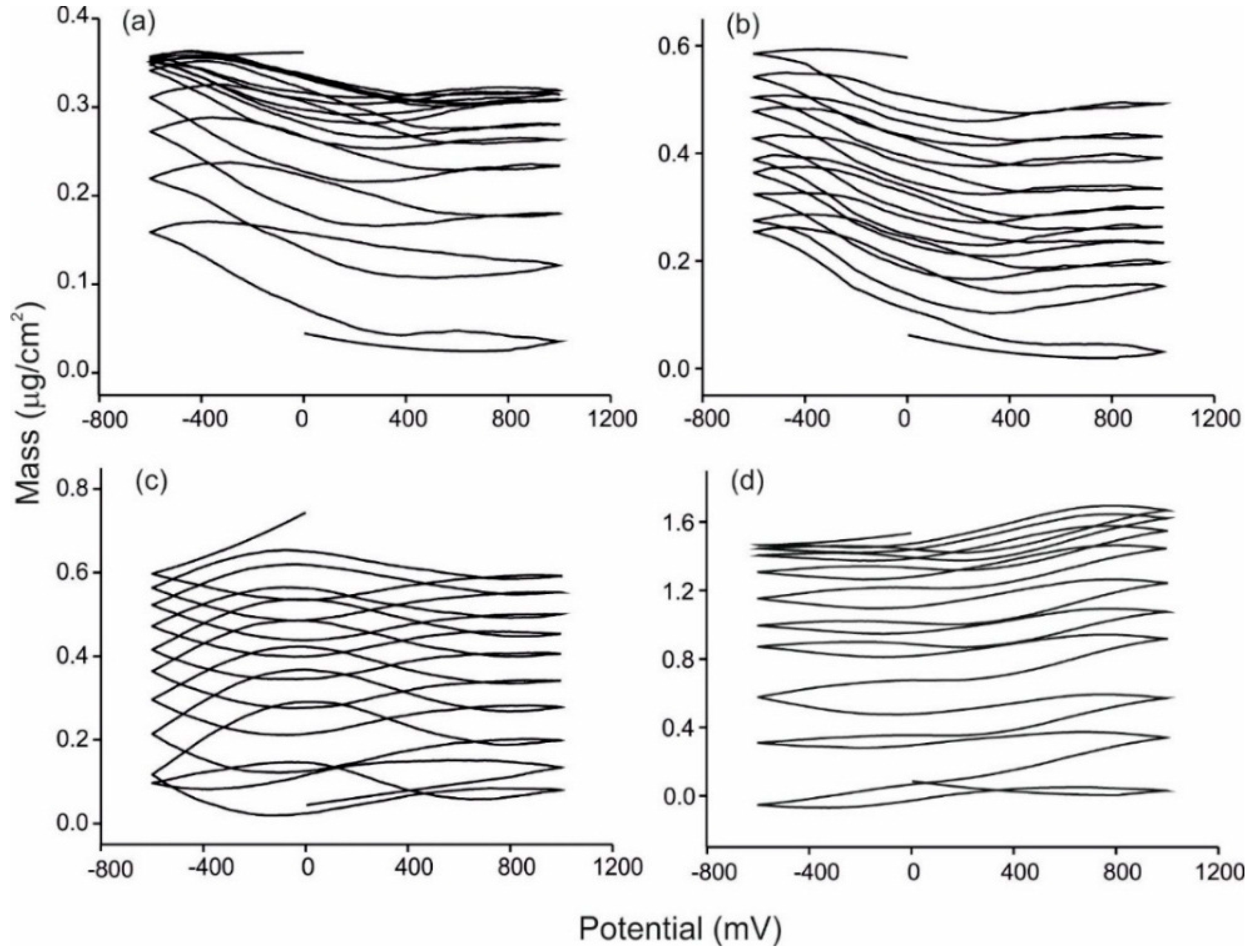
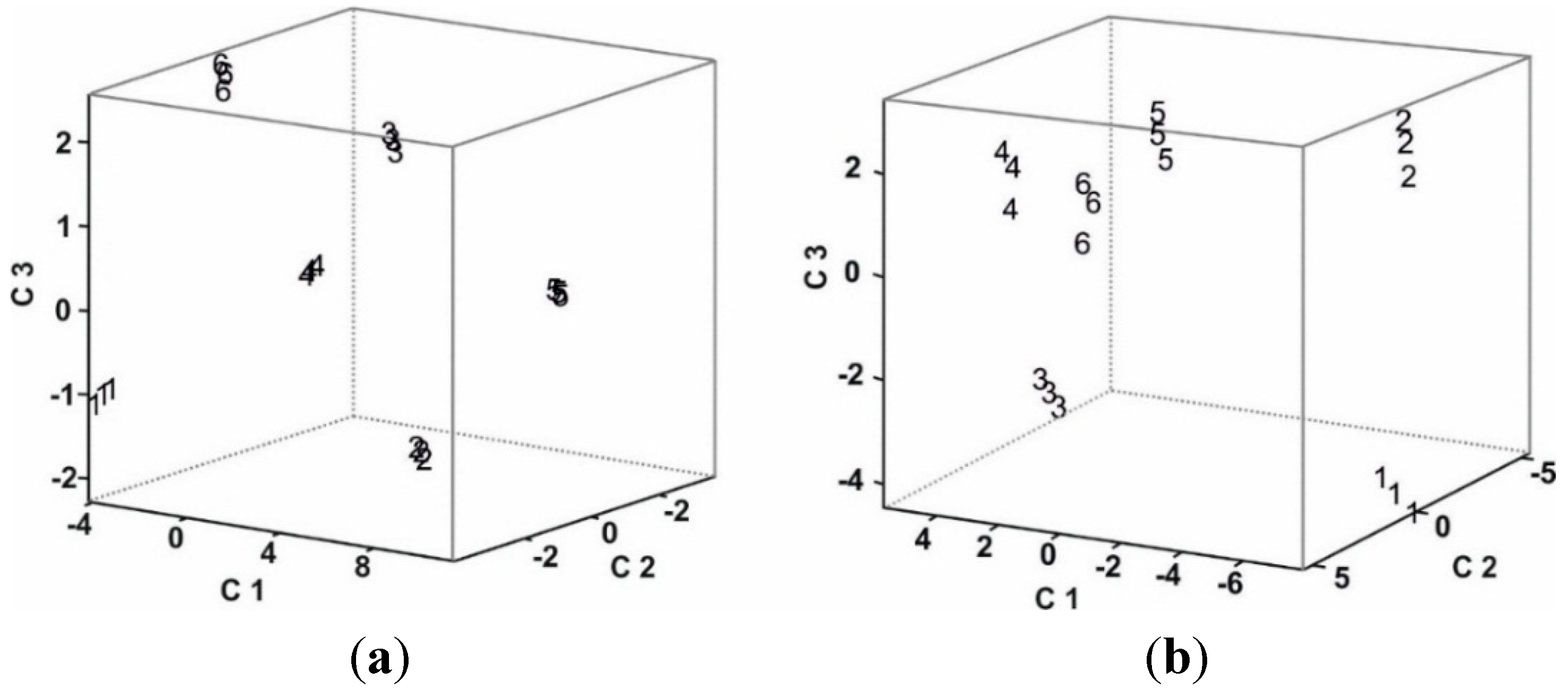
3.4. Statistical Analysis
| Voltammetric Outputs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | R2C (a) | RMSEC (b) | R2P (c) | RMSEP (d) | Number of Components |
| Sugar content | 0.997 | 0.99187 | 0.945 | 4.24917 | 4 |
| Brix degree | 0.996 | 0.09242 | 0.935 | 0.40019 | 4 |
| Degree 16.8 | 0.997 | 0.05894 | 0.946 | 0.25147 | 4 |
| TPI | 0.992 | 0.46538 | 0.983 | 0.68089 | 3 |
| Polyphenolic content | 0.998 | 0.33442 | 0.989 | 1.11841 | 3 |
| Folin-Ciocalteau method | |||||
| Mass Outputs | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | R2C (a) | RMSEC (b) | R2P (c) | RMSEP (d) | Number of Components |
| Sugar content | 0.941 | 4.45005 | 0.839 | 7.31293 | 4 |
| Brix degree | 0.972 | 0.00176 | 0.865 | 0.00291 | 4 |
| Degree 16.8 | 0.941 | 0.26438 | 0.840 | 0.43420 | 4 |
| TPI | 0.961 | 1.02511 | 0.845 | 2.04940 | 5 |
| Polyphenolic content | 0.965 | 1.91428 | 0.921 | 3.0353 | 5 |
| Folin-Ciocalteau method | |||||
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tahara, Y.; Toko, K. Electronic tongues—A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwińska, M.; Wiśniewska, P.; Dymerski, T.; Namieśnik, J.; Wardencki, W. Food analysis using artificial senses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1423–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsanov, D.; Mednova, O.; Vietoris, V.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Legin, A. Towards reliable estimation of an “electronic tongue” predictive ability from PLS regression models in wine analysis. Talanta 2012, 90, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, P.; Casolino, C.; Forina, M. Chemometric Brains for Artificial Tongues. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 57–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ciosek, P.; Wroblewski, W. Potentiometric Electronic Tongues for Foodstuff and Biosample Recognition—An Overview. Sensors 2011, 11, 4688–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scampicchio, M.; Ballabio, D.; Arecchi, A.; Cosio, S.M.; Mannino, S. Amperometric electronic tongue for food analysis. Microchim. Acta 2008, 163, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winquist, F.; Olsson, J.; Eriksson, M. Multicomponent analysis of drinking water by a voltammetric electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 683, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, V.; Arrieta, A.; Fernández-Escudero, J.A.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; de Saja, J.A. Electronic tongue based on chemically modified electrodes and voltammetry for the detection of adulterations in wines. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 118, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceto, X.; Apetrei, C.; del Valle, M.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Evaluation of red wines antioxidant capacity by means of a voltammetric e-tongue with an optimized sensor array. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riul, A.; Dantas, C.A.R.; Miyazaki, C.M.; Oliveira, O.N. Recent advances in electronic tongues. Analyst 2010, 135, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Sanchez, L.; Soto, J.; Martinez-Mañez, R.; Garcia-Breijo, E.; Ibañez, J.; Llobet, E. A novel humid electronic nose combined with an electronic tongue for assessing deterioration of wine. Sens. Actuators A 2011, 171, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, S.; Ballabio, D.; Benedetti, S.; Cosio, M.S. Prediction of Italian red wine sensorial descriptors from electronic nose, electronic tongue and spectrophotometric measurements by means of genetic algorithm regression models. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; Macagnano, A.; Mantini, A.; D’Amico, A.; Ubigli, M.; Legin, A.; Lvova, L.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Vlasov, Y. Application of a combined artificial olfaction and taste system to the quantification of relevant compounds in red wine. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 69, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnitskaya, A.; Rocha, S.M.; Legin, A.; Pereira, V.; Marques, J.C. Evaluation of the feasibility of the electronic tongue as a rapid analytical tool for wine age prediction and quantification of the organic acids and phenolic compounds. The case-study of Madeira wine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 662, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, V.; Hernando, T.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; de Saja, J.A. Electrochemical sensor array made from bisphthalocyanine modified carbon paste electrodes for discrimination of red wines. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 5177–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, N.; Gay, M.; Vidal, S.; Aagaard, O.; de Saja, J.A.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Analysis of the influence of the type of closure in the organoleptic characteristics of a red wine by using an electronic panel. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, V.; Arrieta, A.; Fernandez-Escudero, J.A.; Garcia, H.; Apetrei, C.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; de Saja, J.A. E-tongue based on a hybrid array of voltammetric sensors based on phthalocyanines, perylene derivatives and conducting polymers: Discrimination capability towards red wines elaborated with different variety of grapes. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 115, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apetrei, C.; Apetrei, I.; Nevares, I.; del Alamo, M.; Parra, V.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L.; de Saja, J.A. Using an e-tongue based on voltammetric electrodes to discriminate among red wines aged in oak barrels or aged using alternative methods. Correlation between electrochemical signals and analytical parameters. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legin, A.; Rudnitskaya, A.; Lvova, L.; Vlasov, Y.; di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A. Evaluation of Italian wine by the electronic tongue:recognition, quantitative analysis and correlation with human sensory perception. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 484, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldacci, S.; Matsuno, T.; Toko, K.; Stella, R.; de Rossi, D. Discrimination of wine using taste and smell sensors. Sens. Mater. 1998, 10, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Arrieta, A.A.; Parra, V.; Bernal, A.; Vegas, A.; Villanueva, S.; Gutierrez-Osuna, R.; de Saja, J.A. Fusion of three sensory modalities for the multimodal characterization of red wines. IEEE Sens. J. 2004, 4, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvova, L.; Pudi, R.; Galloni, P.; Lippolis, V.; di Natale, C.; Lundstrom, I.; Paolesse, R. Multi-transduction sensing films for Electronic Tongue applications. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 207, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Llobera, A.; Vila-Planas, J.; Capdevila, F.; Demming, S.; Büttgenbach, S.; Mínguez, S.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C. Hybrid electronic tongue based on optical and electrochemical microsensors for quality control of wine. Analyst 2010, 135, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apetrei, I.M.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Apetrei, C.; Nevares, I.; del Alamo, M.; de Saja, J.A. Monitoring of evolution during red wine aging in oak barrels and alternative method by means of an electronic panel test. Food Res. Int. 2012, 45, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampetti, E.; Pantalei, S.; Macagnano, A.; Proeitti, E.; di Natale, C.; D’Amico, A. Use of multiplexed oscillator in a miniaturized electronic nose based on a multichannel quartz crystal microbalance. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 131, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compagnone, D.; Faieta, M.; Pizzoni, D.; di Natale, C.; Paolesse, R.; van Caelenberg, T.; Beheydt, B.; Pittia, P. Quartz crystal microbalance gas sensor arrays for the quality control of chocolate. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 207, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Advances in electronic-nose technologies developed for biomedical applications. Sensors 2011, 11, 1105–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.; Sankaran, S.; Mallik, S.; Gaddam, B.; Hanson, A.A. Olfactory receptor-based polypeptide sensor for acetic acid VOC detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Lin, C.S.; Chen, S.H.; Ye, R.; Wu, V.C.H. A piezoelectric immunosensor for specific capture and enrichment of viable pathogens by quartz crystal microbalance sensor, followed by detection with antibody-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermolaeva, T.N.; Kalmykova, E.N.; Shashkanova, O.Y. Piezoquartz biosensors for the analysis of environmental objects, foodstuff and for clinical diagnostic. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2008, 78, 2430–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Mo, Z.H.; Choy, J.T.S.; Zhu, D.R.; Fung, Y.S. Piezoelectric quartz crystal sensor for sensing taste-causing compounds in food. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 131, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, P.; Borngraeber, R.; Schroeder, J.; Auge, J. Application of novel sensor electronics for quartz resonators in artificial tongue. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE/EIA International Frequency Control Symposium & Exhibition, Kansas City, MO, USA, 7–9 June 2000; pp. 100–105.
- Gay-Martin, M.; Diez-Arevalo, E.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Saja, J.A.D. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance analysis of the oxidation reaction of phenols found in wines at lutetium bisphthalocyanine electrodes. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 185, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.I.; Chang, Y.P.; Chu, Y.H. Biomolecular interactions and tools for their recognition: Focus on the quartz crystal microbalance and its diverse surface chemistries and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1947–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Plaza, C.; De Saja, J.A.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Bioelectronic tongue based on lipidic nanostructured layers containing phenol oxidases and lutetium bisphthalocyanine for the analysis of grapes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozmen, M.; Ozbek, Z.; Bayrakci, M.; Ertul, S.; Ersoz, M.; Capan, R. Preparation and gas sensing properties of Langmuir-Blodgett thin films of calix[n]arenes: Investigation of cavity effect. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 195, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deligöz, H.; Tieke, B. QCM-D study of layer by layer assembly of polyelectrolyte blend films and their drug loading-release behavior. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 441, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbahar, D.D.; Harbeck, M.; Gumus, G.; Gurol, I.; Ahsen, V. Self-assembly of phthalocyanines on quartz crystal microbalances for QCM liquid sensing applications. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 190, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningsih, P.; Holdsworth, C.Z.; Donne, S.W. Mn-modified polypyrrole thin films for supercapacitor electrodes. Synth. Meth. 2014, 196, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.G.; de Saja, J.A.; Munoz, R.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Multisensor system based on bisphthalocyanine nanowires for the detection of antioxidants. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 68, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.; He, L.H.; Fang, S.M.; Zhang, Z.H. Graphene nanostructures with plasma polymerized allylamine biosensor for selective detection of mercury ions. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 203, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.K.; Liu, C.J.; Hayashi, K. Molecular imprinted polyacrylic acids based QCM sensor array for recognition of organic acids in body odor. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 204, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.H.; Xie, Q.J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.F.; Ma, M.; Yao, S.Z. Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance studies on enzymatic specific activity and direct electrochemistry of immobilized glucose oxidase in the presence of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.M.; Ma, M.; Wang, L.L.; Xie, Q.J.; Cao, Z.J.; Jiang, X.Q.; Yao, S.Z. Highly sensitive and surface-renewable electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance assays of heparin and chondroitin sulfate based on their effects on the electrodeposition of neutral red. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaiyan, N.K.; Obraztsov, L.; Wijesinghe, C.A.; Tran, K.; Kutner, W.; D’Souza, F. Supramolecular Donor-Acceptor Hybrid of Electropolymerized Zinc Porphyrin with Axially Coordinated Fullerene: Formation, Characterization, and Photoelectrochemical Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 8982–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalov, S.; Levi, M.D.; Salitra, G.; Aurbach, D. EQCM as a unique tool for determination of ionic fluxes in microporous carbons as a function of surface charge distribution. J. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 1718–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malitesta, C.; Picca, R.A.; Mazzotta, E.; Guascito, M.R. Tools for the development of electrochemical sensors: An EQCM flow cell with flow focusing. Electroanal 2012, 24, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.M.; Gouveia-Caridade, C.; Soares, D.M.; Brett, C.M.A. Electrochemical and surface characterisation of carbon-film-coated piezoelectric quartz crystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8084–8090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.J.C.; Brett, D.J.L.; Kucernak, A.R.J. An electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance study of platinum phthalocyanine thin films. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2009, 633, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, M.; Erbahar, D.D.; Gurol, I.; Musluoglu, E.; Ahsen, V.; Ozturk, Z.Z. Phthalocyanines as sensitive coatings for QCM sensors operating in liquids for the detection of organic compounds. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 150, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Gay, M.; de Saja, J.A. New insights into sensors based on radical bisphthalocyanines. J. Porphy. Phthalocyan. 2009, 13, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, P.; Pavinatto, F.J.; Oliveira, O.N.; Saez, J.A.D.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L. Detection of catechol using mixed Langmuir-Blodgett films of a phospholipid and phthalocyanines as voltammetric sensors. Analyst 2010, 135, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpati, D.; Alessio, P.; Zanfolim, A.A.; Storti, F.C.; Job, A.E.; Ferreira, M.; Riul, A.; Oliveira, O.N.; Constantino, C.J.L. Exploiting distinct molecular architectures of ultrathin films made with iron phthalocyanine for sensing. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 15275–15282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucolotto, V.; Ferreira, M.; Cordeiro, M.R.; Constantino, C.J.L.; Balogh, D.T.; Zanatta, A.R.; Moreira, W.C.; Oliveira, O.N. Unusual interactions binding iron tetrasulfonated phthalocyanine and poly(allylamine hydrochloride) in layer-by-layer films. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 3733–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIV. Compendium of International Methods of Analysis of Wines and Musts; Organisation Internationale de la Vigneet du Vin: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, P.H.B.; Volpati, D.; Riul, A.; Caetano, W.; Constantino, C.J.L. Layer-by-Layer technique as a new approach to produce nanostructured films containing phospholipids as transducers in sensing applications. Langmuir 2009, 25, 2331–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Osuna, R.; Nagle, H.T. A method for evaluating data-preprocessing techniques for odor classification with an array of gas sensors. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B 1999, 29, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.; Varela, H.; Torresi, R.M.; Tremiliosi, G. Electrode passivation caused by polymerization of different phenolic compounds. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mendez, M.L.; Apetrei, C.; Gay, M.; Medina-Plaza, C.; de Saja, J.A.; Vidal, S.; Aagaard, O.; Ugliano, M.; Wirth, J.; Cheynier, V. Evaluation of oxygen exposure levels and polyphenolic content of red wines using an electronic panel formed by an electronic nose and an electronic tongue. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Hernandez, C.; Medina-Plaza, C.; Garcia-Cabezon, C.; Martin-Pedrosa, F.; Del Valle, I.; De Saja, J.A.; Rodríguez-Méndez, M.L. An Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Multisensor System Based on Phthalocyanine Nanostructured Films: Discrimination of Musts. Sensors 2015, 15, 29233-29249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129233
Garcia-Hernandez C, Medina-Plaza C, Garcia-Cabezon C, Martin-Pedrosa F, Del Valle I, De Saja JA, Rodríguez-Méndez ML. An Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Multisensor System Based on Phthalocyanine Nanostructured Films: Discrimination of Musts. Sensors. 2015; 15(11):29233-29249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129233
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Hernandez, Celia, Cristina Medina-Plaza, Cristina Garcia-Cabezon, Fernando Martin-Pedrosa, Isabel Del Valle, Jose Antonio De Saja, and Maria Luz Rodríguez-Méndez. 2015. "An Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Multisensor System Based on Phthalocyanine Nanostructured Films: Discrimination of Musts" Sensors 15, no. 11: 29233-29249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129233
APA StyleGarcia-Hernandez, C., Medina-Plaza, C., Garcia-Cabezon, C., Martin-Pedrosa, F., Del Valle, I., De Saja, J. A., & Rodríguez-Méndez, M. L. (2015). An Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Multisensor System Based on Phthalocyanine Nanostructured Films: Discrimination of Musts. Sensors, 15(11), 29233-29249. https://doi.org/10.3390/s151129233