A Multi-Point Sensor Based on Optical Fiber for the Measurement of Electrolyte Density in Lead-Acid Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
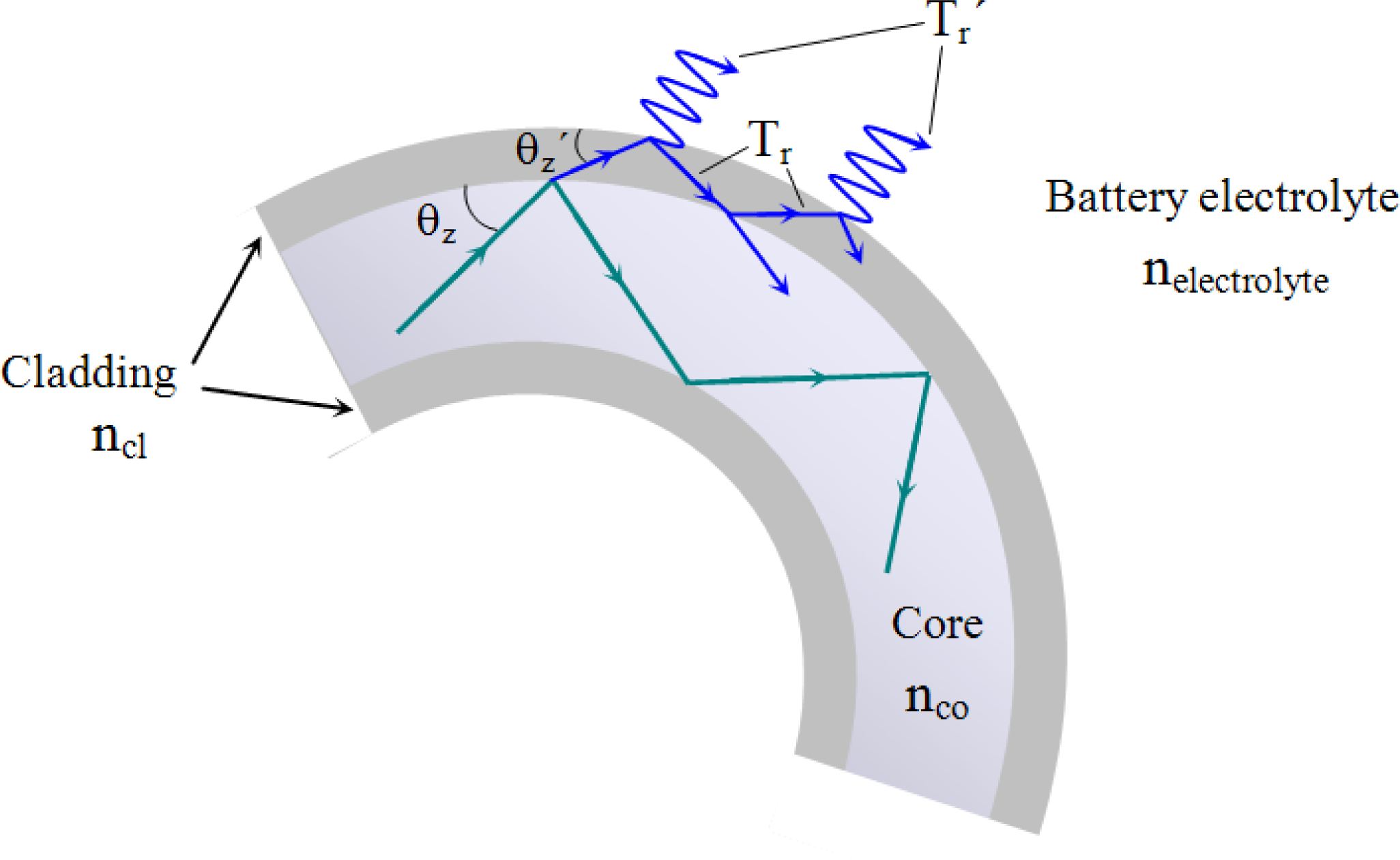
2. Operating Principles
3. Optical Fiber Point Sensor
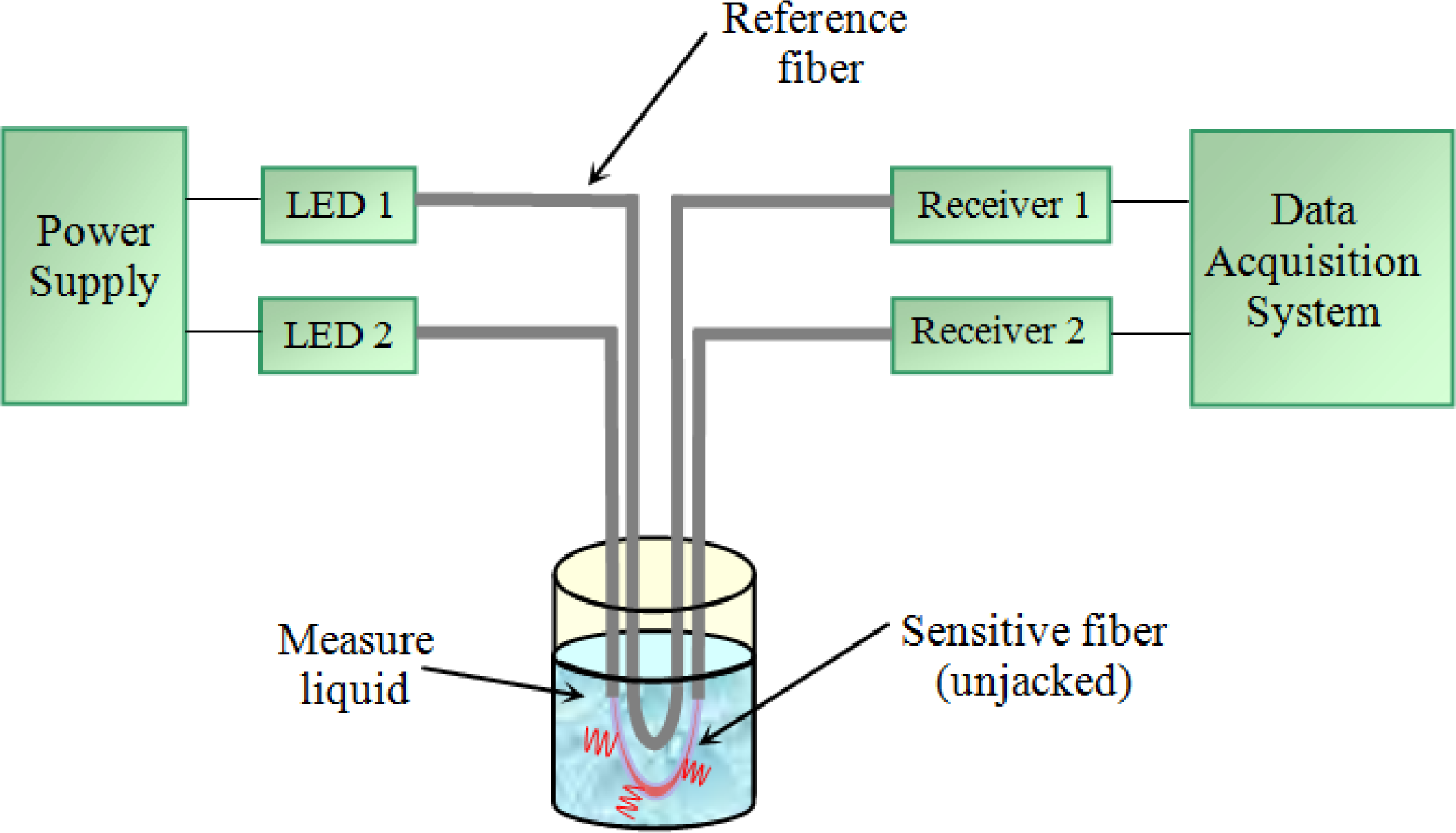
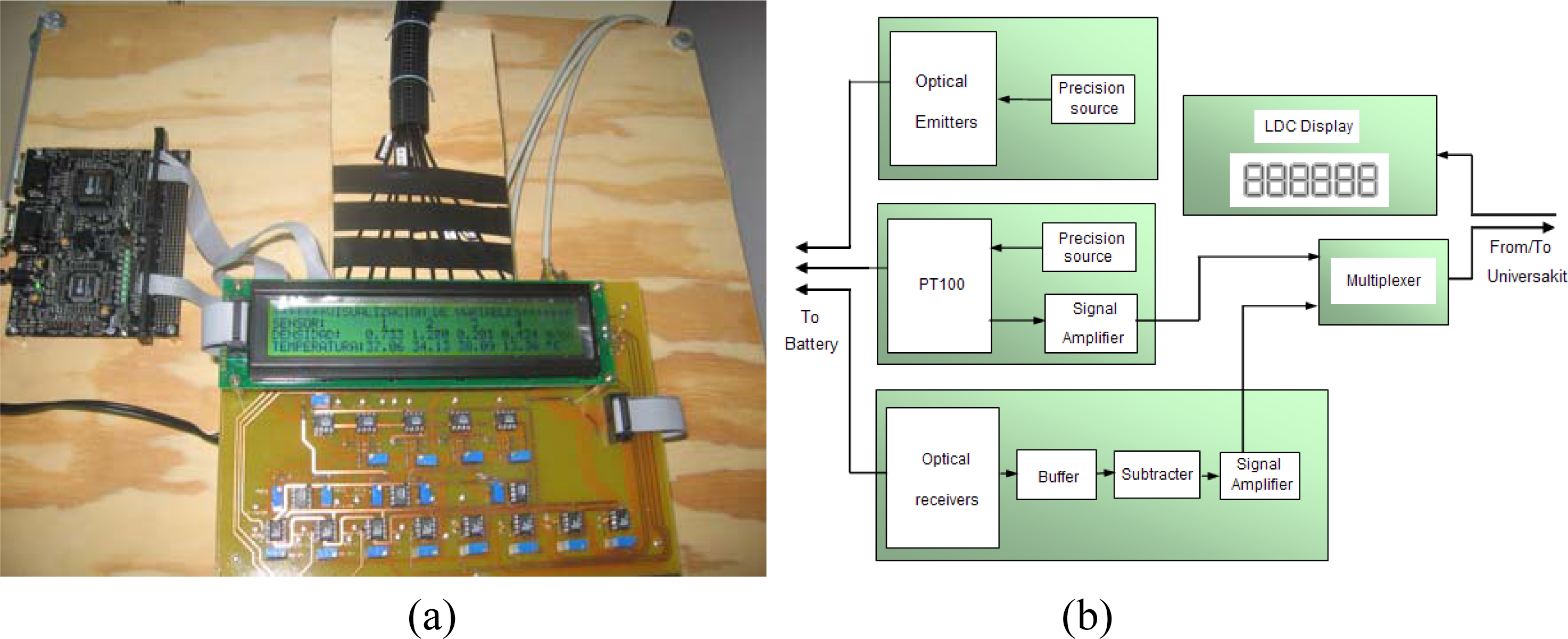
3.1. Sensor configuration
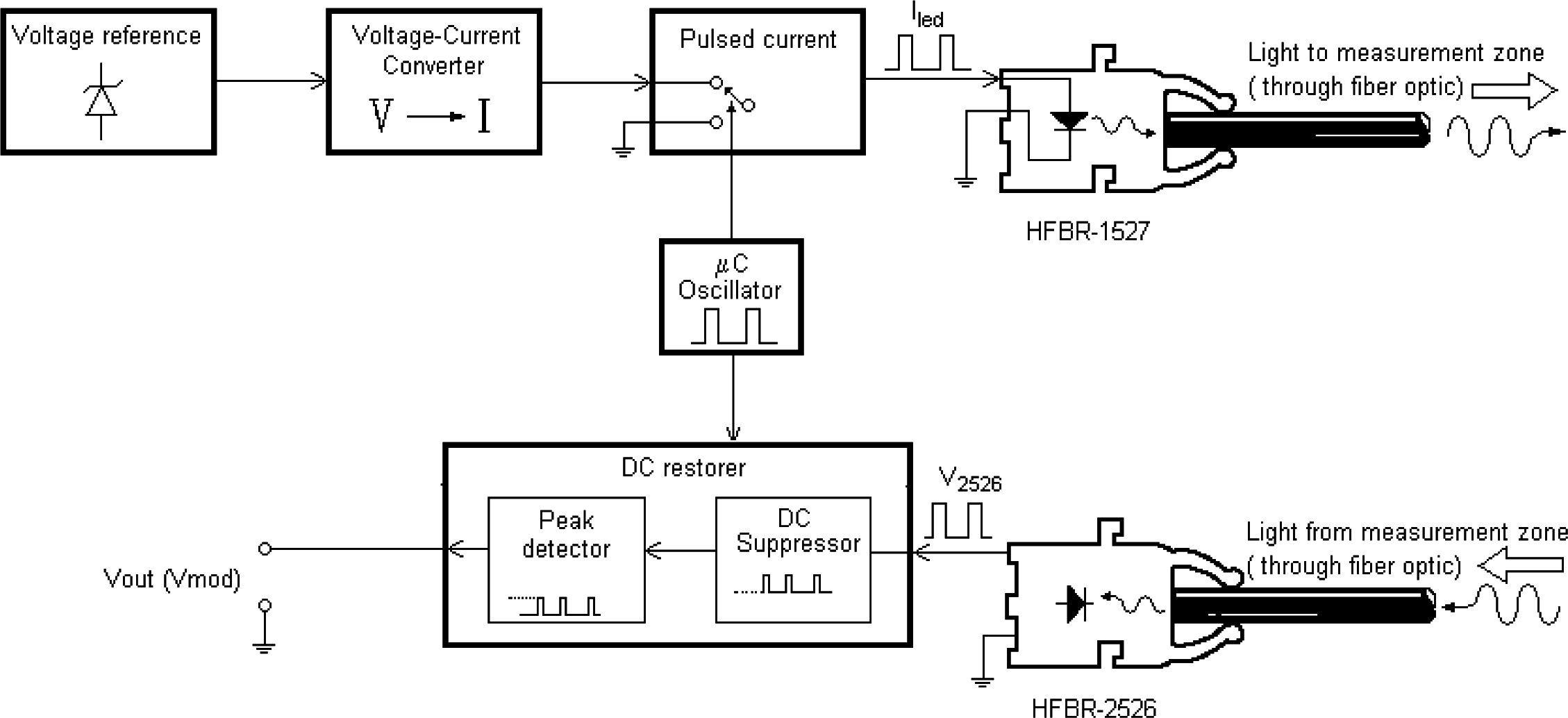
3.2. Electronic system
3.3. Temperature compensation
3.3.1. Temperature compensation by means of Data Processing
3.3.2. Temperature compensation by hardware
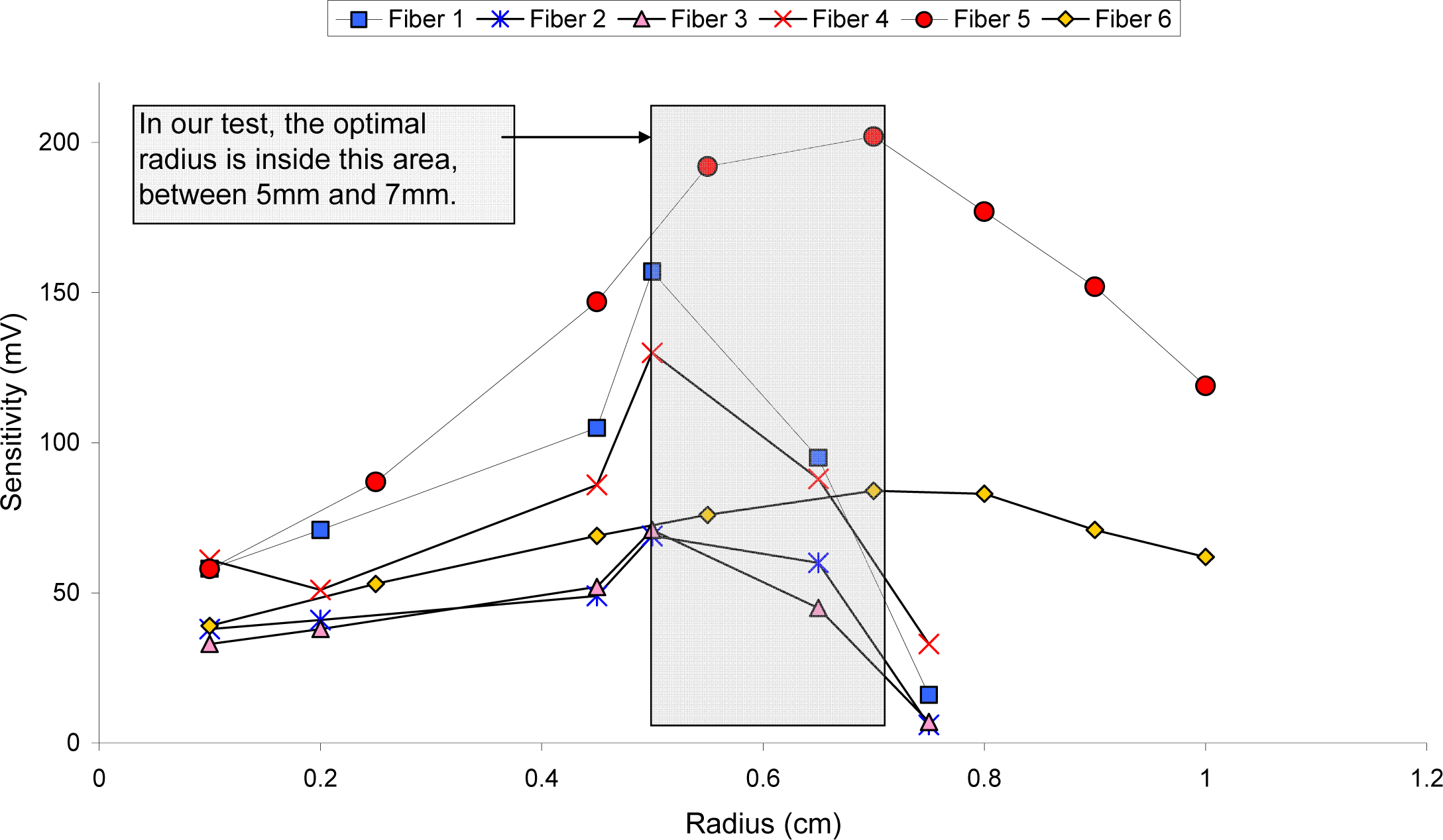
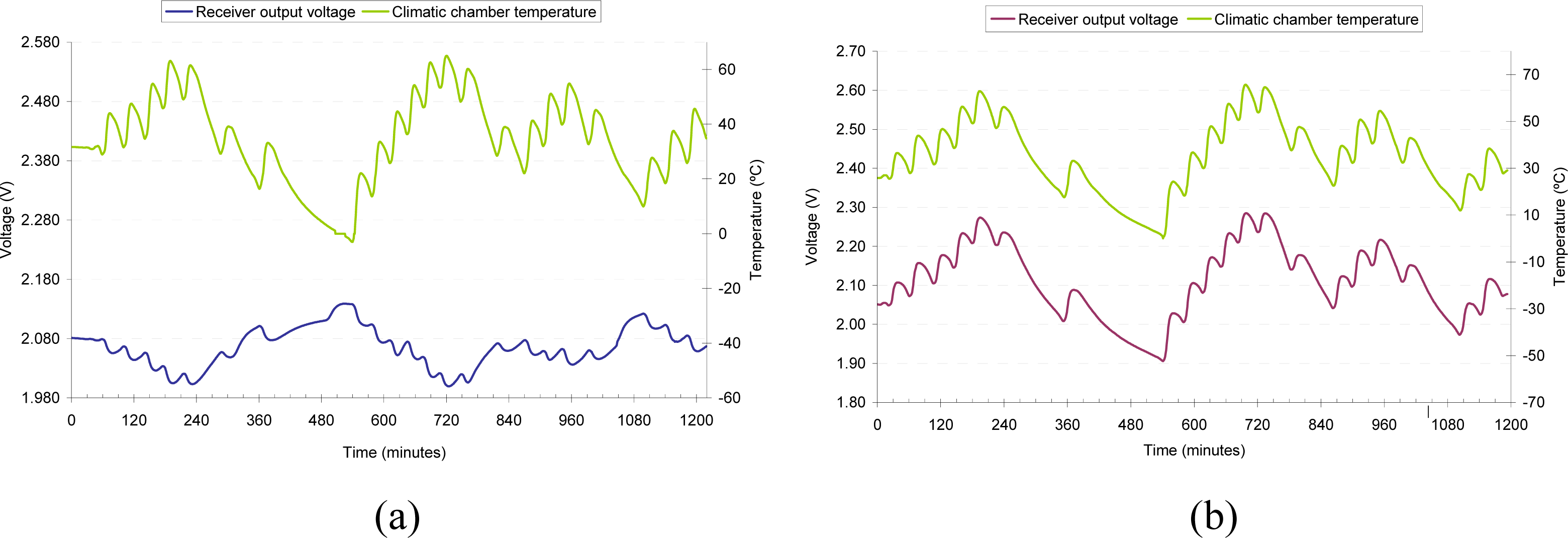
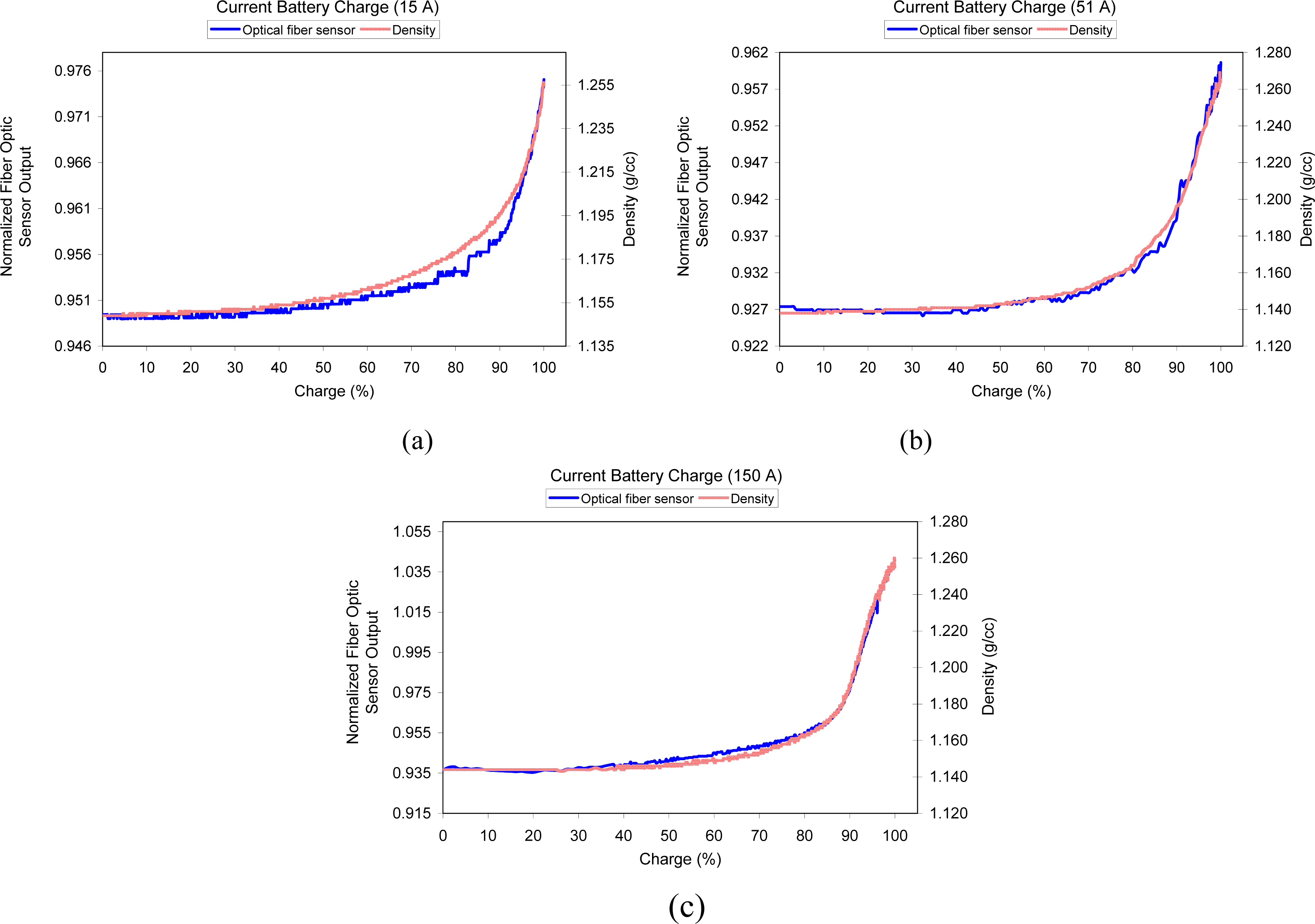
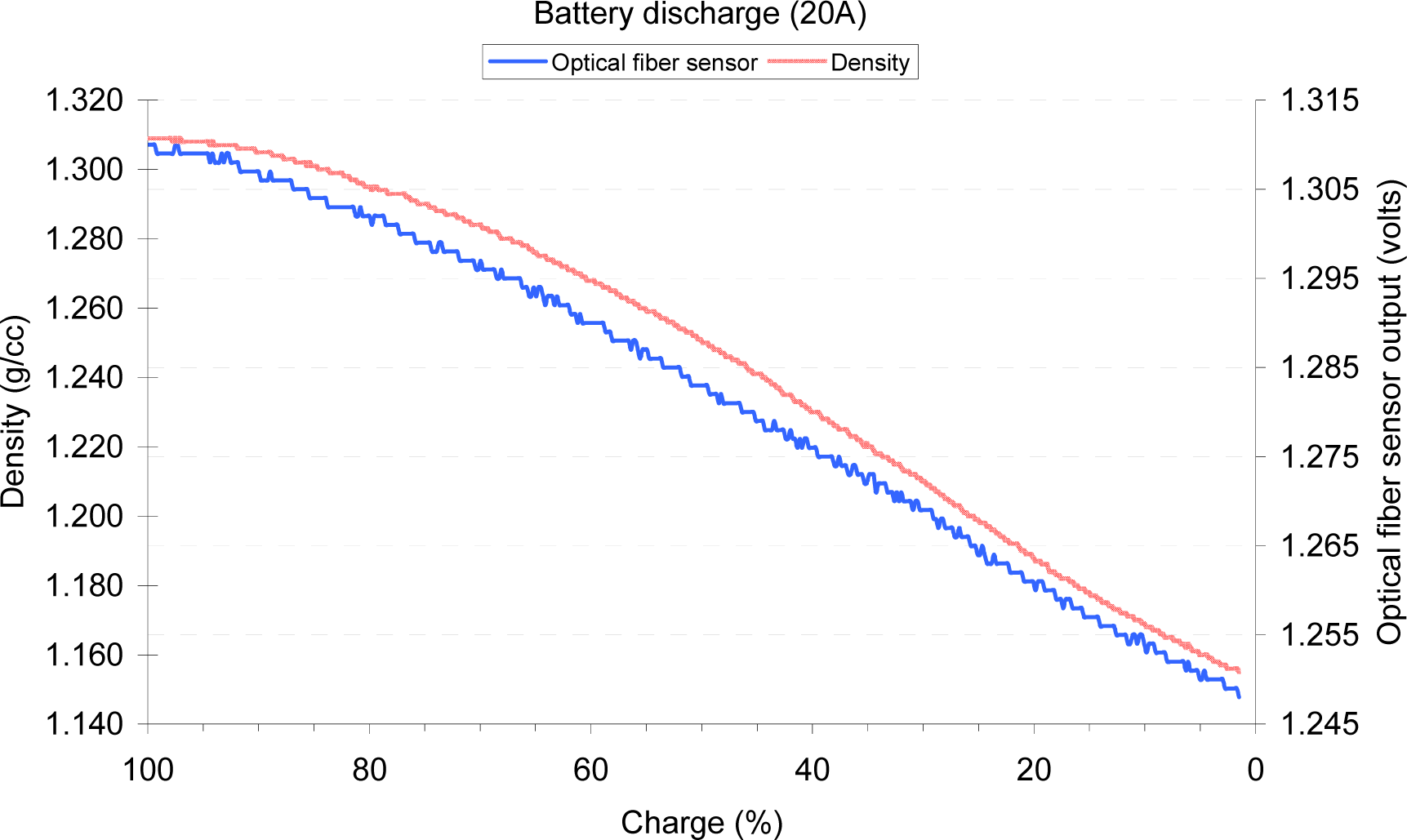
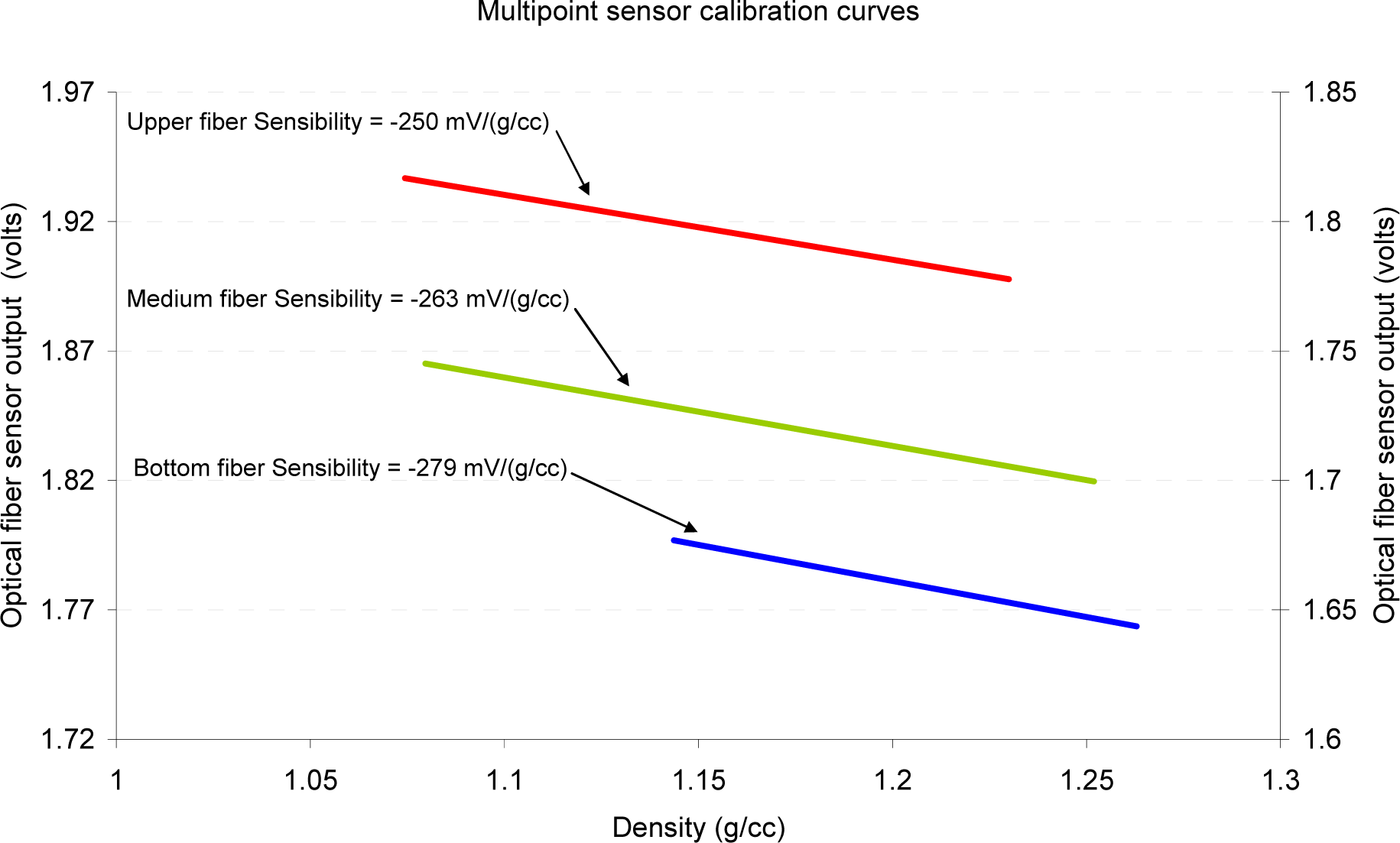
3.4. Results
4. Multi-Point Sensor
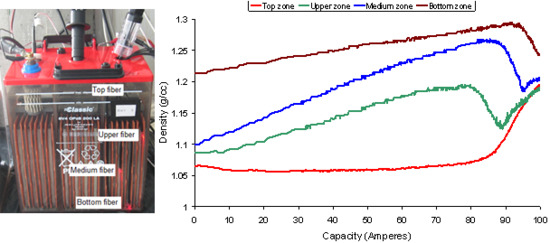
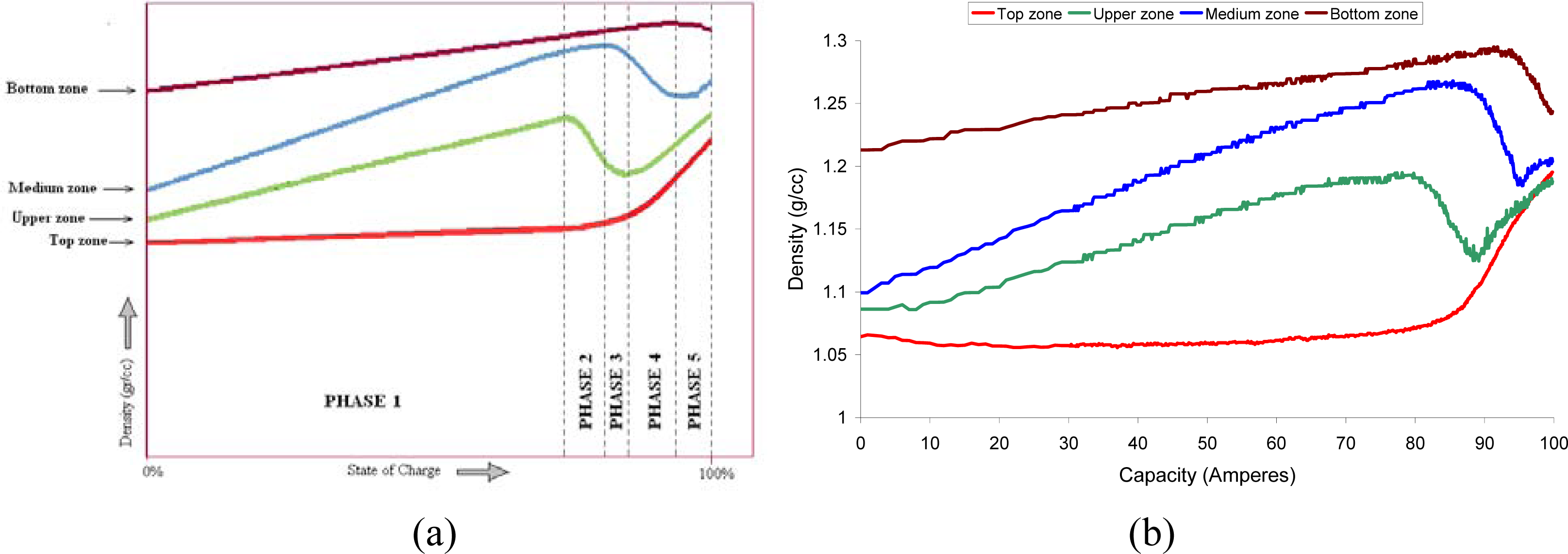
4.1. Measurement of density at several points
- Phase 1: This is the longest phase. Its main characteristic is that the density varies linearly in the four zones of the battery, although with different slopes. The greatest slope is that of the middle and upper zones, whereas the slope in the curve of the top zone is practically zero.
- Phase 2: In this phase a small bubbling appears which makes the density decrease drastically in the upper zone, whereas in the top zone, the slope begins to increase. In the middle zone there is a positive slope, but less than in phase 1. The slope of the density in the bottom zone does not vary.
- Phase 3: In this phase the density of the middle zones begins to decrease, whereas the density in the upper zone begins to stabilize. The slope of the density in the top zone continues to increase and the bottom zone does not change.
- Phase 4: The density of the middle zone decreases dramatically and that of the top zone increases considerably. The density of the upper zone increases again, after the sharp decrease in the two previous phases.
- Phase 5: This phase is observed in a few tests only. During this phase, the density in the bottom zone decreases, and it increases in the other zones. In Figure 17b, this phase can be clearly seen in the real time measurement.
4.2. Electrolyte low-level detection
4.3. Integrated measurement system
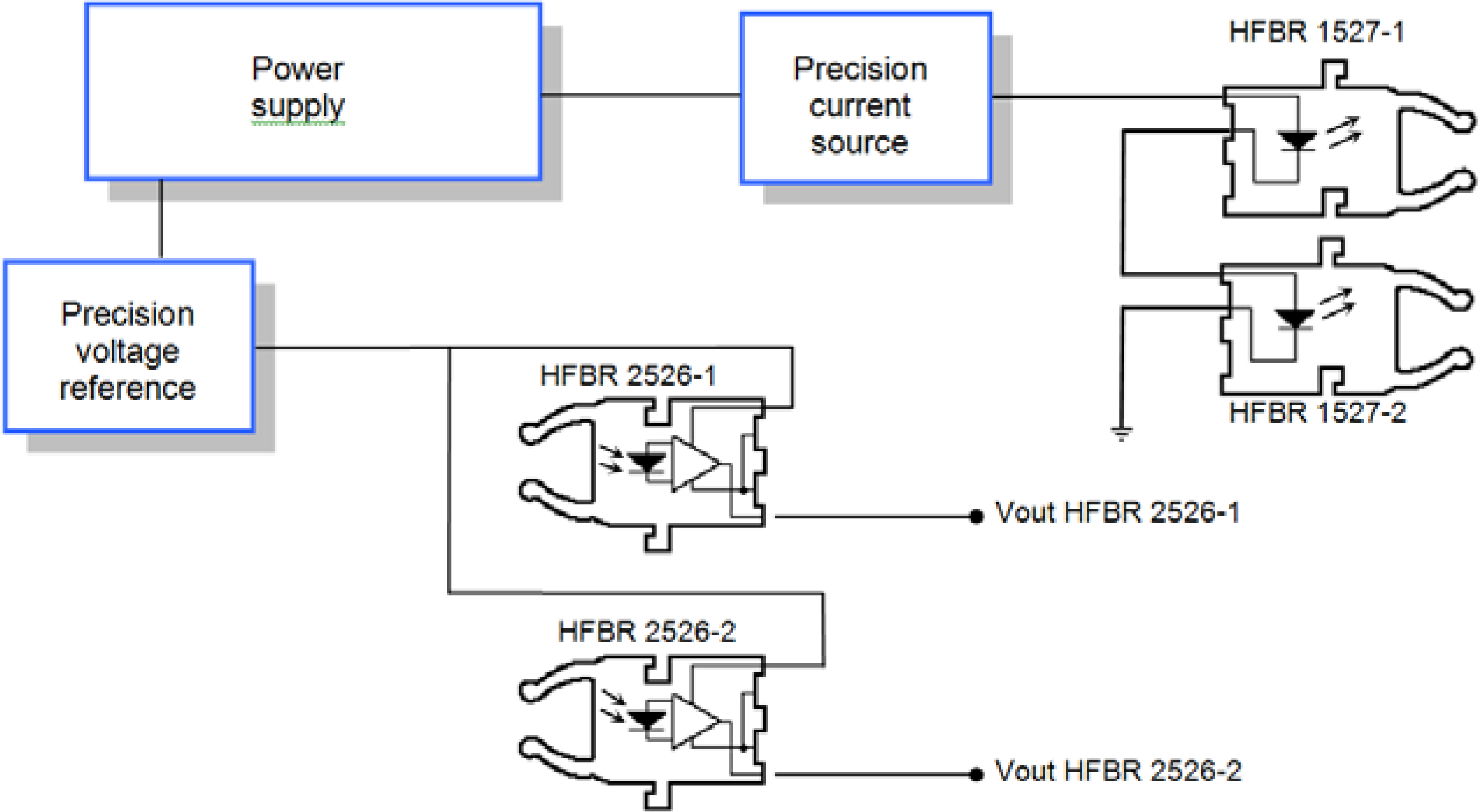
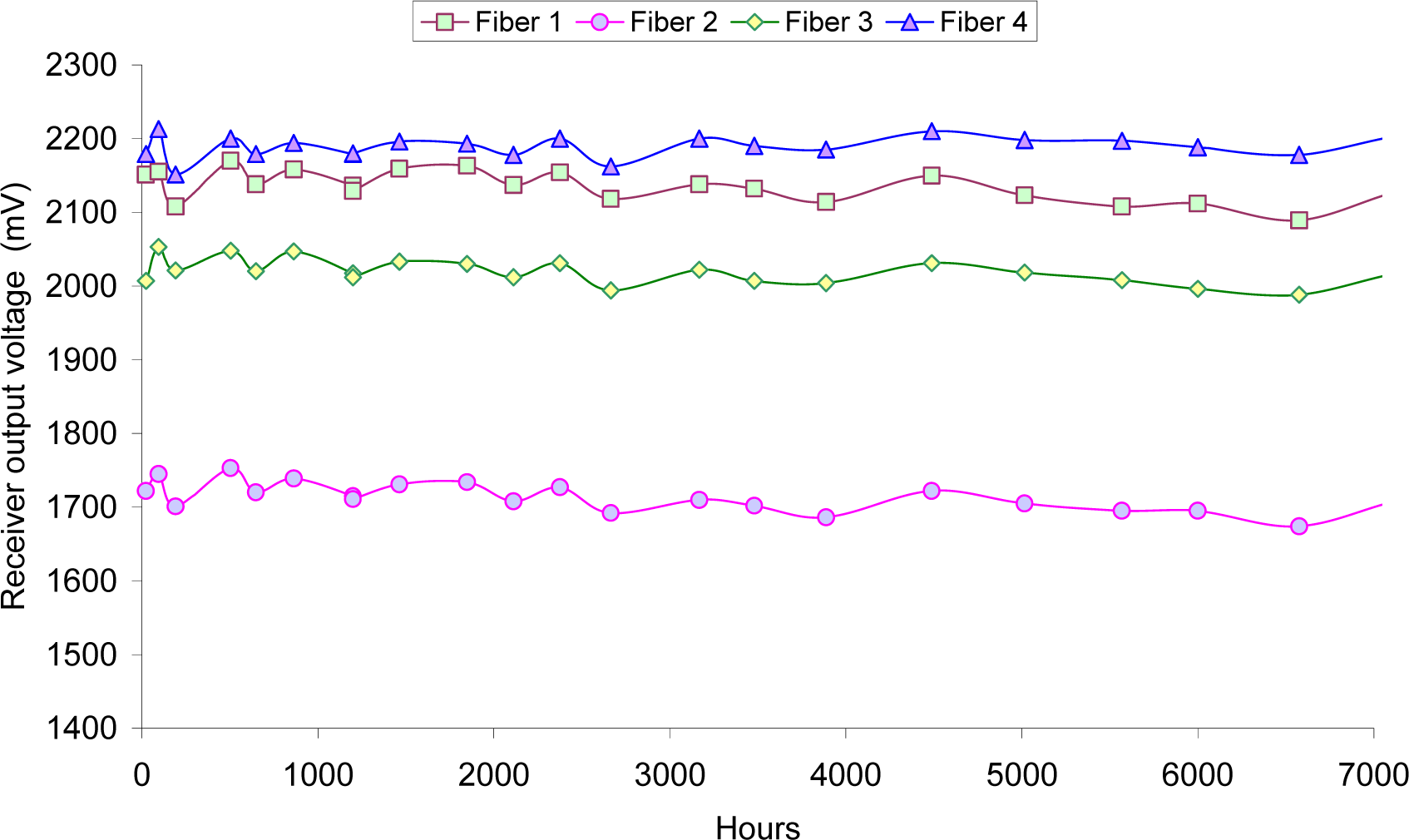
5. Accelerated Testing for Plastic Optical Fibers
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Rand, D.A.J.; Moseley, P.T.; Garche, J.; Parker, C.D. Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid Batteries; Elsevier: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Linden, D.; Reddy, T. Handbook of Batteries, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Piller, S.; Perrin, M.; Jossen, A. Methods for state-of-charge determination and their applications. J. Power Sources 2001, 96, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Takeo, T.; Hattori, H. Optical fiber sensor for measuring refractive Index. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 1982, 21, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar]
- San Martin, J.I; Achaerandio, M.; Gaston, A.; Sevilla, J. Desarrollo de sensores de índice de refracción de líquidos basados en fibra óptica pulida lateralmente. Proceedings of Seminario de Automática, Electrónica Industrial e Instrumentación (SAAEI′98), Pamplona, Spain, September 15–18, 1998; pp. 221–224.
- Hancke, G.P. The measurement of the relative density of homogeneous fluids by means of an optical technique. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas 1992, 41, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. A sensor of sulfuric acid specific gravity for lead-acid batteries. Sens. Actuat. B 2005, 105, 194–198. [Google Scholar]
- Swoboda, C.A.; Fredrickson, D.R.; Gabelnick, S.D.; Cannon, P.H.; Hornstra, F.; Yao, N.P.; Phan, K.A.; Singleterry, M.K. Development of an ultrasonic technique to measure specific gravity in lead-acid battery electrolyte. IEEE Trans. Son. Ultrason 1983, 30, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gayol, A.; Marcos, J.; Nóvoa, R.; Peñalver, C.M.; Pérez, M.C. Resistivity measurements in lead-acid batteries. Proceedings of the 18th International Electric Vehicle Symposium & Exhibition, Berlin, Germany, October 20–24, 2001.
- Dakin, J.; Culshaw, B. Optical Fiber Sensor; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1989; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zubía, J.; Arrúe, J. Plastic optical fibers: An introduction to their technological processes and applications. Opt. Fiber Technol 2001, 7, 101–140. [Google Scholar]
- Harmer, A.L. In optical fiber refractometer using attenuation of cladding modes. Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors, London, UK, April 26–28, 1983.
- Lomer, M.; Quintela, A.; López-Amo, M.; Zubía, J.; López-Higuera, J.M. A quasi-distributed level sensor based on a bent side-polished plastic optical fiber cable. Meas. Sci. Technol 2007, 18, 2261–2267. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherif, M.; Bansal, L.; Yuan, J. Fiber optic sensors for detection of toxic and biological threats. Sensors 2007, 7, 3100–3118. [Google Scholar]
- Montero, D.; Vázquez, C.; Möllers, I.; Arrúe, J.; Jägger, D. A self-referencing intensity based polymer optical fiber sensor for liquid detection. Sensors 2009, 9, 6446–6455. [Google Scholar]
- Armenta, C.; Doria, J.; de Andrés, M.C.; Urrutia, J.; Fullea, J.; Graña, F. A new method of establishing the state of charge of lead-acid batteries with electrolyte circulation. J. Power Sources 1989, 27, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, A.; Love, J. Optical Waveguide Theory, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuse, D. Field deformation and loss caused by curvature of optical fibers. J. Opt. Soc. Am 1976, 66, 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Love, J.; Winkler, C. Power attenuation in bent multimode step-index slab and fiber waveguides. Electron. Lett 1978, 14, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Marcuse, D. Curvature loss formula for optical fibers. J. Opt. Soc. Am 1975, 66, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Gloge, D. Bending loss in multimode fibers with graded and ungraded core index. Appl. Opt 1972, 11, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Ghatak, A.; Sharma, E.; Kompella, J. Exact paths in bent waveguides. Appl. Opt 1988, 27, 3180–3184. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, A.; Love, J. Reflection at a curved dielectric interface—Electromagnetic tunneling. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Tech 1975, 23, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Durana, G.; Zubía, J.; Arrue, J.; Aldabaldetreku, G.; Mateo, J. Dependence of bending losses on cladding thickness in plastic optical fibers. Appl. Opt 2003, 42, 997–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Club Des Fibers Optiques Plastiques. Plastic Optical Fibers. Practical Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, A.; Marcos, J.; Doval, J.; Peñalver, C. An optimized fiber optic sensor for the measurement of the electrolyte density in lead-acid batteries. Proceedings of Eurosensors XIX, Barcelona, Spain, September 11–14, 2005.
- Cao, A.; Marcos, J.; Doval, J.; del Rio, A. Temperature dependence compensation of the optoelectronics components by means of hardware and data processed. Proceedings of POF&MOC 2006, The Joint International Conference on Plastic Optical Fiber & Microoptics, Seoul, Korea, September 11–14, 2006; pp. 126–131.
- Marcos, J.; Álvarez, J.; Doval, J.; Cao, A.; Peñalver, C.; Nogueiras, A.; Lago, A. Management electronics system for fast charging lead-acid batteries. Proceedings of Advanced Automotive Batteries Conference, AABC-05, Honolulu, HI, USA, June 13–17, 2005.
- Marcos, J.; Dios, J.; Cao, A.; Doval, J.; Peñalver, C.; Nogueiras, A.; Lago, A.; Poza, F. Fast lead-acid battery charge strategy. Proceedings of Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC 2006), Dallas, TX, USA, March 19–23, 2006.
- Marcos, J.; Cao, A. 7000 hours accelerated testing for plastic optical fibers in lead-acid batteries applications. Proceedings of the Joint International Conference on Plastic Optical Fiber & Microoptics 2006, Seoul, Korea, September 11–14, 2006; pp. 430–435.
- Volotinen, T.; Griffioen, W.; Gadonna, M.; Limberger, H. Reliability of Optical Fibers and Componentes; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]








© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao-Paz, A.M.; Marcos-Acevedo, J.; Del Río-Vázquez, A.; Martínez-Peñalver, C.; Lago-Ferreiro, A.; Nogueiras-Meléndez, A.A.; Doval-Gandoy, J. A Multi-Point Sensor Based on Optical Fiber for the Measurement of Electrolyte Density in Lead-Acid Batteries. Sensors 2010, 10, 2587-2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100402587
Cao-Paz AM, Marcos-Acevedo J, Del Río-Vázquez A, Martínez-Peñalver C, Lago-Ferreiro A, Nogueiras-Meléndez AA, Doval-Gandoy J. A Multi-Point Sensor Based on Optical Fiber for the Measurement of Electrolyte Density in Lead-Acid Batteries. Sensors. 2010; 10(4):2587-2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100402587
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao-Paz, Ana M., Jorge Marcos-Acevedo, Alfredo Del Río-Vázquez, Carlos Martínez-Peñalver, Alfonso Lago-Ferreiro, Andrés A. Nogueiras-Meléndez, and Jesús Doval-Gandoy. 2010. "A Multi-Point Sensor Based on Optical Fiber for the Measurement of Electrolyte Density in Lead-Acid Batteries" Sensors 10, no. 4: 2587-2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100402587
APA StyleCao-Paz, A. M., Marcos-Acevedo, J., Del Río-Vázquez, A., Martínez-Peñalver, C., Lago-Ferreiro, A., Nogueiras-Meléndez, A. A., & Doval-Gandoy, J. (2010). A Multi-Point Sensor Based on Optical Fiber for the Measurement of Electrolyte Density in Lead-Acid Batteries. Sensors, 10(4), 2587-2608. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100402587